- published: 12 Dec 2009
- views: 347928
-
remove the playlistStem Cell
- remove the playlistStem Cell
- published: 10 Sep 2013
- views: 255588
- published: 30 Apr 2013
- views: 352032
- published: 15 Jan 2014
- views: 55395
- published: 14 Jun 2011
- views: 212980
- published: 27 Apr 2015
- views: 55485
- published: 16 Jul 2014
- views: 42384
- published: 29 Sep 2015
- views: 11677
- published: 25 Mar 2011
- views: 184829
- published: 16 Jul 2015
- views: 46984

Stem cells are biological cells found in all multicellular organisms, that can divide (through mitosis) and differentiate into diverse specialized cell types and can self-renew to produce more stem cells. In mammals, there are two broad types of stem cells: embryonic stem cells, which are isolated from the inner cell mass of blastocysts, and adult stem cells, which are found in various tissues. In adult organisms, stem cells and progenitor cells act as a repair system for the body, replenishing adult tissues. In a developing embryo, stem cells can differentiate into all the specialized cells (these are called pluripotent cells), but also maintain the normal turnover of regenerative organs, such as blood, skin, or intestinal tissues.
There are three sources of autologous adult stem cells: 1) Bone marrow, which requires extraction by harvesting, that is, drilling into bone (typically the femur or iliac crest), 2) Adipose tissue (lipid cells), which requires extraction by liposuction, and 3) Blood, which requires extraction through pheresis, wherein blood is drawn from the donor (similar to a blood donation), passed through a machine that extracts the stem cells and returns other portions of the blood to the donor. Stem cells can also be taken from umbilical cord blood. Of all stem cell types, autologous harvesting involves the least risk. By definition, autologous cells are obtained from one's own body, just as one may bank his or her own blood for elective surgical procedures.
This article is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported License, which means that you can copy and modify it as long as the entire work (including additions) remains under this license.
Stem may refer to:
STEM may refer to:
This article is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported License, which means that you can copy and modify it as long as the entire work (including additions) remains under this license.
Cell(s) may refer to:
This article is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported License, which means that you can copy and modify it as long as the entire work (including additions) remains under this license.
- Loading...

