- published: 23 May 2014
- views: 25698
-
remove the playlistScattering
-
remove the playlistLatest Videos
-
remove the playlistLongest Videos
- remove the playlistScattering
- remove the playlistLatest Videos
- remove the playlistLongest Videos
- published: 02 Apr 2013
- views: 4437
- published: 23 May 2015
- views: 2348
- published: 27 May 2015
- views: 2786
- published: 27 May 2015
- views: 1632
- published: 10 Sep 2010
- views: 69924
- published: 06 May 2010
- views: 159236
- published: 14 Nov 2012
- views: 6469
- published: 18 Jun 2014
- views: 11219
- published: 23 May 2013
- views: 28366
- published: 09 Sep 2014
- views: 4582

Scattering is a general physical process where some forms of radiation, such as light, sound, or moving particles, are forced to deviate from a straight trajectory by one or more localized non-uniformities in the medium through which they pass. In conventional use, this also includes deviation of reflected radiation from the angle predicted by the law of reflection. Reflections that undergo scattering are often called diffuse reflections and unscattered reflections are called specular (mirror-like) reflections
The types of non-uniformities which can cause scattering, sometimes known as scatterers or scattering centers, are too numerous to list, but a small sample includes particles, bubbles, droplets, density fluctuations in fluids, crystallites in polycrystalline solids, defects in monocrystalline solids, surface roughness, cells in organisms, and textile fibers in clothing. The effects of such features on the path of almost any type of propagating wave or moving particle can be described in the framework of scattering theory.
This article is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported License, which means that you can copy and modify it as long as the entire work (including additions) remains under this license.
- Loading...

-
 1:27
1:27Rayleigh Scattering Animation (why the sky is blue)
Rayleigh Scattering Animation (why the sky is blue)Rayleigh Scattering Animation (why the sky is blue)
This is just a mock up, it was never used in a presentation. We were trying to explain scattering in a physical way that makes sense to kids, but also addresses the 1/λ4 wavelength dependence. I want to make clear that I mean blue light is scattering much much more than red, the photon does not partially scatter and continue to move in the same direction. Also, we have already addressed the reason the sky isn't perceived as violet which is why it isn't included. Mie scattering is another video, and perhaps a discussion of light incident could help explain the colors we see at different times of the day. Overall, the physics of light are pretty complex and cool. Maybe we'll do an animation on thin film interference. -
 2:16
2:16Scattering of Light.mp4
Scattering of Light.mp4 -
 15:43
15:43Lesson27: Intro to Scattering +Ion Trap Cooling HW.
Lesson27: Intro to Scattering +Ion Trap Cooling HW.Lesson27: Intro to Scattering +Ion Trap Cooling HW.
Short review of classical scattering + intro to QM Scattering theory. Also.. hints/direction for ion trap cooling homework. Preclass slides by Steve Spicklemire. -
 9:29
9:29Particle Physics (28 of 41) What is a Photon? 12. Rayleigh Scattering (Why is the Sky Blue?)
Particle Physics (28 of 41) What is a Photon? 12. Rayleigh Scattering (Why is the Sky Blue?)Particle Physics (28 of 41) What is a Photon? 12. Rayleigh Scattering (Why is the Sky Blue?)
Visit http://ilectureonline.com for more math and science lectures! In this video I will explain Rayleigh scattering and why is the sky blue? Next video in the Particle Physics series can be seen at: http://youtu.be/uetMkaWUFTs -
 8:18
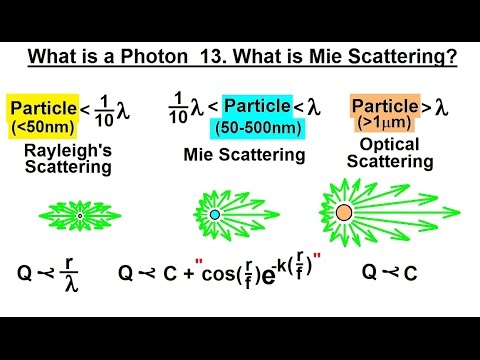
8:18Particle Physics (29 of 41) What is a Photon? 13. Mie Scattering
Particle Physics (29 of 41) What is a Photon? 13. Mie ScatteringParticle Physics (29 of 41) What is a Photon? 13. Mie Scattering
Visit http://ilectureonline.com for more math and science lectures! In this video I will explain Mie scattering of photons scattering off large particles. Next video in the Particle Physics series can be seen at: http://youtu.be/4Lyf2zBSlCo -
 3:27
3:27Particle Physics (30 of 41) What is a Photon? 14. Mie Scattering (Continued 2)
Particle Physics (30 of 41) What is a Photon? 14. Mie Scattering (Continued 2)Particle Physics (30 of 41) What is a Photon? 14. Mie Scattering (Continued 2)
Visit http://ilectureonline.com for more math and science lectures! In this video I will compare Rayleigh's, Mie, and optical scattering. Next video in the Particle Physics series can be seen at: http://youtu.be/ds_JYBjv2g8 -
 5:24
5:24Compton Scattering
Compton ScatteringCompton Scattering
Watch more videos on http://www.brightstorm.com/science/physics SUBSCRIBE FOR All OUR VIDEOS! https://www.youtube.com/subscription_center?add_user=brightstorm2 VISIT BRIGHTSTORM.com FOR TONS OF VIDEO TUTORIALS AND OTHER FEATURES! http://www.brightstorm.com/ LET'S CONNECT! Facebook ► https://www.facebook.com/brightstorm Pinterest ► https://www.pinterest.com/brightstorm/ Google+ ► https://plus.google.com/+brightstorm/ Twitter ► https://twitter.com/brightstorm_ Brightstorm website ► https://www.brightstorm.com/ -
 2:06
2:06Ruther's Alpha Scattering Experiment2
Ruther's Alpha Scattering Experiment2Ruther's Alpha Scattering Experiment2
Follow us at: https://twitter.com/TutorVista Check us out at http://chemistry.tutorvista.com/nuclear-chemistry/rutherford-scattering.html Rutherford Scattering Rutherford bombards a thin gold foil with high fastly moving positively charged alpha particles. Alpha particles are produces from a radioactive source. Whenever the alpha particles pass through the thin foil of gold, the following observations are made by Rutherford. Please like our facebook page http://www.facebook.com/tutorvista -
 42:44
42:4419: Scattering cross section
19: Scattering cross section -
 82:35
82:3513. Scattering Take 2
13. Scattering Take 213. Scattering Take 2
MIT 8.04 Quantum Physics I, Spring 2013 View the complete course: http://ocw.mit.edu/8-04S13 Instructor: Allan Adams In this lecture, Prof. Adams begins with introducing the idea of coherent states. He then continues to discuss one-dimensional scattering problems across potential step and potential barrier. License: Creative Commons BY-NC-SA More information at http://ocw.mit.edu/terms More courses at http://ocw.mit.edu -
 4:42
4:42Physics - Modern Physics (7 of 26) Compton Scattering
Physics - Modern Physics (7 of 26) Compton ScatteringPhysics - Modern Physics (7 of 26) Compton Scattering
Visit http://ilectureonline.com for more math and science lectures! In this video I will show you how to find the wavelength of the scattered photon using the Compton scattering equation. -
 3:15
3:15Dynamic Light Scattering
Dynamic Light ScatteringDynamic Light Scattering
A video demo of Ebatco determining particle size using the Dynamic Light Scattering technique! Please visit us at ebatco.com for more information! -
 3:56
3:56Most Touching OSTs - World of Scattering Flowers
Most Touching OSTs - World of Scattering Flowers -
 8:29
8:29Physics Human Eye part 8 (Scattering of light, coloidal particles, tyndall effect) CBSE class 10 X
Physics Human Eye part 8 (Scattering of light, coloidal particles, tyndall effect) CBSE class 10 XPhysics Human Eye part 8 (Scattering of light, coloidal particles, tyndall effect) CBSE class 10 X
Physics Human Eye part 8 (Scattering of light, coloidal particles, tyndall effect) CBSE class 10 X
- Atomic nucleus
- Backscattering
- Bibcode
- Billiard balls
- Boundary condition
- Bragg diffraction
- Brillouin scattering
- Cell (biology)
- Coherence (physics)
- Compton scattering
- CREIL
- Crystallite
- Density
- Diffuse reflection
- Diffusion
- Doppler shift
- Droplet
- Earth's atmosphere
- Elementary particle
- Ellipsoids
- Feynman diagram
- Fiber
- Fluid
- Fog
- Geometric optics
- Gloss (paint)
- Gold
- Gustav Mie
- Iris (anatomy)
- John H. Seinfeld
- John Wiley & Sons
- Kikuchi line
- Law of reflection
- LIDAR
- Light
- Light scattering
- Liquid bubble
- Lord Rayleigh
- Lustre (mineralogy)
- Maxwell's equations
- Medical ultrasound
- Mie scattering
- Mie theory
- Monocrystal
- Mott scattering
- Nanoparticles
- Nature (journal)
- Neutron scattering
- Particle
- Photon
- Photon diffusion
- Polarization (waves)
- Polycrystal
- Polymerization
- Powder diffraction
- Radar
- Radiation
- Rain drop
- Rainbow
- Raman scattering
- Rayleigh scattering
- Scattering
- Scattering theory
- Semiconductor wafer
- Sound
- Speckle
- Specular
- Spheroids
- Sunlight
- Surface roughness
- Template Scattering
- Thomson scattering
- Trajectory
- Tyndall effect
- Veins
- Wavelength
- Waves
- Weak localization
- Wolf effect
- X-ray
-

