- published: 29 Jun 2014
- views: 34555
-
remove the playlistDiocletian's Palace
-
remove the playlistDiocletian's_palace Travel Guides
-
remove the playlistLatest Videos
-
remove the playlistLongest Videos
- remove the playlistDiocletian's Palace
- remove the playlistDiocletian's_palace Travel Guides
- remove the playlistLatest Videos
- remove the playlistLongest Videos
- published: 04 Jan 2014
- views: 14255
- published: 03 Apr 2013
- views: 4128
- published: 19 Oct 2013
- views: 24416
- published: 06 Apr 2016
- views: 101
- published: 28 Sep 2011
- views: 731
- published: 07 May 2012
- views: 6186
- published: 07 May 2016
- views: 311
- published: 15 Aug 2009
- views: 11449

Diocletian's Palace
Diocletian's Palace (Croatian: Dioklecijanova palača, pronounced [diɔklɛt͡sijǎːnɔʋa pǎlat͡ʃa]) is an ancient palace built by the Roman emperor Diocletian at the turn of the fourth century AD, that today forms about half the old town and city center of Split, in Croatia. While it is referred to as a "palace" because of its intended use as the retirement residence of Diocletian, the term can be misleading as the structure is massive and more resembles a large fortress: about half of it was for Diocletian's personal use, and the rest housed the military garrison.
Diocletian built the massive palace in preparation for his retirement on 1 May 305 AD. It lies in a bay on the south side of a short peninsula running out from the Dalmatian coast, four miles from Salona, the capital of the Roman province of Dalmatia. The terrain slopes gently seaward and is typical karst, consisting of low limestone ridges running east to west with marl in the clefts between them.
History
After the Romans abandoned the site, the Palace remained empty for several centuries. In the 7th century, nearby residents fled to the walled palace in an effort to escape invading Croats. Since then the palace has been occupied, with residents making their homes and businesses within the palace basement and directly in its walls. Today many restaurants and shops, and some homes, can still be found within the walls.
This article is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported License, which means that you can copy and modify it as long as the entire work (including additions) remains under this license.

Diocletian
Diocletian (/ˌdaɪ.əˈkliːʃən/; Latin: Gaius Aurelius Valerius Diocletianus Augustus), born Diocles (245–311), was a Roman emperor from 284 to 305. Born to a family of low status in the Roman province of Dalmatia, Diocletian rose through the ranks of the military to become cavalry commander to the Emperor Carus. After the deaths of Carus and his son Numerian on campaign in Persia, Diocletian was proclaimed emperor. The title was also claimed by Carus' other surviving son, Carinus, but Diocletian defeated him in the Battle of the Margus. Diocletian's reign stabilized the empire and marks the end of the Crisis of the Third Century. He appointed fellow officer Maximian as Augustus, co-emperor, in 286.
Diocletian delegated further on 1 March 293, appointing Galerius and Constantius as Caesars, junior co-emperors. Under this 'tetrarchy', or "rule of four", each emperor would rule over a quarter-division of the empire. Diocletian secured the empire's borders and purged it of all threats to his power. He defeated the Sarmatians and Carpi during several campaigns between 285 and 299, the Alamanni in 288, and usurpers in Egypt between 297 and 298. Galerius, aided by Diocletian, campaigned successfully against Sassanid Persia, the empire's traditional enemy. In 299 he sacked their capital, Ctesiphon. Diocletian led the subsequent negotiations and achieved a lasting and favorable peace.
This article is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported License, which means that you can copy and modify it as long as the entire work (including additions) remains under this license.
- Loading...