-
 6:15
6:15What are stem cells? How can they be used for medical benefit?
What are stem cells? How can they be used for medical benefit?What are stem cells? How can they be used for medical benefit?
What are stem cells? - An short educational film by the Irish Stem Cell Foundation Stem cells are master cells of the body — want to learn more? Visit www.irishstemcellfoundation.org ISCF is an independent not-for-profit organisation whose primary objective is to educate about stem cells, their basic biology and the research and therapies using them. The Foundation will initially focus on education outreach programs, hoping to address the growing problem of bogus stem cell scams being offered to Irish patients over the internet. The Foundation will also assist the development of Irish policy and legislature in this area of medicine and science, ensuring Ireland is informed. The Foundation consists of a broad range of people including Irish doctors, scientists, patient advocates, educators, bioethicists and other associated parties seeking to expand and develop the Irish public's understanding of stem cells. -
 4:11
4:11What are stem cells? - Craig A. Kohn
What are stem cells? - Craig A. KohnWhat are stem cells? - Craig A. Kohn
View full lesson: http://ed.ted.com/lessons/what-are-stem-cells-craig-a-kohn Is personalized medicine for individual bodies in our future? Possibly -- with the use of stem cells, undifferentiated cells with the power to become any tissue in our bodies. Craig A. Kohn describes the role of these incredible, transforming cells and how scientists are harnessing their medical potential. Lesson by Craig A. Kohn, animation by Qa'ed Mai. -
 3:48
3:48Stem Cells
Stem CellsStem Cells
Hank gives you the facts on stem cells - what they are, what they're good for, where they come from, and how they're used in medicine. Like SciShow? Want to help support us, and also get things to put on your walls, cover your torso and hold your liquids? Check out our awesome products over at DFTBA Records: http://dftba.com/artist/52/SciShow -- Looking for SciShow elsewhere on the internet? Facebook: http://www.facebook.com/scishow Twitter: http://www.twitter.com/scishow Tumblr: http://scishow.tumblr.com References for this episode can be found in the Google document here: http://dft.ba/-5DcW -
 7:53
7:53Stem Cells
Stem Cells -
 46:19
46:1923. Stem Cells
23. Stem Cells23. Stem Cells
MIT 7.013 Introductory Biology, Spring 2011 View the complete course: http://ocw.mit.edu/7-013S11 Instructor: Hazel Sive Professor Sive discusses cell fate and differentiation, followed by stem cells. The lecture focuses on defining stem cells, highlighting the key discoveries in research, and discussing therapeutics. License: Creative Commons BY-NC-SA More information at http://ocw.mit.edu/terms More courses at http://ocw.mit.edu -
 15:53
15:53A Stem Cell Story
A Stem Cell StoryA Stem Cell Story
What are stem cells, where do they come from, and what do we really know about them? An award-winning introduction to the world of stem cell research. Innovative hand-drawn animation, beautiful cell photography and documentary interviews capture the fascination and complexity of this cutting-edge area of science. Related resources and lots more stem cell info at http://www.eurostemcell.org/films. If you would like to comment or leave feedback, please do so there. Best TV/video production, Tromsø Science Media Festival. Best short film, Scinema (Australia). Captions in 12 languages. -
 3:17
3:17WHAT CAN STEM CELLS DO?
WHAT CAN STEM CELLS DO?WHAT CAN STEM CELLS DO?
You may have heard of stem cells before, but there is a lot of mystery about what they actually … do. Why is this such a promising new field? Click here to see more videos: http://www.m301.me/lifenoggin Life Noggin is a weekly animated educational series. Whether it's science, pop culture, history or art, we explore it all and have a ton of fun doing it. Follow Us! https://twitter.com/LifeNoggin https://facebook.com/LifeNoggin https://www.LifeNoggin Life Noggin Team: Animation & Designed by: http://www.krofl.com Voiced by: http://youtube.com/patdoesit Written by: https://www.youtube.com/coconutcab Produced by: http://www.twitter.com/IanDokie Sources: Bone marrow transplant: http://www.cancer.net/navigating-cancer-care/how-cancer-treated/bone-marrowstem-cell-transplantation/what-stem-cellbone-marrow-transplantation http://www.nlm.nih.gov/medlineplus/ency/article/003009.htm Gene Expression: http://www.nature.com/scitable/topicpage/gene-expression-14121669 http://www.pa.msu.edu/sciencet/ask_st/060293.html Stem Cells: http://stemcells.nih.gov/info/basics/pages/basics3.aspx http://www.medicalnewstoday.com/info/stem_cell/ -
 2:46
2:46PhytoScience double Stem Cell Philippines Review
PhytoScience double Stem Cell Philippines ReviewPhytoScience double Stem Cell Philippines Review
