- published: 11 Apr 2015
- views: 104460
-
remove the playlistOptimum
- remove the playlistOptimum
- published: 01 Jun 2016
- views: 935
- published: 21 Oct 2014
- views: 131990
- published: 19 Aug 2014
- views: 49274

Mathematical optimization
In mathematics, computer science and operations research, mathematical optimization (alternatively, optimization or mathematical programming) is the selection of a best element (with regard to some criteria) from some set of available alternatives.
In the simplest case, an optimization problem consists of maximizing or minimizing a real function by systematically choosing input values from within an allowed set and computing the value of the function. The generalization of optimization theory and techniques to other formulations comprises a large area of applied mathematics. More generally, optimization includes finding "best available" values of some objective function given a defined domain (or a set of constraints), including a variety of different types of objective functions and different types of domains.
Optimization problems
An optimization problem can be represented in the following way:
Such a formulation is called an optimization problem or a mathematical programming problem (a term not directly related to computer programming, but still in use for example in linear programming – see History below). Many real-world and theoretical problems may be modeled in this general framework. Problems formulated using this technique in the fields of physics and computer vision may refer to the technique as energy minimization, speaking of the value of the function f as representing the energy of the system being modeled.
This article is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported License, which means that you can copy and modify it as long as the entire work (including additions) remains under this license.
- Loading...

