- published: 14 Dec 2014
- views: 190474
-
remove the playlistMotor Oil
- remove the playlistMotor Oil
- published: 19 Jul 2012
- views: 218567
- published: 18 Feb 2015
- views: 71178
- published: 26 Nov 2012
- views: 158858
- published: 13 Apr 2015
- views: 40787
- published: 15 Jun 2012
- views: 193412
- published: 12 May 2015
- views: 14155
- published: 26 Mar 2013
- views: 191400
- published: 29 Jun 2014
- views: 11096
- published: 09 Nov 2012
- views: 102449

Motor oil or engine oil is an oil used for lubrication of various internal combustion engines. The main function is to lubricate moving parts; it also cleans, inhibits corrosion, improves sealing, and cools the engine by carrying heat away from moving parts.
Motor oils are derived from petroleum-based and non-petroleum-synthesized chemical compounds. Motor oils today are mainly blended by using base oils composed of hydrocarbons, polyalphaolefins (PAO), and polyinternal olefins (PIO), thus organic compounds consisting entirely of carbon and hydrogen. The base oils of some high-performance motor oils however contain up to 20% by weight of esters.
Motor oil is a lubricant used in internal combustion engines. These include motor or road vehicles such as cars and motorcycles, heavier vehicles such as buses and commercial vehicles, non-road vehicles such as go-karts, snowmobiles, boats (fixed engine installations and outboards), lawn mowers, large agricultural and construction equipment, locomotives and aircraft and static engines such as electrical generators. In engines, there are parts which move against each other causing friction which wastes otherwise useful power by converting the energy to heat. Contact between moving surfaces also wears away those parts, which could lead to lower efficiency and degradation of the engine. This increases fuel consumption, decreases power output and can, in extreme cases lead to engine failure.
This article is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported License, which means that you can copy and modify it as long as the entire work (including additions) remains under this license.
An oil is any substance that is liquid at ambient temperatures and does not mix with water but may mix with other oils and organic solvents. This general definition includes vegetable oils, volatile essential oils, petrochemical oils, and synthetic oils.
First attested in English 1176, the word oil comes from Old French "oile", from Latin "oleum", which in turn comes from the Greek "ἔλαιον" (elaion), "olive oil, oil" and that from "ἐλαία" (elaia), "olive tree". The earliest attested form of the word is the Mycenaean Greek e-ra-wo, written in Linear B syllabic script.
Organic oils are produced in remarkable diversity by plants, animals, and other organisms through natural metabolic processes. Lipid is the scientific term for the fatty acids, steroids and similar chemicals often found in the oils produced by living things, while oil refers to an overall mixture of chemicals. Organic oils may also contain chemicals other than lipids, including proteins, waxes and alkaloids.
Lipids can be classified by the way that they are made by an organism, their chemical structure and their limited solubility in water compared to oils. They have a high carbon and hydrogen content and are considerably lacking in oxygen compared to other organic compounds and minerals; they tend to be relatively nonpolar molecules, but may include both polar and nonpolar regions as in the case of phospholipids and steroids.
This article is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported License, which means that you can copy and modify it as long as the entire work (including additions) remains under this license.
- Loading...