Experience the Magic of PhytoScience Double Stem Cell Philippines. FB: https://www.facebook.com/PhytosciencePhilippines 2013 Best Selling Double Stem Cell Product in Malaysia and Thailand Now in the Philippines! See Visible Results in Just 14 Days! PHYTOSCIENCE DOUBLE STEM CELL removes the appearance of age lines and restore smooth, radiant, youthful looking skin! PHYTOSCIENCE DOUBLE STEM CELL used A species of apple called the Uttwiler Spatlauber from Northern Switzerland is being heralded as the latest anti-ageing breakthrough. I kid you not – A-list stars including Jennifer Aniston, Michelle Obama and Gwyneth Paltrow have already been reaping the benefits. Product efficacy Delays ageing process Enhances health and vitality Repairs and rejuvenates cell Maintains acid-base balance within body Anti-oxidation Boosts immune system Benefits of Double Stemcell Enhance physical stamina and energy level Repair and regeneration of cells Rejuvenates and activates body cells to raise energy and improve vitality Regulate PH level in our body Anti – Oxidant Improve body immunity system Refine skin texture and improve complexion Delay aging process No side effects - safe, natural and convenient product Pure Vegetarian (Made of only Apple and Grape) Click Here to ORDER PhytoScience Double Stem Cell Therapy Call/TXT/ Viber me @ 09157379217 http://bit.ly/Doublestemcell Are you interested to Become Double Stem Cell Mobile Stockist and Distributors? Contact US ASAP. -
 2:13
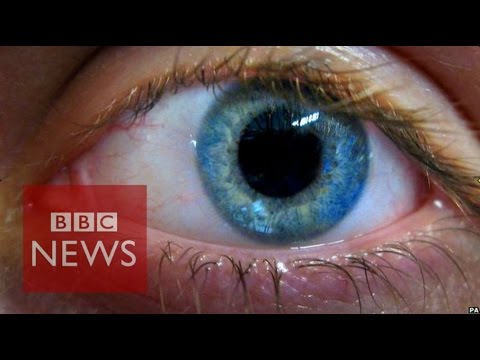
2:13Stem cell cure for blindness tested - BBC News
Stem cell cure for blindness tested - BBC NewsStem cell cure for blindness tested - BBC News
Surgeons in London have used human embryonic stem cells in a pioneering attempt to cure blindness. Cells derived from a donated early embryo were implanted into the retina of a 60-year-old woman with age-related macular degeneration - the most common cause of blindness in the UK. Fergus Walsh reports. Subscribe to BBC News HERE http://bit.ly/1rbfUog Check out our website: http://www.bbc.com/news Facebook: http://www.facebook.com/bbcworldnews Twitter: http://www.twitter.com/bbcworld Instagram: http://instagram.com/bbcnews -
 6:18
6:18Stem Cell Therapy Injections
Stem Cell Therapy InjectionsStem Cell Therapy Injections
Stem Cell therapy, is one form of Comprehensive Prolotherapy available for arthritis treatment, and other chronic pain conditions at Caring Medical and Rehabilitation Services. Our same-day procedure utilizes a person's own mesenchymal stem cells from bone marrow or fat cells to treat degenerated joints. In this video, the stem cell therapy treatment is demonstrated on an athlete with severe osteoarthritis of the knee, by Ross Hauser, MD. Dr. Hauser has specialized in comprehensive Prolotherapy and Orthobiologic treatments since 1993 and treated tens of thousands of patients with excellent success, even patients who have failed surgery, knee replacement, or other treatments for arthritis and pain. To make an appointment with one of our specialists or for an opinion on your case and to learn more about our Stem Cell Prolotherapy, visit us at http://www.caringmedical.com/stem-cell-therapy/ -
 1:07
1:07Stem Cell Animation
Stem Cell AnimationStem Cell Animation
-
 4:09
4:09Why Are Stem Cells So Important?
Why Are Stem Cells So Important?Why Are Stem Cells So Important?
Stem cell research is still very controversial, so why do we want to use stem cells in the first place? Why are they so useful, and what can they do? Read More: Researchers Grow Tiny Beating Human Hearts From Stem Cells http://www.popsci.com/researchers-grow-first-ever-beating-hearts-stem-cells "Stem cells, the jack-of-all-trades building blocks of human tissues, have yet another application in biology research: scientists have been able to grow them into beating cardiac tissue." Key Moments in the Stem-Cell Debate http://www.npr.org/templates/story/story.php?storyId=5252449 "The first embryonic stem cells were isolated in mice in 1981. But it wasn't until 1998 that researchers managed to derive stem cells from human embryos. That kicked into full gear an ethical debate that continues to this day." Stem cell timeline: The history of a medical sensation https://www.newscientist.com/article/dn24970-stem-cell-timeline-the-history-of-a-medical-sensation/ "Stem cells are the cellular putty from which all tissues of the body are made. Ever since human embryonic stem cells were first grown in the lab, researchers have dreamed of using them to repair damaged tissue or create new organs, but such medical uses have also attracted controversy." ____________________ DNews is dedicated to satisfying your curiosity and to bringing you mind-bending stories & perspectives you won't find anywhere else! New videos twice daily. Watch More DNews on TestTube http://testtube.com/dnews Subscribe now! http://www.youtube.com/subscription_center?add_user=dnewschannel DNews on Twitter http://twitter.com/dnews Trace Dominguez on Twitter https://twitter.com/tracedominguez Julia Wilde on Twitter https://twitter.com/julia_sci DNews on Facebook https://facebook.com/DiscoveryNews DNews on Google+ http://gplus.to/dnews Discovery News http://discoverynews.com Download the TestTube App: http://testu.be/1ndmmMq -
 3:57
3:57What is StemCell - Hindi
What is StemCell - Hindi -
 17:54
