- published: 08 Mar 2015
- views: 5752
-
remove the playlistIraqi Prime Minister
-
remove the playlistLatest Videos
-
remove the playlistLongest Videos
- remove the playlistIraqi Prime Minister
- remove the playlistLatest Videos
- remove the playlistLongest Videos
- published: 14 Apr 2015
- views: 9186
- published: 30 Sep 2015
- views: 7648
- published: 08 Jun 2015
- views: 34170
- published: 15 Aug 2014
- views: 1654
- published: 08 Jun 2015
- views: 1926
- published: 17 Feb 2016
- views: 8337
- published: 08 Jun 2015
- views: 4490
- published: 10 Feb 2016
- views: 115
- published: 29 Dec 2015
- views: 97
- published: 09 Jun 2015
- views: 66789

The Prime Minister of Iraq is Iraq's head of government. Prime Minister was originally an appointed office, subsidiary to the head of state, and the nominal leader of the Iraqi parliament. Under the newly adopted constitution the Prime Minister is to be the country's active executive authority. Nouri al-Maliki (formerly Jawad al-Maliki) was selected to be Prime Minister on 21 April 2006.
Under the Iraqi Transitional Government, the Members of the Iraqi National Assembly choose the Presidency Council, including the Prime Minister and the Council of Ministers.
The Presidency Council then shall name a Prime Minister unanimously. According to this, the Presidency Council must agree on a candidate for the post within two weeks. In the event that it fails to do so, the responsibility of naming the Prime Minister reverts to the National Assembly. In that event, the National Assembly must confirm the nomination by a two-thirds majority. If the Prime Minister is unable to nominate his Council of Ministers within one month, the Presidency Council shall name another Prime Minister..
This article is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported License, which means that you can copy and modify it as long as the entire work (including additions) remains under this license.

A prime minister is the most senior minister of cabinet in the executive branch of government in a parliamentary system. In many systems, the prime minister selects and may dismiss other members of the cabinet, and allocates posts to members within the government. In most systems, the prime minister is the presiding member and chairman of the cabinet. In a minority of systems, notably in semi-presidential systems of government, a prime minister is the official who is appointed to manage the civil service and execute the directives of the head of state.
In parliamentary systems fashioned after the Westminster system, the prime minister is the presiding and actual head of the government and head of the executive branch. In such systems, the head of state or the head of state's official representative (i.e. the monarch, president, or governor-general) usually holds a largely ceremonial position, although often with reserve powers.
The prime minister is often, but not always, a member of parliament and is expected with other ministers to ensure the passage of bills through the legislature. In some monarchies the monarch may also exercise executive powers (known as the royal prerogative) which are constitutionally vested in the crown and may be exercised without the approval of parliament.
This article is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported License, which means that you can copy and modify it as long as the entire work (including additions) remains under this license.
- Loading...

