- published: 17 Mar 2016
- views: 11992
-
remove the playlistEvolution
-
remove the playlistLatest Videos
-
remove the playlistLongest Videos
- remove the playlistEvolution
- remove the playlistLatest Videos
- remove the playlistLongest Videos
- published: 11 Jul 2013
- views: 2147750
- published: 10 Oct 2014
- views: 992537
- published: 29 Jan 2014
- views: 1508072
- published: 31 Dec 2015
- views: 2386684
- published: 23 Jan 2016
- views: 916137
- published: 11 Jul 2012
- views: 1033084
- published: 20 Apr 2016
- views: 8312
- published: 19 Apr 2016
- views: 909
- published: 10 Jan 2013
- views: 715008
- published: 20 Apr 2016
- views: 8027
- published: 01 Mar 2014
- views: 96554

Evolution is any change across successive generations in the inherited characteristics of biological populations. Evolutionary processes give rise to diversity at every level of biological organisation, including species, individual organisms and molecules such as DNA and proteins.
Life on Earth originated and then evolved from a universal common ancestor approximately 3.7 billion years ago. Repeated speciation and the divergence of life can be inferred from shared sets of biochemical and morphological traits, or by shared DNA sequences. These homologous traits and sequences are more similar among species that share a more recent common ancestor, and can be used to reconstruct evolutionary histories, using both existing species and the fossil record. Existing patterns of biodiversity have been shaped both by speciation and by extinction.
Charles Darwin was the first to formulate a scientific argument for the theory of evolution by means of natural selection. Evolution by natural selection is a process that is inferred from three facts about populations: 1) more offspring are produced than can possibly survive, 2) traits vary among individuals, leading to differential rates of survival and reproduction, and 3) trait differences are heritable. Thus, when members of a population die they are replaced by the progeny of parents that were better adapted to survive and reproduce in the environment in which natural selection took place. This process creates and preserves traits that are seemingly fitted for the functional roles they perform. Natural selection is the only known cause of adaptation, but not the only known cause of evolution. Other, nonadaptive causes of evolution include mutation and genetic drift.
This article is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported License, which means that you can copy and modify it as long as the entire work (including additions) remains under this license.

William Sanford "Bill" Nye (born November 27, 1955), popularly known as Bill Nye the Science Guy, is an American science educator, comedian, television host, actor, mechanical engineer, and scientist. He is best known as the host of the Disney/PBS children's science show Bill Nye the Science Guy (1993–1998) and for his many subsequent appearances in popular media as a science educator.
William Sanford Nye was born in Washington, D.C., the son of Jacqueline (née Jenkins; c. 1920–2000), a codebreaker during World War II, and Edwin Darby "Ned" Nye (died 1997), also a World War II veteran whose experience in a Japanese prisoner of war camp led him to become a sundial enthusiast. Nye is a fourth-generation Washington, D.C. resident on his father's side of the family. After attending Lafayette Elementary and Alice Deal Junior High in the city, he was accepted to the private Sidwell Friends School on a partial scholarship, graduating in 1973. He studied mechanical engineering at Cornell University, where one of his professors was Carl Sagan, and graduated with a Bachelor of Science in 1977. He was awarded an honorary doctorate by The Johns Hopkins University in May 2008. In May 2011, Nye was awarded an Honorary Doctor of Science degree from Willamette University where he was the keynote speaker for that year's commencement exercises.
This article is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported License, which means that you can copy and modify it as long as the entire work (including additions) remains under this license.

Clinton Richard Dawkins, FRS, FRSL (born 26 March 1941), known as Richard Dawkins, is a British ethologist, evolutionary biologist and author. He is an emeritus fellow of New College, Oxford, and was the University of Oxford's Professor for Public Understanding of Science from 1995 until 2008.
Dawkins came to prominence with his 1976 book The Selfish Gene, which popularised the gene-centered view of evolution and introduced the term meme. In 1982 he introduced an influential concept into evolutionary biology, presented in his book The Extended Phenotype, that the phenotypic effects of a gene are not necessarily limited to an organism's body, but can stretch far into the environment, including the bodies of other organisms.
Dawkins is an atheist, a vice president of the British Humanist Association, and a supporter of the Brights movement. He is well known for his criticism of creationism and intelligent design. In his 1986 book The Blind Watchmaker, he argued against the watchmaker analogy, an argument for the existence of a supernatural creator based upon the complexity of living organisms. Instead, he described evolutionary processes as analogous to a blind watchmaker. He has since written several popular science books, and makes regular television and radio appearances, predominantly discussing these topics. In his 2006 book The God Delusion, Dawkins contends that a supernatural creator almost certainly does not exist and that religious faith is a delusion—"a fixed false belief." As of January 2010 the English-language version has sold more than two million copies and had been translated into 31 languages.
This article is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported License, which means that you can copy and modify it as long as the entire work (including additions) remains under this license.
- Loading...