17:54Stem cell therapy -- beyond the headlines: Timothy Henry at TEDxGrandForks
Stem cell therapy -- beyond the headlines: Timothy Henry at TEDxGrandForksStem cell therapy -- beyond the headlines: Timothy Henry at TEDxGrandForks
There is considerable excitement about the use of stem cells for cardiovascular disease. Stem cells are unspecialized cells with the unique property to self-renew or make copies of themselves and to differentiate into specialized cells. The goal of stem cell therapy is to enhance the body's natural process of regeneration. There are a considerable number of stem cells currently under investigation for patients with heart attacks, angina, heart failure, and peripheral arterial disease. We have made considerable progress but have many questions left to answer. Timothy Henry, MD, FACC, is Chief of Cardiology at Cedars Sinai Heart Institute in Los Angeles, California. Dr. Henry earned his bachelor's degree at the University of North Dakota, graduated from medical school at University of California, San Francisco, in 1982, and was chief medicine resident from 1982--1986 at University of Colorado Health Sciences Center. He completed his training as a cardiology fellow, chief cardiology fellow, and interventional cardiology fellow at University of Minnesota in 1991. His research interests include interventional cardiology, acute myocardial infarction and novel therapies, including stem cell and gene therapy, for patients who are not candidates for standard revascularization techniques. Dr. Henry has published over 250 manuscripts and book chapters and has served on the Research Committee for the Minnesota Affiliate of the AHA and the Emergency Care Committee for the ACC; he currently serves on the Advisory Committee for the AHA Mission: Lifeline Program, the AHA Acute Cardiac Care Committee of the Council on Clinical Cardiology and on the ACC Interventional Subcommittee. He has served as national principal investigator of multiple large, multicenter trials in acute coronary syndromes, myocardial infarction and angiogenesis including several ongoing cardiovascular stem cell trials including RENEW, ALLSTAR and ATHENA. He is also principal investigator for 1 of 7 NIH Clinical Cardiovascular Stem Cell Centers. He is a fellow at ACC and SCAI and a member of Alpha Omega Alpha and the AHA Council on Clinical Cardiology. In the spirit of ideas worth spreading, TEDx is a program of local, self-organized events that bring people together to share a TED-like experience. At a TEDx event, TEDTalks video and live speakers combine to spark deep discussion and connection in a small group. These local, self-organized events are branded TEDx, where x = independently organized TED event. The TED Conference provides general guidance for the TEDx program, but individual TEDx events are self-organized.* (*Subject to certain rules and regulations)
- Adult stem cell
- Alexander Maksimov
- Amniotic fluid
- Amniotic stem cells
- André Gernez
- Angiogenesis
- Anthony Atala
- Autograft
- Autologous
- Berlin
- Biocell Center
- Blastocyst
- Blood vessel
- Bone marrow
- C-myc
- Cancer
- Cancer stem cell
- Cell (biology)
- Cell (journal)
- Cell bank
- Cell culture
- Cell cycle
- Cell differentiation
- Cell division
- Cell line
- Cell potency
- Cord blood
- Decapentaplegic
- Dolly the Sheep
- Electroporation
- Embryo
- Embryonic stem cell
- Embryonic stem cells
- England
- Epiblast
- Ernest McCulloch
- Extracellular matrix
- Father cell
- Femur
- Fibroblasts
- Fibrosis
- Foreskin
- Gail R. Martin
- Gelatin
- Gene therapy
- Germ layer
- Geron Corp.
- Giuseppe Simoni
- Granulation tissue
- Growth factor
- Harvard University
- Holy See
- Human body
- Human genome
- Hwang Woo-Suk
- Ian Wilmut
- Iliac crest
- In vitro
- In vivo
- Inner cell mass
- IPS cells
- Israel
- James Till
- Joseph Altman
- Junying Yu
- Kazutoshi Takahashi
- Kingston University
- Knockout mice
- Kyoto University
- Latin
- Leukemia
- Maggot therapy
- Mario Capecchi
- Martin Evans
- Matthew Kaufman
- Meristem
- Mitochondrial DNA
- Mitosis
- Moratorium (law)
- Morula
- Multiple sclerosis
- Multipotency
- Multipotent
- Mus musculus
- Muscle
- Myc
- Nanog
- Nerve
- Neural stem cell
- Neurogenesis
- Neuron
- Newcastle University
- Oct-4
- Oligopotency
- Oliver Smithies
- Oncogene
- Oocyte
- Organ transplant
- Organisms
- Osservatore Romano
- Parkinson's disease
- Partial cloning
- Patent
- Pheresis
- Placenta
- Plant stem cells
- Pluripotency
- Pluripotent
- Precursor cell
- Progenitor cell
- PubMed Central
- PubMed Identifier
- Roman Catholic
- Russia
- Scar
- Science (journal)
- Shinya Yamanaka
- Shoukhrat Mitalipov
- Somatic
- Sox2
- Spinal cord injuries
- Spore
- Stem cell
- Stem cell laws
- Stem cell line
- Stem cell marker
- Stem Cell Network
- Stem Cell Treatments
- Stem cell treatments
- Template Stem cells
- Teratoma
- The Daily Telegraph
- Therapeutic cloning
- Totipotency
- Totipotent
- Transcription factor
- Tumorigenesis
- UC Irvine
- Umbilical cord blood
- Unipotency
- Unipotent cell
- Vasculogenesis
- WebMD
- Wikipedia Link rot
- Wound healing
- Zygote
-

