- published: 29 Jul 2014
- views: 78377
-
remove the playlistBodice
- remove the playlistBodice
- published: 17 May 2015
- views: 88185
- published: 11 Jun 2013
- views: 194211
- published: 25 Feb 2014
- views: 152420
- published: 20 Mar 2015
- views: 48980
- published: 24 Sep 2012
- views: 260605
- published: 15 Jul 2014
- views: 73656
- published: 16 Jul 2015
- views: 76244
- published: 17 Jul 2015
- views: 39572
- published: 30 Jun 2013
- views: 16489
- published: 30 Apr 2012
- views: 30959
- published: 06 Mar 2015
- views: 42546

A bodice, historically, is an article of clothing for women, covering the body from the neck to the waist. In modern usage it typically refers to a specific type of upper garment common in Europe during the 16th to the 18th century, or to the upper portion of a modern dress to distinguish it from the skirt and sleeves. The term comes from pair of bodies (because the garment was originally made in two pieces that fastened together, frequently by lacing).[citation needed]
In historical usage, particularly in Victorian and early 20th century fashion, a bodice (in earlier sources, body[citation needed]) indicates the upper part of a dress that was constructed in two parts (i.e., with separate skirt and bodice, such as a ballet tutu), but of matching or coordinating fabric with the intention of wearing the two parts as a unit. In dressmaking, the term waist (sometimes given as "dress waist" to distinguish it from a shirtwaist) was also used. During wear, the parts might be connected by hooks and eyes. This construction was standard for fashionable garments from the 18th century until the late 19th century, and had the advantages of allowing a voluminous skirt to be paired with a close-fitting bodice, and of allowing two or more bodices to be worn with the same skirt (e.g., a high-necked bodice and a low-necked bodice allowed the same skirt to serve for both daywear and evening wear). One-piece construction became more common after 1900 due to the trend for looser, more simply-constructed clothing with narrower skirts.
This article is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported License, which means that you can copy and modify it as long as the entire work (including additions) remains under this license.
- Loading...

