- published: 30 Jan 2011
- views: 8482072
-
remove the playlistKingdom Of Ireland
-
remove the playlistKingdom Of Ireland Travel Guides
- remove the playlistKingdom Of Ireland
- remove the playlistKingdom Of Ireland Travel Guides
Please tell us which country and city you'd like to see the weather in.
- published: 25 May 2013
- views: 1294
- published: 02 Mar 2016
- views: 94
- published: 12 Jun 2014
- views: 32233
- published: 24 Aug 2011
- views: 9522
- published: 20 Apr 2015
- views: 771
- published: 26 Oct 2012
- views: 892
- published: 24 May 2014
- views: 10545
- published: 22 Jul 2013
- views: 2754
- published: 20 Jan 2014
- views: 326
- published: 18 Apr 2013
- views: 3397

The Kingdom of Ireland (Irish: Ríoghacht Éireann) refers to the country of Ireland in the period between the proclamation of Henry VIII as King of Ireland by the Crown of Ireland Act 1542 and the Act of Union in 1800. It replaced the Lordship of Ireland, which had been created in 1171. King Henry VIII was recognised as monarch of Ireland by some Protestant powers in Europe, although not by the Catholic monarchies in Europe. However his daughter Mary I was recognised as Queen of Ireland by the pope in 1555. The separate Kingdom of Ireland ceased to exist when Ireland joined with the Kingdom of Great Britain to form the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland in 1801.
The papal bull Laudabiliter of Pope Adrian IV was decreed in 1155. It granted the Angevin King Henry II of England who ruled from Anjou in France, the title Dominus Hibernae. Laudabiliter enabled the king to invade Ireland, in order to bring the country into the European sphere. In return, Henry was required to remit a penny per hearth of the tax roll to the Pope. This was reconfirmed by Adrian's successor Pope Alexander III in 1172.
This article is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported License, which means that you can copy and modify it as long as the entire work (including additions) remains under this license.

Coordinates: 53°20′N 08°00′W / 53.333°N 8°W / 53.333; -8
Ireland (pronounced [ˈaɪrlənd] (![]() listen); Irish: Éire [ˈeːɾʲə] (
listen); Irish: Éire [ˈeːɾʲə] (![]() listen); Ulster Scots: Airlann or Airlan) is an island to the northwest of continental Europe. It is the third-largest island in Europe and the twentieth-largest island on Earth. To its east is the larger island of Great Britain, from which it is separated by the Irish Sea.
listen); Ulster Scots: Airlann or Airlan) is an island to the northwest of continental Europe. It is the third-largest island in Europe and the twentieth-largest island on Earth. To its east is the larger island of Great Britain, from which it is separated by the Irish Sea.
Politically, Ireland is divided between the Republic of Ireland, which covers just under five-sixths of the island, and Northern Ireland, a part of the United Kingdom, which covers the remainder and is located in the northeast of the island. The population of Ireland is approximately 6.4 million. Just under 4.6 million live in the Republic of Ireland and just under 1.8 million live in Northern Ireland.
Relatively low-lying mountains surrounding a central plain epitomise Ireland's geography with several navigable rivers extending inland. The island has lush vegetation, a product of its mild but changeable oceanic climate, which avoids extremes in temperature. Thick woodlands covered the island until the 17th century. Today, it is one of the most deforested areas in Europe. There are twenty-six extant mammal species native to Ireland.
This article is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported License, which means that you can copy and modify it as long as the entire work (including additions) remains under this license.
Radio Stations - Kingdom of Ireland
SEARCH FOR RADIOS
- Loading...

