- published: 14 Dec 2014
- views: 9740
-
remove the playlistSoul (spirit)
- remove the playlistSoul (spirit)
- published: 07 Sep 2014
- views: 3978
- published: 29 Mar 2016
- views: 3195
- published: 10 Oct 2013
- views: 7995
- published: 08 May 2013
- views: 7042
- published: 24 Dec 2015
- views: 7925
- published: 01 Aug 2012
- views: 7226
- published: 31 Aug 2014
- views: 16809
- published: 15 Aug 2013
- views: 35754

The soul – in many traditional spiritual, philosophical, and psychological traditions – is the incorporeal and immortal essence of a person, living thing, or object. Some religions teach that all biological organisms have souls, and others further still that even non-biological entities (such as rivers and mountains) possess souls. This latter belief is called animism.Anima mundi and the Dharmic Ātman are concepts of a "world soul." Some religious thinkers, such as Thomas Aquinas, attribute souls to all organisms but teach that only human souls are immortal.
Soul can function as a synonym for spirit, mind or self; scientific works, in particular, often consider 'soul' as a synonym for 'mind'[citation needed].
The Modern English word soul derived from Old English sáwol, sáwel, first attested to in the 8th century poem Beowulf v. 2820 and in the Vespasian Psalter 77.50, and is cognate with other Germanic and Baltic terms for the same idea, including Gothic saiwala, Old High German sêula, sêla, Old Saxon sêola, Old Low Franconian sêla, sîla, Old Norse sála as well as Lithuanian siela. Further etymology of the Germanic word is uncertain. A more recent suggestion connects it with a root for "binding", Germanic *sailian (OE sēlian, OHG seilen), related to the notion of being "bound" in death, and the practice of ritually binding or restraining the corpse of the deceased in the grave to prevent his or her return as a ghost.
This article is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported License, which means that you can copy and modify it as long as the entire work (including additions) remains under this license.
The English word spirit (from Latin spiritus "breath") has many differing meanings and connotations, most of them relating to a non-corporeal substance contrasted with the material body. The spirit of a living thing usually refers to or explains its consciousness. The notions of a person's "spirit" and "soul" often also overlap, as both contrast with body and both are understood as surviving the bodily death in religion and occultism, and "spirit" can also have the sense of "ghost", i.e. a manifestation of the spirit of a deceased person.
The term may also refer to any incorporeal or immaterial being, such as demons or deities, in Christianity specifically the Holy Spirit experienced by the disciples at Pentecost.
The English word spirit comes from the Latin spiritus, meaning "breath", but also "spirit, soul, courage, vigor", ultimately from a Proto-Indo-European *(s)peis. It is distinguished from Latin anima, "soul." In Greek, this distinction exists between pneuma (πνευμα), "breath, motile air, spirit," and psykhē (ψυχη), "soul."
This article is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported License, which means that you can copy and modify it as long as the entire work (including additions) remains under this license.
- Loading...

