- published: 15 Sep 2009
- views: 2782452
-
remove the playlistSubstitution
- remove the playlistSubstitution
- published: 20 Dec 2015
- views: 31313
- published: 07 Nov 2007
- views: 615223
- published: 01 Oct 2011
- views: 105447
- published: 28 Jan 2015
- views: 171293
- published: 17 Feb 2015
- views: 96946
- published: 20 Mar 2012
- views: 195102
- published: 02 Jul 2014
- views: 57555
- published: 11 Sep 2014
- views: 89079
- published: 10 Mar 2011
- views: 304554
Substitution (logic)
Substitution is a fundamental concept in logic. A substitution is a syntactic transformation on formal expressions. To apply a substitution to an expression means to consistently replace its variable, or placeholder, symbols by other expressions. The resulting expression is called a substitution instance of the original expression.
Propositional logic
Definition
Where Ψ and Φ represent formulas of propositional logic, Ψ is a substitution instance of Φ if and only if Ψ may be obtained from Φ by substituting formulas for symbols in Φ, always replacing an occurrence of the same symbol by an occurrence of the same formula. For example:
is a substitution instance of:
and
is a substitution instance of:
In some deduction systems for propositional logic, a new expression (a proposition) may be entered on a line of a derivation if it is a substitution instance of a previous line of the derivation (Hunter 1971, p. 118). This is how new lines are introduced in some axiomatic systems. In systems that use rules of transformation, a rule may include the use of a substitution instance for the purpose of introducing certain variables into a derivation.
This article is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported License, which means that you can copy and modify it as long as the entire work (including additions) remains under this license.
Substitution
Substitution may refer to:
Science and mathematics
Other uses
This article is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported License, which means that you can copy and modify it as long as the entire work (including additions) remains under this license.

Logic
Logic (from the Ancient Greek: λογική, logike) is the branch of philosophy concerned with the use and study of valid reasoning. The study of logic also features prominently in mathematics and computer science.
Logic was studied in several ancient civilizations, including Greece, India, and China. In the West, logic was established as a formal discipline by Aristotle, who gave it a fundamental place in philosophy. The study of logic was part of the classical trivium, which also included grammar and rhetoric. Logic was further extended by Al-Farabi who categorized it into two separate groups (idea and proof). Later, Avicenna revived the study of logic and developed relationship between temporalis and the implication. In the East, logic was developed by Hindus, Buddhists and Jains.
Logic is often divided into three parts: inductive reasoning, abductive reasoning, and deductive reasoning.
The study of logic
The concept of logical form is central to logic. The validity of an argument is determined by its logical form, not by its content. Traditional Aristotelian syllogistic logic and modern symbolic logic are examples of formal logic.
This article is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported License, which means that you can copy and modify it as long as the entire work (including additions) remains under this license.
- Loading...