Rayleigh Scattering Animation (why the sky is blue)
This is just a mock up, it was never used in a presentation. We were trying to explain scattering in a physical way that makes sense to kids, but also addresses the 1/λ4 wavelength dependence. I want to make clear that I mean blue light is scattering much much more than red, the photon does not partially scatter and continue to move in the same direction. Also, we have already addressed the reason the sky isn't perceived as violet which is why it isn't included. Mie scattering is another video, and perhaps a discussion of light incident could help explain the colors we see at different times of the day. Overall, the physics of light are pretty complex and cool. Maybe we'll do an animation on thin film interference. -

-

Lesson27: Intro to Scattering +Ion Trap Cooling HW.
Short review of classical scattering + intro to QM Scattering theory. Also.. hints/direction for ion trap cooling homework. Preclass slides by Steve Spicklemire. -

Particle Physics (28 of 41) What is a Photon? 12. Rayleigh Scattering (Why is the Sky Blue?)
Visit http://ilectureonline.com for more math and science lectures! In this video I will explain Rayleigh scattering and why is the sky blue? Next video in the Particle Physics series can be seen at: http://youtu.be/uetMkaWUFTs -

Particle Physics (29 of 41) What is a Photon? 13. Mie Scattering
Visit http://ilectureonline.com for more math and science lectures! In this video I will explain Mie scattering of photons scattering off large particles. Next video in the Particle Physics series can be seen at: http://youtu.be/4Lyf2zBSlCo -

Particle Physics (30 of 41) What is a Photon? 14. Mie Scattering (Continued 2)
Visit http://ilectureonline.com for more math and science lectures! In this video I will compare Rayleigh's, Mie, and optical scattering. Next video in the Particle Physics series can be seen at: http://youtu.be/ds_JYBjv2g8 -

