- published: 29 Sep 2016
- views: 73933
-
remove the playlistElectric Charge
-
remove the playlistLatest Videos
-
remove the playlistLongest Videos
- remove the playlistElectric Charge
- remove the playlistLatest Videos
- remove the playlistLongest Videos
- published: 15 May 2014
- views: 33479
- published: 04 Apr 2008
- views: 78613
- published: 23 Jan 2010
- views: 860446
- published: 13 Feb 2015
- views: 168027
- published: 19 Jul 2014
- views: 17414
- published: 10 Nov 2011
- views: 34056

Electric charge
Electric charge is the physical property of matter that causes it to experience a force when placed in an electromagnetic field. There are two types of electric charges: positive and negative. Like charges repel and unlike attract. An object is negatively charged if it has an excess of electrons, and is otherwise positively charged or uncharged. The SI derived unit of electric charge is the coulomb (C). In electrical engineering, however, it is also common to use the ampere-hour (Ah), and in chemistry it is common to use the elementary charge (e) as a unit. The symbol Q often denotes charge. Early knowledge of how charged substances interact is now called classical electrodynamics, and is still accurate for problems that don't require consideration of quantum effects.
The electric charge is a fundamental conserved property of some subatomic particles, which determines their electromagnetic interaction. Electrically charged matter is influenced by, and produces, electromagnetic fields. The interaction between a moving charge and an electromagnetic field is the source of the electromagnetic force, which is one of the four fundamental forces (See also: magnetic field).
This article is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported License, which means that you can copy and modify it as long as the entire work (including additions) remains under this license.
- Loading...