-
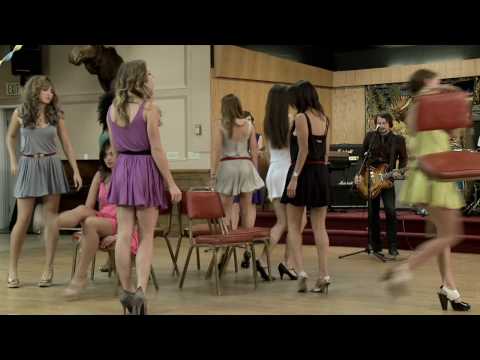 4:49
4:49Silversun Pickups - Substitution
Silversun Pickups - SubstitutionSilversun Pickups - Substitution
"Substitution" [Video] from the album Swoon Download on iTunes: http://smarturl.it/swoon Order Vinyl: http://dangerbirdrecords.merchnow.com/products/160831 Like Silversun Pickups on Facebook http://facebook.com/silversunpickups Follow Silversun Pickups on Twitter http://twitter.com/SSPU Official Silversun Pickups Website http://silversunpickups.com/ Dangerbird Records http://dangerbirdrecords.com http://facebook.com/dangerbirdrecords http://twitter.com/dangerbird -
 5:09
5:09Substitution einfach erklärt – Gleichungen umstellen / lösen
Substitution einfach erklärt – Gleichungen umstellen / lösenSubstitution einfach erklärt – Gleichungen umstellen / lösen
Wat ist dat denn schon wieder für ein hässliches Wort? Substitution? Für was brauch ich die, was macht die und ganz wichtig wie wende ich sie bei Gleichungen an? Das erklären wir euch in diesem Video. Kategorie: Basics Hier kommst du direkt zum nächsten Video: http://bit.ly/LineareGrundlage » ALLE KANÄLE Wirtschaft: http://www.thesimpleeconomics.de Mathe: https://www.youtube.com/TheSimpleMaths Biologie: http://www.thesimplebiology.de Physik: http://www.thesimplephysics.de Chemie: http://www.thesimplechemics.de » MEHR VON UNS Twitter: http://www.twitter.com/thesimpleclub Facebook: http://fb.thesimpleclub.de Alex auf Instagram: http://alex.thesimpleclub.de Nico auf Instagram: http://nico.thesimpleclub.de » WAS IST THE SIMPLE CLUB? Wir sind der Meinung, dass Bildung Spaß machen muss. Deswegen bieten wir dir auf 5 Kanälen die beste und unterhaltsamste Nachhilfe die du im Netz finden kannst: Und das in Mathematik, Biologie, Chemie, Physik und Wirtschaft. In verschiedenen Kategorien und Schwierigkeitsgraden bereiten wir dich auf deine Prüfung vor. Egal ob Schüler oder Student, ob jung oder alt, bei uns findet jeder die passenden Videos. Und das Beste: TheSimpleClub ist und bleibt komplett kostenlos! » CREDITS Ein Konzept von Alexander Giesecke und Nicolai Schork Geschrieben von: Simon Frank Animation: Nicolai Schork Ton: Alexander Giesecke Schnitt & Effekte: Ullrich Köhler -
 2:25
2:25Solving Systems by Substitution - MathHelp.com - Math Help
Solving Systems by Substitution - MathHelp.com - Math HelpSolving Systems by Substitution - MathHelp.com - Math Help
Like my video? Visit http://www.MathHelp.com and let's do the complete lesson together! In this lesson, students learn to solve a system of linear equations by substitution, by first isolating one of the variables in the system, then substituting its value for the corresponding variable in the other equation. -
 11:32
11:32Algebra I Help: Solving Systems of Linear Equations with Substitution 1/2
Algebra I Help: Solving Systems of Linear Equations with Substitution 1/2Algebra I Help: Solving Systems of Linear Equations with Substitution 1/2
http://www.greenemath.com/ In this video, we learn how to solve a system of linear equations using the method of substitution. This method is generally preferred to graphing, since it is sometimes more difficult to determine a solution via graphing. -
 4:51
4:51Integration durch Substitution - Integrale
Integration durch Substitution - IntegraleIntegration durch Substitution - Integrale
Integrale berechnen mit der Substitution – wie soll das gehen? Wie macht man das formal, und wie kann man sich den formalen Quatsch sparen, um einfach nur aufs Ergebnis zu kommen? Das seht ihr hier! Kategorie: Abitur und Studium Hier kommst du direkt zum nächsten Video: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=S5MopJe3iuk&list;=PLjaA00udJtOpEkZF2FX8hTR9iqLpD35Kr&index;=10 » ALLE KANÄLE Wirtschaft: http://www.thesimpleeconomics.de Mathe: https://www.youtube.com/TheSimpleMaths Biologie: http://www.thesimplebiology.de Physik: http://www.thesimplephysics.de Chemie: http://www.thesimplechemics.de The Simple Club: https://www.youtube.com/TheSimpleClub » MEHR VON UNS Twitter: http://www.twitter.com/thesimpleclub Facebook: http://fb.thesimpleclub.de Alex auf Instagram: http://alex.thesimpleclub.de Nico auf Instagram: http://nico.thesimpleclub.de » WAS IST THE SIMPLE CLUB? Wir sind der Meinung, dass Bildung Spaß machen muss. Deswegen bieten wir dir auf 4 Kanälen die beste und unterhaltsamste Nachhilfe die du im Netz finden kannst: Und das in Mathematik, Biologie, Chemie und Physik. In verschiedenen Kategorien und Schwierigkeitsgraden bereiten wir dich auf deine Prüfung vor. Egal ob Schüler oder Student, ob jung oder alt, bei uns findet jeder die passenden Videos. Und das Beste: TheSimpleClub ist und bleibt komplett kostenlos! » CREDITS Ein Konzept von Alexander Giesecke und Nicolai Schork Geschrieben von: Rouven Zeus Visuelle Konzeption: Nicolai Schork Ton: Alexander Giesecke Schnitt & Effekte: Jonas Ressel -
 4:14
4:14Integration durch Substitution 1, Formel, Erklärung, Schreibweise, Mathe by Daniel Jung
Integration durch Substitution 1, Formel, Erklärung, Schreibweise, Mathe by Daniel JungIntegration durch Substitution 1, Formel, Erklärung, Schreibweise, Mathe by Daniel Jung