Compton Scattering
Watch more videos on http://www.brightstorm.com/science/physics SUBSCRIBE FOR All OUR VIDEOS! https://www.youtube.com/subscription_center?add_user=brightstorm2 VISIT BRIGHTSTORM.com FOR TONS OF VIDEO TUTORIALS AND OTHER FEATURES! http://www.brightstorm.com/ LET'S CONNECT! Facebook ► https://www.facebook.com/brightstorm Pinterest ► https://www.pinterest.com/brightstorm/ Google+ ► https://plus.google.com/+brightstorm/ Twitter ► https://twitter.com/brightstorm_ Brightstorm website ► https://www.brightstorm.com/ -

Ruther's Alpha Scattering Experiment2
Follow us at: https://twitter.com/TutorVista Check us out at http://chemistry.tutorvista.com/nuclear-chemistry/rutherford-scattering.html Rutherford Scattering Rutherford bombards a thin gold foil with high fastly moving positively charged alpha particles. Alpha particles are produces from a radioactive source. Whenever the alpha particles pass through the thin foil of gold, the following observations are made by Rutherford. Please like our facebook page http://www.facebook.com/tutorvista -

-

13. Scattering Take 2
MIT 8.04 Quantum Physics I, Spring 2013 View the complete course: http://ocw.mit.edu/8-04S13 Instructor: Allan Adams In this lecture, Prof. Adams begins with introducing the idea of coherent states. He then continues to discuss one-dimensional scattering problems across potential step and potential barrier. License: Creative Commons BY-NC-SA More information at http://ocw.mit.edu/terms More courses at http://ocw.mit.edu -

Physics - Modern Physics (7 of 26) Compton Scattering
Visit http://ilectureonline.com for more math and science lectures! In this video I will show you how to find the wavelength of the scattered photon using the Compton scattering equation. -

Dynamic Light Scattering
A video demo of Ebatco determining particle size using the Dynamic Light Scattering technique! Please visit us at ebatco.com for more information! -

-

Physics Human Eye part 8 (Scattering of light, coloidal particles, tyndall effect) CBSE class 10 X
Physics Human Eye part 8 (Scattering of light, coloidal particles, tyndall effect) CBSE class 10 X -

CH2PH1 Spectroscopy, Topic 7: Raman Scattering
Part of module CH2PH1 at the University of Reading -

Dynamic Light Scattering Theory, Do's & Don'ts, and Data Interpretation
-

-

Into Eternity - The Scattering of Ashes [Full Album]
01 - 00:00 -Novus Inceptum [Intro] 02 - 01:40 -Severe Emotional Distress 03 - 05:35 -Nothing 04 - 09:31 -Timeless Winter 05 - 12:56 -Out 06 - 17:51 -A Past Beyond Memory 07 - 21:30 -Surrounded By Night 08 - 26:38 -Eternal 09 - 29:51 -Pain Through Breathing 10 - 33:43 -Suspension Of Disbelief 11 - 38:12 -Paralyzed © All rights reserved by Into Eternity Into Eternity Official Page: http://www.facebook.com/intoeternityweb Website: www.intoeternity.net My Facebook: http://www.facebook.com/wilkerCF Twitter: @Alemao_CF -

SAXS Part I: Introduction to Biological Small Angle Scattering
SAXS Part I: Introduction to Biological Small Angle Scattering Presenter: Thomas Grant, Postdoctoral Scholar from the Hauptman-Woodward Medical Research Institute Recorded on March 21, 2014 Host: Jason Key -

The Compton Effect (or Compton Scattering)
In this video, I will be showing you the scattering effect as explained by Arthur Compton. This proved once and for all that light behaves as a particle. Light did not behave as a wave in this experiment, unlike the classical wave theory of light and explanation provided by Thomson scattering. -

Bound states, scattering states, and tunneling
An explanation of the difference between bound states and scattering states in quantum mechanics and contrasted to classical mechanics, with a brief introduction to the concept of quantum tunneling. (This lecture is part of a series for a course based on Griffiths' Introduction to Quantum Mechanics. The Full playlist is at http://www.youtube.com/playlist?list=PL65jGfVh1ilueHVVsuCxNXoxrLI3OZAPI.) -

Electron Scattering
Jefferson Lab's Hall A Leader, Cynthia Keppel, explains how nuclear physics experiments are conducted with an electron accelerator. -