-
 1:44
1:44Top 3 Quảng cáo Sữa Optimum mới nhất - Quảng cáo hay cho bé ăn ngoan
Top 3 Quảng cáo Sữa Optimum mới nhất - Quảng cáo hay cho bé ăn ngoanTop 3 Quảng cáo Sữa Optimum mới nhất - Quảng cáo hay cho bé ăn ngoan
Top 3 Quảng cáo sữa Optimum hay nhất, quảng cáo cho bé ăn ngoan http://sieuthisua247.com/gl001/c2011p/8994/11648/sua-dielac-vinamilk.aspx LH mua sữa giá rẻ nhất Hà Nội: 0973.814.735/ 0973.814.628 - http://sieuthisua247.com SIEUTHISUA247.COM - Sữa Bỉm 247: Tập hợp những VIDEO mới nhất, hay nhất về Dinh dưỡng và chăm sóc sức khoẻ cho Bé và cả gia đình SIEUTHISUA247.COM - Sữa Bỉm 247: Địa chỉ Mua SỮA - BỈM Uy tín, BÁN BUÔN + BÁN LẺ RẺ Nhất Hà Nội Ø Dịch vụ giao hàng tận nhà chuyên nghiệp Ø Quà tặng các hãng sữa đầy đủ. Ø LH đặt sữa 0973.814.735/ 0973.814.628 Ø Xem giá sữa khuyến mại tại: http://sieuthisua247.com/gl001/defaul... Hoặc: https://www.facebook.com/SieuThiSua24... Cam kết 100% Hàng Công ty, chính hãng, Chất lượng đảm bảo Mọi chi tiết Vui lòng Liên hệ: SIEUTHISUA247.COM Hệ thống Siêu thị Sữa - Bán hàng Online & Offline giá rẻ nhất • Chuyên cung cấp Sữa bột - Bỉm - Bình Sữa các loại giá rẻ tận gốc, chiết khấu cao, nhiều ưu đãi cho đại lý • Tư vấn - Hướng dẫn mở Shop Sữa,Cửa hàng Sữa Bỉm Miễn phí ĐC Mua hàng: Số 12, Ngõ 52 Đường Phạm Hùng - Mỹ Đình - Từ Liêm - Hà Nội ( Đối diện Trường Mầm Non Mỹ Đình ) Cách bến xe Mỹ Đình 500m về phía Keangnam ĐT: 0984.394.967 - 0979.400.626 - 0978.054.550 Email: sieuthisua247@gmail.com Yahoo: sieuthisua247 Website: sieuthisua247.com - sieuthithuoc247.com - thucphamchucnang247.com ------------------------------------ -
 0:46
0:46Quảng cáo Vinamilk - Sữa bột cao cấp Optimum Gold 4 (45s)
Quảng cáo Vinamilk - Sữa bột cao cấp Optimum Gold 4 (45s) -
 3:48
3:48Bé tập đếm Quảng cáo sữa bột cao cấp Optimum Gold mới nhất 2015
Bé tập đếm Quảng cáo sữa bột cao cấp Optimum Gold mới nhất 2015Bé tập đếm Quảng cáo sữa bột cao cấp Optimum Gold mới nhất 2015
-
 1:01
1:01Optimum: Our Anthem
Optimum: Our AnthemOptimum: Our Anthem
Hello, Tri-State Area. We’re Optimum, and we’re bringing you closer to the content you love. #LetsConnectMore -
 3:21
3:21OPTIMUM - Lately Baby (feat. BRIANNA)
OPTIMUM - Lately Baby (feat. BRIANNA)OPTIMUM - Lately Baby (feat. BRIANNA)
"Lately Baby" Music by Cristian Tarcea & Theodoros Popa Lyrics by Cristian Tarcea & Bianca Nita (Brianna) Buy on iTunes : https://itunes.apple.com/ie/album/lately-baby-feat.-brianna/id934102526 Licensing : office[at]thrace-music.com https://www.facebook.com/weareoptimum https://www.facebook.com/briannamusicofficial Contact (Cristian Tarcea) : christhrace@gmail.com Management & Booking : +40721263042 http://thrace-music.com http://facebook.com/thracemusic Download Extended : http://www61.zippyshare.com/v/31740190/file.html Produced by Thrace Music Photo cover by Irina Munteanu (Skipped Heart Beats) http://www.facebook.com/skippedheartbeats ***DO NOT RE-UPLOAD !*** **Any other video will be deleted. All rights reserved. ©&Ⓟ 2014 TMC (Thrace Music Company) http://thrace-music.com -
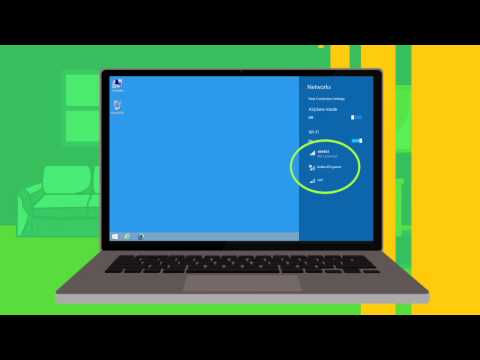 7:47
7:47Tutorial: How to Configure Your Optimum Smart Router
Tutorial: How to Configure Your Optimum Smart RouterTutorial: How to Configure Your Optimum Smart Router
Cool! You just got your new Optimum Online smart router. Now let's help you set it up. Watch this tutorial for instructions, and visit us on Ch. 900, or at https://www.optimum.net/support/ for more helpful solutions. -
 0:31
0:31Vinamilk Dielac Optimum TVC 30s.mov
Vinamilk Dielac Optimum TVC 30s.movVinamilk Dielac Optimum TVC 30s.mov
-
 25:14
25:14Optimum D180x300 lathe project
Optimum D180x300 lathe project -
 2:22
2:22Optimum Nutrition | Quality Supplements
Optimum Nutrition | Quality Supplements -
 1:01
1:01Optimum Triple Play Commercial -- Yeah, it's THAT one!
Optimum Triple Play Commercial -- Yeah, it's THAT one!
Optimum
ALBUMS
- Aerotropolis released: 2013
- Night Slugs Allstars released: 2010
- Night Slugs Allstars, Volume 1 released: 2010
- Modeselektion, Volume 01 released: 2010
- Aqueous Cream / Ampersand released: 2010
- Max Power released: 2010
Aerotropolis
Released 2013- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Mise en place
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Beach Mode (Keep It Simple)
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Mr Cake
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Practice Beats
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Eternal Mode
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Completion V.3
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Manchego
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Let a Smile Be (Y)our Umbrella
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Lights Are Forever
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Mega Church
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Cryo
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Backhand Winners
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen You Won't Find It There
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Zen Sizzle
Night Slugs Allstars, Volume 1
Released 2010- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Square One VIP
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Golds to Get
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen IRL (Bok Bok remix)
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Bust Broke
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Stand Up
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Arpjam
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Seasons
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Liberation Front
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Reclash (dub)
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Broken Embrace
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen (Baby I Don't Know) What You Want
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Booty Slammer
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Wut
Modeselektion, Volume 01
Released 2010- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Das Geheimnis
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen The Unspoken
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen The Assistant Manager
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen The Good Star
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Bierholer
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen The Wind Up
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Pussy Posse
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Space Station Love Affair
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen With Bag and Baggage
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen King of Clubs
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Lyrate
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Hum
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen VW Jetta
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Pitter
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Explorer
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Say Stupid Things
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Kristall
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Pepper Spray (Capsicum edit)
-