-
 5:46
5:46Diocletian's Palace, in Split, Croatia
Diocletian's Palace, in Split, CroatiaDiocletian's Palace, in Split, Croatia
Subscribe to my channel: https://www.youtube.com/user/lindybeige?sub_confirmation=1 More videos here: https://www.youtube.com/playlist?list=PL26F99D743DDB5026 Details on the springs, the Temple of Jupiter, and the vestibule in a forthcoming video. The palace is considered important enough to be a UNESCO world heritage site. Thanks to Josip Pavic for camerawork, advice, and his ability to drive on the wrong side of the road. For those who like to buy merchandise linked to YouTube channels, there may be some stuff in the nearish future from this one. First, though, you might like to go to my Facebook page (see below) and post some suggestions of things that you would buy. Lindybeige: a channel of archaeology, ancient and medieval warfare, rants, swing dance, travelogues, evolution, and whatever else occurs to me to make. ▼ Follow me... Twitter: https://twitter.com/Lindybeige I may have some drivel to contribute to the Twittersphere, plus you get notice of uploads. Facebook:https://www.facebook.com/Lindybeige (it's a 'page' and now seems to be working). Google+: "google.com/+lindybeige" (I think this is working now) website: www.LloydianAspects.co.uk Diocletian's Palace, in Split, Croatia http://www.youtube.com/user/"Lindybeige" -
 3:59
3:59Inside Diocletian's Palace: A Walking Tour in Split, Croatia
Inside Diocletian's Palace: A Walking Tour in Split, CroatiaInside Diocletian's Palace: A Walking Tour in Split, Croatia
When thinking about things to do in Split, Croatia, we chose a walking tour of Diocletian's Palace. This golden crown of Central Dalmatia offers a wealth of insight into 1,700 years of Adriatic history. Join Tricia and I as we explore this amazing UNESCO heritage site with local historian, Dino, followed by a delicious feast at the Konoba Varos restaurant. ______ For translated captions into 60+ languages, click 'CC' in the viewer. Subscribe for more DESTINATIONS with Shawn & Tricia: http://www.youtube.com/subscription_center?add_user=shawnpmitchell For more on this experience from Tricia’s perspective, check out her blog post at: http://triciaannemitchell.com/2014/01/04/diocletian-palace-split-walking-tour/ Connect with Tricia on social media: LinkedIn: https://linkedin.com/in/triciabolyardmitchell Twitter: https://twitter.com/TriciaAMitchell G+: https://google.com/+TriciaAMitchell Connect with Shawn on social media: LinkedIn: https://linkedin.com/in/shawnpmitchell1 Twitter: https://twitter.com/shawnpmitchell G+: https://google.com/+ShawnPMitchell A special thank you to the Central Dalmatia Tourist Board for hosting us on this extraordinary adventure: http://www.dalmatia.hr/en Hat tip to Dino for a phenomenal and informative tour! Arrange for your own tour with Dino through email: dino.ivancic@hotmail.com. -
 6:02
6:02DIOCLETIAN'S PALACE or THE BEACH ? SPLIT DECISIONS ON THE DALMATIAN COAST
DIOCLETIAN'S PALACE or THE BEACH ? SPLIT DECISIONS ON THE DALMATIAN COASTDIOCLETIAN'S PALACE or THE BEACH ? SPLIT DECISIONS ON THE DALMATIAN COAST
A great Mediterranean cruise ends at what is probably the best-preserved Roman palace in the world. (29 July 2012) -
 4:58
4:58Diocletian's Palace | Split, Croatia
Diocletian's Palace | Split, CroatiaDiocletian's Palace | Split, Croatia
Split was the fourth city I visited on my two-week back-packing trip around Croatia. Got to see Diocletian's Palace, an a capella group sing in the Vestbule, climb the steps to the top of the bell tower and regret not rubbing the toe of Grgur Ninski. SPONSOR Hostel Adria Website - http://www.hostel-adria.com/ Email - info(at)hostel-adria.com Phone - 00385 91 1930722 REFERENCES Imported Egyptian Stuff - http://www.croatia-split.com/blog/tourist-sites/sites-in-split-peristil.html Vestibule - http://en.splitculture.hr/location/vestibule http://www.absolute-croatia.com/split-region-dalmatia/split/attractions/item/vestibule-split Grgur Ninski - http://www.croatia-split.com/blog/tourist-sites/sites-in-split-peristil.html This episode is part of the weekly series Burris Film Life - An American filmmaker sharing his expeditions around the world. Subscribe for more! http://youtube.com/subscription_center?add_user=burrisfilm Visit my Youtube Channel! http://youtube.com/BurrisFilm SOCIAL STUFF Facebook - http://www.facebook.com/BurrisFilm Twitter - @BurrisFilm - http://twitter.com/BurrisFilm Instagram - @EvanBurrisTrout - http://www.instagram.com/EvanBurrisTrout Tumblr - http://www.BurrisFilm.tumblr.com Google Plus - http://plus.ly/burrisfilm Website - http://www.BurrisFilm.com Music: Great Dark Spot by Jahzzar/Sketch SOS by Jahzzar/Thruth or Dare by Glass Boy + Mr. Jenkins/Adrienne Interlude #6 by Glass Boy/Enthusiast by Tours. Used rightfully under the Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 License. ©Burris Film 2013 -
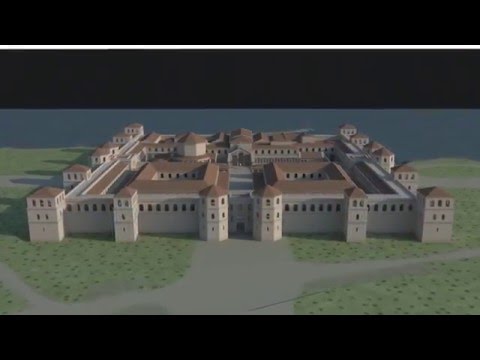 3:52
3:52Diocletian's Palace in 300 AD
Diocletian's Palace in 300 ADDiocletian's Palace in 300 AD
This is my first 3D model constructed fully with Sketchup . . . and then rendered into a movie with VRay for Sketchup. This is a study of Diocletian's Palace as it was in 300 AD, located in what is now Split, Croatia. I am hoping to do further work on this, including some analysis of the ways this complex of buildings works with the natural environment. -
 4:27
4:27Walking Through The Roman Ruins of Diocletians Palace in Split
Walking Through The Roman Ruins of Diocletians Palace in SplitWalking Through The Roman Ruins of Diocletians Palace in Split
http://www.TravelsWithSheila.com The Split Tourist Office hands out a FREE "Discover Split" newspaper that includes a walking map through Diocletian's Palace, built for his retirement. I found the map invaluable and set off today to look for what we thought were the most interesting parts. Diocletian's Palace is not only one of the most imposing Roman ruins in existence but also served as a fortress. The Palace itself was begun around 298 A.D., took 10 years to complete with four gates. Enter through either the Silver Gate, Brass Gate, Gold Gate, or Iron Gate. Come along to see what we saw.... -
 2:18
2:18Palace of Diocletian
Palace of DiocletianPalace of Diocletian
Reconstruction of ancient roman palace of Diocletian, it's now a part of Split, Croatia http://world3dhistory.com/?lang=en - Please visit the site with my reconstructions e-mail: julianvs@yandex.ru -
 6:23
6:23Diocletians Palace - Split Croatia
Diocletians Palace - Split Croatia -
 4:22
4:22Diocletian's Palace part-1
Diocletian's Palace part-1Diocletian's Palace part-1
Diocletian's Palace-once an imperial villa and a roman camp,today a UNESCO WH-site.This is probably the only heritage site in the world that is still inhabited.This video was made by 12-year old pupils. We hope you enjoyed! Thanks for watching! -
 1:54
1:54Split In Your Pocket - Diocletian's Palace (Dioklecijanova palača)
Split In Your Pocket - Diocletian's Palace (Dioklecijanova palača)Split In Your Pocket - Diocletian's Palace (Dioklecijanova palača)
http://split.inyourpocket.com Split In Your Pocket editor Kristina Kovač explores the palace of Roman emperor Diocletian, Split's most important landmark. Construction began in 293 and was completed in ten years and utilized a variety of materials from all around the region, including white stone shipped from the island of Brač to sphinxes transported all the way from Egypt. Diocletian's palace has become the quintessential 'living museum,' as modern shops and citizens live and work inside the walls of the ancient palace complex. The part of the palace known as "the basement" was built during the reign of Diocletian to support the apartments placed above it and, until 1956, was unexplored and cluttered up with the detritus of thousands of years of history. Now, it's been cleaned and opened for visitors. Because it mirrors the floor plan of the original imperial living quarters, a visit to the basement can help visitors envision the layout of the palace. And, because exploring the depths of ancient palaces is difficult work, the steps leading up and out of the northern end of the basement to the Peristyle can be a perfect escape. For more information on sightseeing in Split check out Split In Your Pocket: http://split.inyourpocket.com/Sightseeing/category/63478-Essential_Split.html
Diocletian
ALBUMS
- Gesundrian released: 2014
- Bellum omnium contra omnes released: 2010
- Doom Cult released: 2009
Gesundrian
Released 2014- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Cleaved Asunder
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Wretched Sons
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Summoning Fear
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Traitor’s Gallow
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Steel Jaws
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Wolf Against Serpent
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Beast Atop the Trapezoid
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Zealot’s Poison
Bellum omnium contra omnes
Released 2010- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Black Dominion
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Desolate Earth
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen All Against All
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Might Is Right
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Kingdom of Rats
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Death Tyrant
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Nuclear Vomited
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Blood Aeon
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Infernos
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Fortress of the Unconquerable
Doom Cult
Released 2009- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Doom Cult
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen The Iron Fist
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Oath to Ruin
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Deathstrike Overkill
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Werewolf Directive
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Antichrist Hammerfist
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Bullet Vomited
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Baphocletian
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Heretics
-

