- published: 26 Mar 2015
- views: 55438
-
remove the playlistEconomy Of Singapore
- remove the playlistEconomy Of Singapore
Please tell us which country and city you'd like to see the weather in.
- published: 05 Dec 2013
- views: 284571
- published: 02 Jan 2016
- views: 48426
- published: 26 Jul 2013
- views: 1753
- published: 19 Apr 2016
- views: 113
- published: 26 Mar 2014
- views: 6908
- published: 24 Feb 2015
- views: 56838
- published: 21 May 2015
- views: 169996
- published: 02 May 2009
- views: 16179
- published: 27 Aug 2015
- views: 26494

Singapore has a highly developed capitalist mixed economy; the state owns stakes in firms that comprise perhaps 60% of the GDP through entities such as the sovereign wealth fund Temasek. It has an open business environment, relatively corruption-free and transparent, stable prices, low tax rates (14.2% of GDP) compared to other developed economies, and one of the highest per-capita gross domestic products (GDP) in the world. Its innovative yet steadfast form of economics that combines economic planning with free-market has given it the nickname the Singapore Model. Exports, particularly in electronics and chemicals, and services provide the main source of revenue for the economy, which allows it to purchase natural resources and raw goods which it does not have.
Most companies in Singapore are registered as private limited-liability companies (commonly known as "private limited companies"). A private limited company in Singapore is a separate legal entity, and shareholders are not liable for the company's debts beyond the amount of share capital they have contributed.
This article is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported License, which means that you can copy and modify it as long as the entire work (including additions) remains under this license.

Singapore (![]() i/ˈsɪŋəpɔər/ SI-ngə-pohr), officially the Republic of Singapore, is a Southeast Asian city-state off the southern tip of the Malay Peninsula, 137 kilometres (85 mi) north of the equator. An island country made up of 63 islands, it is separated from Malaysia by the Straits of Johor to its north and from Indonesia's Riau Islands by the Singapore Strait to its south. Singapore is highly urbanised but almost half of the country is covered by greenery. More land is being created for development through land reclamation.
i/ˈsɪŋəpɔər/ SI-ngə-pohr), officially the Republic of Singapore, is a Southeast Asian city-state off the southern tip of the Malay Peninsula, 137 kilometres (85 mi) north of the equator. An island country made up of 63 islands, it is separated from Malaysia by the Straits of Johor to its north and from Indonesia's Riau Islands by the Singapore Strait to its south. Singapore is highly urbanised but almost half of the country is covered by greenery. More land is being created for development through land reclamation.
This article is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported License, which means that you can copy and modify it as long as the entire work (including additions) remains under this license.
Radio Stations - Singapore
SEARCH FOR RADIOS
- Loading...