-
 5:30
5:30Iraqi Prime Minister on ISIS: "We Have to Stop Them"
Iraqi Prime Minister on ISIS: "We Have to Stop Them"Iraqi Prime Minister on ISIS: "We Have to Stop Them"
ABC's Martha Raddatz reports from the front lines of the Iraqi military's fight against ISIS. -
 37:44
37:44President Obama Meets with Iraqi Prime Minister
President Obama Meets with Iraqi Prime MinisterPresident Obama Meets with Iraqi Prime Minister
President Obama holds a bilateral meeting with Iraqi Prime Minister Haider Al-Abadi. April 14, 2015. -
 8:19
8:19Prime Minister Abadi: Iraq welcomes Russia in Islamic State fight
Prime Minister Abadi: Iraq welcomes Russia in Islamic State fightPrime Minister Abadi: Iraq welcomes Russia in Islamic State fight
Iraqi Prime Minister Haider al-Abadi joins chief foreign correspondent Margaret Warner to discuss Russia’s launch of military action in Syria, whether Iraq would allow Russian forces inside its borders to fight the Islamic State and the announcement of a pact to share intelligence with Iran, Syria and Russia. View the Full Story/Transcript: http://www.pbs.org/newshour/bb/prime-minister-abadi-iraq-welcomes-russia-islamic-state-fight/ -
 1:31
1:31President Obama Ignores & Snubs Iraqi Prime Minister Haider al Abadi at G7 Summit | VIDEO
President Obama Ignores & Snubs Iraqi Prime Minister Haider al Abadi at G7 Summit | VIDEOPresident Obama Ignores & Snubs Iraqi Prime Minister Haider al Abadi at G7 Summit | VIDEO
President Obama Ignores & Snubs Iraqi Prime Minister Haider al Abadi at G7 Summit | VIDEO Did Obama give Iraqi PM Abadi the cold shoulder at G7 summit? WASHINGTON – Did President Obama give Iraq’s prime minister the cold shoulder? Video from the G-7 summit in Germany appears to show Iraqi Prime Minister Haider al-Abadi trying to get a word in with the U.S. president after world leaders were gathered for a group photo. Obama can be seen on a bench chatting it up with Italy’s prime minister and Christine Lagarde, the managing director of the IMF – when al-Abadi and his translator take a seat next to Obama. As Obama and the other leaders huddle to talk, Obama appears unaware of Abadi, who awkwardly sits about a foot away with his translator and waits to get the president’s attention. It never happens. When Obama, Lagarde and Italy's Mario Renzi stand up, so does Abadi – though he is still ignored. Finally, Abadi looks at his watch, his translator lifts his hands in the air and shrugs, and the two walk away. The two eventually got to talk. Obama shortly afterward held a formal sit-down meeting with al-Abadi, who has been pleading for additional international assistance in confronting the Islamic State. The two leaders also met at the White House in April but Monday's meeting was the first between the two after ISIS militants took control of Ramadi. Fox, CNN Hype Obama’s ‘Awkward Moment’ with Iraqi PM at G7 Summit As often happens during major gatherings of world leaders, U.S. media is on the lookout today for any hints of “awkwardness” between President Barack Obama and the other prominent figures at today’s G7 Summit in Germany. And they found what they were looking for in a few seconds of video in which Iraq’s new prime minister, Haider al-Abadi, puts in minimal effort to make some pre-meeting small talk with Obama before giving up and walking away. “The president was sort of, sitting down having conversations with other world leaders when the Iraqi prime minister sort of sidled up right behind, obviously waiting to get the president’s attention,” reporter Kevin Corke said. “The president never turned back. Either he didn’t see him or didn’t acknowledge that he was there. And after a certain while, he sort of looked at his watch and his interpreter kind of raised his palms to the sky and say, ‘what gives?’ “An awkward moment to say the least,” he continued. “And we look forward to hearing the president’s explanation for what could certainly be perceived as a snub.” “Yeah, maybe he didn’t see him,” anchor Gregg Jarrett said, dismissing the importance of what has just been reported before changing the subject. Less than 10 minutes later, CNN’s Carol Costello was on the case, calling the “possible snub” a “sign things aren’t going so great” in the discussions between the U.S. and Iraq on how to handle ISIS. “It was awkward, but was it a snub?” she asked reporter Jim Acosta after analyzing the tape. “I think it’s more hashtag awkward,” Acosta said, implying that people are perhaps making too much of the moment. “You know, they try so hard to carefully craft the photo opportunities for these leaders of this G7 Summit and things sometimes go awry and I think that’s the case here.” He pointed out that earlier in the day, Obama did have a choreographed handshake photo-op with al-Abadi. “I think the evidence shows that it’s probably not a snub, just an awkward moment where the president did not even realize that the Iraqi prime minister was behind him,” Acosta concluded. So, to sum up, nothing happened and everything’s cool. 2015 june full footage -
 2:39
2:39Maliki steps down as Iraqi Prime Minister
Maliki steps down as Iraqi Prime MinisterMaliki steps down as Iraqi Prime Minister
Subscribe to our channel http://bit.ly/AJSubscribe Subscribe to our channel http://bit.ly/AJSubscribe Reaching more than 270 million households in over 140 countries across the globe, our viewers trust Al Jazeera English to keep them informed, inspired, and entertained. Our impartial, fact-based reporting wins worldwide praise and respect. It is our unique brand of journalism that the world has come to rely on. We are reshaping global media and constantly working to strengthen our reputation as one of the world's most respected news and current affairs channels. Social Media links: Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/aljazeera Instagram: https://instagram.com/aljazeera/?ref=... Twitter: https://twitter.com/ajenglish Website: http://www.aljazeera.com/ google+: https://plus.google.com/+aljazeera/posts At Al Jazeera English, we focus on people and events that affect people's lives. We bring topics to light that often go under-reported, listening to all sides of the story and giving a 'voice to the voiceless.' Reaching more than 270 million households in over 140 countries across the globe, our viewers trust Al Jazeera English to keep them informed, inspired, and entertained. Our impartial, fact-based reporting wins worldwide praise and respect. It is our unique brand of journalism that the world has come to rely on. We are reshaping global media and constantly working to strengthen our reputation as one of the world's most respected news and current affairs channels. Social Media links: Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/aljazeera Instagram: https://instagram.com/aljazeera/?ref=... Twitter: https://twitter.com/ajenglish Website: http://www.aljazeera.com/ google+: https://plus.google.com/+aljazeera/posts -
 2:01
2:01Did Obama Snub The Iraqi Prime Minister At The G7 Summit-News Brief
Did Obama Snub The Iraqi Prime Minister At The G7 Summit-News BriefDid Obama Snub The Iraqi Prime Minister At The G7 Summit-News Brief
