- published: 28 Aug 2015
- views: 3104612
-
remove the playlistNote
- remove the playlistNote
- published: 07 May 2016
- views: 9233
- published: 13 Aug 2015
- views: 1750928
- published: 06 May 2016
- views: 1750
- published: 20 Aug 2015
- views: 1178927
- published: 06 May 2016
- views: 4784
- published: 04 Mar 2016
- views: 4088
- published: 06 May 2016
- views: 1834
- published: 23 Nov 2015
- views: 336806
- published: 18 Sep 2015
- views: 1879646
- published: 24 Feb 2016
- views: 2650
Abnormality, in the vivid sense of something deviating from the normal or differing from the typical (such as an aberration), is a subjectively defined behavioral characteristic, assigned to those with rare or dysfunctional conditions. Defining who is normal or abnormal is a contentious issue in abnormal psychology.
A common approach to defining abnormality is a Multi-Criteria approach, where all definitions of abnormality are used to determine whether an individuals behavior is abnormal. For example, if an individual is engaging in a particular behavior that is preventing them from 'functioning', breaks a social norm and is statistically infrequent, then psychologists would be prepared to define this individual's behavior as abnormal. A good example of an abnormal behavior assessed by a multi-criteria approach is depression: it is commonly seen as a deviation from ideal mental stability, it often stops the individual from 'functioning' a normal life, and, although it is a relatively common mental disorder, it is still statistically infrequent; most people will not experience significant major depressive disorder in their lifetime 3.
This article is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported License, which means that you can copy and modify it as long as the entire work (including additions) remains under this license.

In music, the term note has two primary meanings:
Notes are the "atoms" of much Western music: discretizations of musical phenomena that facilitate performance, comprehension, and analysis.
The term "note" can be used in both generic and specific senses: one might say either "the piece 'Happy Birthday to You' begins with two notes having the same pitch," or "the piece begins with two repetitions of the same note." In the former case, one uses "note" to refer to a specific musical event; in the latter, one uses the term to refer to a class of events sharing the same pitch.
Two notes with fundamental frequencies in a ratio of any power of two (e.g. half, twice, or four times) are perceived as very similar. Because of that, all notes with these kinds of relations can be grouped under the same pitch class. In traditional music theory pitch classes are represented by the first seven letters of the Latin alphabet (A, B, C, D, E, F and G) (some countries use other names as in the table below). The eighth note, or octave is given the same name as the first, but has double its frequency. The name octave is also used to indicate the span of notes having a frequency ratio of two. To differentiate two notes that have the same pitch class but fall into different octaves, the system of scientific pitch notation combines a letter name with an Arabic numeral designating a specific octave. For example, the now-standard tuning pitch for most Western music, 440 Hz, is named a′ or A4. There are two formal ways to define each note and octave, the Helmholtz system and the Scientific pitch notation.
This article is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported License, which means that you can copy and modify it as long as the entire work (including additions) remains under this license.
- Loading...