Integration durch Substitution 1, Formel, Erklärung, Schreibweise, Stammfunktion bilden, Aufleitung, Integralrechnung, innere, äußere Funktion erkennen Die Integration durch Substitution oder Substitutionsregel ist eine wichtige Methode in der Integralrechnung, um Stammfunktionen und bestimmte Integrale zu berechnen. Durch Einführung einer neuen Integrationsvariablen wird ein Teil des Integranden ersetzt, um das Integral zu vereinfachen und so letztlich auf ein bekanntes oder einfacher handhabbares Integral zurückzuführen. Die Kettenregel aus der Differentialrechnung ist die Grundlage der Substitutionsregel. Ihr Äquivalent für Integrale über mehrdimensionale Funktionen ist der Transformationssatz, der allerdings eine bijektive Substitutionsfunktion voraussetzt. Meine Website: http://daniel-jung.eu/ Mein Social Media: https://www.facebook.com/daniel.jung.520900 https://www.instagram.com/danielskylimit/ https://twitter.com/simplicityyoung Snapchat: jung.daniel Daniel Jung erklärt Mathe in Kürze: Lernkonzept: Mathe lernen durch kurze, auf den Punkt gebrachte Videos zu allen Themen von der 5.Klasse bis zum Studium, sortiert in Themenplaylists für eine intuitive Channelnavigation. Online Nachhilfe, Hilfe in Mathe, Mathe Nachhilfe, einfach erklärt, Onlinenachhilfe https://www.youtube.com/c/mathebydanieljung https://www.studyhelp.de (ABI & UNI Crashkurse) http://www.mathe2go.de/ (Digitales Matheskript, Mathecommunity, Link zu Aufgaben) https://www.youtube.com/user/Studyhelpmedia (Mechanik) https://www.youtube.com/user/OberPrima (YouTuber Mathematik) https://de.serlo.org/ (Übungsaufgaben for FREE) Nachhilfe, online, Mathehilfe, Lernhilfe, Mathe, Hilfe, Onlinehilfe, Lernvideo, Erklärvideo, Nachhilfelehrer, Daniel, Jung, Mathe by Daniel Jung, Daniel Jung, Onlinelehrer, Mathematik, Mathematiknachhilfe, kostenlos, umsonst, schnell, einfach, erklärt, individuell, ausrechnen, berechnen, Schülernachhilfe, Unterricht, Onlineunterricht, Nachhilfeunterricht, persönlicher, Matheaufgaben, besser, lernen, Onlinenachhilfe, Bock, Mathenachhilfe, Erklärung, erklären, geben, mobile, Schüler, Videos, Hausaufgabenhilfe, Abi, Abitur, Grundstudium, Uni, Oberstufe, Grundkurs, Leistungskurs, Mathekurs, Vorkurs, Analysis, Matrix, Matrizen, Lineare Algebra, Stochastik, Wahrscheinlichkeit, Statistik, Analytische, Geometrie, Klassenarbeiten, Klausuren, Vorbereitung, Abiturvorbereitung, auffrischen, wiederholen, aufarbeiten, Taschenrechnereingabe, nacharbeiten, aufholen, Stoff, Mathestoff, Vokabeln, Mathematikvokabeln, Studium, Universität, Schule, Uni Mein erstes Startup (lokale Plattform für Lernen und Lehren) gründete ich 2003 im Bereich Bildung. Dort habe ich selber über 10 Jahre Mathekurse geleitet. Die gesamte Matheschullaufbahn bekommt ihr in kurzen, verständlichen, auf den Punkt gebrachten Lernvideos. Von der 5. bis zur 10. Klasse, Einführungsphase bzw. Jahrgangsstufe 11, Q1/Q2 bzw. Jahrgangsstufe 12/13, Abiturvorbereitung inklusive Berufskolleg Wirtschaft und Verwaltung, Studium, Universitätsmathematik Themen Oberstufe/Abitur/Studium: Analysis (Funktionen & Co.), Stochastik (Wahrscheinlichkeit & Co.), Analytische Geometrie (Vektoren & Co.), Lineare Algebra (Matrizen & Co.), Finanzmathematik, Differentialrechnung, Integralrechnung, Stammfunktion, partielle Integration, Substitutionsmethode, Ableiten, Kettenregel, Produktregel, Quotientenregel, Kurvendiskussion, Symmetrie, Grenzverhalten, Nullstellen, Extrempunkte, Wendepunkte, Hypothesentest, Binomialverteilung, bedingte Wahrscheinlichkeit, Schätzen, Zufallsgrößen, Laplace, Zufallsexperiment, Normalverteilung, Vektoren, Abstand, Lage, Koordinatenform, Geraden, Ebenen, Parameterform, Austauschprozesse, Populationsmatrizen, Koeffizienten, Übergangsprozesse, Fixvektor, Gaußalgorithmus, e-Funktion, ln-Funktion, Steigung, Integrationsverfahren, Differentialgleichung, Vektoranalysis, Taylor, Komplexe Zahlen, Folgen und Reihen, Konvergenz, Determinanten, Gruppen, Vektorräume, Mehrdimensionale Funktionen, Lineare Optimierung, Mengenlehre, Vollständige Induktion, Relationen Themen Unterstufe: Zahlenwelt, Bruchrechnung, Terme, Gleichungen, Zuordnungen, Lineare Funktionen, Prozentrechnung, Dreisatz, Binomische Formeln, Wahrscheinlichkeit, Statistik, Wurzel, Logarithmus, Exponentielles Wachstum, Exponentialfunktionen, Flächen, Körper, Trigonometrie, Pythagoras, Parabeln, quadratische Funktionen, Gleichungssysteme, lösen, Lösungsverfahren, Dreiecke, Vierecke, Pyramide, Quader, Kegel, Würfel, Prisma, Kugel, quadratische Ergänzung, PQ-Formel, Satz von Vieta, Potenzen, Potenzgesetze, Proportionalität Mathe in Kürze, Zeit sparen und Mathe verstehen durch kurze Erklärvideos, dein digitaler Mathe Back Up, jederzeit, überall, sooft wie nötig, Mathe-in-Kürze-Original -
 8:15
8:15How to Solve Systems of Linear Equations by Substitution
How to Solve Systems of Linear Equations by SubstitutionHow to Solve Systems of Linear Equations by Substitution
http://facebook.com/tylersokay http://twitter.com/tylertarver How to Solve Systems of Linear Equations by Substitution -
 4:12
4:12Lineare Substitution zum Integrieren, Stammfunktion bilden, Mathe by Daniel Jung
Lineare Substitution zum Integrieren, Stammfunktion bilden, Mathe by Daniel JungLineare Substitution zum Integrieren, Stammfunktion bilden, Mathe by Daniel Jung
Lineare Substitution um Integrieren, Stammfunktion bilden, Analysis, Mathe by Daniel Jung Meine Website: http://daniel-jung.eu/ Mein Social Media: https://www.facebook.com/daniel.jung.520900 https://www.instagram.com/danielskylimit/ https://twitter.com/simplicityyoung Snapchat: jung.daniel Daniel Jung erklärt Mathe in Kürze: Lernkonzept: Mathe lernen durch kurze, auf den Punkt gebrachte Videos zu allen Themen von der 5.Klasse bis zum Studium, sortiert in Themenplaylists für eine intuitive Channelnavigation. Online Nachhilfe, Hilfe in Mathe, Mathe Nachhilfe, einfach erklärt, Onlinenachhilfe https://www.youtube.com/c/mathebydanieljung https://www.studyhelp.de (ABI & UNI Crashkurse) http://www.mathe2go.de/ (Digitales Matheskript, Mathecommunity, Link zu Aufgaben) https://www.youtube.com/user/Studyhelpmedia (Mechanik) https://www.youtube.com/user/OberPrima (YouTuber Mathematik) Nachhilfe, online, Mathehilfe, Lernhilfe, Mathe, Hilfe, Onlinehilfe, Lernvideo, Erklärvideo, Nachhilfelehrer, Daniel, Jung, Mathe by Daniel Jung, Daniel Jung, Onlinelehrer, Mathematik, Mathematiknachhilfe, kostenlos, umsonst, schnell, einfach, erklärt, individuell, ausrechnen, berechnen, Schülernachhilfe, Unterricht, Onlineunterricht, Nachhilfeunterricht, persönlicher, Matheaufgaben, besser, lernen, Onlinenachhilfe, Bock, Mathenachhilfe, Erklärung, erklären, geben, mobile, Schüler, Videos, Hausaufgabenhilfe, Abi, Abitur, Grundstudium, Uni, Oberstufe, Grundkurs, Leistungskurs, Mathekurs, Vorkurs, Analysis, Matrix, Matrizen, Lineare