- published: 22 Oct 2010
- views: 34822
-
remove the playlistDigital Signal
- remove the playlistDigital Signal
- published: 20 Apr 2013
- views: 20534
- published: 13 May 2010
- views: 57042
- published: 17 Oct 2008
- views: 75919
- published: 24 Feb 2014
- views: 26426
- published: 06 Dec 2011
- views: 83569
- published: 06 Dec 2011
- views: 41763
- published: 15 Aug 2013
- views: 1383
- published: 22 Apr 2008
- views: 181668

A digital signal is a physical signal that is a representation of a sequence of discrete values (a quantified discrete-time signal), for example of an arbitrary bit stream, or of a digitized (sampled and analog-to-digital converted) analog signal. The term digital signal can refer to
A signal that is generated by means of a digital modulation method (digital passband transmission), produced by a modem, is in the first case considered as a digital signal, and in the second case as converted to an analog signal.
In computer architecture and other digital systems, a waveform that switches between two voltage levels representing the two states of a Boolean value (0 and 1) is referred to as a digital signal, even though it is an analog voltage waveform, since it is interpreted in terms of only two levels.
The clock signal is a special digital signal that is used to synchronize digital circuits. The image shown can be considered the waveform of a clock signal. Logic changes are triggered either by the rising edge or the falling edge.
This article is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported License, which means that you can copy and modify it as long as the entire work (including additions) remains under this license.
- Loading...