This past weekend the leaders from the Core G7 nations met in Bavaria, Germany to discuss such topics as the global economy, Russia’s aggression in the Ukraine, the threat of climate change and violent extremism. President Obama and the other world leaders are set to sit down with the Prime Minister of Iraq Haider al-Abadi to discuss efforts to train Iraqi security forces. Obama said that the Pentagon does not yet have a complete plan for training and equipping the Iraqi forces. This is the first meeting since ISIS captured the city of Ramadi. And Al-Abadi has said the Obama administration is not doing enough to help Iraq fight ISIS. And yet here they are, Obama and Al-Abadi sitting on the same bench while Obama is chatting with IMF chief Christine Lagarde and Italy’s Prime Minister Mario Renzi and Obama doesn’t even acknowledge the Iraqi Prime Minister. The Iraqi Prime Minister and his translator were trying to steal a moment with the President, but Obama never turned around which left the two Iraqis visibly frustrated. You can see the translator throw his hands up in annoyance as they walk away. President Obama and Prime Minister al-Abadi eventually did talk shortly afterward at a formal sit-down meeting about the fight against the Islamic State terrorist organization. -
 25:57
25:57Is Iraq ungovernable? | Conflict Zone
Is Iraq ungovernable? | Conflict ZoneIs Iraq ungovernable? | Conflict Zone
http://www.dw.com/conflictzone The Iraqi Prime Minister Haider al-Abadi has a tough job. 'Islamic State' militants are occupying entire regions, corruption is institutionalized and the Sunni-Shia rift is tearing the country apart. "Terrorism is an international problem," al-Abadi insists. But is he doing his fair share of fixing the country? Find out on this week's Conflict Zone with Tim Sebastian. -
 4:29
4:29The Iraqi Prime Minister Haider al Abadi
The Iraqi Prime Minister Haider al AbadiThe Iraqi Prime Minister Haider al Abadi
-
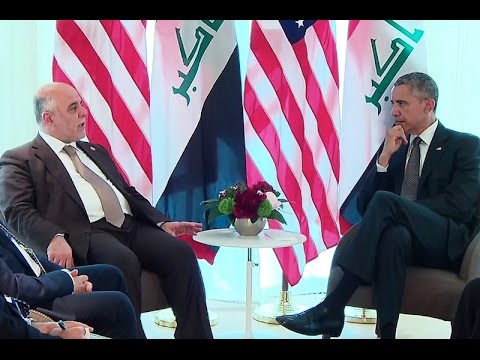 14:38
14:38The President Meets with the Prime Minister of Iraq
The President Meets with the Prime Minister of IraqThe President Meets with the Prime Minister of Iraq
President Obama delivers remarks after meeting with Prime Minister Al-Abadi of Iraq. June 8, 2015. -
 1:55
1:55Pope to Iraqi Prime Minister: Let's seek peace in the midst of the division
Pope to Iraqi Prime Minister: Let's seek peace in the midst of the divisionPope to Iraqi Prime Minister: Let's seek peace in the midst of the division
Follow us on Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/RomeReportsENG/ Click here to receive the latest news: http://smarturl.it/RomeReports Visit our website to learn more: http://www.romereports.com/ They talked about the persecution of Christians and other religious minorities in the Middle East. --------------------- For broadcasting: sales@romereports.com ROME REPORTS, www.romereports.com, is an independent international TV News Agency based in Rome covering the activity of the Pope, the life of the Vatican and current social, cultural and religious debates. Reporting on the Catholic Church requires proximity to the source, in-depth knowledge of the Institution, and a high standard of creativity and technical excellence. As few broadcasters have a permanent correspondent in Rome, ROME REPORTS is geared to inform the public and meet the needs of television broadcasting companies around the world through daily news packages, weekly newsprograms and documentaries. --------------------- Follow us... Our website http://www.romereports.com/ Facebook https://www.facebook.com/RomeReportsENG Twitter https://twitter.com/romereports -
 0:59
0:59Iraqi Prime Minister Visits 'Liberated' Ramadi
Iraqi Prime Minister Visits 'Liberated' RamadiIraqi Prime Minister Visits 'Liberated' Ramadi
On Dec. 29, Prime Minister Haider al-Abadi visited Ramadi and reminded Iraqis that the next operation will be taking Mosul from ISIS -
 1:24
1:24Iraqi PM fails to get Obama’s attention in awkward G7 moment
Iraqi PM fails to get Obama’s attention in awkward G7 momentIraqi PM fails to get Obama’s attention in awkward G7 moment
In an awkward moment at the Group of Seven summit in Germany on Monday, 8 June, Iraqi Prime Minister Haider al-Abadi seeks to get President Barack Obama's attention. Obama, seated on a bench chatting with Italian Prime Minister Mario Renzi and IMF managing director Christine Lagarde appears not to notice when Abadi sits to Obama's left. The president, his back turned to Abadi, continued his huddle with Renzi and Lagarde. Even after Obama, Renzi and Lagarde stand, none acknowledge Abadi nearby. Abadi then checks his watch, his translator gestures, and the two walk away. Obama and Abadi did have a private session later Monday where they discussed the fight against the Islamic State. What are the top stories today? Click to watch: https://www.youtube.com/playlist?list=PLSyY1udCyYqBeDOz400FlseNGNqReKkFd euronews: the most watched news channel in Europe Subscribe! http://www.youtube.com/subscription_center?add_user=euronews euronews is available in 13 languages: https://www.youtube.com/user/euronewsnetwork/channels In English: Website: http://www.euronews.com/news Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/euronews Twitter: http://twitter.com/euronews Google+: http://google.com/+euronews VKontakte: http://vk.com/en.euronews
- Abd al-Karim Qasim
- Abdul Aziz al-Hakim
- Abdul Rahman Arif
- Abdul-Wahab Mirjan
- Achaemenid Assyria
- Adnan Pachachi
- Ahmad Mukhtar Baban
- Ahmed Chalabi
- Ahmed Hassan al-Bakr
- Akkadian Empire
- Al-Faw Peninsula
- Ali Jawdat al-Aiyubi
- Arab Federation
- Arif Abd ar-Razzaq
- Arshad al-Umari
- Assyria
- Assyrian people
- Asuristan
- Ayad Allawi
- Babylonia
- Baghdad
- Cabinet of Iraq
- Central Bank of Iraq
- Christianity in Iraq
- Coat of arms of Iraq
- Constitution of Iraq
- Culture of Iraq
- Demographics of Iraq
- Districts of Iraq
- Economy of Iraq
- Education in Iraq
- Elections in Iraq
- Euphrates
- Excellency
- Ezzedine Salim
- Foreign aid to Iraq
- Geography of Iraq
- Gulf War
- Hamdi al-Pachachi
- Hamrin Mountains
- Head of government
- Head of state
- Health in Iraq
- Hikmat Sulayman
- History of Iraq
- Ibrahim al-Jaafari
- Invasion of Kuwait
- Iran–Iraq War
- Iraq
- Iraq Stock Exchange
- Iraq War
- Iraqi Air Force
- Iraqi Arabic
- Iraqi Armed Forces
- Iraqi Army
- Iraqi cuisine
- Iraqi diaspora
- Iraqi Dinar
- Iraqi insurgency
- Iraqi Kurdistan
- Iraqi Navy
- Iraqi parliament
- Iraqi people
- Iraqi Police
- Iraqi Turkmen
- Islam in Iraq
- Jafar al-Askari
- Jalal Talabani
- Jamil al-Midfai
- Kingdom of Iraq
- Kurdish language
- Kurdistan Parliament
- Lake Habbaniyah
- Lake Hammar
- Lake Milh
- Lake Tharthar
- Languages of Iraq
- Law of Iraq
- Mandaeans
- Mandaeism
- Massoud Barzani
- Media of Iraq
- Mesopotamia
- Mesopotamian Marshes
- Minorities in Iraq
- Mohsen Abdel Hamid
- Music of Iraq
- Muzahim al-Pachachi
- Naji al-Suwaidi
- Naji Shawkat
- Naji Talib
- Neo-Assyrian Empire
- Nouri al-Maliki
- Nureddin Mahmud
- Nuri as-Said
- Official residence
- Oil reserves in Iraq
- Ottoman Iraq
- Parthian Empire
- Politics of Iraq
- Portal Politics
- President of Iraq
- Prime Minister
- Provinces of Iraq
- Religion in Iraq
- Republican Palace
- Roads in Iraq
- Sa'dun Hammadi
- Saddam Hussein
- Sayyid Salih Jabr
- Seleucid Empire
- Shatt al-Arab
- South Azeri language
- Sport in Iraq
- Sumer
- Syrian Desert
- Tahir Yahya
- Tawfiq al-Suwaidi
- Template Iraq topics
- Template IraqiPMs
- Term of office
- Tigris
- Transport in Iraq
- Umm Qasr
- Usama al-Nujayfi
- Yasin al-Hashimi
- Zagros Mountains
-