-
 5:01
5:01Samsung Galaxy Note 5 Hammer & Knife Test!
Samsung Galaxy Note 5 Hammer & Knife Test! -
 4:14
4:14Galaxy Note 6 Lite rumors, iPhone 7 Plus smart connector & more - Pocketnow Daily
Galaxy Note 6 Lite rumors, iPhone 7 Plus smart connector & more - Pocketnow DailyGalaxy Note 6 Lite rumors, iPhone 7 Plus smart connector & more - Pocketnow Daily
Stories: - Apple Music subscriptions go 50 percent off for eligible students http://pocketnow.com/2016/05/06/apple-music-student-discount-50-percent - Asus confirms May 30 ‘Zenvolution’ date, ZenFone 3 smartphone family incoming http://pocketnow.com/2016/05/06/asus-zenfone-3-introduction-may-30 - Meet Queen University’s HoloFlex, a flexible smartphone that produces holograms http://pocketnow.com/2016/05/06/holoflex - iPhone 7 Plus Smart Connector may not get to be http://pocketnow.com/2016/05/06/iphone-7-plus-smart-connect-iphone-pro - Wild rumor calls for Samsung Galaxy Note 6 ‘Lite’ with Snapdragon 820, 4GB RAM http://pocketnow.com/2016/05/06/samsung-galaxy-note-6-lite-rumor-4gb-ram Watch today's Pocketnow Daily as we talk about the recent discounts in Apple Music subscriptions. Then we discuss the Asus event for May 30th, and what we can expect from the "Zenvolution." We then talk about about a very interesting flexible smartphone being built by a university. The rumored iPhone 7 smart connector is next as it might not even make the cut. We end today's show taking about the Samsung Galaxy Note 6 Lite and its rumored specs. All this and more after the break. Subscribe: http://www.youtube.com/subscription_center?add_user=Pocketnowvideo http://www.vessel.com/pocketnow About us: Pocketnow has been a key source of mobile technology news and reviews since its establishment in 2000. With offices on three continents, Pocketnow offers round-the-clock coverage of the mobile technology landscape, from smartphones to tablets to wearables. We aim to be your number-one source for mobile tech news, reviews, comparisons, and commentary. If you love mobile as much as we do, be sure to subscribe! Follow us: http://pocketnow.com http://vessel.com/pocketnow http://twitter.com/pocketnow http://facebook.com/pocketnow http://google.com/+pocketnow http://instagram.com/pocketnow -
 6:22
6:22Samsung Galaxy Note 5 - First Look!
Samsung Galaxy Note 5 - First Look!Samsung Galaxy Note 5 - First Look!
Buy at Amazon: http://geni.us/note5 -|- Note 5 Review: http://goo.gl/BKPj5E The Samsung Galaxy Note 5 follows the lead of the Galaxy S6 in design, but brings some nice additions to the general experience. Best Galaxy Note 5 cases: http://www.androidauthority.com/best-galaxy-note-5-cases-636021/ Talk about Android in our forums: http://www.androidauthority.com/community Subscribe to our YouTube channel: http://www.youtube.com/subscription_center?add_user=androidauthority ---------------------------------------------------- Stay connected to Android Authority: - http://www.androidauthority.com - http://google.com/+androidauthority - http://facebook.com/androidauthority/ - http://twitter.com/androidauth/ - http://instagram.com/androidauthority/ Follow the Team: Josh Vergara: https://plus.google.com/+JoshuaVergara Joe Hindy: https://plus.google.com/+JosephHindy Lanh Nguyen: https://plus.google.com/+LanhNguyenFilms Jayce Broda: https://plus.google.com/+JayceBroda Gary Sims: https://plus.google.com/+GarySims Ash Tailor: https://plus.google.com/+AshTailor -
 5:10
5:10Vật Vờ| So sánh đa nhiệm 4GB RAM của Galaxy Note 5 và OPPO F1 Plus
Vật Vờ| So sánh đa nhiệm 4GB RAM của Galaxy Note 5 và OPPO F1 PlusVật Vờ| So sánh đa nhiệm 4GB RAM của Galaxy Note 5 và OPPO F1 Plus
Giới thiệu, so sánh smartphone Galaxy Note 5 và OPPO F1 Plus mở hộp, so sánh,camera,đánh giá,trải nghiệm Galaxy Note 5 và OPPO F1 Plus Các bạn có thể tìm kiếm video mở hộp, đánh giá chi tiết, hiệu năng, thời lượng pin, camera, so sánh, tư vấn nên mua, sản phẩm Galaxy Note 5 và OPPO F1 Plus tại Vật Vờ channel. ** Xem giá bán Galaxy Note 5 Mỹ cũ: http://www.viettablet.com/samsung-galaxy-note-5-cu-like-new-99 ** Video review, trên tay, các sản phẩm điện thoại, giá bán rẻ nhất, cửa hàng mua uy tín nhất, sản phẩm tốt nhất trong tầm giá và các tư vấn, lời khuyên, video so sánh các sản phẩm cần mua, đánh giá sản phẩm công nghệ, điện thoại di động, máy tính bảng, sản phẩm xách tay Hàn Quốc, Nhật Bản, sản phẩm chính hãng. Các video đánh giá này thuộc quyền sở hữu của Vật Vờ. Liên hệ: Fanpage : https://www.facebook.com/reviewdaos Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/xuanvinh1612 