Top 3 Quảng cáo Sữa Optimum mới nhất - Quảng cáo hay cho bé ăn ngoan
Top 3 Quảng cáo sữa Optimum hay nhất, quảng cáo cho bé ăn ngoan http://sieuthisua247.com/gl001/c2011p/8994/11648/sua-dielac-vinamilk.aspx LH mua sữa giá rẻ nhất Hà Nội: 0973.814.735/ 0973.814.628 - http://sieuthisua247.com SIEUTHISUA247.COM - Sữa Bỉm 247: Tập hợp những VIDEO mới nhất, hay nhất về Dinh dưỡng và chăm sóc sức khoẻ cho Bé và cả gia đình SIEUTHISUA247.COM - Sữa Bỉm 247: Địa chỉ Mua SỮA - BỈM Uy tín, BÁN BUÔN + BÁN LẺ RẺ Nhất Hà Nội Ø Dịch vụ giao hàng tận nhà chuyên nghiệp Ø Quà tặng các hãng sữa đầy đủ. Ø LH đặt sữa 0973.814.735/ 0973.814.628 Ø Xem giá sữa khuyến mại tại: http://sieuthisua247.com/gl001/defaul... Hoặc: https://www.facebook.com/SieuThiSua24... Cam kết 100% Hàng Công ty, chính hãng, Chất lượng đảm bảo Mọi chi tiết Vui lòng Liên hệ: SIEUTHISUA247.COM Hệ thống S... -

-

Bé tập đếm Quảng cáo sữa bột cao cấp Optimum Gold mới nhất 2015
-

Optimum: Our Anthem
Hello, Tri-State Area. We’re Optimum, and we’re bringing you closer to the content you love. #LetsConnectMore -

OPTIMUM - Lately Baby (feat. BRIANNA)
"Lately Baby" Music by Cristian Tarcea & Theodoros Popa Lyrics by Cristian Tarcea & Bianca Nita (Brianna) Buy on iTunes : https://itunes.apple.com/ie/album/lately-baby-feat.-brianna/id934102526 Licensing : office[at]thrace-music.com https://www.facebook.com/weareoptimum https://www.facebook.com/briannamusicofficial Contact (Cristian Tarcea) : christhrace@gmail.com Management & Booking : +40721263042 http://thrace-music.com http://facebook.com/thracemusic Download Extended : http://www61.zippyshare.com/v/31740190/file.html Produced by Thrace Music Photo cover by Irina Munteanu (Skipped Heart Beats) http://www.facebook.com/skippedheartbeats ***DO NOT RE-UPLOAD !*** **Any other video will be deleted. All rights reserved. ©&Ⓟ 2014 TMC (Thrace Music Company) http://thrace-music.com -

Tutorial: How to Configure Your Optimum Smart Router
Cool! You just got your new Optimum Online smart router. Now let's help you set it up. Watch this tutorial for instructions, and visit us on Ch. 900, or at https://www.optimum.net/support/ for more helpful solutions. -