Iraqi Prime Minister on ISIS: "We Have to Stop Them"
ABC's Martha Raddatz reports from the front lines of the Iraqi military's fight against ISIS. -

President Obama Meets with Iraqi Prime Minister
President Obama holds a bilateral meeting with Iraqi Prime Minister Haider Al-Abadi. April 14, 2015. -

Prime Minister Abadi: Iraq welcomes Russia in Islamic State fight
Iraqi Prime Minister Haider al-Abadi joins chief foreign correspondent Margaret Warner to discuss Russia’s launch of military action in Syria, whether Iraq would allow Russian forces inside its borders to fight the Islamic State and the announcement of a pact to share intelligence with Iran, Syria and Russia. View the Full Story/Transcript: http://www.pbs.org/newshour/bb/prime-minister-abadi-iraq-welcomes-russia-islamic-state-fight/ -

President Obama Ignores & Snubs Iraqi Prime Minister Haider al Abadi at G7 Summit | VIDEO
President Obama Ignores & Snubs Iraqi Prime Minister Haider al Abadi at G7 Summit | VIDEO Did Obama give Iraqi PM Abadi the cold shoulder at G7 summit? WASHINGTON – Did President Obama give Iraq’s prime minister the cold shoulder? Video from the G-7 summit in Germany appears to show Iraqi Prime Minister Haider al-Abadi trying to get a word in with the U.S. president after world leaders were gathered for a group photo. Obama can be seen on a bench chatting it up with Italy’s prime minister and Christine Lagarde, the managing director of the IMF – when al-Abadi and his translator take a seat next to Obama. As Obama and the other leaders huddle to talk, Obama appears unaware of Abadi, who awkwardly sits about a foot away with his translator and waits to get the president’s attention.... -

Maliki steps down as Iraqi Prime Minister
Subscribe to our channel http://bit.ly/AJSubscribe Subscribe to our channel http://bit.ly/AJSubscribe Reaching more than 270 million households in over 140 countries across the globe, our viewers trust Al Jazeera English to keep them informed, inspired, and entertained. Our impartial, fact-based reporting wins worldwide praise and respect. It is our unique brand of journalism that the world has come to rely on. We are reshaping global media and constantly working to strengthen our reputation as one of the world's most respected news and current affairs channels. Social Media links: Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/aljazeera Instagram: https://instagram.com/aljazeera/?ref=... Twitter: https://twitter.com/ajenglish Website: http://www.aljazeera.com/ google+: https://plus.google.com/+a... -

Did Obama Snub The Iraqi Prime Minister At The G7 Summit-News Brief
This past weekend the leaders from the Core G7 nations met in Bavaria, Germany to discuss such topics as the global economy, Russia’s aggression in the Ukraine, the threat of climate change and violent extremism. President Obama and the other world leaders are set to sit down with the Prime Minister of Iraq Haider al-Abadi to discuss efforts to train Iraqi security forces. Obama said that the Pentagon does not yet have a complete plan for training and equipping the Iraqi forces. This is the first meeting since ISIS captured the city of Ramadi. And Al-Abadi has said the Obama administration is not doing enough to help Iraq fight ISIS. And yet here they are, Obama and Al-Abadi sitting on the same bench while Obama is chatting with IMF chief Christine Lagarde and Italy’s Prime Minister Mari... -

Is Iraq ungovernable? | Conflict Zone
http://www.dw.com/conflictzone The Iraqi Prime Minister Haider al-Abadi has a tough job. 'Islamic State' militants are occupying entire regions, corruption is institutionalized and the Sunni-Shia rift is tearing the country apart. "Terrorism is an international problem," al-Abadi insists. But is he doing his fair share of fixing the country? Find out on this week's Conflict Zone with Tim Sebastian. -

The Iraqi Prime Minister Haider al Abadi
-

The President Meets with the Prime Minister of Iraq
President Obama delivers remarks after meeting with Prime Minister Al-Abadi of Iraq. June 8, 2015. -

Pope to Iraqi Prime Minister: Let's seek peace in the midst of the division
Follow us on Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/RomeReportsENG/ Click here to receive the latest news: http://smarturl.it/RomeReports Visit our website to learn more: http://www.romereports.com/ They talked about the persecution of Christians and other religious minorities in the Middle East. --------------------- For broadcasting: sales@romereports.com ROME REPORTS, www.romereports.com, is an independent international TV News Agency based in Rome covering the activity of the Pope, the life of the Vatican and current social, cultural and religious debates. Reporting on the Catholic Church requires proximity to the source, in-depth knowledge of the Institution, and a high standard of creativity and technical excellence. As few broadcasters have a permanent correspondent in Rome, ROME ... -

Iraqi Prime Minister Visits 'Liberated' Ramadi
On Dec. 29, Prime Minister Haider al-Abadi visited Ramadi and reminded Iraqis that the next operation will be taking Mosul from ISIS -

Iraqi PM fails to get Obama’s attention in awkward G7 moment
In an awkward moment at the Group of Seven summit in Germany on Monday, 8 June, Iraqi Prime Minister Haider al-Abadi seeks to get President Barack Obama's attention. Obama, seated on a bench chatting with Italian Prime Minister Mario Renzi and IMF managing director Christine Lagarde appears not to notice when Abadi sits to Obama's left. The president, his back turned to Abadi, continued his huddle with Renzi and Lagarde. Even after Obama, Renzi and Lagarde stand, none acknowledge Abadi nearby. Abadi then checks his watch, his translator gestures, and the two walk away. Obama and Abadi did have a private session later Monday where they discussed the fight against the Islamic State. What are the top stories today? Click to watch: https://www.youtube.com/playlist?list=PLSyY1udCyYqBeDOz40...
Iraqi Prime Minister on ISIS: "We Have to Stop Them"
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 5:30
- Updated: 08 Mar 2015
- views: 5752
- published: 08 Mar 2015
- views: 5752
President Obama Meets with Iraqi Prime Minister
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 37:44
- Updated: 14 Apr 2015
- views: 9186
- published: 14 Apr 2015
- views: 9186
Prime Minister Abadi: Iraq welcomes Russia in Islamic State fight
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 8:19
- Updated: 30 Sep 2015
- views: 7648
- published: 30 Sep 2015
- views: 7648
President Obama Ignores & Snubs Iraqi Prime Minister Haider al Abadi at G7 Summit | VIDEO
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 1:31
- Updated: 08 Jun 2015
- views: 34170
- published: 08 Jun 2015
- views: 34170
Maliki steps down as Iraqi Prime Minister
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 2:39
- Updated: 15 Aug 2014
- views: 1654
- published: 15 Aug 2014
- views: 1654
Did Obama Snub The Iraqi Prime Minister At The G7 Summit-News Brief
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 2:01
- Updated: 08 Jun 2015
- views: 1926
- published: 08 Jun 2015
- views: 1926
Is Iraq ungovernable? | Conflict Zone
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 25:57
- Updated: 17 Feb 2016
- views: 8337
- published: 17 Feb 2016
- views: 8337
The Iraqi Prime Minister Haider al Abadi
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 4:29
- Updated: 19 Feb 2016
- views: 252
- published: 19 Feb 2016
- views: 252
The President Meets with the Prime Minister of Iraq
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 14:38
- Updated: 08 Jun 2015
- views: 4490
- published: 08 Jun 2015
- views: 4490
Pope to Iraqi Prime Minister: Let's seek peace in the midst of the division
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 1:55
- Updated: 10 Feb 2016
- views: 115
- published: 10 Feb 2016
- views: 115
Iraqi Prime Minister Visits 'Liberated' Ramadi
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 0:59
- Updated: 29 Dec 2015
- views: 97
- published: 29 Dec 2015
- views: 97
Iraqi PM fails to get Obama’s attention in awkward G7 moment
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 1:24
- Updated: 09 Jun 2015
- views: 66789
- published: 09 Jun 2015
- views: 66789
-