Elastic Neutron Scattering
This video explains the kinematics of elastic neutron scattering in nuclear reactors
Rayleigh Scattering Animation (why the sky is blue)
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 1:27
- Updated: 23 May 2014
- views: 25698
- published: 23 May 2014
- views: 25698
Scattering of Light.mp4
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 2:16
- Updated: 22 Jan 2013
- views: 18205
Lesson27: Intro to Scattering +Ion Trap Cooling HW.
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 15:43
- Updated: 02 Apr 2013
- views: 4437
- published: 02 Apr 2013
- views: 4437
Particle Physics (28 of 41) What is a Photon? 12. Rayleigh Scattering (Why is the Sky Blue?)
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 9:29
- Updated: 23 May 2015
- views: 2348
- published: 23 May 2015
- views: 2348
Particle Physics (29 of 41) What is a Photon? 13. Mie Scattering
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 8:18
- Updated: 27 May 2015
- views: 2786
- published: 27 May 2015
- views: 2786
Particle Physics (30 of 41) What is a Photon? 14. Mie Scattering (Continued 2)
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 3:27
- Updated: 27 May 2015
- views: 1632
- published: 27 May 2015
- views: 1632
Compton Scattering
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 5:24
- Updated: 10 Sep 2010
- views: 69924
- published: 10 Sep 2010
- views: 69924
Ruther's Alpha Scattering Experiment2
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 2:06
- Updated: 06 May 2010
- views: 159236
- published: 06 May 2010
- views: 159236
19: Scattering cross section
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 42:44
- Updated: 14 Nov 2012
- views: 6469
- published: 14 Nov 2012
- views: 6469
13. Scattering Take 2
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 82:35
- Updated: 18 Jun 2014
- views: 11219
- published: 18 Jun 2014
- views: 11219
Physics - Modern Physics (7 of 26) Compton Scattering
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 4:42
- Updated: 23 May 2013
- views: 28366
- published: 23 May 2013
- views: 28366
Dynamic Light Scattering
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 3:15
- Updated: 09 Sep 2014
- views: 4582
- published: 09 Sep 2014
- views: 4582
Most Touching OSTs - World of Scattering Flowers
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 3:56
- Updated: 07 Nov 2013
- views: 93275
Physics Human Eye part 8 (Scattering of light, coloidal particles, tyndall effect) CBSE class 10 X
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 8:29
- Updated: 14 Apr 2013
- views: 24975
- published: 14 Apr 2013
- views: 24975
CH2PH1 Spectroscopy, Topic 7: Raman Scattering
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 7:21
- Updated: 14 Aug 2015
- views: 490
Dynamic Light Scattering Theory, Do's & Don'ts, and Data Interpretation
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 4:16
- Updated: 15 Feb 2011
- views: 14667
- published: 15 Feb 2011
- views: 14667
Rutherford Scattering
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 2:53
- Updated: 02 May 2015
- views: 1116
Into Eternity - The Scattering of Ashes [Full Album]
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 41:24
- Updated: 18 Nov 2012
- views: 41787
- published: 18 Nov 2012
- views: 41787
SAXS Part I: Introduction to Biological Small Angle Scattering
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 49:18
- Updated: 24 Mar 2014
- views: 13692
- published: 24 Mar 2014
- views: 13692
The Compton Effect (or Compton Scattering)
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 12:10
- Updated: 30 Dec 2012
- views: 41457
- published: 30 Dec 2012
- views: 41457
Bound states, scattering states, and tunneling
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 16:39
- Updated: 15 May 2013
- views: 6592
- published: 15 May 2013
- views: 6592
Electron Scattering
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 1:13
- Updated: 03 May 2013
- views: 2816
- published: 03 May 2013
- views: 2816
Elastic Neutron Scattering
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 20:11
- Updated: 04 Sep 2014
- views: 1667
- published: 04 Sep 2014
- views: 1667
-

Gathering Strength Scattering Light
President Matthew Fillier invites us into conversations that matter at this year's Annual Meeting of Maritime Conference, May 26-29, 2016. -

Girl Scattering Pack of Cards
Sexy Girl Scattering Pack of Cards on White Background in Reverse Speed -

Mod-04 Lec-26 X-ray scattering
Materials Characterization by Dr. S. Sankaran, Department of Metallurgical & Materials Engineering,IIT Madras. For more details on NPTEL visit http://nptel.ac.in -

Griffiths Quantum Mechanics Problem 11.10: Born Approximation for Soft Sphere Scattering
Problem from Introduction to Quantum Mechanics, 2nd edition, by David J. Griffiths, Pearson Education, Inc. -

Simulation of Rutherford Scattering using Visual Python
This simulation shows scattering of 50 projectile particles (alpha) from target (gold). The size of target is equal to actual size of gold atom(1.35 A). The size of alpha particles are shown more than actual size. The energy of projectile is around 850 eV. -

Scattering
-

pixels scattering effects
In this video i am going to show you how to do the pixels effects in photoshop. drop your comments and questions below thanks. click on the buttom below to subscribe to my channel for more tutorials simply logon to www.ausgraphics.com.ng like my page on facebook: www.facebook.com/ausgraphics or twitter @ausgraphics007 -

Streuen von Perlen und Scattering der Knospen
-

Minecraft Factions Lab #94: SCATTERING DREAMSQUAD!
HOPE YOU GUYS ENJOYED THE VIDEO! DONT FORGET TO "LICK" DAT LIKE BUTTON (LIKE A PUG) JOIN the Pug Squad today by subscribing! =+= Todays video is about: trolling dreamsquad lol IGN: JustinDaPug - Say hi! Twitter: https://twitter.com/JustinDaPug Upload Schedule: Almost Everyday ranging from 7am to 10am EST! Recording/Editing Software: Camtasia ======================================== Server Ip: play.factionslab.com Shop: shop.factionslab.com Website: factionslab.com ======================================== People you should like totally subscribe to: Aris: https://www.youtube.com/channel/UCpEH3IGS1eoxLKUKuGWCaHQ Blue: https://www.youtube.com/channel/UCp_hqAaKOYKes2Axxud-0AA GFX:https://www.youtube.com/channel/UCDXPusbWH02bZNs2k5b4lWg https://www.youtube.com/channel/UClphoLcduUoc9tgEc... -

Mobile Suit Gundam 00 Ep42 Within the Scattering Light English Subtitle
-

Scattering theory of the chiral magnetic effect in a Weyl semimetal interplay of bulk Weyl cones and
Video abstract for the article ‘Scattering theory of the chiral magnetic effect in a Weyl semimetal: interplay of bulk Weyl cones and surface Fermi arcs‘ by P Baireuther, J A Hutasoit, J Tworzydło and C W J Beenakker (P Baireuther et al 2016 New J. Phys. 18 045009). Read the full article in New Journal of Physics http://iopscience.iop.org/article/10.1088/1367-2630/18/4/045009 -

binary binary scattering
Doppelsterbegegnungen -

Teen Drown While Scattering Ashes Of Dead Relative
In Johor, an 18-year-old teenager has been swept away by waves at Pantai Lido on Wednesday while he was trying to scatter the ash of a dead family member into the sea. The victim, identified as S.Satish from Yong Peng was with other family members at the stretch of beach near the Johor Zoo area to carry out the funeral rites. -

