- published: 15 Jun 2016
- views: 31402
- published: 31 Aug 2011
- views: 5992858
- published: 11 Oct 2013
- views: 517922
- published: 15 Dec 2015
- views: 146622
- published: 15 Jun 2016
- views: 8668
- published: 21 Jan 2016
- views: 507829
- published: 18 Mar 2014
- views: 894057
- published: 10 Aug 2011
- views: 803478
- published: 29 Apr 2014
- views: 270490
- published: 30 May 2014
- views: 3027592
A lens is an optical device which transmits and refracts light, converging or diverging the beam.[citation needed] A simple lens consists of a single optical element. A compound lens is an array of simple lenses (elements) with a common axis; the use of multiple elements allows more optical aberrations to be corrected than is possible with a single element. Lenses are typically made of glass or transparent plastic. Elements which refract electromagnetic radiation outside the visual spectrum are also called lenses: for instance, a microwave lens can be made from paraffin wax.
The variant spelling lense is sometimes seen. While it is listed as an alternative spelling in some dictionaries, most mainstream dictionaries do not list it as acceptable.
The word lens comes from the Latin name of the lentil, because a double-convex lens is lentil-shaped. The genus of the lentil plant is Lens, and the most commonly eaten species is Lens culinaris. The lentil plant also gives its name to a geometric figure.
This article is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported License, which means that you can copy and modify it as long as the entire work (including additions) remains under this license.
Lens or Lense may refer to:
This article is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported License, which means that you can copy and modify it as long as the entire work (including additions) remains under this license.

Optics is the branch of physics which involves the behavior and properties of light, including its interactions with matter and the construction of instruments that use or detect it. Optics usually describes the behavior of visible, ultraviolet, and infrared light. Because light is an electromagnetic wave, other forms of electromagnetic radiation such as X-rays, microwaves, and radio waves exhibit similar properties.
Most optical phenomena can be accounted for using the classical electromagnetic description of light. Complete electromagnetic descriptions of light are, however, often difficult to apply in practice. Practical optics is usually done using simplified models. The most common of these, geometric optics, treats light as a collection of rays that travel in straight lines and bend when they pass through or reflect from surfaces. Physical optics is a more comprehensive model of light, which includes wave effects such as diffraction and interference that cannot be accounted for in geometric optics. Historically, the ray-based model of light was developed first, followed by the wave model of light. Progress in electromagnetic theory in the 19th century led to the discovery that light waves were in fact electromagnetic radiation.
This article is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported License, which means that you can copy and modify it as long as the entire work (including additions) remains under this license.
- Loading...