Instagram: https://www.instagram.com/vatvo69/ Email: xuanvinh1612@gmail.com (Email chỉ để liên hệ hợp tác, không trả lời các thắc mắc tư vấn tình cảm, yêu đương và sản phẩm. Xin cám ơn.) - Video So sánh tốc độ/hiệu năng Galaxy Note 5 và OPPO F1 Plus - Video So sánh vi xử lí Galaxy Note 5 và OPPO F1 Plus - Video So sánh chi tiết Galaxy Note 5 và OPPO F1 Plus - Video So sánh camera Galaxy Note 5 và OPPO F1 Plus - Tư vấn nên mua Galaxy Note 5 và OPPO F1 Plus - Mua Galaxy Note 5 và OPPO F1 Plus ở đâu uy tín, giá rẻ - Mua/bán Galaxy Note 5 và OPPO F1 Plus rẻ nhất Hà Nội/Hồ Chí Minh - Mua Galaxy Note 5 và OPPO F1 Plus ở đâu xách tay Hàn Quốc/Nhật Bản giá tốt - Review/đánh giá chi tiết Galaxy Note 5 và OPPO F1 Plus - Rom cook ổn định, sửa lỗi, tiếng việt cho Galaxy Note 5 và OPPO F1 Plus - Hướng dẫn sử dụng Galaxy Note 5 và OPPO F1 Plus - Các tính năng nổi bật, đặc biệt, hữu ích trên Galaxy Note 5 và OPPO F1 Plus - Galaxy Note 5 và OPPO F1 Plus bền, tốt, cảm ứng mượt, camera chụp đẹp không? - Camera Comparion Galaxy Note 5 và OPPO F1 Plus - Compare Galaxy Note 5 và OPPO F1 Plus - Which on is better Galaxy Note 5 và OPPO F1 Plus - Should i buy Galaxy Note 5 và OPPO F1 Plus -
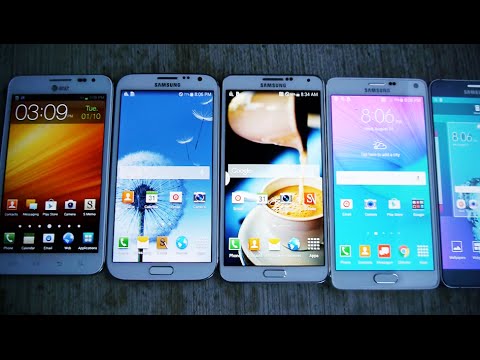 12:19
12:19Samsung Galaxy Note 5 vs 4 vs 3 vs 2 vs 1 Drop Test!
Samsung Galaxy Note 5 vs 4 vs 3 vs 2 vs 1 Drop Test!Samsung Galaxy Note 5 vs 4 vs 3 vs 2 vs 1 Drop Test!
From the first Samsung Galaxy Note 1 released in 2011 to the latest Note 5 released today, which one holds the title as the most durable Note ever drop tested? FACEBOOK: https://www.facebook.com/techrax TWITTER: https://twitter.com/techrax INSTAGRAM: http://instagram.com/techrax -
 3:22
3:22Coolpad Note 3 Plus India | Reasons NOT to BUY | Honest Opinions
Coolpad Note 3 Plus India | Reasons NOT to BUY | Honest OpinionsCoolpad Note 3 Plus India | Reasons NOT to BUY | Honest Opinions
Namaskaar Dosto, is video mein amien aapko Coolpad India ke naye phone ke baare mein bataya hai jo hai Coolpad Note 3 Plus, waise toh yeh naam se naya phone lagta hai but yeh phone Coolpad NOte 3 hi hai bas kuch Minor changes ke saath, aapko isme ek full HD Display mita hai, aur ek naya Gold color, iske alawa aapko Coolpad note 3 aur Coolpad Note 3 Plus ki Price mein 500INR ka difference milta hai. Dosto yeh video koi unboxing nahi hai coolpad note 3 plus ki ya koi Coolpad note 3 plus ka full in depth review nahi hai. Maine aapse apne opinion share kiye hai aur batay ahai ki aapko Coolpad note 3 plus kyu nahi lena chahiye, aapko Performance ekdum acchi nahi milegi, aur batery life bhi average hogi, toh aise mein Meizu m3 note aur Meizu m3 ka wait karna better hoga. Mujhe umeed hai ki Coolpad Note 3 Plus ke baare mein yeh video aapko pasand aategi. Share, Support, Subscribe!!! Subscribe: http://bit.ly/1Wfsvt4 Youtube: http://www.youtube.com/c/TechnicalGuruji Twitter: http://www.twitter.com/technicalguruji Facebook: http://www.facebook.com/technicalguruji Instagram: http://instagram.com/technicalguruji Google Plus: https://plus.google.com/+TechnicalGuruji About : Technical Guruji is a YouTube Channel, where you will find technological videos in Hindi, New Video is Posted Everyday :) -
 11:31
11:31Samsung Galaxy S7 Edge vs Galaxy Note 5 - Speed Test (4K)
Samsung Galaxy S7 Edge vs Galaxy Note 5 - Speed Test (4K)Samsung Galaxy S7 Edge vs Galaxy Note 5 - Speed Test (4K)
Galaxy S7 edge (Exynos 8890) vs note 5 (Exynos 7) speed test. A side by side speed comparison between Samsung Galaxy S7 Edge vs Galaxy Note 5 including boot up, apps opening, multitasking, browsing and fingerprint scanner speed test. ►► Subscribe Now for Daily Tech Videos - http://goo.gl/wj6RxI ►►Join me on social media! ★TWITTER: http://twitter.com/xeetechcare ★INSTAGRAM: http://instagram.com/xeetechcare ★FACEBOOK: http://Facebook.com/xeetechcare ★GOOGLE+: http://plus.google.com/+xeetechcare -
 5:39
5:39Vật Vờ| Đánh giá chi tiết Xiaomi Mi Note Pro: flagship tầm giá 7 triệu
Vật Vờ| Đánh giá chi tiết Xiaomi Mi Note Pro: flagship tầm giá 7 triệuVật Vờ| Đánh giá chi tiết Xiaomi Mi Note Pro: flagship tầm giá 7 triệu