-
 54:11
54:11The difference between soul and spirit.
The difference between soul and spirit.The difference between soul and spirit.
Tom talks about the soul and spirit in us and what it means to be saved. https://www.gofundme.com/tomfischer -
 14:47
14:47Do We Have A Body, Soul, and Spirit? - Pastor Richard Jordan
Do We Have A Body, Soul, and Spirit? - Pastor Richard JordanDo We Have A Body, Soul, and Spirit? - Pastor Richard Jordan
. TO LEARN HOW TO BE SAVED click on "Show more" below. Please visit: http://www.rightdivider.net/speakers/rj/judge/judge.htm This Clip From The Message: "A New Creature In Christ" #882 Order From: "The Message of Grace" PO Box 97, Bloomingdale, IL 60108 (888) 535-2300 -- ( Tags: Mid Acts, Pauline, Dispensational, "Rightly Dividing" Bible, Word of God, 2 Timothy 2:15, Apostle Paul, C.R. Stam, J.C. O'Hair, Joel Finck, Charles F. Baker, Keith R. Blades, ) -- If you need GREAT messages to help you grow in your faith click on the links below... http://helpersofyourjoy.com/?page_id=59 http://columbusbiblechurch.org/ http://www.rightlydividing.org/MP3_grace/mp3.htm http://shorewoodbiblechurch.org/ You Tube: http://www.youtube.com/user/TheMessageofGrace http://www.youtube.com/user/norcalgrace http://www.youtube.com/user/BookstoreAtShorewood/videos -- [HOW TO BE SAVED] After you die do you think you will you go to Heaven or Hell? We all DESERVE to go to HELL because of what we have done WRONG in this life! "As it is written, There is none righteous, no, not one:" (Romans 3:10) "For all have sinned and come short of the glory of God." (Romans 3:23) -- The "Good News" is that God LOVES us and wants to SAVE US from going to that terrible place called hell. Check this verse out from the Bible... "For this is good and acceptable in the sight of God our Saviour; Who will have ALL men to be saved, and to come unto the knowledge of the truth." (1 Timothy 2:3-4) -- After we DIE it will be TOO LATE to be saved! "And as it is appointed unto men once to die, but after this the JUDGMENT" (Hebrews 9:27) -- God's solution for our sin is THE CROSS... "But God commendeth his love toward us, in that, while we were yet sinners, Christ died for us." (Romans 5:8) "...Christ died for our sins according to the scriptures; and that he was buried, and that he rose again the third day according to the scriptures." (I Corinthians 15:3,4) "In whom we have redemption through his blood, the forgiveness of sins, according to the riches of His grace;" (Ephesians 1:7) -- SALVATION is God's FREE GIFT to us... "For the wages of sin is death; but the GIFT of God is eternal life through Jesus Christ our Lord." (Romans 6:23) -- The Result of our faith is PEACE WITH GOD... "Therefore being justified by faith, we have peace with God through our Lord Jesus Christ." (Romans 5:1) "For by grace are ye saved through faith; and that not of yourselves: it is the gift of God: Not of works, lest any man should boast." (Ephesians 2:8,9) -- At this very moment you have the responsibility of making a decision. You can be saved right now: Simply make the decision in your heart to trust completely and exclusively in the blood of the Lord Jesus Christ as the total payment to God for your sins. The moment you do, God will forgive you all your sins and save you from spending eternity in the Lake of Fire. -- After we are saved we are SEALED (kept safe by God) by Being given God's Holy Spirit to be with us until we go to be in heaven... "In whom [Christ] ye also trusted, after that ye heard the word of truth, the gospel of your salvation: in whom also after that ye believed, ye were sealed with that Holy Spirit of promise..." (Ephesians 1:13) -- "He that believeth on the Son hath everlasting life: and he that believeth NOT the Son shall not see life; but the wrath of God abideth on him." (John 3:36) Do not use links below. For meta data: http://www.intouch.org/ http://www.insight.org/ http://rickwarren.org/ http://www.gty.org/ http://www.lwf.org/site/PageServer http://www.billhybels.org/ http://www.focusonthefamily.com/ http://www.cbn.com/700club/ http://billygraham.org/ http://www.equip.org/ -