-
 3:55
3:55Proof of evolution that you can find on your body
Proof of evolution that you can find on your bodyProof of evolution that you can find on your body
You have your mom's smile, your dad's eyes, and the ear muscles of a Triassic mammal. Subscribe to our channel! http://goo.gl/0bsAjO Forty-two percent of Americans say that humans were created in their present form within the past 10,000 years — a percentage that hasn't changed much since 1982, when Gallup started polling views on evolution. Several lines of evidence, from the fossil record, comparative anatomy, and genetics, tell another story. But you don't have to read all the research to find signs of our evolutionary history — you can see it in the vestigial structures in each of our bodies, like the third molars that no longer fit in our mouths. For a few other examples, check out the video above. Vox.com is a news website that helps you cut through the noise and understand what's really driving the events in the headlines. Check out http://www.vox.com to get up to speed on everything from Kurdistan to the Kim Kardashian app. Check out our full video catalog: http://goo.gl/IZONyE Follow Vox on Twitter: http://goo.gl/XFrZ5H Or on Facebook: http://goo.gl/U2g06o -
 11:48
11:48How Evolution works
How Evolution worksHow Evolution works
The mechanisms of evolution explained in one video. The theory of evolution explains how the enormous variety of life could come into existence. How it is possible for primitive life forms to spawn the millions of different creatures, that exist today. Unfortunately, evolution is often misunderstood, because it's mechanisms seem counter intuitive. By using visualizations, infographics and appealing characters, the viewer is more likely to understand it the complex information. More than that, by presenting the information in an entertaining way, the information is more likely to sink in. Short videos, explaining things. For example Evolution, the Universe, Stock Market or controversial topics like Fracking. Because we love science. We would love to interact more with you, our viewers to figure out what topics you want to see. If you have a suggestion for future videos or feedback, drop us a line! :) We're a bunch of Information designers from munich, visit us on facebook or behance to say hi! https://www.facebook.com/Kurzgesagt https://www.behance.net/kurzgesagt How Evolution Works Help us caption & translate this video! http://amara.org/v/Co7a/ -
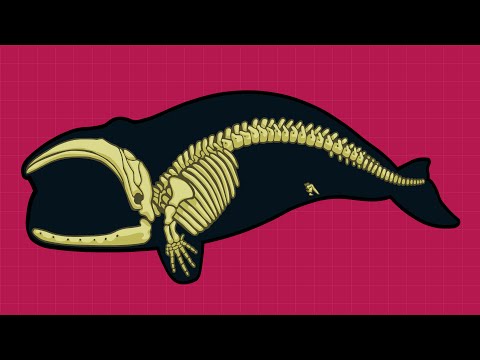 11:22
11:22What is the Evidence for Evolution?
What is the Evidence for Evolution?What is the Evidence for Evolution?
Support Stated Clearly on Patreon: https://www.patreon.com/statedclearly Biologists teach that all living things on Earth are related. Is there any solid evidence to back this claim? Join us as we explore the facts! We start with a close look at the origin of whales from land mammals, and then touch on the origins of several other critters, including our own species. If you want to learn more about whale fossils and evolution, we have articles for you to enjoy on our website! http://statedclearly.com/articles/category/evolution To learn more about whale embryos, check out the work of Dr. Hans Thewissen here: http://web.neomed.edu/web/anatomy/DLDD/index.html For an in-depth view of whale evolution, read Dr. Hans Thewissen's new book "The Walking Whales" http://www.ucpress.edu/book.php?isbn=9780520277069 Corrections: Dolphin embryos shown in this animation come from spotted dolphins. Adult is a dusky dolphin. Photo of bowhead whale pelvis comes from the Department of Wildlife Management, Barrow, Alaska -
 44:56
44:56Evolution The Evolution of humans documentary 2014
Evolution The Evolution of humans documentary 2014Evolution The Evolution of humans documentary 2014
Evolution The Evolution of Shape HD documentary Evolution is the change in the inherited characteristics of biological populations over successive generations. Evolutionary processes give rise to diversity at every level of biological organisation, including species, individual organisms and molecules such as DNA and proteins.[1] All life on Earth is descended from a last universal ancestor that lived approximately 3.8 billion years ago. Repeated speciation and the divergence of life can be inferred from shared sets of biochemical and morphological traits, or by shared DNA sequences.[2] These homologous traits and sequences are more similar among species that share a more recent common ancestor, and can be used to reconstruct evolutionary histories, using both existing species and the fossil record. Existing patterns of biodiversity have been shaped both by speciation and by extinction.[3] Charles Darwin was the first to formulate a scientific argument for the theory of evolution by means of natural selection. Evolution by natural selection is a process inferred from three facts about populations: 1) more offspring are produced than can possibly survive, 2) traits vary among individuals, leading to different rates of survival and reproduction, and 3) trait differences are heritable.[4] Thus, when members of a population die they are replaced by the progeny of parents better adapted to survive and reproduce in the environment in which natural selection takes place. This process creates and preserves traits that are seemingly fitted for the functional roles they perform.[5] Natural selection is the only known cause of adaptation, but not the only known cause of evolution. Other, nonadaptive causes of evolution include mutation and genetic drift.[6] In the early 20th century, genetics was integrated with Darwin's theory of evolution by natural selection through the discipline of population genetics. The importance of natural selection as a cause of evolution was accepted into other branches of biology. Moreover, previously held notions about evolution, such as orthogenesis and "progress" became obsolete.[7] Scientists continue to study various aspects of evolution by forming and testing hypotheses, constructing scientific theories, using observational data, and performing experiments in both the field and the laboratory. Biologists agree that descent with modification is one of the most reliably established facts in science.[8] Discoveries in evolutionary biology have made a significant impact not just within the traditional branches of biology, but also in other academic disciplines (e.g., anthropology and psychology) and on society at large.[9][10] -
 7:45
7:4510 Unsolved Mysteries Of Evolution
10 Unsolved Mysteries Of Evolution10 Unsolved Mysteries Of Evolution
Since Charles Darwin published his groundbreaking work on evolution, scientists have been trying to answer how we came to be the species that we are. From why we walk on 2 legs, to what we'll evolve into next, AllTime 10s answers the top 10 unsolved mysteries of evolution. Click to Subscribe.. http://bit.ly/WTVC4x Check out the best of Alltime10s - https://www.youtube.com/playlist?list=PLec1lxRhYOzt2qqqnFBIpUm63wr5yhLF6 Where else to find All Time 10s... Facebook: http://ow.ly/3FNFR Twitter: http://ow.ly/3FNMk -
 7:00
7:007 MYTHS You Still Believe About EVOLUTION
7 MYTHS You Still Believe About EVOLUTION7 MYTHS You Still Believe About EVOLUTION
Subscribe! New videos Monday and Friday!►http://bit.ly/SantoroSubscribe Snapchat: https://snapchat.com/add/MatthewSantoro Facebook Page: http://fb.com/MatthewSantoroOfficial Facebook Profile: http://fb.com/MatthewMSantoro Periscope: http://periscope.tv/MatthewSantoro Instagram: http://instagr.am/MatthewSantoro Twitter: http://twitter.com/MatthewSantoro Vine: http://vine.co/MatthewSantoro Podcast: http://bit.ly/SantoroiTunes My Gaming Channel►http://bit.ly/SantoroGamingSubscribe My Vlog Channel►http://bit.ly/SantoroVlogsSubscribe Writers: Matthew Santoro Jim Vaylin Editor: Brock Sumner -
 112:05
112:05Evolution - What Darwin Never Knew - NOVA PBS Documentary
Evolution - What Darwin Never Knew - NOVA PBS DocumentaryEvolution - What Darwin Never Knew - NOVA PBS Documentary
DOWNLOAD BOOK ( pdf ): http://www.mediafire.com/?39l9wwiurjns48y READ ON-LINE: http://archive.org/stream/originofspecies00darwuoft#page/n0/mode/2up -
 18:41
18:41CAN WE BEAT THE HACKERS?! - Minecraft EVOLUTION #2 with Vikkstar & Woofless
CAN WE BEAT THE HACKERS?! - Minecraft EVOLUTION #2 with Vikkstar & WooflessCAN WE BEAT THE HACKERS?! - Minecraft EVOLUTION #2 with Vikkstar & Woofless
We face some Hackers in Minecraft Evolution. Can we win?! My Gaming Channel: http://www.youtube.com/VikkstarPlays Follow me on TWITTER: http://twitter.com/#!/Vikkstar123 Like my Facebook Page: http://www.facebook.com/Vikkstar123 My Instagram: http://instagram.com/Vikkstagram The Pack: https://www.youtube.com/Lachlan https://www.youtube.com/PrestonPlayz https://www.youtube.com/MrWoofless https://www.youtube.com/JeromeASF https://www.youtube.com/TheBajanCanadian My Servers: http://arkhamnetwork.org/ IP: mc.arkhamnetwork.org http://treasurewars.net/ IP: treasurewars.net My capture card: http://e.lga.to/v Follow me on Twitch for Livestreams: http://www.twitch.tv/vikkstar123 Check out my other channels linked below: FPS & More: http://www.youtube.com/Vikkstar123 Lets Play: http://www.youtube.com/VikkstarPlays -
 35:07
35:07The Evolution of the Parasitical Class: Past, Present and Future
The Evolution of the Parasitical Class: Past, Present and FutureThe Evolution of the Parasitical Class: Past, Present and Future
Stefan Molyneux breaks down the origin of the parasitical class which uses language to manipulate and control human beings. What is the truth about the past, present and future of interspecies human parasitism? Freedomain Radio is 100% funded by viewers like you. Please support the show by signing up for a monthly subscription or making a one time donation at: http://www.freedomainradio.com/donate Get more from Stefan Molyneux and Freedomain Radio including books, podcasts and other info at: http://www.freedomainradio.com Amazon Affiliate Links US: http://www.fdrurl.com/Amazon Canada: http://www.fdrurl.com/AmazonCanada UK: http://www.fdrurl.com/AmazonUK -
 8:53
8:53What is Evolution?
What is Evolution?What is Evolution?
Support Stated Clearly on Patreon: https://www.patreon.com/statedclearly Evolution is often considered a complex and controversial topic but it's actually a very simple concept to understand. Watch this short animation to see how evolution works. Share it with your friends on Facebook who might be confused or may have been mislead about the evolutionary process. You can learn more about genetics and evolution by visiting our website at http://www.statedclearly.com This video is our first animation with illustrations from the talented Rosemary Mosco. If you don't already know her work, make sure to check out her website at http://BirdAndMoon.com You'll love her biology comics, posters and t-shirts. This video features custom music by AD at Proof Avenue. Check his other work at http://ProofAvenue.com Sources: The definition of Evolution: "Genetic change in a population of organisms; in general, evolution leads to progressive change from simple to complex." - Biology, Seventh Edition, Raven, Johnson, Losos, Singer (college textbook) pg G-6 glossary "Descent with modification...change in the genetic composition of a population from generation to generation." - Biology Eighth Edition, Campbell, Reece (college textbook) pg G-14 glossary "Biological evolution, simply put, is descent with modification. This definition encompasses small-scale evolution (changes in gene frequency in a population from one generation to the next) and large-scale evolution (the descent of different species from a common ancestor over many generations). Evolution helps us to understand the history of life." University of California Berkley http://evolution.berkeley.edu/evosite/evo101/IIntro.shtml Dogs evolved from wolves: http://news.bbc.co.uk/2/hi/science/nature/2498669.stm Thanks to Hedvig Francke for providing Closed Captions in Swedish. -
 10:48
10:48Minecraft Evolution #7 - Un gioco rovinato... w/ Tech4play JacoRollo
Minecraft Evolution #7 - Un gioco rovinato... w/ Tech4play JacoRolloMinecraft Evolution #7 - Un gioco rovinato... w/ Tech4play JacoRollo
Alle 18 esce un video lezzo, non perdetevelo :D Tech4Play: https://www.youtube.com/user/Tech4Play JacoRollo: https://www.youtube.com/user/JacoRollo Instagram: https://instagram.com/luca.marcacci/ IP: IP Server: eu.mineplex.com --------------------------------------------------------------------------------- Server di gioco e TeamSpeak 3: TrinityHosting: http://www.trinityhosting.it/aff.php?aff=021 Codice sconto del 5% su server minecraft superiori a 1GB di RAM: Deh Codice sconto del 15% su VPS: Lezzo --------------------------------------------------------------------------------- Info e link utili: Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/pages/Metano007/762668557115304 Ask: http://ask.fm/Metano007 Google+: https://plus.google.com/u/0/b/102974627985251070040/102974627985251070040/about Steam: http://steamcommunity.com/id/metano007 Skype: Metano007 --------------------------------------------------------------------------------- -
 56:39
56:39EVOLUTION - GREAT TRANSFORMATIONS - NOVA - Discovery/History/Science (documentary)
EVOLUTION - GREAT TRANSFORMATIONS - NOVA - Discovery/History/Science (documentary)EVOLUTION - GREAT TRANSFORMATIONS - NOVA - Discovery/History/Science (documentary)
evolution - great transformations - nova (documentary). thanks for watching. history life discovery science technology tech learning education national nature geographic earth planet channel universe culture civilization civilisation archaeology ancient discoveries creation creationism darwin caveman neanderthal ape human humans man evolve animal animals prehistoric dinosaur dinosaurs biology zoology -
 11:44
11:44Evolution: It's a Thing - Crash Course Biology #20
Evolution: It's a Thing - Crash Course Biology #20Evolution: It's a Thing - Crash Course Biology #20
Hank gets real with us in a discussion of evolution - it's a thing, not a debate. Gene distribution changes over time, across successive generations, to give rise to diversity at every level of biological organization. Crash Course Biology is now available on DVD! http://dft.ba/-8css Like CrashCourse on Facebook: http://www.facebook.com/YouTubeCrashCourse Follow CrashCourse on Twitter: http://www.twitter.com/TheCrashCourse Table of Contents 1) The Theory of Evolution 1:49 2) Fossils 2:42 3) Homologous Structures 4:36 4) Biogeography 7:02 5) Direct Observation 8:52 References for this episode can be found in the Google document here: http://dft.ba/-2Oyu evolution, theory, biology, science, crashcourse, genetics, gene, facts, fossil, fossil record, dinosaur, extinct, extinction, organism, dorudon, rodhocetus, vestigial, structure, similarity, homologous structure, related, relationship, morganucodon, fore limb, hind limb, vertebrate, molecule, DNA, RNA, chimpanzee, fruit fly, biogeography, marsupial, finches, direct observation, drug resistance, resistance, selective pressure, italian wall lizard Support CrashCourse on Subbable: http://subbable.com/crashcourse -
 16:17
16:17Evolution #23 z Hunterem
Evolution #23 z Hunterem
- Abiogenesis
- Abiotic
- Actuality
- Adaptation
- Adaptive radiation
- Albinism
- Albino
- Allele
- Allele frequency
- Almost Like a Whale
- Amino acid
- Amniote
- Amphibian
- Anagenesis
- Anatomy
- Anaximander
- Ant
- Anthoxanthum
- Antibiotic
- Antibody
- Ape
- Apes
- Arabidopsis thaliana
- Archaea
- Arthropod
- Artificial life
- Artificial selection
- ArXiv
- Assortative mating
- Astrobiology
- Atmosphere
- Atom
- August Weismann
- Bacillus subtilis
- Bacteria
- Baldwin effect
- Baleen whale
- Bat
- BBC
- Bdelloidea
- Bee
- Biased sample
- Bibcode
- Bimodal distribution
- Biochemistry
- Biocoenosis
- Biodiversity
- Biogeography
- Bioinformatics
- Biological system
- Biology
- Biomass
- Biomass (ecology)
- Biomechanics
- Biomolecule
- Biophysics
- Biosphere
- Biostatistics
- Biotic component
- Bird
- Blending inheritance
- Book Evolution
- Botany
- Brian Charlesworth
- Brown algae
- Butterfly evolution
- Cambrian explosion
- Carbohydrates
- Carcinogenesis
- Caricature
- Carl Bergstrom
- Carl Zimmer
- Carolus Linnaeus
- Cat gap
- Category Biology
- Cell (biology)
- Cell biology
- Cell nucleus
- Cell signalling
- Cell theory
- Charles Darwin
- Chemical biology
- Chicken
- Chloroplast
- Chromatin
- Chromosome
- Chronobiology
- Cichlid
- Citric acid
- Cladistics
- Cladogenesis
- Classical genetics
- Co-evolution
- Coccyx
- Coevolution
- Colony (biology)
- Common descent
- Common Garter Snake
- Community ecology
- Comparative anatomy
- Computer science
- Cone cell
- Conservation biology
- Convergent evolution
- Cosmos
- CRC Press
- Creation myths
- Creationism
- Creationist
- Cretaceous
- Crocodile
- Crystallin
- Cyanobacteria
- Cytoplasm
- Daniel Dennett
- Darwin's finches
- Darwinism
- Deborah Charlesworth
- Deep homology
- Derek Briggs
- Dinosaur
- Directed evolution
- Disruptive selection
- Divergent evolution
- Divinity
- DNA
- DNA methylation
- Dollo's law
- Domain (biology)
- Domestication
- Donkey
- Double helix
- Douglas J. Futuyma
- Earth
- Earth science
- Ecological genetics
- Ecological niche
- Ecology
- Ecosystem
- Ecosystem ecology
- Ediacara biota
- Edward Larson
- Embryogenesis
- Empedocles
- Endospore
- Endosymbiont
- Energy
- Enzyme
- Epidemiology
- Epigenetic
- Epigenetics
- Epperson v. Arkansas
- Erasmus Darwin
- Ernst W. Mayr
- Escherichia coli
- Eukaryote
- Eusociality
- Evolution
- Evolution of ageing
- Evolution of birds
- Evolution of cells
- Evolution of fungi
- Evolution of hair
- Evolution of insects
- Evolution of mammals
- Evolution of plants
- Evolution of spiders
- Evolution of the eye
- Evolution strategy
- Evolutionary biology
- Evolutionary ethics
- Evolvability
- Exaptation
- Experiments
- Explanatory
- Extinction
- Extinction event
- Eye
- Eye colour
- Eörs Szathmáry
- Fact
- Fecundity
- Fitness (biology)
- Flagella
- Flavobacterium
- Flipper (anatomy)
- Food chain
- Fossil
- Fossil record
- Founder effect
- Francis Crick
- Function (biology)
- Fungus
- Galápagos Islands
- Garrett Hardin
- Gene
- Gene duplication
- Gene family
- Gene flow
- Gene product
- Generation
- Genes
- Genetic algorithm
- Genetic assimilation
- Genetic disorder
- Genetic diversity
- Genetic drift
- Genetic engineering
- Genetic hitchhiking
- Genetic linkage
- Genetic material
- Genetic programming
- Genetic variation
- Genetics
- Genome
- Genomics
- Genotype
- Georges Cuvier
- Germ cell
- Germline
- Global warming
- Glossary of ecology
- Glycolysis
- Goose bumps
- Gray tree frog
- Gregor Mendel
- Group selection
- H. Allen Orr
- Habitat
- Handicap principle
- Haplotype
- Heredity
- Heritability
- Histology
- Homeostasis
- Homininae
- Homology (biology)
- Horse
- Host (biology)
- Hugo de Vries
- Human biology
- Human evolution
- Human vestigiality
- Hybrid (biology)
- Hybrid speciation
- Hydrogenosome
- Idealism
- Immune system
- Immunology
- Inbreeding
- Inference
- Infertility
- Ingo Rechenberg
- Insect
- Intelligent design
- J.B.S. Haldane
- James D. Watson
- Jerry A. Coyne
- Jerry Coyne
- John Henry Holland
- John Maynard Smith
- John Ray
- Jonathan Eisen
- JSTOR
- Kin selection
- Lamarck
- Laws of nature
- Leg
- Life
- Lipids
- Locus (genetics)
- Macroevolution
- Macromolecule
- Mammal
- Marcel Dekker
- Marine biology
- Materialism
- Maupertuis
- McGraw Hill
- Meiosis
- Mendelian genetics
- Metabolic pathway
- Metabolism
- Mexican tetra
- Michael Ghiselin
- Microbiology
- Microevolution
- Microorganism
- Middle Ages
- Mitochondrion
- Mitosis
- Modern humans
- Modern science
- Modularity (biology)
- Molecular Biology
- Molecular biology
- Molecular clock
- Molecular evolution
- Molecular genetics
- Molecular machine
- Molecule
- Monkey
- Morphology (biology)
- Mosaic evolution
- Mouse
- Mule
- Mutation
- Mycology
- Mycorrhiza
- Myxobacteria
- Nanobiotechnology
- Natural selection
- Natural theology
- Nature (philosophy)
- Neo-Darwinian
- Neuroculture
- Neuroscience
- Neutral mutation
- Niche construction
- Nick Barton
- Norms of reaction
- Nucleic Acids
- Nucleobase
- Nucleotide
- Nutrition
- Nylon
- Offspring
- Organ (anatomy)
- Organelle
- Organism
- Orthogenesis
- Oxygen
- Paleontology
- Pangenesis
- Parallel evolution
- Parasitology
- Pathogen
- Pathology
- Pentachlorophenol
- Peppered moth
- Pesticide
- Peter J. Bowler
- Pharmacology
- Phenotype
- Phenotypic trait
- Photosynthesis
- Phylogenetic
- Phylogenetic tree
- Phylogenetics
- Phylum
- Physical cosmology
- Physiology
- Pigment
- Plant
- Pollen
- Polyketide synthase
- Polymer
- Polyploidy
- Population
- Population Ecology
- Population genetics
- Portal Biology
- Predation
- Prehistoric fish
- Primate
- Primitive reflexes
- Prions
- Prokaryote
- Prometheus Books
- Protein
- Protein domain
- Protein structure
- Proteins
- Pseudogene
- Pseudoscience
- PubMed Central
- PubMed Identifier
- Quantum biology
- Random walk
- Religion
- Reptile
- Resource (biology)
- Richard Dawkins