Xiaomi Mi Note Pro Các bạn có thể tìm kiếm video mở hộp, đánh giá chi tiết, hiệu năng, thời lượng pin, camera, so sánh, tư vấn nên mua, sản phẩm Xiaomi Mi Note Pro tại Vật Vờ channel. Xem giá bán Xiaomi Mi Note Pro mới 100%: http://www.viettablet.com/xiaomi-mi-note-pro - Video Đánh giá, review chi tiết Xiaomi Mi Note Pro chính hãng/xách tay - Có nên mua Xiaomi Mi Note Pro không? - Mua Xiaomi Mi Note Pro ở đâu giá tốt, uy tín? - Xiaomi Mi Note Pro xách tay ở đâu giá rẻ, uy tín, chất lượng? - Video Mở hộp Xiaomi Mi Note Pro hàng chính hãng/xách tay - Video Đánh giá, review chi tiết Xiaomi Mi Note Pro hàng chính hãng, chất lượng - Video Đánh giá chi tiết camera Xiaomi Mi Note Pro - Video Đánh giá chi tiết thời lượng pin Xiaomi Mi Note Pro - Video đánh giá chất khả năng chơi game Xiaomi Mi Note Pro - Giá tiền, giá bán xách tay/chính hãng của Xiaomi Mi Note Pro - Mua Xiaomi Mi Note Pro ở đâu rẻ nhất được tặng kèm cái gì - Mua Xiaomi Mi Note Pro rẻ nhất Hà Nội/Hồ chí Minh - Hướng dẫn sử dụng Xiaomi Mi Note Pro - Các tính năng nổi bật, đặc biệt, hữu ích trên Xiaomi Mi Note Pro - Hướng dẫn mua/kiểm tra/check Xiaomi Mi Note Pro cũ/2hand/second hand/qua sử dụng - Xiaomi Mi Note Pro bền, tốt, cảm ứng mượt, camera chụp đẹp không? - Review Xiaomi Mi Note Pro - What new on Xiaomi Mi Note Pro - Shoud i buy Xiaomi Mi Note Pro - Where to buy Xiaomi Mi Note Pro - Battery test/Game test/Camera test/review Xiaomi Mi Note Pro ** Video review, trên tay, các sản phẩm điện thoại, giá bán rẻ nhất, cửa hàng mua uy tín nhất, sản phẩm tốt nhất trong tầm giá và các tư vấn, lời khuyên, video so sánh các sản phẩm cần mua, đánh giá sản phẩm công nghệ, điện thoại di động, máy tính bảng, sản phẩm xách tay Hàn Quốc, Nhật Bản, sản phẩm chính hãng. Các video đánh giá này thuộc quyền sở hữu của Vật Vờ. Liên hệ: Fanpage : https://www.facebook.com/reviewdaos Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/xuanvinh1612 Instagram: @vatvo69 Email: reviewdao@gmail.com -
 13:47
13:47Galaxy Note 5 vs iPhone 6s Plus
Galaxy Note 5 vs iPhone 6s PlusGalaxy Note 5 vs iPhone 6s Plus
Buy Note 5: http://geni.us/3tcI -|- Buy iPhone 6S Plus: http://geni.us/23n1 -|- Read more: http://goo.gl/lURBFq How does the current Samsung flagship fare against the latest large smartphone from Apple? Here is a look at the Samsung Galaxy Note 5 vs iPhone 6S Plus! Talk about Android in our forums: http://www.androidauthority.com/community Subscribe to our YouTube channel: http://www.youtube.com/subscription_center?add_user=androidauthority ---------------------------------------------------- Stay connected to Android Authority: - http://www.androidauthority.com - http://google.com/+androidauthority - http://facebook.com/androidauthority/ - http://twitter.com/androidauth/ - http://instagram.com/androidauthority/ Follow the Team: Josh Vergara: https://plus.google.com/+JoshuaVergara Joe Hindy: https://plus.google.com/+JosephHindy Lanh Nguyen: https://plus.google.com/+LanhNguyenFilms Jayce Broda: https://plus.google.com/+JayceBroda Gary Sims: https://plus.google.com/+GarySims Ash Tailor: https://plus.google.com/+AshTailor -
 9:08
9:08Samsung Galaxy Note 5 Review!
Samsung Galaxy Note 5 Review!Samsung Galaxy Note 5 Review!
Galaxy Note 5: Samsung's slightly larger premium Android flagship! Galaxy Note 5 (Sapphire): http://amzn.to/1Yi4YGr dBrand Note 5 skin: https://dbrand.com/shop/galaxy-note-5 Video Gear I use: http://amzn.com/lm/R3B571T7PT4PWM?tag=m0494a-20 Intro Track: Deadmau5 - Slow Down, Start Over ~ http://twitter.com/MKBHD http://google.com/+MarquesBrownlee http://facebook.com/MarquesBrownlee http://facebook.com/MKBHD http://instagram.com/MKBHD -
 6:25
6:25Samsung Galaxy S7 vs Galaxy Note 5 Hands On Comparison
Samsung Galaxy S7 vs Galaxy Note 5 Hands On ComparisonSamsung Galaxy S7 vs Galaxy Note 5 Hands On Comparison
Buy the Note 5: http://geni.us/Note5 | Full comparison: http://goo.gl/JFkdcP Join us as we take a quick look at the Samsung Galaxy S7 vs the Samsung Galaxy Note 5! Talk about Android in our forums: http://www.androidauthority.com/community Subscribe to our YouTube channel: http://www.youtube.com/subscription_center?add_user=androidauthority ---------------------------------------------------- Stay connected to Android Authority: - http://www.androidauthority.com - http://google.com/+androidauthority - http://facebook.com/androidauthority/ - http://twitter.com/androidauth/ - http://instagram.com/androidauthority/ Follow the Team: Josh Vergara: https://plus.google.com/+JoshuaVergara Joe Hindy: https://plus.google.com/+JosephHindy Lanh Nguyen: https://plus.google.com/+LanhNguyenFilms Jayce Broda: https://plus.google.com/+JayceBroda Gary Sims: https://plus.google.com/+GarySims Ash Tailor: https://plus.google.com/+AshTailor -
 5:06
5:06Samsung Galaxy Note 6, HTC 10 Launch Dates, Google Now Gets New Voice - Android Weekly
Samsung Galaxy Note 6, HTC 10 Launch Dates, Google Now Gets New Voice - Android Weekly
-