-
 5:28
5:28Lesson 1 - Basic bodice
Lesson 1 - Basic bodiceLesson 1 - Basic bodice
This is Lesson 1 of our INTRODUCTION to PATTERNMAKING tutorials. There is a slight mistake with darts calculations, where it says bw/3 should say b/3... For more materials visit our website designbylot13.weebly.com -
 7:50
7:50How To Drape A Sweetheart Strapless Bodice (Professional Version)
How To Drape A Sweetheart Strapless Bodice (Professional Version)How To Drape A Sweetheart Strapless Bodice (Professional Version)
In this video I show you how to drape a sweetheart strapless bodice. Perfect for an inspiring fashion designer, or a sewer who wants to advance there skills. Items used in this tutorial: -1/2 Yards of muslin fabric -Ruler -Push Pins -1/8" Ribbon Tape -Pencil or Marker -Dress Form Loved this video. **hit the subscribe button for more tutorials** Previously on Redesign Your Clothes: https://youtu.be/97ru--vq1Z8 Do you have an item of clothing you want to redesign? Leave a comment with detailed description of the item of clothing so I can help redesign. -Facebook Fanpage: https://www.facebook.com/RedesignYourClothes -Instagram:http://instagram.com/RedesignYourClothes --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- My other social platform -Daniela Tabois Online Website:http://stores.danielatabois.com/ -Daniela Tabois Facebook :https://www.facebook.com/pages/Daniela-Tabois/188242627857255 -Pinterest:http://pinterest.com/dtabois/ -Instagram:http://instagram.com/danielatabois -Twitter:https://twitter.com/Daniela_Tabois -Tumblr:http://danielatabois.tumblr.com/ NOTE: All Items in this video are all purchase by me -
 15:21
15:21DIY-Basic Pattern Tutorial: The Bodice
DIY-Basic Pattern Tutorial: The BodiceDIY-Basic Pattern Tutorial: The Bodice
For those of you who would like to learn how to construct your own bodice, Black Diamond has created a tutorial for you. This basic pattern tutorial will show you how to construct a bodice from scratch. We also have an ad-free(it only cost $1.99) version of this tutorial on https://curious.com/blackdiamond/diy-basic-bodice-pattern?ref=8OjHYsvNSQ4 . It helps us help you by allowing us to make more pattern making tutorials. it also comes with a few extras that Curious.com makes it easy to do such as measurement calculators and equipment lists etc. Like us on Facebook at http://www.facebook.com/Black.Diamond.by.bd -
 29:25
29:25Fit 2 Stitch - Season 1 Episode 1 - The Bodice and Why Darts are a Woman's Best Friend
Fit 2 Stitch - Season 1 Episode 1 - The Bodice and Why Darts are a Woman's Best FriendFit 2 Stitch - Season 1 Episode 1 - The Bodice and Why Darts are a Woman's Best Friend
Join host Peggy Sagers as she clearly explains turning flat fabric into 3 dimensional clothing that anyone can understand. This is the first of 13 episodes in the 100 series of "Fit 2 Stitch", now being shown on public television stations all over the US. Contact your local public television stations for local times. A DVD series of all 13 shows is available for sale at Public television home page. -- http://www.fit2stitch.com. Educational sewing home page. -- http://www.silhouettepatterns.com Silhouette Buddies on Facebook! -- https://www.facebook.com/pages/Silhouette-Patterns/129772940391590 -
 5:06
5:06Making a Bodice Overlay: The Fluffy Feathered Dress, Part Three
Making a Bodice Overlay: The Fluffy Feathered Dress, Part ThreeMaking a Bodice Overlay: The Fluffy Feathered Dress, Part Three
For more information and a detailed write up on this project, check out the links below! I have a very detailed blog post that goes through the process of making this dress. It can be read here: https://doxiequeen1.wordpress.com/2015/03/20/making-a-fluffy-feathered-dress-part-three/ I also have a blog post about making the skirt, which is here: https://doxiequeen1.wordpress.com/2015/02/27/making-a-fluffy-feathered-dress-part-one/ And a video that corresponds with it: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=vq6wW7Bhpo4 The same applies to the dress, The blog post is here: https://doxiequeen1.wordpress.com/2015/03/06/making-a-fluffy-feathered-dress-part-two/ And the video is here!: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=1VD-2oxzo7M If you are interested in seeing more of my work or contacting me, I'll leave links to my various sites below! Tumblr: http://doxiequeen1.tumblr.com/ Blog: https://doxiequeen1.wordpress.com Portfolio: http://angelaclayton.crevado.com/ Email: AngelaCostumery@gmail.com The music does not belong to me, it is titled "University of Chicago Orc. - 4 - Appassionato " by Johannes Brahms. The song was acquired through Musopen. Sorry for the coughing and fuzzy background noise in the track- finding royalty free, free music that is the right length and not overly dramatic has been a challenge. The fuzzy sound was barely there in imovie, I don't know what happened! I definitely won't be using it again. Thank you for watching and reading! -
 9:56
9:56Sweetheart Bodice - How to add lining and how to hem edges
Sweetheart Bodice - How to add lining and how to hem edgesSweetheart Bodice - How to add lining and how to hem edges
Hello its April :) Just wanted to make this video to clear up some questions on the simple sweetheart top tutorial! Keep in mind it is only a video on how to attach lining and how to hem the top if you aren't putting in a lining. If you guys have any questions please comment down below or you can contact my other social networks :D FACEBOOK: http://www.facebook.com/pages/Coolirpa/386007438128797 MY TUMBLR: http://coolirpa.tumblr.com/ MY TWITTER: https://twitter.com/coolirpa -