-
 3:40
3:40Motor Oil Myths & FAQs - Synthetic vs Conventional
Motor Oil Myths & FAQs - Synthetic vs ConventionalMotor Oil Myths & FAQs - Synthetic vs Conventional
Choosing the best, whether synthetic or conventional, engine oil is highly controversial and debated. Motor oil is surrounded with myths and questions. Shell helps answer the following: - What does 5W-30 mean? - Why should I change my oil? - What is the typical composition of motor oil? - Are aftermarket oil additives needed? - What does synthetic oil mean? - Can you mix synthetic with conventional oil? - Can synthetic be used to break in an engine? - What causes sludge? - Why should I use the viscosity grade that the manufacturer recommends? Related Videos: Trackside Lab Formula 1 - http://youtu.be/6G8XP8L-MFE Shell Technology Center - http://youtu.be/pUr7-Ug1Uqc Please feel free to rate, comment, and subscribe! And don't forget to check out my Facebook page: http://www.facebook.com/engineeringexplained To help create more videos, check out my Patreon page! http://www.patreon.com/engineeringexplained Also check out my official website: Make suggestions, participate in forums, learn through logically ordered lessons, read FAQs, and plan your future! http://www.howdoesacarwork.com Now on Twitter: http://www.twitter.com/jasonfenske13 NEW VIDEO EVERY WEDNESDAY! -
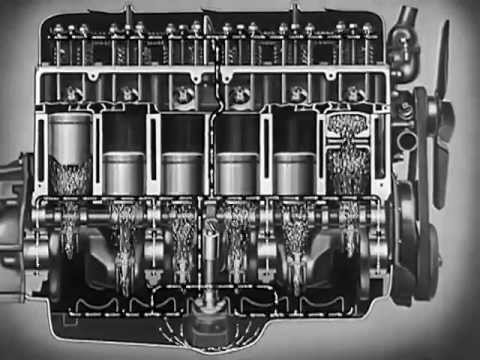 10:40
10:40Motor Oil: "Riding the Film" 1937 Chevrolet Engine Lubrication 11min
Motor Oil: "Riding the Film" 1937 Chevrolet Engine Lubrication 11minMotor Oil: "Riding the Film" 1937 Chevrolet Engine Lubrication 11min
more at http://auto-parts.quickfound.net/ "Motorists really ride on a film of oil, because all the moving parts of the engine are kept slipping over each other by a thin film of oil." 'Possibly footage from 1936 Winter Olympics in Germany. Cross country skiers riding over wood bridge through snowy forest; VS skier riding down hill. Great LS ski jumper in tuck position skiing down long steep ramp of jump; cut to ski jumper flying through the air; LS ski jumper lands jump, camera pans over to audience in bleachers, Nazi flag with swastika insignia hangs by bleachers. Two men on sleds dive head first down track away from camera; VS people riding on sleds; VS of the luges racing through luge course. Great shot sailboat-like sled glides over camera on ice; VS men sledding on sailboat-like sleds; VS ice skating; high-angle pair figure skating. CU ice, blade of figure skate slides up to camera; camera zooms into CU blade of ice skate against ice; CU figure skate blade against ice with superimposed arrows to aid in audio tracks explanation of the physics of ice skating. CU figure skate with moving projection background to make skate appear as though it is gliding over the ice. Boy about 12 slides down slide into pool; formally dressed men women and children on Coney Island ride with boat sliding to shoot into water. CU disembodied arm opens filing cabinet drawer then takes bar of soap and soaps edge of drawer then opens and closes the filing cabinet door. Great shot of the disembarking of a huge late 1930s ocean liner, audience watches as ship enters water. CU scientist for an experiment pours oil for lubrication from a metal kettle onto small ramp then releases a black from top of ramp letting it slide to the bottom. Train engineer lubricating various parts of train. CU disembodied hand dabs finger tip in glass container filled with oil; CU disembodied forefinger with oil on it is pinched together with the thumb; VS scientist does experiment with flywheel bearing and various methods of lubrication. CU of an engine, cover of engine dissolves from shot revealing cross-section of an engine exposing pumping cylinders; VS graphic illustrations of a running engine and the pathway of oil through the engines various parts. Camera zooms in on cross-section of running engine to main bearings, superimposed arrows in shot identify the bearings next to the crank shaft; cut to cartoon illustrating the main bearing receiving oil in a running engine. CU cross-section of a running engine, camera zooms in on the cam shaft; CU valves opening and closing; cartoon of cross-section of running engine. CU running engine; CU oil being poured into gears; VS cartoon of running engine and the locations where oil enters the system. Great shot old locomotive producing large black cloud of smoke heads toward camera alongside tracks; train speeds by camera, "New York Central" painted on side of train. Great shot two men, one greasy mechanic and one filmmaker behind movie camera filming with a stroboscope a running engine; CU SLO MO of oil dripping around spinning crank shaft of engine; cartoon animation shows cross section of running engine with pumping cylinder. Scientist wearing a long white lab coat holds a hose attached to an engine; scientist turns on nozzle of hose and sprays oil from the engine onto a blank blackboard; CU disembodied hand holding hose spraying oil in a somewhat phallic gesture; CU oil spraying on board. VS CU various running engine parts, superimposed over various CU shots is a shot of oil slowly dripping from top to bottom of frame.' Public domain film from the Library of Congress Prelinger Archive, slightly cropped to remove uneven edges, with the aspect ratio corrected, and mild video noise reduction applied. The soundtrack was also processed with volume normalization, noise reduction, clipping reduction, and equalization (the resulting sound, though not perfect, is far less noisy than the original). http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Motor_oil ...Motor oils are derived from petroleum-based and non-petroleum-synthesized chemical compounds. Motor oils today are mainly blended by using base oils composed of hydrocarbons, polyalphaolefins (PAO), and polyinternal olefins (PIO), thus organic compounds consisting entirely of carbon and hydrogen. The base oils of some high-performance motor oils however contain up to 20% by weight of esters... Lubricating oil creates a separating film between surfaces of adjacent moving parts to minimize direct contact between them, decreasing heat caused by friction and reducing wear, thus protecting the engine... -
 20:45
20:45Straight Talk About Motor Oil
Straight Talk About Motor OilStraight Talk About Motor Oil
-
 2:29
2:29Don't Destroy Your Engine With Bad Motor Oil
Don't Destroy Your Engine With Bad Motor OilDon't Destroy Your Engine With Bad Motor Oil
Motor oil -
 2:07
2:07How does car engine oil work?
How does car engine oil work?How does car engine oil work?
The journey of oil around a car engine takes as little as five seconds. In this time it protects critical engine parts, preventing damage. This short film take us on this incredible journey, truly demonstrating oil in action. For more information, please visit www.castrol.com. -
 8:45
8:45Choosing the Best Motor Oil for your Vehicle
Choosing the Best Motor Oil for your VehicleChoosing the Best Motor Oil for your Vehicle
In this edition I cover how to choose the best motor oil for your vehicle and your budget. We will be looking at API certified vs. Uncertified, the different weights of oils and how to choose which weight is correct for your vehicle, and also tips on choosing between Conventional, Synthetic Blends, or Fully Synthetic oils. Plus we do an experiment to help you better understand how multi-weight and straight weight oils differer at different temperatures. If you have any questions, leave a comment below and I will be glad to answer it! Cheers, Drake -
 8:34
8:34-20 motor oil test
-20 motor oil test-20 motor oil test
