










- Loading...

-
Glycoproteins
Glycoproteins -
079-Glycoproteins
079-Glycoproteins079-Glycoproteins
Overview of glycoprotein structure and distinction between O and N glycoslyation. -
Synthesis of glycoprotein
Synthesis of glycoproteinSynthesis of glycoprotein
For more information, log on to- http://shomusbiology.weebly.com/ Download the study materials here- http://shomusbiology.weebly.com/bio-materials.html Polys... -
Cell Membranes
Cell MembranesCell Membranes
015 - Cell Membranes Paul Andersen explains how cells are selectively permeable with the help of their cell membrane. The main constituents of the cell membr... -
Ebola virus envelope glycoprotein secondary structure
Ebola virus envelope glycoprotein secondary structureEbola virus envelope glycoprotein secondary structure
This is another upload of our continuing animations showing the Ebola virus envelope glycoprotein. These two small clips move the viewer around the side over top complex then underneath the complex showing symmetry of the secondary structure. Animation by RenderingReality.com contact us at tomcaruso@renderingreality.com -
Tools for Glycoprotein Analysis
Tools for Glycoprotein AnalysisTools for Glycoprotein Analysis
This tutorial introduces the function N- and O-glycans, and discusses enzymes used in deglycosylation. -
36-6 Protein Structure and Structural Carbohydrates: Glycoproteins
36-6 Protein Structure and Structural Carbohydrates: Glycoproteins36-6 Protein Structure and Structural Carbohydrates: Glycoproteins
(c) 2012 edX Lecture by Prof. Cima, MIT, taken form the edX course : 3.091x Introduction to Solid State Chemistry http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-n... -
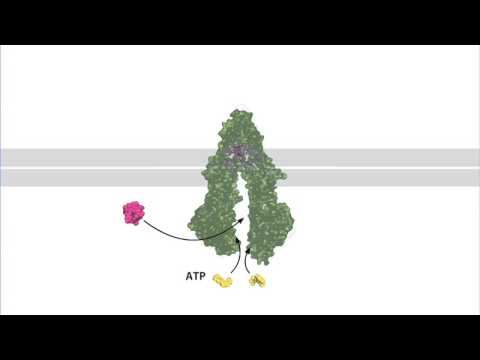
Multidrug ABC transporter, P-glycoprotein (with sound)
Multidrug ABC transporter, P-glycoprotein (with sound)Multidrug ABC transporter, P-glycoprotein (with sound)
P-glycoprotein removes anticancer drugs from cytoplasm and confers multidrug resistance to cancer cells. It has a tandem repeat structure with 6 transmembran... -
Animated Glycoprotein
Animated GlycoproteinAnimated Glycoprotein
Animated Glycoprotein By Amin Mahpour Based on NMR structure determined by Slynko, V., Schubert, M., Numao, S., Kowarik, M., Aebi, M., Allain, F.H. Published... -
Drug Export by the Multi Drug Resistance Pump
Drug Export by the Multi Drug Resistance PumpDrug Export by the Multi Drug Resistance Pump
Transmembrane drug efflux pumps can remove chemotherapeutic drugs from inside a cancer cell, thereby reducing intracellular drug concentration, which generat... -
AHA: Glycoprotein IIb/IIIa Drugs Come Out Even for PCI
AHA: Glycoprotein IIb/IIIa Drugs Come Out Even for PCIAHA: Glycoprotein IIb/IIIa Drugs Come Out Even for PCI
Marc Cohen, M.D., Beth Israel Medical Center, Newark, N.J. http://www.medpagetoday.com ORLANDO, Nov. 5 -- One glycoprotein IIb/IIIa inhibitor may be just as ... -
SMU biochemist creates dynamic model of human P-glycoprotein
SMU biochemist creates dynamic model of human P-glycoproteinSMU biochemist creates dynamic model of human P-glycoprotein
SMU biologists Pia Vogel and John Wise are using the computational power of SMU's high-performance supercomputer to screen millions of drug compounds in hope... -
Model of alpha2-HS-glycoprotein (Ahsg)
Model of alpha2-HS-glycoprotein (Ahsg)Model of alpha2-HS-glycoprotein (Ahsg)