-
 9:42
9:42Electric Charge: Crash Course Physics #25
Electric Charge: Crash Course Physics #25Electric Charge: Crash Course Physics #25
Moving on to our unit on the Physics of Electricity, it's time to talk about charge. What is charge? Is there a positive and negative charge? What do those things mean? In this episode, Shini talks about electrostatic forces, electrical charge, Coulomb's law, and the force between charged particles. Get your own Crash Course Physics mug from DFTBA: http://store.dftba.com/products/crash... The Latest from PBS Digital Studios: https://www.youtube.com/playlist?list... -- Produced in collaboration with PBS Digital Studios: http://youtube.com/pbsdigitalstudios -- Want to find Crash Course elsewhere on the internet? Facebook - http://www.facebook.com/YouTubeCrashC... Twitter - http://www.twitter.com/TheCrashCourse Tumblr - http://thecrashcourse.tumblr.com Support CrashCourse on Patreon: http://www.patreon.com/crashcourse CC Kids: http://www.youtube.com/crashcoursekids -
 4:19
4:19Electric Charge
Electric ChargeElectric Charge
006 - Electric Charge In this video Paul Andersen introduces electric charge. Electric charge has been studies by humans and was generalized by scientists such as Benjamin Franklin. The amount of charge in a system is conserved but individual charges can move through a conductor as current. Do you speak another language? Help me translate my videos: http://www.bozemanscience.com/translations/ Music Attribution Title: String Theory Artist: Herman Jolly http://sunsetvalley.bandcamp.com/track/string-theory All of the images are licensed under creative commons and public domain licensing: Dilmen, Nevit. English: A Lemon Battery Is a Device Used in Experiments Proposed in Many Science Textbooks around the World, First Discovered by Josh Balestri. It Is Made by Inserting Two Different Metallic Objects, for Example a Zinc and a Copper Strip, into a Lemon. The Copper Stripserves as the Positive Electrode or Cathode and Zinc Strip as the Electron-Producing Negative Electrode or Anode. These Two Objects Work as Electrodes, Causing an Electrochemical Reaction Which Generates a Small Potential Difference. Red Wire: Positive Electrode. Black Wire: Negative Electrode. White Wire: Connector., 2011. Own work. http://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Lemon_batteries_circuit_1390001_nevit.jpg. en.wikipedia, Akimbomidget Original uploader was Akimbomidget at. English: Made by Akimbomidget... For Wikipedia Usage., June 10, 2007. Transferred from en.wikipedia; transferred to Commons by User:Sreejithk2000 using CommonsHelper. http://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:A_Cell_and_a_Battery_symbol.svg. "File:Benjamin West, English (born America) - Benjamin Franklin Drawing Electricity from the Sky - Google Art Project.jpg." Wikipedia, the Free Encyclopedia. Accessed May 3, 2014. http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/File:Benjamin_West,_English_(born_America)_-_Benjamin_Franklin_Drawing_Electricity_from_the_Sky_-_Google_Art_Project.jpg. Hariadhi. English: A Feather of Chicken Taken from Photograph Studio for Study, November 6, 2007. Own work. http://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Feather2.jpg. Libricool. Deutsch: Stola Aus Golden Island Fuchs, 2009. Own work. http://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Golden_Island_Fox_fur_cape_1.jpg. Martin, David. Portrait of Benjamin Franklin. Oil on canvas on panel, 1767. White House. http://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Benjamin_Franklin_1767.jpg. Sebakoamber. English: Borneo Amber from Beradai Coal Mine, Merit-Pila, Sarawak, Malaysia. This Amber Is Dated to the Tertiary Period, 15-17 Millions Years Old. Apparently This Amber Was Found in a Coal Seam Which Is Dated to the Middle Miocene Epoch. Very Tough but Also Very Difficult to Bring the Mirror-like Polished. This Variety Can Withstand a Lot of Impact on Hard Floor., November 27, 2008. Own work. http://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Borneo_amber_from_Beradai_Coal_Mine,_Merit-Pila,_Sarawak.jpg. USA, Ken Bosma from Green Valley, Arizona. You Should Get a Charge out of This., August 31, 2008. Electric Slide Uploaded by Pieter Kuiper. http://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Static_slide.jpg. -
 2:47
2:47Basics of Electric Charge
Basics of Electric ChargeBasics of Electric Charge
An educational segment about electrons, protons, electrostatics, and the Coulomb. Helpful articles: http://www.matrix.edu.au/6-common-mistakes-hsc-physics-students-make-in-exams/ http://www.matrix.edu.au/how-to-achieve-99-95-atar/ http://www.matrix.edu.au/chemical-reactions-year-12-chemistry-students-must-k... http://www.matrix.edu.au/all-about-atar-scaling/ -
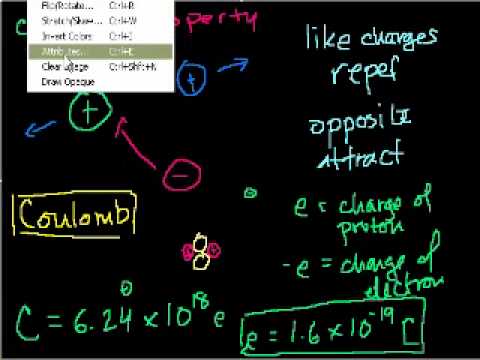 14:02
14:02Electrostatics (part 1): Introduction to Charge and Coulomb's Law
Electrostatics (part 1): Introduction to Charge and Coulomb's LawElectrostatics (part 1): Introduction to Charge and Coulomb's Law
Introduction to Charge and Coulomb's Law (video from May 2008 that I forgot to upload) More free lessons at: http://www.khanacademy.org/video?v=NXMgvrS8Gr8 -
 47:14
47:148.02x - Lect 1 - Electric Charges and Forces - Coulomb's Law - Polarization
8.02x - Lect 1 - Electric Charges and Forces - Coulomb's Law - Polarization8.02x - Lect 1 - Electric Charges and Forces - Coulomb's Law - Polarization
What holds our world together? Electric Charges (Historical), Polarization, Electric Force, Coulomb's Law, Van de Graaff, Great Demos Assignments Lecture 1, 2, 3, 4 and 5: http://freepdfhosting.com/2cb4aad955.pdf Solutions Lecture 1, 2, 3, 4 and 5: http://freepdfhosting.com/75b96693f2.pdf -
 15:53
15:53Introduction to Electric Charge (Friction, Conduction, Induction) | Doc Physics
Introduction to Electric Charge (Friction, Conduction, Induction) | Doc PhysicsIntroduction to Electric Charge (Friction, Conduction, Induction) | Doc Physics
This shows some things that one can do with electrons. -
 4:12
4:12The Flow of Electric Charge
The Flow of Electric Charge -
 64:47
64:47Electric Charge and Electric Field Part 1
Electric Charge and Electric Field Part 1Electric Charge and Electric Field Part 1
Electricity and magnetism. Charge, atoms, Coulomb force, vector, dipole, electric field. -
 8:34
8:34Electric Charges
Electric ChargesElectric Charges
In this video, I will demonstrate some realistic experiments that many children may have done as a game, but they have never asked the reason. First, I will show three simple experiments that they can easily do at home: 1- Rub two balloons on my hair. When I close them, they repel each other 2- Rub a balloon on my hair. Then roll a soda can toward the balloon. 3- This time, I will rub a balloon through my hair, and then try to bend a stream of water using it to different directions Now that they are excited, I will start explaining the reason. I will give a simple introduction about the positive and negative charges. Then I will draw how the charges are placed on the balloon, and how they redistribute the charges on nearby objects. -
 106:54
106:54XII_1.Electric charge(2013)
XII_1.Electric charge(2013)
-

