- published: 28 Jan 2012
- views: 31401
-
remove the playlistEuclid's Elements
-
remove the playlistLatest Videos
-
remove the playlistLongest Videos
- remove the playlistEuclid's Elements
- remove the playlistLatest Videos
- remove the playlistLongest Videos
- published: 28 Feb 2012
- views: 729643
- published: 01 Apr 2009
- views: 20704
- published: 22 Oct 2010
- views: 24358
- published: 01 Aug 2015
- views: 220
- published: 18 Mar 2015
- views: 1319
- published: 28 Jan 2012
- views: 30009
- published: 19 Feb 2014
- views: 3223
- published: 23 Feb 2014
- views: 1803

Euclid's Elements
Euclid's Elements (Ancient Greek: Στοιχεῖα Stoicheia) is a mathematical and geometric treatise consisting of 13 books written by the ancient Greek mathematician Euclid in Alexandria, Ptolemaic Egypt c. 300 BC. It is a collection of definitions, postulates (axioms), propositions (theorems and constructions), and mathematical proofs of the propositions. The thirteen books cover Euclidean geometry and the ancient Greek version of elementary number theory. The work also includes an algebraic system that has become known as geometric algebra, which is powerful enough to solve many algebraic problems, including the problem of finding the square root of a number. The Elements is the second oldest extant Greek mathematical treatises after Autolycus' On the Moving Sphere, and it is the oldest extant axiomatic deductive treatment of mathematics. It has proven instrumental in the development of logic and modern science. According to Proclus the term "element" was used to describe a theorem that is all-pervading and helps furnishing proofs of many other theorems. The word 'element' is in the Greek language the same as 'letter'. This suggests that theorems in the Elements should be seen as standing in the same relation to geometry as letters to language. Later commentators give a slightly different meaning to the term 'element', emphasizing how the propositions have progressed in small steps, and continued to build on previous propositions in a well-defined order.
This article is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported License, which means that you can copy and modify it as long as the entire work (including additions) remains under this license.

Euclid
Euclid (/ˈjuːklɪd/; Greek: Εὐκλείδης, Eukleidēs Ancient Greek: [eu̯.klěː.dɛːs]; fl. 300 BCE), sometimes called Euclid of Alexandria to distinguish him from Euclid of Megara, was a Greek mathematician, often referred to as the "father of geometry". He was active in Alexandria during the reign of Ptolemy I (323–283 BCE). His Elements is one of the most influential works in the history of mathematics, serving as the main textbook for teaching mathematics (especially geometry) from the time of its publication until the late 19th or early 20th century. In the Elements, Euclid deduced the principles of what is now called Euclidean geometry from a small set of axioms. Euclid also wrote works on perspective, conic sections, spherical geometry, number theory and rigor.
Euclid is the anglicized version of the Greek name Εὐκλείδης, which means "renowned, glorious".
Life
Very few original references to Euclid survive, so little is known about his life. The date, place and circumstances of both his birth and death are unknown and may only be estimated roughly relative to other figures mentioned alongside him. He is rarely mentioned by name by other Greek mathematicians from Archimedes onward, who usually call him "ὁ στοιχειώτης" ("the author of Elements"). The few historical references to Euclid were written centuries after he lived, by Proclus c. 450 AD and Pappus of Alexandria c. 320 AD.
This article is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported License, which means that you can copy and modify it as long as the entire work (including additions) remains under this license.
- Loading...

