- published: 06 Nov 2007
- views: 334529
-
remove the playlistEngine Displacement
- remove the playlistEngine Displacement
- published: 07 Jan 2015
- views: 2682
- published: 09 Oct 2014
- views: 715
- published: 23 Jul 2015
- views: 444
- published: 27 Sep 2013
- views: 616111
- published: 26 May 2014
- views: 933
- published: 06 Nov 2013
- views: 1809
- published: 28 Feb 2016
- views: 40
- published: 26 Aug 2014
- views: 987

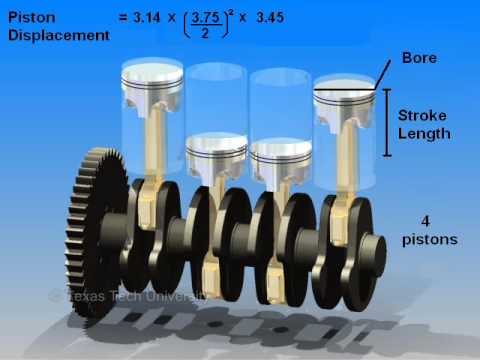
Engine displacement is the volume swept by all the pistons inside the cylinders of an internal combustion engine in a single movement from top dead centre (TDC) to bottom dead centre (BDC). It is commonly specified in cubic centimeters (cc), litres (l), or (mainly in North America) cubic inches (CID). Engine displacement does not include the total volume of the combustion chamber.
Engine displacement is determined from the bore and stroke of an engine's cylinders. The bore is the diameter of the circular chambers cut into the cylinder block.
To simplify:
Examples: The 427 Chevy bore is 4.312 in, and the stroke is 3.65 in, therefore the displacement for this eight-cylinder engine is:
Or: (4.312 in)2 × 0.7854 × 3.65 in × 8 = 426.4 cu in
If the bore is 10 cm and the stroke is 5 cm with four cylinders, the calculation is:
In the United States, the cubic inch was the commonly used unit of measurement until the 1980s by the manufacturers to express the displacement of engines for cars, trucks, etc. (e.g., the "426" in 426 HEMI refers to 426 cubic inches displaced). It is still used for this purpose in the context of the classic-car hobby, auto racing, and so forth.[citation needed]
This article is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported License, which means that you can copy and modify it as long as the entire work (including additions) remains under this license.
- Loading...