What are stem cells? How can they be used for medical benefit?
What are stem cells? - An short educational film by the Irish Stem Cell Foundation Stem cells are master cells of the body — want to learn more? Visit www.irishstemcellfoundation.org ISCF is an independent not-for-profit organisation whose primary objective is to educate about stem cells, their basic biology and the research and therapies using them. The Foundation will initially focus on education outreach programs, hoping to address the growing problem of bogus stem cell scams being offered to Irish patients over the internet. The Foundation will also assist the development of Irish policy and legislature in this area of medicine and science, ensuring Ireland is informed. The Foundation consists of a broad range of people including Irish doctors, scientists, patient advocates... -

What are stem cells? - Craig A. Kohn
View full lesson: http://ed.ted.com/lessons/what-are-stem-cells-craig-a-kohn Is personalized medicine for individual bodies in our future? Possibly -- with the use of stem cells, undifferentiated cells with the power to become any tissue in our bodies. Craig A. Kohn describes the role of these incredible, transforming cells and how scientists are harnessing their medical potential. Lesson by Craig A. Kohn, animation by Qa'ed Mai. -

Stem Cells
Hank gives you the facts on stem cells - what they are, what they're good for, where they come from, and how they're used in medicine. Like SciShow? Want to help support us, and also get things to put on your walls, cover your torso and hold your liquids? Check out our awesome products over at DFTBA Records: http://dftba.com/artist/52/SciShow -- Looking for SciShow elsewhere on the internet? Facebook: http://www.facebook.com/scishow Twitter: http://www.twitter.com/scishow Tumblr: http://scishow.tumblr.com References for this episode can be found in the Google document here: http://dft.ba/-5DcW -

-

23. Stem Cells
MIT 7.013 Introductory Biology, Spring 2011 View the complete course: http://ocw.mit.edu/7-013S11 Instructor: Hazel Sive Professor Sive discusses cell fate and differentiation, followed by stem cells. The lecture focuses on defining stem cells, highlighting the key discoveries in research, and discussing therapeutics. License: Creative Commons BY-NC-SA More information at http://ocw.mit.edu/terms More courses at http://ocw.mit.edu -

A Stem Cell Story
What are stem cells, where do they come from, and what do we really know about them? An award-winning introduction to the world of stem cell research. Innovative hand-drawn animation, beautiful cell photography and documentary interviews capture the fascination and complexity of this cutting-edge area of science. Related resources and lots more stem cell info at http://www.eurostemcell.org/films. If you would like to comment or leave feedback, please do so there. Best TV/video production, Tromsø Science Media Festival. Best short film, Scinema (Australia). Captions in 12 languages. -

WHAT CAN STEM CELLS DO?
You may have heard of stem cells before, but there is a lot of mystery about what they actually … do. Why is this such a promising new field? Click here to see more videos: http://www.m301.me/lifenoggin Life Noggin is a weekly animated educational series. Whether it's science, pop culture, history or art, we explore it all and have a ton of fun doing it. Follow Us! https://twitter.com/LifeNoggin https://facebook.com/LifeNoggin https://www.LifeNoggin Life Noggin Team: Animation & Designed by: http://www.krofl.com Voiced by: http://youtube.com/patdoesit Written by: https://www.youtube.com/coconutcab Produced by: http://www.twitter.com/IanDokie Sources: Bone marrow transplant: http://www.cancer.net/navigating-cancer-care/how-cancer-treated/bone-marrowstem-cell-transpl... -

PhytoScience double Stem Cell Philippines Review
Experience the Magic of PhytoScience Double Stem Cell Philippines. FB: https://www.facebook.com/PhytosciencePhilippines 2013 Best Selling Double Stem Cell Product in Malaysia and Thailand Now in the Philippines! See Visible Results in Just 14 Days! PHYTOSCIENCE DOUBLE STEM CELL removes the appearance of age lines and restore smooth, radiant, youthful looking skin! PHYTOSCIENCE DOUBLE STEM CELL used A species of apple called the Uttwiler Spatlauber from Northern Switzerland is being heralded as the latest anti-ageing breakthrough. I kid you not – A-list stars including Jennifer Aniston, Michelle Obama and Gwyneth Paltrow have already been reaping the benefits. Product efficacy Delays ageing process Enhances health and vitality Repairs and rejuvenates cell Maintains acid-base balance ... -

Stem cell cure for blindness tested - BBC News
Surgeons in London have used human embryonic stem cells in a pioneering attempt to cure blindness. Cells derived from a donated early embryo were implanted into the retina of a 60-year-old woman with age-related macular degeneration - the most common cause of blindness in the UK. Fergus Walsh reports. Subscribe to BBC News HERE http://bit.ly/1rbfUog Check out our website: http://www.bbc.com/news Facebook: http://www.facebook.com/bbcworldnews Twitter: http://www.twitter.com/bbcworld Instagram: http://instagram.com/bbcnews -

Stem Cell Therapy Injections
Stem Cell therapy, is one form of Comprehensive Prolotherapy available for arthritis treatment, and other chronic pain conditions at Caring Medical and Rehabilitation Services. Our same-day procedure utilizes a person's own mesenchymal stem cells from bone marrow or fat cells to treat degenerated joints. In this video, the stem cell therapy treatment is demonstrated on an athlete with severe osteoarthritis of the knee, by Ross Hauser, MD. Dr. Hauser has specialized in comprehensive Prolotherapy and Orthobiologic treatments since 1993 and treated tens of thousands of patients with excellent success, even patients who have failed surgery, knee replacement, or other treatments for arthritis and pain. To make an appointment with one of our specialists or for an opinion on your case and to lear... -