-
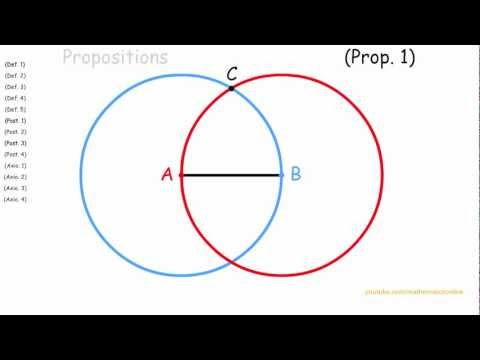 2:03
2:03Euclid's elements: proposition 1
Euclid's elements: proposition 1Euclid's elements: proposition 1
Learn this proposition with interactive step-by-step here: http://pythagoreanmath.com/euclids-elements-book-1-proposition-1/ Buy my app! https://itunes.apple.com/us/app/euclids-elements-book-1/id717831746?ls=1&mt;=8 visit my site: http://www.pythagoreanmath.com Playlist of Euclid's Elements in link below: http://www.youtube.com/playlist?list=PLFC65BA76F7142E9D With any straight line you can always create a perfect equilateral triangle. -
 8:23
8:23Euclid as the father of geometry | Introduction to Euclidean geometry | Geometry | Khan Academy
Euclid as the father of geometry | Introduction to Euclidean geometry | Geometry | Khan AcademyEuclid as the father of geometry | Introduction to Euclidean geometry | Geometry | Khan Academy
We don't normally delve too far into history when talking about math, but sometimes it's important to have perspective about how some of our math concepts came about and how influential they have become. Watch the next lesson: https://www.khanacademy.org/math/geometry/intro_euclid/v/language-and-notation-of-basic-geometry?utm_source=YT&utm;_medium=Desc&utm;_campaign=Geometry Geometry on Khan Academy: We are surrounded by space. And that space contains lots of things. And these things have shapes. In geometry we are concerned with the nature of these shapes, how we define them, and what they teach us about the world at large--from math to architecture to biology to astronomy (and everything in between). Learning geometry is about more than just taking your medicine ("It's good for you!"), it's at the core of everything that exists--including you. Having said all that, some of the specific topics we'll cover include angles, intersecting lines, right triangles, perimeter, area, volume, circles, triangles, quadrilaterals, analytic geometry, and geometric constructions. Wow. That's a lot. To summarize: it's difficult to imagine any area of math that is more widely used than geometry. About Khan Academy: Khan Academy offers practice exercises, instructional videos, and a personalized learning dashboard that empower learners to study at their own pace in and outside of the classroom. We tackle math, science, computer programming, history, art history, economics, and more. Our math missions guide learners from kindergarten to calculus using state-of-the-art, adaptive technology that identifies strengths and learning gaps. We've also partnered with institutions like NASA, The Museum of Modern Art, The California Academy of Sciences, and MIT to offer specialized content. For free. For everyone. Forever. #YouCanLearnAnything Subscribe to Khan Academy’s Geometry channel: https://www.youtube.com/channel/UCD3OtKxPRUFw8kzYlhJXa1Q?sub_confirmation=1 Subscribe to Khan Academy: https://www.youtube.com/subscription_center?add_user=khanacademy -
 9:05
9:05MathFoundations19: Euclid's Elements
MathFoundations19: Euclid's ElementsMathFoundations19: Euclid's Elements
Euclid's book `The Elements' is the most famous and important mathematics book of all time. To begin to lay the foundations of geometry properly, we first have to make contact with Euclid's thinking. Here we look at the basic set-up of Definitions, Axioms and Postulates, and some of the highlights from Books I,II and III. This lecture is part of the MathFoundations series, which tries to lay out proper foundations for mathematics, and will not shy away from discussing the serious logical difficulties entwined in modern pure mathematics. The full playlist is at http://www.youtube.com/playlist?list=PL5A714C94D40392AB&feature;=view_all My research papers can be found at my Research Gate page, at https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Norman_Wildberger. I also have a blog at http://njwildberger.com/, where I will discuss lots of foundational issues, along with other things, and you can check out my webpages at http://web.maths.unsw.edu.au/~norman/. Of course if you want to support all these bold initiatives, become a Patron of this Channel at https://www.patreon.com/njwildberger?ty=h . -
 12:22
12:22Greek Mathematics (Part 1)
Greek Mathematics (Part 1)Greek Mathematics (Part 1)
A documentary about ancient Greek mathematics, focusing on Euclid's Elements. (Part 1) -
 9:45
9:45Euclid's Elements: Book I: A Book Review
Euclid's Elements: Book I: A Book ReviewEuclid's Elements: Book I: A Book Review
A review, summary, analysis, and overview of Book I of Euclid's Elements! -Jake E. Stief The Long Haired Freaky Dude Feel free to contact me with any question or comments, negative or positive. Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/people/Jake-E-Stief-FannPage/100003466311227 Twitter: @crazyjake451 Instagram: LongHairedFreakyDude Email: crazyjake451@yahoo.com -
 16:55
16:55Euclid's Elements: The Solution to the Parallel Postulate | Hermetic Geometry
Euclid's Elements: The Solution to the Parallel Postulate | Hermetic GeometryEuclid's Elements: The Solution to the Parallel Postulate | Hermetic Geometry