 10:33
10:33How to Sew Lining in a Bodice
How to Sew Lining in a BodiceHow to Sew Lining in a Bodice
Learn what it takes to add a lining to a bodice for a professional looking garment. WEBSITE: https://www.professorpincushion.com BLOG: https://www.professorpincushion.com/professorpincushion/bodice-lining/ -
 8:08
8:08Pattern Cutting - Flat Pattern Drafting, the Bodice Block part 1
Pattern Cutting - Flat Pattern Drafting, the Bodice Block part 1Pattern Cutting - Flat Pattern Drafting, the Bodice Block part 1
Pattern Cutting. How to Draft Sewing Patterns to your own Measurements. Flat Pattern Drafting. Equipment, Taking Measurements and Drafting First Steps - View my Pattern Cutting Pages here - https://angelakane.com/sewing_patterns/pattern-cutting/ NOTE: The Pattern Cutting Variables can be found here along with a FULL TRANSCRIPT OF THE VIDEOS. Pattern cutting can be complicated - just follow the instructions and practice and then you will understand what is going on. https://angelakane.com/sewing_patterns/pattern-cutting/ PDF Sewing Patterns from https://angelakane.com/sewing_patterns/ Learn Sewing with me. Follow my How To Sew Tutorials for Beginners. Sewing Patterns and Sewing eBooks for Novice Sewers and the more experienced seamstress. -
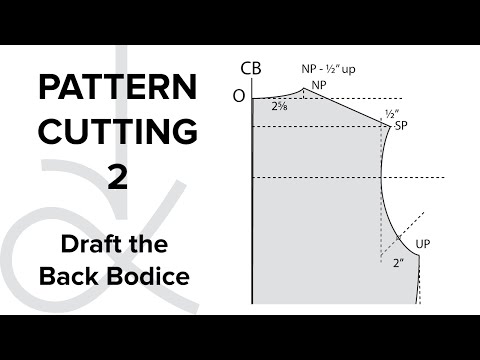 6:01
6:01Pattern Cutting - Flat Pattern Drafting, the Bodice Block part 2
Pattern Cutting - Flat Pattern Drafting, the Bodice Block part 2Pattern Cutting - Flat Pattern Drafting, the Bodice Block part 2
Pattern Cutting. How to Draft Sewing Patterns to your own Measurements. Flat Pattern Drafting - Drafting The Back Bodice, Neckline, Armhole and Side Seam. NOTE: The Pattern Cutting Variables can be found here along with a FULL TRANSCRIPT OF THE VIDEOS. Pattern cutting can be complicated - just follow the instructions and practice and then you will understand what is going on. https://angelakane.com/sewing_patterns/pattern-cutting/ PDF Sewing Patterns from https://angelakane.com/sewing_patterns/ Learn Sewing with me. Follow my How To Sew Tutorials for Beginners. Sewing Patterns and Sewing eBooks for Novice Sewers and the more experienced seamstress. -
 11:59
11:59DIY: Sewing Your Own Bodice With Pattern
DIY: Sewing Your Own Bodice With PatternDIY: Sewing Your Own Bodice With Pattern
Hey guys, Am back with another DIY Sewing project. Today we will be Sewing a Bodice with a patter I got online, I am going to put the link to the web site for pattern if u want to buy it. This video am going to explain how to use a pattern and how to sew your bodice. Hope u like it, and do leave your comments behind. Thank you for Watching . Web Sites For Pattern http://butterick.mccall.com/b5601-products-13743.php?page_id=155http://www.amazon.com/arts-crafts-sewing/dp/B005QSUYMK http://www.ebay.co.uk/itm/Butterick-Sewing-Pattern-B5601-sizes-6-20-/230918746266?pt=UK_Crafts_SewingPatterns_EH&var;=&hash;=item7b6d859009 http://www.bizrate.com/butterick-patterns-b5601-misses-misses-2718965880/shop -
 8:06
8:06BODICE.wmv
BODICE.wmvBODICE.wmv
HOW TO DRAFT BODICE AT YOUR MEASUREMENTS, FREE BODICE PATTERN DRAFTING. -
 6:39
6:39Making a Bodice : The Fluffy Feathered Dress, Part Two
Making a Bodice : The Fluffy Feathered Dress, Part TwoMaking a Bodice : The Fluffy Feathered Dress, Part Two
For more information and a detailed write up on this project, check out the links below! I have a very detailed blog post that goes through the process of making this dress. It can be read here: https://doxiequeen1.wordpress.com/2015/03/06/making-a-fluffy-feathered-dress-part-two/ I also have a blog post about making the skirt, which is here: https://doxiequeen1.wordpress.com/2015/02/27/making-a-fluffy-feathered-dress-part-one/ And a video that corresponds with it: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=vq6wW7Bhpo4 This video and the blog post linked above are the second part in a three part series about making this dress. If you enjoyed it, and would like to see more I would suggest subscribing to my channel! If you are interested in seeing more of my work or contacting me, I'll leave links to my various sites below! Tumblr: http://doxiequeen1.tumblr.com/ Blog: https://doxiequeen1.wordpress.com Portfolio: http://angelaclayton.crevado.com/ Email: AngelaCostumery@gmail.com The music does not belong to me, it is titled "University of Chicago Orc. - 4 - Allegretto grazioso" by Johannes Brahms. The song was acquired through Musopen. Sorry for the coughing and background noise in the track- finding royalty free, free music that is the right length and not overly dramatic has been a challenge. Thank you for watching and reading! -
 19:39
19:39Origami bamboo bodice tutorial TR cutting
Origami bamboo bodice tutorial TR cutting -
 9:19
9:19(RYC) 28: DIY Sweetheart Strapless Bustier
(RYC) 28: DIY Sweetheart Strapless Bustier(RYC) 28: DIY Sweetheart Strapless Bustier