 8:45
8:45Soul vs Spirit - John Paul Jackson
Soul vs Spirit - John Paul Jackson -
 5:04
5:04Spirit Soul & Body - Animation Part 1
Spirit Soul & Body - Animation Part 1Spirit Soul & Body - Animation Part 1
To subscribe to Andrew’s email newsletter: http://www.awmi.net/youtube-subscribe/ This is the 1st animation of the teaching Spirit, Soul and Body, which is a foundational truth that is essential for understanding how much God loves you and believing what He says about you in His Word. Each person is made up of three different parts: spirit, soul, and body. Learn how these three parts relate to God and to each other. At salvation your spirit is totally changed, but your soul and body is not yet redeemed. This series will teach you how to release the life that is already in your spirit, into your physical body and emotions. ==================================== Andrew Wommack Ministries http://www.awmi.net/ https://www.facebook.com/AWMinistries https://twitter.com/andrewwommack https://instagram.com/andrewwommack/ https://www.pinterest.com/andrewwommack/ ====================================================== https://youtu.be/b5aAGTNWNBA -
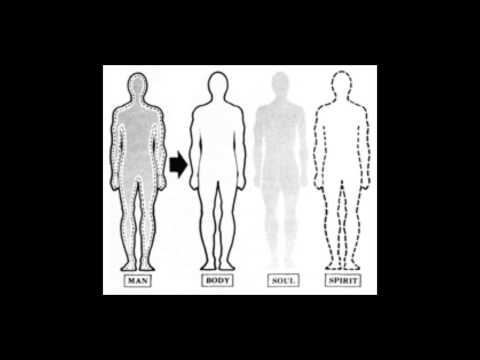 73:00
73:00The Trinity: Body, Soul, and Spirit
The Trinity: Body, Soul, and Spirit -
 8:14
8:14What is the Difference Between Soul and Spirit?
What is the Difference Between Soul and Spirit?What is the Difference Between Soul and Spirit?
Student Question: What is the difference between soul and spirit? -
 4:59
4:59What does the Bible say about our Body Soul Spirit?
What does the Bible say about our Body Soul Spirit?What does the Bible say about our Body Soul Spirit?
What does the Bible say about our Body, Soul and Spirit? What happens when we are born again? How does this affect me in my walk with the Lord? Why do I still sin if I have been born again? -
 69:02
69:02Going Beyond the Soul to Spirit by Zac Poonen
Going Beyond the Soul to Spirit by Zac PoonenGoing Beyond the Soul to Spirit by Zac Poonen
Website: http://www.sermonindex.net Google+: https://www.google.com/+SermonindexNet The work and ministry of sermonindex can be encapsulated in this one word: REVIVAL. sermonindex is not a organisation, business, or any attempt by man to build something for God. It is rather a expression of a heart burden to see the Church revived and brought back to holiness, purity, and power with God. "The mission of SermonIndex is the preservation and propogation of classical vintage preaching and the promotion of genuine biblical revival to this generation." -
 12:27
12:27Why You Do What You Do - How body, soul, and spirit work
Why You Do What You Do - How body, soul, and spirit workWhy You Do What You Do - How body, soul, and spirit work
http://christianhomeandfamily.com - Human behavior can be confusing. Add to that the influence of being a fallen human being and the sinful habits we develop - and you can go "tilt" trying to figure it out. This screencast is designed to help you understand what the Bible says about how your body, soul, and spirit work together - and how the entrance of the Holy Spirit into your life can make all the difference! MUSIC USED BY PERMISSION of Adam Rey - http://www.heyreyguitar.com Christian Home and Family exists to help you make Christ the center of your home. Contact Carey with your questions, counseling needs, suggestions, and comments. TWITTER: http://christianhomeandfamily.com/twitter PODCAST: http://christianhomeandfamily.com/podcast FACEBOOK: http://christianhomeandfamily.com/facebook VOICEMAIL: http://christianhomeandfamily.com/voicemail PHONE: 719-966-7744 -