Three-dimensional folding model of rat Ahsg showing at lower left in marine blue, the putative epitope HRTHHDLRHAFS that mediates interaction with the beta-s... -
Biotech Support Group Glycoprotein Enrichment Reagent Kit
Biotech Support Group Glycoprotein Enrichment Reagent KitBiotech Support Group Glycoprotein Enrichment Reagent Kit
Biotech Support Group NuGel™ Glycoprotein Enrichment PBA Kit With Phenyl Boronic Acid NuGel™ Matrix Glycoprotein Enrichment & Detection Glycoprotein Sample P...
- Activin and inhibin
- Agarose
- Aggrecan
- Alpha-fetoprotein
- Alpha-Mannosidase
- Alpha-mannosidosis
- Amino acid
- Aminosugar
- Antibody
- Antifreeze protein
- Antigen
- Apolipoprotein H
- Asialoglycoprotein
- Asparagine
- ATC code A16
- Avidin
- Beta-galactosidase
- Beta-mannosidase
- Beta-mannosidosis
- Biglycan
- Biochemistry
- Blood plasma
- Bone
- Brevican
- CA-125
- Calcium
- Calnexin
- Calreticulin
- CD164
- CD43
- CD44
- CD70
- Ceruloplasmin
- Chondroitin sulfate
- Clusterin
- Collagen
- Complementary DNA
- Connective tissue
- CSPG4
- CSPG5
- Cytosol
- Decorin
- Deoxy sugar
- Dermatan sulfate
- Dolichol kinase
- Egg white
- Electrophoresis
- Endoglycosidase
- Endothelium
- Enzyme
- ER Oxidoreductin
- Erythropoietin
- Exoglycosidase
- Female Sperm Storage
- Fibromodulin
- Fucose
- Fucosidase
- Fucosidosis
- Galactose
- Galactosialidosis
- GCS1
- Glucose
- Glycans
- Glycocalyx
- Glycoconjugate
- Glycoform
- Glycopeptide
- Glycophorin
- Glycophorin C
- Glycoprotein
- Glycoproteinosis
- Glycosylation
- Gp120
- Gp41
- Haptoglobin
- Hemopexin
- Hemostasis
- Heparan sulfate
- Hexosaminidase
- Hexose
- Histocompatibility
- Hormone
- Hydrolysis
- Hydroxyl
- Hydroxylysine
- Hydroxyproline
- I-cell disease
- Immune system
- Intrinsic factor
- Keratan sulfate
- Keratocan
- Lactoferrin
- Lectin
- Lumican
- Luteinizing hormone
- Lysosomal enzymes
- Mammal
- Mannose
- Mannose-6-phosphate
- Mannosidase
- Mannosidosis
- Mass spectrometry
- Metabolism
- Methylation
- Miraculin
- Molecular mass
- MUC1
- MUC13
- MUC15
- MUC17
- MUC19
- MUC2
- MUC20
- MUC3A
- MUC3B
- MUC4
- MUC5AC
- MUC5B
- MUC6
- MUC7
- MUC8
- Mucin
- Mucolipidosis
- Mucoprotein
- Myelin protein zero
- N-Acetylglucosamine
- NAGA (gene)
- Neuraminic acid
- Neuraminidase
- Neurocan
- NMR spectroscopy
- Notch signaling
- Oligosaccharide
- Oocyte
- Orosomucoid
- Osteonectin
- Ovomucin
- Oxygen
- P-glycoprotein
- Pentose
- Peptide
- Peptidoglycan
- Perlecan
- Phosphatase
- Phospholipase
- Phytohaemagglutinin
- Platelet
- Platelet factor 4
- Protein
- Protein C
- Protein folding
- Protein S
- Proteoglycan
- Proteolysis
- PubMed Identifier
- Radioactive decay
- Salla disease
- Schindler disease
- Selectin
- Serine
- Sialic acid
- Sialidosis
- Sialoglycoprotein
- SLC17A5
- SMC3 (gene)
- Sperm
- Syndecan 1
- T cell
- Template Alcohols
- Template AminoAcids
- Template Eicosanoids
- Template Fatty acids
- Template Glycolysis
- Template Glycosides
- Template Lipids
- Template Metabolism
- Template Urea cycle
- Testican
- Threonine
- Thrombopoietin
- Thrombosis
- Thyroglobulin
- Transcortin
- Transferrin
- Uteroglobin
- Versican
- Viscosity
- Vitronectin
- White blood cell
- Xylose
- Zona pellucida
-
Glycoproteins
GlycoproteinsGlycoproteins
Get the App! http://bit.ly/eGzKcn. -
079-Glycoproteins
079-Glycoproteins079-Glycoproteins