Hey guys! I'm coming back to you with part 2 of the Sweetheart Drape bodice. In this video I show you how to sew a sweetheart strapless bustier. Perfect for summer and I think I'm going to sew a sundress for myself. Let me know if you would like to see a DIY on that. Items used in this tutorial: -1/2- 1 Yards of non stretch fabric -1/2 -1 Yard of non stretch lining -Expose zipper -1 Yard of 1/4" boning -Fabric scissors Blog Post on this Tutioral:http://redesignyourclothes.com/2015/06/07/how-to-sew-a-sweetheart-strapless-bodice/ Loved this video. **hit the subscribe button for more tutorials** Previously on Redesign Your Clothes: https://youtu.be/PFW7_nLamSY Do you have an item of clothing you want to redesign? Leave a comment with detailed description of the item of clothing so I can help redesign. -Facebook Fanpage: https://www.facebook.com/RedesignYourClothes -Instagram:http://instagram.com/RedesignYourClothes --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- My other social platform -Daniela Tabois Online Website:http://stores.danielatabois.com/ -Daniela Tabois Facebook :https://www.facebook.com/pages/Daniela-Tabois/188242627857255 -Pinterest:http://pinterest.com/dtabois/ -Instagram:http://instagram.com/danielatabois -Twitter:https://twitter.com/Daniela_Tabois -Tumblr:http://danielatabois.tumblr.com/ NOTE: All Items in this video are all purchase by me
- A-line
- Abaya
- Aboyne dress
- Academic dress
- Adaptive clothing
- Agnes Sorel
- Anglo-Saxon dress
- Anorak
- Aodai
- Apron
- Ascot tie
- Athletic shoe
- Babydoll
- Back closure
- Balaclava (clothing)
- Balgha
- Ball gown
- Ballerina skirt
- Ballet tutu
- Banyan (clothing)
- Baro't saya
- Barong Tagalog
- Batik
- Bedgown
- Bell-bottoms
- Belly chain
- Belt (clothing)
- Beret
- Bermuda shorts
- Bikini
- Bishop sleeve
- Black tie
- Blanket sleeper
- Blazer
- Blouse
- Boardshorts
- Bodice
- Bolo tie
- Bondage pants
- Bonnet (headgear)
- Boot
- Bow tie
- Boxer briefs
- Boxer shorts
- Braccae
- Brassiere
- Breeches
- Breeching (boys)
- Briefs
- Brunswick (clothing)
- Buckle
- Bunad
- Bustle
- Bustline
- Button
- Buttonhole
- Byzantine dress
- Cagoule (raincoat)
- Cap
- Capri pants
- Caraco
- Cargo pants
- Chaps
- Chemise
- Cheongsam
- Chiton (costume)
- Chlamys
- Clerical clothing
- Cloak
- Close-bodied gown
- Clothing
- Clothing in Africa
- Clothing material
- Clothing terminology
- Coat (clothing)
- Cocktail dress
- Coin purse
- Collar (clothing)
- Corsage (bodice)
- Corselet
- Corset
- Costume
- Cotton
- Court dress
- Court shoe
- Cravat
- Crop top
- Crown (headgear)
- Cuff
- Cufflink
- Culottes
- Cycling shorts
- Dashiki
- Deel (clothing)
- Deely bobber
- Dhoti
- Diaper
- Dickey (garment)
- Dirndl
- Djellaba
- Doublet (clothing)
- Dress
- Dress code
- Dress pants
- Dress shirt
- Dress shoe
- Dressmaking
- Duffle coat
- Duster (clothing)
- Débutante dress
- Earring
- Elastomer
- Europe
- Evening gown
- Exomis
- Farthingale
- Fascinator
- Fashion
- Fashion accessory
- Fillet (clothing)
- Flip-flops
- Fly (clothing)
- Footwear
- Formal wear
- Frock
- Frock coat
- Fur clothing
- Fustanella
- Gaiters
- Gho
- Glove
- Goggle jacket
- Gown
- Greatcoat
- Guernsey (clothing)
- Gymslip
- Gákti
- Hairnet
- Hairpin (fashion)
- Halterneck
- Han Chinese clothing
- Hanbok
- Handbag
- Hat
- Headband
- Headscarf
- Headwear
- Helmet
- Hemline
- Henley shirt
- Highland dress
- Himation
- Hobble skirt
- Hood (headgear)
- Hoodie
- Hook-and-eye closure
- Hose (clothing)
- Hosiery
- Houppelande
- Ironing
- Izaar
- Jacket
- Jacket lapel
- Jean skirt
- Jeans
- Jellabiya
- Jerkin (garment)
- Jersey (clothing)
- Jilbāb
- Job skirt
- Jodhpurs
- Jumper (dress)
- Jumpsuit
- Justacorps
- Kasaya (clothing)
- Kebaya
- Kente cloth
- Kerchief
- Kilt
- Kimono
- Kira (Bhutan)
- Laundry
- Leather
- Leather jacket
- Leather skirt
- Lederhosen
- Leg warmer
- Leggings
- Linen
- Lingerie
- Little black dress
- Locking clothing
- Loincloth
- Long underwear
- Mao suit
- Mask
- Maternity clothing
- Men's skirts
- Microskirt
- Miniskirt
- Morning dress
- Muff (handwarmer)
- National costume
- National dress
- Necklace
- Neckline
- Necktie
- Negligee
- Nightcap (garment)
- Nightgown
- Nightshirt
- Nightwear
- Nylon
- One-piece swimsuit
- Open drawers
- Opera coat
- Outerwear
- Overall
- Overcoat
- Pajamas
- Palla (garment)
- Panties
- Pantsuit
- Parachute pants
- Pea coat
- Peignoir
- Pencil skirt
- Peplos
- Petticoat
- Phat pants
- Phragmites
- Pocket watch
- Poet shirt
- Polo neck
- Polo shirt
- Polonaise (clothing)
- Polyester
- Poncho
- Poodle skirt
- Prairie skirt
- Rah-rah skirt
- Raincoat
- Rayon
- Red Sea rig
- Redingote
- Renaissance Fair
- Revers
- Reversible garment
- Robe
- Sack-back gown
- Sampot
- Sandal (footwear)
- Sarafan
- Sari
- Sarong
- Scarf
- Scrubs (clothing)
- Shalwar kameez
- Shawl
- Sherwani
- Shirt
- Shoe
- Shoe buckle
- Shorts
- Shoulder strap
- Shrug (clothing)
- Silk
- Ski suit
- Skirt
- Skort
- Sleeve
- Sleeved blanket
- Sleeveless shirt
- Sleeveless sweater
- Slip (clothing)
- Slipper
- Smock-frock
- Snap fastener
- Snood (headgear)
- Sock
- Spandex
- Sportcoat
- Sports visor
- Square leg suit
- Stocking
- Stola
- Strap
- Stroller (style)
- Suit (clothing)
- Sumptuary law
- Sundress
- Sunglasses
- Suspenders
- Sweater
- Sweatpants
- Swim briefs
- Swim cap
- Swim diaper
- Swimsuit
- T-shirt
- Tangzhuang
- Tea gown
- Teddy (lingerie)
- Template Clothing
- Temple garment
- Thawb
- Tiara
- Tights
- Toga
- Top (clothing)
- Train (clothing)
- Trench coat
- Trousers
- Trunks (clothing)
- Tube top
- Tunic
- Turban
- Tuxedo
- Twinset
- Undergarment
- Undershirt
- Uniform
- Ushanka
- Veil
- Velcro
- Victorian fashion
- Vietnamese clothing
- Waist (clothing)
- Waistcoat
- Waistline (clothing)
- Wedding dress
- Wetsuit
- Whalebone
- White coat
- White tie
- Wig
- Windbreaker
- Windpants
- Women wearing pants
- Wool
- Wrap (clothing)
- Wrap dress
- Zipper
- Áo bà ba
- Áo tứ thân
- Þjóðbúningurinn
-