Diocletian's Palace, in Split, Croatia
Subscribe to my channel: https://www.youtube.com/user/lindybeige?sub_confirmation=1 More videos here: https://www.youtube.com/playlist?list=PL26F99D743DDB5026 Details on the springs, the Temple of Jupiter, and the vestibule in a forthcoming video. The palace is considered important enough to be a UNESCO world heritage site. Thanks to Josip Pavic for camerawork, advice, and his ability to drive on the wrong side of the road. For those who like to buy merchandise linked to YouTube channels, there may be some stuff in the nearish future from this one. First, though, you might like to go to my Facebook page (see below) and post some suggestions of things that you would buy. Lindybeige: a channel of archaeology, ancient and medieval warfare, rants, swing dance, travelogues, evolution,... -

Inside Diocletian's Palace: A Walking Tour in Split, Croatia
When thinking about things to do in Split, Croatia, we chose a walking tour of Diocletian's Palace. This golden crown of Central Dalmatia offers a wealth of insight into 1,700 years of Adriatic history. Join Tricia and I as we explore this amazing UNESCO heritage site with local historian, Dino, followed by a delicious feast at the Konoba Varos restaurant. ______ For translated captions into 60+ languages, click 'CC' in the viewer. Subscribe for more DESTINATIONS with Shawn & Tricia: http://www.youtube.com/subscription_center?add_user=shawnpmitchell For more on this experience from Tricia’s perspective, check out her blog post at: http://triciaannemitchell.com/2014/01/04/diocletian-palace-split-walking-tour/ Connect with Tricia on social media: LinkedIn: https://linkedin.com/in/tric... -

DIOCLETIAN'S PALACE or THE BEACH ? SPLIT DECISIONS ON THE DALMATIAN COAST
A great Mediterranean cruise ends at what is probably the best-preserved Roman palace in the world. (29 July 2012) -

Diocletian's Palace | Split, Croatia
Split was the fourth city I visited on my two-week back-packing trip around Croatia. Got to see Diocletian's Palace, an a capella group sing in the Vestbule, climb the steps to the top of the bell tower and regret not rubbing the toe of Grgur Ninski. SPONSOR Hostel Adria Website - http://www.hostel-adria.com/ Email - info(at)hostel-adria.com Phone - 00385 91 1930722 REFERENCES Imported Egyptian Stuff - http://www.croatia-split.com/blog/tourist-sites/sites-in-split-peristil.html Vestibule - http://en.splitculture.hr/location/vestibule http://www.absolute-croatia.com/split-region-dalmatia/split/attractions/item/vestibule-split Grgur Ninski - http://www.croatia-split.com/blog/tourist-sites/sites-in-split-peristil.html This episode is part of the weekly series Burris Film Life - An Americ... -