Electric Charge: Crash Course Physics #25
Moving on to our unit on the Physics of Electricity, it's time to talk about charge. What is charge? Is there a positive and negative charge? What do those things mean? In this episode, Shini talks about electrostatic forces, electrical charge, Coulomb's law, and the force between charged particles. Get your own Crash Course Physics mug from DFTBA: http://store.dftba.com/products/crash... The Latest from PBS Digital Studios: https://www.youtube.com/playlist?list... -- Produced in collaboration with PBS Digital Studios: http://youtube.com/pbsdigitalstudios -- Want to find Crash Course elsewhere on the internet? Facebook - http://www.facebook.com/YouTubeCrashC... Twitter - http://www.twitter.com/TheCrashCourse Tumblr - http://thecrashcourse.tumblr.com Support CrashCourse on Patreon: ...
published: 29 Sep 2016 -

Electric Charge
006 - Electric Charge In this video Paul Andersen introduces electric charge. Electric charge has been studies by humans and was generalized by scientists such as Benjamin Franklin. The amount of charge in a system is conserved but individual charges can move through a conductor as current. Do you speak another language? Help me translate my videos: http://www.bozemanscience.com/translations/ Music Attribution Title: String Theory Artist: Herman Jolly http://sunsetvalley.bandcamp.com/track/string-theory All of the images are licensed under creative commons and public domain licensing: Dilmen, Nevit. English: A Lemon Battery Is a Device Used in Experiments Proposed in Many Science Textbooks around the World, First Discovered by Josh Balestri. It Is Made by Inserting Two Different M...
published: 15 May 2014 -

Basics of Electric Charge
An educational segment about electrons, protons, electrostatics, and the Coulomb. Helpful articles: http://www.matrix.edu.au/6-common-mistakes-hsc-physics-students-make-in-exams/ http://www.matrix.edu.au/how-to-achieve-99-95-atar/ http://www.matrix.edu.au/chemical-reactions-year-12-chemistry-students-must-k... http://www.matrix.edu.au/all-about-atar-scaling/
published: 04 Apr 2008 -

Electrostatics (part 1): Introduction to Charge and Coulomb's Law
Introduction to Charge and Coulomb's Law (video from May 2008 that I forgot to upload) More free lessons at: http://www.khanacademy.org/video?v=NXMgvrS8Gr8
published: 23 Jan 2010 -