-

Galaxy Note 6 Lite rumors, iPhone 7 Plus smart connector & more - Pocketnow Daily
Stories: - Apple Music subscriptions go 50 percent off for eligible students http://pocketnow.com/2016/05/06/apple-music-student-discount-50-percent - Asus confirms May 30 ‘Zenvolution’ date, ZenFone 3 smartphone family incoming http://pocketnow.com/2016/05/06/asus-zenfone-3-introduction-may-30 - Meet Queen University’s HoloFlex, a flexible smartphone that produces holograms http://pocketnow.com/2016/05/06/holoflex - iPhone 7 Plus Smart Connector may not get to be http://pocketnow.com/2016/05/06/iphone-7-plus-smart-connect-iphone-pro - Wild rumor calls for Samsung Galaxy Note 6 ‘Lite’ with Snapdragon 820, 4GB RAM http://pocketnow.com/2016/05/06/samsung-galaxy-note-6-lite-rumor-4gb-ram Watch today's Pocketnow Daily as we talk about the recent discounts in Apple Music subscriptions. Then we... -

Samsung Galaxy Note 5 - First Look!
Buy at Amazon: http://geni.us/note5 -|- Note 5 Review: http://goo.gl/BKPj5E The Samsung Galaxy Note 5 follows the lead of the Galaxy S6 in design, but brings some nice additions to the general experience. Best Galaxy Note 5 cases: http://www.androidauthority.com/best-galaxy-note-5-cases-636021/ Talk about Android in our forums: http://www.androidauthority.com/community Subscribe to our YouTube channel: http://www.youtube.com/subscription_center?add_user=androidauthority ---------------------------------------------------- Stay connected to Android Authority: - http://www.androidauthority.com - http://google.com/+androidauthority - http://facebook.com/androidauthority/ - http://twitter.com/androidauth/ - http://instagram.com/androidauthority/ Follow the Team: Josh Vergara: https://pl... -