- RNA
- RNA interference
- RNA world hypothesis
- Rod cell
- Ronald Fisher
- Rough Guides
- Rough-skinned newt
- Sampling error
- Science (journal)
- Scientific American
- Scientific consensus
- Scientific method
- Scientific theory
- Scopes Trial
- Sean B. Carroll
- Selectable marker
- Selective sweep
- Sewall Wright
- Sex
- Sexual reproduction
- Sexual selection
- Signal transduction
- Slime mold
- Sociobiology
- Somatic cell
- Somatic cells
- Speciation
- Species problem
- Species selection
- Sphingobium
- Sponge
- Stephen C. Stearns
- Stephen Jay Gould
- Sun tanning
- Sunburn
- Symbiogenesis
- Symbiosis
- Sympatric speciation
- Systematics
- Systems biology
- TalkOrigins Archive
- Taxonomy
- Teleology
- Teleonomy
- Template Biology nav
- Template Evolution
- Termite
- Tetrodotoxin
- The Selfish Gene
- Theism
- Theistic evolution
- Theory of forms
- Thomas Henry Huxley
- Tissue (biology)
- Toxicology
- Trait (biology)
- Transitional fossil
- Transitional fossils
- Transposon
- Tyrannosaurus rex
- Unit of selection
- Universal Darwinism
- Variance
- Vermiform appendix
- Vestigial structure
- Vestigiality
- Viral evolution
- Virus
- Wikipedia Media help
- Will Provine
- William Paley
- Wisdom teeth
- WP Books
- Zoology
- Anaximander
- August Weismann
- Brian Charlesworth
- Carl Bergstrom
- Carl Zimmer
- Charles Darwin
- Daniel Dennett
- Deborah Charlesworth
- Derek Briggs
- Empedocles
- Erasmus Darwin
- Eörs Szathmáry
- Francis Crick
- Garrett Hardin
- Georges Cuvier
- Gregor Mendel
- Hugo de Vries
- Ingo Rechenberg
- Jerry Coyne
- John Henry Holland
- John Maynard Smith
- John Ray
- Jonathan Eisen
- Michael Ghiselin
- Nick Barton
- Richard Dawkins
- Ronald Fisher
- Sewall Wright
- Stephen Jay Gould
- Thomas Henry Huxley
- Will Provine
- William Paley
Evolutions, John Filmography
-
2013, role: editor
Henderson, 'Evolution' Filmography
-
1937, role: actor , character name: Himself
Evolution
Cast
- Liam Neeson
- Cornelius Garrett
- John Quentin
- Matthew Radford
- Eleanor Ogbourne
- Andy Henderson
- Anthony Carrick
- Jane Cunliffe
- Chris Larkin
- Joshua Losey
- Tobias Vaughan
- Manon Eames
- John Walters
- Ian Shaw
- Roger Brierley
- Will Fawcett
- Andrew Heath
- Mark Tandy
- Season 1
-
Play in Full Screen
Episode 1: Darwin's Dangerous Idea
USA:2002...
-
Play in Full Screen
Episode 2: Great Transformations
USA:2002...
-
Play in Full Screen
Episode 3: Extinction!
USA:2002...
-
Play in Full Screen
Episode 4: The Evolutionary Arms Race
USA:2002...
-
Play in Full Screen
Episode 5: Why Sex?
USA:2002...
-
Play in Full Screen
Episode 6: The Mind's Big Bang
USA:2002...
-
Play in Full Screen
Episode 7: What About God?
USA:2002...
Matching books:
Evolution
ALBUMS
- Oscillating Phenomena released: 1997
- Shiva Technology released: 1996
Oscillating Phenomena
Released 1997- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Riding High (Bullet 350 mix)
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Fifth-Dimensional Craft
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Flower of Life
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Water Spirit
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Genetic Engeneering
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Alien Phenomenon
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Warriors of Light
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Akhunathon
Shiva Technology
Released 1996- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen The Experience of Taking a Step Into Someone's Dream
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Tribalism
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Peyote
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Here We Go
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Sub-Marine
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Goa (remix)
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Exotic Planet
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Cuzco
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Ritual Trance
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Sparkling Sun
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Equilibrium
Evolution
ALBUMS
- Tontraeger Fuer Synapsen Massage released:
- Mystera IX released:
Tontraeger Fuer Synapsen Massage
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Astrogator
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Comala
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Fill 4
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Clavius
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Trobriand
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Marmion Island
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen The FX Ov Smmøp
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Interlude RmX
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Symphony In E
Mystera IX
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Divano
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Light and Shadow
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Quo Vadis
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Journey to Schambala
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen To Be Free
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Child in Time
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Caislean Oir
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Aqua Marine
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Lesiem
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Ave Maria Unio Mystica
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Sunrise
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Mists of Avalon
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Gloria
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Minja
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Fountain of Secrets
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Danza La Luna
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Mother Nature Ballade
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen To the Moon
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen La Lune
Evolution
ALBUMS
- Intercity Woman, Volume 2 released: 2009
- The River of Constant Change released: 1996
- Harbour of Joy: A Tribute to Camel released: 1996
Intercity Woman, Volume 2
Released 2009- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Big Girls Don't Cry
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Coming Home
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Tied Down
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen This Is the Life
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen What You Give Is What You Get
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Annie
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Remedy
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen My Sweetness
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen The Circus Song
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Don't Dream It's Over
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Good Morning Angel
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Don"T Fade Away
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Every Little Thing (He) Does Is Magic
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen The Way It Is/Mayby Tonight
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Hometown Glory
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Crime
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Bang Bang
The River of Constant Change
Released 1996- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Horizons
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Looking for Someone
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen The Light Dies Down On Broadway
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Entangled
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Watcher Of The Skies
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Visions Of Angels
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Dancing With The Moonlit Knight
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen White Mountain
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen No Son of Mine
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen In the Rapids
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Wot Gorilla?
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Afterglow
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen The Chamber Of 32 Doors
Harbour of Joy: A Tribute to Camel
Released 1996- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Pressure Points
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen First Light
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Ice
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Nimrodel
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Long Goodbyes
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Rain Dances
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Rhayader
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Lady Fantasy
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Fritha Alone
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Harbour of Tears
Evolution
ALBUMS
- In The Groove released: 2004
- Brit Rock released:
- Chilled Beats released:
In The Groove
Released 2004- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Anubis
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Bend Your Mind
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Boogie Down
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Bouff
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Bubble Dancer
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Changes
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Charlene
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Crazy
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Da Roots (Folk mix)
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Dawn
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Delirium
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Disconnected
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Disconnected ~Hyper~
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Disconnected ~Mobius~
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen DJ Party
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Do U Love Me
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Don't Promise Me
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Don't Promise Me ~Happiness~
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Dreams of Passion
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Drifting Away
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Driving Force Classical
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Euphoria
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Fly Away
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Fly With Me
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Flying High
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Hand of Time
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Hardcore of the North
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Hip Hop Jam
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Hybrid
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen I Think I Like That Sound
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen I'll Get There Anyway
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Infection
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen July
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Kagami
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Kiss Me Red
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Land of the Rising Sun
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Lemmings on the Run
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Let Me Be the One
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Let My Love Go Blind
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Mellow
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Mouth
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen My Favourite Game
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Mythology
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen No 1 Nation
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Normal
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Not Worth the Paper
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Oasis
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen On a Day Like Today
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen PA Theme
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Pandemonium
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Perfect
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Queen of Light
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Remember December
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen ROM-eo & Juli8
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Solina
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Tell
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Tension
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen The Beginning
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen The Game
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Torn
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Touch Me
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Tough Enough
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Turn It On
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Utopia
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen VerTex
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Walking on Fire (Blank & Jones remix)
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Which MC Was That?
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen While tha Rekkid Spinz
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Why Me
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Xuxa
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Zodiac
Brit Rock
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Guitarmageddon
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Foolz Errand
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Doctor Rocker
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen High as a Kite
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Lost' N' Found
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Dirty Torque
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Free-For-All
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen A Right Touch
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen These Are the Days
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen No Harm Done
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Go for Broke
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Bring It On
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Mad for It
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Old Rope
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Sweet as a Nut
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Guitarmageddon
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Foolz Errand
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Doctor Rocker
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen High as a Kite
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Lost' N' Found
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Dirty Torque
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Free-For-All
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen A Right Touch
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen These Are the Days
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen No Harm Done
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Go for Broke
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Bring It On
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Mad for It
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Old Rope
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Sweet as a Nut
Chilled Beats
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Pleasure Island
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Chill Pill
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Liquid Gold
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen True Color
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Sweet Heat
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Shaderunner
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Smoke Without Fire
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen The Last Sun
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Almost Heaven
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Born to Be Mild
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Chiba Fever
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Moondown
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Solar Quest
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Hed 2 Hed
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Aquaphonic Tonic
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Pleasure Island (30 second version)
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Chill Pill (30 second version)
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Liquid Gold (30 second version)
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen True Color (30 second version)
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Sweet Heat (30 second version)
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Shaderunner (30 second version)
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Smoke Without Fire (30 second version)
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen The Last Sun (30 second version)
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Almost Heaven (30 second version)
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Born to Be Mild (30 second version)
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Chiba Fever (30 second version)
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Moondown (30 second version)
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Solar Quest (30 second version)
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Hed 2 Hed (30 second version)
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Aquaphonic Tonic (30 second version)
Evolution
ALBUMS
- Unnatural Selection released: 2002
Unnatural Selection
Released 2002- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Numb
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Mexican Dawn
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Better House Music
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Walking On Fire
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Firewyre
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Crocodile Man
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Solina
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Blaster
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Phoenix
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Making Sense
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Walking (Ambient)
E-Volution
ALBUMS
- Dance July 2007 released: 2007
Dance July 2007
Released 2007- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen The Creeps (Get on the Dancefloor) (Vandalism vocal mix)
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen A Neverending Dream (Buzz Junkies mix)
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen The Year of the Cat (Alex Gaudino & Paul Sander mix)
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Sign Your Name (Soul Corporation club mix)
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Gimme Your Love (Bob Roberts remix)
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Come Tomorrow (Soul Seekerz club mix)
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen I Don't Wanna See You Again (Starchaser remix)
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Sunstaring (Digital Dog mix)
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen So Good (Shaolin Master remix)
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Estrella (original mix)
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Get the Party Started (North vs. N West remix)
Evo-lution
ALBUMS
- Changing Memories released: 2011
Changing Memories
Released 2011- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen The Beginning
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Lies
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Im Himmel
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Society of Today
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Träume
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Terminator
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Unendlichkeit
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Absolving Me
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Für Dich & Mich
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Black Day
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Stuck on Love
-

