- published: 03 Jun 2015
- views: 22098
-
remove the playlistDwdm
- remove the playlistDwdm
- published: 22 May 2011
- views: 85834
- published: 30 Mar 2015
- views: 76393
- published: 29 Apr 2016
- views: 6217
- published: 08 Oct 2014
- views: 17162
- published: 05 Mar 2015
- views: 11832
- published: 26 Oct 2012
- views: 100524
- published: 12 May 2017
- views: 417
WDM
WDM may refer to:
People
This article is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported License, which means that you can copy and modify it as long as the entire work (including additions) remains under this license.

Wavelength-division multiplexing
In fiber-optic communications, wavelength-division multiplexing (WDM) is a technology which multiplexes a number of optical carrier signals onto a single optical fiber by using different wavelengths (i.e., colors) of laser light. This technique enables bidirectional communications over one strand of fiber, as well as multiplication of capacity.
The term wavelength-division multiplexing is commonly applied to an optical carrier (which is typically described by its wavelength), whereas frequency-division multiplexing typically applies to a radio carrier (which is more often described by frequency). Since wavelength and frequency are tied together through a simple directly inverse relationship, in which the product of frequency and wavelength equals c (the propagation speed of light), the two terms actually describe the same concept.
WDM systems
A WDM system uses a multiplexer at the transmitter to join the several signals together, and a demultiplexer at the receiver to split them apart. With the right type of fiber it is possible to have a device that does both simultaneously, and can function as an optical add-drop multiplexer. The optical filtering devices used have conventionally been etalons (stable solid-state single-frequency Fabry–Pérot interferometers in the form of thin-film-coated optical glass).
This article is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported License, which means that you can copy and modify it as long as the entire work (including additions) remains under this license.
- Loading...