-
 1:05
1:053D Engine Displacement Video - English units
3D Engine Displacement Video - English units3D Engine Displacement Video - English units
A quick engine displacement lesson in 3D form. If you are a teacher using this in or for your class, please message me, I'd love to know if it was effective! Thanks! -
 1:42
1:42Engine Displacement
Engine Displacement -
 5:59
5:59Engine displacement
Engine displacementEngine displacement
Engine displacement is the volume swept by all the pistons inside the cylinders of a reciprocating engine in a single movement from top dead centre (TDC) to bottom dead centre (BDC). It is commonly specified in cubic centimetres (cc or cm3), litres (l), or (mainly in North America) cubic inches (CID). Engine displacement does not include the total volume of the combustion chamber. This video is targeted to blind users. Attribution: Article text available under CC-BY-SA Creative Commons image source in video -
 3:20
3:20Engine Displacement
Engine DisplacementEngine Displacement
Description -
 1:44
1:44Engine Displacement using CC and Liters
Engine Displacement using CC and LitersEngine Displacement using CC and Liters
Description -
 6:20
6:20Toby's Kitchen: What is engine displacement? (Re-Released)
Toby's Kitchen: What is engine displacement? (Re-Released)Toby's Kitchen: What is engine displacement? (Re-Released)
This video was originally released back in 2009. However, back then on YT there wasn't an issue using copyright music. The original video had copyright music being used so I've rendered this video again without using any music but I've left it otherwise unchanged What is engine displacement? How do you calculate it? How do they know an engine is 250cc or 300cc, how can you actually calculate the engine size? ****************************************************************** Subscribe to Opferman Motors for trail riding, dirt bikes, motorcycle events, mechanics, rebuilding engines, Maicos, Hondas, Kawasakis, Suzukis, Yamahas, Husqvarnas, KTMs, and more! The channel for vintage dirtbikes ******************* Opferman Motors on the Web ******************* Opferman Motors http://www.maicowerk.com Tillamook Singletrack Magazine http://www.tillamooksingletrackmagazi... Opferman Motors on Facebook https://www.facebook.com/maicowerk Tillamook Single Track Magazine on Facebook https://www.facebook.com/tillamooksin... Motorcycle and dirtbike restorations Facebook Group https://www.facebook.com/groups/motor... -
 8:26
8:26Turbo vs V8 Drifting! Is There a Replacement for Displacement? - HOT ROD Unlimited Ep. 42
Turbo vs V8 Drifting! Is There a Replacement for Displacement? - HOT ROD Unlimited Ep. 42Turbo vs V8 Drifting! Is There a Replacement for Displacement? - HOT ROD Unlimited Ep. 42
On this episode of Hot Rod Unlimited we go drifting! In recent years, the swap of the GM Lsx motor has become more and more common, so we decided to check out the effects in the world of drifting at Englishtown, New Jersey during Club Loose's Freedom Moves event. Staff editor Brandan Gillogly speaks to three regulars at Club Loose about their setups and opinions on cars with and without V8's, and what suits them best. HOT ROD Unlimited appears every other Friday on the Motor Trend channel. http://www.youtube.com/motortrend Subscribe now to make sure you're in on all the action! http://www.youtube.com/subscription_center?add_user=motortrend Facebook - http://facebook.com/motortrendmag & http://facebook.com/hotrodmag Twitter - http://twitter.com/motortrend Google+ - https://plus.google.com/1018679678590... Website - http://www.motortrend.com & http://www.hotrod.com -
 8:34
8:34how to calculate engine displacement from ci to liters
how to calculate engine displacement from ci to litershow to calculate engine displacement from ci to liters
if you have been through high school or middle school this should seem familiar units to metric conversions using formulas. Its not hard but one of the dumbest things I hear from other kids my age is that they dont need to know math to become a mechanic. Especially if you are an engine expert like me, I know engines and mostly engines. You can give me your car engine and ill fix it but you cant give me the car itself cause i cant fix that! -
 1:06
1:06How Calculate Compression-Ratio, Engine Displacement + more!
How Calculate Compression-Ratio, Engine Displacement + more!How Calculate Compression-Ratio, Engine Displacement + more!
Want to calculate Compression Ratio right from your Phone or Tablet? Have no Internet connection and still need to calculate compression or displacement? Want to save compression-ratio combos in your device and retrieve at a later date? ...well then waste no time and download now! iOS: http://appstore.com/enginetoolbox Google Play: https://play.google.com/store/apps/details?id=com.mexicanchevyshotmail.com.mexicanchevys.engine2lbx ...or visit website at http://www.istudiomobile.com/compression_ratio_calculator.html -
 6:31
6:31Tessellated Displacement Material for Landscape Actors for Unreal Engine 4
Tessellated Displacement Material for Landscape Actors for Unreal Engine 4Tessellated Displacement Material for Landscape Actors for Unreal Engine 4
This can be purchase on the Unreal Engine 4 Marketplace -
 2:09
2:09Engine Displacement Explained and Calculated .12. JMSpeedshop !
Engine Displacement Explained and Calculated .12. JMSpeedshop !Engine Displacement Explained and Calculated .12. JMSpeedshop !
how to calculated engine displacement and what value's are needed to do when you going for a rebore of the cilinders and getting bigger bore or different cranksahft with longer stroke it is always handy to do a calulation how much it will influence on your displacement formula: displacement 1 cilinder= (bore2)X(0,25XPI)X Stroke= then multiple to the amount of cilinders and you will have the full displacement. bore is the diameter of the cilinder the stroke is 2 times the offset of the crankshaft to the crankpin where the big end of the rod is connected if there are any question leave a comment. if you like the video's please like it and if you want more, please don't forget to subscribe to the page and visit the main page of JMSpeedshop ! on youtube -
 1:14
1:14Source engine - displacement mapping
Source engine - displacement mappingSource engine - displacement mapping
CS:GO project: http://csgo.gamebanana.com/prefabs/6744 Dispgen: http://www.chaosincarnate.net/cannonfodder/cftools.php?program=dispgen Music: Marshland Melodies - Risen 3: Titan Lords Dispgen is a program that creates displacements from heightmaps. Source Engine has a lot of limits, also for displacements, but you can use them for details and 3D skyboxes. -
 7:01
7:01Low Poly Assets From Displacement Maps - Part 2
Low Poly Assets From Displacement Maps - Part 2Low Poly Assets From Displacement Maps - Part 2
In this tutorial, we take the game asset we created in Part 1 and import it into Unreal Engine 4 -
 9:10
9:10Engine compression ratio and displacement calculation
Engine compression ratio and displacement calculationEngine compression ratio and displacement calculation
11th part of the Oldsmobile 455 marine engine build. The worked over cylinder heads are looked at in this video. Timing marks, compression and displacement are also looked at in this video. If you want to skip right to the math go to 6:18 in the video. Thanks for watching.
- Aircraft engine
- Aircraft fuel system
- Alternator
- Annunciator panel
- Autofeather
- Auxiliary power unit
- Avgas
- Blade pitch
- Bore (engine)
- Camshaft
- Carburetor
- Carburetor heat
- Chrysler Hemi engine
- Chrysler LA engine
- Chrysler RB engine
- Combustion chamber
- Compression ratio
- Connecting rod
- Crankpin
- Crankshaft
- Cylinder (engine)
- Cylinder block
- Cylinder head
- Dead centre
- Diameter
- Diesel fuel
- Dual ignition
- Electrical generator
- Engine displacement
- Engine tuning
- Flight data recorder
- Ford 335 engine
- Ford 385 engine
- Ford FE engine
- Ford Windsor engine
- Four-stroke engine
- Fuel injection
- Gascolator
- Glass cockpit
- GM Iron Duke engine
- Gnome Monosoupape
- Gudgeon pin
- Hobbs meter
- Horsepower
- Hydraulic fluid
- Hydraulic tappet
- Ignition system
- Ignition timing
- Inlet manifold
- Intercooler
- Litre
- Magneto
- Main bearing
- Manifold vacuum
- Moped
- Nissan Teana
- Nissan VQ engine
- Nominal size
- Obturator ring
- Oldsmobile V8 engine
- Overhead camshaft
- Overhead valve
- Petrol
- Piston
- Piston ring
- Poppet valve
- Pressure carburetor
- Propeller (aircraft)
- Propeller governor
- Reciprocating engine
- Recoil start
- Rocker arm
- Rotary engine
- Scimitar propeller
- Sleeve valve
- Spark plug
- Spinner (aircraft)
- Starter motor
- Stroke (engine)
- Supercharger
- Tachometer
- Tappet
- Throttle
- Turbocharger
- Two-stroke engine
- V6 engine
- V8 engine
- Valve timing
- Volume
- Wankel engine
-