-
 4:49
4:49Digital and Analog Signals (Austin Lutz)
Digital and Analog Signals (Austin Lutz) -
 12:42
12:42What is the Difference between Analog and Digital Signal? Explained !!!!
What is the Difference between Analog and Digital Signal? Explained !!!!What is the Difference between Analog and Digital Signal? Explained !!!!
One of the unsolved queries of students : Difference between Analog and Digital signal Watch the video from TechnoLionX to get your answer Click thumbs and Subscribe for more :) -
 5:25
5:2501 - Introduction to Digital Signal Processing
01 - Introduction to Digital Signal Processing01 - Introduction to Digital Signal Processing
We review some concepts from analog signal processing and introduce the terminology and notation of digital signal processing. Don't worry too much about understanding every equation just yet. This lecture is adapted from the ECE 410: Digital Signal Processing course notes developed by David Munson and Andrew Singer -
 54:19
54:19Lecture -7 Transmission of Digital Signal - I
Lecture -7 Transmission of Digital Signal - ILecture -7 Transmission of Digital Signal - I
Lecture Series on Data Communication by Prof.A. Pal, Department of Computer Science Engineering,IIT Kharagpur. For more details on NPTEL visit http://nptel.iitm.ac.in -
 20:12
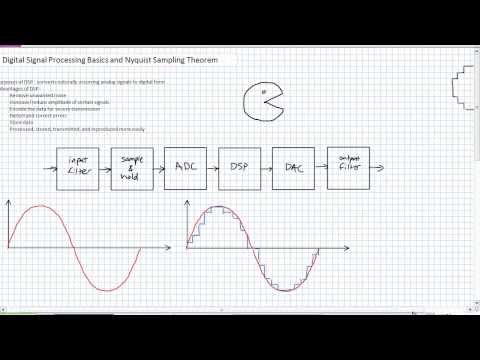
20:12Digital Signal Processing Basics and Nyquist Sampling Theorem
Digital Signal Processing Basics and Nyquist Sampling TheoremDigital Signal Processing Basics and Nyquist Sampling Theorem
A video by Jim Pytel for Renewable Energy Technology students at Columbia Gorge Community College -
 17:42
17:42Lec 1 | MIT RES.6-008 Digital Signal Processing, 1975
Lec 1 | MIT RES.6-008 Digital Signal Processing, 1975Lec 1 | MIT RES.6-008 Digital Signal Processing, 1975
Lecture 1: Introduction Instructor: Alan V. Oppenheim View the complete course: http://ocw.mit.edu/RES6-008S11 License: Creative Commons BY-NC-SA More information at http://ocw.mit.edu/terms More courses at http://ocw.mit.edu -
 36:56
36:56Lec 2 | MIT RES.6-008 Digital Signal Processing, 1975
Lec 2 | MIT RES.6-008 Digital Signal Processing, 1975Lec 2 | MIT RES.6-008 Digital Signal Processing, 1975
Lecture 2: Discrete-time signals and systems, part 1 Instructor: Alan V. Oppenheim View the complete course: http://ocw.mit.edu/RES6-008S11 License: Creative Commons BY-NC-SA More information at http://ocw.mit.edu/terms More courses at http://ocw.mit.edu -
 13:34
13:34Analog and Digital Signal Conversions Part 1
Analog and Digital Signal Conversions Part 1 -
 6:58
6:58Cyber People - Digital Signal Processor
Cyber People - Digital Signal ProcessorCyber People - Digital Signal Processor
ZYX Music Italo Disco, 1988 Amazon Download: http://www.amazon.de/Digital-Signal-Processor-Remix/dp/B002RXOS4M/ref=sr_1_1?ie=UTF8&qid;=1376557427&sr;=8-1&keywords;=cyber+people+digital+signal+processor iTunes: https://itunes.apple.com/de/album/zyx-italo-disco-collection-1/id364584603 -
 55:26
55:26Lecture 2 - Digital Signal Processing Introduction Contd
Lecture 2 - Digital Signal Processing Introduction ContdLecture 2 - Digital Signal Processing Introduction Contd
Lecture Series on Digital Signal Processing by Prof.S. C Dutta Roy, Department of Electrical Engineering, IIT Delhi. For More details on NPTEL visit http://nptel.iitm.ac.in -
 8:27
8:27Digital Signal Processors (DSPs) Explained
Digital Signal Processors (DSPs) ExplainedDigital Signal Processors (DSPs) Explained
High Level Explanation of Digital Signal Processors (DSPs) -
 85:25
85:25Digital Signal Processing Using Matlab 1 (Basic Signals and Operations)
Digital Signal Processing Using Matlab 1 (Basic Signals and Operations)Digital Signal Processing Using Matlab 1 (Basic Signals and Operations)
Basic signals and basic operations on signals -
 2:33
2:33Audio Control DQ61 Digital Signal Processor
Audio Control DQ61 Digital Signal ProcessorAudio Control DQ61 Digital Signal Processor
Test Report of the Audio Control DQ61 Digital Signal Processor by Garry Springgay. -
 25:27
25:27Lecture 1 - Digital Signal Processing Introduction
Lecture 1 - Digital Signal Processing IntroductionLecture 1 - Digital Signal Processing Introduction
Lecture Series on Digital Signal Processing by Prof.S. C Dutta Roy, Department of Electrical Engineering, IIT Delhi. For More details on NPTEL visit http://nptel.iitm.ac.in
- 4B3T
- 4B5B
- 64b 66b encoding
- 6b 8b encoding
- 8b 10b encoding
- Alfred Vail
- Analog signal
- ARPANET
- Baseband
- Baud
- Beacon
- Bipolar encoding
- Bit rate
- Bit stream
- BITNET
- Boolean logic
- Category Line codes
- Charles Wheatstone
- Claude Chappe
- Clock signal
- CMOS
- Coaxial cable
- Coded mark inversion
- Computer network
- Conditioned Diphase
- Delay encoding
- Dependent territory
- Digital
- Digital modulation
- Digital signal
- Digital transmission
- Digitize
- Discrete-time signal
- Drum (communication)
- Electric current
- Electric potential
- Electrical telegraph
- Elisha Gray
- Ethernet
- Fax
- FidoNet
- Geography
- Guglielmo Marconi
- Heliograph
- History of radio
- Hybrid ternary code
- Hydraulic telegraph
- Internet
- Invention
- Johann Philipp Reis
- John Logie Baird
- Lee De Forest
- Line code
- Line coding
- Local area network
- Logic level
- Manchester code
- Mass media
- Microwave
- MLT-3 encoding
- Mobile telephony
- Modem
- Modified AMI code
- Modulation
- Nikola Tesla
- Non-return-to-zero
- On-off keying
- Optical fiber
- Packet switching
- Passband
- Philo Farnsworth
- Photophone
- Pulse train
- Quantification
- Radio network
- Radio waves
- Radiotelephone
- Reginald Fessenden
- Return-to-zero
- Schmitt trigger
- Semaphore line
- Serial communication
- Signal (electronics)
- Sovereign state
- Sovereign territory
- Synchronization
- TC-PAM
- Telecommunication
- Telegraphy
- Telephone line
- Television network
- Telex
- Template Asia topic
- The Telephone Cases
- Tim Berners-Lee
- Transition time
- Transmission medium
- Unipolar encoding
- Vcc
- Videotelephony
- Vint Cerf
- Vladimir K. Zworykin
- Waveform
- Wide area network
- Wireless network
- World Wide Web
-