Iraqi army launches Falluja operation | DW News
It is only day one of operations to retake the ISIS stronghold but Iraq's Prime Minister Haider al-Abadi is confident of victory. More News: http://www.dw.com/en/program/dw-news/s-3232-9798 -

Falluja operation against Islamic State going on successfully - Abadi.
FULL SCRIPT TO FOLLOW EDITORS PLEASE NOTE: THIS EDIT CONTAINS MATERIAL WHICH WAS ORIGINALLY 4:3 An Iraqi army offensive to retake Falluja from Islamic State militants is "going on successfully", Prime Minister Haider al-Abadi says. SHOWS: NEAR FALLUJA, IRAQ (MAY 23, 2016) (ORIGINALLY 4:3) (IRAQIYA TV - ACCESS ALL) 1. VARIOUS OF CONVOY OF MILITARY VEHICLES ESCORTING IRAQI PRIME MINISTER, HAIDER AL-ABADI, DRIVING ON ROAD TO FALLUJA OPERATIONS COMMAND / PLUME OF BLACK SMOKE AT FAR DISTANCE 2. COLUMN OF MILITARY CONVOY OF ABADI DRIVING ON ROAD 3. MILITARY VEHICLE ESCORTING ABADI'S WHITE ARMOURED VEHICLE 4. MILITARY VEHICLES DRIVING 5. VEHICLES OUTSIDE FALLUJA OPERATIONS COMMAND 6. MILITARY OFFICIALS AND JOURNALISTS ENTERING FALLUJA OPERATIONS COMMAND HEADQUARTERS 7. MILITARY OFFICIAL... -

Iraqi army tells Fallujah residents to flee city
Iraqi prime minister announce start of military offensive to retake the city of Fallujah from ISIL -

Iraqi army regains more ground from Daesh terrorists
Iraqi forces are pushing ahead with their fight against Daesh terrorists, regaining more areas from the Takfiri group. In its latest series of offensives, the Iraqi army backed by the Popular Mobilization Units, managed to liberate the city of Karmah northeast of Fallujah in Anbar province. The army says dozens of terrorists were killed in the operation. Prime Minister Haider al-Abadi visited the front line to monitor the situation on the ground. He hailed the efforts by the Iraqi troops against ISIL terrorists. Watch Live: http://www.presstv.ir/live.html Twitter: http://twitter.com/PressTV LiveLeak: http://www.liveleak.com/c/PressTV Facebook: http://www.facebook.com/PRESSTV Google+: http://plus.google.com/+VideosPTV Instagram: http://instagram.com/presstv... -

Iraqi forces battle ISIL militants outside Fallujah
Iraq's Prime Minister, Haider al-Abadi, has celebrated what he had called "big successes" for government troops who launched an offensive on Monday to retake the city of Fallujah from ISIL. Citizens were advised to evacuate the city before the offensive started. The city has been controlled by ISIL since January 2014. Subscribe to us on Youtube: https://www.youtube.com/user/CCTVNEWSbeijing Download for IOS: https://itunes.apple.com/us/app/cctvnews-app/id922456579?l=zh&ls;=1&mt;=8 Download for Android: https://play.google.com/store/apps/details?id=com.imib.cctv Follow us on: Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/cctvnewschina Twitter: https://twitter.com/CCTVNEWS Google+: https://plus.google.com/+CCTVNEWSbeijing Tumblr: http://cctvnews.tumblr.com/ Weibo: http://weibo.com/cctvnewsbeijing -

Raw: Iraq Claims Advances in IS Fallujah Fight
Iraq's Prime Minister Haider al-Abadi hailed "big successes" by government troops after launching an offensive to retake Fallujah from Islamic State group militants on Monday. AP filmed Iraqi troops taking part in the offensive. (May 24) Subscribe for more Breaking News: http://smarturl.it/AssociatedPress Get updates and more Breaking News here: http://smarturl.it/APBreakingNews The Associated Press is the essential global news network, delivering fast, unbiased news from every corner of the world to all media platforms and formats. AP’s commitment to independent, comprehensive journalism has deep roots. Founded in 1846, AP has covered all the major news events of the past 165 years, providing high-quality, informed reporting of everything from wars and elections to championship game... -

Iraqi forces free several villages in Fallujah region
The Iraqi prime minister has lauded advances made by security forces against Daesh around Fallujah as he visits the front line to monitor progress being made against the terrorists. Haider al-Abadi, symbolically wearing the black uniform of Iraq’s counter-terrorism forces, conferred with top commanders at the Fallujah Operation command headquarters. The Iraqi security forces along with tribal and Hashd al-Sha’abi fighters, have retaken several villages. They include the Shahabi and Dawaiah regions around Garma, which is the main supply route for Daesh terrorists. Iraqi Defense minister Khaled al-Obeidi confirmed that the Takfiri terrorist defenses were crumbling in the city as government reinforcements continue to pour into the area. Fallujah, located in Iraq’s western Anbar province fel... -