3D Engine Displacement Video - English units
A quick engine displacement lesson in 3D form. If you are a teacher using this in or for your class, please message me, I'd love to know if it was effective! Thanks! -

-

Engine displacement
Engine displacement is the volume swept by all the pistons inside the cylinders of a reciprocating engine in a single movement from top dead centre (TDC) to bottom dead centre (BDC). It is commonly specified in cubic centimetres (cc or cm3), litres (l), or (mainly in North America) cubic inches (CID). Engine displacement does not include the total volume of the combustion chamber. This video is targeted to blind users. Attribution: Article text available under CC-BY-SA Creative Commons image source in video -

Engine Displacement
Description -

Engine Displacement using CC and Liters
Description -

Toby's Kitchen: What is engine displacement? (Re-Released)
This video was originally released back in 2009. However, back then on YT there wasn't an issue using copyright music. The original video had copyright music being used so I've rendered this video again without using any music but I've left it otherwise unchanged What is engine displacement? How do you calculate it? How do they know an engine is 250cc or 300cc, how can you actually calculate the engine size? ****************************************************************** Subscribe to Opferman Motors for trail riding, dirt bikes, motorcycle events, mechanics, rebuilding engines, Maicos, Hondas, Kawasakis, Suzukis, Yamahas, Husqvarnas, KTMs, and more! The channel for vintage dirtbikes ******************* Opferman Motors on the Web ******************* Opferman Motors http://www.mai... -

Turbo vs V8 Drifting! Is There a Replacement for Displacement? - HOT ROD Unlimited Ep. 42
On this episode of Hot Rod Unlimited we go drifting! In recent years, the swap of the GM Lsx motor has become more and more common, so we decided to check out the effects in the world of drifting at Englishtown, New Jersey during Club Loose's Freedom Moves event. Staff editor Brandan Gillogly speaks to three regulars at Club Loose about their setups and opinions on cars with and without V8's, and what suits them best. HOT ROD Unlimited appears every other Friday on the Motor Trend channel. http://www.youtube.com/motortrend Subscribe now to make sure you're in on all the action! http://www.youtube.com/subscription_center?add_user=motortrend Facebook - http://facebook.com/motortrendmag & http://facebook.com/hotrodmag Twitter - http://twitter.com/motortrend Google+ - https://plus.google.co... -

how to calculate engine displacement from ci to liters
if you have been through high school or middle school this should seem familiar units to metric conversions using formulas. Its not hard but one of the dumbest things I hear from other kids my age is that they dont need to know math to become a mechanic. Especially if you are an engine expert like me, I know engines and mostly engines. You can give me your car engine and ill fix it but you cant give me the car itself cause i cant fix that! -