-
 3:36
3:36England Fans do the Show in Lens near Lille - Euro 2016 waiting for England Wales game the next day
England Fans do the Show in Lens near Lille - Euro 2016 waiting for England Wales game the next day -
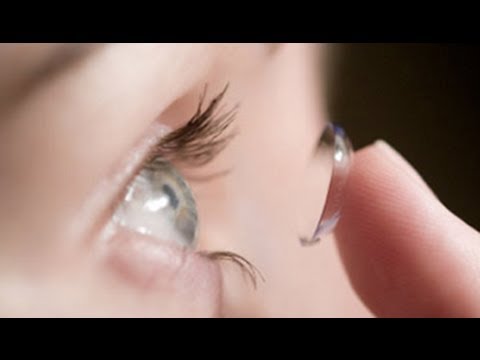 4:04
4:04How To Apply Contact Lenses
How To Apply Contact LensesHow To Apply Contact Lenses
Want to see more? You could follow my blog? It's free! :D http://www.bloglovin.com/en/blog/2609935/klairedelys/follow The lenses I use are coloured contacts, NOT for my vision. They're meant for cosplaying, dressing up or just a one-off. They are not meant to be worn constantly. You should ALWAYS check with an optician before purchasing lenses just to make sure they're ok. If you have a history of eye problems, if your eyes are different shapes, of if the lenses just don't feel right DO NOT USE THEM. Always keep your tools clean. I always wash the tweezers after using them and make sure that the lens cases are super clean. I learned at lot of new tips and tricks for this video from Earaness, check him out his makeup is awesome!: http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=IJ2m8Bi3LVE&feature;=related I've said this in the video but I just want to say it again, ALWAYS check with an optician before doing anything with your eyes. -------------------------------------------------------------- Where else to find me: Website/Blog: http://www.klairedelys.com Twitter: http://twitter.com/KlairedeLys Facebook Page: https://www.facebook.com/pages/Klaire-de-Lys/128984429746?ref=ts My second Channel: http://www.youtube.com/user/KlairedeLysdotcom Deviant Art Account: http://klairedelys.deviantart.com/ Google+ : https://plus.google.com/u/0/stream?tab=G#109311808933297815502/posts Tumblr: http://klairedelys.tumblr.com/ -------------------------------------------------------------- What I used: -Contact lenses (single colour grey): http://www.funkylenses.co.uk/patterns.html -Lens Tweezers can be found on e-Bay :) -(And for those of you asking the earrings here is the seller I bought them from): http://www.ebay.co.uk/itm/Earrings-Large-Brass-Key-STEAMPUNK-/130568795393?pt=UK_Jewellery_Watches_CostumeJewellery_CA&hash;=item1e6681b501 Just as a precaution I'm going to paste the FAQ's from the contact lens company I buy my lenses from: Soak your Funky Eyes in solution for at least 2 hours before wearing them. PLEASE DO NOT OVERWEAR. On the first day, wear for no more than 4 hours, you may then increase this by 2 hours each day but never wear them overnight. DO NOT share this product DO NOT let this product dry out. DO NOT wear or use our products if damaged. DO dispose of this product 30 days after opening. FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS. Q : How do I put them in? A : The product comes with detailed instructions. Q : Is it hard to put in? A : We provide simple to follow instructions on the product. Q : How long do they last? A : When unopened the product has a three year life span, however as soon as the vial is opened the product has a thirty day life span during these thirty days you can wear them as oftern as you want. Q : Do I need an eye test? A : Here at Funky Eyes we believe everybody should have an eye test for their peace of mind. However you do NOT need an eye test to wear them. Q : I wear glasses does this mean I can't use this type of product? A: As our product does not alter your vision there is no reason why you can't wear them at the same time as your glasses. Q: I wear contact lenses, can I wear patterns or colours over or under them? A: No if you wear contacts to correct your vision you will need to purchase prescription colour or pattern contact lenses from your optician. -
 19:57
19:57Understanding Camera Lenses
Understanding Camera LensesUnderstanding Camera Lenses
DSLR Lens guide. This video teaches how to understand everything about camera lenses, which can be very difficult starting out. Topics covered include zoom lenses, prime lenses, wide angle, mid range, and telephoto lenses. As well as focal length, background compression, bokeh, UV filters, and all the rings, switches, buttons and what they do. Also going over all the letters and numbers and what they mean. Also here are some links to things I referred to in the video High quality UV filters - http://www.amazon.com/dp/B0000BZLBQ/ref=as_li_ss_til?tag=wwwnewtograph-20&camp;=0&creative;=0&linkCode;=as4&creativeASIN;=B0000BZLBQ&adid;=1GVAG7R6XK46QAS2SWYZ Lens pen (for cleaning lenses) - http://www.amazon.com/dp/B007G5NNOW/ref=as_li_ss_til?tag=wwwnewtograph-20&camp;=0&creative;=0&linkCode;=as4&creativeASIN;=B007G5NNOW&adid;=0Y0WV9J7CYM4AAEHTHFQ -