Algebra, Stochastik, Wahrscheinlichkeit, Statistik, Analytische, Geometrie, Klassenarbeiten, Klausuren, Vorbereitung, Abiturvorbereitung, auffrischen, wiederholen, aufarbeiten, Taschenrechnereingabe, nacharbeiten, aufholen, Stoff, Mathestoff, Vokabeln, Mathematikvokabeln, Studium, Universität, Schule, Uni Mein erstes Startup (lokale Plattform für Lernen und Lehren) gründete ich 2003 im Bereich Bildung. Dort habe ich selber über 10 Jahre Mathekurse geleitet. Die gesamte Matheschullaufbahn bekommt ihr in kurzen, verständlichen, auf den Punkt gebrachten Lernvideos. Von der 5. bis zur 10. Klasse, Einführungsphase bzw. Jahrgangsstufe 11, Q1/Q2 bzw. Jahrgangsstufe 12/13, Abiturvorbereitung inklusive Berufskolleg Wirtschaft und Verwaltung, Studium, Universitätsmathematik Themen Oberstufe/Abitur/Studium: Analysis (Funktionen & Co.), Stochastik (Wahrscheinlichkeit & Co.), Analytische Geometrie (Vektoren & Co.), Lineare Algebra (Matrizen & Co.), Finanzmathematik, Differentialrechnung, Integralrechnung, Stammfunktion, partielle Integration, Substitutionsmethode, Ableiten, Kettenregel, Produktregel, Quotientenregel, Kurvendiskussion, Symmetrie, Grenzverhalten, Nullstellen, Extrempunkte, Wendepunkte, Hypothesentest, Binomialverteilung, bedingte Wahrscheinlichkeit, Schätzen, Zufallsgrößen, Laplace, Zufallsexperiment, Normalverteilung, Vektoren, Abstand, Lage, Koordinatenform, Geraden, Ebenen, Parameterform, Austauschprozesse, Populationsmatrizen, Koeffizienten, Übergangsprozesse, Fixvektor, Gaußalgorithmus, e-Funktion, ln-Funktion, Steigung, Integrationsverfahren, Differentialgleichung, Vektoranalysis, Taylor, Komplexe Zahlen, Folgen und Reihen, Konvergenz, Determinanten, Gruppen, Vektorräume, Mehrdimensionale Funktionen, Lineare Optimierung, Mengenlehre, Vollständige Induktion, Relationen Themen Unterstufe: Zahlenwelt, Bruchrechnung, Terme, Gleichungen, Zuordnungen, Lineare Funktionen, Prozentrechnung, Dreisatz, Binomische Formeln, Wahrscheinlichkeit, Statistik, Wurzel, Logarithmus, Exponentielles Wachstum, Exponentialfunktionen, Flächen, Körper, Trigonometrie, Pythagoras, Parabeln, quadratische Funktionen, Gleichungssysteme, lösen, Lösungsverfahren, Dreiecke, Vierecke, Pyramide, Quader, Kegel, Würfel, Prisma, Kugel, quadratische Ergänzung, PQ-Formel, Satz von Vieta, Potenzen, Potenzgesetze, Proportionalität Mathe in Kürze, Zeit sparen und Mathe verstehen durch kurze Erklärvideos, dein digitaler Mathe Back Up, jederzeit, überall, sooft wie nötig, Mathe-in-Kürze-Original -
 6:10
6:10Algebra 36 - Solving Systems of Equations by Substitution
Algebra 36 - Solving Systems of Equations by SubstitutionAlgebra 36 - Solving Systems of Equations by Substitution
A system of two equations in x and y can be solved by rearranging one equation to represent x in terms of y, and then substituting this expression for x into the other equation to create an equation with only the variable y. This equation can then be solved to find y's value which can then be substituted back into either equation to find the value of x. -
 4:39
4:39The substitution method | Systems of equations | 8th grade | Khan Academy
The substitution method | Systems of equations | 8th grade | Khan AcademyThe substitution method | Systems of equations | 8th grade | Khan Academy
The Substitution Method Practice this lesson yourself on KhanAcademy.org right now: https://www.khanacademy.org/math/cc-eighth-grade-math/cc-8th-systems-topic/cc-8th-systems-with-substitution/e/systems_of_equations_with_substitution?utm_source=YT&utm;_medium=Desc&utm;_campaign=8thgrade Watch the next lesson: https://www.khanacademy.org/math/cc-eighth-grade-math/cc-8th-systems-topic/cc-8th-systems-with-substitution/v/substitution-method-2?utm_source=YT&utm;_medium=Desc&utm;_campaign=8thgrade Missed the previous lesson? https://www.khanacademy.org/math/cc-eighth-grade-math/cc-8th-systems-topic/cc-8th-systems-with-substitution/v/solving-systems-by-substitution-3?utm_source=YT&utm;_medium=Desc&utm;_campaign=8thgrade 8th grade on Khan Academy: 8th grade is all about tackling the meat of algebra and getting exposure to some of the foundational concepts in geometry. If you get this stuff (and you should because you're incredibly persistent), the rest of your life will be easy. Okay, maybe not your whole life, but at least your mathematical life. Seriously, if you really get the equations and functions stuff we cover here, most of high school will feel intuitive, even relaxing. (Content was selected for this grade level based on a typical curriculum in the United States.) About Khan Academy: Khan Academy offers practice exercises, instructional videos, and a personalized learning dashboard that empower learners to study at their own pace in and outside of the classroom. We tackle math, science, computer programming, history, art history, economics, and more. Our math missions guide learners from kindergarten to calculus using state-of-the-art, adaptive technology that identifies strengths and learning gaps. We've also partnered with institutions like NASA, The Museum of Modern Art, The California Academy of Sciences, and MIT to offer specialized content. For free. For everyone. Forever. #YouCanLearnAnything Subscribe to Khan Academy’s 8th grade channel: https://www.youtube.com/channel/UCq341CBxj87C7AY_zu2qPlQ?sub_confirmation=1 Subscribe to Khan Academy: https://www.youtube.com/subscription_center?add_user=khanacademy
-
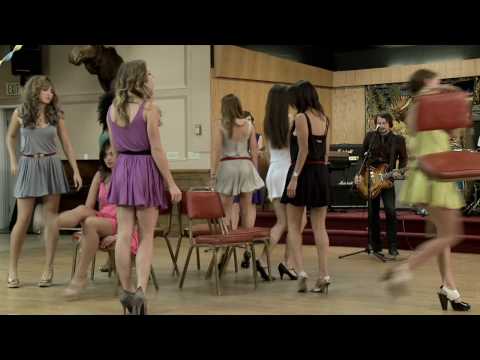
Silversun Pickups - Substitution
"Substitution" [Video] from the album Swoon Download on iTunes: http://smarturl.it/swoon Order Vinyl: http://dangerbirdrecords.merchnow.com/products/160831 Like Silversun Pickups on Facebook http://facebook.com/silversunpickups Follow Silversun Pickups on Twitter http://twitter.com/SSPU Official Silversun Pickups Website http://silversunpickups.com/ Dangerbird Records http://dangerbirdrecords.com http://facebook.com/dangerbirdrecords http://twitter.com/dangerbird -