8.02x - Lect 1 - Electric Charges and Forces - Coulomb's Law - Polarization
What holds our world together? Electric Charges (Historical), Polarization, Electric Force, Coulomb's Law, Van de Graaff, Great Demos Assignments Lecture 1, 2, 3, 4 and 5: http://freepdfhosting.com/2cb4aad955.pdf Solutions Lecture 1, 2, 3, 4 and 5: http://freepdfhosting.com/75b96693f2.pdf
published: 13 Feb 2015 -

Introduction to Electric Charge (Friction, Conduction, Induction) | Doc Physics
This shows some things that one can do with electrons.
published: 13 Dec 2012 -

-

Electric Charge and Electric Field Part 1
Electricity and magnetism. Charge, atoms, Coulomb force, vector, dipole, electric field.
published: 19 Jul 2014 -

Electric Charges
In this video, I will demonstrate some realistic experiments that many children may have done as a game, but they have never asked the reason. First, I will show three simple experiments that they can easily do at home: 1- Rub two balloons on my hair. When I close them, they repel each other 2- Rub a balloon on my hair. Then roll a soda can toward the balloon. 3- This time, I will rub a balloon through my hair, and then try to bend a stream of water using it to different directions Now that they are excited, I will start explaining the reason. I will give a simple introduction about the positive and negative charges. Then I will draw how the charges are placed on the balloon, and how they redistribute the charges on nearby objects.
published: 10 Nov 2011 -

Electric Charge: Crash Course Physics #25
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 9:42
- Updated: 29 Sep 2016
- views: 73933
- published: 29 Sep 2016
- views: 73933
Electric Charge
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 4:19
- Updated: 15 May 2014
- views: 33479
- published: 15 May 2014
- views: 33479
Basics of Electric Charge
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 2:47
- Updated: 04 Apr 2008
- views: 78613
- published: 04 Apr 2008
- views: 78613
Electrostatics (part 1): Introduction to Charge and Coulomb's Law
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 14:02
- Updated: 23 Jan 2010
- views: 860446
- published: 23 Jan 2010
- views: 860446
8.02x - Lect 1 - Electric Charges and Forces - Coulomb's Law - Polarization
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 47:14
- Updated: 13 Feb 2015
- views: 168027
- published: 13 Feb 2015
- views: 168027
Introduction to Electric Charge (Friction, Conduction, Induction) | Doc Physics
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 15:53
- Updated: 13 Dec 2012
- views: 28047
- published: 13 Dec 2012
- views: 28047
The Flow of Electric Charge
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 4:12
- Updated: 22 May 2013
- views: 14126
Electric Charge and Electric Field Part 1
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 64:47
- Updated: 19 Jul 2014
- views: 17414
- published: 19 Jul 2014
- views: 17414
Electric Charges
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 8:34
- Updated: 10 Nov 2011
- views: 34056
- published: 10 Nov 2011
- views: 34056
XII_1.Electric charge(2013)
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 106:54
- Updated: 26 Mar 2013
- views: 149158
-

electric charges
published: 08 Sep 2016 -

Electric Charge
published: 14 May 2013 -

Electric charge
This is a video on electric charge and charge carriers.
published: 23 Jul 2014 -