Iraqi PM Announces Military Operation To Retake Fallujah
From: https://www.youtube.com/user/france24english May 23, 2016 - Subscribe to France 24 now : http://f24.my/youtubeEN FRANCE 24 live news stream: all the latest news 24/7 http://f24.my/YTliveEN Iraqi Prime Minister Haider al-Abadi announced the launching of an offensive to retake the Islamic State group's stronghold of Fallujah. The military told residents on Sunday to get ready to leave before fighting started. Visit our website : http://www.france24.com Subscribe to our YouTube channel : http://f24.my/youtubeEN Like us on Facebook : https://www.facebook.com/FRANCE24.English Follow us on Twitter : https://twitter.com/France24_en --- PigmineNews.com: http://www.pigminenews.com PigmineNews on mobile: http://www.pigminenews.com/mobile PigmineNews on Facebook: http://www.facebook.com... -

Iraq Military enter Fallujah to retake city from ISIS
Baghdad -- Iraq's prime minister hailed "big successes" Monday by government troops after launching an offensive to retake Fallujah from Islamic State militants, but the operation promises to be one of the toughest challenges yet for the country's struggling security forces. Troops recaptured some agricultural areas in Garma, a district along the northeastern edge of Fallujah, under intensified Iraqi airstrikes and heavy artillery, said Col. Mahmoud al-Mardhi, who leads Shiite militia forces in the operation. U.S.-led coalition forces carried out two airstrikes, the Pentagon said, part of an aerial campaign that has seen an average of two bombings a day over the past week in the city about 40 miles, 65 kilometers, west of Baghdad. Prime Minister Haider al-Abadi toured the Fallujah fron... -

Iraqi forces free several villages in Fallujah
The Iraqi army and allied troops liberate several key regions around Fallujah as they press on with their massive offensive to free the city from Daesh terrorists. The army, counter-terrorism and police troops, along with tribal and Hashd al-Sha’abi fighters, have retaken several villages. They include the Shahabi and Dawaiah regions around Garma, which is the main supply route for Daesh terrorists. Iraqi Defense minister Khaled al-Obeidi confirmed that the Takfiri terrorist defenses were collapsing in the city as Iraqi government reinforcements continue to pour into the area. Iraqi Prime minister Haider al-Abadi, meanwhile, hailed the operation as a big success. Fallujah, located in Iraq’s western Anbar province fell to Daesh terrorists in the summer of 20-14. Up to 600 Takfiris are estim... -

Iraqi forces clash with ISIL while retaking Fallujah
Iraqi forces have clashed with ISIL militants near Fallujah while bombing the city's central district. The battle took place in the initial hours of an offensive announced earlier by Prime Minister Haider al-Abadi to retake the city from ISIL. Subscribe to us on Youtube: https://www.youtube.com/user/CCTVNEWSbeijing Download for IOS: https://itunes.apple.com/us/app/cctvnews-app/id922456579?l=zh&ls;=1&mt;=8 Download for Android: https://play.google.com/store/apps/details?id=com.imib.cctv Follow us on: Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/cctvnewschina Twitter: https://twitter.com/CCTVNEWS Google+: https://plus.google.com/+CCTVNEWSbeijing Tumblr: http://cctvnews.tumblr.com/ Weibo: http://weibo.com/cctvnewsbeijing -

Operation to free Falluja from ISIS starts
Iraqi Prime Minister Haider al-Abadi took to live television early Monday to announce the start of an operation to recapture the city of Falluja from ISIS. Speaking on Iraqi state TV from the military's Joint Operations Command in Baghdad, Abadi said Iraqi security forces would provide safe passage for civilians to leave the city during the operation.
Iraqi army launches Falluja operation | DW News
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 1:21
- Updated: 24 May 2016
- views: 36
- published: 24 May 2016
- views: 36
Falluja operation against Islamic State going on successfully - Abadi.
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 3:07
- Updated: 24 May 2016
- views: 0
- published: 24 May 2016
- views: 0
Iraqi army tells Fallujah residents to flee city
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 2:08
- Updated: 24 May 2016
- views: 0
- published: 24 May 2016
- views: 0
Iraqi army regains more ground from Daesh terrorists
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 1:31
- Updated: 24 May 2016
- views: 33
- published: 24 May 2016
- views: 33
Iraqi forces battle ISIL militants outside Fallujah
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 0:31
- Updated: 24 May 2016
- views: 128
- published: 24 May 2016
- views: 128
Raw: Iraq Claims Advances in IS Fallujah Fight
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 0:59
- Updated: 24 May 2016
- views: 683
- published: 24 May 2016
- views: 683
Iraqi forces free several villages in Fallujah region
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 1:21
- Updated: 24 May 2016
- views: 754
- published: 24 May 2016
- views: 754
Iraqi PM Announces Military Operation To Retake Fallujah
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 1:48
- Updated: 24 May 2016
- views: 13
- published: 24 May 2016
- views: 13
Iraq Military enter Fallujah to retake city from ISIS
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 1:00
- Updated: 23 May 2016
- views: 119
- published: 23 May 2016
- views: 119
Iraqi forces free several villages in Fallujah
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 0:47
- Updated: 23 May 2016
- views: 110
- published: 23 May 2016
- views: 110
Iraqi forces clash with ISIL while retaking Fallujah
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 1:03
- Updated: 23 May 2016
- views: 35
- published: 23 May 2016
- views: 35
Operation to free Falluja from ISIS starts
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 2:23
- Updated: 23 May 2016
- views: 6
- published: 23 May 2016
- views: 6
-

Davos 2015 A Vision for Iraq - Prime Minister Al Abadi
http://americancontractor.com Haïdar Al Abadi, Prime Minister of Iraq Introduced by Klaus Schwab, Founder and Executive Chairman, World Economic Forum Moderator Charlie Rose, Anchor, CBS News, USA http://www.weforum.org/ -

Statesmen's Forum: Iraqi Prime Minister Haider Al-Abadi
H.E. Dr. Haider Al-Abadi Prime Minister of the Republic of Iraq Introduction by: Dr. John Hamre CSIS President and CEO Moderated by: Dr. Jon B. Alterman Senior Vice President, Zbigniew Brzezinski Chair in Global Security and Geostrategy, and Director, CSIS Middle East Program H.E. Dr. Haider Al-Abadi is prime minister of the Republic of Iraq, a position he has held since September 2014. Prior to this, he served as deputy speaker of parliament, and minister of communications in the Iraqi Governing Council. He was also elected to the Iraqi parliament in 2005 and 2010 as a representative of Baghdad, and has chaired the parliament’s finance committee and committee for economy and investment. Before returning to Iraq in 2003, Dr. Al-Abadi worked as a high-tech transportation design and deve... -