Substitution einfach erklärt – Gleichungen umstellen / lösen
Wat ist dat denn schon wieder für ein hässliches Wort? Substitution? Für was brauch ich die, was macht die und ganz wichtig wie wende ich sie bei Gleichungen an? Das erklären wir euch in diesem Video. Kategorie: Basics Hier kommst du direkt zum nächsten Video: http://bit.ly/LineareGrundlage » ALLE KANÄLE Wirtschaft: http://www.thesimpleeconomics.de Mathe: https://www.youtube.com/TheSimpleMaths Biologie: http://www.thesimplebiology.de Physik: http://www.thesimplephysics.de Chemie: http://www.thesimplechemics.de » MEHR VON UNS Twitter: http://www.twitter.com/thesimpleclub Facebook: http://fb.thesimpleclub.de Alex auf Instagram: http://alex.thesimpleclub.de Nico auf Instagram: http://nico.thesimpleclub.de » WAS IST THE SIMPLE CLUB? Wir sind der Meinung, dass Bildung Spaß machen muss... -

Solving Systems by Substitution - MathHelp.com - Math Help
Like my video? Visit http://www.MathHelp.com and let's do the complete lesson together! In this lesson, students learn to solve a system of linear equations by substitution, by first isolating one of the variables in the system, then substituting its value for the corresponding variable in the other equation. -