-
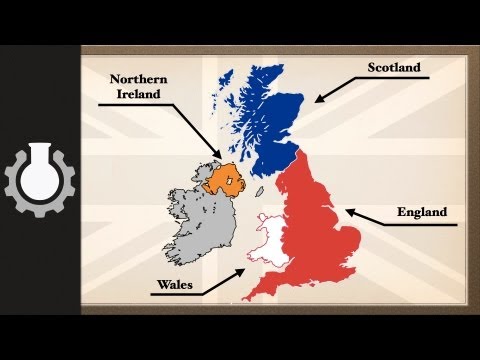 5:15
5:15The Difference between the United Kingdom, Great Britain and England Explained
The Difference between the United Kingdom, Great Britain and England Explained -
 36:46
36:46Crusader Kings 2 - Irish Campaign - Part 7: The Kingdom Of Ireland
Crusader Kings 2 - Irish Campaign - Part 7: The Kingdom Of IrelandCrusader Kings 2 - Irish Campaign - Part 7: The Kingdom Of Ireland
I play Crusader Kings 2, which is a grand strategy game set in the middle ages, where you must keep your dynasty alive through the plots and wars through the centuries. I am playing as the Duke of Munster, this is my first proper campaign in Crusader Kings 2, so tips and advice are generally appreciated in the comments section. if you're interested in total war, check out these campaigns I've done: Arnor Campaign http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=fYk51vHGHp0 Eriador Campaign http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=PYAfVY197Bc Rohan Campaign http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=KZh-8emkuGg Mordor Campaign http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Yyb6O0Rpy7Y High Elves Campaign http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=AsHCXE-8X7I ● Subscribe: http://www.youtube.com/subscription_center?add_user=CosmicContrarian ● Facebook: http://www.facebook.com/CosmicContrarian ● Steam Group: http://steamcommunity.com/groups/CosmicContrarian ● Twitter Sub Box: https://twitter.com/CosmiContrarian ● Twitch: http://www.twitch.tv/cosmiccontrarian -
 9:46
9:46History of United Kingdom and Ireland - Timelapse (301BC - 2016)
History of United Kingdom and Ireland - Timelapse (301BC - 2016)History of United Kingdom and Ireland - Timelapse (301BC - 2016)
Thanks to http://geacron.com/ you are able to see a timelapse of United Kingdom and Ireland. As an initial starting point was taken year of 301 BC. In 9 minutes you can see how United Kingdom and Ireland created through history. Of course, you can call this video as history of Scotland, Wales and Northern Ireland History of Scotland Timelapse History of Wales Timelapse History of Northern Ireland Timelapse -
 1:36
1:36How To Draw Map Of United Kingdom And Ireland
How To Draw Map Of United Kingdom And Ireland -
 10:21
10:21The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland | ArtArsDJ HomeStudio
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland | ArtArsDJ HomeStudioThe United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland | ArtArsDJ HomeStudio
This is my homework for college. This video will tell and show you England in all its glory! Subscribe to the channel! ПОДПИШИСЬ! Сreator/Создатель: https://vk.com/arseny_pavlov and https://vk.com/id161926359 RU:Это моё домашнее задание по английскому языку, так что может быть кому нибудь пригодится Кратко о видео: В данном ролике я отобрал лучшие на мой взгляд ролики про Англию (около 10 роликов) принадлежащие разным авторам. Информация взята с Wikipedia, а озвучивала текст специальная программа! /Great Britain/Time Lapse/ P.S. Made with love! ------------------------------------------- ||||РЕКЛАМА|||| Узнай, какие тайны скрыты в Брянских лесах? https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=C1yDLGOhJOk&list;=PLVJOibtk8lrshCcXxP8CflQjmPSjQcelN ------------------------------------------- Click here to subscribe to our channel. We have many interesting! https://www.youtube.com/channel/UCD1fgqr9yZ6syGtWZMp498w RU: Все видео и аудио материалы, представленные в данном ролике, принадлежат их законным авторам и правообладателям. ENG: All video and audio material presented in this video belong to their rightful copyright holders. Music: The National Anthem (arr. Elgar); Coldplay - Clocks; (London) Alexey Romeo - mfx tumbler; (Wales) Lisa Mitchell – Neopolitan Dreams (Nilow Remix); (Glasgow) -