Proof of evolution that you can find on your body
You have your mom's smile, your dad's eyes, and the ear muscles of a Triassic mammal. Subscribe to our channel! http://goo.gl/0bsAjO Forty-two percent of Americans say that humans were created in their present form within the past 10,000 years — a percentage that hasn't changed much since 1982, when Gallup started polling views on evolution. Several lines of evidence, from the fossil record, comparative anatomy, and genetics, tell another story. But you don't have to read all the research to find signs of our evolutionary history — you can see it in the vestigial structures in each of our bodies, like the third molars that no longer fit in our mouths. For a few other examples, check out the video above. Vox.com is a news website that helps you cut through the noise and understand wha... -

How Evolution works
The mechanisms of evolution explained in one video. The theory of evolution explains how the enormous variety of life could come into existence. How it is possible for primitive life forms to spawn the millions of different creatures, that exist today. Unfortunately, evolution is often misunderstood, because it's mechanisms seem counter intuitive. By using visualizations, infographics and appealing characters, the viewer is more likely to understand it the complex information. More than that, by presenting the information in an entertaining way, the information is more likely to sink in. Short videos, explaining things. For example Evolution, the Universe, Stock Market or controversial topics like Fracking. Because we love science. We would love to interact more with you, our viewers t... -

What is the Evidence for Evolution?
Support Stated Clearly on Patreon: https://www.patreon.com/statedclearly Biologists teach that all living things on Earth are related. Is there any solid evidence to back this claim? Join us as we explore the facts! We start with a close look at the origin of whales from land mammals, and then touch on the origins of several other critters, including our own species. If you want to learn more about whale fossils and evolution, we have articles for you to enjoy on our website! http://statedclearly.com/articles/category/evolution To learn more about whale embryos, check out the work of Dr. Hans Thewissen here: http://web.neomed.edu/web/anatomy/DLDD/index.html For an in-depth view of whale evolution, read Dr. Hans Thewissen's new book "The Walking Whales" http://www.ucpress.edu/book.php?i... -