How Calculate Compression-Ratio, Engine Displacement + more!
Want to calculate Compression Ratio right from your Phone or Tablet? Have no Internet connection and still need to calculate compression or displacement? Want to save compression-ratio combos in your device and retrieve at a later date? ...well then waste no time and download now! iOS: http://appstore.com/enginetoolbox Google Play: https://play.google.com/store/apps/details?id=com.mexicanchevyshotmail.com.mexicanchevys.engine2lbx ...or visit website at http://www.istudiomobile.com/compression_ratio_calculator.html -

Tessellated Displacement Material for Landscape Actors for Unreal Engine 4
This can be purchase on the Unreal Engine 4 Marketplace -

Engine Displacement Explained and Calculated .12. JMSpeedshop !
how to calculated engine displacement and what value's are needed to do when you going for a rebore of the cilinders and getting bigger bore or different cranksahft with longer stroke it is always handy to do a calulation how much it will influence on your displacement formula: displacement 1 cilinder= (bore2)X(0,25XPI)X Stroke= then multiple to the amount of cilinders and you will have the full displacement. bore is the diameter of the cilinder the stroke is 2 times the offset of the crankshaft to the crankpin where the big end of the rod is connected if there are any question leave a comment. if you like the video's please like it and if you want more, please don't forget to subscribe to the page and visit the main page of JMSpeedshop ! on youtube -

Source engine - displacement mapping
CS:GO project: http://csgo.gamebanana.com/prefabs/6744 Dispgen: http://www.chaosincarnate.net/cannonfodder/cftools.php?program=dispgen Music: Marshland Melodies - Risen 3: Titan Lords Dispgen is a program that creates displacements from heightmaps. Source Engine has a lot of limits, also for displacements, but you can use them for details and 3D skyboxes. -

Low Poly Assets From Displacement Maps - Part 2
In this tutorial, we take the game asset we created in Part 1 and import it into Unreal Engine 4 -

Engine compression ratio and displacement calculation
11th part of the Oldsmobile 455 marine engine build. The worked over cylinder heads are looked at in this video. Timing marks, compression and displacement are also looked at in this video. If you want to skip right to the math go to 6:18 in the video. Thanks for watching. -

-

2016 Ducati 959 Panigale Reviews - Engine Displacement 955cc
1 . 2016 Ducati 959 Panigale The 2016 Ducati 959 Panigale saw engineers give a beefed up bottom-end and mid-range by increasing piston stroke 3.6mm to 60.8mm, netting a power 57cc increase. New exhaust pipes, and associated fuel/ignition mapping complement the set-up, and also meet the stricter Euro 4 emission standards being implemented next year. The 959 is claimed to produce 157 horsepower and nearly 80 lb-ft of torque at the crank. The chassis and suspension are the same as before, but the body panels see a few aesthetic tweaks highlighted by a wider front snout, with bigger air intake scoops. The tail section and rear view mirrors were also re-shaped and the junior Panigale also benefits from a more grippy set of machined aluminum. Standard electronics include eight-way adjustable tr... -

My Homemade LTD Stirling Engine (Displacement type) Part 1 of 2
My First Stirling Engine. I was very happy to see it work on the first try without any tunning. Running on heat from an electric range. Made mostly from a computer hard drive, and other computer parts. It took only a few hours of work. the displacement chamber expands a little losing compression, cause the sheet metal is so thin. I'm working on fixing the problem. though the heat sinks helped a little. :) -

My Homemade LTD Stirling Engine (Displacement type) Part 2 of 2
Take 2, after some slight modifications. Running a little better. My First Stirling Engine. I was very happy to see it work on the first try without any tunning. Running on heat from an electric range. Made mostly from a computer hard drive, and other computer parts. It took only a few hours of work. the displacement chamber expands a little losing compression, cause the sheet metal is so thin. I'm working on fixing the problem. though the heat sinks helped a litte. :) -

engine displacement.wmv
CC, engine displacement -

Source Engine Displacement Maps [SFM]
This feature has been available to us for 5 years now yet Valve has no documentation of it or any public information. Reading through the alienswarm source code I discovered that it was possible and Narry future put it to test and these are the results. Will be documented soon. Narry's video http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=UXKviuIeDYQ -