-

What is the Difference between Analog and Digital Signal? Explained !!!!
One of the unsolved queries of students : Difference between Analog and Digital signal Watch the video from TechnoLionX to get your answer Click thumbs and Subscribe for more :) -

01 - Introduction to Digital Signal Processing
We review some concepts from analog signal processing and introduce the terminology and notation of digital signal processing. Don't worry too much about understanding every equation just yet. This lecture is adapted from the ECE 410: Digital Signal Processing course notes developed by David Munson and Andrew Singer -

Lecture -7 Transmission of Digital Signal - I
Lecture Series on Data Communication by Prof.A. Pal, Department of Computer Science Engineering,IIT Kharagpur. For more details on NPTEL visit http://nptel.iitm.ac.in -

Digital Signal Processing Basics and Nyquist Sampling Theorem
A video by Jim Pytel for Renewable Energy Technology students at Columbia Gorge Community College -

Lec 1 | MIT RES.6-008 Digital Signal Processing, 1975
Lecture 1: Introduction Instructor: Alan V. Oppenheim View the complete course: http://ocw.mit.edu/RES6-008S11 License: Creative Commons BY-NC-SA More information at http://ocw.mit.edu/terms More courses at http://ocw.mit.edu -
Lec 2 | MIT RES.6-008 Digital Signal Processing, 1975
Lecture 2: Discrete-time signals and systems, part 1 Instructor: Alan V. Oppenheim View the complete course: http://ocw.mit.edu/RES6-008S11 License: Creative Commons BY-NC-SA More information at http://ocw.mit.edu/terms More courses at http://ocw.mit.edu -

-

Cyber People - Digital Signal Processor
ZYX Music Italo Disco, 1988 Amazon Download: http://www.amazon.de/Digital-Signal-Processor-Remix/dp/B002RXOS4M/ref=sr_1_1?ie=UTF8&qid;=1376557427&sr;=8-1&keywords;=cyber+people+digital+signal+processor iTunes: https://itunes.apple.com/de/album/zyx-italo-disco-collection-1/id364584603 -

Lecture 2 - Digital Signal Processing Introduction Contd
Lecture Series on Digital Signal Processing by Prof.S. C Dutta Roy, Department of Electrical Engineering, IIT Delhi. For More details on NPTEL visit http://nptel.iitm.ac.in -

Digital Signal Processors (DSPs) Explained
High Level Explanation of Digital Signal Processors (DSPs) -

Digital Signal Processing Using Matlab 1 (Basic Signals and Operations)
Basic signals and basic operations on signals -

Audio Control DQ61 Digital Signal Processor
Test Report of the Audio Control DQ61 Digital Signal Processor by Garry Springgay. -

Lecture 1 - Digital Signal Processing Introduction
Lecture Series on Digital Signal Processing by Prof.S. C Dutta Roy, Department of Electrical Engineering, IIT Delhi. For More details on NPTEL visit http://nptel.iitm.ac.in -

Using Digital Signal Processing on Icom HF Radios
This video goes into detail on how to use Digital Signal processing on the following Icom HF radios: IC-7000, IC-7200, IC-7410, IC-7600, IC-7700, IC-7800 and the IC-9100. For more information on any of these radios, please visit -- http://www.icomamerica.com/amateur -