Lesson 1 - Basic bodice
This is Lesson 1 of our INTRODUCTION to PATTERNMAKING tutorials. There is a slight mistake with darts calculations, where it says bw/3 should say b/3... For more materials visit our website designbylot13.weebly.com -

How To Drape A Sweetheart Strapless Bodice (Professional Version)
In this video I show you how to drape a sweetheart strapless bodice. Perfect for an inspiring fashion designer, or a sewer who wants to advance there skills. Items used in this tutorial: -1/2 Yards of muslin fabric -Ruler -Push Pins -1/8" Ribbon Tape -Pencil or Marker -Dress Form Loved this video. **hit the subscribe button for more tutorials** Previously on Redesign Your Clothes: https://youtu.be/97ru--vq1Z8 Do you have an item of clothing you want to redesign? Leave a comment with detailed description of the item of clothing so I can help redesign. -Facebook Fanpage: https://www.facebook.com/RedesignYourClothes -Instagram:http://instagram.com/RedesignYourClothes -----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------... -

DIY-Basic Pattern Tutorial: The Bodice
For those of you who would like to learn how to construct your own bodice, Black Diamond has created a tutorial for you. This basic pattern tutorial will show you how to construct a bodice from scratch. We also have an ad-free(it only cost $1.99) version of this tutorial on https://curious.com/blackdiamond/diy-basic-bodice-pattern?ref=8OjHYsvNSQ4 . It helps us help you by allowing us to make more pattern making tutorials. it also comes with a few extras that Curious.com makes it easy to do such as measurement calculators and equipment lists etc. Like us on Facebook at http://www.facebook.com/Black.Diamond.by.bd -

Fit 2 Stitch - Season 1 Episode 1 - The Bodice and Why Darts are a Woman's Best Friend
Join host Peggy Sagers as she clearly explains turning flat fabric into 3 dimensional clothing that anyone can understand. This is the first of 13 episodes in the 100 series of "Fit 2 Stitch", now being shown on public television stations all over the US. Contact your local public television stations for local times. A DVD series of all 13 shows is available for sale at Public television home page. -- http://www.fit2stitch.com. Educational sewing home page. -- http://www.silhouettepatterns.com Silhouette Buddies on Facebook! -- https://www.facebook.com/pages/Silhouette-Patterns/129772940391590 -

Making a Bodice Overlay: The Fluffy Feathered Dress, Part Three
For more information and a detailed write up on this project, check out the links below! I have a very detailed blog post that goes through the process of making this dress. It can be read here: https://doxiequeen1.wordpress.com/2015/03/20/making-a-fluffy-feathered-dress-part-three/ I also have a blog post about making the skirt, which is here: https://doxiequeen1.wordpress.com/2015/02/27/making-a-fluffy-feathered-dress-part-one/ And a video that corresponds with it: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=vq6wW7Bhpo4 The same applies to the dress, The blog post is here: https://doxiequeen1.wordpress.com/2015/03/06/making-a-fluffy-feathered-dress-part-two/ And the video is here!: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=1VD-2oxzo7M If you are interested in seeing more of my work or contacting me, I'l... -

Sweetheart Bodice - How to add lining and how to hem edges
Hello its April :) Just wanted to make this video to clear up some questions on the simple sweetheart top tutorial! Keep in mind it is only a video on how to attach lining and how to hem the top if you aren't putting in a lining. If you guys have any questions please comment down below or you can contact my other social networks :D FACEBOOK: http://www.facebook.com/pages/Coolirpa/386007438128797 MY TUMBLR: http://coolirpa.tumblr.com/ MY TWITTER: https://twitter.com/coolirpa -

How to Sew Lining in a Bodice
Learn what it takes to add a lining to a bodice for a professional looking garment. WEBSITE: https://www.professorpincushion.com BLOG: https://www.professorpincushion.com/professorpincushion/bodice-lining/ -

Pattern Cutting - Flat Pattern Drafting, the Bodice Block part 1
Pattern Cutting. How to Draft Sewing Patterns to your own Measurements. Flat Pattern Drafting. Equipment, Taking Measurements and Drafting First Steps - View my Pattern Cutting Pages here - https://angelakane.com/sewing_patterns/pattern-cutting/ NOTE: The Pattern Cutting Variables can be found here along with a FULL TRANSCRIPT OF THE VIDEOS. Pattern cutting can be complicated - just follow the instructions and practice and then you will understand what is going on. https://angelakane.com/sewing_patterns/pattern-cutting/ PDF Sewing Patterns from https://angelakane.com/sewing_patterns/ Learn Sewing with me. Follow my How To Sew Tutorials for Beginners. Sewing Patterns and Sewing eBooks for Novice Sewers and the more experienced seamstress. -