 2:50
2:50How To: Put in Scleral Sabertooth 22mm Contact Lens
How To: Put in Scleral Sabertooth 22mm Contact LensHow To: Put in Scleral Sabertooth 22mm Contact Lens
Simple tutorial on how to put in scleral Sabertooth 22mm contact lenses in by Colour VUE - Bianca Jay Xx -
 1:53
1:53France: English lager louts defy alcohol ban in Lens *EXPLICIT*
France: English lager louts defy alcohol ban in Lens *EXPLICIT*France: English lager louts defy alcohol ban in Lens *EXPLICIT*
English football fans continued to disobey the imposed alcohol ban in Lens, Wednesday, as they gathered ahead of their next Group B tie with Wales which kicks off on Thursday at the Bollaert stadium. SOT, Barman (French): "We can sell beer below five per cent. This is the condition they have imposed on us. And we can sell it for takeaway in plastic cups." SOT, Shop owner (French): "I find the prohibition of selling alcohol totally ridiculous. As a little store, I have no right to sell alcohol, not even beer less than 5 per cent, while bars and restaurants have this right to sell beer under five per cent. I think this means killing the feast of football." Video ID: 20160615-052 Video on Demand: http://www.ruptly.tv Contact: cd@ruptly.tv Twitter: http://twitter.com/Ruptly Facebook: http://www.facebook.com/Ruptly -
 5:01
5:01THÁCH THẢO 4 | Đeo lens | Ngọc Thảo
THÁCH THẢO 4 | Đeo lens | Ngọc ThảoTHÁCH THẢO 4 | Đeo lens | Ngọc Thảo
Subscribe ► http://bit.ly/ThaoTube ----------------------------------------------- Phở Đặc Biệt ► https://www.facebook.com/tobuuphat Ngọc Thảo ► http://www.facebook.com/ngocthaovn Instagram ► http://instagram.com/ngocthao_official -
 4:58
4:58Lens Nasıl Takılır Çıkartılır ve Temizlenir
Lens Nasıl Takılır Çıkartılır ve TemizlenirLens Nasıl Takılır Çıkartılır ve Temizlenir
Yeni versiyon eskisinde lens çıkarma yoktu. Kusura bakmayın yeniden lens nasıl takılır videosu sizlerle Kanalıma abone olmak için bu linke tıklayınız http://goo.gl/kXfGWo Tüm MAKYAJ Videoları Playlistim https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Lr6dcc7wrnI&list;=PLQ3DzVb2YFIlrAOUQOjjIFilvZSvaQtgs Tüm SAÇ MODELLERİ Playlist http://www.youtube.com/playlist?list=PLQ3DzVb2YFIkBnE5HVYTSMaakAfY8xaWT Tüm MANİKÜR Videoları Playlistim https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=2YuwrpouY4s&list;=PLC7F4AF2880C90928 Tüm İPUÇLARI Playlistim https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=U8jjll-bEKI&list;=PLQ3DzVb2YFIls_gEzFhoDdFSksf-SkPvT Tüm ALIŞVERİŞ ve ÜRÜN Tanıtımı Playlistim https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=52QKUdNagko&list;=PLQ3DzVb2YFIlvaxQX7VjoUH_dZjQ5u5jw Tüm TAG Videoları Playlistim https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ixQUMRCBbaU&list;=PLQ3DzVb2YFInJEzIDCxjt6RXLEaVj1aS1 Aşağıdaki linklerden beni takip edebilirsiniz. Facebook: http://www.facebook.com/nelervarneler Blog: www.sebibebi.com instagram: sebibebi Pinterest: pinterest.com/sebile Twitter: sebibebicom Dailymotion Offical:www.dailymotion.com/sebibebi İş İçin İletişim: sebibebimakeup@gmail.com -
 7:45
7:45All about lenses for beginners
All about lenses for beginnersAll about lenses for beginners
http://www.mccordall.com/photography/ A look at lenses for the beginner, explaining focal length aperture and all the lens markings and what they mean. -
 9:01
9:01Lens Kullanımı: Lensler Nasıl Takılır? Nasıl Çıkarılır?
Lens Kullanımı: Lensler Nasıl Takılır? Nasıl Çıkarılır?Lens Kullanımı: Lensler Nasıl Takılır? Nasıl Çıkarılır?
Yeni videolardan haberdar olmak için kanalıma abone olun: http://goo.gl/ZCAeSZ Benimle iletişim kurabileceğiniz diğer adresler: Instagram: sulekaraok Blog: sulekaraok.blogspot.com Twitter:: sulekaraok Mail: sule.karaok@gmail.com Makyajlar - http://goo.gl/rckgH7 Bitenler - http://goo.gl/fKIg0U Favoriler - http://goo.gl/RIU0C7 Nasıl Yapılır? - http://goo.gl/ZUpzq9 Alışveriş - http://goo.gl/6L8nIm Tag Videoları - http://goo.gl/CBY4OO Kitaplığımda Ne Var? - http://goo.gl/vBLQRe Ürün İncelemeleri - http://goo.gl/0gwQxl Vlog - http://goo.gl/BOfyuz Outfit of the Day - http://goo.gl/hyarzS -