Vinamilk Dielac Optimum TVC 30s.mov
-

-

-

Top 3 Quảng cáo Sữa Optimum mới nhất - Quảng cáo hay cho bé ăn ngoan
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 1:44
- Updated: 11 Apr 2015
- views: 104460
- published: 11 Apr 2015
- views: 104460
Quảng cáo Vinamilk - Sữa bột cao cấp Optimum Gold 4 (45s)
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 0:46
- Updated: 27 Mar 2015
- views: 1459347
Bé tập đếm Quảng cáo sữa bột cao cấp Optimum Gold mới nhất 2015
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 3:48
- Updated: 14 Nov 2015
- views: 24599
- published: 14 Nov 2015
- views: 24599
Optimum: Our Anthem
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 1:01
- Updated: 01 Jun 2016
- views: 935
- published: 01 Jun 2016
- views: 935
OPTIMUM - Lately Baby (feat. BRIANNA)
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 3:21
- Updated: 21 Oct 2014
- views: 131990
- published: 21 Oct 2014
- views: 131990
Tutorial: How to Configure Your Optimum Smart Router
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 7:47
- Updated: 19 Aug 2014
- views: 49274
- published: 19 Aug 2014
- views: 49274
Vinamilk Dielac Optimum TVC 30s.mov
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 0:31
- Updated: 28 May 2012
- views: 816719
- published: 28 May 2012
- views: 816719
Optimum D180x300 lathe project
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 25:14
- Updated: 22 Apr 2013
- views: 46119
Optimum Nutrition | Quality Supplements
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 2:22
- Updated: 06 Aug 2014
- views: 2274535
Optimum Triple Play Commercial -- Yeah, it's THAT one!
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 1:01
- Updated: 27 Mar 2008
- views: 74430
- Playlist
- Chat
- Playlist
- Chat

Top 3 Quảng cáo Sữa Optimum mới nhất - Quảng cáo hay cho bé ăn ngoan
- Report rights infringement
- published: 11 Apr 2015
- views: 104460

Quảng cáo Vinamilk - Sữa bột cao cấp Optimum Gold 4 (45s)
- Report rights infringement
- published: 27 Mar 2015
- views: 1459347

Bé tập đếm Quảng cáo sữa bột cao cấp Optimum Gold mới nhất 2015
- Report rights infringement
- published: 14 Nov 2015
- views: 24599

Optimum: Our Anthem
- Report rights infringement
- published: 01 Jun 2016
- views: 935

OPTIMUM - Lately Baby (feat. BRIANNA)
- Report rights infringement
- published: 21 Oct 2014
- views: 131990

Tutorial: How to Configure Your Optimum Smart Router
- Report rights infringement
- published: 19 Aug 2014
- views: 49274

Vinamilk Dielac Optimum TVC 30s.mov
- Report rights infringement
- published: 28 May 2012
- views: 816719

Optimum D180x300 lathe project
- Report rights infringement
- published: 22 Apr 2013
- views: 46119

Optimum Nutrition | Quality Supplements
- Report rights infringement
- published: 06 Aug 2014
- views: 2274535

Optimum Triple Play Commercial -- Yeah, it's THAT one!
- Report rights infringement
- published: 27 Mar 2008
- views: 74430
What happened in Turkey? Everything we know about military coup attempt to overthrow Erdogan
Edit The Independent 16 Jul 2016Turkish coup attempt largely over, says government
Edit The Irish Times 16 Jul 2016Nice Terrorist Attack: At Least 77 Dead, Police Kill Suspect
Edit WorldNews.com 15 Jul 2016Honor Killing: Pakistani Social Media Star Strangled to Death by brother
Edit Voa News 16 Jul 2016Tom Brady Ends Four-Game Suspension Fight
Edit Newsday 16 Jul 2016Pence: 'I Accept Your Invitation to Run, Serve'
Edit Newsday 16 Jul 2016Maintenance: Regular check-ups key to building immunity
Edit Indian Express 16 Jul 2016How to watch the LA Galaxy vs. Houston Dynamo match in English on UniMás with SAP (Los Angeles Galaxy)
Edit Public Technologies 16 Jul 2016Diet diary: Strenuous workout, low protein intake weaken immunity
Edit Indian Express 16 Jul 2016Land Rover U.S. Eventing Team Finishes Sixth at CICO3* Aachen (USEF - United States Equestrian Federation Inc)
Edit Public Technologies 16 Jul 2016Africa: Mobile App for Rain Forecasts Raising Farmers' Yields
Edit All Africa 15 Jul 2016The freedom of cutting down on choices
Edit Financial Times 15 Jul 2016Obama: 'Heavier Hearts' For Nice
Edit Newsday 15 Jul 2016- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- Next page »