Diocletian's Palace in 300 AD
This is my first 3D model constructed fully with Sketchup . . . and then rendered into a movie with VRay for Sketchup. This is a study of Diocletian's Palace as it was in 300 AD, located in what is now Split, Croatia. I am hoping to do further work on this, including some analysis of the ways this complex of buildings works with the natural environment. -

Walking Through The Roman Ruins of Diocletians Palace in Split
http://www.TravelsWithSheila.com The Split Tourist Office hands out a FREE "Discover Split" newspaper that includes a walking map through Diocletian's Palace, built for his retirement. I found the map invaluable and set off today to look for what we thought were the most interesting parts. Diocletian's Palace is not only one of the most imposing Roman ruins in existence but also served as a fortress. The Palace itself was begun around 298 A.D., took 10 years to complete with four gates. Enter through either the Silver Gate, Brass Gate, Gold Gate, or Iron Gate. Come along to see what we saw.... -

Palace of Diocletian
Reconstruction of ancient roman palace of Diocletian, it's now a part of Split, Croatia http://world3dhistory.com/?lang=en - Please visit the site with my reconstructions e-mail: julianvs@yandex.ru -

-

Diocletian's Palace part-1
Diocletian's Palace-once an imperial villa and a roman camp,today a UNESCO WH-site.This is probably the only heritage site in the world that is still inhabited.This video was made by 12-year old pupils. We hope you enjoyed! Thanks for watching! -

Split In Your Pocket - Diocletian's Palace (Dioklecijanova palača)
http://split.inyourpocket.com Split In Your Pocket editor Kristina Kovač explores the palace of Roman emperor Diocletian, Split's most important landmark. Construction began in 293 and was completed in ten years and utilized a variety of materials from all around the region, including white stone shipped from the island of Brač to sphinxes transported all the way from Egypt. Diocletian's palace has become the quintessential 'living museum,' as modern shops and citizens live and work inside the walls of the ancient palace complex. The part of the palace known as "the basement" was built during the reign of Diocletian to support the apartments placed above it and, until 1956, was unexplored and cluttered up with the detritus of thousands of years of history. Now, it's been cleaned and open...
Diocletian's Palace, in Split, Croatia
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 5:46
- Updated: 29 Jun 2014
- views: 34555
- published: 29 Jun 2014
- views: 34555
Inside Diocletian's Palace: A Walking Tour in Split, Croatia
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 3:59
- Updated: 04 Jan 2014
- views: 14255
- published: 04 Jan 2014
- views: 14255
DIOCLETIAN'S PALACE or THE BEACH ? SPLIT DECISIONS ON THE DALMATIAN COAST
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 6:02
- Updated: 03 Apr 2013
- views: 4128
- published: 03 Apr 2013
- views: 4128
Diocletian's Palace | Split, Croatia
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 4:58
- Updated: 19 Oct 2013
- views: 24416
- published: 19 Oct 2013
- views: 24416
Diocletian's Palace in 300 AD
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 3:52
- Updated: 06 Apr 2016
- views: 101
- published: 06 Apr 2016
- views: 101
Walking Through The Roman Ruins of Diocletians Palace in Split
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 4:27
- Updated: 28 Sep 2011
- views: 731
- published: 28 Sep 2011
- views: 731
Palace of Diocletian
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 2:18
- Updated: 07 May 2012
- views: 6186
- published: 07 May 2012
- views: 6186
Diocletians Palace - Split Croatia
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 6:23
- Updated: 14 Jan 2007
- views: 7119
Diocletian's Palace part-1
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 4:22
- Updated: 07 May 2016
- views: 311
- published: 07 May 2016
- views: 311
Split In Your Pocket - Diocletian's Palace (Dioklecijanova palača)
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 1:54
- Updated: 15 Aug 2009
- views: 11449
- published: 15 Aug 2009
- views: 11449
-

Croatia Travel Guide : Wedding Ceremony at Palace of Diocletian, Split, Croatia
Croatia Travel Guide : Wedding Ceremony at Palace of Diocletian, Split, Croatia. The Palac Dioklecjans, Center point, Split, Croatia Location : Diocletian's Palace Google map https://goo.gl/maps/ScZ5j4Be4ys http://www.taluitamtawan.com/journey/Croatia/ ลากกระเป๋าท่องโลก เที่ยวยุโรป โครเอเชีย เที่ยวเองได้ ตอน ร่วมฉลองงานมงคลสมรส งานแต่งงาน ที่ Diocletian's Palace Center Point of The World Heritage Site, Split, Croatia สนุกสนานมากครับ ตะลุยตามตะวัน รีวิวให้ชม พอเป็นแนวทาง ท่องเที่ยว โครเอเชีย ครับ Travel Guide & Review by : http://www.TaluiTamtawan.Com https://www.facebook.com/taluitamtawan https://www.youtube.com/user/taluitamtawan https://plus.google.com/+TaluitamtawanTraveller/ https://instagram.com/taluitamtawan/ http://taluitamtawan.blogspot.com/ https://vimeo.com/taluitamtawan -