Skip the history and go straight to the problem: 11:40 Professor Raymond Flood's "From One to Many Geometries" lecture. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=n8uAH6xCcOk Euclid's Elements From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia Euclid's Elements (Ancient Greek: Στοιχεῖα Stoicheia) is a mathematical and geometric treatise consisting of 13 books written by the ancient Greek mathematician Euclid in Alexandria c. 300 BC. It is a collection of definitions, postulates (axioms), propositions (theorems and constructions), and mathematical proofs of the propositions. The thirteen books cover Euclidean geometry and the ancient Greek version of elementary number theory. The work also includes an algebraic system that has become known as geometric algebra, which is powerful enough to solve many algebraic problems, including the problem of finding the square root of a number. With the exception of Autolycus' On the Moving Sphere, the Elements is one of the oldest extant Greek mathematical treatises, and it is the oldest extant axiomatic deductive treatment of mathematics. It has proven instrumental in the development of logic and modern science. According to Proclus the term "element" was used to describe a theorem that is all-pervading and helps furnishing proofs of many other theorems. The word 'element' is in the Greek language the same as 'letter'. This suggests that theorems in the Elements should be seen as standing in the same relation to geometry as letters to language. Later commentators give a slightly different meaning to the term 'element', emphasizing how the propositions have progressed in small steps, and continued to build on previous propositions in a well-defined order. Euclid's Elements has been referred to as the most successful and influential textbook ever written. Being first set in type in Venice in 1482, it is one of the very earliest mathematical works to be printed after the invention of the printing press and was estimated by Carl Benjamin Boyer to be second only to the Bible in the number of editions published, with the number reaching well over one thousand. For centuries, when the quadrivium was included in the curriculum of all university students, knowledge of at least part of Euclid's Elements was required of all students. Not until the 20th century, by which time its content was universally taught through other school textbooks, did it cease to be considered something all educated people had read. -
 5:36
5:36Euclid's Elements Book 1 - Introduction
Euclid's Elements Book 1 - IntroductionEuclid's Elements Book 1 - Introduction
Euclid's 5 postulates, common notions, etc -
 3:48
3:48Euclid's elements: definitions, postulates, and axioms
Euclid's elements: definitions, postulates, and axiomsEuclid's elements: definitions, postulates, and axioms
Learn step-by-step here: http://pythagoreanmath.com/euclids-elements/ Buy my app! https://itunes.apple.com/us/app/euclids-elements-book-1/id717831746?ls=1&mt;=8 visit my site: http://www.pythagoreanmath.com Playlist of Euclid's Elements in link below: http://www.youtube.com/playlist?list=PLFC65BA76F7142E9D This is an ameatuer introduction to Euclid's elements. -
 2:17
2:17Euclid's Elements Book 1 - Proposition 1
Euclid's Elements Book 1 - Proposition 1Euclid's Elements Book 1 - Proposition 1
How to construct an equilateral triangle from a given line segment -
 3:24
3:24Euclid's Elements Book 1 - Proposition 7
Euclid's Elements Book 1 - Proposition 7Euclid's Elements Book 1 - Proposition 7
Given two straight lines extending from another straight line, these two straight lines can meet at one point above the specified line, and one point only. Or more simply, the apex of a given triangle can exist only at one point.
Euclid
ALBUMS
- Rodentagogue: The Best of Dark Roots Music Vol.2 released: 2010
- Schlagstrom!, Volume 5 released: 2010
- Carthage released: 2003
Rodentagogue: The Best of Dark Roots Music Vol.2
Released 2010- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen The Dead Walk the Streets
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Grandfather
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Man With No Name
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Billy Bible and the Beast Boy
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Devil on My Shoulder
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Revelations
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Red Ships
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Carthage
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Sithe
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Demons
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Tinder
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Playing Dead to Be Invited to the Vulture Dinner Party
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Ears to the Snake
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen The Foes of the Righteous Will Be Condemned
Schlagstrom!, Volume 5
Released 2010- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Lower Twelve
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Pump90 Beta
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Ekkofisk
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen A Relic of Endosymbiotic Origin
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen You Are the Key
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen The Cure
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Deep Sea Defenders (Esperanza version)
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Nerven ohne Fleisch
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen B.W. (version)
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Un passage égaré
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Strategie und Struktur
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Swamp Theme
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Kranke Schwester
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Painkiller
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Be Sexual
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Kakato Geri
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen A Bizarre Break in Character
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Sociopath
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Ostkreuz
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Rastlos
Carthage
Released 2003- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Little Dove
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Carthage
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Rocky Trail
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen A Better Life
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Fare Thee Well
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen [unknown]
-