 5:15
5:15Mongolian Music - Healing Soul Spirit Song
Mongolian Music - Healing Soul Spirit Song -
 34:01
34:01Ian Clayton - Splitting Soul & Spirit (Company of Burning Hearts)
Ian Clayton - Splitting Soul & Spirit (Company of Burning Hearts)Ian Clayton - Splitting Soul & Spirit (Company of Burning Hearts)
Splitting Soul & Spirit - Ian Clayton Re-up from: http://companyofburninghearts.podomatic.com/entry/2011-10-03T17_44_05-07_00 Company of Burning Hearts http://companyofburninghearts.wordpress.com Son of Thunder is the Itinerant Ministry of Ian Clayton http://www.sonofthunder.org -
 31:15
31:15Andrew Wommack: Spirit, Soul & Body - Week 1 - Session 1
Andrew Wommack: Spirit, Soul & Body - Week 1 - Session 1Andrew Wommack: Spirit, Soul & Body - Week 1 - Session 1
This DVD album was recorded from the Gospel Truth TV broadcast. Each DVD contains one week of programming. Please note that while they do cover the same material as a CD album, they are not exactly the same. This teaching is a foundational truth that is essential for understanding how much God loves you and believing what He says about you in His Word. Each person is made up of three different parts: spirit, soul, and body. Learn how these three parts relate to God and to each other. At salvation your spirit is totally changed, but your soul and body is not yet redeemed. This series will teach you how to release the life that is already in your spirit, into your physical body and emotions.
- Abrahamic religions
- Acosmism
- Adib Taherzadeh
- Afterlife
- Agnosticism
- Ahl-e Haqq
- Albrecht Ritschl
- Alvin Plantinga
- Ancient Greece
- Angel
- Anglicanism
- Anima
- Anima mundi
- Animal
- Animism
- Annihilationism
- Anselm of Canterbury
- Anthony Kenny
- Antireligion
- Antony Flew
- Apophatic theology
- Apostasy
- Apostles' Creed
- Argument from beauty
- Argument from degree
- Argument from desire
- Argument from love
- Argument from reason
- Aristotelianism
- Aristotle
- Atheism
- Atheist's Wager
- Atma Siddhi
- Atman (Jainism)
- Augustine of Hippo
- Augustinian theodicy
- Averroes
- Avicenna
- Avicennism
- Ayyavazhi
- B. Alan Wallace
- Bahá'u'lláh
- Bahá'í Faith
- Baltic languages
- Baron d'Holbach
- Baruch Spinoza
- Basalt
- Behavior
- Beowulf
- Bertrand Russell
- Biblical Hebrew
- Birth control
- Blaise Pascal
- Boethius
- Book of Genesis
- Bosom of Abraham
- Brahma Kumaris
- Brahman
- Broca's area
- Buddha-nature
- Buddhism
- Bön
- Cao Dai
- Cartesianism
- Category Religion
- Catholicism
- Celtic polytheism
- Chabad.org
- Charles Hartshorne
- Chaya (soul)
- Cheondoism
- Christadelphians
- Christian humanism
- Christian salvation
- Christianity
- Clergy
- Cognition
- Comparative religion
- Confucianism
- Consciousness
- Conservative Judaism
- Creationism (soul)
- Daniel Dennett
- David Chalmers
- David Hume
- Deism
- Deity
- Demiurge
- Demon
- Descartes
- Desiderius Erasmus
- Desire (philosophy)
- Desire realms
- Determinism
- Dharma
- Disability
- Discordianism
- Divine judgment
- Divine simplicity
- Dream
- Druze
- Dualism
- Dvaita
- East Asian religions
- Ecclesiology
- Eckankar
- Edward Conze
- Egyptian soul
- Ekam
- Embryo
- Emil Brunner
- Emotion
- Epistemology
- Ernst Cassirer
- Ernst Haeckel
- Ernst Troeltsch
- Eros (concept)
- Erwin Rohde