Croatia Travel Guide : Diociletian Palace - Port - Train Station. split, Croatia
Croatia Travel Guide : Diocletian Palace & The World Heritage Site & Port & Train Station @ Center point, Split, Croatia ลากกระเป๋าท่องโลก เที่ยวยุโรป โครเอเชีย เที่ยวเองได้ ตอน เดินเล่นท่าเรือ เมืองเก่า ปราสาท สถานีรถไฟ Split ครับ ตะลุยตามตะวัน รีวิวให้ชม พอเป็นแนวทาง ท่องเที่ยว โครเอเชีย ครับ Travel Guide & Review by : http://www.TaluiTamtawan.Com https://www.facebook.com/taluitamtawan https://www.youtube.com/user/taluitamtawan https://plus.google.com/+TaluitamtawanTraveller/ https://instagram.com/taluitamtawan/ http://taluitamtawan.blogspot.com/ https://vimeo.com/taluitamtawan -

Split (Croatia) Vacation Travel Video Guide
Travel video about destination Split in Croatia. Split is the Croatian Republic’s second largest city and the financial and cultural centre of Dalmatia. It has a harbour for ferries, cruise liners and greets tourists from all over the world but the origin and importance of this city date back to Roman emperor, Diocletian who, planning for his retirement, wanted to build a grand property near to his hometown of Salona, a palace along the lines of a Roman castrum. The palace subsequently became an ancient city and the mausoleum a Christian cathedral to which a Venetian campanile was later added. An ingenious system of pillars, corridors, arches and vaulted ceilings, support the palace. Over the centuries, the large basement rooms remained almost untouched and only a few have been renovated... -

Top Tourist Attractions in Croatia: Travel Guide
http://ultramodern-home.ru Top Tourist Attractions and beautiful places in Croatia: Travel Guide Ancient City Walls Dubrovnik, Diocletian's Palace Split, Cavtat Old Town, Dubrovnik Cable Car, Old Town Rovinj, Plitvice Lakes, Porec Old Town, The Arena in Pula, Trogir Historic Site, Zagreb -

Croatia Travel: Split, Marjan Hill and Diocletian's Palace
On May 1, 2012 we embarked on an excursion from Zadar to Split, Croatia's second largest city. Split is a beautiful coastal city with a long history. Archeological research indicates that the area was inhabited as early as the 6th century BC. After a brief stroll along the beautiful waterfront and the old downtown, we embarked on a walk up Marjan Hill which is covered in a dense pine forest and provides sweeping views over the city and the coastal areas and islands that are located off the coast. Once arrived at the top, we realized that there was a huge festival on top of the hill with thousands of people attending. Food was being prepared and children could enjoy rides and different types of entertainment. On the way back to the city, incredible panoramic vistas opened up of the downtown... -

Croatia Travel Guide : Thailand in the eyes of European & Croatian
Croatia Travel Guide : Thailand in the eyes of European & Croatian @ Trogir & Split, Croatia. Diocletian's Palace The UNESCO World Heritage Site Designated 1979 Location : 43.50813 16.44019 ลากกระเป๋าท่องเที่ยวยุโรป โครเอเชีย เที่ยวเองได้ ตอน มุมมอง ขาวสปริท ชาวโดรเอเชีย ชาวยุโรป ต่อ ประเทศไทย ครับ ตะลุยตามตะวัน ได้มีโอกาส คุยกับหลายๆ ท่าน จึง รีวิวให้ ชม ครับ Travel Guide & Review by : http://www.TaluiTamtawan.Com https://www.facebook.com/taluitamtawan https://www.youtube.com/user/taluitamtawan https://plus.google.com/+TaluitamtawanTraveller/ https://instagram.com/taluitamtawan/ http://taluitamtawan.blogspot.com/ https://vimeo.com/taluitamtawan
Croatia Travel Guide : Wedding Ceremony at Palace of Diocletian, Split, Croatia
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 2:48
- Updated: 20 Jun 2015
- views: 2960
- published: 20 Jun 2015
- views: 2960
Croatia Travel Guide : Diociletian Palace - Port - Train Station. split, Croatia
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 0:07
- Updated: 14 Jun 2015
- views: 140
- published: 14 Jun 2015
- views: 140
Split (Croatia) Vacation Travel Video Guide
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 9:40
- Updated: 21 Dec 2015
- views: 4604
- published: 21 Dec 2015
- views: 4604
Top Tourist Attractions in Croatia: Travel Guide
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 1:40
- Updated: 03 May 2016
- views: 392
- published: 03 May 2016
- views: 392
Croatia Travel: Split, Marjan Hill and Diocletian's Palace
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 1:36
- Updated: 09 Aug 2012
- views: 217
- published: 09 Aug 2012
- views: 217
Croatia Travel Guide : Thailand in the eyes of European & Croatian
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 3:12
- Updated: 29 Jun 2015
- views: 122
- published: 29 Jun 2015
- views: 122
-

Inside the walls of the Diocletian Palace, Split, Croatia
Absolutely beautiful. -

Everyday Roman Drama in Diocletian's Palace, Split, Croatia (abakprithibi.com)
Diocletian's Palace, An ancient palace built by the Roman emperor Diocletian.In the old town and city center of Split, every day at noon they perform a Roman Drama to say welcome. Split is a beautiful city of central Dalmatia. Visited by Bengali (Bangla) travel blog www.abakprithibi.com -