How To Increase Horsepower - Explained
How can you increase horsepower? There are several fundamental principles if you are going to increase the acceleration of your car, aside from obviously shedding some weight. I'll explain some different methods of how to increase horsepower. Related Videos HP vs. Torque: http://youtu.be/fgLNO3ThGD4 Engine HP vs. Wheel HP: http://youtu.be/BOFVnkrkQ6k Please feel free to rate, comment, and subscribe! And don't forget to check out my Facebook page: http://www.facebook.com/engineeringexplained Also check out my official website: Make suggestions, participate in forums, enter for Car of the Month, learn through logically ordered lessons, read FAQs, and plan your future! http://www.howdoesacarwork.com NEW VIDEOS EVERY WEDNESDAY! -

School Engine with Displacement Lubricator (HD)
First steam test of the Polish "School Engine" since fitting silicone piston rings and a displacement lubricator. -

Kawasaki ZX14R INCREASED ENGINE DISPLACEMENT
ZX-14R 2012
3D Engine Displacement Video - English units
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 1:05
- Updated: 06 Nov 2007
- views: 334529
- published: 06 Nov 2007
- views: 334529
Engine Displacement
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 1:42
- Updated: 07 Jan 2015
- views: 2682
- published: 07 Jan 2015
- views: 2682
Engine displacement
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 5:59
- Updated: 09 Oct 2014
- views: 715
- published: 09 Oct 2014
- views: 715
Engine Displacement
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 3:20
- Updated: 17 Nov 2015
- views: 22
Engine Displacement using CC and Liters
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 1:44
- Updated: 17 Nov 2015
- views: 143
Toby's Kitchen: What is engine displacement? (Re-Released)
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 6:20
- Updated: 23 Jul 2015
- views: 444
- published: 23 Jul 2015
- views: 444
Turbo vs V8 Drifting! Is There a Replacement for Displacement? - HOT ROD Unlimited Ep. 42
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 8:26
- Updated: 27 Sep 2013
- views: 616111
- published: 27 Sep 2013
- views: 616111
how to calculate engine displacement from ci to liters
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 8:34
- Updated: 26 May 2014
- views: 933
- published: 26 May 2014
- views: 933
How Calculate Compression-Ratio, Engine Displacement + more!
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 1:06
- Updated: 06 Nov 2013
- views: 1809
- published: 06 Nov 2013
- views: 1809
Tessellated Displacement Material for Landscape Actors for Unreal Engine 4
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 6:31
- Updated: 22 Feb 2015
- views: 10544
Engine Displacement Explained and Calculated .12. JMSpeedshop !
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 2:09
- Updated: 28 Feb 2016
- views: 40
- published: 28 Feb 2016
- views: 40
Source engine - displacement mapping
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 1:14
- Updated: 26 Aug 2014
- views: 987
- published: 26 Aug 2014
- views: 987
Low Poly Assets From Displacement Maps - Part 2
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 7:01
- Updated: 21 Feb 2015
- views: 2078
- published: 21 Feb 2015
- views: 2078
Engine compression ratio and displacement calculation
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 9:10
- Updated: 08 May 2011
- views: 17758
- published: 08 May 2011
- views: 17758
Operating on the Testing Bench(Engine Displacement : 80cc)
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 1:07
- Updated: 10 Jan 2008
- views: 14739
2016 Ducati 959 Panigale Reviews - Engine Displacement 955cc
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 2:18
- Updated: 17 Dec 2015
- views: 120
- published: 17 Dec 2015
- views: 120
My Homemade LTD Stirling Engine (Displacement type) Part 1 of 2
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 5:46
- Updated: 17 Sep 2008
- views: 7499
- published: 17 Sep 2008
- views: 7499
My Homemade LTD Stirling Engine (Displacement type) Part 2 of 2
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 2:22
- Updated: 17 Sep 2008
- views: 2244
- published: 17 Sep 2008
- views: 2244
engine displacement.wmv
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 1:16
- Updated: 15 Apr 2012
- views: 806
- published: 15 Apr 2012
- views: 806
Source Engine Displacement Maps [SFM]
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 0:39
- Updated: 18 Jun 2013
- views: 2043
- published: 18 Jun 2013
- views: 2043
How To Increase Horsepower - Explained
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 5:24
- Updated: 27 Feb 2013
- views: 332229
- published: 27 Feb 2013
- views: 332229
School Engine with Displacement Lubricator (HD)
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 7:20
- Updated: 02 Aug 2014
- views: 541
- published: 02 Aug 2014
- views: 541
Kawasaki ZX14R INCREASED ENGINE DISPLACEMENT
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 1:25
- Updated: 11 Oct 2011
- views: 1030
- Playlist
- Chat
- Playlist
- Chat