 5:43
5:43Learn English in the United Kingdom and Ireland with Kaplan
Learn English in the United Kingdom and Ireland with KaplanLearn English in the United Kingdom and Ireland with Kaplan
Come and join Kaplan International Colleges in the UK and Ireland! http://bit.ly/KIC-UK Find out what our staff and students have to say about Kaplan's 10 English schools located throughout the UK and Ireland. This includes destinations such as London, Edinburgh, Oxford, Cambridge and Dublin to name a few. Our staff are dedicated qualified professionals working hard to provide the best education for our students. Meet our qualified teaching staff and their language students. Explore all the Kaplan school facilities as well as our wide range of accommodation options. In the UK and Ireland Kaplan also has social coordinators to ensure our students also have a great time outside of the classroom. Watch our video to find out more! -
 5:16
5:16History of the United Kingdom and Ireland Flags | ASL - American Sign Language
History of the United Kingdom and Ireland Flags | ASL - American Sign LanguageHistory of the United Kingdom and Ireland Flags | ASL - American Sign Language
A brief history of how the flag of the United Kingdom or Great Britain came to be. Also included is the Ireland Flag. Explained in American Sign Language (ASL). -
 5:08
5:08Power Grid: Northern Europe/United Kingdom & Ireland Overview - Spiel 2012
Power Grid: Northern Europe/United Kingdom & Ireland Overview - Spiel 2012Power Grid: Northern Europe/United Kingdom & Ireland Overview - Spiel 2012
http://boardgamegeek.com/boardgameexpansion/131184/power-grid-northern-europeunited-kingdom-ireland -
 4:58
4:58Wild Atlantic Way - Kerry - Ireland's Spectacular Kingdom
Wild Atlantic Way - Kerry - Ireland's Spectacular KingdomWild Atlantic Way - Kerry - Ireland's Spectacular Kingdom
Wild Atlantic Way - Kerry - Ireland's Spectacular Kingdom Music: The Kerry The Kingdom Orchestral Suite -
 2:32
2:32United Kingdom vs. Great Britain vs. Ireland
United Kingdom vs. Great Britain vs. IrelandUnited Kingdom vs. Great Britain vs. Ireland
Just a short geography lesson because a lot of people do not understand or know the difference between the United Kingdom, Great Britain and why there are "two Ireland's". I hope you enjoy! :) ****I AM NOT A GEOGRAPHY TEACHER! Follow Me On Twitter: https://twitter.com/saraparamo Add Me On Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/YouMeAtSixFan -
 37:12
37:12United Kingdom and Ireland Regional 5v5 Cup
United Kingdom and Ireland Regional 5v5 CupUnited Kingdom and Ireland Regional 5v5 Cup
Mostly from the perspective of the north/south west team. Matches: 00:13 - East England V.S. North/South West 05:49 - London V.S. North/South West 09:16 - Scotland V.S. North/South West 13:54 - Yorkshire V.S. North/South West 20:52 - North East V.S. North/South West 28:26 - Ireland V.S. North/South West 32:57 - South East V.S. North/South West 36:18 - Final Round and Scores -
 16:10