 8:14
8:14How to : Open, Store, Clean, Check, Put On, Remove and Re-wetting Contact Lens
How to : Open, Store, Clean, Check, Put On, Remove and Re-wetting Contact LensHow to : Open, Store, Clean, Check, Put On, Remove and Re-wetting Contact Lens
Hope you find it helpful.♥ --------- --------- --------- Please comment, share, like, fav, and SUBSCRIBE, if you think it's worth! --------- --------- --------- *Never rinse your contacts in regular tap water. This will just make them dirty.* *If your eyes are gritty or sore or red, do NOT put your contacts in.* *Always remove your contacts prior to sleeping.* *Do not swim or soak in a hot tub when wearing your lens. * *Clean your lens before wearing it everytime.* *When wearing makeup and contact lenses, make sure you put in the contact lenses in first, so they will not get contaminated. * *If discomfort persists, IMMEDIATELY remove your lenses and contact your eye care practitioner.* ** Always seek medical advice from your Optician if you have any problem.** (*)Color Contacts = Vassen Lucky Clover Cocoro Brown Contact Lenses http://bit.ly/1kKSXpX (*)1395 Contact Lens Travel Kit Case(Sweet Yellow Biscuit) http://bit.ly/1k2I6Yo Encore All-in-One Multi Purpose Solution (*)Barrel Style Contact lens WASHERS Case (White) http://bit.ly/1rgAirf (*)Rohto Lycee Eye Drops for Contact Lens http://bit.ly/1wloBzp (This is the one I used in video) ================== New Packaging for Rohto Lycee Eye Drops http://bit.ly/1tI1Rdp ( in New Packaging ) ================== (*)Items were comes from ♥ LoveShoppingHolics ♥ http://www.loveshoppingholics.com/ Music; Meditation Impromptu 01 by Kevin MacLeod (incompetech.com)
- Achromat
- Achromatic lens
- Afocal system
- Ancient Egypt
- Anti-fog
- Aperture
- Apochromat
- Aristophanes
- Aspheric lens
- Assyria
- Astigmatism
- Axial symmetry
- Axicon
- Back focal plane
- Barrel distortion
- BBC
- Binoculars
- Bokeh
- Burning-glass
- Camera
- Camera lens
- Catadioptric system
- Chester Moore Hall
- Chromatic aberration
- Collimated light
- Coma (optics)
- Comet
- Contact lens
- Corrective lens
- Corrective lenses
- Curved mirror
- Cylindrical lens
- David Brewster
- Defocus aberration
- Dielectric lens
- Diffraction
- Diffraction-limited
- Dioptre
- Dispersion (optics)
- Distortion (optics)
- Doublet (lens)
- Droplets
- Egyptian hieroglyphs
- Emerald
- England
- Eyeglasses
- Eyepiece
- F-number
- Field curvature
- Fluorite
- Focal length
- Focal power
- Focus (optics)
- Fresnel lens
- Fröjel
- Gladiator
- Glass
- Golden Gate Bridge
- Gotland
- GPL
- Gradient index lens
- Gravitational lens
- History of optics
- Human eye
- Human eyeball
- Hyperopia
- Image
- Infinity
- Italy
- John Dollond
- JSTOR
- Lens (anatomy)
- Lens (genus)
- Lens (geometry)
- Lens (optics)
- Lens antenna
- Lentil
- Light
- Light beam
- List of lens designs
- Magnification
- Magnifying glass
- Meniscus corrector
- Microlens
- Microscope
- Microwave
- Monk
- Monocular
- Movie projector
- Myopia
- Nero
- Netherlands
- Nimrud lens
- Numerical aperture
- Optical aberration
- Optical coating
- Optical lens design
- Optical lenticular
- Optical microscope
- Optical power
- Optical sensor
- Optical telescope
- Optics
- Paraffin wax
- Photochromic lens
- Photographic film
- Photographic lens
- Photography
- Photovoltaic cell
- Plastic
- Pliny the Elder
- Point source
- Pole lathe
- Presbyopia
- Prime lens
- Principal plane
- Prism (optics)
- Prosthetic
- PubMed Identifier
- Radar
- Radio astronomy
- Rain
- Rayleigh criterion
- Reading stone
- Real image
- Refracting telescope
- Refraction
- Refractive index
- Roman Empire
- Seal (emblem)
- Seneca the Younger
- Sign convention
- Simple lens
- Spectacles
- Spherical aberration
- Sun
- Sunglass lens
- Sunglasses
- Superlens
- Surface vertex
- Sweden
- Telescope
- The Clouds
- Thin lens
- Tilt (optics)
- Toric lens
- Transmittance
- University of Oxford
- Vacuum
- Viking
- Virtual image
- Visby lenses
- Visual impairment
- Visual spectrum
- Water
- Wiktionary concave
- Wiktionary convex
- Zoom lens
-