-
 2:13
2:13Why Singapore became an economic success
Why Singapore became an economic successWhy Singapore became an economic success
When it started life as an independent, separate country in 1965, Singapore’s prospects did not look good. Tiny and underdeveloped, it had no natural resources and a population of relatively recent immigrants with little shared history. The country’s first prime minister, the late Lee Kuan Yew is credited with transforming it. He called one volume of his memoirs, “From Third World to First”. Why did Singapore become an economic success? First, its strategic location and natural harbour helped. It is at the mouth of the Malacca Strait, through which perhaps 40% of world maritime trade passes. It was an important trading post in the 14th century, and again from the 19th, when British diplomat Sir Stamford Raffles founded the modern city. Now it is at the heart of one of the world’s most dynamic regions. Under Mr Lee, Singapore made the most of these advantages. Second, under Mr Lee, Singapore welcomed foreign trade and investment. Multinationals found Singapore a natural hub and were encouraged to expand and prosper. Third, the government was kept small, efficient and honest—qualities absent in most of Singapore’s neighbours. It regularly tops surveys for the ease of doing business. But the island city is not ideal. Although clean and orderly, it has harsh judicial punishments, a tame press and illiberal social policies. Homosexual acts, for example, remain illegal. Protest demonstrations are rarely permitted. Mr Lee saw his authoritarian style of government as an essential ingredient in Singapore’s success, emphasizing the island’s vulnerability in a potentially hostile neighbourhood. But younger people now question whether Singapore really is that fragile, and resent the restrictions on their freedom. -
 13:21
13:21SINGAPORE AIRLINES | SINGAPORE-ZURICH | A380 | ECONOMY CLASS
SINGAPORE AIRLINES | SINGAPORE-ZURICH | A380 | ECONOMY CLASSSINGAPORE AIRLINES | SINGAPORE-ZURICH | A380 | ECONOMY CLASS
Hi guys! I visited Singapore for a few days this october. The outbound flight was on Swiss, and I could use my miles to get upgraded to business class. But that report is coming soon. This one is the return flight to Zurich on Singapore Airlines A380, since I never tried SQ economy I decided to save money (or save my parents money ;)) and I booked SQ economy! I was expecting a nice experience since it is a 5* Airline, and I wasn't disappointed! SQ Economy is easily comparable to other airlines premium economy, but have a look yourself in my report! I really enjoyed every second in that economy seat! (except the dinner lol). Please enjoy! If you have a question, don't hesitate to ask! You can also find me on Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/pages/Amandeuce-Aviation/933332023376326 Twitter: https://twitter.com/amandeuce Instagram: https://instagram.com/travelswithamandeuce -
![Premium Economy on Singapore Airlines | Full Review! | SYD-SIN-SYD [HD] Inflightexpert; updated 02 Jan 2016; published 02 Jan 2016](http://web.archive.org./web/20160622090837im_/http://i.ytimg.com/vi/7jd3y6M8aso/0.jpg) 24:11
24:11Premium Economy on Singapore Airlines | Full Review! | SYD-SIN-SYD [HD] Inflightexpert
Premium Economy on Singapore Airlines | Full Review! | SYD-SIN-SYD [HD] InflightexpertPremium Economy on Singapore Airlines | Full Review! | SYD-SIN-SYD [HD] Inflightexpert
Take a look and tell me what you think of the new Premium Economy class on Singapore Airlines?!? Premium Economy Class is a great way to fly - especially on SQ. A very comfortable product coupled with the legendary Singapore Airlines attention to detail and service. I'll show you everything you want to see: including the seat and it's various functions, the food (including 'Book the Cook'), the champagne (yes, SQ offers French bubbles to customers in Premium Economy Class) and many other features that make this a very pleasant journey. Perhaps the best feature is the generous legroom and the 2-4-2 configuration - especially if you are in a pair on either side and you know the person next to you. If you are thinking about investing in Premium Economy, particularly on a long haul flight onto Europe or to the USA, then I hope this video may help you decide if you think it is worth the extra $. I should also mention that in addition to everything you see in this video, Premium Economy customers on Singapore Airlines also have access to dedicated priority check-in counters as well as priority baggage handling, both of which are usually reserved for status customers and/or customers in Business/First. Overall, I find SQ's Premium Economy offering to be very impressive - it certainly feels like more of a watered down business class rather than an upgraded economy class or economy plus. See what you think! DISCLAIMER: Music by Epidemic Sound (http://www.epidemicsound.com). ***You are most welcome to share this video on social media, though