16:10Let's Play Crusader Kings II - Kingdom of Ireland & Empire of Britannia - Part 1
Let's Play Crusader Kings II - Kingdom of Ireland & Empire of Britannia - Part 1Let's Play Crusader Kings II - Kingdom of Ireland & Empire of Britannia - Part 1
Hello there, and welcome to my Let's Play of Crusader Kings II! Crusader Kings II is a grand strategy game set in the High and Late Middle Ages developed by Paradox Development Studio and published by Paradox Interactive as a sequel to Crusader Kings. It was released for Microsoft Windows on 14 February 2012 to positive reviews. A Mac OS X version, Paradox Interactive's first in-house development for Mac OS X, was released on 24 May 2012. The game contains numerous historical figures such as William the Conqueror, Harold Godwinson, Harald Hardrada, El Cid, Constantine X Doukas, Alexios I Komnenos, Richard I of England and Saladin. In this Let's Play, Greenbeard and I take on the roles of Denmark and Sweden respectively from the date of William the Conqueror (26th December 1066) and we fully intend to conquer the whole of Scandinavia, if not the entirety of the known world at the time! Join me as I, in running alongside my Multiplayer Let's Play with Greenbeard, try to form the Kingdom of Ireland and then the Empire of Britannia from the small but powerful Duchy of Connacht. There will be blood, sweat, and tears as we cut our way through our enemies flesh, plot our way through their courts and talk our way into the mistresses bedroom! For Ireland, for Britannia! Tags: Crusader Kings II, Crusader Kings 2, Crusader Kings, Crusader, Kings, Crusades, 1066, Grand-strategy, Grand-strategy games, Sweden, Denmark, Scandinavia, Europe, Multiplayer, Dual Commentary, Kylarnatia, Greenbeard, The Gentleman Who Prefers Blondes, TheRealTubClub, HD, Let's Play, Ireland, Britannia, Connacht, Duchy, Kingdom, Empire, War, Espionage, Plotting -
 23:09
23:09Let's Play Crusader Kings II - Kingdom of Ireland & Empire of Britannia - Part 2
Let's Play Crusader Kings II - Kingdom of Ireland & Empire of Britannia - Part 2Let's Play Crusader Kings II - Kingdom of Ireland & Empire of Britannia - Part 2
Hello there, and welcome to my Let's Play of Crusader Kings II! Crusader Kings II is a grand strategy game set in the High and Late Middle Ages developed by Paradox Development Studio and published by Paradox Interactive as a sequel to Crusader Kings. It was released for Microsoft Windows on 14 February 2012 to positive reviews. A Mac OS X version, Paradox Interactive's first in-house development for Mac OS X, was released on 24 May 2012. The game contains numerous historical figures such as William the Conqueror, Harold Godwinson, Harald Hardrada, El Cid, Constantine X Doukas, Alexios I Komnenos, Richard I of England and Saladin. In this Let's Play, Greenbeard and I take on the roles of Denmark and Sweden respectively from the date of William the Conqueror (26th December 1066) and we fully intend to conquer the whole of Scandinavia, if not the entirety of the known world at the time! Join me as I, in running alongside my Multiplayer Let's Play with Greenbeard, try to form the Kingdom of Ireland and then the Empire of Britannia from the small but powerful Duchy of Connacht. There will be blood, sweat, and tears as we cut our way through our enemies flesh, plot our way through their courts and talk our way into the mistresses bedroom! For Ireland, for Britannia! Tags: Crusader Kings II, Crusader Kings 2, Crusader Kings, Crusader, Kings, Crusades, 1066, Grand-strategy, Grand-strategy games, Sweden, Denmark, Scandinavia, Europe, Multiplayer, Dual Commentary, Kylarnatia, Greenbeard, The Gentleman Who Prefers Blondes, TheRealTubClub, HD, Let's Play, Ireland, Britannia, Connacht, Duchy, Kingdom, Empire, War, Espionage, Plotting -