130717 Split Diocletian Palace Plaza 1 F 4824 SOUND Effect
-

130717 Split Diocletian Palace Plaza 1 R 4824 SOUND Effect
-

130717 Split Diocletian Palace Plaza 2 4824 SOUND Effect
-

Split Diocletians palace - Selfie video
-

Diocletian's Palace walls (Split)
-

Apartment Diocletians Palace Split Croatia
-

Diocletian's Palace, Split
We spent 2 full days in Split and it was awesome. Diocletian's Palace is massive. Encompassing an area that would make modern day Palace's jealous. Entrance is free, I suggest to find a good tour group before, our tour guide was actually quite awful. The seafood is fresh and can be found all over the city. Just take a walk around and eat wherever you like. Grab a swim at the local beaches, they area sandy once you pass some rocks. The water in July was warm, around 75F. Parking is problematic, I suggest you find a lot and leave the car as the city is very walkable. -

Guest house Diocletian Palace Experience Split Croatia
Inside the walls of the Diocletian Palace, Split, Croatia
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 0:53
- Updated: 24 Jul 2016
- views: 0
Everyday Roman Drama in Diocletian's Palace, Split, Croatia (abakprithibi.com)
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 2:57
- Updated: 23 Jul 2016
- views: 8
- published: 23 Jul 2016
- views: 8
130717 Split Diocletian Palace Plaza 1 F 4824 SOUND Effect
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 1:53
- Updated: 22 Jul 2016
- views: 0
- published: 22 Jul 2016
- views: 0
130717 Split Diocletian Palace Plaza 1 R 4824 SOUND Effect
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 1:53
- Updated: 22 Jul 2016
- views: 0
- published: 22 Jul 2016
- views: 0
130717 Split Diocletian Palace Plaza 2 4824 SOUND Effect
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 2:02
- Updated: 22 Jul 2016
- views: 0
- published: 22 Jul 2016
- views: 0
Split Diocletians palace - Selfie video
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 0:18
- Updated: 18 Jul 2016
- views: 3
- published: 18 Jul 2016
- views: 3
Diocletian's Palace walls (Split)
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 0:42
- Updated: 16 Jul 2016
- views: 2
- published: 16 Jul 2016
- views: 2
Apartment Diocletians Palace Split Croatia
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 4:10
- Updated: 13 Jul 2016
- views: 1
- published: 13 Jul 2016
- views: 1
Diocletian's Palace, Split
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 9:43
- Updated: 12 Jul 2016
- views: 23
- published: 12 Jul 2016
- views: 23
Guest house Diocletian Palace Experience Split Croatia
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 1:58
- Updated: 08 Jul 2016
- views: 0
- published: 08 Jul 2016
- views: 0
-

Split | Beaches, Diocletian's palace, Riva quay
--- All information about this video see below ---- In this video you will see beaches, street strolls, old center, Diocletian's palace, views from Marjan hill and Riva quay. ---- All parts ---- First part: Beaches, Diocletian's palace, Riva quay - https://youtu.be/OFuu6zObNBU Second part: Adriatic sea, Riva quay, Marjan hill - https://youtu.be/UrQH0FaMSFE Third part: Old city stroll, panoramic view from Marjan hill - https://youtu.be/ihvOg3DER-Y Fourth part: A stroll along the Riva quay - https://youtu.be/RBMhoZw7NZc -

Dalmatia (Documentary, Discovery, History)
A trip on the clear waters of the Adriatic from the north to the south of Croatia. Stopovers at : Opatija, a former Imperial high society resort town, Pula and its Roman theatre, Zadar and its churches, Split and the ruins of Diocletian's palace, Korcula, Marco Polo's city, and finally Dubrovnik, rival to Venice with its countless treasures. Stopover will take you on prodigious trips across the most marvelous oceans and rivers of the world. Travel with us as we explore not just the waters of the world, but also the mythical cruise ships, legendary liners, magnificent sailboats and fascinating traditional vessels that take us from place to place. Subscribe to our channel: http://www.youtube.com/subscription_center?add_user=StopovertvHD Add us to your G+ circles: https://plus.google.com/b/... -

22. Rome Redux: The Tetrarchic Renaissance
Roman Architecture (HSAR 252) Professor Kleiner characterizes third-century Rome as an "architectural wasteland" due to the rapid change of emperors, continuous civil war, and a crumbling economy. There was no time to build and the only major architectural commission was a new defensive wall. The crisis came to an end with the rise of Diocletian, who created a new form of government called the Tetrarchy, or four-man rule, with two leaders in the East and two in the West. Diocletian and his colleagues instituted a major public and private building campaign in Rome and the provinces, which reflected the Empire's renewed stability. Professor Kleiner begins with Diocletian's commissions in Rome--a five-column monument dedicated to the tenth anniversary of the formation of the Tetrarchy, the... -

Sail Ho Croatia Episode 3: SPLIT – TROGIR
Episode 03: SPLIT – TROGIR We'll explore magical city of Split, monumental Diocletian's Palace, introduce you to beautiful marinas in the region, show you the fastest way of traveling within Croatia and much more. https://www.facebook.com/sailho.croatia -

Split | Old city stroll, panoramic view from Marjan hill
--- All information about this video see below ---- In this video you will see a stroll in the old city, panoramic view from the Marjan hill and a sunset. ---- All parts ---- First part: Beaches, Diocletian's palace, Riva quay - https://youtu.be/OFuu6zObNBU Second part: Adriatic sea, Riva quay, Marjan hill - https://youtu.be/UrQH0FaMSFE Third part: Old city stroll, panoramic view from Marjan hill - https://youtu.be/ihvOg3DER-Y Fourth part: A stroll along the Riva quay - https://youtu.be/RBMhoZw7NZc -