please do not copy and/or publish without my express prior authorisation*** WHO IS INFLIGHTEXPERT? Hi - I'm David from Australia. I do a few different things for work, and my great passion in life is helping people improve the appearance of their skin! I also love to fly and enjoy to share my journeys here as 'Inflightexpert' on YouTube. If you may be interested in knowing more, then I encourage you to visit my website here: http://www.primafacieskincare.com Read amazing testimonials here (including those from my YouTube subscribers who use my amazing anti-acne product!): http://www.primafacieskincare.com/results.html Follow me on Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/PrimafacieSkin Follow me on twitter @inflightexpert #Inflightexpert -
 3:41
3:41Singapore is world's second fastest growing economy
Singapore is world's second fastest growing economySingapore is world's second fastest growing economy
Singapore's economy expanded 14.7 percent in 2010, making it one of the fastest-growing economies in the world.Prime Minister Lee Hsien Loong said this is the best growth on record ever for the country. -
 20:37
20:37Singapore Airlines A350-900 | Economy Class Review
Singapore Airlines A350-900 | Economy Class ReviewSingapore Airlines A350-900 | Economy Class Review
A flight review of Singapore Airlines flight SQ118 from Singapore to Kuala Lumpur onboard the Airbus A350-900. ___________________ Enjoyed this video? Share it on social media › https://youtu.be/6k8iiwegdxI Subscribe › http://www.youtube.com/subscription_c... Find me on Facebook › https://www.facebook.com/rva.aviation Follow me on Instagram › https://www.instagram.com/flycruise_singapore Google+ › https://www.google.com/+rva9495 ____________________________________ Thanks for the support. As always, more videos coming soon! -
 25:58
25:58How The PAP Will Crash The Singapore Economy
How The PAP Will Crash The Singapore EconomyHow The PAP Will Crash The Singapore Economy
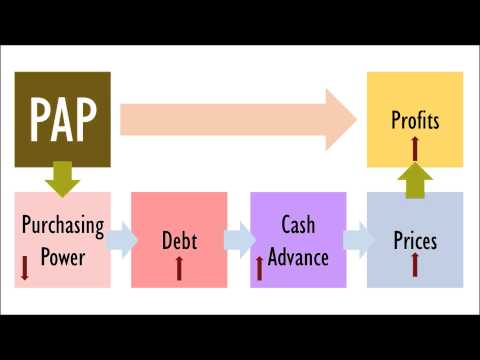
Because of the PAP's want to make profits, it has devised ways to make more money out of Singaporeans while Singaporeans are forced to live more and more difficult lives. Today, Singaporeans receive the lowest wages among the developed countries while the richest in Singapore earns the highest salaries. Yet, the rich pays the lowest tax and CPF in Singapore while the poor and middle-income pay more tax and CPF than they do and have a much smaller purchasing power. Meanwhile, income inequality in Singapore has risen to the widest among the developed countries and there are proven side effects. Watch this video to understand how the PAP is corrupting the Singapore economy and how the "solutions" that they had introduced are half-baked and would only allow them to earn more profits. At the end of the video, find out what solutions need to be taken in Singapore to allow Singapore to restart ourselves and move towards a growth that would benefit all of Singaporeans and allow us to work together towards shared growth. You can read more in this article: http://thehearttruths.com/2014/03/19/truth-exposed-how-the-pap-will-crash-the-singapore-economy/ You can also join the Facebook event page for the 3 May 2014 event here: https://www.facebook.com/events/527069484078804/ -
 19:44
19:44SINGAPORE AIRLINES AIRBUS A380 AUCKLAND-SINGAPORE ECONOMY CLASS
SINGAPORE AIRLINES AIRBUS A380 AUCKLAND-SINGAPORE ECONOMY CLASSSINGAPORE AIRLINES AIRBUS A380 AUCKLAND-SINGAPORE ECONOMY CLASS
Hi guys, here's a new report of my vacation in Australia and New Zealand. The route is Auckland-Singapore. This route is only operated by the Airbus A380 during summer. As usual on Singapore Airlines, the flight was amazing, the FA were very nice, the plane was super spacious and the food was great! Always a pleasure to travel with them! I also had the chance to visit Changi for a few hours: swimming pool, shops, restaurants, gardens... what an amazing place! Hope you'll enjoy it, and see you in the sky! *** FLIGHT INFORMATIONS *** Airline: Singapore Airlines SQ SIA Aircraft: Airbus A380-841 Registration number: 9V-SKB (second ever delivered A380!) Delivery date: January 11, 2008 Flight Number: SQ286 Date: 13.01.2015 Flight duration: 9h40 -
 2:18
2:18Singapore Airlines Premium Economy Class - The Unveil Event
Singapore Airlines Premium Economy Class - The Unveil EventSingapore Airlines Premium Economy Class - The Unveil Event
Singapore Airlines is proud to unveil the new Premium Economy Class at a launch event held on 21 May 2015 in Singapore. Now, be among the first to experience A Great New Way to Fly - book today: www.siapremiumeconomy.com -
 12:53
12:53101 East - Singapore's economy - Part 1
101 East - Singapore's economy - Part 1101 East - Singapore's economy - Part 1