- Esotericism
- Essence
- Eternal damnation
- Eternal death
- Ethical egoism
- Ethics in religion
- Euthyphro dilemma
- Evangelicalism
- Evangelism
- Exclusivism
- Exegesis
- Existence of God
- Existentialism
- F. M. Cornford
- Faith
- Feminist theology
- Fetus
- Final cause
- Finnish paganism
- Fire worship
- First actuality
- Five worlds
- Fourth Way
- Francis Crick
- Frederick Buechner
- Free will
- Freedom of religion
- Friedrich Nietzsche
- Fundamentalism
- George Gurdjieff
- George Santayana
- Germanic paganism
- Ghost in the machine
- Gilbert Ryle
- Gilgul
- Gnosticism
- God
- God in Buddhism
- God in Christianity
- God in Hinduism
- God in Islam
- God in Jainism
- God in Mormonism
- God in Sikhism
- Gothic language
- Goths
- Guru Granth Sahib
- Gurung Dharma
- Hades
- Harald Høffding
- Heart
- Heaven
- Hebrew
- Helena Blavatsky
- Hell
- Hell in Christianity
- Henotheism
- Heraclitus
- Hereward Carrington
- Hinduism
- Hippolyte Baraduc
- History of religions
- Hoa Hao
- Holy Spirit
- Homer
- Hossein Nasr
- Humanism
- Hun and po
- I (pronoun)
- I-Kuan Tao
- Ibn al-Nafis
- Immanuel Kant
- Immortality
- Inclusivism
- Inconsistent triad
- Incorporeality
- Indian religions
- Indigenous religion
- Intelligence
- Intentional stance
- Intentionality
- Iranian religions
- Irenaean theodicy
- Irreligion
- Islam
- J. L. Mackie
- Jain philosophy
- Jainism
- James Hillman
- Javanese beliefs
- Jean Calvin
- Jean-Luc Marion
- Jehovah's Witnesses
- Jiva
- Judaism
- Jungian archetypes
- Kabbalah
- Kami
- Karaite Judaism
- Karl Barth
- Karl Marx
- Karma in Buddhism
- Karma in Hinduism
- Kashrut
- Koine Greek
- Kuttamuwa
- Language-game
- Last Judgment
- LaVeyan Satanism
- Lev Shestov
- Life
- Life expectancy
- Life form
- List of deities
- List of philosophies
- Lithuanian language
- Liturgy
- Logical positivism
- Loyal Rue
- Ludwig Feuerbach
- Mahayana
- Maimonides
- Maltheism
- Mandaeism
- Manichaeism
- Martin Buber
- Martin Lings
- Martin Luther
- Materialism
- Matter
- Mazdak
- Meditation
- Meher Baba
- Mental process
- Mikveh
- Mind
- Mind uploading
- Mind-body dualism
- Mind-body problem
- Minority religion
- Miracle
- Mircea Eliade
- Mirror neuron
- Missionary
- Mithraic mysteries
- Mitzvot
- Monasticism
- Monism
- Monk
- Monotheism
- Mormonism
- Motivation
- Muslim philosopher
- Mysticism
- Mythology
- Nafs
- National church
- Natural evil
- Natural-law argument
- Nature worship
- Nefesh habehamit
- Neopaganism
- Neoplatonism
- Nephesh
- Neshama
- Neuroscience
- Neurotheology
- New Age
- New Thought
- Nondualism
- Nontheism
- Nous
- Nun
- Object (philosophy)
- Occam's razor
- Old Dutch
- Old English
- Old High German
- Old Norse
- Old Saxon
- Oliver Leaman
- Omnipotence paradox
- On the Soul
- Ontological
- Ontological argument
- Ordination
- Organ (anatomy)
- Oriental Orthodoxy
- Orthodox Judaism
- Orthodoxy
- Orthopraxy
- Outline of religion
- Oxymoron
- Paleolithic religion
- Pandeism
- Panentheism
- Pantheism
- Paradise
- Parapsychologists
- Particular judgment
- Pascal's Wager
- Paul Tillich
- Paul Twitchell
- Pavel Florensky
- Perennial philosophy
- Persian people
- Personal god
- Peter Geach
- Philippine mythology
- Philosophical zombie
- Philosophy of mind
- Photographed
- Pindar
- Plato
- Pneuma
- Polynesian mythology
- Polytheism
- Portal Philosophy
- Portal Religion
- Prakriti
- Prayer
- Pre-existence
- Prehistoric religion
- Problem of evil
- Problem of Hell
- Process theology
- Proselytism
- Protestanism
- Protestantism
- Psyche (psychology)
- Psychic
- Psychologist
- Psychology
- Psychopathology
- Psychotherapy
- Purgatory
- Purusha
- Pythagoreanism
- Qualia
- Rastafari movement
- Ravidassia religion