We did a test at -20 between all of these oils let me know what you think in the comments and if we missed a brand you think we should test -
 8:14
8:14How to Choose Between Synthetic and Conventional Motor Oil
How to Choose Between Synthetic and Conventional Motor OilHow to Choose Between Synthetic and Conventional Motor Oil
On this community episode Ben and Russ answer Matt's questions about motor oil. Which is better, conventional or synthetic oil? Matt also asks whether he should use synthetic in his vehicles. Subscribe! http://bit.ly/subscribecaranddriver Tune in to the new Car and Driver Channel on YouTube and follow Popular Mechanics associate auto editor Ben Wojdyla as he leads viewers, step by step, through repairs and upgrades on the Saturday Mechanic show. Got car questions? Email Ben, and he may answer them on the air. Connect with Ben Wojdyla: Facebook: http://www.facebook.com/#!/ben.wojdyla Twitter: http://twitter.com/#!/Ben_Wojdyla Youtube: http://www.youtube.com/user/bwojdyla Connect To Popular Mechanics: http://www.facebook.com/popularmechanics http://twitter.com/#!/popmech Connect to Car and Driver: Subscribe! http://bit.ly/subscribecaranddriver Twitter: http://bit.ly/tweetcaranddriver Facebook: http://on.fb.me/facebookcaranddriver -
 4:01
4:01Best Price Motor Oil Comparison ~ Walmart vs O'Reilly's ~ Automotive Video
Best Price Motor Oil Comparison ~ Walmart vs O'Reilly's ~ Automotive VideoBest Price Motor Oil Comparison ~ Walmart vs O'Reilly's ~ Automotive Video
Best Price Motor Oil Comparison ~ Walmart vs O'Reilly's ~ Automotive Video http://www.hipstercars.com Oil, Transmission Fluid Power Steering Brake etc all consumables where do you Buy. Auto Parts and Fluids are not cheap. in Business its Good to Shop around Shop & Save at Wal-Mart. It is amazing just how much money you can save when you buy at walmart. Even oil compared to any auto parts store it is a big difference in prices. It seems that everything is cheaper at Wal-Mart and I do most all of my shopping there for food and supplies. Make sure and keep an eye out for more great videos coming up. THANK YOU For watching and Make sure to stay in Touch at these Social Media Links below Add me on YouTube, Facebook, Twitter & Instagram. http://www.youtube.com/subscription_center?add_user=cerealmarshmallows http://www.facebook.com/nathanwratislaw https://instagram.com/cerealmarshmallows/ http://www.twitter.com/1ownercarguy Make sure and visit Some of My Websites Below I do All Sorts of Unique Things..;-) www.1ownercarguy.com www.cerealmarshmallows.com www.hipstercars.com Send Me Hate Mail or Goodies & Stuff to show on Youtube 1 Owner Car Guy (Nathan Wratislaw) PO Box 2505 Lakeside, CA 92040 No Ticking items please..;-) "Motor Oil" "Auto Parts" Parts "Auto Parts Store" -
 1:19
1:19Pennzoil - Conventional vs Synthetic Motor Oil
Pennzoil - Conventional vs Synthetic Motor OilPennzoil - Conventional vs Synthetic Motor Oil
Pennzoil Technology Manager Bob Sutherland and Lubricants Technology Managers Mark Ferner and Allison Falender talk about how Pennzoil Platinum synthetic motor oil performs better than all other leading brands in extreme heat and extreme cold temperatures. Based on ASTM Sequence IIIG piston deposit test using SAE 5W-30. Does not apply to Pennzoil Platinum® 0W20. Pennzoil Platinum® keeps pistons up to 8% cleaner than Mobil 1; up to 17% cleaner than Valvoline® SynPower®; and up to 20% cleaner than Castrol® EDGE® with SYNTEC®. Learn More: http://www.pz4.me/1w -
 3:31
3:31What do motor oil numbers mean?
What do motor oil numbers mean?What do motor oil numbers mean?
Learn what 5W-30 means on that bottle of oil you are putting in your engine. Why does it matter what weight of oil you use? When it's ok to change oil viscosity depending on where you live and how you drive. Visit http://www.autoeducation.com/autoshop101/oil-change.htm for more information. -
 5:12
5:12Choosing the Right Oil Type
Choosing the Right Oil TypeChoosing the Right Oil Type
How do you decide what motor oil is right for the life of your engine? -
 3:56
3:56Free energy and heating - waste motor oil stove experiment prototype
Free energy and heating - waste motor oil stove experiment prototypeFree energy and heating - waste motor oil stove experiment prototype
A waste motor oil stove i have build and experimented with. Please excuse the poor construction details and quality of assembly. It is only a prototype used to test the working principle. I think it will be good to heat up a garage, a small workshop, a barn or any other place where is waste motor oil available. -
 13:36
13:36All About Motor Oil for Your Gasoline Fuel Car
All About Motor Oil for Your Gasoline Fuel CarAll About Motor Oil for Your Gasoline Fuel Car
***Sponsored Video*** Amazon links to the oil shown in this here video↓ http://www.amazon.com/gp/product/B0123EL2OI/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp;=1789&creative;=9325&creativeASIN;=B0123EL2OI&linkCode;=as2&tag;=httpwwwyou00f-20&linkId;=QG44S6K57RBEZZHL Check out Shanna's videos on the Pennzoil YouTube account here → https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Sloh8cWxVhM&list;=PLLJ-AgGEakKSPf0WumAWZLChp6FI34Zu- Connect with me socially on these social media spaces Facebook → https://www.facebook.com/briansmobile1 Instagram → https://instagram.com/briansmobile1/ Twitter → https://twitter.com/briansmobile1/ Who's the BOSS? Get'em to donate here! It's tax deductible! These folks help kids like my daughter to stop having seizures so they can develop properly! Glut1 Foundation → http://www.g1dfoundation.org/ways-to-give/donate/ I love mail! (or maybe just riding the motorcycle to get it!) Drop me a letter! P.O. Box 282 Cedar Valley, UT 84013 All About Motor Oil for Your Gasoline Fuel Car
- 1,2-Dichloroethane
- 3,000 mile myth
- Acidity
- Alkalinity
- Antifreeze
- Atom
- AW additive
- BMW
- Brake fluid
- Butyl rubber
- Carbon
- Catalytic
- Catalytic converter
- Citroën
- Classic car
- Coke (fuel)
- Combustion chamber
- Connecting rod
- Convection
- Corrosion
- Corrosion inhibitor
- Crankcase
- Crankshaft
- Crude oil
- Cylinder (engine)
- Cylinder head
- Detergent
- Dexos
- Diesel engine
- Diesel fuel
- Dispersant
- Ecalene
- Edmonton Oilers
- Engine cooling
- EP additive
- Ester
- Esters
- Ethylenediamine
- Europe
- European Union
- Filling station
- Flash point
- Foam
- Ford Motor Company
- Four-stroke engine
- Friction
- Fuel card
- Fuel efficiency
- Full service
- Gasoline
- Gasoline engine
- Gear oil
- Gear pump
- General Motors
- Glass bottle
- GM 3800 engine
- Heat
- How-to
- Hydrocarbon
- Hydrocracking
- Hydrogen
- Journal bearings
- Lubricant
- Lubrication
- Mercedes-Benz
- Metal deactivator
- Mineral oil
- Mobil 1
- Molecule
- Molybdenum disulfide
- Motive power
- Motor oil
- Motorcycle oil
- Moving parts
- MTBE controversy
- Nitromethane
- NOACK volatility
- Oil
- Oil filter
- Oil pan
- Oil refinery
- Oil sludge
- Organic compounds
- Oxidation
- Oxygen
- Pay at the pump
- PCV valve
- Petroleum
- Peugeot
- Phosphorus
- Piston ring
- Pistons
- Plastic bottle
- Poise
- Polyalkylene glycol
- Polyalpha-olefins
- Polyalphaolefin
- Polyethylene
- Polymer
- Polyol
- Porsche
- PSA Peugeot Citroën
- PTFE
- Rust
- Snow blower
- Soot
- Stokes (unit)
- Sulfur
- Sump
- Synthetic lubricants
- Synthetic oils
- Talk Motor oil
- Template Motor fuel
- Tetraethyllead
- Tetranitromethane
- Total Acid Number
- Total Base Number
- Turbocharger
- TV documentary
- Two-stroke engine
- Two-stroke oil
- Viscosity
- Viscosity index
- Volkswagen Group
- Wear
- WikiHow
- WP references
- WP Verifiability
- Zinc
- Zinc dithiophosphate
-