Ash Scattering at Sea by Airplane
Scattering Ashes at Sea by Air near Pebble Beach, California with landings at Half Moon Bay and Monterey. -

Octane Render Subsurface Scattering (SSS)
уроки на русском -

21. BLENDER TUTORIAL - SUSBSURFACE - SCATTERING - BLACKPARASITE.COM
http://www.blackparasite.com http://black-parasite.blogspot.com We have BLENDER, 3DS MAX, AUTODESK MAYA, MUDBOX, AFTER EFFECT, Z BRUSH, FLASH, PHOTOSHOP, CORELDRAW, 3D UNITY, CINEMA 4D, 3d printing AND MORE TUTORIALS.. PLEASE SUBSCRIBE US ON http://youtube.com/c/blackparasitecom -

-

Numerical simulation of the scattering of sound by a convected vortex
The harmonic sound field emitted by a monopole source is scattered by an inviscid vortex convected through the domain by a uniform mean flow. The scattering phenomenon is responsible for a spatial redistribution of the acoustic energy and it also alters the spectral content of the sound field. In the top frame, the colour contours represent the total pressure fluctuation. In the bottom frame, the colour contours represent the scattered pressure fluctuation (corresponding to the difference between the total pressure fluctuations obtained from simulations with and without the vortex) magnified by a factor 15. The black lines are velocity contours depicting the vortex. This simulation has been realised by V. Clair and G. Gabard at the ISVR (Institute of Sound and Vibration Research), using ... -

SUB SURFACE SCATTERING - MODELO ORGANICO EN JADE
-

N1144 5in Scattering
-

Biomedical Applications of Light Scattering McGraw Hill Biophotonics
-

SaicoPVP Factions Skeleton [EP:04] Scattering Cartel Walls !!!
Scattering Cartel Walls Its Fun LOL :) GG Dudes ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- Server IP : Play .Saicopvp.com Ts IP For SaicoPVP : Ts.Saicopvp.com ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- Song : Ivan B Edge Of The World ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- People With Me : Bipz -

Neutron Imaging and Applications A Reference for the Imaging Community Neutron Scattering Applicatio
Gathering Strength Scattering Light
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 5:33
- Updated: 15 Apr 2016
- views: 5
- published: 15 Apr 2016
- views: 5
Girl Scattering Pack of Cards
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 0:04
- Updated: 15 Apr 2016
- views: 0
- published: 15 Apr 2016
- views: 0
Mod-04 Lec-26 X-ray scattering
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 45:03
- Updated: 15 Apr 2016
- views: 2
- published: 15 Apr 2016
- views: 2
Griffiths Quantum Mechanics Problem 11.10: Born Approximation for Soft Sphere Scattering
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 18:33
- Updated: 15 Apr 2016
- views: 2
- published: 15 Apr 2016
- views: 2
Simulation of Rutherford Scattering using Visual Python
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 0:54
- Updated: 14 Apr 2016
- views: 8
- published: 14 Apr 2016
- views: 8
Scattering
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 0:43
- Updated: 14 Apr 2016
- views: 1
- published: 14 Apr 2016
- views: 1
pixels scattering effects
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 5:54
- Updated: 14 Apr 2016
- views: 4
- published: 14 Apr 2016
- views: 4
Streuen von Perlen und Scattering der Knospen
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 0:19
- Updated: 14 Apr 2016
- views: 0
- published: 14 Apr 2016
- views: 0
Minecraft Factions Lab #94: SCATTERING DREAMSQUAD!
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 10:55
- Updated: 14 Apr 2016
- views: 61
- published: 14 Apr 2016
- views: 61
Mobile Suit Gundam 00 Ep42 Within the Scattering Light English Subtitle
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 21:57
- Updated: 14 Apr 2016
- views: 1
- published: 14 Apr 2016
- views: 1
Scattering theory of the chiral magnetic effect in a Weyl semimetal interplay of bulk Weyl cones and
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 5:21
- Updated: 14 Apr 2016
- views: 4
- published: 14 Apr 2016
- views: 4
binary binary scattering
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 0:25
- Updated: 14 Apr 2016
- views: 10
- published: 14 Apr 2016
- views: 10
Teen Drown While Scattering Ashes Of Dead Relative
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 0:45
- Updated: 14 Apr 2016
- views: 7
- published: 14 Apr 2016
- views: 7
Ash Scattering at Sea by Airplane
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 3:34
- Updated: 14 Apr 2016
- views: 9
- published: 14 Apr 2016
- views: 9
Octane Render Subsurface Scattering (SSS)
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 69:16
- Updated: 13 Apr 2016
- views: 172
- published: 13 Apr 2016
- views: 172
21. BLENDER TUTORIAL - SUSBSURFACE - SCATTERING - BLACKPARASITE.COM
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 14:26
- Updated: 13 Apr 2016
- views: 4
- published: 13 Apr 2016
- views: 4
របាំបាចផ្កា ជូនសិរី | scattering flower and Glorying dance by Cambodian Khmer
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 8:12
- Updated: 13 Apr 2016
- views: 8
Numerical simulation of the scattering of sound by a convected vortex
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 0:07
- Updated: 11 Apr 2016
- views: 2
- published: 11 Apr 2016
- views: 2
SUB SURFACE SCATTERING - MODELO ORGANICO EN JADE
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 0:06
- Updated: 10 Apr 2016
- views: 130
- published: 10 Apr 2016
- views: 130
N1144 5in Scattering
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 0:10
- Updated: 08 Apr 2016
- views: 0
- published: 08 Apr 2016
- views: 0
Biomedical Applications of Light Scattering McGraw Hill Biophotonics
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 0:17
- Updated: 07 Apr 2016
- views: 0
- published: 07 Apr 2016
- views: 0
SaicoPVP Factions Skeleton [EP:04] Scattering Cartel Walls !!!
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 4:06
- Updated: 06 Apr 2016
- views: 106
- published: 06 Apr 2016
- views: 106
Neutron Imaging and Applications A Reference for the Imaging Community Neutron Scattering Applicatio
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 0:32
- Updated: 05 Apr 2016
- views: 1
- published: 05 Apr 2016
- views: 1
-