 20:40
20:40Let's Play Crusader Kings II - Kingdom of Ireland & Empire of Britannia - Part 14
Let's Play Crusader Kings II - Kingdom of Ireland & Empire of Britannia - Part 14Let's Play Crusader Kings II - Kingdom of Ireland & Empire of Britannia - Part 14
Hello there, and welcome to my Let's Play of Crusader Kings II! Crusader Kings II is a grand strategy game set in the High and Late Middle Ages developed by Paradox Development Studio and published by Paradox Interactive as a sequel to Crusader Kings. It was released for Microsoft Windows on 14 February 2012 to positive reviews. A Mac OS X version, Paradox Interactive's first in-house development for Mac OS X, was released on 24 May 2012. The game contains numerous historical figures such as William the Conqueror, Harold Godwinson, Harald Hardrada, El Cid, Constantine X Doukas, Alexios I Komnenos, Richard I of England and Saladin. In this Let's Play, Greenbeard and I take on the roles of Denmark and Sweden respectively from the date of William the Conqueror (26th December 1066) and we fully intend to conquer the whole of Scandinavia, if not the entirety of the known world at the time! Join me as I, in running alongside my Multiplayer Let's Play with Greenbeard, try to form the Kingdom of Ireland and then the Empire of Britannia from the small but powerful Duchy of Connacht. There will be blood, sweat, and tears as we cut our way through our enemies flesh, plot our way through their courts and talk our way into the mistresses bedroom! For Ireland, for Britannia! Tags: Crusader Kings II, Crusader Kings 2, Crusader Kings, Crusader, Kings, Crusades, 1066, Grand-strategy, Grand-strategy games, Sweden, Denmark, Scandinavia, Europe, Multiplayer, Dual Commentary, Kylarnatia, Greenbeard, The Gentleman Who Prefers Blondes, TheRealTubClub, HD, Let's Play, Ireland, Britannia, Connacht, Duchy, Kingdom, Empire, War, Espionage, Plotting
- Acts of Union 1800
- Anglo-Irish
- Anglo-Irish Treaty
- Annulment
- Aos Sí
- Auregnais
- Barmbrack
- Barrister
- Battle of Clontarf
- Battle of Glenmama
- Beltane
- Bishop
- Black Death
- Blazoned
- Boxty
- Brigid's cross
- Britain (name)
- British Isles
- British people
- Camogie
- Canon law
- Celtic languages
- Celtic Tiger
- Champ (food)
- Channel Islands
- Charles I of England
- Church of England
- Cities in Ireland
- Climate of Ireland
- Clàrsach
- Coddle
- Colcannon
- College Green
- Common Travel Area
- Confederate Ireland
- Constitution of 1782
- Cornish language
- Cornish people
- Counties of Ireland
- Crest (heraldry)
- Crown Dependencies
- Culture of Ireland
- Céilidh
- D'Hondt method
- Desmond Rebellions
- Disestablishment
- Drisheen
- Dublin
- Dublin Lockout
- Dublin University
- Dáil Éireann
- Easter Rising
- Echtra
- Edward VI of England
- England
- English language
- English people
- Fauna of Ireland
- Fenian Cycle
- Fenian Rising
- Flight of the Earls
- France
- French language
- Full breakfast
- Gaelic football
- Gaelic handball
- Gaelic Ireland
- Gaels
- Geography of Ireland
- Germanic languages
- Goody (dessert)