Subscribe to our channel http://bit.ly/AJSubscribe Some speculate that Singapore could take years to recover from the impact of the global economic downturn. Tharman Shanmugaratnam, Singapore's finance minister, talks to 101 East about the challenges facing Singapore's economy. At Al Jazeera English, we focus on people and events that affect people's lives. We bring topics to light that often go under-reported, listening to all sides of the story and giving a 'voice to the voiceless.' Reaching more than 270 million households in over 140 countries across the globe, our viewers trust Al Jazeera English to keep them informed, inspired, and entertained. Our impartial, fact-based reporting wins worldwide praise and respect. It is our unique brand of journalism that the world has come to rely on. We are reshaping global media and constantly working to strengthen our reputation as one of the world's most respected news and current affairs channels. Social Media links: Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/aljazeera Instagram: https://instagram.com/aljazeera/?ref=... Twitter: https://twitter.com/ajenglish Website: http://www.aljazeera.com/ google+: https://plus.google.com/+aljazeera/posts -
 1:58
1:58SINGAPORE AIRLINES NEW PREMIUM ECONOMY
SINGAPORE AIRLINES NEW PREMIUM ECONOMYSINGAPORE AIRLINES NEW PREMIUM ECONOMY
Singapore Airlines are introducing new premium economy class seating into their fleet. www.thetraveltrunk.net was invited to Heathrow Airport in London to have a close up look at a premium economy cabin in one of its A380 aircraft. The route from London to Singapore will have yet more aircraft fitted with this new class of seating their Boing 777's will also have premium economy seats
- 5 C's of Singapore
- Agriculture
- APEC Australia 1989
- APEC Australia 2007
- APEC Brunei 2000
- APEC Canada 1997
- APEC Chile 2004
- APEC Indonesia 1994
- APEC Indonesia 2013
- APEC Japan 1995
- APEC Japan 2010
- APEC Malaysia 1998
- APEC Mexico 2002
- APEC Peru 2008
- APEC Russia 2012
- APEC Singapore 1990
- APEC Singapore 2009
- APEC Thailand 1992
- APEC Thailand 2003
- APEC Vietnam 2006
- Arab Singaporean
- ASEAN
- Banking in Singapore
- Battle of Singapore
- Beaches of Singapore
- Beverage
- Bilateral aid
- Biopolis
- Biotechnology
- Brunei
- Budget
- Burma
- Cabinet of Singapore
- Capitalist
- Chek Jawa
- Chemical
- Chemicals
- Chile
- Chinese Singaporean
- Chinese Taipei
- Cinema of Singapore
- Commerce
- Companies
- Consumer price index
- Copra
- Corruption
- Cuisine of Singapore
- Culture of Singapore
- Dance in Singapore
- Democracy Index
- Dependent territory
- Driving in Singapore
- Dual economy
- Economic planning
- Economy of Abkhazia
- Economy of Armenia
- Economy of Asia
- Economy of Australia
- Economy of Bahrain
- Economy of Bhutan
- Economy of Brunei
- Economy of Burma
- Economy of Cambodia
- Economy of Canada
- Economy of Chile
- Economy of Cyprus
- Economy of Egypt
- Economy of Hong Kong
- Economy of India
- Economy of Indonesia
- Economy of Iran
- Economy of Iraq
- Economy of Israel
- Economy of Japan
- Economy of Jordan
- Economy of Kuwait
- Economy of Laos
- Economy of Lebanon
- Economy of Macau
- Economy of Malaysia
- Economy of Mexico
- Economy of Mongolia
- Economy of Nepal
- Economy of Oman
- Economy of Pakistan
- Economy of Palestine
- Economy of Peru
- Economy of Qatar
- Economy of Russia
- Economy of Singapore
- Economy of Sri Lanka
- Economy of Syria
- Economy of Taiwan
- Economy of Thailand
- Economy of Turkey
- Economy of Vietnam
- Economy of Yemen
- Electronics
- Entrepot trade
- Entrepôt
- European Union
- Export
- Fauna of Singapore
- Financial service
- Fiscal year
- Fitch Group
- Flag of Singapore
- Flora of Singapore
- Food
- Foreign investment
- Four Asian Tigers
- Free-market
- Freedom House
- Fusionopolis
- Gini coefficient
- GlaxoSmithKline
- Globalization
- Heritage Foundation
- History of Singapore
- Hong Kong
- Human Rights Watch
- Indians in Singapore
- Indonesia
- Industry
- Inflation
- Infrastructure
- International trade
- Japan
- Jordan
- JTC Corporation
- Law of Singapore
- Lee Kuan-Yew
- Majulah Singapura
- Malays in Singapore
- Malaysia
- Manufacturing
- Merck & Co.
- Merlion
- Mixed economy
- Moody's
- Music of Singapore
- National Day Parade
- Natural resources
- Oil drilling
- Oil refining
- Orchid
- Pediatric
- Peranakan
- Peru
- Petroleum refining
- Pfizer
- Places in Singapore
- Political corruption
- Port
- Port of Hong Kong
- Port of Rotterdam
- Port of Singapore
- Portal Singapore
- Poverty line
- PRC
- Press Freedom Index
- Raw material
- Refine
- Rubber
- SARS
- Service (economics)
- SGD
- Ship
- Singapore
- Singapore Airlines
- Singapore dollar
- Singapore English
- Singapore Exchange
- Singapore government
- Skill
- Smoking in Singapore
- Sook Ching massacre
- South Korea
- Sport in Singapore
- Standard & Poor's
- Straits Settlements
- Symbol of Singapore
- Telecommunications
- Temasek Holdings
- Template Asia topic
- The Economist
- Tourism in Singapore
- Trade union
- Tripartism
- Unemployment
- United Nations
- United States
- United States dollar
- Vaccines
- Vanda Miss Joaquim
- Wafer fabrication
- Women in Singapore
- World Bank
- World Economic Forum
-