-

How To Apply Contact Lenses
Want to see more? You could follow my blog? It's free! :D http://www.bloglovin.com/en/blog/2609935/klairedelys/follow The lenses I use are coloured contacts, NOT for my vision. They're meant for cosplaying, dressing up or just a one-off. They are not meant to be worn constantly. You should ALWAYS check with an optician before purchasing lenses just to make sure they're ok. If you have a history of eye problems, if your eyes are different shapes, of if the lenses just don't feel right DO NOT USE THEM. Always keep your tools clean. I always wash the tweezers after using them and make sure that the lens cases are super clean. I learned at lot of new tips and tricks for this video from Earaness, check him out his makeup is awesome!: http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=IJ2m8Bi3LVE&feature;=rela... -

Understanding Camera Lenses
DSLR Lens guide. This video teaches how to understand everything about camera lenses, which can be very difficult starting out. Topics covered include zoom lenses, prime lenses, wide angle, mid range, and telephoto lenses. As well as focal length, background compression, bokeh, UV filters, and all the rings, switches, buttons and what they do. Also going over all the letters and numbers and what they mean. Also here are some links to things I referred to in the video High quality UV filters - http://www.amazon.com/dp/B0000BZLBQ/ref=as_li_ss_til?tag=wwwnewtograph-20&camp;=0&creative;=0&linkCode;=as4&creativeASIN;=B0000BZLBQ&adid;=1GVAG7R6XK46QAS2SWYZ Lens pen (for cleaning lenses) - http://www.amazon.com/dp/B007G5NNOW/ref=as_li_ss_til?tag=wwwnewtograph-20&camp;=0&creative;=0&linkCode;=as4&creativ;... -

How To: Put in Scleral Sabertooth 22mm Contact Lens
Simple tutorial on how to put in scleral Sabertooth 22mm contact lenses in by Colour VUE - Bianca Jay Xx -

France: English lager louts defy alcohol ban in Lens *EXPLICIT*
English football fans continued to disobey the imposed alcohol ban in Lens, Wednesday, as they gathered ahead of their next Group B tie with Wales which kicks off on Thursday at the Bollaert stadium. SOT, Barman (French): "We can sell beer below five per cent. This is the condition they have imposed on us. And we can sell it for takeaway in plastic cups." SOT, Shop owner (French): "I find the prohibition of selling alcohol totally ridiculous. As a little store, I have no right to sell alcohol, not even beer less than 5 per cent, while bars and restaurants have this right to sell beer under five per cent. I think this means killing the feast of football." Video ID: 20160615-052 Video on Demand: http://www.ruptly.tv Contact: cd@ruptly.tv Twitter: http://twitter.com/Ruptly Faceboo... -

THÁCH THẢO 4 | Đeo lens | Ngọc Thảo
Subscribe ► http://bit.ly/ThaoTube ----------------------------------------------- Phở Đặc Biệt ► https://www.facebook.com/tobuuphat Ngọc Thảo ► http://www.facebook.com/ngocthaovn Instagram ► http://instagram.com/ngocthao_official -

Lens Nasıl Takılır Çıkartılır ve Temizlenir
Yeni versiyon eskisinde lens çıkarma yoktu. Kusura bakmayın yeniden lens nasıl takılır videosu sizlerle Kanalıma abone olmak için bu linke tıklayınız http://goo.gl/kXfGWo Tüm MAKYAJ Videoları Playlistim https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Lr6dcc7wrnI&list;=PLQ3DzVb2YFIlrAOUQOjjIFilvZSvaQtgs Tüm SAÇ MODELLERİ Playlist http://www.youtube.com/playlist?list=PLQ3DzVb2YFIkBnE5HVYTSMaakAfY8xaWT Tüm MANİKÜR Videoları Playlistim https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=2YuwrpouY4s&list;=PLC7F4AF2880C90928 Tüm İPUÇLARI Playlistim https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=U8jjll-bEKI&list;=PLQ3DzVb2YFIls_gEzFhoDdFSksf-SkPvT Tüm ALIŞVERİŞ ve ÜRÜN Tanıtımı Playlistim https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=52QKUdNagko&list;=PLQ3DzVb2YFIlvaxQX7VjoUH_dZjQ5u5jw Tüm TAG Videoları Playlistim https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ixQUMRCBbaU&l;... -

All about lenses for beginners
http://www.mccordall.com/photography/ A look at lenses for the beginner, explaining focal length aperture and all the lens markings and what they mean. -

Lens Kullanımı: Lensler Nasıl Takılır? Nasıl Çıkarılır?
Yeni videolardan haberdar olmak için kanalıma abone olun: http://goo.gl/ZCAeSZ Benimle iletişim kurabileceğiniz diğer adresler: Instagram: sulekaraok Blog: sulekaraok.blogspot.com Twitter:: sulekaraok Mail: sule.karaok@gmail.com Makyajlar - http://goo.gl/rckgH7 Bitenler - http://goo.gl/fKIg0U Favoriler - http://goo.gl/RIU0C7 Nasıl Yapılır? - http://goo.gl/ZUpzq9 Alışveriş - http://goo.gl/6L8nIm Tag Videoları - http://goo.gl/CBY4OO Kitaplığımda Ne Var? - http://goo.gl/vBLQRe Ürün İncelemeleri - http://goo.gl/0gwQxl Vlog - http://goo.gl/BOfyuz Outfit of the Day - http://goo.gl/hyarzS -