-
 39:28
39:28Tutorial DWDM & Packet Optical Fundamentals Troubleshooting the Transmission Layer
Tutorial DWDM & Packet Optical Fundamentals Troubleshooting the Transmission LayerTutorial DWDM & Packet Optical Fundamentals Troubleshooting the Transmission Layer
Speakes: Peter Landon, BTI This tutorial will cover three different areas, Dense Wave Division Multiplexing, Packet Optical technology, and performance monitoring. This introduction of technologies will lead into a practical overview of methods to debug and troubleshoot optical networks, for both new and existing installations. Examples will include debug techniques for real-life issues and various solutions will be discussed. - See more at: https://www.nanog.org/meetings/nanog64/agenda#sthash.Dz9Xz6Qx.dpuf -
 7:08
7:08DWDM Fiber Optics Presentation
DWDM Fiber Optics PresentationDWDM Fiber Optics Presentation
In this video we describe a brief history of fiber optics and how it got to Dense Wavelength Division Multiplexing or DWDM. We also give a high level overview of how a DWDM system works. -
 4:10
4:10SONET, DWDM, and CWDM - CompTIA Network+ N10-006 - 1.4
SONET, DWDM, and CWDM - CompTIA Network+ N10-006 - 1.4SONET, DWDM, and CWDM - CompTIA Network+ N10-006 - 1.4
Network+ Training Course Index: http://professormesser.link/n10006 Professor Messer’s Course Notes: http://professormesser.link/n10006cn Frequently Asked Questions: http://professormesser.link/faq - - - - - Carrier networks are all about large bandwidths over large distances. In this video, you’ll learn about SONET and WDM networks. - - - - - Download entire video course: http://professormesser.link/006vdyt Get the course on MP3 audio: http://professormesser.link/006adyt Subscribe to get the latest videos: http://professormesser.link/yt Calendar of live events: http://www.professormesser.com/calendar/ FOLLOW PROFESSOR MESSER: Professor Messer official website: http://www.professormesser.com/ Twitter: http://www.professormesser.com/twitter Facebook: http://www.professormesser.com/facebook Instagram: http://www.professormesser.com/instagram Google +: http://www.professormesser.com/googleplus -
 55:13
55:13On-Demand: DWDM Systems
On-Demand: DWDM SystemsOn-Demand: DWDM Systems
Senior sales executive for the Adtell Group, Frank McClatchy presents the topics: Fiber Fundamentals, Evolution of WDM, DWDM Parameters to Validate, Optical Spectrum Analyzers, Fiber Certification. Webinar Date: 04-27-2016 View our webinar archive at: http://www.fiberoptic.com/webinar -
 3:36
3:36Training in DWDM AND SDH
Training in DWDM AND SDHTraining in DWDM AND SDH
-
 3:42
3:42CWDM VS DWDM Transmission Systems
CWDM VS DWDM Transmission SystemsCWDM VS DWDM Transmission Systems
WDM is really a technology which multiplexes multiple optical signals on one fiber by utilizing different wavelengths,or colors,of laser light to carry the various signals. -
 5:23
5:23Multiplexing WDM and DWDM
Multiplexing WDM and DWDMMultiplexing WDM and DWDM
Multiplexing Technique used in Optical domain -
 1:12:22
1:12:22APRICOT 2015 - DWDM & Packet Optical Fundamentals: How to troubleshoot the Transmission Layer
APRICOT 2015 - DWDM & Packet Optical Fundamentals: How to troubleshoot the Transmission LayerAPRICOT 2015 - DWDM & Packet Optical Fundamentals: How to troubleshoot the Transmission Layer
Location: Room 502 + 503 This tutorial will cover three different areas, Dense Wave Division Multiplexing, Packet Optical technology, specifically metro Ethernet, and performance monitoring. This introduction of technologies will lead into a practical overview of methods to debug and troubleshoot optical networks, for both new and existing installations. Examples will include debug techniques for real-life issues and possible solutions will be discussed. Agenda Peter Landon (BTI Systems) -
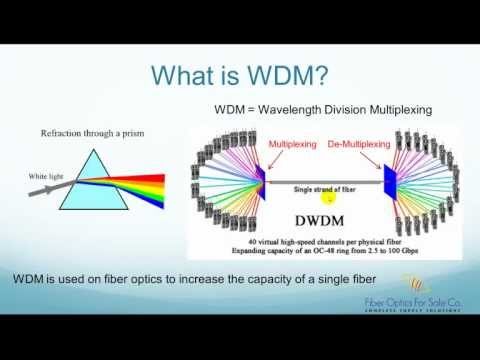 4:34
4:34What is WDM (Wavelength Division Multiplexer)? - FO4SALE.COM
What is WDM (Wavelength Division Multiplexer)? - FO4SALE.COMWhat is WDM (Wavelength Division Multiplexer)? - FO4SALE.COM
http://www.fiberoptics4sale.com WDM stands for Wavelength Division Multiplexing. WDM is the most important and most popular method to increase the capacity of a single strand of fiber. As we all have learned from elementary school science, a white light beam can be separated into individual colored light beams by a prism, as shown in this picture. Vice versa, individual colored light beams can also be combined into a single white light beam by the prism, that is if we use the prism in the reverse direction. WDM uses this same idea. Traditionally, only one colored light was used on a single strand of fiber to carry the information, such as 1550nm light. However, starting from the early 1990s, the Internet boom pushed service providers to find a method to increase the capacity on their network in the most economical way. That is when WDM devices were invented. As shown in the right side picture, in a WDM system, many different colored lights are combined by a WDM multiplexing device and put into a single strand of fiber, each color is called a channel. On the receiving side, each color is separated into its own channel by a WDM de-multiplexing device. It shows that a single fiber's capacity is increased by 40 times with a 40 channel WDM. The beauty of WDM is that you only need to upgrade the end equipment, no need to dig up trenches to bury more fibers, which is much more costly. So how are WDM devices made? This picture shows a 3 channel WDM device based on thin-film filters. Thin-film filters are a piece of flat surface glass with optical coatings on it. The optical coatings are designed to pass and reflect certain colored lights. This is a de-multiplexing WDM device, which means that it separates combined colored lights from a single fiber into separate individual fibers. But if used in the reverse direction, it can also combine different colored lights from individual fibers into a single fiber. As shown, three colored lights, which are 1510nm, 1530nm and 1570nm, come from a single strand of fiber 1. The GRIN lens collimates the light so it won't diverge into a large un-controlled beam. Filter 1 is designed to pass 1530nm and 1510nm, but reflect 1570nm. So when the light hits filter 1, 1570nm is reflected and re-focused into fiber 2 by the GRIN lens. Now the light has 1530nm and 1510nm in it, and it keeps going until it hits filter 2. Filter 2 is designed to pass 1510nm but reflect 1530nm, so 1510nm light passes and is focused into fiber 3 by the 2nd GRIN lens. On the other hand, 1530nm light is reflected by filter 2, passes filter 1 again, and is focused into fiber 4 by the 1st GRIN lens. Why isn't 1530nm focused into fiber 2? That is because the filters have a thickness, so there is a offset on the vertical direction. We just talked about a 3 channel WDM device. Thin-film filter based WDMs can be cascaded together to get higher channel counts, such as 4, 8, 16, 32 channels. The right side picture shows a 8 channel WDM device. The left picture shows how it's made by cascading several WDMs together. In additional to thin-film filter based WDMs, there are also fused fiber based WDMs, Arrayed Waveguide Grating based WDMs, Interleaver based WDMs, etc. They use different mechanisms to separate the colored lights. So there you have it. Please don't forget to visit http://www.fiberoptics4sale.com for more free fiber optic tutorials. I will see you in the next video! -
 6:41
6:41CommScope: CWDM vs. DWDM
CommScope: CWDM vs. DWDMCommScope: CWDM vs. DWDM
As CommScope's Wes Oxlee explains, mobile network operators who choose coarse wave division multiplexing fiber deployments have the option to upgrade to dense wave division multiplexing with an overlay at a later time.
-