Stem Cell Animation
-

Why Are Stem Cells So Important?
Stem cell research is still very controversial, so why do we want to use stem cells in the first place? Why are they so useful, and what can they do? Read More: Researchers Grow Tiny Beating Human Hearts From Stem Cells http://www.popsci.com/researchers-grow-first-ever-beating-hearts-stem-cells "Stem cells, the jack-of-all-trades building blocks of human tissues, have yet another application in biology research: scientists have been able to grow them into beating cardiac tissue." Key Moments in the Stem-Cell Debate http://www.npr.org/templates/story/story.php?storyId=5252449 "The first embryonic stem cells were isolated in mice in 1981. But it wasn't until 1998 that researchers managed to derive stem cells from human embryos. That kicked into full gear an ethical debate that co... -

-

Stem cell therapy -- beyond the headlines: Timothy Henry at TEDxGrandForks
There is considerable excitement about the use of stem cells for cardiovascular disease. Stem cells are unspecialized cells with the unique property to self-renew or make copies of themselves and to differentiate into specialized cells. The goal of stem cell therapy is to enhance the body's natural process of regeneration. There are a considerable number of stem cells currently under investigation for patients with heart attacks, angina, heart failure, and peripheral arterial disease. We have made considerable progress but have many questions left to answer. Timothy Henry, MD, FACC, is Chief of Cardiology at Cedars Sinai Heart Institute in Los Angeles, California. Dr. Henry earned his bachelor's degree at the University of North Dakota, graduated from medical school at University of Calif... -

How Do Stem Cells Work? - Bang Goes the Theory - BBC
Liz Bonnin investigates new stem-cell research that could change the face of organ transplant surgery. Absorbing clip from series 5 of BBC 1 series Bang Goes the Theory Investigating the science behind the headlines and making sense of the everyday issues that matter to us all. http://www.bbc.co.uk/programmes/b00lwxj1 Subscribe to the BBC Worldwide channel: http://bit.ly/yqBWhy BBC Worldwide Channel: http://www.youtube.com/BBCWorldwide -

Hair Regrowth Treatment - Stem Cell Hair Restoration Technique
For more details about Stem Cell Hair Restoration Technique and to view results of Scissorboy's hair transplant, visit http://www.scissorboy.com Balding and thinning hair has always been a curse for men and women as they age. In December 2010 ScissorBoy learned about a promising new procedure developed by Dr. Coen Gho of the Hair Science Institute in the Netherlands that may be the solution many have been waiting for. Dr. Gho has developed a process that uses your own hair to produce new hair that can fill in balding and thinning parts of your head. This hair regrowth treatment is also know as Stem Cell Hair Restoration Technique or Follicular Unit Extraction. In this cosmetology education video, ScissorBoy becomes a patient of Dr. Gho to get back his receding hairline using this hair ... -

Stem Cell Treatment- Dave Palumbo Regenerates Shoulder Injuries
Dave Palumbo visits Dr Eric Siegel for Stem Cell therapy for chronic shoulder arthritis. Is this the new therapy wave of the future? Find out what the procedure entails and how it's performed! -

New heart built with stem cells
An entire functional heart was created using a heart 'shell' and stem cells. This has been done in the rat & pig, with hopes of using a pig's heart 'shell' for people. Livers, kidneys, and pancreas (much harder) are in the works. They "injected the empty sac with heart cells from newborn rats. Within days, the cells had multiplied to flesh out the heart, which began beating on its own. "We've taken organs from cadavers, removed all the cells, put cells back in and been able to reanimate what was previously a dead organ," said molecular biologist Doris Taylor, director of the Center for Cardiovascular Repair at the University of Minnesota. "What that means, we hope, is that one day if you need a new organ, we'll be able to take your cells, transplant them into this framework or s... -

Science Friction: Stem Cell Research
The third instalment of RTÉ's documentary series, 'Science Friction' where science and society collide, explores one of the most controversial issues in the history of science: the human embryo and its use in the ground-breaking field of stem cell research. In this episode, presenter Liz Bonnin embarks on a journey to meet the different people, both within and outside the science community, whose lives are touched by the controversy surrounding the embryo. Liz talks to 22-year-old Geoff Harte, who was left paralysed after breaking his neck in a school rugby match, and now believes that stem cells may one day help him to walk again. We also hear from Stephen Sullivan, a Harvard based Irish scientist who uses frozen embryos left over as a result of IVF treatment, as a source of stem cell... -