Mod-01 Lec-06 Quantum Theory of collisions Differential scattering cross section,Partial wave
Special/Select Topics in the Theory of Atomic Collisions and Spectroscopy by Prof. P.C. Deshmukh,Department of Physics,IIT Madras.For more details on NPTEL visit http://nptel.ac.in -

8.02x - Lect 30 - Polarizers, Malus' Law, Light Scattering, Blue Skies, Red Sunsets
Polarizers, Malus's Law, Brewster Angle, Polarization by Reflection and Scattering, Why is the sky blue, why are clouds white and sunsets red? Great demos! Assignments Lecture 29, 30 and 31: http://freepdfhosting.com/7d76b7e131.pdf Solutions Lecture 29, 30 and 31: http://freepdfhosting.com/cc1c6d39d1.pdf -

SubSurface Scattering In Cycles
I go over the SubSurface Scattering node in Cycles and how it can give your fleshy models an edge in realism. I also go over a very basic skin shader. A more complex and realistic shader can be found here:http://blenderartists.org/forum/showthread.php?287516-Arnold-skin-shader-ported-to-Cycles Check out this video and others at my website: www.enigmatoots.co.uk. Feel free to contact me there or by emailing me at enigmatoots@hotmail.co.uk :) Keep up to date on twitter: https://twitter.com/Enigma_Toots Follow me on Google+: https://plus.google.com/+EnigmatootsCoUk/ Good Luck with your Blenderations and have a nice day :) -

Stéphane Mallat: "Scattering Invariant Deep Networks for Classification, Pt. 1"
Graduate Summer School 2012: Deep Learning, Feature Learning "Scattering Invariant Deep Networks for Classification, Pt. 1" Stéphane Mallat, École Polytechnique Institute for Pure and Applied Mathematics, UCLA July 18, 2012 For more information: https://www.ipam.ucla.edu/programs/summer-schools/graduate-summer-school-deep-learning-feature-learning/?tab=overview -

FISH - Scattering Crows LIVE 2004
Live in Europe 2004. Filmed at the Town and Country Club Bradford April 6th 2004. -

-

Lecture - 30 Scattering Matrix
Lecture Series on Circuit theory by Prof.S. C Dutta Roy, Department of Electrical Engineering, IIT Delhi. For More details on NPTEL visit http://nptel.iitm.ac.in -

Mod-01 Lec-14 Scattering of nucleons
Nuclear Physics: Fundamentals and Applications by Prof. H.C. Verma,Department of Physics,IIT Kanpur.For more details on NPTEL visit http://nptel.ac.in -

Lesson28: More Scattering Theory (improved)
More scattering theory, including plane wave decomposition and partial scattering amplitudes. Improved demo showing plane wave decomposition. Preclass slides by Steve Spicklemire. (Note... the next two lessons are review and exam.. so no new slides) See you again at lesson 31! -

Lesson31: More Scattering! This time with movies!
Phase Shifts, Scattering Length, low energy limit. Lots of visualizations, hard sphere and soft sphere scattering, probability current profiles, and more! Pre-class slides by Steve Spicklemire -

Impact parameter and scattering angle - Relation by Dilip Sir
this video explains scattering angle, impact parameter and relation between them -

Subsurface Scattering In Cinema 4D
In this tutorial we take a look at the Subsurface Scattering Shader in Cinema 4D. We learn about it's settings and what they mean. We also look at how we can optimise those settings so we can reduce render times. -

The Booze Cruise III: The Scattering [[Full Movie]]
The gang is BACK (with a tag-along) to scatter Elsie's ashes and celebrate Grace and Morris's 40th anniversary. A series of cock-ups once more adds flavour to their journey, as always. Cast: Neil Pearson, Mark Benton, Brian Murphy, Anne Reid, Karen Henthorn, Amanda Abbington, Ian Richardson. Aired on ITV Producers: Granada Yorkshire, Water Lane Productions, Yorkshire Television (YTV) -

Scattering & Gathering of Israel
Many Christians today feel Israelites do not matter and God has turned his back on them, while making the Gentiles the new church. Does the Bible really support this thought? www,FountainOfIsrael.com email questions to FOIBibleStudies@inbox.com -

Subsurface Scattering In Octane Cinema 4D
Check out how to use subsurface scattering in Octane for Cinema 4D to use in your own projects! Please comment below for any questions. Follow along for $0.99 here: https://gumroad.com/l/iJYMX HDRI free pack by Maxime Roz: http://www.maximeroz.com/hdri-free-pack Be sure to check out his packs on gumroad!! Amazing quality! brandon@glasshandfilms.com www.glasshandfilms.com Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/brandon.clem... Glass Hand Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/glasshandfil... Instagram: @thebranclem Glass Hand Instagram: @glasshandfilms Twitter: @thebranclem -

Lecture - 31 Scattering Parameters of a Two-port
Lecture Series on Circuit theory by Prof.S. C Dutta Roy, Department of Electrical Engineering, IIT Delhi. For More details on NPTEL visit http://nptel.iitm.ac.in -

Dynamic light scattering for nanoparticle characterization
Dynamic light scattering for nanoparticle characterization Prof. Gabriel Popescu, UIUC Powerpoint: http://light.ece.illinois.edu/nbss11/_Lecture_Notes/04_DLS_PPT.pdf -