Overview of glycoprotein structure and distinction between O and N glycoslyation. -
Synthesis of glycoprotein
Synthesis of glycoproteinSynthesis of glycoprotein
For more information, log on to- http://shomusbiology.weebly.com/ Download the study materials here- http://shomusbiology.weebly.com/bio-materials.html Polys... -
Cell Membranes
Cell MembranesCell Membranes
015 - Cell Membranes Paul Andersen explains how cells are selectively permeable with the help of their cell membrane. The main constituents of the cell membr... -
Ebola virus envelope glycoprotein secondary structure
Ebola virus envelope glycoprotein secondary structureEbola virus envelope glycoprotein secondary structure
This is another upload of our continuing animations showing the Ebola virus envelope glycoprotein. These two small clips move the viewer around the side over top complex then underneath the complex showing symmetry of the secondary structure. Animation by RenderingReality.com contact us at tomcaruso@renderingreality.com -
Tools for Glycoprotein Analysis
Tools for Glycoprotein AnalysisTools for Glycoprotein Analysis
This tutorial introduces the function N- and O-glycans, and discusses enzymes used in deglycosylation. -
36-6 Protein Structure and Structural Carbohydrates: Glycoproteins
36-6 Protein Structure and Structural Carbohydrates: Glycoproteins36-6 Protein Structure and Structural Carbohydrates: Glycoproteins
(c) 2012 edX Lecture by Prof. Cima, MIT, taken form the edX course : 3.091x Introduction to Solid State Chemistry http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-n... -
Multidrug ABC transporter, P-glycoprotein (with sound)
Multidrug ABC transporter, P-glycoprotein (with sound)Multidrug ABC transporter, P-glycoprotein (with sound)
P-glycoprotein removes anticancer drugs from cytoplasm and confers multidrug resistance to cancer cells. It has a tandem repeat structure with 6 transmembran... -
Animated Glycoprotein
Animated GlycoproteinAnimated Glycoprotein
Animated Glycoprotein By Amin Mahpour Based on NMR structure determined by Slynko, V., Schubert, M., Numao, S., Kowarik, M., Aebi, M., Allain, F.H. Published... -
Drug Export by the Multi Drug Resistance Pump
Drug Export by the Multi Drug Resistance PumpDrug Export by the Multi Drug Resistance Pump
Transmembrane drug efflux pumps can remove chemotherapeutic drugs from inside a cancer cell, thereby reducing intracellular drug concentration, which generat... -
AHA: Glycoprotein IIb/IIIa Drugs Come Out Even for PCI
AHA: Glycoprotein IIb/IIIa Drugs Come Out Even for PCIAHA: Glycoprotein IIb/IIIa Drugs Come Out Even for PCI
Marc Cohen, M.D., Beth Israel Medical Center, Newark, N.J. http://www.medpagetoday.com ORLANDO, Nov. 5 -- One glycoprotein IIb/IIIa inhibitor may be just as ... -
SMU biochemist creates dynamic model of human P-glycoprotein
SMU biochemist creates dynamic model of human P-glycoproteinSMU biochemist creates dynamic model of human P-glycoprotein
SMU biologists Pia Vogel and John Wise are using the computational power of SMU's high-performance supercomputer to screen millions of drug compounds in hope... -
Model of alpha2-HS-glycoprotein (Ahsg)
Model of alpha2-HS-glycoprotein (Ahsg)Model of alpha2-HS-glycoprotein (Ahsg)
Three-dimensional folding model of rat Ahsg showing at lower left in marine blue, the putative epitope HRTHHDLRHAFS that mediates interaction with the beta-s... -