- Grattan's Parliament
- Great Britain
- Green Ensign
- Guernsey
- Guernésiais
- Guinness
- Halloween
- Hebrides
- Henry Grattan
- Henry II of England
- Heraldry
- Hiberno-English
- Hiberno-Normans
- History of England
- History of Ireland
- History of Jersey
- History of Scotland
- History of Wales
- Holy See
- House of Plantagenet
- Hurling
- Imbolc
- Immram
- Inner Hebrides
- Ireland
- Ireland 1536–1691
- Ireland 1691–1801
- Ireland 1801–1922
- Irish annals
- Irish calendar
- Irish Civil War
- Irish coffee
- Irish cream
- Irish cuisine
- Irish dance
- Irish diaspora
- Irish fiction
- Irish Free State
- Irish House of Lords
- Irish language
- Irish literature
- Irish martial arts
- Irish Mist
- Irish mythology
- Irish name
- Irish nationalism
- Irish Patriot Party
- Irish people
- Irish poetry
- Irish Republic
- Irish republicanism
- Irish road bowling
- Irish rock
- Irish Sign Language
- Irish stepdance
- Irish stew
- Irish theatre
- Irish Travellers
- Irish whiskey
- Irish Wolfhound
- Islands of the Clyde
- Isle of Man
- Isles of Scilly
- James I of England
- Jersey
- Jig
- Jèrriais
- King of England
- King of Scots
- King's Inns
- Kingdom of England
- Kingdom of Ireland
- Kingdom of Scotland
- Land War
- Languages of Ireland
- Laudabiliter
- Leinster
- List of Irish flags
- List of Irish people
- List of Irish ports
- Lordship of Ireland
- Lughnasadh
- Manx language
- Manx people
- Mary I of England
- Monarchy
- Monarchy of Ireland
- Munster Republic
- Music of Ireland
- Mythological Cycle
- Norman Ireland
- Northern Ireland
- Northern Isles
- Oireachtas
- Orkney
- Outer Hebrides
- Papal bull
- Penal Laws
- Penal Laws (Ireland)
- Personal union
- Plantation of Ulster
- Poitín
- Pope
- Pope Adrian IV
- Pope Alexander III
- Pope Clement VII
- Pope Paul III
- Portal Ireland
- Poynings' Law
- Prehistoric Ireland
- Presbyterians
- President of Ireland
- Provinces of Ireland
- Red Hand of Ulster
- Republic of Ireland
- Rivers of Ireland
- Romance languages
- Romanichal
- Rounders
- Saint Patrick's Day
- Saint Patrick's Flag
- Samhain
- Scotland
- Scots language
- Scottish Gaelic
- Scottish people
- Sean-nós dance
- Seanad Éireann
- Sercquiais
- Set dance
- Shamrock
- Shelta
- Shetland
- Silken Thomas
- Skirts and kidneys
- Soda bread
- Sovereign state
- Sport in Ireland
- State Church
- The Protectorate
- The Troubles
- The Twelfth
- Tithe War
- Transport in Ireland
- Triads of Ireland
- Tuatha Dé Danann
- Ulster Cycle
- Ulster loyalism
- Ulster Scots people
- Unionism in Ireland
- United Kingdom
- Viceroy
- Wales
- Welsh language
- Welsh people
- Wren Day
- Éire
- College Green
- Confederate Ireland
- Crown Dependencies
- Desmond Rebellions
- Dublin
- England
- France
- Great Britain
- Guernsey
- Hebrides
- Inner Hebrides
- Ireland
- Irish Free State
- Isle of Man
- Jersey
- Kingdom of England
- Kingdom of Ireland
- Leinster
- Lordship of Ireland
- Northern Ireland
- Oireachtas
- Orkney
- Outer Hebrides
- Republic of Ireland
- Scotland
- Shetland
- United Kingdom
- Wales
- British people
- Charles I of England
- Cornish people
- Edward VI of England
- English people
- Gaels
- Henry Grattan
- Henry II of England
- House of Plantagenet
- Irish Civil War
- Irish people
- List of Irish people
- Manx people
- Mary I of England
- Pope Adrian IV
- Pope Alexander III
- Pope Clement VII
- Pope Paul III
- Romanichal
- Scottish people
- Tuatha Dé Danann
- Ulster Scots people
- Welsh people
-