Evolution The Evolution of humans documentary 2014
Evolution The Evolution of Shape HD documentary Evolution is the change in the inherited characteristics of biological populations over successive generations. Evolutionary processes give rise to diversity at every level of biological organisation, including species, individual organisms and molecules such as DNA and proteins.[1] All life on Earth is descended from a last universal ancestor that lived approximately 3.8 billion years ago. Repeated speciation and the divergence of life can be inferred from shared sets of biochemical and morphological traits, or by shared DNA sequences.[2] These homologous traits and sequences are more similar among species that share a more recent common ancestor, and can be used to reconstruct evolutionary histories, using both existing species and the fo... -

10 Unsolved Mysteries Of Evolution
Since Charles Darwin published his groundbreaking work on evolution, scientists have been trying to answer how we came to be the species that we are. From why we walk on 2 legs, to what we'll evolve into next, AllTime 10s answers the top 10 unsolved mysteries of evolution. Click to Subscribe.. http://bit.ly/WTVC4x Check out the best of Alltime10s - https://www.youtube.com/playlist?list=PLec1lxRhYOzt2qqqnFBIpUm63wr5yhLF6 Where else to find All Time 10s... Facebook: http://ow.ly/3FNFR Twitter: http://ow.ly/3FNMk -

7 MYTHS You Still Believe About EVOLUTION
Subscribe! New videos Monday and Friday!►http://bit.ly/SantoroSubscribe Snapchat: https://snapchat.com/add/MatthewSantoro Facebook Page: http://fb.com/MatthewSantoroOfficial Facebook Profile: http://fb.com/MatthewMSantoro Periscope: http://periscope.tv/MatthewSantoro Instagram: http://instagr.am/MatthewSantoro Twitter: http://twitter.com/MatthewSantoro Vine: http://vine.co/MatthewSantoro Podcast: http://bit.ly/SantoroiTunes My Gaming Channel►http://bit.ly/SantoroGamingSubscribe My Vlog Channel►http://bit.ly/SantoroVlogsSubscribe Writers: Matthew Santoro Jim Vaylin Editor: Brock Sumner -

Evolution - What Darwin Never Knew - NOVA PBS Documentary
DOWNLOAD BOOK ( pdf ): http://www.mediafire.com/?39l9wwiurjns48y READ ON-LINE: http://archive.org/stream/originofspecies00darwuoft#page/n0/mode/2up -

CAN WE BEAT THE HACKERS?! - Minecraft EVOLUTION #2 with Vikkstar & Woofless
We face some Hackers in Minecraft Evolution. Can we win?! My Gaming Channel: http://www.youtube.com/VikkstarPlays Follow me on TWITTER: http://twitter.com/#!/Vikkstar123 Like my Facebook Page: http://www.facebook.com/Vikkstar123 My Instagram: http://instagram.com/Vikkstagram The Pack: https://www.youtube.com/Lachlan https://www.youtube.com/PrestonPlayz https://www.youtube.com/MrWoofless https://www.youtube.com/JeromeASF https://www.youtube.com/TheBajanCanadian My Servers: http://arkhamnetwork.org/ IP: mc.arkhamnetwork.org http://treasurewars.net/ IP: treasurewars.net My capture card: http://e.lga.to/v Follow me on Twitch for Livestreams: http://www.twitch.tv/vikkstar123 Check out my other channels linked below: FPS & More: http://www.youtube.com/Vikkstar123 Lets Play: http://www.yout... -

The Evolution of the Parasitical Class: Past, Present and Future
Stefan Molyneux breaks down the origin of the parasitical class which uses language to manipulate and control human beings. What is the truth about the past, present and future of interspecies human parasitism? Freedomain Radio is 100% funded by viewers like you. Please support the show by signing up for a monthly subscription or making a one time donation at: http://www.freedomainradio.com/donate Get more from Stefan Molyneux and Freedomain Radio including books, podcasts and other info at: http://www.freedomainradio.com Amazon Affiliate Links US: http://www.fdrurl.com/Amazon Canada: http://www.fdrurl.com/AmazonCanada UK: http://www.fdrurl.com/AmazonUK -

What is Evolution?
Support Stated Clearly on Patreon: https://www.patreon.com/statedclearly Evolution is often considered a complex and controversial topic but it's actually a very simple concept to understand. Watch this short animation to see how evolution works. Share it with your friends on Facebook who might be confused or may have been mislead about the evolutionary process. You can learn more about genetics and evolution by visiting our website at http://www.statedclearly.com This video is our first animation with illustrations from the talented Rosemary Mosco. If you don't already know her work, make sure to check out her website at http://BirdAndMoon.com You'll love her biology comics, posters and t-shirts. This video features custom music by AD at Proof Avenue. Check his other work at http://Pr... -

Minecraft Evolution #7 - Un gioco rovinato... w/ Tech4play JacoRollo
Alle 18 esce un video lezzo, non perdetevelo :D Tech4Play: https://www.youtube.com/user/Tech4Play JacoRollo: https://www.youtube.com/user/JacoRollo Instagram: https://instagram.com/luca.marcacci/ IP: IP Server: eu.mineplex.com --------------------------------------------------------------------------------- Server di gioco e TeamSpeak 3: TrinityHosting: http://www.trinityhosting.it/aff.php?aff=021 Codice sconto del 5% su server minecraft superiori a 1GB di RAM: Deh Codice sconto del 15% su VPS: Lezzo --------------------------------------------------------------------------------- Info e link utili: Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/pages/Metano007/762668557115304 Ask: http://ask.fm/Metano007 Google+: https://plus.google.com/u/0/b/102974627985251070040/102974627985251070040/about S... -

EVOLUTION - GREAT TRANSFORMATIONS - NOVA - Discovery/History/Science (documentary)
evolution - great transformations - nova (documentary). thanks for watching. history life discovery science technology tech learning education national nature geographic earth planet channel universe culture civilization civilisation archaeology ancient discoveries creation creationism darwin caveman neanderthal ape human humans man evolve animal animals prehistoric dinosaur dinosaurs biology zoology -

Evolution: It's a Thing - Crash Course Biology #20
Hank gets real with us in a discussion of evolution - it's a thing, not a debate. Gene distribution changes over time, across successive generations, to give rise to diversity at every level of biological organization. Crash Course Biology is now available on DVD! http://dft.ba/-8css Like CrashCourse on Facebook: http://www.facebook.com/YouTubeCrashCourse Follow CrashCourse on Twitter: http://www.twitter.com/TheCrashCourse Table of Contents 1) The Theory of Evolution 1:49 2) Fossils 2:42 3) Homologous Structures 4:36 4) Biogeography 7:02 5) Direct Observation 8:52 References for this episode can be found in the Google document here: http://dft.ba/-2Oyu evolution, theory, biology, science, crashcourse, genetics, gene, facts, fossil, fossil record, dinosaur, extinct, extinction, organis... -

-

Bill Nye, Ken Ham Debate Creation vs. Evolution
The debate between Bill Nye and Ken Ham on the question "Is Creation A Viable Model of Origins?" was held at the Creation Museum in Petersburg, Kentucky. Ken Ham, founder and CEO of the Young Earth creationist (YEC) ministry Answers in Genesis (AiG), challenged Bill Nye, a science educator best known for hosting the 1990s hit television series "Bill Nye the Science Guy", to the debate after taking exception to a video featuring Nye lamenting the refusal of a large segment of the U.S. population to accept the theory of evolution. -

-

The 12 Days of Evolution - Complete Series!
All 12 days… in ONE video! Prefer the individual videos? Go here: http://bit.ly/OKTBS12daysPL ↓ More info and sources below ↓ I *highly* recommend these books: “Undeniable” by Bill Nye http://amzn.to/1TK3wZs “Why Evolution Is True” by Jerry Coyne http://amzn.to/1TK3zV3 WEBSITES/TEACHING RESOURCES: - Berkeley’s “Understanding Evolution” http://evolution.berkeley.edu/evolibrary/home.php - The National Center for Science Education http://ncse.com/ Don’t miss a single one of our 12 Days of Evolution! Follow along with this playlist: https://www.youtube.com/playlist?list=PLsmqeqKj7M-rZe1C9PUon8V-VQ1tZj5NF Darwin illustration credit: Nicku / Shutterstock Have an idea for an episode or an amazing science question you want answered? Leave a comment or check us out at the links bel... -

Richard Dawkins Teaching Evolution to Religious Students
Dawkins teaching evolution to a year 11 (ages 14-15) class at Park High School, London. He answers several questions of the students, most of whom doubt evolution. -

The Amazing Evolution Of Spider-Man In Movies [Documentary]
Here is our amazing in depth evolution of Spider-Man in movies. Subscribe to our channel : http://goo.gl/ho3Hg6 Check Out These Other Amazing Videos: DOCU: Who Really is the Deadliest Marvel Superhero? https://youtu.be/hRX9Rz_G1EA DOCU: Batman V Superman: How Batman Can Beat Superman Even if He Loses https://youtu.be/rrJkw-aV560 No matter how many heroes may be re-imagined, rebooted, or replaced, and with more and more comic book superheroes being introduced every year, Spider-Man remains one of the most beloved, relatable, and recognizable around the world. Taking that kind of success and moving it to the big screen is harder than it sounds, as a few directors have already learned - with more lessons still coming. As Spider-Man makes his journey to the Marvel Cinematic Universe, what b... -

Evolution of Super Smash Bros. INTROS
The Super Smash Bros. series is the biggest video game crossover franchise. Today, we're going through the intro cutscenes of all games in the beloved series. Music Let's Brawl by Tonindo https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=GGtv5yRmWic Our YouTube Network: http://www.unionforgamers.com/apply?referral=z6prcktnosv1ai -