The Cancer Stem Cell Theory
The European Cancer Stem Cell Research Institute at Cardiff University believes that cancer stem cells are responsible for the spread and regrowth of tumours. This animation demonstrates how cancer stem cells proliferate. The aim of the Institute is to develop more personalised approaches to treatment for patients with cancer by aiding faster and cheaper drug development and delivering better diagnostic tools to help detect cancer earlier. This short animation was created by Alan Dimery, one of our valued supporters with input from final-year undergraduate student Sophie Hopkins. -

Stem cells basics animation
This stem cells animation explains about stem cell therapy. http://shomusbiology.com/ Download the study materials here- http://shomusbiology.com/bio-materials.html Remember Shomu’s Biology is created to spread the knowledge of life science and biology by sharing all this free biology lectures video and animation presented by Suman Bhattacharjee in YouTube. All these tutorials are brought to you for free. Please subscribe to our channel so that we can grow together. You can check for any of the following services from Shomu’s Biology- Buy Shomu’s Biology lecture DVD set- www.shomusbiology.com/dvd-store Shomu’s Biology assignment services – www.shomusbiology.com/assignment -help Join Online coaching for CSIR NET exam – www.shomusbiology.com/net-coaching We are social. Find us on different ... -

dr. Boenjamin Setiawan, PhD., Bicara Soal Stem Cell
KLIKDOKTER.com dan metrotvnews.com berkesempatan mewawancarai salah satu praktisi peneliti stem cell ternama di Indonesia. -

The future of healthcare: On-demand personalized stem cell therapy | Dr. Yael Porat | TEDxJerusalem
The future of medicine is here today. Dr. Yael Porat, CEO of BioGenCell (www.BioGenCell.net), describes the development of a groundbreaking technology for the automated production of personalized stem-cell therapies. These products, derived from the patient’s own blood, will be available on demand within 24 hours, to save lives and restore the quality of life for the billion people worldwide with blood vessel diseases including heart disease, stroke, PAD and dementia. Yael Porat, PhD, is founder and CEO of BioGenCell Ltd (www.BioGenCell.net), a biotechnology company focusing on stem cell therapy and regenerative medicine. Dr. Porat earned her PhD in immunology from the Sackler School of Medicine, Tel-Aviv University. Prior to founding BioGenCell, she served as head of the Global Bi...
What are stem cells? How can they be used for medical benefit?
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 6:15
- Updated: 12 Dec 2009
- views: 347928
- published: 12 Dec 2009
- views: 347928
What are stem cells? - Craig A. Kohn
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 4:11
- Updated: 10 Sep 2013
- views: 255588
- published: 10 Sep 2013
- views: 255588
Stem Cells
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 3:48
- Updated: 30 Apr 2013
- views: 352032
- published: 30 Apr 2013
- views: 352032
Stem Cells
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 7:53
- Updated: 05 Jun 2007
- views: 586409
23. Stem Cells
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 46:19
- Updated: 15 Jan 2014
- views: 55395
- published: 15 Jan 2014
- views: 55395
A Stem Cell Story
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 15:53
- Updated: 14 Jun 2011
- views: 212980
- published: 14 Jun 2011
- views: 212980
WHAT CAN STEM CELLS DO?
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 3:17
- Updated: 27 Apr 2015
- views: 55485
- published: 27 Apr 2015
- views: 55485
PhytoScience double Stem Cell Philippines Review
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 2:46
- Updated: 16 Jul 2014
- views: 42384
- published: 16 Jul 2014
- views: 42384
Stem cell cure for blindness tested - BBC News
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 2:13
- Updated: 29 Sep 2015
- views: 11677
- published: 29 Sep 2015
- views: 11677
Stem Cell Therapy Injections
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 6:18
- Updated: 25 Mar 2011
- views: 184829
- published: 25 Mar 2011
- views: 184829
Stem Cell Animation
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 1:07
- Updated: 07 Nov 2013
- views: 45873
- published: 07 Nov 2013
- views: 45873
Why Are Stem Cells So Important?
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 4:09
- Updated: 16 Jul 2015
- views: 46984
- published: 16 Jul 2015
- views: 46984
What is StemCell - Hindi
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 3:57
- Updated: 27 Jul 2015
- views: 9590
Stem cell therapy -- beyond the headlines: Timothy Henry at TEDxGrandForks
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 17:54
- Updated: 17 Mar 2014
- views: 34534
- published: 17 Mar 2014
- views: 34534
How Do Stem Cells Work? - Bang Goes the Theory - BBC
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 4:03
- Updated: 17 Apr 2013
- views: 101536
- published: 17 Apr 2013
- views: 101536
Hair Regrowth Treatment - Stem Cell Hair Restoration Technique
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 4:53
- Updated: 12 Mar 2012
- views: 914404
- published: 12 Mar 2012
- views: 914404
Stem Cell Treatment- Dave Palumbo Regenerates Shoulder Injuries
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 25:37
- Updated: 13 Mar 2016
- views: 504
- published: 13 Mar 2016
- views: 504
New heart built with stem cells
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 1:51
- Updated: 27 Apr 2008
- views: 161287
- published: 27 Apr 2008
- views: 161287
Science Friction: Stem Cell Research
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 54:44
- Updated: 22 Aug 2012
- views: 76247
- published: 22 Aug 2012
- views: 76247
The Cancer Stem Cell Theory
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 2:52
- Updated: 03 Feb 2015
- views: 7961
- published: 03 Feb 2015
- views: 7961
Stem cells basics animation
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 3:39
- Updated: 26 Dec 2012
- views: 20677
- published: 26 Dec 2012
- views: 20677
dr. Boenjamin Setiawan, PhD., Bicara Soal Stem Cell
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 11:23
- Updated: 22 Feb 2014
- views: 2845
- published: 22 Feb 2014
- views: 2845
The future of healthcare: On-demand personalized stem cell therapy | Dr. Yael Porat | TEDxJerusalem
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 10:56
- Updated: 08 May 2015
- views: 4082
- published: 08 May 2015
- views: 4082
- Playlist
- Chat
- Playlist
- Chat