-

Crusader Kings 2 - Irish Campaign - Part 7: The Kingdom Of Ireland
I play Crusader Kings 2, which is a grand strategy game set in the middle ages, where you must keep your dynasty alive through the plots and wars through the centuries. I am playing as the Duke of Munster, this is my first proper campaign in Crusader Kings 2, so tips and advice are generally appreciated in the comments section. if you're interested in total war, check out these campaigns I've done: Arnor Campaign http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=fYk51vHGHp0 Eriador Campaign http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=PYAfVY197Bc Rohan Campaign http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=KZh-8emkuGg Mordor Campaign http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Yyb6O0Rpy7Y High Elves Campaign http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=AsHCXE-8X7I ● Subscribe: http://www.youtube.com/subscription_center?add_user=CosmicContrarian ● Facebook... -

History of United Kingdom and Ireland - Timelapse (301BC - 2016)
Thanks to http://geacron.com/ you are able to see a timelapse of United Kingdom and Ireland. As an initial starting point was taken year of 301 BC. In 9 minutes you can see how United Kingdom and Ireland created through history. Of course, you can call this video as history of Scotland, Wales and Northern Ireland History of Scotland Timelapse History of Wales Timelapse History of Northern Ireland Timelapse -

-

The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland | ArtArsDJ HomeStudio
This is my homework for college. This video will tell and show you England in all its glory! Subscribe to the channel! ПОДПИШИСЬ! Сreator/Создатель: https://vk.com/arseny_pavlov and https://vk.com/id161926359 RU:Это моё домашнее задание по английскому языку, так что может быть кому нибудь пригодится Кратко о видео: В данном ролике я отобрал лучшие на мой взгляд ролики про Англию (около 10 роликов) принадлежащие разным авторам. Информация взята с Wikipedia, а озвучивала текст специальная программа! /Great Britain/Time Lapse/ P.S. Made with love! ------------------------------------------- ||||РЕКЛАМА|||| Узнай, какие тайны скрыты в Брянских лесах? https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=C1yDLGOhJOk&list;=PLVJOibtk8lrshCcXxP8CflQjmPSjQcelN -----------------------------------------... -

Learn English in the United Kingdom and Ireland with Kaplan
Come and join Kaplan International Colleges in the UK and Ireland! http://bit.ly/KIC-UK Find out what our staff and students have to say about Kaplan's 10 English schools located throughout the UK and Ireland. This includes destinations such as London, Edinburgh, Oxford, Cambridge and Dublin to name a few. Our staff are dedicated qualified professionals working hard to provide the best education for our students. Meet our qualified teaching staff and their language students. Explore all the Kaplan school facilities as well as our wide range of accommodation options. In the UK and Ireland Kaplan also has social coordinators to ensure our students also have a great time outside of the classroom. Watch our video to find out more! -

History of the United Kingdom and Ireland Flags | ASL - American Sign Language
A brief history of how the flag of the United Kingdom or Great Britain came to be. Also included is the Ireland Flag. Explained in American Sign Language (ASL). -

Power Grid: Northern Europe/United Kingdom & Ireland Overview - Spiel 2012
http://boardgamegeek.com/boardgameexpansion/131184/power-grid-northern-europeunited-kingdom-ireland -

Wild Atlantic Way - Kerry - Ireland's Spectacular Kingdom
Wild Atlantic Way - Kerry - Ireland's Spectacular Kingdom Music: The Kerry The Kingdom Orchestral Suite -

United Kingdom vs. Great Britain vs. Ireland
Just a short geography lesson because a lot of people do not understand or know the difference between the United Kingdom, Great Britain and why there are "two Ireland's". I hope you enjoy! :) ****I AM NOT A GEOGRAPHY TEACHER! Follow Me On Twitter: https://twitter.com/saraparamo Add Me On Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/YouMeAtSixFan -

United Kingdom and Ireland Regional 5v5 Cup
Mostly from the perspective of the north/south west team. Matches: 00:13 - East England V.S. North/South West 05:49 - London V.S. North/South West 09:16 - Scotland V.S. North/South West 13:54 - Yorkshire V.S. North/South West 20:52 - North East V.S. North/South West 28:26 - Ireland V.S. North/South West 32:57 - South East V.S. North/South West 36:18 - Final Round and Scores -

Let's Play Crusader Kings II - Kingdom of Ireland & Empire of Britannia - Part 1
Hello there, and welcome to my Let's Play of Crusader Kings II! Crusader Kings II is a grand strategy game set in the High and Late Middle Ages developed by Paradox Development Studio and published by Paradox Interactive as a sequel to Crusader Kings. It was released for Microsoft Windows on 14 February 2012 to positive reviews. A Mac OS X version, Paradox Interactive's first in-house development for Mac OS X, was released on 24 May 2012. The game contains numerous historical figures such as William the Conqueror, Harold Godwinson, Harald Hardrada, El Cid, Constantine X Doukas, Alexios I Komnenos, Richard I of England and Saladin. In this Let's Play, Greenbeard and I take on the roles of Denmark and Sweden respectively from the date of William the Conqueror (26th December 1066) and we fu... -

Let's Play Crusader Kings II - Kingdom of Ireland & Empire of Britannia - Part 2
Hello there, and welcome to my Let's Play of Crusader Kings II! Crusader Kings II is a grand strategy game set in the High and Late Middle Ages developed by Paradox Development Studio and published by Paradox Interactive as a sequel to Crusader Kings. It was released for Microsoft Windows on 14 February 2012 to positive reviews. A Mac OS X version, Paradox Interactive's first in-house development for Mac OS X, was released on 24 May 2012. The game contains numerous historical figures such as William the Conqueror, Harold Godwinson, Harald Hardrada, El Cid, Constantine X Doukas, Alexios I Komnenos, Richard I of England and Saladin. In this Let's Play, Greenbeard and I take on the roles of Denmark and Sweden respectively from the date of William the Conqueror (26th December 1066) and we fu... -