Euclid's elements: proposition 1
Learn this proposition with interactive step-by-step here: http://pythagoreanmath.com/euclids-elements-book-1-proposition-1/ Buy my app! https://itunes.apple.com/us/app/euclids-elements-book-1/id717831746?ls=1&mt;=8 visit my site: http://www.pythagoreanmath.com Playlist of Euclid's Elements in link below: http://www.youtube.com/playlist?list=PLFC65BA76F7142E9D With any straight line you can always create a perfect equilateral triangle. -

Euclid as the father of geometry | Introduction to Euclidean geometry | Geometry | Khan Academy
We don't normally delve too far into history when talking about math, but sometimes it's important to have perspective about how some of our math concepts came about and how influential they have become. Watch the next lesson: https://www.khanacademy.org/math/geometry/intro_euclid/v/language-and-notation-of-basic-geometry?utm_source=YT&utm;_medium=Desc&utm;_campaign=Geometry Geometry on Khan Academy: We are surrounded by space. And that space contains lots of things. And these things have shapes. In geometry we are concerned with the nature of these shapes, how we define them, and what they teach us about the world at large--from math to architecture to biology to astronomy (and everything in between). Learning geometry is about more than just taking your medicine ("It's good for you!"), i... -

MathFoundations19: Euclid's Elements
Euclid's book `The Elements' is the most famous and important mathematics book of all time. To begin to lay the foundations of geometry properly, we first have to make contact with Euclid's thinking. Here we look at the basic set-up of Definitions, Axioms and Postulates, and some of the highlights from Books I,II and III. This lecture is part of the MathFoundations series, which tries to lay out proper foundations for mathematics, and will not shy away from discussing the serious logical difficulties entwined in modern pure mathematics. The full playlist is at http://www.youtube.com/playlist?list=PL5A714C94D40392AB&feature;=view_all My research papers can be found at my Research Gate page, at https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Norman_Wildberger. I also have a blog at http://njwildberg... -

Greek Mathematics (Part 1)
A documentary about ancient Greek mathematics, focusing on Euclid's Elements. (Part 1) -

Euclid's Elements: Book I: A Book Review
A review, summary, analysis, and overview of Book I of Euclid's Elements! -Jake E. Stief The Long Haired Freaky Dude Feel free to contact me with any question or comments, negative or positive. Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/people/Jake-E-Stief-FannPage/100003466311227 Twitter: @crazyjake451 Instagram: LongHairedFreakyDude Email: crazyjake451@yahoo.com -

Euclid's Elements: The Solution to the Parallel Postulate | Hermetic Geometry
Skip the history and go straight to the problem: 11:40 Professor Raymond Flood's "From One to Many Geometries" lecture. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=n8uAH6xCcOk Euclid's Elements From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia Euclid's Elements (Ancient Greek: Στοιχεῖα Stoicheia) is a mathematical and geometric treatise consisting of 13 books written by the ancient Greek mathematician Euclid in Alexandria c. 300 BC. It is a collection of definitions, postulates (axioms), propositions (theorems and constructions), and mathematical proofs of the propositions. The thirteen books cover Euclidean geometry and the ancient Greek version of elementary number theory. The work also includes an algebraic system that has become known as geometric algebra, which is powerful enough to solve many algebraic p... -

Euclid's Elements Book 1 - Introduction
Euclid's 5 postulates, common notions, etc -

Euclid's elements: definitions, postulates, and axioms
Learn step-by-step here: http://pythagoreanmath.com/euclids-elements/ Buy my app! https://itunes.apple.com/us/app/euclids-elements-book-1/id717831746?ls=1&mt;=8 visit my site: http://www.pythagoreanmath.com Playlist of Euclid's Elements in link below: http://www.youtube.com/playlist?list=PLFC65BA76F7142E9D This is an ameatuer introduction to Euclid's elements. -

Euclid's Elements Book 1 - Proposition 1
How to construct an equilateral triangle from a given line segment -

Euclid's Elements Book 1 - Proposition 7
Given two straight lines extending from another straight line, these two straight lines can meet at one point above the specified line, and one point only. Or more simply, the apex of a given triangle can exist only at one point.
Euclid's elements: proposition 1
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 2:03
- Updated: 28 Jan 2012
- views: 31401
- published: 28 Jan 2012
- views: 31401
Euclid as the father of geometry | Introduction to Euclidean geometry | Geometry | Khan Academy
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 8:23
- Updated: 28 Feb 2012
- views: 729643
- published: 28 Feb 2012
- views: 729643
MathFoundations19: Euclid's Elements
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 9:05
- Updated: 01 Apr 2009
- views: 20704
- published: 01 Apr 2009
- views: 20704
Greek Mathematics (Part 1)
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 12:22
- Updated: 22 Oct 2010
- views: 24358
- published: 22 Oct 2010
- views: 24358
Euclid's Elements: Book I: A Book Review
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 9:45
- Updated: 01 Aug 2015
- views: 220
- published: 01 Aug 2015
- views: 220
Euclid's Elements: The Solution to the Parallel Postulate | Hermetic Geometry
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 16:55
- Updated: 18 Mar 2015
- views: 1319
- published: 18 Mar 2015
- views: 1319
Euclid's Elements Book 1 - Introduction
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 5:36
- Updated: 20 Feb 2014
- views: 4656
Euclid's elements: definitions, postulates, and axioms
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 3:48
- Updated: 28 Jan 2012
- views: 30009
- published: 28 Jan 2012
- views: 30009
Euclid's Elements Book 1 - Proposition 1
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 2:17
- Updated: 19 Feb 2014
- views: 3223
- published: 19 Feb 2014
- views: 3223
Euclid's Elements Book 1 - Proposition 7
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 3:24
- Updated: 23 Feb 2014
- views: 1803
- published: 23 Feb 2014
- views: 1803
-