Tutorial DWDM & Packet Optical Fundamentals Troubleshooting the Transmission Layer
Speakes: Peter Landon, BTI This tutorial will cover three different areas, Dense Wave Division Multiplexing, Packet Optical technology, and performance monitoring. This introduction of technologies will lead into a practical overview of methods to debug and troubleshoot optical networks, for both new and existing installations. Examples will include debug techniques for real-life issues and various solutions will be discussed. - See more at: https://www.nanog.org/meetings/nanog64/agenda#sthash.Dz9Xz6Qx.dpuf
published: 03 Jun 2015 -

DWDM Fiber Optics Presentation
In this video we describe a brief history of fiber optics and how it got to Dense Wavelength Division Multiplexing or DWDM. We also give a high level overview of how a DWDM system works.
published: 22 May 2011 -

SONET, DWDM, and CWDM - CompTIA Network+ N10-006 - 1.4
Network+ Training Course Index: http://professormesser.link/n10006 Professor Messer’s Course Notes: http://professormesser.link/n10006cn Frequently Asked Questions: http://professormesser.link/faq - - - - - Carrier networks are all about large bandwidths over large distances. In this video, you’ll learn about SONET and WDM networks. - - - - - Download entire video course: http://professormesser.link/006vdyt Get the course on MP3 audio: http://professormesser.link/006adyt Subscribe to get the latest videos: http://professormesser.link/yt Calendar of live events: http://www.professormesser.com/calendar/ FOLLOW PROFESSOR MESSER: Professor Messer official website: http://www.professormesser.com/ Twitter: http://www.professormesser.com/twitter Facebook: http://www.professormesser.com/facebook...
published: 30 Mar 2015 -

On-Demand: DWDM Systems
Senior sales executive for the Adtell Group, Frank McClatchy presents the topics: Fiber Fundamentals, Evolution of WDM, DWDM Parameters to Validate, Optical Spectrum Analyzers, Fiber Certification. Webinar Date: 04-27-2016 View our webinar archive at: http://www.fiberoptic.com/webinar
published: 29 Apr 2016 -

Training in DWDM AND SDH
published: 23 Aug 2016 -

CWDM VS DWDM Transmission Systems
WDM is really a technology which multiplexes multiple optical signals on one fiber by utilizing different wavelengths,or colors,of laser light to carry the various signals.
published: 08 Oct 2014 -

-

APRICOT 2015 - DWDM & Packet Optical Fundamentals: How to troubleshoot the Transmission Layer
Location: Room 502 + 503 This tutorial will cover three different areas, Dense Wave Division Multiplexing, Packet Optical technology, specifically metro Ethernet, and performance monitoring. This introduction of technologies will lead into a practical overview of methods to debug and troubleshoot optical networks, for both new and existing installations. Examples will include debug techniques for real-life issues and possible solutions will be discussed. Agenda Peter Landon (BTI Systems)
published: 05 Mar 2015 -

What is WDM (Wavelength Division Multiplexer)? - FO4SALE.COM
http://www.fiberoptics4sale.com WDM stands for Wavelength Division Multiplexing. WDM is the most important and most popular method to increase the capacity of a single strand of fiber. As we all have learned from elementary school science, a white light beam can be separated into individual colored light beams by a prism, as shown in this picture. Vice versa, individual colored light beams can also be combined into a single white light beam by the prism, that is if we use the prism in the reverse direction. WDM uses this same idea. Traditionally, only one colored light was used on a single strand of fiber to carry the information, such as 1550nm light. However, starting from the early 1990s, the Internet boom pushed service providers to find a method to increase the capacity on their ne...
published: 26 Oct 2012 -