How to : Open, Store, Clean, Check, Put On, Remove and Re-wetting Contact Lens
Hope you find it helpful.♥ --------- --------- --------- Please comment, share, like, fav, and SUBSCRIBE, if you think it's worth! --------- --------- --------- *Never rinse your contacts in regular tap water. This will just make them dirty.* *If your eyes are gritty or sore or red, do NOT put your contacts in.* *Always remove your contacts prior to sleeping.* *Do not swim or soak in a hot tub when wearing your lens. * *Clean your lens before wearing it everytime.* *When wearing makeup and contact lenses, make sure you put in the contact lenses in first, so they will not get contaminated. * *If discomfort persists, IMMEDIATELY remove your lenses and contact your eye care practitioner.* ** Always seek medical advice from your Optician if you have any problem.** (*)Color Co...
England Fans do the Show in Lens near Lille - Euro 2016 waiting for England Wales game the next day
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 3:36
- Updated: 15 Jun 2016
- views: 31402
How To Apply Contact Lenses
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 4:04
- Updated: 31 Aug 2011
- views: 5992858
- published: 31 Aug 2011
- views: 5992858
Understanding Camera Lenses
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 19:57
- Updated: 11 Oct 2013
- views: 517922
- published: 11 Oct 2013
- views: 517922
How To: Put in Scleral Sabertooth 22mm Contact Lens
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 2:50
- Updated: 15 Dec 2015
- views: 146622
- published: 15 Dec 2015
- views: 146622
France: English lager louts defy alcohol ban in Lens *EXPLICIT*
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 1:53
- Updated: 15 Jun 2016
- views: 8668
- published: 15 Jun 2016
- views: 8668
THÁCH THẢO 4 | Đeo lens | Ngọc Thảo
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 5:01
- Updated: 21 Jan 2016
- views: 507829
- published: 21 Jan 2016
- views: 507829
Lens Nasıl Takılır Çıkartılır ve Temizlenir
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 4:58
- Updated: 18 Mar 2014
- views: 894057
- published: 18 Mar 2014
- views: 894057
All about lenses for beginners
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 7:45
- Updated: 10 Aug 2011
- views: 803478
- published: 10 Aug 2011
- views: 803478
Lens Kullanımı: Lensler Nasıl Takılır? Nasıl Çıkarılır?
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 9:01
- Updated: 29 Apr 2014
- views: 270490
- published: 29 Apr 2014
- views: 270490
How to : Open, Store, Clean, Check, Put On, Remove and Re-wetting Contact Lens
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 8:14
- Updated: 30 May 2014
- views: 3027592
- published: 30 May 2014
- views: 3027592
-

-

Geometric Optics - A Level Physics
Continuing the A Level Physics revision series with geometric optics. The lens formula. Real and virtual images. Convex and Concave lenses and mirrors. -

Geometric Optics Intuition with Mirrors and Lenses Concave Convex Diverging Converging | Doc Physics
This video has it all. Seriously, all of it. But no math, and no ray tracing. But maybe you just want to understand. Who can blame you? Just look at the light in that thumbnail bending away from the normal to the surface as it exits the plastic. All of geometric optics with lenses stems from that simple effect. -

Physics: optics of lenses and mirrors (1)
Physics: Introduction to geometric optics for lenses and mirrors. Concave, convex, converging, diverging; real, virtual; upright, inverted, magnified, shrunk. Sign conventions for focal length, image distance, object distance, magnification. The lens/mirror equation; the magnification equation. Introduction to ray tracing. This is a recording of a tutoring session, posted with the student's permission. These videos are offered on a "pay-what-you-like" basis. You can pay for the use of the videos at my website: http://www.freelance-teacher.com/videos.htm For printable documents containing the "handout" and problems discussed in this video series, go to my website. For a list of all the available video series, arranged in suggested viewing order, go to my website. For a playl... -

Shop Talk: Affordable Optics
Are affordable sights good? Do they work? Are they a good option for more expensive options? We talk about affordable optics in this episode of Shop Talk. Copper Custom: http://www.coppercustom.com MAC on Instagram: http://www.instagram.com/militaryarms MAC on Facebook: http://www.facebook.com/militaryarms -