Homes for Sale - 7600 Euclid Ave, Madeira, OH 45243
For more information about this property, please contact Maureen Pippin, Sibcy Cline Realtors, 513-703-1993 or mpippin@sibcycline.com Asking Price : $775,000 Details: New Construction! Total lifestyle buy, walkability, food, shops, post office! 1st floor master-2 bedrooms + 2 baths + loft on 2nd. Top drawer materials & finishes-Great 3 house enclave in the heart of downtown Madeira-Fabulous kitchen/great room. Ready to go! See more details about this property at http://www.sibcycline.com/scmp.asp?mls=1501054&b=CIN&sender=CirclePix View all our videos at https://www.youtube.com/user/sibcyclinerealestate Visit our web site at: http://www.sibcycline.com Follow us on Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/SibcyClineRealtors Follow us on Pinterest: http://www.pinterest.com/sibcyc... -

Home For Sale: 27190 Shirley Ave Euclid, OH 44132-2047
For more information visit http://www.century21.com/oh/euclid/27190-shirley-ave-44132/property-C2148BERB 27190 Shirley Ave Euclid, OH, 44132-2047 MLS# 3770239 Beds: 4 | Baths: 1 | Sq Ft: 1,562 Welcome Home ............ Youll love it. This awesome 4 bed room Bungalow boasts a brand new gorgeous eat in kitchen with granite counter tops, glass back splash, stainless steel sink and all stainless steel appliances. A brand new bath room.... Wow. Updated Electrical panel, all new switches, new grounded outlets, new gfcis and all new lighting fixtures. New carpeting in all of the bed rooms. New allure flooring in the kitchen and living room. The entire home has been tastefully painted. There are several new windows on the first floor and newer windows on the second floor. An attached two car ... -

-

Euclid Motel, Bay City, USA
-

274 Euclid Ave, Lynn MA 01904 - Single Family Home - Real Estate - For Sale -
274 Euclid Ave, Lynn MA 01904 Single Family Home Real Estate For Sale Spacious older colonial in a good neighborhood offers 6 rooms,3 BRS.,1 full bath first floor. Living room, Dining room (could be converted to two rooms1st floor BR?!) with sliders to deck, rear 70's addition with updated oak kitchen with door to deck and newer large full bathroom rear of house (has electric heat).Open stairway at entry to 2nd floor with three goodsized bedrooms and pulldown stair to attic.Low ceiling basement with no water history. LARGE level fenced rear yard with deck. Two car sidebyside parking front of house with some asphalt beyond fence for additional parking if desired.Walkable location close to schools,Magnolia Park,Sluice Pond,Wyoma Square stores and restaurants, public transportation. Conv... -

Commercial for rent - 601 Euclid Ave, Helena, MT 59601
Listing Site: Property Site: http://tour.circlepix.com/home/L98TW7 Current State Farm lease space. 1500 sq ft. Can be combined with Unit G (additional 500 sq ft) for $2000 month. Other units available in building. Bedrooms: 0 Bathrooms: 0 Square Feet: 0 Price: $1,500 MLS ID: 294175 For more information about this property, please contact ALICE SANTOS at 406-449-2181 or alicesantos@mt.net. You can also text 3296921 to 67299. COMPANY SOCIAL MEDIA: ------------------------------------------ http://helenakw.yourkwoffice.com/ Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/KellerWilliamsMontana YouTube: http://www.youtube.com/helenakellerwilliams REALTOR SOCIAL MEDIA: ------------------------------------------ http://alicesantos.com Last modified: 07/06/2016 09:38:03 pm -

Commercial for rent - 601 Euclid, Helena, MT 59601
Listing Site: Property Site: http://tour.circlepix.com/home/LA5NK8 Units D and G. Offered combined. Has access to bathroom and kitchen. Perfect place if your business is in need of office space. Bedrooms: 0 Bathrooms: 0 Square Feet: 0 Price: $2,000 MLS ID: 294174 For more information about this property, please contact ALICE SANTOS at 406-449-2181 or alicesantos@mt.net. You can also text 3296917 to 67299. COMPANY SOCIAL MEDIA: ------------------------------------------ http://helenakw.yourkwoffice.com/ Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/KellerWilliamsMontana YouTube: http://www.youtube.com/helenakellerwilliams REALTOR SOCIAL MEDIA: ------------------------------------------ http://alicesantos.com Last modified: 07/06/2016 09:32:02 pm -