Biotech Support Group Glycoprotein Enrichment Reagent Kit
Biotech Support Group Glycoprotein Enrichment Reagent KitBiotech Support Group Glycoprotein Enrichment Reagent Kit
Biotech Support Group NuGel™ Glycoprotein Enrichment PBA Kit With Phenyl Boronic Acid NuGel™ Matrix Glycoprotein Enrichment & Detection Glycoprotein Sample P... -
Ebola glycoprotein secondary structures
Ebola glycoprotein secondary structuresEbola glycoprotein secondary structures
In this animation, we show the surface and secondary structures of the pre-fusion Ebola glycoprotein complex found on the virus surface. Scientists have been studying the structural configuration and the specific functions of certain regions responsible for binding to the host cell and fusion to the endosome wall. Animation by RenderingReality.com The below source has been extremely helpful in this animation. The Primed Ebolavirus Glycoprotein (19-Kilodalton GP1,2): Sequence and Residues Critical for Host Cell Binding http://jvi.asm.org/content/83/7/2883.full Derek Dube, Matthew B. Brecher , Sue E. Delos, Sean C. Rose, Edward W. Park, K -
Cool movie of human a2-HS-glycoprotein (fetuin A) insulin receptor face
Cool movie of human a2-HS-glycoprotein (fetuin A) insulin receptor faceCool movie of human a2-HS-glycoprotein (fetuin A) insulin receptor face
-
Mutational Analysis of the Putative Fusion Domain of Ebola Virus Glycoprotein
Mutational Analysis of the Putative Fusion Domain of Ebola Virus GlycoproteinMutational Analysis of the Putative Fusion Domain of Ebola Virus Glycoprotein
http://jvi.asm.org/content/73/10/8907.short -
HIV Envelope Glycoprotein: Fusion and Inhibition
HIV Envelope Glycoprotein: Fusion and InhibitionHIV Envelope Glycoprotein: Fusion and Inhibition
This is an entry in the RCSB PDB Video Challenge 2014 "Structural View of HIV/AIDS". -
Glycoprotein
GlycoproteinGlycoprotein
Glycoproteins are proteins that contain oligosaccharide chains (glycans) covalently attached to polypeptide side-chains. The carbohydrate is attached to the protein in a cotranslational or posttranslational modification. This process is known as glycosylation. Secreted extracellular proteins are often glycosylated. In proteins that have segments extending extracellularly, the extracellular segments are also glycosylated. Glycoproteins are often important integral membrane proteins, where they play a role in cell–cell interactions. Glycoproteins are also formed in the cytosol, but their functions and the pathways producing these modifications -
Glycoprotein Engineering
Glycoprotein EngineeringGlycoprotein Engineering
-
Beta 2 GLYCOPROTEIN 1 IgM ELISA kit
Beta 2 GLYCOPROTEIN 1 IgM ELISA kitBeta 2 GLYCOPROTEIN 1 IgM ELISA kit
http://www.rapidtest.com/index.php?i=Beta-2-Glycoprotein-1-IgM-ELISA-kit&id;=18&cat;=8 Autoimmune Disease ELISA kits: Beta 2 GLYCOPROTEIN 1 IgM ELISA kit ELISA... -
How to Say or Pronounce P-Glycoprotein
How to Say or Pronounce P-GlycoproteinHow to Say or Pronounce P-Glycoprotein
Get those medical secrets: http://www.health101.pw/Medical-Secrets.shtml This video shows you how to say or pronounce P-Glycoprotein. Audio is from cancer.gov. -
Pronounce Medical Words ― P―Glycoprotein
Pronounce Medical Words ― P―GlycoproteinPronounce Medical Words ― P―Glycoprotein
This video shows you how to say P―Glycoprotein. How would you pronounce P―Glycoprotein?