Pattern Cutting - Flat Pattern Drafting, the Bodice Block part 2
Pattern Cutting. How to Draft Sewing Patterns to your own Measurements. Flat Pattern Drafting - Drafting The Back Bodice, Neckline, Armhole and Side Seam. NOTE: The Pattern Cutting Variables can be found here along with a FULL TRANSCRIPT OF THE VIDEOS. Pattern cutting can be complicated - just follow the instructions and practice and then you will understand what is going on. https://angelakane.com/sewing_patterns/pattern-cutting/ PDF Sewing Patterns from https://angelakane.com/sewing_patterns/ Learn Sewing with me. Follow my How To Sew Tutorials for Beginners. Sewing Patterns and Sewing eBooks for Novice Sewers and the more experienced seamstress. -

DIY: Sewing Your Own Bodice With Pattern
Hey guys, Am back with another DIY Sewing project. Today we will be Sewing a Bodice with a patter I got online, I am going to put the link to the web site for pattern if u want to buy it. This video am going to explain how to use a pattern and how to sew your bodice. Hope u like it, and do leave your comments behind. Thank you for Watching . Web Sites For Pattern http://butterick.mccall.com/b5601-products-13743.php?page_id=155http://www.amazon.com/arts-crafts-sewing/dp/B005QSUYMK http://www.ebay.co.uk/itm/Butterick-Sewing-Pattern-B5601-sizes-6-20-/230918746266?pt=UK_Crafts_SewingPatterns_EH&var;=&hash;=item7b6d859009 http://www.bizrate.com/butterick-patterns-b5601-misses-misses-2718965880/shop -

BODICE.wmv
HOW TO DRAFT BODICE AT YOUR MEASUREMENTS, FREE BODICE PATTERN DRAFTING. -

Making a Bodice : The Fluffy Feathered Dress, Part Two
For more information and a detailed write up on this project, check out the links below! I have a very detailed blog post that goes through the process of making this dress. It can be read here: https://doxiequeen1.wordpress.com/2015/03/06/making-a-fluffy-feathered-dress-part-two/ I also have a blog post about making the skirt, which is here: https://doxiequeen1.wordpress.com/2015/02/27/making-a-fluffy-feathered-dress-part-one/ And a video that corresponds with it: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=vq6wW7Bhpo4 This video and the blog post linked above are the second part in a three part series about making this dress. If you enjoyed it, and would like to see more I would suggest subscribing to my channel! If you are interested in seeing more of my work or contacting me, I'll leave links... -

-

(RYC) 28: DIY Sweetheart Strapless Bustier
Hey guys! I'm coming back to you with part 2 of the Sweetheart Drape bodice. In this video I show you how to sew a sweetheart strapless bustier. Perfect for summer and I think I'm going to sew a sundress for myself. Let me know if you would like to see a DIY on that. Items used in this tutorial: -1/2- 1 Yards of non stretch fabric -1/2 -1 Yard of non stretch lining -Expose zipper -1 Yard of 1/4" boning -Fabric scissors Blog Post on this Tutioral:http://redesignyourclothes.com/2015/06/07/how-to-sew-a-sweetheart-strapless-bodice/ Loved this video. **hit the subscribe button for more tutorials** Previously on Redesign Your Clothes: https://youtu.be/PFW7_nLamSY Do you have an item of clothing you want to redesign? Leave a comment with detailed description of the item of clothing so I ca... -

How to Pattern a Bodice Block (Front)
Hey everyone! Today we're going to be drafting the front half of our basic bodice block! Accurate measuring is the key to getting a successful pattern with minimal fit issues!!! For step-by-step instructions: http://goo.gl/6Afo4J Blog: http://awlnighter.com/ Music: http://goo.gl/4XaGF1 Edited with: Adobe Premiere Pro CC 2014 Camera: Canon Rebel FTC: This video was not sponsored. -

How to sew facings to the bodice around the armholes
This short video tutorial is to demonstrate how to sew the facings to the bodice around the armholes in two separate steps. As described in Pattern A of Feminine Wardrobe. http://www.japanesesewingbooks.com/2013/06/06/short-video-tutorial-for-pattern-a-of-feminine-wardrobe For more free patterns and tutorials, as well as reviews on Japanese sewing pattern and craft books, visit www.JapaneseSewingBooks.com -

Pattern Drafting Tutorial - Strapless Bodice
It's very hard to find strapless outfits that fit perfectly and offer good coverage, especially if your chest isn't proportionate to the rest of your body! This tutorial is for those looking to create a nice fitting strapless bodice. It utilises a bodice block, which should have already been constructed to your measurements, with very little or 0 bust ease. You will also need your bust radius, which should be measured from your bust point to the bottom of your bust. I only cover how to draft the pattern pieces and have assumed that viewers know basic sewing terminology and understand how to construct the garments. I hope you enjoy the video! Any feedback will be appreciated thanks! ALSO DON'T FORGET TO SUBSCRIBE!! Follow me: Instagram: elewafashion Facebook: Ẹlẹwa Twitter: ElewaFashi... -