-

Wandering through the Medieval city inside the 2000 year old Roman Emperor's palace.
The Roman Emperor just before Constantine was the last to sacrifice and persecute Christians. His name was Diocletian, he was born in the town of Solan on the Adriatic coast. When he retired he had a massive fortified palace built for himself on forested land on the Adriatic sea 6kms from where he was born in Solan. The palace's front wall was built along the water so ships could arrive and deliver right at the main gate. After he passed away his palace was used by the Roman government for official functions and gatherings until eventually as the power and influence of the Romans receded his palace was left abandoned. The palace stayed empty and unused for several hundred years. Around the year 600 Solan was attacked and the residents took refuge in the old empty palace and never left.... -

The Croatian Coast Dalmatia Vacation Travel Video Guide • Great Destinations
A picturesque country, which is blessed by an unfathomable natural richness. Its charm, beside the coast full of bays, the warm watered fjords and reefs, high cliffs and the green hills is made up also by its artistic and historical values. On the Dalmatian Coast the romantic cities of Zadar and Trogir and the Saint Jacob cathedral of Sibenik make us remember to the past. In Split, one can take a look at emperor Diocletian’s unique palace. Among the natural beauties the crystal clear waters, waterfalls, caves and rapids of the Krka National Park are on top. Crikvenica introduce us to the mood of a spa in the monarchy, while the whole travel is crowned by the Queen of the Adriatic, Dubrovnik. Blue sky, glimmering sea, lovely islands, and wonderful landscape. They say that the heart of the t... -

Diocletian
Ryan M. Reeves (PhD Cambridge) is Assistant Professor of Historical Theology at Gordon-Conwell Theological Seminary. Twitter: https://twitter.com/RyanMReeves Instagram: https://instagram.com/ryreeves4/ Website: http://www.gordonconwell.edu/academics/view-faculty-member.cfm?faculty_id=15906&grp;_id=8947 For the entire course on 'Church History: Reformation to Modern', see the playlist: https://www.youtube.com/playlist?list=PLRgREWf4NFWY1ZaP-falnLFIR9texgvjR -

발칸여행 4국. 4일차[크로아티아Croatia Travel-Dubrovnik.Split[두브로브니크,스플리트]
발칸4국 여행 4일차[크로아티아 여행] Croatia Travel-Dubrovnik.Split[두브로브니크,스플리트] 성곽,보트관광, 디오클레시안 궁전, 아카펠라 Palace of Diocletian, Acappella CafePort
Split | Beaches, Diocletian's palace, Riva quay
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 24:48
- Updated: 06 Nov 2015
- views: 18
- published: 06 Nov 2015
- views: 18
Dalmatia (Documentary, Discovery, History)
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 60:45
- Updated: 26 Feb 2014
- views: 13911
- published: 26 Feb 2014
- views: 13911
22. Rome Redux: The Tetrarchic Renaissance
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 73:42
- Updated: 14 Sep 2009
- views: 10891
- published: 14 Sep 2009
- views: 10891
Sail Ho Croatia Episode 3: SPLIT – TROGIR
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 29:09
- Updated: 13 Dec 2015
- views: 1009
- published: 13 Dec 2015
- views: 1009
Split | Old city stroll, panoramic view from Marjan hill
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 25:41
- Updated: 07 Nov 2015
- views: 13
- published: 07 Nov 2015
- views: 13
Split, Croatia
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 20:26
- Updated: 21 Mar 2016
- views: 4
Wandering through the Medieval city inside the 2000 year old Roman Emperor's palace.
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 34:43
- Updated: 16 Apr 2013
- views: 1188
- published: 16 Apr 2013
- views: 1188
The Croatian Coast Dalmatia Vacation Travel Video Guide • Great Destinations
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 59:00
- Updated: 24 Feb 2015
- views: 24204
- published: 24 Feb 2015
- views: 24204
Diocletian
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 29:37
- Updated: 31 May 2014
- views: 17231
- published: 31 May 2014
- views: 17231
발칸여행 4국. 4일차[크로아티아Croatia Travel-Dubrovnik.Split[두브로브니크,스플리트]
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 22:13
- Updated: 23 Jul 2016
- views: 31
- published: 23 Jul 2016
- views: 31
- Playlist
- Chat
- Playlist
- Chat

Diocletian's Palace, in Split, Croatia
- Report rights infringement
- published: 29 Jun 2014
- views: 34555

Inside Diocletian's Palace: A Walking Tour in Split, Croatia
- Report rights infringement
- published: 04 Jan 2014
- views: 14255

DIOCLETIAN'S PALACE or THE BEACH ? SPLIT DECISIONS ON THE DALMATIAN COAST
- Report rights infringement
- published: 03 Apr 2013
- views: 4128

Diocletian's Palace | Split, Croatia
- Report rights infringement
- published: 19 Oct 2013
- views: 24416

Diocletian's Palace in 300 AD
- Report rights infringement
- published: 06 Apr 2016
- views: 101

Walking Through The Roman Ruins of Diocletians Palace in Split
- Report rights infringement
- published: 28 Sep 2011
- views: 731

Palace of Diocletian
- Report rights infringement
- published: 07 May 2012
- views: 6186