Physics 111: Laser Induced Fluorescence and Raman Scattering (LIF)
Physics 111 Advanced Laboratory. Professor Sumner Davis This video accompanied the Laser Induced Fluorescence and Raman Scattering Experiment, providing students with an introduction to the theory, apparatus, and procedures. This experiment is no longer in use in the Physics 111 lab. Molecules in the gaseous state can absorb light when the frequency or photon energy matches the energy difference between two levels. A short time later, the molecules decay to lower energy states and emit photons (fluorescent light) with energies corresponding to energy differences between states. The lower states can be the same as or different from the original state. Observation of frequencies of light absorbed or of these fluorescence photons can tell us about the energy level structure of the molecul...
Mod-01 Lec-06 Quantum Theory of collisions Differential scattering cross section,Partial wave
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 40:29
- Updated: 06 May 2014
- views: 2275
- published: 06 May 2014
- views: 2275
8.02x - Lect 30 - Polarizers, Malus' Law, Light Scattering, Blue Skies, Red Sunsets
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 51:24
- Updated: 14 Feb 2015
- views: 3465
- published: 14 Feb 2015
- views: 3465
SubSurface Scattering In Cycles
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 22:28
- Updated: 22 Jul 2014
- views: 12215
- published: 22 Jul 2014
- views: 12215
Stéphane Mallat: "Scattering Invariant Deep Networks for Classification, Pt. 1"
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 64:48
- Updated: 26 Aug 2015
- views: 550
- published: 26 Aug 2015
- views: 550
FISH - Scattering Crows LIVE 2004
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 99:38
- Updated: 22 Aug 2013
- views: 18298
- published: 22 Aug 2013
- views: 18298
Comsol Multiphysics 5 tutorial for beginners: Scattering Cross Section of a Si nanoparticle
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 33:24
- Updated: 19 Feb 2015
- views: 9702
Lecture - 30 Scattering Matrix
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 56:02
- Updated: 29 Apr 2008
- views: 29922
- published: 29 Apr 2008
- views: 29922
Mod-01 Lec-14 Scattering of nucleons
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 57:48
- Updated: 25 Mar 2014
- views: 3437
- published: 25 Mar 2014
- views: 3437
Lesson28: More Scattering Theory (improved)
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 20:34
- Updated: 05 Apr 2013
- views: 3781
- published: 05 Apr 2013
- views: 3781
Lesson31: More Scattering! This time with movies!
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 28:22
- Updated: 11 Apr 2013
- views: 1384
- published: 11 Apr 2013
- views: 1384
Impact parameter and scattering angle - Relation by Dilip Sir
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 26:59
- Updated: 22 Dec 2014
- views: 1635
- published: 22 Dec 2014
- views: 1635
Subsurface Scattering In Cinema 4D
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 34:03
- Updated: 30 Sep 2015
- views: 635
- published: 30 Sep 2015
- views: 635
The Booze Cruise III: The Scattering [[Full Movie]]
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 92:14
- Updated: 11 Feb 2014
- views: 26149
- published: 11 Feb 2014
- views: 26149
Scattering & Gathering of Israel
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 55:32
- Updated: 30 Nov 2014
- views: 1007
- published: 30 Nov 2014
- views: 1007
Subsurface Scattering In Octane Cinema 4D
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 34:54
- Updated: 17 Oct 2015
- views: 4085
- published: 17 Oct 2015
- views: 4085
Lecture - 31 Scattering Parameters of a Two-port
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 54:02
- Updated: 29 Apr 2008
- views: 40455
- published: 29 Apr 2008
- views: 40455
Dynamic light scattering for nanoparticle characterization
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 53:23
- Updated: 13 Jun 2012
- views: 5970
- published: 13 Jun 2012
- views: 5970
Physics 111: Laser Induced Fluorescence and Raman Scattering (LIF)
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 64:43
- Updated: 08 Mar 2012
- views: 8350
- published: 08 Mar 2012
- views: 8350
- Playlist
- Chat
- Playlist
- Chat

Rayleigh Scattering Animation (why the sky is blue)
- Report rights infringement
- published: 23 May 2014
- views: 25698

Scattering of Light.mp4
- Report rights infringement
- published: 22 Jan 2013
- views: 18205

Lesson27: Intro to Scattering +Ion Trap Cooling HW.
- Report rights infringement
- published: 02 Apr 2013
- views: 4437

Particle Physics (28 of 41) What is a Photon? 12. Rayleigh Scattering (Why is the Sky Blue?)
- Report rights infringement
- published: 23 May 2015
- views: 2348

Particle Physics (29 of 41) What is a Photon? 13. Mie Scattering
- Report rights infringement
- published: 27 May 2015
- views: 2786

Particle Physics (30 of 41) What is a Photon? 14. Mie Scattering (Continued 2)
- Report rights infringement
- published: 27 May 2015
- views: 1632

Compton Scattering
- Report rights infringement
- published: 10 Sep 2010
- views: 69924

Ruther's Alpha Scattering Experiment2
- Report rights infringement
- published: 06 May 2010
- views: 159236

19: Scattering cross section
- Report rights infringement
- published: 14 Nov 2012
- views: 6469

13. Scattering Take 2
- Report rights infringement
- published: 18 Jun 2014
- views: 11219

Physics - Modern Physics (7 of 26) Compton Scattering
- Report rights infringement
- published: 23 May 2013
- views: 28366

Dynamic Light Scattering
- Report rights infringement
- published: 09 Sep 2014
- views: 4582

Most Touching OSTs - World of Scattering Flowers
- Report rights infringement
- published: 07 Nov 2013
- views: 93275