Why Singapore became an economic success
When it started life as an independent, separate country in 1965, Singapore’s prospects did not look good. Tiny and underdeveloped, it had no natural resources and a population of relatively recent immigrants with little shared history. The country’s first prime minister, the late Lee Kuan Yew is credited with transforming it. He called one volume of his memoirs, “From Third World to First”. Why did Singapore become an economic success? First, its strategic location and natural harbour helped. It is at the mouth of the Malacca Strait, through which perhaps 40% of world maritime trade passes. It was an important trading post in the 14th century, and again from the 19th, when British diplomat Sir Stamford Raffles founded the modern city. Now it is at the heart of one of the world’s most... -

SINGAPORE AIRLINES | SINGAPORE-ZURICH | A380 | ECONOMY CLASS
Hi guys! I visited Singapore for a few days this october. The outbound flight was on Swiss, and I could use my miles to get upgraded to business class. But that report is coming soon. This one is the return flight to Zurich on Singapore Airlines A380, since I never tried SQ economy I decided to save money (or save my parents money ;)) and I booked SQ economy! I was expecting a nice experience since it is a 5* Airline, and I wasn't disappointed! SQ Economy is easily comparable to other airlines premium economy, but have a look yourself in my report! I really enjoyed every second in that economy seat! (except the dinner lol). Please enjoy! If you have a question, don't hesitate to ask! You can also find me on Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/pages/Amandeuce-Aviation/933332023376326 Tw... -