Electric Charge 3
published: 16 Aug 2016 -

Electric Charge and Electric Field
published: 07 Sep 2016 -

Electrical Charge Project
published: 19 Sep 2016 -

ELECTROSTATICS (electric charge)
published: 05 Nov 2016 -

AIM 9 Electrical Charge
published: 31 May 2016 -

Electric charge and coulomb's law
published: 13 Mar 2015 -

ELECTRICAL CHARGES AND FIELDS
published: 06 May 2015
electric charges
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 4:32
- Updated: 08 Sep 2016
- views: 0
- published: 08 Sep 2016
- views: 0
Electric Charge
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 1:10:42
- Updated: 14 May 2013
- views: 3300
- published: 14 May 2013
- views: 3300
Electric charge
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 23:14
- Updated: 23 Jul 2014
- views: 94
- published: 23 Jul 2014
- views: 94
Electric Charge 3
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 4:37
- Updated: 16 Aug 2016
- views: 0
- published: 16 Aug 2016
- views: 0
Electric Charge and Electric Field
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 47:59
- Updated: 07 Sep 2016
- views: 1
- published: 07 Sep 2016
- views: 1
Electrical Charge Project
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 0:22
- Updated: 19 Sep 2016
- views: 5
- published: 19 Sep 2016
- views: 5
ELECTROSTATICS (electric charge)
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 1:03:23
- Updated: 05 Nov 2016
- views: 8
- published: 05 Nov 2016
- views: 8
AIM 9 Electrical Charge
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 11:36
- Updated: 31 May 2016
- views: 15
- published: 31 May 2016
- views: 15
Electric charge and coulomb's law
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 22:50
- Updated: 13 Mar 2015
- views: 358
- published: 13 Mar 2015
- views: 358
ELECTRICAL CHARGES AND FIELDS
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 2:39:00
- Updated: 06 May 2015
- views: 60
- published: 06 May 2015
- views: 60
-

-

Discussion With CPI Narayana On Electricity Charges
Discussion With CPI Narayana On Electricity Charges
published: 05 Apr 2013 -

Electric charges and fields NCERT exercise part 1
published: 12 Mar 2016 -

Electric Charge and Electric Field Part 1
Electricity and magnetism. Charge, atoms, Coulomb force, vector, dipole, electric field.
published: 19 Jul 2014 -

-

Electric Charge and Motion
Electric charges and their response to external electric fields; the electric dipole and its response to external electric fields.
published: 28 Jan 2015
XII Physics Lessons- Electric Charge
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 1:25:06
- Updated: 05 Apr 2014
- views: 188
Discussion With CPI Narayana On Electricity Charges
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 36:10
- Updated: 05 Apr 2013
- views: 296
Electric charges and fields NCERT exercise part 1
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 37:01
- Updated: 12 Mar 2016
- views: 28
- published: 12 Mar 2016
- views: 28
Electric Charge and Electric Field Part 1
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 1:04:47
- Updated: 19 Jul 2014
- views: 17467
- published: 19 Jul 2014
- views: 17467
XII-1.01.Electric Charge (2014) Pradeep Kshetrapal Physics
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 1:09:27
- Updated: 12 Apr 2014
- views: 183154
Electric Charge and Motion
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 51:30
- Updated: 28 Jan 2015
- views: 317
- published: 28 Jan 2015
- views: 317
- Playlist
- Chat
- Playlist
- Chat

Electric Charge: Crash Course Physics #25
- Report rights infringement
- published: 29 Sep 2016
- views: 73933

Electric Charge
- Report rights infringement
- published: 15 May 2014
- views: 33479

Basics of Electric Charge
- Report rights infringement
- published: 04 Apr 2008
- views: 78613

Electrostatics (part 1): Introduction to Charge and Coulomb's Law
- Report rights infringement
- published: 23 Jan 2010
- views: 860446

8.02x - Lect 1 - Electric Charges and Forces - Coulomb's Law - Polarization
- Report rights infringement
- published: 13 Feb 2015
- views: 168027

Introduction to Electric Charge (Friction, Conduction, Induction) | Doc Physics
- Report rights infringement
- published: 13 Dec 2012
- views: 28047

The Flow of Electric Charge
- Report rights infringement
- published: 22 May 2013
- views: 14126

Electric Charge and Electric Field Part 1
- Report rights infringement
- published: 19 Jul 2014
- views: 17414

Electric Charges
- Report rights infringement
- published: 10 Nov 2011
- views: 34056