Vật Vờ| So sánh đa nhiệm 4GB RAM của Galaxy Note 5 và OPPO F1 Plus
Giới thiệu, so sánh smartphone Galaxy Note 5 và OPPO F1 Plus mở hộp, so sánh,camera,đánh giá,trải nghiệm Galaxy Note 5 và OPPO F1 Plus Các bạn có thể tìm kiếm video mở hộp, đánh giá chi tiết, hiệu năng, thời lượng pin, camera, so sánh, tư vấn nên mua, sản phẩm Galaxy Note 5 và OPPO F1 Plus tại Vật Vờ channel. ** Xem giá bán Galaxy Note 5 Mỹ cũ: http://www.viettablet.com/samsung-galaxy-note-5-cu-like-new-99 ** Video review, trên tay, các sản phẩm điện thoại, giá bán rẻ nhất, cửa hàng mua uy tín nhất, sản phẩm tốt nhất trong tầm giá và các tư vấn, lời khuyên, video so sánh các sản phẩm cần mua, đánh giá sản phẩm công nghệ, điện thoại di động, máy tính bảng, sản phẩm xách tay Hàn Quốc, Nhật Bản, sản phẩm chính hãng. Các video đánh giá này thuộc quyền sở hữu của Vật Vờ. Liên hệ: Fanpage : ... -

Samsung Galaxy Note 5 vs 4 vs 3 vs 2 vs 1 Drop Test!
From the first Samsung Galaxy Note 1 released in 2011 to the latest Note 5 released today, which one holds the title as the most durable Note ever drop tested? FACEBOOK: https://www.facebook.com/techrax TWITTER: https://twitter.com/techrax INSTAGRAM: http://instagram.com/techrax -

Coolpad Note 3 Plus India | Reasons NOT to BUY | Honest Opinions
Namaskaar Dosto, is video mein amien aapko Coolpad India ke naye phone ke baare mein bataya hai jo hai Coolpad Note 3 Plus, waise toh yeh naam se naya phone lagta hai but yeh phone Coolpad NOte 3 hi hai bas kuch Minor changes ke saath, aapko isme ek full HD Display mita hai, aur ek naya Gold color, iske alawa aapko Coolpad note 3 aur Coolpad Note 3 Plus ki Price mein 500INR ka difference milta hai. Dosto yeh video koi unboxing nahi hai coolpad note 3 plus ki ya koi Coolpad note 3 plus ka full in depth review nahi hai. Maine aapse apne opinion share kiye hai aur batay ahai ki aapko Coolpad note 3 plus kyu nahi lena chahiye, aapko Performance ekdum acchi nahi milegi, aur batery life bhi average hogi, toh aise mein Meizu m3 note aur Meizu m3 ka wait karna better hoga. Mujhe umeed hai ki Coolp... -

Samsung Galaxy S7 Edge vs Galaxy Note 5 - Speed Test (4K)
Galaxy S7 edge (Exynos 8890) vs note 5 (Exynos 7) speed test. A side by side speed comparison between Samsung Galaxy S7 Edge vs Galaxy Note 5 including boot up, apps opening, multitasking, browsing and fingerprint scanner speed test. ►► Subscribe Now for Daily Tech Videos - http://goo.gl/wj6RxI ►►Join me on social media! ★TWITTER: http://twitter.com/xeetechcare ★INSTAGRAM: http://instagram.com/xeetechcare ★FACEBOOK: http://Facebook.com/xeetechcare ★GOOGLE+: http://plus.google.com/+xeetechcare -

Vật Vờ| Đánh giá chi tiết Xiaomi Mi Note Pro: flagship tầm giá 7 triệu
Xiaomi Mi Note Pro Các bạn có thể tìm kiếm video mở hộp, đánh giá chi tiết, hiệu năng, thời lượng pin, camera, so sánh, tư vấn nên mua, sản phẩm Xiaomi Mi Note Pro tại Vật Vờ channel. Xem giá bán Xiaomi Mi Note Pro mới 100%: http://www.viettablet.com/xiaomi-mi-note-pro - Video Đánh giá, review chi tiết Xiaomi Mi Note Pro chính hãng/xách tay - Có nên mua Xiaomi Mi Note Pro không? - Mua Xiaomi Mi Note Pro ở đâu giá tốt, uy tín? - Xiaomi Mi Note Pro xách tay ở đâu giá rẻ, uy tín, chất lượng? - Video Mở hộp Xiaomi Mi Note Pro hàng chính hãng/xách tay - Video Đánh giá, review chi tiết Xiaomi Mi Note Pro hàng chính hãng, chất lượng - Video Đánh giá chi tiết camera Xiaomi Mi Note Pro - Video Đánh giá chi tiết thời lượng pin Xiaomi Mi Note Pro - Video đánh giá chất khả năng chơi game X... -