Algebra I Help: Solving Systems of Linear Equations with Substitution 1/2
http://www.greenemath.com/ In this video, we learn how to solve a system of linear equations using the method of substitution. This method is generally preferred to graphing, since it is sometimes more difficult to determine a solution via graphing. -

Integration durch Substitution - Integrale
Integrale berechnen mit der Substitution – wie soll das gehen? Wie macht man das formal, und wie kann man sich den formalen Quatsch sparen, um einfach nur aufs Ergebnis zu kommen? Das seht ihr hier! Kategorie: Abitur und Studium Hier kommst du direkt zum nächsten Video: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=S5MopJe3iuk&list;=PLjaA00udJtOpEkZF2FX8hTR9iqLpD35Kr&index;=10 » ALLE KANÄLE Wirtschaft: http://www.thesimpleeconomics.de Mathe: https://www.youtube.com/TheSimpleMaths Biologie: http://www.thesimplebiology.de Physik: http://www.thesimplephysics.de Chemie: http://www.thesimplechemics.de The Simple Club: https://www.youtube.com/TheSimpleClub » MEHR VON UNS Twitter: http://www.twitter.com/thesimpleclub Facebook: http://fb.thesimpleclub.de Alex auf Instagram: http://alex.thesimpleclub.de Nic... -