Premium Economy on Singapore Airlines | Full Review! | SYD-SIN-SYD [HD] Inflightexpert
Take a look and tell me what you think of the new Premium Economy class on Singapore Airlines?!? Premium Economy Class is a great way to fly - especially on SQ. A very comfortable product coupled with the legendary Singapore Airlines attention to detail and service. I'll show you everything you want to see: including the seat and it's various functions, the food (including 'Book the Cook'), the champagne (yes, SQ offers French bubbles to customers in Premium Economy Class) and many other features that make this a very pleasant journey. Perhaps the best feature is the generous legroom and the 2-4-2 configuration - especially if you are in a pair on either side and you know the person next to you. If you are thinking about investing in Premium Economy, particularly on a long haul flig... -

Singapore is world's second fastest growing economy
Singapore's economy expanded 14.7 percent in 2010, making it one of the fastest-growing economies in the world.Prime Minister Lee Hsien Loong said this is the best growth on record ever for the country. -

Singapore Airlines A350-900 | Economy Class Review
A flight review of Singapore Airlines flight SQ118 from Singapore to Kuala Lumpur onboard the Airbus A350-900. ___________________ Enjoyed this video? Share it on social media › https://youtu.be/6k8iiwegdxI Subscribe › http://www.youtube.com/subscription_c... Find me on Facebook › https://www.facebook.com/rva.aviation Follow me on Instagram › https://www.instagram.com/flycruise_singapore Google+ › https://www.google.com/+rva9495 ____________________________________ Thanks for the support. As always, more videos coming soon! -

How The PAP Will Crash The Singapore Economy
Because of the PAP's want to make profits, it has devised ways to make more money out of Singaporeans while Singaporeans are forced to live more and more difficult lives. Today, Singaporeans receive the lowest wages among the developed countries while the richest in Singapore earns the highest salaries. Yet, the rich pays the lowest tax and CPF in Singapore while the poor and middle-income pay more tax and CPF than they do and have a much smaller purchasing power. Meanwhile, income inequality in Singapore has risen to the widest among the developed countries and there are proven side effects. Watch this video to understand how the PAP is corrupting the Singapore economy and how the "solutions" that they had introduced are half-baked and would only allow them to earn more profits. At the... -

SINGAPORE AIRLINES AIRBUS A380 AUCKLAND-SINGAPORE ECONOMY CLASS
Hi guys, here's a new report of my vacation in Australia and New Zealand. The route is Auckland-Singapore. This route is only operated by the Airbus A380 during summer. As usual on Singapore Airlines, the flight was amazing, the FA were very nice, the plane was super spacious and the food was great! Always a pleasure to travel with them! I also had the chance to visit Changi for a few hours: swimming pool, shops, restaurants, gardens... what an amazing place! Hope you'll enjoy it, and see you in the sky! *** FLIGHT INFORMATIONS *** Airline: Singapore Airlines SQ SIA Aircraft: Airbus A380-841 Registration number: 9V-SKB (second ever delivered A380!) Delivery date: January 11, 2008 Flight Number: SQ286 Date: 13.01.2015 Flight duration: 9h40 -

Singapore Airlines Premium Economy Class - The Unveil Event
Singapore Airlines is proud to unveil the new Premium Economy Class at a launch event held on 21 May 2015 in Singapore. Now, be among the first to experience A Great New Way to Fly - book today: www.siapremiumeconomy.com -

101 East - Singapore's economy - Part 1
Subscribe to our channel http://bit.ly/AJSubscribe Some speculate that Singapore could take years to recover from the impact of the global economic downturn. Tharman Shanmugaratnam, Singapore's finance minister, talks to 101 East about the challenges facing Singapore's economy. At Al Jazeera English, we focus on people and events that affect people's lives. We bring topics to light that often go under-reported, listening to all sides of the story and giving a 'voice to the voiceless.' Reaching more than 270 million households in over 140 countries across the globe, our viewers trust Al Jazeera English to keep them informed, inspired, and entertained. Our impartial, fact-based reporting wins worldwide praise and respect. It is our unique brand of journalism that the world has come to rely... -