-

-

Pearl Jam - Do the Evolution
Music video by Pearl Jam performing Do The Evolution. (C) 1998 SONY BMG MUSIC ENTERTAINMENT
Proof of evolution that you can find on your body
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 3:55
- Updated: 17 Mar 2016
- views: 11992
- published: 17 Mar 2016
- views: 11992
How Evolution works
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 11:48
- Updated: 11 Jul 2013
- views: 2147750
- published: 11 Jul 2013
- views: 2147750
What is the Evidence for Evolution?
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 11:22
- Updated: 10 Oct 2014
- views: 992537
- published: 10 Oct 2014
- views: 992537
Evolution The Evolution of humans documentary 2014
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 44:56
- Updated: 29 Jan 2014
- views: 1508072
- published: 29 Jan 2014
- views: 1508072
10 Unsolved Mysteries Of Evolution
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 7:45
- Updated: 31 Dec 2015
- views: 2386684
- published: 31 Dec 2015
- views: 2386684
7 MYTHS You Still Believe About EVOLUTION
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 7:00
- Updated: 23 Jan 2016
- views: 916137
- published: 23 Jan 2016
- views: 916137
Evolution - What Darwin Never Knew - NOVA PBS Documentary
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 112:05
- Updated: 11 Jul 2012
- views: 1033084
- published: 11 Jul 2012
- views: 1033084
CAN WE BEAT THE HACKERS?! - Minecraft EVOLUTION #2 with Vikkstar & Woofless
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 18:41
- Updated: 20 Apr 2016
- views: 8312
- published: 20 Apr 2016
- views: 8312
The Evolution of the Parasitical Class: Past, Present and Future
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 35:07
- Updated: 19 Apr 2016
- views: 909
- published: 19 Apr 2016
- views: 909
What is Evolution?
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 8:53
- Updated: 10 Jan 2013
- views: 715008
- published: 10 Jan 2013
- views: 715008
Minecraft Evolution #7 - Un gioco rovinato... w/ Tech4play JacoRollo
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 10:48
- Updated: 20 Apr 2016
- views: 8027
- published: 20 Apr 2016
- views: 8027
EVOLUTION - GREAT TRANSFORMATIONS - NOVA - Discovery/History/Science (documentary)
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 56:39
- Updated: 01 Mar 2014
- views: 96554
- published: 01 Mar 2014
- views: 96554
Evolution: It's a Thing - Crash Course Biology #20
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 11:44
- Updated: 11 Jun 2012
- views: 650868
- published: 11 Jun 2012
- views: 650868
Evolution #23 z Hunterem
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 16:17
- Updated: 20 Apr 2016
- views: 7324
Bill Nye, Ken Ham Debate Creation vs. Evolution
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 150:18
- Updated: 22 Feb 2014
- views: 203494
- published: 22 Feb 2014
- views: 203494
The science of Human evolution
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 54:43
- Updated: 11 Jan 2015
- views: 194537
The 12 Days of Evolution - Complete Series!
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 18:04
- Updated: 28 Dec 2015
- views: 87869
- published: 28 Dec 2015
- views: 87869
Richard Dawkins Teaching Evolution to Religious Students
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 52:27
- Updated: 16 Nov 2014
- views: 1108018
- published: 16 Nov 2014
- views: 1108018
The Amazing Evolution Of Spider-Man In Movies [Documentary]
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 8:17
- Updated: 03 Apr 2016
- views: 2016
- published: 03 Apr 2016
- views: 2016
Evolution of Super Smash Bros. INTROS
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 8:00
- Updated: 19 Apr 2016
- views: 2590
- published: 19 Apr 2016
- views: 2590
Evolution - Part 2 of 7 - Great Transformations (PBS Documentary)[HD 720p]
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 56:38
- Updated: 28 Jul 2012
- views: 202438
Korn - Evolution
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 3:46
- Updated: 03 Apr 2008
- views: 12719663
Pearl Jam - Do the Evolution
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 4:01
- Updated: 25 Oct 2009
- views: 14582922
- published: 25 Oct 2009
- views: 14582922
-

-

-

Pro Evolution Soccer 2016 myClub_20160420114252
Q pasada PES 2016 myClub https://store.playstation.com/#!/es-es/tid=CUSA03663_00 -

SynthRar - EVOLUTION
Ma musique en ligne (téléchargement gratuit) MUSIC FREE DOWNLOAD https://soundcloud.com/synthrar http://synthrar.wix.com/synthrar ¤ Encourager ma Création Musicale ¤ -

-

-

DIE EVOLUTION DER ROLLENSPIELE Let's Play Evoland #01
-

Swiss Replica Watches Replica Breitling Chronomat Evolution SSRG White Numeral Dial on Bracelet A775
http://www.puretimeclone.com -

Swiss Replica Watches Replica Breitling Chronomat Evolution SSRG Blue Numeral Dial A7750 sku0785
http://www.puretimeclone.com -

Swiss Replica Watches Replica Breitling Chronomat Evolution SSRG White Dial A7750 sku0789
http://www.puretimeclone.com -

Swiss Replica Watches Replica Breitling Chronomat Evolution SSRG Blue Stick Dial on Bracelet A7750
http://www.puretimeclone.com -

Pro Evolution Soccer 2016_بيس 2016 بطولة يورو امم اوروبا جولة التصفيات الاولى
-

Swiss Replica Watches Replica Breitling Chronomat Evolution SSRG Black Numeral Dial A7750 sku0794
http://www.puretimeclone.com -

Swiss Replica Watches Replica Breitling Chronomat Evolution SSRG Black Numeral Dial on Bracelet A775
http://www.puretimeclone.com -

Swiss Replica Watches Replica Breitling Chronomat Evolution SSRG Blue Dial A7750 sku0783
http://www.puretimeclone.com -

Swiss Replica Watches Replica Breitling Chronomat Evolution SS White Numeral Dial on Brown Leather S
http://www.puretimeclone.com -

Swiss Replica Watches Replica Breitling Chronomat Evolution SS White Stick Dial on Brown Leather Str
http://www.puretimeclone.com -

Swiss Replica Watches Replica Breitling Chronomat Evolution SS RG Black Dial A7750 sku0792
http://www.puretimeclone.com -

Swiss Replica Watches Replica Breitling Chronomat Evolution SS RG White Numeral Dial A7750 sku0793
http://www.puretimeclone.com -

ROBOT... UNICORN... PERO QUE? - Robot Unicorn Attack Evolution
Sin comentarios, vean por ustedes mismos El juego http://www.adultswim.com/games/web/robot-unicorn-attack-evolution La musica https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=lWqJTKdznaM https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=NMVZ6hAuwNI tuiter: https://twitter.com/Electrofantasia feisbuk: https://www.facebook.com/electrofantasia/?ref=aymt_homepage_panel gugel plus: https://plus.google.com/u/0/b/102012827134350644523/102012827134350644523/posts Sugerencias y opiniones en los comentarios... dale like si the ha gustado y suscribete para mas -

. love your self lyrics . perfect girl evolution شارة دراما
شارة دراما perfect girl evolution طلب احد المتابعين -

Swiss Replica Watches Replica Breitling Chronomat Evolution SS Grey Stick Dial on Black Leather Stra
http://www.puretimeclone.com -

Swiss Replica Watches Replica Breitling Chronomat Evolution SS Grey Stick Dial on Bracelet A7750 sku
http://www.puretimeclone.com
Pro Evolution Soccer 2016
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 1:57
- Updated: 20 Apr 2016
- views: 0
Pro Evolution Soccer 2016_20160420184105
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 0:55
- Updated: 20 Apr 2016
- views: 0
Pro Evolution Soccer 2016 myClub_20160420114252
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 2:48
- Updated: 20 Apr 2016
- views: 0
- published: 20 Apr 2016
- views: 0
SynthRar - EVOLUTION
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 2:46
- Updated: 20 Apr 2016
- views: 2
- published: 20 Apr 2016
- views: 2
Pro Evolution Soccer 2016 Scorpion kick miss
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 0:27
- Updated: 20 Apr 2016
- views: 1
🐣Chicken Evolution🐣
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 9:46
- Updated: 20 Apr 2016
- views: 5
DIE EVOLUTION DER ROLLENSPIELE Let's Play Evoland #01
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 15:52
- Updated: 20 Apr 2016
- views: 0
- published: 20 Apr 2016
- views: 0
Swiss Replica Watches Replica Breitling Chronomat Evolution SSRG White Numeral Dial on Bracelet A775
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 1:19
- Updated: 20 Apr 2016
- views: 0
Swiss Replica Watches Replica Breitling Chronomat Evolution SSRG Blue Numeral Dial A7750 sku0785
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 1:25
- Updated: 20 Apr 2016
- views: 0
Swiss Replica Watches Replica Breitling Chronomat Evolution SSRG White Dial A7750 sku0789
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 1:36
- Updated: 20 Apr 2016
- views: 0
Swiss Replica Watches Replica Breitling Chronomat Evolution SSRG Blue Stick Dial on Bracelet A7750
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 1:53
- Updated: 20 Apr 2016
- views: 0
Pro Evolution Soccer 2016_بيس 2016 بطولة يورو امم اوروبا جولة التصفيات الاولى
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 15:00
- Updated: 20 Apr 2016
- views: 0
- published: 20 Apr 2016
- views: 0
Swiss Replica Watches Replica Breitling Chronomat Evolution SSRG Black Numeral Dial A7750 sku0794
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 1:27
- Updated: 20 Apr 2016
- views: 0
Swiss Replica Watches Replica Breitling Chronomat Evolution SSRG Black Numeral Dial on Bracelet A775
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 1:54
- Updated: 20 Apr 2016
- views: 0
Swiss Replica Watches Replica Breitling Chronomat Evolution SSRG Blue Dial A7750 sku0783
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 1:40
- Updated: 20 Apr 2016
- views: 0
Swiss Replica Watches Replica Breitling Chronomat Evolution SS White Numeral Dial on Brown Leather S
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 1:47
- Updated: 20 Apr 2016
- views: 0
Swiss Replica Watches Replica Breitling Chronomat Evolution SS White Stick Dial on Brown Leather Str
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 1:05
- Updated: 20 Apr 2016
- views: 0
Swiss Replica Watches Replica Breitling Chronomat Evolution SS RG Black Dial A7750 sku0792
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 1:35
- Updated: 20 Apr 2016
- views: 0
Swiss Replica Watches Replica Breitling Chronomat Evolution SS RG White Numeral Dial A7750 sku0793
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 1:43
- Updated: 20 Apr 2016
- views: 0
ROBOT... UNICORN... PERO QUE? - Robot Unicorn Attack Evolution
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 10:39
- Updated: 20 Apr 2016
- views: 0
- published: 20 Apr 2016
- views: 0
. love your self lyrics . perfect girl evolution شارة دراما
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 1:51
- Updated: 20 Apr 2016
- views: 65
- published: 20 Apr 2016
- views: 65
Swiss Replica Watches Replica Breitling Chronomat Evolution SS Grey Stick Dial on Black Leather Stra
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 1:36
- Updated: 20 Apr 2016
- views: 0
Swiss Replica Watches Replica Breitling Chronomat Evolution SS Grey Stick Dial on Bracelet A7750 sku
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 1:20
- Updated: 20 Apr 2016
- views: 0
-