Digital signal processor
A digital signal processor (DSP) is a specialized microprocessor (or a SIP block), with its architecture optimized for the operational needs of digital signal processing. The goal of DSPs is usually to measure, filter and/or compress continuous real-world analog signals. Most general-purpose microprocessors can also execute digital signal processing algorithms successfully, but dedicated DSPs usually have better power efficiency thus they are more suitable in portable devices such as mobile phones because of power consumption constraints. DSPs often use special memory architectures that are able to fetch multiple data and/or instructions at the same time. This video is targeted to blind users. Attribution: Article text available under CC-BY-SA Creative Commons image source in video -

Digital Electronics: 1) Digital versus Analog signals
Bill Kleitz, author of Digital Electronics: A Practical Approach (Prentice-Hall), discusses digital versus analog signals. http://www.amazon.com/William-Kleitz/e/B001IQWPDU/ -

Digital Signal Processing 1: Signals and Systems - Prof E. Ambikairajah
Digital Signal Processing - Signals and Systems - Electronic Whiteboard-Based Lecture - Lecture notes available from: http://tv.unsw.edu.au/school/electrical-engineering-and-telecommunications -

Multirate Digital Signal Processing part 1A
-

Digital Signal Processing - Convolution
example for present project Digital Signal Processing Thai-Nichi Institute of Technology --------- made by: https://www.facebook.com/ExKONx3 thank music Cap-cell [NEXX] METEORITE ARK [NEXX] -

Lecture - 8 Digital Signal Processors
Lecture series on Embedded Systems by Dr.Santanu Chaudhury,Dept. of Electrical Engineering, IIT Delhi . For more details on NPTEL visit http://nptel.iitm.ac.in -

AudioControl New Hi-Res Digital Signal Processors (DSP) | DM-608 & DM810 | Car Audio | CES 2016
This year AudioControl debuts two brand new DSPs, the DM-608 and the DM-810. These units give you 6-8 channels of RCA input and 8-10 channels of RCA output, all controllable when the unit is connected to a computer. The units feature AudioControl's AccuBASS and M.I.L.c. Source Clip technology, as well as full control over each channel with a 30-band EQ and time alignment. Available later in 2016 Get more information on these units: DM-608: http://www.sonicelectronix.com/item_107759_AudioControl-DM-608.html DM-810: http://www.sonicelectronix.com/item_107761_AudioControl-DM-810.html Shop AudioControl: http://www.sonicelectronix.com/m54-audiocontrol.html - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - Sonic Electronix always strives to be the premiere... -