XII_1.Electric charge(2013)
- Report rights infringement
- published: 26 Mar 2013
- views: 149158
- Playlist
- Chat

electric charges
- Report rights infringement
- published: 08 Sep 2016
- views: 0

Electric Charge
- Report rights infringement
- published: 14 May 2013
- views: 3300

Electric charge
- Report rights infringement
- published: 23 Jul 2014
- views: 94

Electric Charge 3
- Report rights infringement
- published: 16 Aug 2016
- views: 0

Electric Charge and Electric Field
- Report rights infringement
- published: 07 Sep 2016
- views: 1

Electrical Charge Project
- Report rights infringement
- published: 19 Sep 2016
- views: 5

ELECTROSTATICS (electric charge)
- Report rights infringement
- published: 05 Nov 2016
- views: 8

AIM 9 Electrical Charge
- Report rights infringement
- published: 31 May 2016
- views: 15

Electric charge and coulomb's law
- Report rights infringement
- published: 13 Mar 2015
- views: 358

ELECTRICAL CHARGES AND FIELDS
- Report rights infringement
- published: 06 May 2015
- views: 60
- Playlist
- Chat

XII Physics Lessons- Electric Charge
- Report rights infringement
- published: 05 Apr 2014
- views: 188

Discussion With CPI Narayana On Electricity Charges
- Report rights infringement
- published: 05 Apr 2013
- views: 296

Electric charges and fields NCERT exercise part 1
- Report rights infringement
- published: 12 Mar 2016
- views: 28

Electric Charge and Electric Field Part 1
- Report rights infringement
- published: 19 Jul 2014
- views: 17467

XII-1.01.Electric Charge (2014) Pradeep Kshetrapal Physics
- Report rights infringement
- published: 12 Apr 2014
- views: 183154

Electric Charge and Motion
- Report rights infringement
- published: 28 Jan 2015
- views: 317
Admire Trump’s Honor – What Democrats Get Wrong About Donald Trump And His Followers
Edit WorldNews.com 18 Nov 2016Farmers Shocked By What Was Inside Captured Snake
Edit Opposing Views 17 Nov 2016Man who dissolved in Yellowstone hot spring slipped while checking temperature to take bath
Edit Chicago Tribune 18 Nov 2016Trump Names Sessions, Pompeo For Attorney General, CIA
Edit WorldNews.com 18 Nov 2016Pakistan's war exercise near India border flaunts China-made attack helicopter
Edit International Business Times 18 Nov 2016LG&E; Bringing New Energy to Butchertown (PPL Corporation)
Edit Public Technologies 18 Nov 2016LG&E; bringing new energy to Butchertown (LG&E; and KU Energy LLC)
Edit Public Technologies 18 Nov 2016Plug-in electric vehicles: A consumer wish list (University of Michigan)
Edit Public Technologies 18 Nov 2016PSC Approves Change in KCPL-GMO RESRAM Charge (Missouri Public Service Commission)
Edit Public Technologies 18 Nov 2016Smart Fortwo Electric Drive impressions: an ideal city commuter
Edit TechRadar 18 Nov 2016Eco-friendly car service opens
Edit NJ dot com 18 Nov 20162 EV chargers added at airport center
Edit Star Advertiser 18 Nov 2016Sierra Club Files Antitrust Complaint Concerning the NEXUS Gas Pipeline (Sierra Club)
Edit Public Technologies 18 Nov 2016Eversource still sunny on solar
Edit Boston Herald 18 Nov 2016ATCO Is Giving the Gift of Free Energy in January
Edit Stockhouse 18 Nov 2016A bicycle that charges up deliveries for startups
Edit The Times of India 18 Nov 2016Extra charges fund AEP reliability-improvement projects; some question value
Edit The Columbus Dispatch 18 Nov 2016Tesla Vote Favoring a SolarCity Merger Won't Stop Likely Political Headwinds
Edit The Street 18 Nov 2016- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- Next page »