Press Availability with Iraqi Prime Minister and French Foreign Minister
Press availability following the international conference, "Combating the Islamic State Group" in Paris with Deputy Secretary of State Antony J. Blinken, Iraqi Prime Minister Haider al-Abadi and French Foreign Minister Laurent Fabius in Paris, France on June 2, 2015. Transcript available at http://www.state.gov/s/d/2015/243095.htm. -

Iraq's Transition: Remarks by Iraqi Prime Minister H.E. Mr. Noori al-Maliki
Date: October 31, 2013 Iraq has made significant progress since the last of U.S. troops left the country in December 2011, but continues to face serious challenges. Iraq's economy became stronger, provincial and regional elections were organized, and the country has made steady steps toward regaining its regional and international stature. At the same time, the country is struggling with high levels of violence and other spillover effects from Syria, as it tries to hold national elections in 2014 and find a workable common vision of governance. On October 31, Iraqi Prime Minister Noori al-Maliki joined USIP for a discussion on his country's future. Details: http://bit.ly/1a0ZqmK Speakers: Jim Marshall, Opening Remarks and Moderator President, U.S. Institute of Peace Amb. Beth Jones, I... -

H.E. Dr. Haider Al-Abadi, Prime Minister of the Republic of Iraq, gave speech in Berlin
H.E. Dr. Haider Al-Abadi, Prime Minister of the Republic of Iraq, gave a speech in Berlin on domestic and foreign policy challenges of Iraq on 6 February upon invitation of Körber Foundation. The ensuing discussion was moderated by Dr. Thomas Paulsen, Member of the Executive Board, Körber Foundation. -

Bush and Iraq Prime Minister Maliki Sign the Strategic Framework Agreement and Security Agreement
-

Iraqi Deputy Prime Minister Al-Eissawi on Political Developments Since the Surge
Iraqi security forces are increasingly capable of maintaining the relative calm in Iraq, and U.S. role is shifting toward providing logistical support and training, which is a “tremendous change in the mission” according to Iraq’s Deputy Prime Minister Rafe H. Al-Eissawi. -

Governance and Stability in Iraq - Deputy Prime Minister of the Republic of Iraq
Date: January 14, 2014 The United States Institute of Peace (USIP), the National Defense University (NDU), and the Iraqi American Community Center (IAC) hosted H.E. Mr. Saleh al-Mutlaq, Deputy Prime Minister of the Republic of Iraq, and members of the Iraqi Council of Representatives for public remarks and a discussion on governance, services, transition, and peace and stability in Iraq. To watch the discussion with members of the Iraqi Council of Representatives, visit: http://youtu.be/1rsd4Xde80Q For more details about this event, visit: http://www.usip.org/events/governance-and-stability-in-iraq-0 Speakers: William B. Taylor, Opening Remarks Vice President for Middle East and Africa, U.S. Institute of Peace H.E. Mr. Saleh al-Mutlaq, Keynote Remarks Deputy Prime Minister of the Repu... -

(Arabic) Governance and Stability in Iraq - Deputy Prime Minister of the Republic of Iraq
Arabic language version Date: January 14, 2014 The United States Institute of Peace (USIP), the National Defense University (NDU), and the Iraqi American Community Center (IAC) hosted H.E. Mr. Saleh al-Mutlaq, Deputy Prime Minister of the Republic of Iraq, and members of the Iraqi Council of Representatives for public remarks and a discussion on governance, services, transition, and peace and stability in Iraq. To watch the discussion with members of the Iraqi Council of Representatives, visit: http://youtu.be/1rsd4Xde80Q For more details about this event, visit: http://www.usip.org/events/governance-and-stability-in-iraq-0 Speakers: William B. Taylor, Opening Remarks Vice President for Middle East and Africa, U.S. Institute of Peace H.E. Mr. Saleh al-Mutlaq, Keynote Remarks Deputy P... -

Prime Minister's Press Conference - Iraq
Davos 2015 A Vision for Iraq - Prime Minister Al Abadi
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 32:40
- Updated: 08 Feb 2015
- views: 3160
- published: 08 Feb 2015
- views: 3160
Statesmen's Forum: Iraqi Prime Minister Haider Al-Abadi
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 64:47
- Updated: 16 Apr 2015
- views: 7626
- published: 16 Apr 2015
- views: 7626
Press Availability with Iraqi Prime Minister and French Foreign Minister
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 24:49
- Updated: 02 Jun 2015
- views: 345
- published: 02 Jun 2015
- views: 345
Iraq's Transition: Remarks by Iraqi Prime Minister H.E. Mr. Noori al-Maliki
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 62:50
- Updated: 05 Nov 2013
- views: 856
- published: 05 Nov 2013
- views: 856
H.E. Dr. Haider Al-Abadi, Prime Minister of the Republic of Iraq, gave speech in Berlin
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 59:24
- Updated: 06 Feb 2015
- views: 12618
- published: 06 Feb 2015
- views: 12618
Bush and Iraq Prime Minister Maliki Sign the Strategic Framework Agreement and Security Agreement
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 27:42
- Updated: 03 May 2012
- views: 243
- published: 03 May 2012
- views: 243
Iraqi Deputy Prime Minister Al-Eissawi on Political Developments Since the Surge
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 66:01
- Updated: 03 Mar 2016
- views: 2
- published: 03 Mar 2016
- views: 2
Governance and Stability in Iraq - Deputy Prime Minister of the Republic of Iraq
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 59:53
- Updated: 22 Jan 2014
- views: 392
- published: 22 Jan 2014
- views: 392
(Arabic) Governance and Stability in Iraq - Deputy Prime Minister of the Republic of Iraq
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 59:55
- Updated: 23 Jan 2014
- views: 102
- published: 23 Jan 2014
- views: 102
Prime Minister's Press Conference - Iraq
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 35:20
- Updated: 03 Oct 2014
- views: 3430
- published: 03 Oct 2014
- views: 3430
- Playlist
- Chat
- Playlist
- Chat

Iraqi Prime Minister on ISIS: "We Have to Stop Them"
- Report rights infringement
- published: 08 Mar 2015
- views: 5752

President Obama Meets with Iraqi Prime Minister
- Report rights infringement
- published: 14 Apr 2015
- views: 9186