What are stem cells? How can they be used for medical benefit?
- Report rights infringement
- published: 12 Dec 2009
- views: 347928

What are stem cells? - Craig A. Kohn
- Report rights infringement
- published: 10 Sep 2013
- views: 255588

Stem Cells
- Report rights infringement
- published: 30 Apr 2013
- views: 352032


23. Stem Cells
- Report rights infringement
- published: 15 Jan 2014
- views: 55395

A Stem Cell Story
- Report rights infringement
- published: 14 Jun 2011
- views: 212980

WHAT CAN STEM CELLS DO?
- Report rights infringement
- published: 27 Apr 2015
- views: 55485

PhytoScience double Stem Cell Philippines Review
- Report rights infringement
- published: 16 Jul 2014
- views: 42384

Stem cell cure for blindness tested - BBC News
- Report rights infringement
- published: 29 Sep 2015
- views: 11677

Stem Cell Therapy Injections
- Report rights infringement
- published: 25 Mar 2011
- views: 184829

Stem Cell Animation
- Report rights infringement
- published: 07 Nov 2013
- views: 45873

Why Are Stem Cells So Important?
- Report rights infringement
- published: 16 Jul 2015
- views: 46984

What is StemCell - Hindi
- Report rights infringement
- published: 27 Jul 2015
- views: 9590

Stem cell therapy -- beyond the headlines: Timothy Henry at TEDxGrandForks
- Report rights infringement
- published: 17 Mar 2014
- views: 34534
Indonesian Singer Dies After Cobra Bites Her Onstage
Edit WorldNews.com 08 Apr 2016N Korea says it can now 'reduce US to ashes'
Edit The Times of India 09 Apr 2016Belgian Police Capture Paris Attacks Suspect Mohamed Abrini
Edit WorldNews.com 08 Apr 2016Planet Nine's profile fleshed out
Edit BBC News 08 Apr 2016Man dies after falling while trying to slide down escalator handrail
Edit Atlanta Journal 08 Apr 2016Ottawa Hospital's experimental new stem cell treatment a world first
Edit Canada Dot Com 09 Apr 2016American doctors make new esophagus using stents and skin
Edit Seattle Post-Intelligence 09 Apr 2016American doctors make new organs in a laboratory
Edit Khaleej Times 09 Apr 2016'Step forward' in battle against blood disorders
Edit Belfast Telegraph 08 Apr 2016Stem cell storage company goes into liquidation
Edit Australian Broadcasting Corporation 08 Apr 2016Swiss Luxury Skin Care Brand Brings Tech Infused Anti-Aging Collection to US
Edit PR Newswire 08 Apr 2016Married profs mix music, neuroscience at UCF
Edit Orlando Sentinel 08 Apr 2016World's First Cloned Dog Snuppy Dies at Age 10 (Seoul National University)
Edit Public Technologies 08 Apr 2016Coimbatore orthopaedic hospital to open research centre
Edit The Times of India 08 Apr 2016CORONEO Australia New Zealand Distribution Partnership (Admedus Ltd)
Edit Public Technologies 08 Apr 2016Science minister responds after NRC shakeup, but with few details
Edit Canada Dot Com 08 Apr 2016Safer stem cell-derived therapy for brain radiation recovery
Edit Science Daily 07 Apr 2016Medicare to cover stem cell transplantation for sickle cell disease (University of Illinois at Chicago)
Edit Public Technologies 07 Apr 2016- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- Next page »