Motor Oil Myths & FAQs - Synthetic vs Conventional
Choosing the best, whether synthetic or conventional, engine oil is highly controversial and debated. Motor oil is surrounded with myths and questions. Shell helps answer the following: - What does 5W-30 mean? - Why should I change my oil? - What is the typical composition of motor oil? - Are aftermarket oil additives needed? - What does synthetic oil mean? - Can you mix synthetic with conventional oil? - Can synthetic be used to break in an engine? - What causes sludge? - Why should I use the viscosity grade that the manufacturer recommends? Related Videos: Trackside Lab Formula 1 - http://youtu.be/6G8XP8L-MFE Shell Technology Center - http://youtu.be/pUr7-Ug1Uqc Please feel free to rate, comment, and subscribe! And don't forget to check out my Facebook page: http://www.facebook.com/... -

Motor Oil: "Riding the Film" 1937 Chevrolet Engine Lubrication 11min
more at http://auto-parts.quickfound.net/ "Motorists really ride on a film of oil, because all the moving parts of the engine are kept slipping over each other by a thin film of oil." 'Possibly footage from 1936 Winter Olympics in Germany. Cross country skiers riding over wood bridge through snowy forest; VS skier riding down hill. Great LS ski jumper in tuck position skiing down long steep ramp of jump; cut to ski jumper flying through the air; LS ski jumper lands jump, camera pans over to audience in bleachers, Nazi flag with swastika insignia hangs by bleachers. Two men on sleds dive head first down track away from camera; VS people riding on sleds; VS of the luges racing through luge course. Great shot sailboat-like sled glides over camera on ice; VS men sledding on sailboat-like... -