Prime Minister Abadi: Iraq welcomes Russia in Islamic State fight
- Report rights infringement
- published: 30 Sep 2015
- views: 7648

President Obama Ignores & Snubs Iraqi Prime Minister Haider al Abadi at G7 Summit | VIDEO
- Report rights infringement
- published: 08 Jun 2015
- views: 34170

Maliki steps down as Iraqi Prime Minister
- Report rights infringement
- published: 15 Aug 2014
- views: 1654

Did Obama Snub The Iraqi Prime Minister At The G7 Summit-News Brief
- Report rights infringement
- published: 08 Jun 2015
- views: 1926

Is Iraq ungovernable? | Conflict Zone
- Report rights infringement
- published: 17 Feb 2016
- views: 8337

The Iraqi Prime Minister Haider al Abadi
- Report rights infringement
- published: 19 Feb 2016
- views: 252

The President Meets with the Prime Minister of Iraq
- Report rights infringement
- published: 08 Jun 2015
- views: 4490

Pope to Iraqi Prime Minister: Let's seek peace in the midst of the division
- Report rights infringement
- published: 10 Feb 2016
- views: 115

Iraqi Prime Minister Visits 'Liberated' Ramadi
- Report rights infringement
- published: 29 Dec 2015
- views: 97

Iraqi PM fails to get Obama’s attention in awkward G7 moment
- Report rights infringement
- published: 09 Jun 2015
- views: 66789
- Playlist
- Chat

Iraqi army launches Falluja operation | DW News
- Report rights infringement
- published: 24 May 2016
- views: 36

Falluja operation against Islamic State going on successfully - Abadi.
- Report rights infringement
- published: 24 May 2016
- views: 0

Iraqi army tells Fallujah residents to flee city
- Report rights infringement
- published: 24 May 2016
- views: 0

Iraqi army regains more ground from Daesh terrorists
- Report rights infringement
- published: 24 May 2016
- views: 33

Iraqi forces battle ISIL militants outside Fallujah
- Report rights infringement
- published: 24 May 2016
- views: 128

Raw: Iraq Claims Advances in IS Fallujah Fight
- Report rights infringement
- published: 24 May 2016
- views: 683

Iraqi forces free several villages in Fallujah region
- Report rights infringement
- published: 24 May 2016
- views: 754

Iraqi PM Announces Military Operation To Retake Fallujah
- Report rights infringement
- published: 24 May 2016
- views: 13

Iraq Military enter Fallujah to retake city from ISIS
- Report rights infringement
- published: 23 May 2016
- views: 119

Iraqi forces free several villages in Fallujah
- Report rights infringement
- published: 23 May 2016
- views: 110

Iraqi forces clash with ISIL while retaking Fallujah
- Report rights infringement
- published: 23 May 2016
- views: 35

Operation to free Falluja from ISIS starts
- Report rights infringement
- published: 23 May 2016
- views: 6
- Playlist
- Chat

Davos 2015 A Vision for Iraq - Prime Minister Al Abadi
- Report rights infringement
- published: 08 Feb 2015
- views: 3160

Statesmen's Forum: Iraqi Prime Minister Haider Al-Abadi
- Report rights infringement
- published: 16 Apr 2015
- views: 7626

Press Availability with Iraqi Prime Minister and French Foreign Minister
- Report rights infringement
- published: 02 Jun 2015
- views: 345

Iraq's Transition: Remarks by Iraqi Prime Minister H.E. Mr. Noori al-Maliki
- Report rights infringement
- published: 05 Nov 2013
- views: 856

H.E. Dr. Haider Al-Abadi, Prime Minister of the Republic of Iraq, gave speech in Berlin
- Report rights infringement
- published: 06 Feb 2015
- views: 12618

Bush and Iraq Prime Minister Maliki Sign the Strategic Framework Agreement and Security Agreement
- Report rights infringement
- published: 03 May 2012
- views: 243

Iraqi Deputy Prime Minister Al-Eissawi on Political Developments Since the Surge
- Report rights infringement
- published: 03 Mar 2016
- views: 2

Governance and Stability in Iraq - Deputy Prime Minister of the Republic of Iraq
- Report rights infringement
- published: 22 Jan 2014
- views: 392

(Arabic) Governance and Stability in Iraq - Deputy Prime Minister of the Republic of Iraq
- Report rights infringement
- published: 23 Jan 2014
- views: 102

Prime Minister's Press Conference - Iraq
- Report rights infringement
- published: 03 Oct 2014
- views: 3430
World War III will be fought over water
Edit Quartz 24 May 2016Failure Is Not An Option: IS Commanders, Militants Executed For Missing Goals
Edit WorldNews.com 24 May 2016Forensic Official: EgyptAir 804 Brought Down By Explosion
Edit WorldNews.com 24 May 2016'Keurig Of Cannabis' Seen As Sign Legalized Pot Is Becoming Depressingly Unhip
Edit WorldNews.com 24 May 2016U.S. Justice Department Decides Dylann Roof Will Face Death Penalty If Convicted
Edit WorldNews.com 24 May 2016Itinerary for Tuesday, May 24, 2016 (Office of the Prime Minister of Canada)
Edit Public Technologies 25 May 2016Is the UK’s Iraq Inquiry Set to “savage” Tony Blair?
Edit Dissident Voice 25 May 2016Trudeau to take day off in Japan to celebrate wedding anniversary
Edit Toronto Sun 25 May 2016Spokesperson's Press Briefing (May 24, 2016) (Ministry of Foreign Affairs and Trade of the Republic of Korea)
Edit Public Technologies 25 May 2016Editorial: Seeds of doubt, finally
Edit Yahoo Daily News 25 May 2016Readout of Vice President Biden’s Meeting with Prime Minister Dacian Ciolos of Romania (President of the United States)
Edit Public Technologies 25 May 2016BJP plans six rallies in in Odisha soon
Edit The Times of India 25 May 2016Japan PM Shinzo Abe to meet Obama, Cameron ahead of G7 summit
Edit Indian Express 25 May 2016Canada PM Justin Trudeau's popularity soars
Edit Deccan Chronicle 25 May 2016Seven stories in the news today, May 24
Edit Topix 25 May 2016Japan PM Abe to meet with Obama, Cameron ahead of G7 summit
Edit Reuters 25 May 2016Depp's war of words with Australian deputy leader continues
Edit Seattle Post-Intelligence 25 May 2016- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- Next page »