- Duration: 1:34
- Updated: 25 Jul 2014

- Duration: 4:20
- Updated: 27 Jul 2014
- published: 11 Jun 2014
- views: 110
- author: Fundamentals of Biochemistry

- Duration: 8:08
- Updated: 03 Sep 2014
- published: 06 Nov 2012
- views: 2854
- author: Suman Bhattacharjee

- Duration: 11:04
- Updated: 06 Sep 2014
- published: 08 Jul 2011
- views: 190211
- author: Bozeman Science

- Duration: 0:23
- Updated: 23 Sep 2014
- published: 23 Sep 2014
- views: 0

- Duration: 5:48
- Updated: 24 Aug 2014
- published: 26 Mar 2012
- views: 3846
- author: New England Biolabs

- Duration: 3:00
- Updated: 01 Apr 2014
- published: 02 Jan 2013
- views: 496
- author: Respect Chemistry

- Duration: 4:37
- Updated: 12 May 2014
- published: 07 Feb 2013
- views: 2510
- author: StructureForBiology

- Duration: 0:07
- Updated: 26 Jun 2013
- published: 05 Feb 2009
- views: 2371
- author: MOLPAPER

- Duration: 2:10
- Updated: 03 Sep 2014
- published: 24 Jun 2013
- views: 4263
- author: Dr. Reginald Halaby

- Duration: 2:58
- Updated: 12 Mar 2014
- published: 31 Jan 2008
- views: 1421
- author: MedPageToday

- Duration: 1:26
- Updated: 25 Feb 2014
- published: 03 May 2012
- views: 2389
- author: SMUVideo

- Duration: 0:32
- Updated: 18 May 2013
- published: 24 Sep 2011
- views: 262
- author: Anton-Scott Goustin

- Duration: 0:36
- Updated: 04 Jan 2014
- published: 01 Jan 2014
- views: 20
- author: BiotechSupportGroup

- Duration: 0:13
- Updated: 07 Oct 2014
- published: 07 Oct 2014
- views: 8

- Duration: 0:33
- Updated: 18 May 2013
http://wn.com/Cool_movie_of_human_a2-HS-glycoprotein_(fetuin_A)_insulin_receptor_face

- Duration: 0:54
- Updated: 08 Oct 2014
- published: 08 Oct 2014
- views: 14

- Duration: 2:25
- Updated: 30 May 2014
- published: 30 May 2014
- views: 116
- author: SChavva24

- Duration: 4:16
- Updated: 28 Oct 2014
- published: 28 Oct 2014
- views: 1

- Duration: 2:02
- Updated: 15 Aug 2013
- published: 20 Jun 2013
- views: 24
- author: autoimmuneELISAkit

- Duration: 0:11
- Updated: 02 Jan 2014
- published: 15 Aug 2013
- views: 59
- author: Barrett Oneal

- Duration: 0:11
- Updated: 06 May 2014
- published: 06 May 2014
- views: 3
- Playlist
- Chat

Glycoproteins
Get the App! http://bit.ly/eGzKcn.- published: 10 Jun 2012
- views: 5125
- author: MenteonLearning

079-Glycoproteins
Overview of glycoprotein structure and distinction between O and N glycoslyation.- published: 11 Jun 2014
- views: 110
- author: Fundamentals of Biochemistry

Synthesis of glycoprotein
For more information, log on to- http://shomusbiology.weebly.com/ Download the study materials here- http://shomusbiology.weebly.com/bio-materials.html Polys...- published: 06 Nov 2012
- views: 2854
- author: Suman Bhattacharjee

Cell Membranes
015 - Cell Membranes Paul Andersen explains how cells are selectively permeable with the help of their cell membrane. The main constituents of the cell membr...- published: 08 Jul 2011
- views: 190211
- author: Bozeman Science

Ebola virus envelope glycoprotein secondary structure
This is another upload of our continuing animations showing the Ebola virus envelope glycoprotein. These two small clips move the viewer around the side over top complex then underneath the complex showing symmetry of the secondary structure. Animation by RenderingReality.com contact us at tomcaruso@renderingreality.com- published: 23 Sep 2014
- views: 0

Tools for Glycoprotein Analysis
This tutorial introduces the function N- and O-glycans, and discusses enzymes used in deglycosylation.- published: 26 Mar 2012
- views: 3846
- author: New England Biolabs

36-6 Protein Structure and Structural Carbohydrates: Glycoproteins
(c) 2012 edX Lecture by Prof. Cima, MIT, taken form the edX course : 3.091x Introduction to Solid State Chemistry http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-n...- published: 02 Jan 2013
- views: 496
- author: Respect Chemistry

Multidrug ABC transporter, P-glycoprotein (with sound)
P-glycoprotein removes anticancer drugs from cytoplasm and confers multidrug resistance to cancer cells. It has a tandem repeat structure with 6 transmembran...- published: 07 Feb 2013
- views: 2510
- author: StructureForBiology

Animated Glycoprotein
Animated Glycoprotein By Amin Mahpour Based on NMR structure determined by Slynko, V., Schubert, M., Numao, S., Kowarik, M., Aebi, M., Allain, F.H. Published...- published: 05 Feb 2009
- views: 2371
- author: MOLPAPER