Straight Talk About Motor Oil
-

Don't Destroy Your Engine With Bad Motor Oil
Motor oil -

How does car engine oil work?
The journey of oil around a car engine takes as little as five seconds. In this time it protects critical engine parts, preventing damage. This short film take us on this incredible journey, truly demonstrating oil in action. For more information, please visit www.castrol.com. -

Choosing the Best Motor Oil for your Vehicle
In this edition I cover how to choose the best motor oil for your vehicle and your budget. We will be looking at API certified vs. Uncertified, the different weights of oils and how to choose which weight is correct for your vehicle, and also tips on choosing between Conventional, Synthetic Blends, or Fully Synthetic oils. Plus we do an experiment to help you better understand how multi-weight and straight weight oils differer at different temperatures. If you have any questions, leave a comment below and I will be glad to answer it! Cheers, Drake -

-20 motor oil test
We did a test at -20 between all of these oils let me know what you think in the comments and if we missed a brand you think we should test -

How to Choose Between Synthetic and Conventional Motor Oil
On this community episode Ben and Russ answer Matt's questions about motor oil. Which is better, conventional or synthetic oil? Matt also asks whether he should use synthetic in his vehicles. Subscribe! http://bit.ly/subscribecaranddriver Tune in to the new Car and Driver Channel on YouTube and follow Popular Mechanics associate auto editor Ben Wojdyla as he leads viewers, step by step, through repairs and upgrades on the Saturday Mechanic show. Got car questions? Email Ben, and he may answer them on the air. Connect with Ben Wojdyla: Facebook: http://www.facebook.com/#!/ben.wojdyla Twitter: http://twitter.com/#!/Ben_Wojdyla Youtube: http://www.youtube.com/user/bwojdyla Connect To Popular Mechanics: http://www.facebook.com/popularmechanics http://twitter.com/#!/popmech Connect to Car... -

Best Price Motor Oil Comparison ~ Walmart vs O'Reilly's ~ Automotive Video
Best Price Motor Oil Comparison ~ Walmart vs O'Reilly's ~ Automotive Video http://www.hipstercars.com Oil, Transmission Fluid Power Steering Brake etc all consumables where do you Buy. Auto Parts and Fluids are not cheap. in Business its Good to Shop around Shop & Save at Wal-Mart. It is amazing just how much money you can save when you buy at walmart. Even oil compared to any auto parts store it is a big difference in prices. It seems that everything is cheaper at Wal-Mart and I do most all of my shopping there for food and supplies. Make sure and keep an eye out for more great videos coming up. THANK YOU For watching and Make sure to stay in Touch at these Social Media Links below Add me on YouTube, Facebook, Twitter & Instagram. http://www.youtube.com/subscription_center?add_user=cere... -