How Fiber Optics Work
How Fiber Optics Work Bill uses a bucket of propylene glycol to show how a fiber optic cable works and how engineers send signal across oceans. How Light Bulbs Work http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=SQIYXqnq-sU How Does a Microwave Oven Work http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=9_v6uOYWU68 How Lasers Work http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=BP6Cl39TgQk How Fiber Optics Work https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=9VmA2S2XiCo How does a lead-acid battery work https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ovWoajfIi94 How does a smoke detector work https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=I3FTuu-V8Is How the Smartphone works http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=3wZQ0aZw3LI How an atomic clock works http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=35LHWJOtVCU How digital camera works http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=CrpYqi0r5kY How does a hard drive works https:... -

Thoughts on Rifle Optics
Support this Channel: http://patreon.com/JamesYeager Yeager Gear: https://tacticalresponse.com/collections/gear Training NEAR YOU: http://www.TacticalResponse.com Yeager's Amazon Shop: http://astore.amazon.com/jamyeasyou-20 Please visit our CHANNEL SPONSORS and keep in mind I only recommend quality gear. Support them because they support you and use the coupon codes when available. TELL THEM JAMES YEAGER SENT YOU! http://www.AR500Armor.com http://www.BreakThroughClean.com http://www.GorillaAmmo.com http://www.KeyBar.us/ http://www.MidwestIndustriesInc.com http://www.NSRtactical.com http://shop.TheTacticalMedic.com FACEBOOK: http://www.facebook.com/JamesYeagerofTacticalResponse Twitter and Instagram: MFCEOYeager -

16. Ray or Geometrical Optics I
For more information about Professor Shankar's book based on the lectures from this course, Fundamentals of Physics: Mechanics, Relativity, and Thermodynamics, visit http://bit.ly/1jFIqNu. Fundamentals of Physics, II (PHYS 201) Geometric optics is discussed as an approximation to wave theory when the wavelength is very small compared to other lengths in the problem (such as the size of openings). Many results of geometric optics involving reflection, refraction (mirrors and lenses) are derived in a unified way using Fermat's Principle of Least Time. 00:00 - Chapter 1. Light as an Electromagnetic Phenomenon 07:17 - Chapter 2. Review of Geometrical (Classical) Optics 21:50 - Chapter 3. Fermat's Principle of Least Time and its Corollaries Complete course materials are available at the Ope... -

5 Things You Need to Know When Buying a Scope - Vortex Optics
Steve, from Vortex Optics teaches Destinee about five things to consider when buying a scope. Check out Vortex Optics at: http://www.vortexoptics.com/ Or on Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/vortexoptics -

How It's Made, Fiber Optics.
Physics - Optics: Lenses (1 of 4) Converging Lens
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 4:45
- Updated: 30 Apr 2013
- views: 66417
Geometric Optics - A Level Physics
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 36:43
- Updated: 03 May 2012
- views: 55658
- published: 03 May 2012
- views: 55658
Geometric Optics Intuition with Mirrors and Lenses Concave Convex Diverging Converging | Doc Physics
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 7:01
- Updated: 01 Mar 2013
- views: 45275
- published: 01 Mar 2013
- views: 45275
Physics: optics of lenses and mirrors (1)
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 10:48
- Updated: 03 May 2009
- views: 178952
- published: 03 May 2009
- views: 178952
Shop Talk: Affordable Optics
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 14:35
- Updated: 05 Jun 2014
- views: 162933
- published: 05 Jun 2014
- views: 162933
How Fiber Optics Work
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 5:36
- Updated: 23 Feb 2014
- views: 400036
- published: 23 Feb 2014
- views: 400036
Thoughts on Rifle Optics
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 13:46
- Updated: 10 Dec 2015
- views: 74646
- published: 10 Dec 2015
- views: 74646
16. Ray or Geometrical Optics I
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 73:21
- Updated: 24 Mar 2011
- views: 78461
- published: 24 Mar 2011
- views: 78461
5 Things You Need to Know When Buying a Scope - Vortex Optics
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 14:16
- Updated: 04 Oct 2015
- views: 62379
- published: 04 Oct 2015
- views: 62379
How It's Made, Fiber Optics.
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 4:47
- Updated: 16 Nov 2011
- views: 623985
- published: 16 Nov 2011
- views: 623985
- Playlist
- Chat
- Playlist
- Chat

England Fans do the Show in Lens near Lille - Euro 2016 waiting for England Wales game the next day
- Report rights infringement
- published: 15 Jun 2016
- views: 31402