Commercial for rent - 601 Euclid, Helena, MT 59601
Listing Site: Property Site: http://tour.circlepix.com/home/XX4KC5 500 sq ft space for rent inside the State Farm building. It has access to a bathroom and kitchen and also has its own access outside. Can be combined with Unit D for a 2000 sq ft lease space ($2000 month). Other lease space available in building. Bedrooms: 0 Bathrooms: 0 Square Feet: 0 Price: $500 MLS ID: 294176 For more information about this property, please contact ALICE SANTOS at 406-449-2181 or alicesantos@mt.net. You can also text 3296920 to 67299. COMPANY SOCIAL MEDIA: ------------------------------------------ http://helenakw.yourkwoffice.com/ Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/KellerWilliamsMontana YouTube: http://www.youtube.com/helenakellerwilliams REALTOR SOCIAL MEDIA: --------------------... -

[PDF] "DOWNLOAD" Euclid's Elements Free
[PDF] DOWNLOAD: http://bestebookpdf.com/1888009195 Book PDF EPUB FREE Euclid's Elements More from MTV: Official MTV Website: http://www.mtv.com/ Like MTV: https://www.facebook.com/MTV MTV on Tumblr: http://mtv.tumblr.com/ MTV Instagram: http://instagram.com/mtv MTV on Pinterest: http://www.pinterest.com/mtv/ Shows + Pop Culture + Music + Celebrity. VH1: We complete you. Connect with VH1 Online VH1 Official Site: http://vh1.com, Follow @VH1 on Twitter: http://twitter.com/VH1, Find VH1 on Facebook: http://facebook.com/VH1, Find VH1 on Tumblr : http://vh1.tumblr.com, Follow VH1 on Instagram : http://instagram.com/vh1, Find VH1 on Google + : http://plus.google.com/+vh1, Follow VH1 on Pinterest : http://pinterest.com/vh1 http://instagram.com/darkavengerc86 https://twitter.com/DarkAvengerC8... -

Tour Bus on Euclid & 9th Streets NW (7/6/16)
Homes for Sale - 7600 Euclid Ave, Madeira, OH 45243
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 1:20
- Updated: 07 Jul 2016
- views: 0
- published: 07 Jul 2016
- views: 0
Home For Sale: 27190 Shirley Ave Euclid, OH 44132-2047
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 3:33
- Updated: 07 Jul 2016
- views: 0
- published: 07 Jul 2016
- views: 0
616 EUCLID AVE MOBILE, AL 36606
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 0:24
- Updated: 07 Jul 2016
- views: 0
Euclid Motel, Bay City, USA
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 0:46
- Updated: 07 Jul 2016
- views: 0
- published: 07 Jul 2016
- views: 0
274 Euclid Ave, Lynn MA 01904 - Single Family Home - Real Estate - For Sale -
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 5:24
- Updated: 07 Jul 2016
- views: 2
- published: 07 Jul 2016
- views: 2
Commercial for rent - 601 Euclid Ave, Helena, MT 59601
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 0:34
- Updated: 07 Jul 2016
- views: 0
- published: 07 Jul 2016
- views: 0
Commercial for rent - 601 Euclid, Helena, MT 59601
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 0:38
- Updated: 07 Jul 2016
- views: 0
- published: 07 Jul 2016
- views: 0
Commercial for rent - 601 Euclid, Helena, MT 59601
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 0:26
- Updated: 07 Jul 2016
- views: 0
- published: 07 Jul 2016
- views: 0
[PDF] "DOWNLOAD" Euclid's Elements Free
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 0:00
- Updated: 07 Jul 2016
- views: 0
- published: 07 Jul 2016
- views: 0
Tour Bus on Euclid & 9th Streets NW (7/6/16)
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 1:09
- Updated: 07 Jul 2016
- views: 6
- published: 07 Jul 2016
- views: 6
-

Euclid's Big Problem - Numberphile
Trisecting angles and calculating cube roots was a big problem for Euclid and his cohorts. Discussed by Zsuzsanna Dancso at MSRI. TRISECT WITH ORIGAMI: http://youtu.be/SL2lYcggGpc CIRCLE THE SQUARE: http://youtu.be/CMP9a2J4Bqw NUMBERPHILE Website: http://www.numberphile.com/ Numberphile on Facebook: http://www.facebook.com/numberphile Numberphile tweets: https://twitter.com/numberphile Numberphile is supported by the Mathematical Sciences Research Institute (MSRI): http://bit.ly/MSRINumberphile Videos by Brady Haran Support us on Patreon: http://www.patreon.com/numberphile Brady's videos subreddit: http://www.reddit.com/r/BradyHaran/ A run-down of Brady's channels: http://www.bradyharan.com Sign up for (occasional) emails: http://eepurl.com/YdjL9 -