3D Engine Displacement Video - English units
- Report rights infringement
- published: 06 Nov 2007
- views: 334529

Engine Displacement
- Report rights infringement
- published: 07 Jan 2015
- views: 2682

Engine displacement
- Report rights infringement
- published: 09 Oct 2014
- views: 715

Engine Displacement using CC and Liters
- Report rights infringement
- published: 17 Nov 2015
- views: 143

Toby's Kitchen: What is engine displacement? (Re-Released)
- Report rights infringement
- published: 23 Jul 2015
- views: 444

Turbo vs V8 Drifting! Is There a Replacement for Displacement? - HOT ROD Unlimited Ep. 42
- Report rights infringement
- published: 27 Sep 2013
- views: 616111

how to calculate engine displacement from ci to liters
- Report rights infringement
- published: 26 May 2014
- views: 933

How Calculate Compression-Ratio, Engine Displacement + more!
- Report rights infringement
- published: 06 Nov 2013
- views: 1809

Tessellated Displacement Material for Landscape Actors for Unreal Engine 4
- Report rights infringement
- published: 22 Feb 2015
- views: 10544

Engine Displacement Explained and Calculated .12. JMSpeedshop !
- Report rights infringement
- published: 28 Feb 2016
- views: 40

Source engine - displacement mapping
- Report rights infringement
- published: 26 Aug 2014
- views: 987

Low Poly Assets From Displacement Maps - Part 2
- Report rights infringement
- published: 21 Feb 2015
- views: 2078

Engine compression ratio and displacement calculation
- Report rights infringement
- published: 08 May 2011
- views: 17758
CBS’ ‘60 Minutes’ Vindicates Trump But Republican Purge Continues
Edit WorldNews.com 11 Apr 2016NASA Scientists Regain Control Of Kepler, Trying To Figure Out Outage Cause
Edit WorldNews.com 11 Apr 2016New Study Suggests Bible Could Have Been Written Earlier Than Previously Thought
Edit WorldNews.com 12 Apr 2016Egypt gives Saudi Arabia 2 islands in a show of gratitude
Edit The Times of India 11 Apr 2016Immigrant students blocked from enrolling in school in the US: Report
Edit Deccan Herald 11 Apr 2016Porsche 911 Enthusiasts Get Rare Opportunity To Bid On Classic Vehicles
Edit Inquisitr 05 Apr 2016Charging poles to tap e-car growth (Shanghai Municipal Government)
Edit Public Technologies 02 Apr 2016Yokohama Rubber’s Support for Motor Sports in 2016 (YRC - Yokohama Rubber Co Ltd)
Edit Public Technologies 30 Mar 2016Opel Astra TCR Celebrates Race Debut on Persian Gulf (Adam Opel GmbH)
Edit Public Technologies 23 Mar 2016Millard Bill Updating ATV Restrictions Gains Bipartisan Support (David R Millard)
Edit Public Technologies 21 Mar 2016Millard Bill Updating ATV Restrictions Gains Bipartisan Support (Pennsylvania House Republican Caucus)
Edit Public Technologies 21 Mar 2016Considering the Lexus NX 200t? Take a look at these, too
Edit Canada Dot Com 17 Mar 2016Fit for Job & Family: The Station Wagon with that Little Bit Extra (Adam Opel GmbH)
Edit Public Technologies 16 Mar 2016Global Motorcycles, Scooters and Mopeds Industry
Edit PR Newswire 16 Mar 2016The new Mercedes-Benz CLA and CLA Shooting Brake: Update for a designer gem (Daimler AG)
Edit Public Technologies 15 Mar 20162017 Acura NSX Press Kit - Sport Hybrid Power Unit (American Honda Motor Co Inc)
Edit Public Technologies 14 Mar 2016Cult Car ŠKODA 1000 MBX Celebrates 50 Years (Skoda Auto as)
Edit Public Technologies 08 Mar 2016Audi SQ7 TDI: Driving Innovation (Audi AG)
Edit Public Technologies 03 Mar 2016- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- Next page »