Pennzoil - Conventional vs Synthetic Motor Oil
Pennzoil Technology Manager Bob Sutherland and Lubricants Technology Managers Mark Ferner and Allison Falender talk about how Pennzoil Platinum synthetic motor oil performs better than all other leading brands in extreme heat and extreme cold temperatures. Based on ASTM Sequence IIIG piston deposit test using SAE 5W-30. Does not apply to Pennzoil Platinum® 0W20. Pennzoil Platinum® keeps pistons up to 8% cleaner than Mobil 1; up to 17% cleaner than Valvoline® SynPower®; and up to 20% cleaner than Castrol® EDGE® with SYNTEC®. Learn More: http://www.pz4.me/1w -

What do motor oil numbers mean?
Learn what 5W-30 means on that bottle of oil you are putting in your engine. Why does it matter what weight of oil you use? When it's ok to change oil viscosity depending on where you live and how you drive. Visit http://www.autoeducation.com/autoshop101/oil-change.htm for more information. -

Choosing the Right Oil Type
How do you decide what motor oil is right for the life of your engine? -

Free energy and heating - waste motor oil stove experiment prototype
A waste motor oil stove i have build and experimented with. Please excuse the poor construction details and quality of assembly. It is only a prototype used to test the working principle. I think it will be good to heat up a garage, a small workshop, a barn or any other place where is waste motor oil available. -

All About Motor Oil for Your Gasoline Fuel Car
***Sponsored Video*** Amazon links to the oil shown in this here video↓ http://www.amazon.com/gp/product/B0123EL2OI/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp;=1789&creative;=9325&creativeASIN;=B0123EL2OI&linkCode;=as2&tag;=httpwwwyou00f-20&linkId;=QG44S6K57RBEZZHL Check out Shanna's videos on the Pennzoil YouTube account here → https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Sloh8cWxVhM&list;=PLLJ-AgGEakKSPf0WumAWZLChp6FI34Zu- Connect with me socially on these social media spaces Facebook → https://www.facebook.com/briansmobile1 Instagram → https://instagram.com/briansmobile1/ Twitter → https://twitter.com/briansmobile1/ Who's the BOSS? Get'em to donate here! It's tax deductible! These folks help kids like my daughter to stop having seizures so they can develop properly! Glut1 Foundation → http://www.g1dfoundation.org/wa... -

-

Mobil 1 vs. Liqui Moly - Synthetic Motor Oil Review - Bundys Garage
Tests performed to Mobil 1 and Liqui Moly to see which ones takes the abuse best. You decide which one wins, let me know in the comments below. Mobile 1 Oil Website: www.mobiloil.com Liqui Moly Website: www.liqui-moly.com Questions, Comments, Conceerns email me at: bundysgarage@gmail.com Musis by Randall Kent All Rights Reserved Copyright 2014 Bundys Garage DISCLAIMER - DISCLAIMER - DISCLAIMER Due to factors beyond the control of BundysGarage, it cannot guarantee against unauthorized modifications of this information, or improper use of this information. BundysGarage assumes no liability for property damage or injury incurred as a result of any of the information contained in this video. BundysGarage recommends safe practices when working with power tools, automotive lifts, liftin... -

Can I use Transmission Fluid as Motor Oil?
Fact or Myth? Can using Automatic Transmission fluid as a temporary substitute hurt the internal components of my engine or does it help De-carbonize its components? In this video I add 1 quart of ATF as an experiment to see what kind of effects if any are derived from it. -

Sludge Buildup From Not Changing Motor Oil - LT1 Engine
What happens when you don't change your engine oil? Sludge buildup as you see here. This LT1 has one of the worst cases of sludge buildup that we've ever seen. If you wait until 10,000 miles or more before changing your oil, your oil may turn to sludge which causes damage to your engine like it did this one. The conventional wisdom is to change your car’s motor oil every 3,000 to 5,000 miles or at least once a year. -

How used motor oil is recycled
-

-

How to Change Honda CRV Engine Motor Oil
How to change the engine oil for a Honda CRV. The same concept applies to all cars. For this car, I used 4.5 quarts of 0W20 full synthetic motor oil. I also changed the oil filter. I change the oil roughly every 7500 miles. I also rotate my car tires whenever I change the engine oil. Thanks for watching. http://www.AwkwardHamster.com http://twitter.com/AwkwardHamster https://www.facebook.com/AwkwardHamster https://plus.google.com/+AwkwardHamster/ -