Drug Export by the Multi Drug Resistance Pump
Transmembrane drug efflux pumps can remove chemotherapeutic drugs from inside a cancer cell, thereby reducing intracellular drug concentration, which generat...- published: 24 Jun 2013
- views: 4263
- author: Dr. Reginald Halaby

AHA: Glycoprotein IIb/IIIa Drugs Come Out Even for PCI
Marc Cohen, M.D., Beth Israel Medical Center, Newark, N.J. http://www.medpagetoday.com ORLANDO, Nov. 5 -- One glycoprotein IIb/IIIa inhibitor may be just as ...- published: 31 Jan 2008
- views: 1421
- author: MedPageToday

SMU biochemist creates dynamic model of human P-glycoprotein
SMU biologists Pia Vogel and John Wise are using the computational power of SMU's high-performance supercomputer to screen millions of drug compounds in hope...- published: 03 May 2012
- views: 2389
- author: SMUVideo

Model of alpha2-HS-glycoprotein (Ahsg)
Three-dimensional folding model of rat Ahsg showing at lower left in marine blue, the putative epitope HRTHHDLRHAFS that mediates interaction with the beta-s...- published: 24 Sep 2011
- views: 262
- author: Anton-Scott Goustin

Biotech Support Group Glycoprotein Enrichment Reagent Kit
Biotech Support Group NuGel™ Glycoprotein Enrichment PBA Kit With Phenyl Boronic Acid NuGel™ Matrix Glycoprotein Enrichment & Detection Glycoprotein Sample P...- published: 01 Jan 2014
- views: 20
- author: BiotechSupportGroup

Ebola glycoprotein secondary structures
In this animation, we show the surface and secondary structures of the pre-fusion Ebola glycoprotein complex found on the virus surface. Scientists have been studying the structural configuration and the specific functions of certain regions responsible for binding to the host cell and fusion to the endosome wall. Animation by RenderingReality.com The below source has been extremely helpful in this animation. The Primed Ebolavirus Glycoprotein (19-Kilodalton GP1,2): Sequence and Residues Critical for Host Cell Binding http://jvi.asm.org/content/83/7/2883.full Derek Dube, Matthew B. Brecher , Sue E. Delos, Sean C. Rose, Edward W. Park, Kathryn L. Schornberg Jens H. Kuhn, Judith M. White- published: 07 Oct 2014
- views: 8

Cool movie of human a2-HS-glycoprotein (fetuin A) insulin receptor face
- published: 13 Jul 2010
- views: 937
- author: Anton-Scott Goustin

Mutational Analysis of the Putative Fusion Domain of Ebola Virus Glycoprotein
http://jvi.asm.org/content/73/10/8907.short- published: 08 Oct 2014
- views: 14

HIV Envelope Glycoprotein: Fusion and Inhibition
This is an entry in the RCSB PDB Video Challenge 2014 "Structural View of HIV/AIDS".- published: 30 May 2014
- views: 116
- author: SChavva24
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- Next page »

Glycoproteins are proteins that contain oligosaccharide chains (glycans) covalently attached to polypeptide side-chains. The carbohydrate is attached to the protein in a cotranslational or posttranslational modification. This process is known as glycosylation. In proteins that have segments extending extracellularly, the extracellular segments are often glycosylated. Glycoproteins are often important integral membrane proteins, where they play a role in cell–cell interactions. Glycoproteins are also formed in the cytosol, but their functions and the pathways producing these modifications in this compartment are less well understood.
There are two types of glycoproteins:
Monosaccharides commonly found in eukaryotic glycoproteins include:
The sugar group(s) can assist in protein folding or improve proteins' stability.
One example of glycoproteins found in the body is mucins, which are secreted in the mucus of the respiratory and digestive tracts. The sugars attached to mucins give them considerable water-holding capacity and also make them resistant to proteolysis by digestive enzymes.
This article is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported License, which means that you can copy and modify it as long as the entire work (including additions) remains under this license.
![[u'Glycoprotein Engineering'][0].replace('](http://web.archive.org./web/20141118121316im_/http://i.ytimg.com/vi/qTuIVH9ttXs/0.jpg)