Sound Design Tutorial w/ BT Pt. 1: Digital Signal Processing Using Mac OS X Terminal
Learn more about Dubspot's Sound Design Program: http://www.dubspot.com/sound-design/ Last year Dubspot presented a special sound design workshop with electronic producer and software programmer BT. Check out part one of a two-part video recap. Head over to our blog for more info: http://blog.dubspot.com/?p=63756 Check out our channel page for more tutorials, reviews, recaps, interviews, see what our partners are up to and more! And stay up to date with our latest videos by subscribing! http://www.youtube.com/subscription_center?add_user=DubSpot If you have any questions, comments or suggestions from this video please share them with us in the comments section below :) Never miss a beat by following us here! Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/DubSpot Instagram: http://statigr.am/dubspo...
Digital and Analog Signals (Austin Lutz)
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 4:49
- Updated: 22 Oct 2010
- views: 34822
What is the Difference between Analog and Digital Signal? Explained !!!!
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 12:42
- Updated: 20 Apr 2013
- views: 20534
- published: 20 Apr 2013
- views: 20534
01 - Introduction to Digital Signal Processing
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 5:25
- Updated: 13 May 2010
- views: 57042
- published: 13 May 2010
- views: 57042
Lecture -7 Transmission of Digital Signal - I
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 54:19
- Updated: 17 Oct 2008
- views: 75919
- published: 17 Oct 2008
- views: 75919
Digital Signal Processing Basics and Nyquist Sampling Theorem
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 20:12
- Updated: 24 Feb 2014
- views: 26426
- published: 24 Feb 2014
- views: 26426
Lec 1 | MIT RES.6-008 Digital Signal Processing, 1975
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 17:42
- Updated: 06 Dec 2011
- views: 83569
- published: 06 Dec 2011
- views: 83569
Lec 2 | MIT RES.6-008 Digital Signal Processing, 1975
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 36:56
- Updated: 06 Dec 2011
- views: 41763
- published: 06 Dec 2011
- views: 41763
Analog and Digital Signal Conversions Part 1
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 13:34
- Updated: 04 Sep 2011
- views: 27205
Cyber People - Digital Signal Processor
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 6:58
- Updated: 15 Aug 2013
- views: 1383
- published: 15 Aug 2013
- views: 1383
Lecture 2 - Digital Signal Processing Introduction Contd
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 55:26
- Updated: 22 Apr 2008
- views: 181668
- published: 22 Apr 2008
- views: 181668
Digital Signal Processors (DSPs) Explained
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 8:27
- Updated: 31 May 2010
- views: 26371
Digital Signal Processing Using Matlab 1 (Basic Signals and Operations)
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 85:25
- Updated: 07 Sep 2015
- views: 1528
Audio Control DQ61 Digital Signal Processor
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 2:33
- Updated: 08 Dec 2013
- views: 13074
- published: 08 Dec 2013
- views: 13074
Lecture 1 - Digital Signal Processing Introduction
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 25:27
- Updated: 18 Mar 2010
- views: 299498
- published: 18 Mar 2010
- views: 299498
Using Digital Signal Processing on Icom HF Radios
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 8:43
- Updated: 22 Mar 2013
- views: 7330
- published: 22 Mar 2013
- views: 7330
Digital signal processor
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 15:37
- Updated: 03 Oct 2014
- views: 3274
- published: 03 Oct 2014
- views: 3274
Digital Electronics: 1) Digital versus Analog signals
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 8:39
- Updated: 05 Mar 2010
- views: 29042
- published: 05 Mar 2010
- views: 29042
Digital Signal Processing 1: Signals and Systems - Prof E. Ambikairajah
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 72:59
- Updated: 24 Mar 2009
- views: 84328
- published: 24 Mar 2009
- views: 84328
Multirate Digital Signal Processing part 1A
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 36:54
- Updated: 29 Aug 2013
- views: 1899
- published: 29 Aug 2013
- views: 1899
Digital Signal Processing - Convolution
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 1:35
- Updated: 23 Sep 2013
- views: 3305
- published: 23 Sep 2013
- views: 3305
Lecture - 8 Digital Signal Processors
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 55:48
- Updated: 16 Apr 2008
- views: 38883
- published: 16 Apr 2008
- views: 38883
AudioControl New Hi-Res Digital Signal Processors (DSP) | DM-608 & DM810 | Car Audio | CES 2016
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 2:06
- Updated: 18 Jan 2016
- views: 2865
- published: 18 Jan 2016
- views: 2865
Sound Design Tutorial w/ BT Pt. 1: Digital Signal Processing Using Mac OS X Terminal
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 8:44
- Updated: 20 May 2014
- views: 19855
- published: 20 May 2014
- views: 19855
- Playlist
- Chat
- Playlist
- Chat

Digital and Analog Signals (Austin Lutz)
- Report rights infringement
- published: 22 Oct 2010
- views: 34822

What is the Difference between Analog and Digital Signal? Explained !!!!
- Report rights infringement
- published: 20 Apr 2013
- views: 20534

01 - Introduction to Digital Signal Processing
- Report rights infringement
- published: 13 May 2010
- views: 57042

Lecture -7 Transmission of Digital Signal - I
- Report rights infringement
- published: 17 Oct 2008
- views: 75919

Digital Signal Processing Basics and Nyquist Sampling Theorem
- Report rights infringement
- published: 24 Feb 2014
- views: 26426