SINGAPORE AIRLINES NEW PREMIUM ECONOMY
Singapore Airlines are introducing new premium economy class seating into their fleet. www.thetraveltrunk.net was invited to Heathrow Airport in London to have a close up look at a premium economy cabin in one of its A380 aircraft. The route from London to Singapore will have yet more aircraft fitted with this new class of seating their Boing 777's will also have premium economy seats
Why Singapore became an economic success
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 2:13
- Updated: 26 Mar 2015
- views: 55438
- published: 26 Mar 2015
- views: 55438
SINGAPORE AIRLINES | SINGAPORE-ZURICH | A380 | ECONOMY CLASS
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 13:21
- Updated: 05 Dec 2013
- views: 284571
- published: 05 Dec 2013
- views: 284571
Premium Economy on Singapore Airlines | Full Review! | SYD-SIN-SYD [HD] Inflightexpert
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 24:11
- Updated: 02 Jan 2016
- views: 48426
- published: 02 Jan 2016
- views: 48426
Singapore is world's second fastest growing economy
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 3:41
- Updated: 26 Jul 2013
- views: 1753
- published: 26 Jul 2013
- views: 1753
Singapore Airlines A350-900 | Economy Class Review
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 20:37
- Updated: 19 Apr 2016
- views: 113
- published: 19 Apr 2016
- views: 113
How The PAP Will Crash The Singapore Economy
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 25:58
- Updated: 26 Mar 2014
- views: 6908
- published: 26 Mar 2014
- views: 6908
SINGAPORE AIRLINES AIRBUS A380 AUCKLAND-SINGAPORE ECONOMY CLASS
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 19:44
- Updated: 24 Feb 2015
- views: 56838
- published: 24 Feb 2015
- views: 56838
Singapore Airlines Premium Economy Class - The Unveil Event
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 2:18
- Updated: 21 May 2015
- views: 169996
- published: 21 May 2015
- views: 169996
101 East - Singapore's economy - Part 1
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 12:53
- Updated: 02 May 2009
- views: 16179
- published: 02 May 2009
- views: 16179
SINGAPORE AIRLINES NEW PREMIUM ECONOMY
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 1:58
- Updated: 27 Aug 2015
- views: 26494
- published: 27 Aug 2015
- views: 26494
- Playlist
- Chat
- Playlist
- Chat

Why Singapore became an economic success
- Report rights infringement
- published: 26 Mar 2015
- views: 55438

SINGAPORE AIRLINES | SINGAPORE-ZURICH | A380 | ECONOMY CLASS
- Report rights infringement
- published: 05 Dec 2013
- views: 284571

Premium Economy on Singapore Airlines | Full Review! | SYD-SIN-SYD [HD] Inflightexpert
- Report rights infringement
- published: 02 Jan 2016
- views: 48426

Singapore is world's second fastest growing economy
- Report rights infringement
- published: 26 Jul 2013
- views: 1753

Singapore Airlines A350-900 | Economy Class Review
- Report rights infringement
- published: 19 Apr 2016
- views: 113

How The PAP Will Crash The Singapore Economy
- Report rights infringement
- published: 26 Mar 2014
- views: 6908

SINGAPORE AIRLINES AIRBUS A380 AUCKLAND-SINGAPORE ECONOMY CLASS
- Report rights infringement
- published: 24 Feb 2015
- views: 56838

Singapore Airlines Premium Economy Class - The Unveil Event
- Report rights infringement
- published: 21 May 2015
- views: 169996

101 East - Singapore's economy - Part 1
- Report rights infringement
- published: 02 May 2009
- views: 16179

SINGAPORE AIRLINES NEW PREMIUM ECONOMY
- Report rights infringement
- published: 27 Aug 2015
- views: 26494