Synthetic Oil Basics
Technically, Synthetic Oil originates as traditional mineral based motor oil. What separates the two is the level of advanced engineering, refinement and criteria that goes into this modern engine lubricant. In short, there is no other routine maintenance contributor that can provide better protection, performance and longevity than today's Synthetic Motor Oils Extreme Weather Protection: Under early morning sub-zero winter starts or summertime high temperature stop-and-go traffic, Synthetic Oils are engineered to deliver vital engine protection and reliable performance year-round. Cold Weather Pour Test: In this laboratory test, a Synthetic-Oil and a Synthetic-Mineral-Blend have been frozen overnight at minus 40 below. This pour test illustrates conclusively the cold-start read... -

Should you switch to full synthetic motor oil? - Auto Information Series
Full synthetic motor oil is better for the internal moving parts of your automobile motor. It usually lubricates the motor better, extends your oil change intervals, and may even increase your mpg. The savings will usually out weigh the cost of the better oil. This video explains why some people experience oil leaks when they switch to full synthetic motor oil.
Motor Oil Myths & FAQs - Synthetic vs Conventional
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 3:40
- Updated: 14 Dec 2014
- views: 190474
- published: 14 Dec 2014
- views: 190474
Motor Oil: "Riding the Film" 1937 Chevrolet Engine Lubrication 11min
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 10:40
- Updated: 19 Jul 2012
- views: 218567
- published: 19 Jul 2012
- views: 218567
Straight Talk About Motor Oil
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 20:45
- Updated: 31 Oct 2012
- views: 73824
- published: 31 Oct 2012
- views: 73824
Don't Destroy Your Engine With Bad Motor Oil
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 2:29
- Updated: 13 Aug 2013
- views: 92644
- published: 13 Aug 2013
- views: 92644
How does car engine oil work?
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 2:07
- Updated: 18 Feb 2015
- views: 71178
- published: 18 Feb 2015
- views: 71178
Choosing the Best Motor Oil for your Vehicle
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 8:45
- Updated: 26 Nov 2012
- views: 158858
- published: 26 Nov 2012
- views: 158858
-20 motor oil test
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 8:34
- Updated: 13 Apr 2015
- views: 40787
- published: 13 Apr 2015
- views: 40787
How to Choose Between Synthetic and Conventional Motor Oil
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 8:14
- Updated: 15 Jun 2012
- views: 193412
- published: 15 Jun 2012
- views: 193412
Best Price Motor Oil Comparison ~ Walmart vs O'Reilly's ~ Automotive Video
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 4:01
- Updated: 12 May 2015
- views: 14155
- published: 12 May 2015
- views: 14155
Pennzoil - Conventional vs Synthetic Motor Oil
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 1:19
- Updated: 26 Mar 2013
- views: 191400
- published: 26 Mar 2013
- views: 191400
What do motor oil numbers mean?
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 3:31
- Updated: 29 Jun 2014
- views: 11096
- published: 29 Jun 2014
- views: 11096
Choosing the Right Oil Type
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 5:12
- Updated: 09 Nov 2012
- views: 102449
- published: 09 Nov 2012
- views: 102449
Free energy and heating - waste motor oil stove experiment prototype
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 3:56
- Updated: 04 Jul 2013
- views: 175511
- published: 04 Jul 2013
- views: 175511
All About Motor Oil for Your Gasoline Fuel Car
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 13:36
- Updated: 23 Mar 2016
- views: 1352
- published: 23 Mar 2016
- views: 1352
Is Synthetic Motor Oil Good for Everyday Cars?
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 4:18
- Updated: 03 Mar 2009
- views: 141694
Mobil 1 vs. Liqui Moly - Synthetic Motor Oil Review - Bundys Garage
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 12:15
- Updated: 26 Jul 2014
- views: 98251
- published: 26 Jul 2014
- views: 98251
Can I use Transmission Fluid as Motor Oil?
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 5:13
- Updated: 04 Jan 2015
- views: 8558
- published: 04 Jan 2015
- views: 8558
Sludge Buildup From Not Changing Motor Oil - LT1 Engine
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 0:52
- Updated: 02 Oct 2014
- views: 26392
- published: 02 Oct 2014
- views: 26392
How used motor oil is recycled
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 7:27
- Updated: 21 Feb 2015
- views: 4600
- published: 21 Feb 2015
- views: 4600
veggie oil instead of motor oil
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 4:32
- Updated: 17 Dec 2011
- views: 8199
How to Change Honda CRV Engine Motor Oil
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 9:41
- Updated: 27 Aug 2014
- views: 26482
- published: 27 Aug 2014
- views: 26482
Synthetic Oil Basics
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 4:18
- Updated: 10 Dec 2011
- views: 554050
- published: 10 Dec 2011
- views: 554050
Should you switch to full synthetic motor oil? - Auto Information Series
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 9:51
- Updated: 11 Oct 2013
- views: 17973
- published: 11 Oct 2013
- views: 17973
- Playlist
- Chat
- Playlist
- Chat