Diocletians Palace - Split Croatia
- Report rights infringement
- published: 14 Jan 2007
- views: 7119

Diocletian's Palace part-1
- Report rights infringement
- published: 07 May 2016
- views: 311

Split In Your Pocket - Diocletian's Palace (Dioklecijanova palača)
- Report rights infringement
- published: 15 Aug 2009
- views: 11449
- Playlist
- Chat

Croatia Travel Guide : Wedding Ceremony at Palace of Diocletian, Split, Croatia
- Report rights infringement
- published: 20 Jun 2015
- views: 2960

Croatia Travel Guide : Diociletian Palace - Port - Train Station. split, Croatia
- Report rights infringement
- published: 14 Jun 2015
- views: 140

Split (Croatia) Vacation Travel Video Guide
- Report rights infringement
- published: 21 Dec 2015
- views: 4604

Top Tourist Attractions in Croatia: Travel Guide
- Report rights infringement
- published: 03 May 2016
- views: 392

Croatia Travel: Split, Marjan Hill and Diocletian's Palace
- Report rights infringement
- published: 09 Aug 2012
- views: 217

Croatia Travel Guide : Thailand in the eyes of European & Croatian
- Report rights infringement
- published: 29 Jun 2015
- views: 122
- Playlist
- Chat

Inside the walls of the Diocletian Palace, Split, Croatia
- Report rights infringement
- published: 24 Jul 2016
- views: 0

Everyday Roman Drama in Diocletian's Palace, Split, Croatia (abakprithibi.com)
- Report rights infringement
- published: 23 Jul 2016
- views: 8

130717 Split Diocletian Palace Plaza 1 F 4824 SOUND Effect
- Report rights infringement
- published: 22 Jul 2016
- views: 0

130717 Split Diocletian Palace Plaza 1 R 4824 SOUND Effect
- Report rights infringement
- published: 22 Jul 2016
- views: 0

130717 Split Diocletian Palace Plaza 2 4824 SOUND Effect
- Report rights infringement
- published: 22 Jul 2016
- views: 0

Split Diocletians palace - Selfie video
- Report rights infringement
- published: 18 Jul 2016
- views: 3

Diocletian's Palace walls (Split)
- Report rights infringement
- published: 16 Jul 2016
- views: 2

Apartment Diocletians Palace Split Croatia
- Report rights infringement
- published: 13 Jul 2016
- views: 1

Diocletian's Palace, Split
- Report rights infringement
- published: 12 Jul 2016
- views: 23

Guest house Diocletian Palace Experience Split Croatia
- Report rights infringement
- published: 08 Jul 2016
- views: 0
- Playlist
- Chat

Split | Beaches, Diocletian's palace, Riva quay
- Report rights infringement
- published: 06 Nov 2015
- views: 18

Dalmatia (Documentary, Discovery, History)
- Report rights infringement
- published: 26 Feb 2014
- views: 13911

22. Rome Redux: The Tetrarchic Renaissance
- Report rights infringement
- published: 14 Sep 2009
- views: 10891

Sail Ho Croatia Episode 3: SPLIT – TROGIR
- Report rights infringement
- published: 13 Dec 2015
- views: 1009

Split | Old city stroll, panoramic view from Marjan hill
- Report rights infringement
- published: 07 Nov 2015
- views: 13

Split, Croatia
- Report rights infringement
- published: 21 Mar 2016
- views: 4

Wandering through the Medieval city inside the 2000 year old Roman Emperor's palace.
- Report rights infringement
- published: 16 Apr 2013
- views: 1188

The Croatian Coast Dalmatia Vacation Travel Video Guide • Great Destinations
- Report rights infringement
- published: 24 Feb 2015
- views: 24204

Diocletian
- Report rights infringement
- published: 31 May 2014
- views: 17231

발칸여행 4국. 4일차[크로아티아Croatia Travel-Dubrovnik.Split[두브로브니크,스플리트]
- Report rights infringement
- published: 23 Jul 2016
- views: 31
Rapper Kasper Knight shot himself in the face in the name of publicity
Edit NZ Herald 26 Jul 2016'Laughing gas' kills newborn in Sydney hospital
Edit BBC News 26 Jul 2016THE PALACES’ ART COLLECTIONS
Edit The Jakarta Post 26 Jul 2016Alexandra Palace 'secret theatre' fundraising campaign launched
Edit BBC News 26 Jul 2016Museum a model of flood control
Edit China Daily 26 Jul 2016The intimate-living concept is our interpretation of luxury: Ashish Vohra
Edit DNA India 26 Jul 2016Display of queen's wardrobe includes outfit she wore at Great Wall in 1986
Edit China Daily 26 Jul 2016August 6th: Valencia Visit Selhurst (Crystal Palace Football Club (2000) Ltd)
Edit Public Technologies 26 Jul 2016Renovation of Southampton's iconic Bargate now complete (Southampton City Council)
Edit Public Technologies 26 Jul 2016Theatre Review: Harry Potter and the Cursed Child
Edit Scotsman 26 Jul 2016Prince George feeding his dog ice cream made the internet mad
Edit New York Post 26 Jul 2016Salman Khan didn't kill chinkaras, too
Edit DNA India 26 Jul 2016UN rapporteur Rhona Smith defends approach
Edit Topix 26 Jul 2016Iwan Thomas, left, and Prince Harry at the Heads Together barbecue at Kensington Palace
Edit Topix 26 Jul 2016- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- Next page »