What's the point of Geometry? - Euclid
Buy the ipad edition of Euclid, the Man who invented Geometry - http://bit.ly/euclid_geometry_ibook Buy signed copies of the book http://bit.ly/SignedEuclidBook Geometry lies at the root of all drawing, so it's good to know a little about it. This is the first video in a series which will explain the basics of Euclid's Elements of Geometry. Don't be scared - It's quite fun! The drawings and script are the basis of the book and ebook, Euclid, The Man Who Invented Geometry. If you have thoughts about this video or the project please share in the comments box below. with award winning illustrator, Shoo Rayner, who has illustrated well over 200 children's books for famous authors and for his own stories. See Shoo's books on amazon.com http://amzn.to/Jp6YEW and on amazon.co.uk http://amzn.... -

Euclid Biography
Euclid 300 B.C. http://www.cloudbiography.com Euclid was an ancient Greek mathematician. See a related article at Britannica.com: http://www.britannica.com/EBchecked/topic/194880/Euclid All content is either in the public domain or licensed pursuant to a Creative Commons Attribution License http://creativecommons.org/licenses/ Attribution: http://cloudbiography.com/attribution.html -

-

-

FamousMathProbs 12: Euclid's construction problems I
Euclid's treatise the Elements is easily the greatest mathematical text of all time. Book I lays out basics of planar geometry, with an alternation between theory and practice, where practice means solving explicit construction problems with straight-edge and compass. In this lecture we look at most of these problems, sometimes departing from Euclid's order and presentation, but not from his spirit. These are problems which come up repeatedly when working with modern dynamic geometry packages such as Geometer's Sketchpad, C.a.R., Geogebra, etc.A study of them not only enhances our appreciation for the logical structure of mathematics, but also the importance of constructing mathematical objects before we theorize about them---- a point that is somewhat diminished in the modern formulation... -

-

Probing the Dark Sector with Euclid
The past decade has seen the emergence of the so-called "concordance model" of cosmology. In this model, the Universe started about 13.7 billion years ago in a Big Bang and is now dominated by dark matter and dark energy. Together this poorly understood "dark sector" makes up about 95% of the Universe, but the nature of these phenomena remains elusive. Weak gravitational lensing, whereby the observed shapes of background galaxies are slightly distorted by foreground dark matter has proven to be one of the most useful ways to measure dark matter and dark energy. I'll explain the basics of weak lensing and outline some key weak lensing results. Finally, I'll discuss The European Space Agency's Euclid mission. NASA has recently agreed to partner on this ambitious mission to measure the dark s... -

Euclid's Big Problem - Numberphile
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 16:51
- Updated: 12 Dec 2014
- views: 542604
- published: 12 Dec 2014
- views: 542604
What's the point of Geometry? - Euclid
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 3:19
- Updated: 15 Jun 2012
- views: 92015
- published: 15 Jun 2012
- views: 92015
Euclid Biography
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 1:36
- Updated: 29 May 2012
- views: 9218
- published: 29 May 2012
- views: 9218
Euclid Dump Trucks Jake Braking Down Hill At Quarry
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 5:10
- Updated: 09 Oct 2013
- views: 17174
Euclid S7 Scraper - 2014 HCEA National Meet
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 2:43
- Updated: 12 Aug 2014
- views: 8592
FamousMathProbs 12: Euclid's construction problems I
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 41:50
- Updated: 18 Apr 2013
- views: 8170
- published: 18 Apr 2013
- views: 8170
Euclid 201LD Documentary
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 7:15
- Updated: 30 Jun 2011
- views: 55542
Probing the Dark Sector with Euclid
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 75:15
- Updated: 05 Jan 2014
- views: 20719
- published: 05 Jan 2014
- views: 20719
1965 Euclid C 6-5 DOZER
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 9:42
- Updated: 30 Apr 2011
- views: 49549
- Playlist
- Chat
- Playlist
- Chat

Euclid's elements: proposition 1
- Report rights infringement
- published: 28 Jan 2012
- views: 31401

Euclid as the father of geometry | Introduction to Euclidean geometry | Geometry | Khan Academy
- Report rights infringement
- published: 28 Feb 2012
- views: 729643

MathFoundations19: Euclid's Elements
- Report rights infringement
- published: 01 Apr 2009
- views: 20704

Greek Mathematics (Part 1)
- Report rights infringement
- published: 22 Oct 2010
- views: 24358

Euclid's Elements: Book I: A Book Review
- Report rights infringement
- published: 01 Aug 2015
- views: 220

Euclid's Elements: The Solution to the Parallel Postulate | Hermetic Geometry
- Report rights infringement
- published: 18 Mar 2015
- views: 1319

Euclid's Elements Book 1 - Introduction
- Report rights infringement
- published: 20 Feb 2014
- views: 4656