Motor Oil Myths & FAQs - Synthetic vs Conventional
- Report rights infringement
- published: 14 Dec 2014
- views: 190474

Motor Oil: "Riding the Film" 1937 Chevrolet Engine Lubrication 11min
- Report rights infringement
- published: 19 Jul 2012
- views: 218567

Straight Talk About Motor Oil
- Report rights infringement
- published: 31 Oct 2012
- views: 73824

Don't Destroy Your Engine With Bad Motor Oil
- Report rights infringement
- published: 13 Aug 2013
- views: 92644

How does car engine oil work?
- Report rights infringement
- published: 18 Feb 2015
- views: 71178

Choosing the Best Motor Oil for your Vehicle
- Report rights infringement
- published: 26 Nov 2012
- views: 158858

-20 motor oil test
- Report rights infringement
- published: 13 Apr 2015
- views: 40787

How to Choose Between Synthetic and Conventional Motor Oil
- Report rights infringement
- published: 15 Jun 2012
- views: 193412

Best Price Motor Oil Comparison ~ Walmart vs O'Reilly's ~ Automotive Video
- Report rights infringement
- published: 12 May 2015
- views: 14155

Pennzoil - Conventional vs Synthetic Motor Oil
- Report rights infringement
- published: 26 Mar 2013
- views: 191400

What do motor oil numbers mean?
- Report rights infringement
- published: 29 Jun 2014
- views: 11096

Choosing the Right Oil Type
- Report rights infringement
- published: 09 Nov 2012
- views: 102449

Free energy and heating - waste motor oil stove experiment prototype
- Report rights infringement
- published: 04 Jul 2013
- views: 175511

All About Motor Oil for Your Gasoline Fuel Car
- Report rights infringement
- published: 23 Mar 2016
- views: 1352
-
Lyrics list:text lyricsplay full screenplay karaoke
John Robert Charlton Arrested For Murder After Police Identify Dismembered Body Of Missing Seattle Mom
Edit Inquisitr 12 Apr 2016Famous Woman Biker Veenu Paliwal Dies in a Fatal Road Accident
Edit Pinkvilla 12 Apr 2016Trump denounces ‘rigged’ Republican primary process
Edit Press TV 12 Apr 2016Russell Westbrook, Kevin Durant spoil Kobe Bryant’s final game in Oklahoma City
Edit LA Daily News 12 Apr 2016New Study Suggests Bible Could Have Been Written Earlier Than Previously Thought
Edit WorldNews.com 12 Apr 2016Gang lays 1.5-km underground pipe to steal from BPCL depot
Edit The Times of India 12 Apr 2016Household Hazardous Waste Day, April 23rd 9 AM to 1 PM Athens Community Center (City of Athens, OH)
Edit Public Technologies 12 Apr 2016PUBLIC NOTICE: Storm Drain Marking Project - Preserving our Waterways (City of Molalla, OR)
Edit Public Technologies 12 Apr 2016Kicked-out roommate accused of setting fire to Iowa house
Edit San Francisco Chronicle 08 Apr 2016LUKOIL BECOMES A PRIORITY MOTOR OIL SUPPLIER IN RUSSIA (OAO Lukoil)
Edit Public Technologies 07 Apr 2016Household Waste Collection Day – April 16 (City of Dublin, OH)
Edit Public Technologies 07 Apr 2016Free Household Hazardous Waste Collection Event April 30 in Harrisburg (Oregon Department of Environmental Quality)
Edit Public Technologies 07 Apr 2016Free Household Hazardous Waste Collection Event April 23 in Reedsport (Oregon Department of Environmental Quality)
Edit Public Technologies 07 Apr 2016Proposed Rate Changes for Sewer and Garbage Customers (City of Bakersfield, CA)
Edit Public Technologies 07 Apr 2016Driving Costs Hit Six-Year Low, Finds AAA (AAA - American Automobile Association)
Edit Public Technologies 07 Apr 2016Driving Costs Hit Six-Year Low, AAA Finds (Automobile Club of Southern California)
Edit Public Technologies 07 Apr 2016Sales of Gazpromneft Lubricants G-Energy motor oils up two thirds in 2015 (OAO Gazprom Neft)
Edit Public Technologies 06 Apr 2016Quest Resource Adds the Two Largest Automotive Aftermarket Retailers to Its Portfolio of Clients
Edit Stockhouse 06 Apr 2016- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- Next page »