CD9 - EVOLUTION (álbum completo)
"Evolution" 1. Déjà Vu 0:00 2. I Feel Alive (Spanish Version) 3:05 3. Placer Culposo 6:29 4. Lo Que Te Hace Perfecta 9:44 5. Shakespeare y Serenatas 13:19 6. Error Perfecto 16:47 7. Dime 20:04 8. Peligrosa 23:19 9. Uno Mismo 26:35 10. A Tu Lado 29:55 11. Own the Night 33:30 12. I Feel Alive (English Version) 36:43 13. Guilty Pleasure 40:06 14. Jaw Dropper 43:19 15. Best Bad Move 46:36 -

Evolution 2001 Movie
A firefighting cadet two college professors, and a geeky sexy government scientist work against an alien organism that has been rapidly evolving ever since its arrival on Earth inside a meteor. -

Ape To Man: Evolution Documentary History Channel
Subscribe now to ScienceNET! Apologies for the bad quality. It's a tremendous documentary so I still wanted to post it. Couldn't find a better version. Follow us on Twitter: http://twitter.com/ScienceNetDaily Like us on Facebook: http://www.facebook.com/sciencenetdaily Follow us on Google+: http://plus.google.com/114075690126383757791 Instagram: sciencenetdaily -

EVOLUTION - HOW EYES EVOLVED - NOVA - Discovery/History/Science (documentary) HD
evolution - how eyes evolved - nova (documentary) HD. thanks for watching. history life discovery science technology tech learning education national nature geographic earth planet channel universe culture civilization civilisation archaeology ancient discoveries creation creationism darwin caveman neanderthal ape human humans man evolve animal animals prehistoric dinosaur dinosaurs biology zoology eye sight seeing vision predator prey -

Evolution The Greatest Lie EVER Told !!! Evolution Debunked by White Rabbit of The CTN
Evolution is the greatest lie ever told to humanity! So many blindly believe this lie because they have been brainwashed to believe it is scientific fact! When in reality science proves it to be wrong! In this video I share with you an awesome video from CTN team member white rabbit who debunks this supposed fact! Please share this video! God Bless and STAY VIGILANT !!! For more info on this topic - https://www.youtube.com/playlist?list=PLz9SyBDerhgjfzXDQf7RobY2md0jXAR57 SUBSCRIBE TO TVC YouTube Channels: TVC Biblical Studies Channel Please Subscribe and Join us! https://www.youtube.com/channel/UCPgtwcH4mWP8KHpPwy54QwQ The Godly Bros https://www.youtube.com/channel/UCfxyfS98YVHRfRFhh_QlXQw TVC Backup Channel https://www.youtube.com/channel/UCHKHC9bVGr49vuv1WyPp_5Q TVC Healthy Livi... -

Why Evolution is True and Why Many People Still Don't Believe It (Jerry Coyne, 2012)
Jerry Coyne, a professor of Ecology and Evolution at the University of Chicago and author of the seminal book, Why Evolution is True, is one of the world's most eloquent defenders of evolutionary science in the face of legal, religious, and cultural opposition. In this talk, Coyne explored the evidence for evolution, why Americans are so resistant to accepting the theory, and what can be done to make the country more evolution-friendly. His book, Why Evolution is True:http://www.amazon.com/Why-Evolution-True-Jerry-Coyne/dp/0143116649/ref=tmm_pap_title_0 and blog: http://whyevolutionistrue.wordpress.com/ Frequently asked questions about evolution: http://www.pbs.org/wgbh/evolution/library/faq/index.html Evolution: Fact and Theory: http://www.actionbioscience.org/evolution/lenski.html E... -

Evolution: What the Fossils Say (by Donald Prothero)
Is evolution a fact? How do the claims of creationists stack up against the fossil record and the actual science? Dr. Donald Prothero presents the evidence in a presentation based on his 2007 book (and more recent findings). Prothero is a paleontologist, geologist, author and science educator. He holds a Ph.D in geological sciences from Columbia University, and he has authored over 300 scientific papers and 30 books. He is currently a research associate in vertebrate paleontology at the Natural History Museum of Los Angeles County. www.donaldprothero.com -

-

FIRE SHARK!! || Hungry Shark Evolution - Ep 22 HD
Out of all the newly released sharks I have to say this is the best. It can fly, breathe fire and also launch a huge meteor strike... whats not to love??? ❤❤❤ For Exclusive Updates you can find them all here ❤❤❤ ❤ Facebook: http://on.fb.me/1CSf5Yd ❤ Instagram: http://bit.ly/1Uavyxc ❤ Twitter: http://bit.ly/16adMa1 ❤ Twitch: www.twitch.tv/agamingbeaver Take control of a very Hungry Shark in this action packed aquatic adventure. Survive as long as possible by eating everything that gets in your way! Many different sharks to collect and evolve, including the Hammerhead, Great White and Megalodon! -

History BBc Documentary : The evolution of man 2015 - Full Documentary
History Documentary : The evolution of man 2015 -

EVOLUTION - THE EVOLUTION OF SIZE - NOVA - Discovery/History/Science (documentary) HD
evolution - the evolution of size - nova (documentary) HD. thanks for watching. history life discovery science technology tech learning education national nature geographic earth planet channel universe culture civilization civilisation archaeology ancient discoveries creation creationism darwin caveman neanderthal ape human humans man evolve animal animals prehistoric dinosaur dinosaurs biology zoology big large giant bigger biggest small -

Evolution of First Levels in Mario games
The Mario series is considered to be the King of Platformers for its amazing and innovative level design. In this episode of 'Evolution of Gaming' we're going through the first level of every Mario game. Music To the Stars by Stephan Wells, Laura Intravia https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=xii-VZmfhvQ Our YouTube Network: http://www.unionforgamers.com/apply?referral=z6prcktnosv1ai -

Information, Evolution, and intelligent Design - With Daniel Dennett
Daniel Dennett explores the first steps towards a unified theory of information, through common threads in the convergence of evolution, learning, and engineering. Subscribe for regular science talks: http://bit.ly/RiSubscRibe Watch the Q&A; now: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=beKC_7rlTuw The concept of information is fundamental to all areas of science, and ubiquitous in daily life in the Internet Age. However, it is still not well understood despite being recognised for more than 40 years. In this talk, Daniel Dennett explores steps towards a unified theory of information, through common threads in evolution, learning, and engineering. This event was the first in a series on the theme of 'Convergence', exploring the links between neuroscience, philosophy and artificial intelligence. If... -

FIRST EVOLUTION! [4] - PIXELMON W/Ash & Amy!
Hello Everybody! Welcome to a new PIXELMON series! In this awesome adventure Ash & Amy will be joining me! If you don't know much about pixelmon let me explain: Pixelmon is an awesome mod that enables players to play pokemon in a minecraft world! Letting players train, battle and evolve Pokemon! Get 15% off your very own Pixelmon server over at Nitrous Networks using promo code Pixelmon - https://nitrous-networks.com/minecraft Squiddy T-Shirts UK - http://iballisticsquid.spreadshirt.co.uk/ Squiddy T-Shirts US - http://iballisticsquid.spreadshirt.com Subscribe - http://www.youtube.com/iballisticsquid Twitter - https://twitter.com/iBallisticSquid Facebook - http://www.facebook.com/pages/IBallisticSquid/164520893684505 -