Galaxy Note 5 vs iPhone 6s Plus
Buy Note 5: http://geni.us/3tcI -|- Buy iPhone 6S Plus: http://geni.us/23n1 -|- Read more: http://goo.gl/lURBFq How does the current Samsung flagship fare against the latest large smartphone from Apple? Here is a look at the Samsung Galaxy Note 5 vs iPhone 6S Plus! Talk about Android in our forums: http://www.androidauthority.com/community Subscribe to our YouTube channel: http://www.youtube.com/subscription_center?add_user=androidauthority ---------------------------------------------------- Stay connected to Android Authority: - http://www.androidauthority.com - http://google.com/+androidauthority - http://facebook.com/androidauthority/ - http://twitter.com/androidauth/ - http://instagram.com/androidauthority/ Follow the Team: Josh Vergara: https://plus.google.com/+JoshuaVergara Joe ... -

Samsung Galaxy Note 5 Review!
Galaxy Note 5: Samsung's slightly larger premium Android flagship! Galaxy Note 5 (Sapphire): http://amzn.to/1Yi4YGr dBrand Note 5 skin: https://dbrand.com/shop/galaxy-note-5 Video Gear I use: http://amzn.com/lm/R3B571T7PT4PWM?tag=m0494a-20 Intro Track: Deadmau5 - Slow Down, Start Over ~ http://twitter.com/MKBHD http://google.com/+MarquesBrownlee http://facebook.com/MarquesBrownlee http://facebook.com/MKBHD http://instagram.com/MKBHD -

Samsung Galaxy S7 vs Galaxy Note 5 Hands On Comparison
Buy the Note 5: http://geni.us/Note5 | Full comparison: http://goo.gl/JFkdcP Join us as we take a quick look at the Samsung Galaxy S7 vs the Samsung Galaxy Note 5! Talk about Android in our forums: http://www.androidauthority.com/community Subscribe to our YouTube channel: http://www.youtube.com/subscription_center?add_user=androidauthority ---------------------------------------------------- Stay connected to Android Authority: - http://www.androidauthority.com - http://google.com/+androidauthority - http://facebook.com/androidauthority/ - http://twitter.com/androidauth/ - http://instagram.com/androidauthority/ Follow the Team: Josh Vergara: https://plus.google.com/+JoshuaVergara Joe Hindy: https://plus.google.com/+JosephHindy Lanh Nguyen: https://plus.google.com/+LanhNguyenFilms Jayc... -

Samsung Galaxy Note 5 Hammer & Knife Test!
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 5:01
- Updated: 28 Aug 2015
- views: 3104612
Galaxy Note 6 Lite rumors, iPhone 7 Plus smart connector & more - Pocketnow Daily
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 4:14
- Updated: 07 May 2016
- views: 9233
- published: 07 May 2016
- views: 9233
Samsung Galaxy Note 5 - First Look!
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 6:22
- Updated: 13 Aug 2015
- views: 1750928
- published: 13 Aug 2015
- views: 1750928
Vật Vờ| So sánh đa nhiệm 4GB RAM của Galaxy Note 5 và OPPO F1 Plus
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 5:10
- Updated: 06 May 2016
- views: 1750
- published: 06 May 2016
- views: 1750
Samsung Galaxy Note 5 vs 4 vs 3 vs 2 vs 1 Drop Test!
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 12:19
- Updated: 20 Aug 2015
- views: 1178927
- published: 20 Aug 2015
- views: 1178927
Coolpad Note 3 Plus India | Reasons NOT to BUY | Honest Opinions
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 3:22
- Updated: 06 May 2016
- views: 4784
- published: 06 May 2016
- views: 4784
Samsung Galaxy S7 Edge vs Galaxy Note 5 - Speed Test (4K)
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 11:31
- Updated: 04 Mar 2016
- views: 4088
- published: 04 Mar 2016
- views: 4088
Vật Vờ| Đánh giá chi tiết Xiaomi Mi Note Pro: flagship tầm giá 7 triệu
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 5:39
- Updated: 06 May 2016
- views: 1834
- published: 06 May 2016
- views: 1834
Galaxy Note 5 vs iPhone 6s Plus
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 13:47
- Updated: 23 Nov 2015
- views: 336806
- published: 23 Nov 2015
- views: 336806
Samsung Galaxy Note 5 Review!
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 9:08
- Updated: 18 Sep 2015
- views: 1879646
- published: 18 Sep 2015
- views: 1879646
Samsung Galaxy S7 vs Galaxy Note 5 Hands On Comparison
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 6:25
- Updated: 24 Feb 2016
- views: 2650
- published: 24 Feb 2016
- views: 2650
Samsung Galaxy Note 6, HTC 10 Launch Dates, Google Now Gets New Voice - Android Weekly
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 5:06
- Updated: 28 Mar 2016
- views: 1904
- Playlist
- Chat
- Playlist
- Chat