DIY - Basic Pattern Tutorial: The Mens Bodice
Learn how to make a Men's Basic Bodice pattern from scratch. BD shows you what equipment and material you need, Which measurements you need, how to measure them and then how to use them to construct the pattern. This Men's bodice pattern is fully compatible with the Sleeve pattern made in https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=vaKzUifoszg Like us on Facebook at http://www.facebook.com/Black.Diamond.by.bd -

-

How to Draw a Basic Bodice Front Part 1 - How to Make your own Sewing Patterns
http://www.surefitdesigns.com http://www.sfdLearningCenter.com Learn how to draw the Sure-Fit Designs Bodice Front pattern Part 1. See center front, the neck curve and shoulder line being drawn to your body dimensions. The end result is your body blueprint or sloper drawn to your exact measurements. Sure-Fit Designs™ offers an easy fitting and pattern system to make your own sewing patterns. How to draw a bodice. Learn how the Sure-Fit Designs™ fitting, sewing and designing system can benefit you to achieve a well-fitting pattern for pants, blouses, skirts, dresses, jackets, shirts, children's wear and men's pants. At http://www.sfdLearningCenter.com, you'll find free sewing and fitting assistance with complete instructional content. The Sure-Fit Designs™ fitting and sewing system is... -

Easy and fast basic bodice block pattern (No Darts)
I demonstrated how to make this easy basic bodice block pattern with no darts. You can use this pattern to make designs like non fitting garments like shift dresses and t-shirts. It will also be suitable to make designs that require stretch fabrics. This tutorial is very straight forward, concise and easy. I will be using this pattern for some of my future tutorials so it will be easier and faster for you to follow my tutorials. I will definitely be posting another version of this pattern with darts as well as other patterns for dresses, jackets, skirts, pants etc. Stay tuned for more. Don't forget to follow me on instagram and Facebook @temymarie https://www.instagram.com/temymarie/ https://www.facebook.com/temymarie/ -

Pivoting the bodice darts pattern DD
Make creative bodice styles, just by pivoting the basic darts all around the bodice block. change them to gathers or seams. -

How to sew a gathered skirt into a dress bodice PREVIEW| BurdaStyle
Lesson 1 - Basic bodice
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 5:28
- Updated: 29 Jul 2014
- views: 78377
- published: 29 Jul 2014
- views: 78377
How To Drape A Sweetheart Strapless Bodice (Professional Version)
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 7:50
- Updated: 17 May 2015
- views: 88185
- published: 17 May 2015
- views: 88185
DIY-Basic Pattern Tutorial: The Bodice
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 15:21
- Updated: 11 Jun 2013
- views: 194211
- published: 11 Jun 2013
- views: 194211
Fit 2 Stitch - Season 1 Episode 1 - The Bodice and Why Darts are a Woman's Best Friend
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 29:25
- Updated: 25 Feb 2014
- views: 152420
- published: 25 Feb 2014
- views: 152420
Making a Bodice Overlay: The Fluffy Feathered Dress, Part Three
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 5:06
- Updated: 20 Mar 2015
- views: 48980
- published: 20 Mar 2015
- views: 48980
Sweetheart Bodice - How to add lining and how to hem edges
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 9:56
- Updated: 24 Sep 2012
- views: 260605
- published: 24 Sep 2012
- views: 260605
How to Sew Lining in a Bodice
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 10:33
- Updated: 15 Jul 2014
- views: 73656
- published: 15 Jul 2014
- views: 73656
Pattern Cutting - Flat Pattern Drafting, the Bodice Block part 1
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 8:08
- Updated: 16 Jul 2015
- views: 76244
- published: 16 Jul 2015
- views: 76244
Pattern Cutting - Flat Pattern Drafting, the Bodice Block part 2
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 6:01
- Updated: 17 Jul 2015
- views: 39572
- published: 17 Jul 2015
- views: 39572
DIY: Sewing Your Own Bodice With Pattern
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 11:59
- Updated: 30 Jun 2013
- views: 16489
- published: 30 Jun 2013
- views: 16489
BODICE.wmv
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 8:06
- Updated: 30 Apr 2012
- views: 30959
- published: 30 Apr 2012
- views: 30959
Making a Bodice : The Fluffy Feathered Dress, Part Two
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 6:39
- Updated: 06 Mar 2015
- views: 42546
- published: 06 Mar 2015
- views: 42546
Origami bamboo bodice tutorial TR cutting
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 19:39
- Updated: 15 Nov 2015
- views: 23485
(RYC) 28: DIY Sweetheart Strapless Bustier
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 9:19
- Updated: 07 Jun 2015
- views: 32364
- published: 07 Jun 2015
- views: 32364
How to Pattern a Bodice Block (Front)
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 5:59
- Updated: 18 Sep 2015
- views: 836
- published: 18 Sep 2015
- views: 836
How to sew facings to the bodice around the armholes
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 10:42
- Updated: 05 Jun 2013
- views: 39885
- published: 05 Jun 2013
- views: 39885
Pattern Drafting Tutorial - Strapless Bodice
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 5:29
- Updated: 10 Jan 2016
- views: 626
- published: 10 Jan 2016
- views: 626
DIY - Basic Pattern Tutorial: The Mens Bodice
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 14:12
- Updated: 20 Jul 2014
- views: 14254
- published: 20 Jul 2014
- views: 14254
How to Measure For Bodice Block Pattern Making (Free Sample)
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 7:37
- Updated: 01 Jun 2009
- views: 229303
How to Draw a Basic Bodice Front Part 1 - How to Make your own Sewing Patterns
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 6:40
- Updated: 22 Jun 2015
- views: 6167
- published: 22 Jun 2015
- views: 6167
Easy and fast basic bodice block pattern (No Darts)
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 9:55
- Updated: 18 Feb 2016
- views: 716
- published: 18 Feb 2016
- views: 716
Pivoting the bodice darts pattern DD
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 14:27
- Updated: 21 Aug 2013
- views: 54542
- published: 21 Aug 2013
- views: 54542
How to sew a gathered skirt into a dress bodice PREVIEW| BurdaStyle
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 2:26
- Updated: 10 Oct 2014
- views: 8441
- published: 10 Oct 2014
- views: 8441
- Playlist
- Chat
- Playlist
- Chat