- Raëlism
- Reason
- Reform Judaism
- Reincarnate
- Reinhold Niebuhr
- Relative term
- Religion
- Religious behaviour
- Religious belief
- Religious conversion
- Religious education
- Religious fanaticism
- Religious humanism
- Religious language
- Religious naturalism
- Religious philosophy
- Religious pluralism
- Religious studies
- Religious symbolism
- Religious terrorism
- Religious violence
- Religious war
- René Descartes
- René Guénon
- Resurrection
- Richard Swinburne
- Ritual
- Robert Todd Carroll
- Routledge
- Ruach
- Rudolf Otto
- Rudolf Steiner
- Russell's teapot
- Sacrifice
- Saint Paul
- Sam'al
- Samaritan
- Samkhya
- Sanskrit
- Schism (religion)
- Scholasticism
- Scientific
- Scientology
- Second Coming
- Secular humanism
- Secular theology
- Secularism
- Secularization
- Seicho-no-Ie
- Self (philosophy)
- Self (spirituality)
- Self-awareness
- Self-consciousness
- Sense
- Septuagint
- Sergei Bulgakov
- Shadow (psychology)
- Shaivism
- Shaktism
- Shamanism
- Shia Islam
- Shinto
- Sikhism
- Slavic mythology
- Smartism
- Socrates
- Soul
- Soul dualism
- Soul in the Bible
- Spirit
- Spirituality
- State religion
- Stele
- Store consciousness
- Substance theory
- Sufism
- Summa Theologica
- Sunni Islam
- Supernatural
- Supreme being
- Surat Shabd Yoga
- Syncretism
- Søren Kierkegaard
- Taoism
- Tenrikyo
- Terence
- Tevilah
- The Times
- Theism
- Thelema
- Theocracy
- Theodicy
- Theological veto
- Theology
- Theories of religion
- Theory of mind
- Theosophy
- Theravada
- Thomas Aquinas
- Thomas Chubb
- Thomas Nagel
- Thought experiment
- Thumos
- Tibetan Buddhism
- Timeline of religion
- Toleration
- Torah
- Traducianism
- Transcendentalism
- Transhumanism
- Transtheistic
- Tzadik
- Ulfilas
- Unconsciousness
- Unification Church
- Universal salvation
- Universalism
- Unmoved mover
- Utne Reader
- Vaishnavism
- Vajrayana
- Verificationism
- Vespasian Psalter
- Visishtadvaita
- Vitalism
- Vulgate
- Waheguru
- Water and religion
- Wealth and religion
- Western philosophy
- Western world
- Wicca
- Wikipedia Link rot
- Wikipedia Vagueness
- William Alston
- William Bouguereau
- William James
- William L. Rowe
- William Lane Craig
- William Whewell
- William Wollaston
- Women and religion
- Worship
- Yazidi
- Yechidah
- Yin and yang
- Yogacara
- Zen
- Zoroastrianism
- Zurvanism
- Ātman (Hinduism)
- אֱלֹהִ֔ים
- 三魂七魄
- Adib Taherzadeh
- Albrecht Ritschl
- Alvin Plantinga
- Anselm of Canterbury
- Anthony Kenny
- Antony Flew
- Aristotle
- Augustine of Hippo
- Averroes
- Avicenna
- Baruch Spinoza
- Bertrand Russell
- Blaise Pascal
- Boethius
- Charles Hartshorne
- Daniel Dennett
- David Chalmers
- David Hume
- Desiderius Erasmus
- Edward Conze
- Emil Brunner
- Ernst Cassirer
- Ernst Haeckel
- Ernst Troeltsch
- Erwin Rohde
- Francis Crick
- Frederick Buechner
- Friedrich Nietzsche
- George Gurdjieff
- George Santayana
- Gilbert Ryle
- Goths
- Harald Høffding
- Helena Blavatsky
- Heraclitus
- Hereward Carrington
- Homer
- Hossein Nasr
- Immanuel Kant
- James Hillman
- Karl Barth
- Karl Marx
- Kuttamuwa
- Lev Shestov
- Loyal Rue
- Ludwig Feuerbach
- Maimonides
- Manichaeism
- Martin Buber
- Martin Lings
- Martin Luther
- Mazdak
- Meher Baba
- Mircea Eliade
- Oliver Leaman
- Paul Tillich
- Paul Twitchell
- Pavel Florensky
- Persian people
- Peter Geach
- Pindar
- Plato
- Reinhold Niebuhr
- René Descartes
- René Guénon
- Richard Swinburne
- Robert Todd Carroll
- Rudolf Otto
- Rudolf Steiner
- Sergei Bulgakov
- Socrates
- Søren Kierkegaard
- Terence
- Thomas Aquinas
- Thomas Chubb
- Thomas Nagel
- Ulfilas
- William Alston
- William James
- William Lane Craig
- William Whewell
- William Wollaston
- Yazidi
-