Lec 1 | MIT RES.6-008 Digital Signal Processing, 1975
- Report rights infringement
- published: 06 Dec 2011
- views: 83569
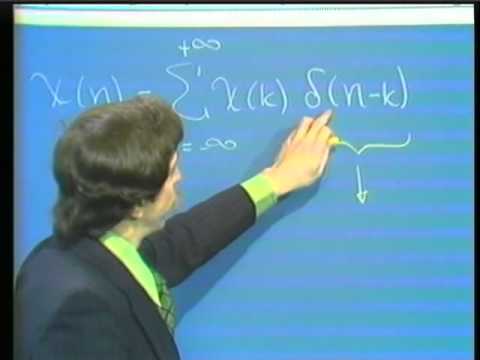
Lec 2 | MIT RES.6-008 Digital Signal Processing, 1975
- Report rights infringement
- published: 06 Dec 2011
- views: 41763


Cyber People - Digital Signal Processor
- Report rights infringement
- published: 15 Aug 2013
- views: 1383

Lecture 2 - Digital Signal Processing Introduction Contd
- Report rights infringement
- published: 22 Apr 2008
- views: 181668

Digital Signal Processors (DSPs) Explained
- Report rights infringement
- published: 31 May 2010
- views: 26371

Digital Signal Processing Using Matlab 1 (Basic Signals and Operations)
- Report rights infringement
- published: 07 Sep 2015
- views: 1528

Audio Control DQ61 Digital Signal Processor
- Report rights infringement
- published: 08 Dec 2013
- views: 13074

Lecture 1 - Digital Signal Processing Introduction
- Report rights infringement
- published: 18 Mar 2010
- views: 299498
Cynthia Lee Fontaine on her "Drag Race" elimination and battle with cancer
Edit The Examiner 22 Mar 2016Islamic State issues statement promising ‘dark days’ ahead
Edit Indian Express 23 Mar 2016
Have Norwegian Scientists Solved The Mystery Behind The Bermuda Triangle?
Edit WorldNews.com 23 Mar 2016Scientists Puzzled, Delighted By What's Happening At Jupiter's North Pole
Edit WorldNews.com 23 Mar 2016Europe’s security dysfunction again exploited
Edit Stars and Stripes 23 Mar 2016Brussels shows Europe's shockingly dysfunctional approach to security (Commentary)
Edit Syracuse 23 Mar 2016Ignatius: The dark path to Brussels
Edit Herald Tribune 23 Mar 2016Ignatius: Intelligence failures paved the dark path to Brussels
Edit Herald Tribune 23 Mar 2016Fujitsu Significantly Expands Its 1FINITY Series of Optical Transmission System Equipment (Fujitsu Ltd)
Edit Public Technologies 23 Mar 2016Bristol and Lund set a new world record in 5G wireless spectrum efficiency (University of Bristol)
Edit Public Technologies 23 Mar 2016Fujitsu Develops 400 Gbps Optical Transceiver Architecture (Fujitsu Ltd)
Edit Public Technologies 22 Mar 2016MaxLinear Introduces MxL9103, a 28Gbaud Linear TIA for 100Gbps/400Gbps Fiber-Optic Data Center Applications (MaxLinear Inc)
Edit Public Technologies 22 Mar 2016Coriant Successfully Demonstrates 200G and 400G Single-Lambda Transmission in Live Network Trial (Coriant America Inc)
Edit Public Technologies 22 Mar 2016Bonnie Ferri to Receive Regents’ Teaching and Learning Award (GeorgiaTech - Georgia Institute of Technology)
Edit Public Technologies 22 Mar 2016NeoPhotonics to Conduct Three Demonstrations Enabled by New Products for High Speed 100G to 400G Telecom and Datacenter Networks (NeoPhotonics Corporation)
Edit Public Technologies 21 Mar 2016Advantech Launches WISE-4012: Cost-effective Analog IoT Wireless I/O Modules (ADVANTECH Co Ltd)
Edit Public Technologies 18 Mar 2016NeoPhotonics Announces Sample Availability of 100G Class 3 Coherent Pluggable CFP2-ACO (NeoPhotonics Corporation)
Edit Public Technologies 18 Mar 2016- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- Next page »