CommScope: CWDM vs. DWDM
As CommScope's Wes Oxlee explains, mobile network operators who choose coarse wave division multiplexing fiber deployments have the option to upgrade to dense wave division multiplexing with an overlay at a later time.
published: 12 May 2017
Tutorial DWDM & Packet Optical Fundamentals Troubleshooting the Transmission Layer
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 39:28
- Updated: 03 Jun 2015
- views: 22098
- published: 03 Jun 2015
- views: 22098
DWDM Fiber Optics Presentation
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 7:08
- Updated: 22 May 2011
- views: 85834
- published: 22 May 2011
- views: 85834
SONET, DWDM, and CWDM - CompTIA Network+ N10-006 - 1.4
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 4:10
- Updated: 30 Mar 2015
- views: 76393
- published: 30 Mar 2015
- views: 76393
On-Demand: DWDM Systems
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 55:13
- Updated: 29 Apr 2016
- views: 6217
- published: 29 Apr 2016
- views: 6217
Training in DWDM AND SDH
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 3:36
- Updated: 23 Aug 2016
- views: 8008
- published: 23 Aug 2016
- views: 8008
CWDM VS DWDM Transmission Systems
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 3:42
- Updated: 08 Oct 2014
- views: 17162
- published: 08 Oct 2014
- views: 17162
Multiplexing WDM and DWDM
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 5:23
- Updated: 20 Nov 2016
- views: 2426
APRICOT 2015 - DWDM & Packet Optical Fundamentals: How to troubleshoot the Transmission Layer
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 1:12:22
- Updated: 05 Mar 2015
- views: 11832
- published: 05 Mar 2015
- views: 11832
What is WDM (Wavelength Division Multiplexer)? - FO4SALE.COM
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 4:34
- Updated: 26 Oct 2012
- views: 100524
- published: 26 Oct 2012
- views: 100524
CommScope: CWDM vs. DWDM
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 6:41
- Updated: 12 May 2017
- views: 417
- published: 12 May 2017
- views: 417

- Playlist
- Chat

- Playlist
- Chat

Tutorial DWDM & Packet Optical Fundamentals Troubleshooting the Transmission Layer
- Report rights infringement
- published: 03 Jun 2015
- views: 22098

DWDM Fiber Optics Presentation
- Report rights infringement
- published: 22 May 2011
- views: 85834

SONET, DWDM, and CWDM - CompTIA Network+ N10-006 - 1.4
- Report rights infringement
- published: 30 Mar 2015
- views: 76393

On-Demand: DWDM Systems
- Report rights infringement
- published: 29 Apr 2016
- views: 6217

Training in DWDM AND SDH
- Report rights infringement
- published: 23 Aug 2016
- views: 8008

CWDM VS DWDM Transmission Systems
- Report rights infringement
- published: 08 Oct 2014
- views: 17162

Multiplexing WDM and DWDM
- Report rights infringement
- published: 20 Nov 2016
- views: 2426

APRICOT 2015 - DWDM & Packet Optical Fundamentals: How to troubleshoot the Transmission Layer
- Report rights infringement
- published: 05 Mar 2015
- views: 11832

What is WDM (Wavelength Division Multiplexer)? - FO4SALE.COM
- Report rights infringement
- published: 26 Oct 2012
- views: 100524

CommScope: CWDM vs. DWDM
- Report rights infringement
- published: 12 May 2017
- views: 417
-
Lyrics list:lyrics
-
The Veldt, Deadmau5
-
Telemiscommunications, Deadmau5
-
Sofi Needs A Ladder, Deadmau5
-
Raise Your Weapon, Deadmau5
-
Professional Griefers, Deadmau5
-
One Trick Pony, Deadmau5
-
I Like Soda, Deadmau5
-
Ghosts N Stuff, Deadmau5
-
Bad Selection, Deadmau5
-
Arguru, Deadmau5
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
The Veldt
HappyLife, with the machines
Scattered around the room
Look what they made, they made it for me
Happy Technology
Outside, the lions roam
Feeding on remains
We'll never leave, look at us now
So in love with the way we are
Here
The World That The Children Made
The World That the Children Made
Here
The World That The Children Made
Here
The World That The Children Made
Every night, they rock us to sleep
Digital family
Is it real, or is it a dream?
Can you believe in machines?
Outside, the beating sun
Can you hear the screams?
We'll never leave, look at us now
So in love with the way we are
Here
The World That The Children Made
The World That the Children Made
Here
The World That The Children Made
Here
The World That The Children Made
Here
The World That The Children Made
Here
The World That The Children Made
HappyLife, with the machines
Scattered around the room
Look what they made, they made it for me
Happy Technology
Outside, the lions roam
Feeding on remains
We'll never leave, look at us now
So in love with the way we are
Here
The World That The Children Made
The World That the Children Made
Here
The World That The Children Made
Here
The World That The Children Made
Here
The World That The Children Made
Here