CD9 - EVOLUTION (álbum completo)
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 49:41
- Updated: 20 Mar 2016
- views: 8225
- published: 20 Mar 2016
- views: 8225
Evolution 2001 Movie
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 101:42
- Updated: 26 Dec 2013
- views: 228101
- published: 26 Dec 2013
- views: 228101
Ape To Man: Evolution Documentary History Channel
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 89:55
- Updated: 19 Apr 2014
- views: 2299233
- published: 19 Apr 2014
- views: 2299233
EVOLUTION - HOW EYES EVOLVED - NOVA - Discovery/History/Science (documentary) HD
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 44:56
- Updated: 01 Mar 2014
- views: 118790
- published: 01 Mar 2014
- views: 118790
Evolution The Greatest Lie EVER Told !!! Evolution Debunked by White Rabbit of The CTN
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 39:17
- Updated: 12 Nov 2014
- views: 80108
- published: 12 Nov 2014
- views: 80108
Why Evolution is True and Why Many People Still Don't Believe It (Jerry Coyne, 2012)
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 65:33
- Updated: 09 Jun 2012
- views: 386420
- published: 09 Jun 2012
- views: 386420
Evolution: What the Fossils Say (by Donald Prothero)
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 81:31
- Updated: 05 Nov 2015
- views: 57192
- published: 05 Nov 2015
- views: 57192
David Berlinski Explains Problems With Evolution.
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 37:42
- Updated: 10 Aug 2013
- views: 67334
FIRE SHARK!! || Hungry Shark Evolution - Ep 22 HD
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 26:43
- Updated: 07 Apr 2016
- views: 65409
- published: 07 Apr 2016
- views: 65409
History BBc Documentary : The evolution of man 2015 - Full Documentary
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 49:14
- Updated: 28 Jan 2015
- views: 73380
EVOLUTION - THE EVOLUTION OF SIZE - NOVA - Discovery/History/Science (documentary) HD
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 44:56
- Updated: 01 Mar 2014
- views: 56345
- published: 01 Mar 2014
- views: 56345
Evolution of First Levels in Mario games
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 24:19
- Updated: 09 Mar 2016
- views: 2130
- published: 09 Mar 2016
- views: 2130
Information, Evolution, and intelligent Design - With Daniel Dennett
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 61:45
- Updated: 13 May 2015
- views: 59674
- published: 13 May 2015
- views: 59674
FIRST EVOLUTION! [4] - PIXELMON W/Ash & Amy!
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 30:57
- Updated: 14 Apr 2016
- views: 8865
- published: 14 Apr 2016
- views: 8865
Creationism Vs Evolution Debate Ken Ham And Bill Nye 2014[Full]
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 152:19
- Updated: 27 Mar 2014
- views: 154983
- Playlist
- Chat
- Playlist
- Chat

Proof of evolution that you can find on your body
- Report rights infringement
- published: 17 Mar 2016
- views: 11992

How Evolution works
- Report rights infringement
- published: 11 Jul 2013
- views: 2147750

What is the Evidence for Evolution?
- Report rights infringement
- published: 10 Oct 2014
- views: 992537

Evolution The Evolution of humans documentary 2014
- Report rights infringement
- published: 29 Jan 2014
- views: 1508072

10 Unsolved Mysteries Of Evolution
- Report rights infringement
- published: 31 Dec 2015
- views: 2386684

7 MYTHS You Still Believe About EVOLUTION
- Report rights infringement
- published: 23 Jan 2016
- views: 916137

Evolution - What Darwin Never Knew - NOVA PBS Documentary
- Report rights infringement
- published: 11 Jul 2012
- views: 1033084

CAN WE BEAT THE HACKERS?! - Minecraft EVOLUTION #2 with Vikkstar & Woofless
- Report rights infringement
- published: 20 Apr 2016
- views: 8312

The Evolution of the Parasitical Class: Past, Present and Future
- Report rights infringement
- published: 19 Apr 2016
- views: 909

What is Evolution?
- Report rights infringement
- published: 10 Jan 2013
- views: 715008

Minecraft Evolution #7 - Un gioco rovinato... w/ Tech4play JacoRollo
- Report rights infringement
- published: 20 Apr 2016
- views: 8027

EVOLUTION - GREAT TRANSFORMATIONS - NOVA - Discovery/History/Science (documentary)
- Report rights infringement
- published: 01 Mar 2014
- views: 96554

Evolution: It's a Thing - Crash Course Biology #20
- Report rights infringement
- published: 11 Jun 2012
- views: 650868

Evolution #23 z Hunterem
- Report rights infringement
- published: 20 Apr 2016
- views: 7324
- Playlist
- Chat

Pro Evolution Soccer 2016
- Report rights infringement
- published: 20 Apr 2016
- views: 0

Pro Evolution Soccer 2016_20160420184105
- Report rights infringement
- published: 20 Apr 2016
- views: 0

Pro Evolution Soccer 2016 myClub_20160420114252
- Report rights infringement
- published: 20 Apr 2016
- views: 0

SynthRar - EVOLUTION
- Report rights infringement
- published: 20 Apr 2016
- views: 2

Pro Evolution Soccer 2016 Scorpion kick miss
- Report rights infringement
- published: 20 Apr 2016
- views: 1

🐣Chicken Evolution🐣
- Report rights infringement
- published: 20 Apr 2016
- views: 5

DIE EVOLUTION DER ROLLENSPIELE Let's Play Evoland #01
- Report rights infringement
- published: 20 Apr 2016
- views: 0

Swiss Replica Watches Replica Breitling Chronomat Evolution SSRG White Numeral Dial on Bracelet A775
- Report rights infringement
- published: 20 Apr 2016
- views: 0

Swiss Replica Watches Replica Breitling Chronomat Evolution SSRG Blue Numeral Dial A7750 sku0785
- Report rights infringement
- published: 20 Apr 2016
- views: 0

Swiss Replica Watches Replica Breitling Chronomat Evolution SSRG White Dial A7750 sku0789
- Report rights infringement
- published: 20 Apr 2016
- views: 0

Swiss Replica Watches Replica Breitling Chronomat Evolution SSRG Blue Stick Dial on Bracelet A7750
- Report rights infringement
- published: 20 Apr 2016
- views: 0

Pro Evolution Soccer 2016_بيس 2016 بطولة يورو امم اوروبا جولة التصفيات الاولى
- Report rights infringement
- published: 20 Apr 2016
- views: 0

Swiss Replica Watches Replica Breitling Chronomat Evolution SSRG Black Numeral Dial A7750 sku0794
- Report rights infringement
- published: 20 Apr 2016
- views: 0

Swiss Replica Watches Replica Breitling Chronomat Evolution SSRG Black Numeral Dial on Bracelet A775
- Report rights infringement
- published: 20 Apr 2016
- views: 0
- Playlist
- Chat

CD9 - EVOLUTION (álbum completo)
- Report rights infringement
- published: 20 Mar 2016
- views: 8225

Evolution 2001 Movie
- Report rights infringement
- published: 26 Dec 2013
- views: 228101

Ape To Man: Evolution Documentary History Channel
- Report rights infringement
- published: 19 Apr 2014
- views: 2299233

EVOLUTION - HOW EYES EVOLVED - NOVA - Discovery/History/Science (documentary) HD
- Report rights infringement
- published: 01 Mar 2014
- views: 118790

Evolution The Greatest Lie EVER Told !!! Evolution Debunked by White Rabbit of The CTN
- Report rights infringement
- published: 12 Nov 2014
- views: 80108

Why Evolution is True and Why Many People Still Don't Believe It (Jerry Coyne, 2012)
- Report rights infringement
- published: 09 Jun 2012
- views: 386420

Evolution: What the Fossils Say (by Donald Prothero)
- Report rights infringement
- published: 05 Nov 2015
- views: 57192

David Berlinski Explains Problems With Evolution.
- Report rights infringement
- published: 10 Aug 2013
- views: 67334

FIRE SHARK!! || Hungry Shark Evolution - Ep 22 HD
- Report rights infringement
- published: 07 Apr 2016
- views: 65409

History BBc Documentary : The evolution of man 2015 - Full Documentary
- Report rights infringement
- published: 28 Jan 2015
- views: 73380

EVOLUTION - THE EVOLUTION OF SIZE - NOVA - Discovery/History/Science (documentary) HD
- Report rights infringement
- published: 01 Mar 2014
- views: 56345

Evolution of First Levels in Mario games
- Report rights infringement
- published: 09 Mar 2016
- views: 2130

Information, Evolution, and intelligent Design - With Daniel Dennett
- Report rights infringement
- published: 13 May 2015
- views: 59674

FIRST EVOLUTION! [4] - PIXELMON W/Ash & Amy!
- Report rights infringement
- published: 14 Apr 2016
- views: 8865
-
Lyrics list:text lyricsplay full screenplay karaoke
Victoria Wood dead: Comedian dies aged 62 from cancer
Edit The Independent 20 Apr 2016Death Toll In Kabul Suicide Bombing Rises Overnight to 64
Edit WorldNews.com 20 Apr 2016Mass killer Breivik’s human rights violated in prison
Edit The Irish Times 20 Apr 2016For Workers It Is The Beginning Of History, Not The End
Edit WorldNews.com 20 Apr 2016Houston flooding: 7 dead, 1,200 rescued -- and more rain to come
Edit CNN 20 Apr 2016Annual Mineral Resources and Ore Reserves Statement (Evolution Mining Limited)
Edit Public Technologies 21 Apr 2016March 2016 Quarterly Report (Evolution Mining Limited)
Edit Public Technologies 21 Apr 2016How do these monkey teeth fill in gaps in American primate evolution?
Edit The Christian Science Monitor 21 Apr 2016North Carolina's transgender bathroom law could be overturned very soon
Edit Business Insider 21 Apr 2016Soon, a policy to regulate app-based cab services
Edit The Hindu 21 Apr 2016War an outdated way to settle differences: Kamal
Edit The Hindu 21 Apr 2016NCI Launches a Platform to Submit Research Ideas for Cancer Moonshot Initiative (USC Norris Comprehensive Cancer Center)
Edit Public Technologies 21 Apr 2016War is an outdated way to settle differences: Kamal
Edit The Hindu 21 Apr 2016Andreas Ivanschitz finds his spot, Seattle Sounders reap the rewards (Seattle Sounders FC)
Edit Public Technologies 21 Apr 2016Pacific Magazines & Skylanders partner for augmented reality cover (MPA - Magazine Publishers of Australia)
Edit Public Technologies 21 Apr 2016How Shakespeare’s works were nearly lost to us
Edit New York Post 21 Apr 2016EVOLUTION OF THE FOOTBALLER: EPISODE ONE (Norwich City FC plc)
Edit Public Technologies 20 Apr 2016Ancient DNA reveals evolution of giant bears in the Americas (The University of Adelaide)
Edit Public Technologies 20 Apr 2016- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- Next page »