How To Apply Contact Lenses
- Report rights infringement
- published: 31 Aug 2011
- views: 5992858

Understanding Camera Lenses
- Report rights infringement
- published: 11 Oct 2013
- views: 517922

How To: Put in Scleral Sabertooth 22mm Contact Lens
- Report rights infringement
- published: 15 Dec 2015
- views: 146622

France: English lager louts defy alcohol ban in Lens *EXPLICIT*
- Report rights infringement
- published: 15 Jun 2016
- views: 8668

THÁCH THẢO 4 | Đeo lens | Ngọc Thảo
- Report rights infringement
- published: 21 Jan 2016
- views: 507829

Lens Nasıl Takılır Çıkartılır ve Temizlenir
- Report rights infringement
- published: 18 Mar 2014
- views: 894057

All about lenses for beginners
- Report rights infringement
- published: 10 Aug 2011
- views: 803478

Lens Kullanımı: Lensler Nasıl Takılır? Nasıl Çıkarılır?
- Report rights infringement
- published: 29 Apr 2014
- views: 270490

How to : Open, Store, Clean, Check, Put On, Remove and Re-wetting Contact Lens
- Report rights infringement
- published: 30 May 2014
- views: 3027592
- Playlist
- Chat

Physics - Optics: Lenses (1 of 4) Converging Lens
- Report rights infringement
- published: 30 Apr 2013
- views: 66417

Geometric Optics - A Level Physics
- Report rights infringement
- published: 03 May 2012
- views: 55658

Geometric Optics Intuition with Mirrors and Lenses Concave Convex Diverging Converging | Doc Physics
- Report rights infringement
- published: 01 Mar 2013
- views: 45275

Physics: optics of lenses and mirrors (1)
- Report rights infringement
- published: 03 May 2009
- views: 178952

Shop Talk: Affordable Optics
- Report rights infringement
- published: 05 Jun 2014
- views: 162933

How Fiber Optics Work
- Report rights infringement
- published: 23 Feb 2014
- views: 400036

Thoughts on Rifle Optics
- Report rights infringement
- published: 10 Dec 2015
- views: 74646

16. Ray or Geometrical Optics I
- Report rights infringement
- published: 24 Mar 2011
- views: 78461

5 Things You Need to Know When Buying a Scope - Vortex Optics
- Report rights infringement
- published: 04 Oct 2015
- views: 62379

How It's Made, Fiber Optics.
- Report rights infringement
- published: 16 Nov 2011
- views: 623985
[VIDEO]: Texas Woman Awakens From Surgery With British Accent
Edit WorldNews.com 23 Jun 2016High turnout reported as Britons cast vote in EU referendum
Edit The Guardian 24 Jun 2016Is Donald Trump right about Hillary Clinton?
Edit CNN 23 Jun 2016[VIDEO]: Gunman Killed After Allegedly Taking Hostages At German Cinema
Edit WorldNews.com 23 Jun 2016As Polls Close, UKIP's Nigel Farage Concedes Defeat For Brexit Referendum
Edit WorldNews.com 23 Jun 2016Lifestyle blogger Marianna Hewitt offers summer beauty tips
Edit The Examiner 24 Jun 2016Metabones (sort of) adds support for Sony AF modes to its Canon lens adapters
Edit Digital Trends 24 Jun 2016Celtics select Jaylen Brown with No. 3 overall pick in draft
Edit Colorado Springs Gazette 24 Jun 2016MREPC to participate in SEMICON West, San Francisco (Malaysian Rubber Export Promotion Council)
Edit Public Technologies 24 Jun 2016Marrying superconductors, lasers, and Bose-Einstein condensates (Chapman University)
Edit Public Technologies 24 Jun 2016Topcon selected to join IBM Watson Health global medical imaging collaborative (Topcon Corporation)
Edit Public Technologies 24 Jun 2016Chattisgarh: Maoists killed 70 BJP workers in 2 yrs, says Chief Minister Raman Singh
Edit Indian Express 24 Jun 2016Icelandic strongman calls Portugal's Ronaldo a 'p---y'
Edit Toronto Sun 24 Jun 2016Maradona: Portugal too dependent on Ronaldo
Edit FourFourTwo 24 Jun 2016Cristiano Ronaldo return to form gives Portugal timely boost
Edit Indian Express 24 Jun 2016LeEco’s Le Max2 outshines Samsung Galaxy S7 and iPhone 6s Plus with CDLA technology
Edit Indian Express 24 Jun 2016Don't blink over North Korea
Edit CNN 24 Jun 2016- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- Next page »