Euclid's elements: definitions, postulates, and axioms
- Report rights infringement
- published: 28 Jan 2012
- views: 30009

Euclid's Elements Book 1 - Proposition 1
- Report rights infringement
- published: 19 Feb 2014
- views: 3223

Euclid's Elements Book 1 - Proposition 7
- Report rights infringement
- published: 23 Feb 2014
- views: 1803
- Playlist
- Chat

Homes for Sale - 7600 Euclid Ave, Madeira, OH 45243
- Report rights infringement
- published: 07 Jul 2016
- views: 0

Home For Sale: 27190 Shirley Ave Euclid, OH 44132-2047
- Report rights infringement
- published: 07 Jul 2016
- views: 0


Euclid Motel, Bay City, USA
- Report rights infringement
- published: 07 Jul 2016
- views: 0

274 Euclid Ave, Lynn MA 01904 - Single Family Home - Real Estate - For Sale -
- Report rights infringement
- published: 07 Jul 2016
- views: 2

Commercial for rent - 601 Euclid Ave, Helena, MT 59601
- Report rights infringement
- published: 07 Jul 2016
- views: 0

Commercial for rent - 601 Euclid, Helena, MT 59601
- Report rights infringement
- published: 07 Jul 2016
- views: 0

Commercial for rent - 601 Euclid, Helena, MT 59601
- Report rights infringement
- published: 07 Jul 2016
- views: 0

[PDF] "DOWNLOAD" Euclid's Elements Free
- Report rights infringement
- published: 07 Jul 2016
- views: 0

Tour Bus on Euclid & 9th Streets NW (7/6/16)
- Report rights infringement
- published: 07 Jul 2016
- views: 6
- Playlist
- Chat

Euclid's Big Problem - Numberphile
- Report rights infringement
- published: 12 Dec 2014
- views: 542604

What's the point of Geometry? - Euclid
- Report rights infringement
- published: 15 Jun 2012
- views: 92015

Euclid Biography
- Report rights infringement
- published: 29 May 2012
- views: 9218


Euclid S7 Scraper - 2014 HCEA National Meet
- Report rights infringement
- published: 12 Aug 2014
- views: 8592

FamousMathProbs 12: Euclid's construction problems I
- Report rights infringement
- published: 18 Apr 2013
- views: 8170


Probing the Dark Sector with Euclid
- Report rights infringement
- published: 05 Jan 2014
- views: 20719

1965 Euclid C 6-5 DOZER
- Report rights infringement
- published: 30 Apr 2011
- views: 49549
New US police shooting in Minnesota as protests continue in Baton Rouge
Edit BBC News 07 Jul 2016Chilcot's blind spot: Iraq War report buries oil evidence, fails to address motive
Edit Open Democracy 07 Jul 2016UN Secretary-General Ban Ki-Moon Urges Peaceful Negotiation To End Waterway Standoff
Edit WorldNews.com 07 Jul 2016Theresa May, Andrea Leadsom To Contest For Tory Leadership, Prime Minister
Edit WorldNews.com 07 Jul 2016Dark Horse For Trump Vice President? Ivanka Trump
Edit WorldNews.com 07 Jul 2016Derren Brown's Ghost Train at Thorpe Park - first-look photos
Edit Digital Spy 08 Jul 2016Art in the Library Opens New Exhibit (City of Hillsboro, OR)
Edit Public Technologies 08 Jul 2016Julyfest: Abjects // All Kings and Queens // Strangefruit
Edit Skiddle 08 Jul 2016Couple sues architect for copying custom dream home
Edit New York Post 08 Jul 2016City & BMTS Secure $2.7 Million Main St. Improvement Grant (City of Binghamton, NY)
Edit Public Technologies 08 Jul 2016Souterrain Presents - Jovel + Miller Blue + Taliwhoah tickets
Edit Skiddle 08 Jul 2016UK troops bound for east Europe in Nato show of strength
Edit Scotsman 08 Jul 2016British troops to be deployed to eastern Europe amid Nato concerns over Putin
Edit Belfast Telegraph 08 Jul 2016Rowan School of Osteopathic Medicine Offers Free Course on Osteopathic Medicine (Rowan University)
Edit Public Technologies 08 Jul 2016Sadio Cissokho & Golden Kora Band / Iguanas / DJ Fenomeno Show
Edit Skiddle 08 Jul 2016The question Bangladesh must answer
Edit CNN 08 Jul 2016Rockstar Games Was The Last Major Publisher To Allow A Game To Be Backwards Compatible On Xbox One
Edit ThisGenGaming 08 Jul 2016Mayor Kasim Reed Celebrates Groundbreaking for the Martin Luther King, Jr. Recreation and Aquatic Center (City of Atlanta, GA)
Edit Public Technologies 08 Jul 2016- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- Next page »