The difference between soul and spirit.
Tom talks about the soul and spirit in us and what it means to be saved. https://www.gofundme.com/tomfischer -

Do We Have A Body, Soul, and Spirit? - Pastor Richard Jordan
. TO LEARN HOW TO BE SAVED click on "Show more" below. Please visit: http://www.rightdivider.net/speakers/rj/judge/judge.htm This Clip From The Message: "A New Creature In Christ" #882 Order From: "The Message of Grace" PO Box 97, Bloomingdale, IL 60108 (888) 535-2300 -- ( Tags: Mid Acts, Pauline, Dispensational, "Rightly Dividing" Bible, Word of God, 2 Timothy 2:15, Apostle Paul, C.R. Stam, J.C. O'Hair, Joel Finck, Charles F. Baker, Keith R. Blades, ) -- If you need GREAT messages to help you grow in your faith click on the links below... http://helpersofyourjoy.com/?page_id=59 http://columbusbiblechurch.org/ http://www.rightlydividing.org/MP3_grace/mp3.htm http://shorewoodbiblechurch.org/ You Tube: http://www.youtube.com/user/TheMessageofGrace http://www.youtube.com/user/n... -

-

Spirit Soul & Body - Animation Part 1
To subscribe to Andrew’s email newsletter: http://www.awmi.net/youtube-subscribe/ This is the 1st animation of the teaching Spirit, Soul and Body, which is a foundational truth that is essential for understanding how much God loves you and believing what He says about you in His Word. Each person is made up of three different parts: spirit, soul, and body. Learn how these three parts relate to God and to each other. At salvation your spirit is totally changed, but your soul and body is not yet redeemed. This series will teach you how to release the life that is already in your spirit, into your physical body and emotions. ==================================== Andrew Wommack Ministries http://www.awmi.net/ https://www.facebook.com/AWMinistries https://twitter.com/andrewwommack http... -

-

What is the Difference Between Soul and Spirit?
Student Question: What is the difference between soul and spirit? -

What does the Bible say about our Body Soul Spirit?
What does the Bible say about our Body, Soul and Spirit? What happens when we are born again? How does this affect me in my walk with the Lord? Why do I still sin if I have been born again? -

Going Beyond the Soul to Spirit by Zac Poonen
Website: http://www.sermonindex.net Google+: https://www.google.com/+SermonindexNet The work and ministry of sermonindex can be encapsulated in this one word: REVIVAL. sermonindex is not a organisation, business, or any attempt by man to build something for God. It is rather a expression of a heart burden to see the Church revived and brought back to holiness, purity, and power with God. "The mission of SermonIndex is the preservation and propogation of classical vintage preaching and the promotion of genuine biblical revival to this generation." -

Why You Do What You Do - How body, soul, and spirit work
http://christianhomeandfamily.com - Human behavior can be confusing. Add to that the influence of being a fallen human being and the sinful habits we develop - and you can go "tilt" trying to figure it out. This screencast is designed to help you understand what the Bible says about how your body, soul, and spirit work together - and how the entrance of the Holy Spirit into your life can make all the difference! MUSIC USED BY PERMISSION of Adam Rey - http://www.heyreyguitar.com Christian Home and Family exists to help you make Christ the center of your home. Contact Carey with your questions, counseling needs, suggestions, and comments. TWITTER: http://christianhomeandfamily.com/twitter PODCAST: http://christianhomeandfamily.com/podcast FACEBOOK: http://christianhomeandfamily.com/face... -

-

Ian Clayton - Splitting Soul & Spirit (Company of Burning Hearts)
Splitting Soul & Spirit - Ian Clayton Re-up from: http://companyofburninghearts.podomatic.com/entry/2011-10-03T17_44_05-07_00 Company of Burning Hearts http://companyofburninghearts.wordpress.com Son of Thunder is the Itinerant Ministry of Ian Clayton http://www.sonofthunder.org -

Andrew Wommack: Spirit, Soul & Body - Week 1 - Session 1
This DVD album was recorded from the Gospel Truth TV broadcast. Each DVD contains one week of programming. Please note that while they do cover the same material as a CD album, they are not exactly the same. This teaching is a foundational truth that is essential for understanding how much God loves you and believing what He says about you in His Word. Each person is made up of three different parts: spirit, soul, and body. Learn how these three parts relate to God and to each other. At salvation your spirit is totally changed, but your soul and body is not yet redeemed. This series will teach you how to release the life that is already in your spirit, into your physical body and emotions.
The difference between soul and spirit.
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 54:11
- Updated: 14 Dec 2014
- views: 9740
- published: 14 Dec 2014
- views: 9740
Do We Have A Body, Soul, and Spirit? - Pastor Richard Jordan
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 14:47
- Updated: 07 Sep 2014
- views: 3978
- published: 07 Sep 2014
- views: 3978
Soul vs Spirit - John Paul Jackson
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 8:45
- Updated: 29 Jul 2013
- views: 33535
Spirit Soul & Body - Animation Part 1
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 5:04
- Updated: 29 Mar 2016
- views: 3195
- published: 29 Mar 2016
- views: 3195
The Trinity: Body, Soul, and Spirit
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 73:00
- Updated: 14 Mar 2013
- views: 18003
What is the Difference Between Soul and Spirit?
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 8:14
- Updated: 10 Oct 2013
- views: 7995
- published: 10 Oct 2013
- views: 7995
What does the Bible say about our Body Soul Spirit?
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 4:59
- Updated: 08 May 2013
- views: 7042
- published: 08 May 2013
- views: 7042
Going Beyond the Soul to Spirit by Zac Poonen
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 69:02
- Updated: 24 Dec 2015
- views: 7925
- published: 24 Dec 2015
- views: 7925
Why You Do What You Do - How body, soul, and spirit work
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 12:27
- Updated: 01 Aug 2012
- views: 7226
- published: 01 Aug 2012
- views: 7226
Mongolian Music - Healing Soul Spirit Song
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 5:15
- Updated: 08 Jan 2013
- views: 784369
Ian Clayton - Splitting Soul & Spirit (Company of Burning Hearts)
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 34:01
- Updated: 31 Aug 2014
- views: 16809
- published: 31 Aug 2014
- views: 16809
Andrew Wommack: Spirit, Soul & Body - Week 1 - Session 1
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 31:15
- Updated: 15 Aug 2013
- views: 35754
- published: 15 Aug 2013
- views: 35754
- Playlist
- Chat
- Playlist
- Chat