Samsung Galaxy Note 5 Hammer & Knife Test!
- Report rights infringement
- published: 28 Aug 2015
- views: 3104612

Galaxy Note 6 Lite rumors, iPhone 7 Plus smart connector & more - Pocketnow Daily
- Report rights infringement
- published: 07 May 2016
- views: 9233

Samsung Galaxy Note 5 - First Look!
- Report rights infringement
- published: 13 Aug 2015
- views: 1750928

Vật Vờ| So sánh đa nhiệm 4GB RAM của Galaxy Note 5 và OPPO F1 Plus
- Report rights infringement
- published: 06 May 2016
- views: 1750

Samsung Galaxy Note 5 vs 4 vs 3 vs 2 vs 1 Drop Test!
- Report rights infringement
- published: 20 Aug 2015
- views: 1178927

Coolpad Note 3 Plus India | Reasons NOT to BUY | Honest Opinions
- Report rights infringement
- published: 06 May 2016
- views: 4784

Samsung Galaxy S7 Edge vs Galaxy Note 5 - Speed Test (4K)
- Report rights infringement
- published: 04 Mar 2016
- views: 4088

Vật Vờ| Đánh giá chi tiết Xiaomi Mi Note Pro: flagship tầm giá 7 triệu
- Report rights infringement
- published: 06 May 2016
- views: 1834

Galaxy Note 5 vs iPhone 6s Plus
- Report rights infringement
- published: 23 Nov 2015
- views: 336806

Samsung Galaxy Note 5 Review!
- Report rights infringement
- published: 18 Sep 2015
- views: 1879646

Samsung Galaxy S7 vs Galaxy Note 5 Hands On Comparison
- Report rights infringement
- published: 24 Feb 2016
- views: 2650

Samsung Galaxy Note 6, HTC 10 Launch Dates, Google Now Gets New Voice - Android Weekly
- Report rights infringement
- published: 28 Mar 2016
- views: 1904
[UPDATE]: Egyptian, French Authorities Open EgyptAir Investigations, Bodies Recovered
Edit WorldNews.com 19 May 2016[UPDATE]: Egyptian Aviation Minister: Terrorist Attack Took Down EgyptAir Jet
Edit WorldNews.com 19 May 2016Hey Naysayers...Once In A Blue Moon A Reality Saturday
Edit WorldNews.com 19 May 2016Report: Defunct Trump University, Saudi Arabia Still Bring In Cash For Billionaire
Edit WorldNews.com 19 May 2016US B52 bomber crashes on Guam, all crew safe
Edit Gulf News 19 May 2016Universal Health Services, Inc. Announces Offering Of Senior Secured Notes
Edit PR Newswire 19 May 2016Tesoro Logistics issues $700 million in senior notes
Edit Business Journal 19 May 2016Fitch Rates Oceanwide's Proposed USD Senior Notes 'B(EXP)'
Edit Reuters 19 May 2016Kid’s hilarious note to mom to find out about her surprise gift goes viral
Edit Deccan Chronicle 19 May 2016'Jealous' Bancroft student charged with sending threatening notes to peers
Edit Worcester Telegram 19 May 2016Tempur Sealy Launches Proposed $500 Million Senior Notes Offering
Edit PR Newswire 19 May 2016Tempur Sealy Announces Pricing Of Upsized $600 Million Senior Notes Offering
Edit PR Newswire 19 May 2016Notes of Kofola S.A. VAR/2018, ISIN CZ0000000351 - Results of Noteholders Meeting convened 17.5.2016 (Kofola SA)
Edit Public Technologies 19 May 2016Team Baywatch Cherishes working with Priyanka, Shares a Pic & Appreciation Note!
Edit Pinkvilla 19 May 2016Will take call on tightening P-Note norms soon: Sebi chief
Edit The Times of India 19 May 2016- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- Next page »