Physics Human Eye part 8 (Scattering of light, coloidal particles, tyndall effect) CBSE class 10 X
- Report rights infringement
- published: 14 Apr 2013
- views: 24975
- Playlist
- Chat

Gathering Strength Scattering Light
- Report rights infringement
- published: 15 Apr 2016
- views: 5

Girl Scattering Pack of Cards
- Report rights infringement
- published: 15 Apr 2016
- views: 0

Mod-04 Lec-26 X-ray scattering
- Report rights infringement
- published: 15 Apr 2016
- views: 2

Griffiths Quantum Mechanics Problem 11.10: Born Approximation for Soft Sphere Scattering
- Report rights infringement
- published: 15 Apr 2016
- views: 2

Simulation of Rutherford Scattering using Visual Python
- Report rights infringement
- published: 14 Apr 2016
- views: 8

Scattering
- Report rights infringement
- published: 14 Apr 2016
- views: 1

pixels scattering effects
- Report rights infringement
- published: 14 Apr 2016
- views: 4

Streuen von Perlen und Scattering der Knospen
- Report rights infringement
- published: 14 Apr 2016
- views: 0

Minecraft Factions Lab #94: SCATTERING DREAMSQUAD!
- Report rights infringement
- published: 14 Apr 2016
- views: 61

Mobile Suit Gundam 00 Ep42 Within the Scattering Light English Subtitle
- Report rights infringement
- published: 14 Apr 2016
- views: 1

Scattering theory of the chiral magnetic effect in a Weyl semimetal interplay of bulk Weyl cones and
- Report rights infringement
- published: 14 Apr 2016
- views: 4

binary binary scattering
- Report rights infringement
- published: 14 Apr 2016
- views: 10

Teen Drown While Scattering Ashes Of Dead Relative
- Report rights infringement
- published: 14 Apr 2016
- views: 7

Ash Scattering at Sea by Airplane
- Report rights infringement
- published: 14 Apr 2016
- views: 9
- Playlist
- Chat

Mod-01 Lec-06 Quantum Theory of collisions Differential scattering cross section,Partial wave
- Report rights infringement
- published: 06 May 2014
- views: 2275

8.02x - Lect 30 - Polarizers, Malus' Law, Light Scattering, Blue Skies, Red Sunsets
- Report rights infringement
- published: 14 Feb 2015
- views: 3465

SubSurface Scattering In Cycles
- Report rights infringement
- published: 22 Jul 2014
- views: 12215

Stéphane Mallat: "Scattering Invariant Deep Networks for Classification, Pt. 1"
- Report rights infringement
- published: 26 Aug 2015
- views: 550

FISH - Scattering Crows LIVE 2004
- Report rights infringement
- published: 22 Aug 2013
- views: 18298

Comsol Multiphysics 5 tutorial for beginners: Scattering Cross Section of a Si nanoparticle
- Report rights infringement
- published: 19 Feb 2015
- views: 9702

Lecture - 30 Scattering Matrix
- Report rights infringement
- published: 29 Apr 2008
- views: 29922

Mod-01 Lec-14 Scattering of nucleons
- Report rights infringement
- published: 25 Mar 2014
- views: 3437

Lesson28: More Scattering Theory (improved)
- Report rights infringement
- published: 05 Apr 2013
- views: 3781

Lesson31: More Scattering! This time with movies!
- Report rights infringement
- published: 11 Apr 2013
- views: 1384

Impact parameter and scattering angle - Relation by Dilip Sir
- Report rights infringement
- published: 22 Dec 2014
- views: 1635

Subsurface Scattering In Cinema 4D
- Report rights infringement
- published: 30 Sep 2015
- views: 635

The Booze Cruise III: The Scattering [[Full Movie]]
- Report rights infringement
- published: 11 Feb 2014
- views: 26149

Scattering & Gathering of Israel
- Report rights infringement
- published: 30 Nov 2014
- views: 1007
-
Lyrics list:text lyricsplay full screenplay karaoke
New earthquake hits southern Japan
Edit Al Jazeera 15 Apr 2016Istanbul 2005 Final Inspires Liverpool to Beat Dortmund in Seven-goal Thriller
Edit Community news 15 Apr 2016NY Post Editorial Board Endorses 'Rookie' Donald Trump In Republican Primary
Edit WorldNews.com 15 Apr 2016In A Constellation Far, Far Away, This Galaxy Is A Ruthless Cannibal Eating Its Neighbors
Edit Inquisitr 15 Apr 2016Power crews working to restore electricity in Ohio and Kentucky April 3, 2016 (Duke Energy Corporation)
Edit Public Technologies 16 Apr 2016Power crews working to restore electricity in Indiana April 3, 2016 (Duke Energy Corporation)
Edit Public Technologies 16 Apr 2016Ten things to do at Epcot Flower and Garden Festival: Event runs thru May 30
Edit The Examiner 16 Apr 20169 men in hooch murder
Edit Topix 16 Apr 2016Tornados Clinch Sixth Consecutive 20-Win Season, Blow Past Blazers 19-1 (Concordia Texas Athletics)
Edit Public Technologies 16 Apr 2016185 years through the lens
Edit Sydney Morning Herald 16 Apr 2016Keystone Outlasts Marywood in Pitchers Duel, 1-0 (Marywood University Pacers)
Edit Public Technologies 16 Apr 2016Softball Opens Series With Ozarks With 8-0 Victory (The University of Texas at Dallas Athletics)
Edit Public Technologies 16 Apr 2016Attack of the holly leaf miner
Edit The Guardian 16 Apr 2016Blowin' in the wind: Phelps wins 200 fly at Arizona meet
Edit Springfield News-Sun 16 Apr 2016Zola and Darling Dazzle in Softball Sweep of Clarion (IUP Crimson Hawks)
Edit Public Technologies 16 Apr 2016- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- Next page »