Lesson 1 - Basic bodice
- Report rights infringement
- published: 29 Jul 2014
- views: 78377

How To Drape A Sweetheart Strapless Bodice (Professional Version)
- Report rights infringement
- published: 17 May 2015
- views: 88185

DIY-Basic Pattern Tutorial: The Bodice
- Report rights infringement
- published: 11 Jun 2013
- views: 194211

Fit 2 Stitch - Season 1 Episode 1 - The Bodice and Why Darts are a Woman's Best Friend
- Report rights infringement
- published: 25 Feb 2014
- views: 152420

Making a Bodice Overlay: The Fluffy Feathered Dress, Part Three
- Report rights infringement
- published: 20 Mar 2015
- views: 48980

Sweetheart Bodice - How to add lining and how to hem edges
- Report rights infringement
- published: 24 Sep 2012
- views: 260605

How to Sew Lining in a Bodice
- Report rights infringement
- published: 15 Jul 2014
- views: 73656

Pattern Cutting - Flat Pattern Drafting, the Bodice Block part 1
- Report rights infringement
- published: 16 Jul 2015
- views: 76244

Pattern Cutting - Flat Pattern Drafting, the Bodice Block part 2
- Report rights infringement
- published: 17 Jul 2015
- views: 39572

DIY: Sewing Your Own Bodice With Pattern
- Report rights infringement
- published: 30 Jun 2013
- views: 16489

BODICE.wmv
- Report rights infringement
- published: 30 Apr 2012
- views: 30959

Making a Bodice : The Fluffy Feathered Dress, Part Two
- Report rights infringement
- published: 06 Mar 2015
- views: 42546

Origami bamboo bodice tutorial TR cutting
- Report rights infringement
- published: 15 Nov 2015
- views: 23485

(RYC) 28: DIY Sweetheart Strapless Bustier
- Report rights infringement
- published: 07 Jun 2015
- views: 32364
-
Lyrics list:text lyricsplay full screenplay karaoke
Why isn't the killing of 1.5 million Armenians officially called a 'genocide'?
Edit The Independent 25 Apr 2016Koch: Clinton May Be Better Candidate Than Current GOP
Edit WorldNews.com 25 Apr 2016Former CIA Operative Faces Extradition To Italy For 2003 Extraordinary Rendition
Edit WorldNews.com 25 Apr 2016Saudi link? White House set to release secret pages from 9/11 probe
Edit Indiatoday 25 Apr 2016Selfies, puns and codpieces galore at the Shakespeare street festival
Edit The Guardian 24 Apr 2016Fifty shades of Sunny Leone
Edit The Times of India 24 Apr 2016Kim Kardashian wears incredibly low-cut corset top and white leggings on family outing in Miami
Edit The Daily Mail 23 Apr 2016Check Out Our Top 9 Picks from the Bridal Fashion Week Spring 2017, just for you!
Edit Pinkvilla 21 Apr 2016Gowns Aside, The Huntsman: Winter’s War Will Kill You with Boredom
Edit Time Magazine 21 Apr 2016The 9 sexiest shows on US TV that we can't believe were allowed to happen, from Game of Thrones to Rome
Edit Digital Spy 20 Apr 2016The Winterhalter Exhibit at MFAH May Inspire You to Buy a Dress
Edit Houston Press 19 Apr 2016Royal 17th century wardrobe found in the Wadden Sea (Universiteit van Amsterdam)
Edit Public Technologies 18 Apr 2016Yay or Nay : Mahira Khan in Manish Malhotra
Edit Pinkvilla 17 Apr 2016mid-range style
Edit The National 17 Apr 2016Kenzie's Closet: More than a prom dress
Edit Springfield News-Sun 17 Apr 2016- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- Next page »