Integration durch Substitution 1, Formel, Erklärung, Schreibweise, Mathe by Daniel Jung
Integration durch Substitution 1, Formel, Erklärung, Schreibweise, Stammfunktion bilden, Aufleitung, Integralrechnung, innere, äußere Funktion erkennen Die Integration durch Substitution oder Substitutionsregel ist eine wichtige Methode in der Integralrechnung, um Stammfunktionen und bestimmte Integrale zu berechnen. Durch Einführung einer neuen Integrationsvariablen wird ein Teil des Integranden ersetzt, um das Integral zu vereinfachen und so letztlich auf ein bekanntes oder einfacher handhabbares Integral zurückzuführen. Die Kettenregel aus der Differentialrechnung ist die Grundlage der Substitutionsregel. Ihr Äquivalent für Integrale über mehrdimensionale Funktionen ist der Transformationssatz, der allerdings eine bijektive Substitutionsfunktion voraussetzt. Meine Website: http://dani... -

How to Solve Systems of Linear Equations by Substitution
http://facebook.com/tylersokay http://twitter.com/tylertarver How to Solve Systems of Linear Equations by Substitution -

Lineare Substitution zum Integrieren, Stammfunktion bilden, Mathe by Daniel Jung
Lineare Substitution um Integrieren, Stammfunktion bilden, Analysis, Mathe by Daniel Jung Meine Website: http://daniel-jung.eu/ Mein Social Media: https://www.facebook.com/daniel.jung.520900 https://www.instagram.com/danielskylimit/ https://twitter.com/simplicityyoung Snapchat: jung.daniel Daniel Jung erklärt Mathe in Kürze: Lernkonzept: Mathe lernen durch kurze, auf den Punkt gebrachte Videos zu allen Themen von der 5.Klasse bis zum Studium, sortiert in Themenplaylists für eine intuitive Channelnavigation. Online Nachhilfe, Hilfe in Mathe, Mathe Nachhilfe, einfach erklärt, Onlinenachhilfe https://www.youtube.com/c/mathebydanieljung https://www.studyhelp.de (ABI & UNI Crashkurse) http://www.mathe2go.de/ (Digitales Matheskript, Mathecommunity, Link zu Aufgaben) https://www.youtube.com/... -

Algebra 36 - Solving Systems of Equations by Substitution
A system of two equations in x and y can be solved by rearranging one equation to represent x in terms of y, and then substituting this expression for x into the other equation to create an equation with only the variable y. This equation can then be solved to find y's value which can then be substituted back into either equation to find the value of x. -

The substitution method | Systems of equations | 8th grade | Khan Academy
The Substitution Method Practice this lesson yourself on KhanAcademy.org right now: https://www.khanacademy.org/math/cc-eighth-grade-math/cc-8th-systems-topic/cc-8th-systems-with-substitution/e/systems_of_equations_with_substitution?utm_source=YT&utm;_medium=Desc&utm;_campaign=8thgrade Watch the next lesson: https://www.khanacademy.org/math/cc-eighth-grade-math/cc-8th-systems-topic/cc-8th-systems-with-substitution/v/substitution-method-2?utm_source=YT&utm;_medium=Desc&utm;_campaign=8thgrade Missed the previous lesson? https://www.khanacademy.org/math/cc-eighth-grade-math/cc-8th-systems-topic/cc-8th-systems-with-substitution/v/solving-systems-by-substitution-3?utm_source=YT&utm;_medium=Desc&utm;_campaign=8thgrade 8th grade on Khan Academy: 8th grade is all about tackling the meat of algebra ...
Silversun Pickups - Substitution
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 4:49
- Updated: 15 Sep 2009
- views: 2782452
- published: 15 Sep 2009
- views: 2782452
Substitution einfach erklärt – Gleichungen umstellen / lösen
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 5:09
- Updated: 20 Dec 2015
- views: 31313
- published: 20 Dec 2015
- views: 31313
Solving Systems by Substitution - MathHelp.com - Math Help
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 2:25
- Updated: 07 Nov 2007
- views: 615223
- published: 07 Nov 2007
- views: 615223
Algebra I Help: Solving Systems of Linear Equations with Substitution 1/2
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 11:32
- Updated: 01 Oct 2011
- views: 105447
- published: 01 Oct 2011
- views: 105447
Integration durch Substitution - Integrale
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 4:51
- Updated: 28 Jan 2015
- views: 171293
- published: 28 Jan 2015
- views: 171293
Integration durch Substitution 1, Formel, Erklärung, Schreibweise, Mathe by Daniel Jung
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 4:14
- Updated: 17 Feb 2015
- views: 96946
- published: 17 Feb 2015
- views: 96946
How to Solve Systems of Linear Equations by Substitution
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 8:15
- Updated: 20 Mar 2012
- views: 195102
- published: 20 Mar 2012
- views: 195102
Lineare Substitution zum Integrieren, Stammfunktion bilden, Mathe by Daniel Jung
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 4:12
- Updated: 02 Jul 2014
- views: 57555
- published: 02 Jul 2014
- views: 57555
Algebra 36 - Solving Systems of Equations by Substitution
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 6:10
- Updated: 11 Sep 2014
- views: 89079
- published: 11 Sep 2014
- views: 89079
The substitution method | Systems of equations | 8th grade | Khan Academy
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 4:39
- Updated: 10 Mar 2011
- views: 304554
- published: 10 Mar 2011
- views: 304554
- Playlist
- Chat
- Playlist
- Chat
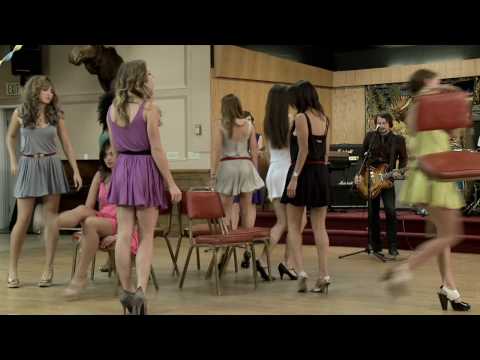
Silversun Pickups - Substitution
- Report rights infringement
- published: 15 Sep 2009
- views: 2782452