The difference between soul and spirit.
- Report rights infringement
- published: 14 Dec 2014
- views: 9740

Do We Have A Body, Soul, and Spirit? - Pastor Richard Jordan
- Report rights infringement
- published: 07 Sep 2014
- views: 3978

Soul vs Spirit - John Paul Jackson
- Report rights infringement
- published: 29 Jul 2013
- views: 33535

Spirit Soul & Body - Animation Part 1
- Report rights infringement
- published: 29 Mar 2016
- views: 3195

The Trinity: Body, Soul, and Spirit
- Report rights infringement
- published: 14 Mar 2013
- views: 18003

What is the Difference Between Soul and Spirit?
- Report rights infringement
- published: 10 Oct 2013
- views: 7995

What does the Bible say about our Body Soul Spirit?
- Report rights infringement
- published: 08 May 2013
- views: 7042

Going Beyond the Soul to Spirit by Zac Poonen
- Report rights infringement
- published: 24 Dec 2015
- views: 7925

Why You Do What You Do - How body, soul, and spirit work
- Report rights infringement
- published: 01 Aug 2012
- views: 7226


Ian Clayton - Splitting Soul & Spirit (Company of Burning Hearts)
- Report rights infringement
- published: 31 Aug 2014
- views: 16809

Andrew Wommack: Spirit, Soul & Body - Week 1 - Session 1
- Report rights infringement
- published: 15 Aug 2013
- views: 35754
[VIDEOS]: Behind-The-Scenes Scenario May Prevent Trump, Clinton Presidency: Report
Edit WorldNews.com 18 May 2016“In New Republican Party We Trust” As Democrats Face Contested Convention
Edit WorldNews.com 18 May 2016A mysterious ocean on a frozen moon just became our best shot at finding alien life
Edit Business Insider 18 May 2016'First Chibok girl found' in Nigeria
Edit BBC News 18 May 2016US scientists say major earthquake likely in Jammu & Kashmir
Edit The Times of India 18 May 2016Blues, Soul, Reggae with Dom Pipkin
Edit Skiddle 19 May 2016Heavy Jams
Edit Skiddle 19 May 2016Colin Roy Swing & Motown Night
Edit Skiddle 19 May 2016Quantic
Edit Skiddle 19 May 2016Mara Simpson full band Album Release Show
Edit Skiddle 19 May 2016Algo Mas tickets
Edit Skiddle 19 May 2016Blade joining Daredevil, Jessica Jones, Luke Cage, Iron Fist on Netflix?
Edit The Examiner 19 May 2016Pagoda: Brame & Hamo tickets
Edit Skiddle 19 May 2016Week 13 Players of the Week Announced (IFL - Indoor Football League)
Edit Public Technologies 19 May 2016Emily Saunders - The Voice Mix
Edit Skiddle 19 May 2016Reflective 'Home Of The Bassline' tickets
Edit Skiddle 19 May 2016Demon’s Souls Servers and Website Offline
Edit TechRaptor 18 May 2016- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- Next page »