Substitution einfach erklärt – Gleichungen umstellen / lösen
- Report rights infringement
- published: 20 Dec 2015
- views: 31313

Solving Systems by Substitution - MathHelp.com - Math Help
- Report rights infringement
- published: 07 Nov 2007
- views: 615223

Algebra I Help: Solving Systems of Linear Equations with Substitution 1/2
- Report rights infringement
- published: 01 Oct 2011
- views: 105447

Integration durch Substitution - Integrale
- Report rights infringement
- published: 28 Jan 2015
- views: 171293

Integration durch Substitution 1, Formel, Erklärung, Schreibweise, Mathe by Daniel Jung
- Report rights infringement
- published: 17 Feb 2015
- views: 96946

How to Solve Systems of Linear Equations by Substitution
- Report rights infringement
- published: 20 Mar 2012
- views: 195102

Lineare Substitution zum Integrieren, Stammfunktion bilden, Mathe by Daniel Jung
- Report rights infringement
- published: 02 Jul 2014
- views: 57555

Algebra 36 - Solving Systems of Equations by Substitution
- Report rights infringement
- published: 11 Sep 2014
- views: 89079

The substitution method | Systems of equations | 8th grade | Khan Academy
- Report rights infringement
- published: 10 Mar 2011
- views: 304554
Rodrigo Duterte: Philippines president calls Barack Obama a 'son of a bitch'
Edit The Independent 05 Sep 2016Mozambique shows 3 new pieces of suspected MH370 debris
Edit Deccan Chronicle 05 Sep 2016Obama and Putin Hold Meeting at G-20
Edit Voa News 05 Sep 2016World's Largest Primate Now Considered "Critically Endangered"
Edit IFL Science 05 Sep 2016Lower Rates No Substitute For Broader Policy Reforms: Raghuram Rajan
Edit NDTV 05 Sep 201605 September 2016 - Press release REACH is the dominant driver for substitution - more action is needed (ECHA - European Chemical Agency)
Edit Public Technologies 05 Sep 2016Rhetoric of this year's presidential campaign is no substitute for thoughtful policy
Edit Las Vegas Sun 05 Sep 2016Fourth substitute experiment in Scottish Cup
Edit BBC News 05 Sep 2016Wiggle Insurance Garmin Competition (Wiggle Ltd)
Edit Public Technologies 05 Sep 2016Mane ends Liverpool injury fears after Klopp call (Liverpool Football Club and Athletic Grounds plc)
Edit Public Technologies 05 Sep 2016LOAN WATCH: Six youngsters in action (West Bromwich Albion Football Club plc)
Edit Public Technologies 05 Sep 2016PS4 NPL: Canberra FC set up 2015 GF Rematch (ACT Football Federation Inc)
Edit Public Technologies 05 Sep 2016International Round-Up (Barnsley Football Club Ltd)
Edit Public Technologies 05 Sep 2016DOUGHTY HELPS SWINDON TO POINT (Queens Park Rangers Football & Athletic Club Ltd)
Edit Public Technologies 05 Sep 2016Caps Utd Close Gap
Edit All Africa 05 Sep 2016Sadio Mane returns to Liverpool FC injury-free despite scare during international duty with Senegal
Edit The Daily Mail 05 Sep 2016- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- Next page »