Let's Play Crusader Kings II - Kingdom of Ireland & Empire of Britannia - Part 14
Hello there, and welcome to my Let's Play of Crusader Kings II! Crusader Kings II is a grand strategy game set in the High and Late Middle Ages developed by Paradox Development Studio and published by Paradox Interactive as a sequel to Crusader Kings. It was released for Microsoft Windows on 14 February 2012 to positive reviews. A Mac OS X version, Paradox Interactive's first in-house development for Mac OS X, was released on 24 May 2012. The game contains numerous historical figures such as William the Conqueror, Harold Godwinson, Harald Hardrada, El Cid, Constantine X Doukas, Alexios I Komnenos, Richard I of England and Saladin. In this Let's Play, Greenbeard and I take on the roles of Denmark and Sweden respectively from the date of William the Conqueror (26th December 1066) and we fu... -

Let's Play Crusader Kings II - Kingdom of Ireland & Empire of Britannia - Part 45
Hello there, and welcome to my Let's Play of Crusader Kings II! Please Comment, Like, Share and Subscribe! Thank you so much! Crusader Kings II is a grand strategy game set in the High and Late Middle Ages developed by Paradox Development Studio and published by Paradox Interactive as a sequel to Crusader Kings. It was released for Microsoft Windows on 14 February 2012 to positive reviews. A Mac OS X version, Paradox Interactive's first in-house development for Mac OS X, was released on 24 May 2012. The game contains numerous historical figures such as William the Conqueror, Harold Godwinson, Harald Hardrada, El Cid, Constantine X Doukas, Alexios I Komnenos, Richard I of England and Saladin. In this Let's Play, Greenbeard and I take on the roles of Denmark and Sweden respectively from th... -

Let's Play Crusader Kings II - Kingdom of Ireland & Empire of Britannia - Part 50
++NOTICE: This is old footage from and old play-through. You've been warned!++ Hello there, and welcome to my Let's Play of Crusader Kings II! Please Comment, Like, Share and Subscribe! Thank you so much! Crusader Kings II is a grand strategy game set in the High and Late Middle Ages developed by Paradox Development Studio and published by Paradox Interactive as a sequel to Crusader Kings. It was released for Microsoft Windows on 14 February 2012 to positive reviews. A Mac OS X version, Paradox Interactive's first in-house development for Mac OS X, was released on 24 May 2012. The game contains numerous historical figures such as William the Conqueror, Harold Godwinson, Harald Hardrada, El Cid, Constantine X Doukas, Alexios I Komnenos, Richard I of England and Saladin. In this Let's Pla... -

Let's Play Medieval 2: Total War | The Kingdom of Ireland #1 | Thus the Irish march to war
-

The United Kingdom of Great Britain & Northern Ireland - A History of Origins
This documentary explains the origins of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland. You have to go back to the Norman conquest of England and the Battle of Hastings in 1066. The UK that we know today was then formed in 1922 when the Anglo-Irish Treaty took effect. -

Conor McGregor steals Jose Aldo's UFC Belt during Dublin Press Conference
The UFC 189 world tour reaches it's last stop, the hometown of Conor McGregor Dublin,Ireland. McGregor steals Aldo's belt after the champion claims he is the king of Dublin. -

Survey of Special Collections and Archives in the United Kingdom and Ireland
In this video, Program Officer Jackie Dooley and Senior Program Merrilee Proffitt discuss the report, Survey of Special Collections and Archives in the United Kingdom and Ireland. The report, produced in collaboration by OCLC Research and RLUK, builds on the foundation established by Taking Our Pulse: The OCLC Research Survey of Special Collections and Archives, a report published in 2010 that provides a rigorous, evidence-based appraisal of the state of special collections in the US and Canada. The survey provides both evidence and a basis for action as part of the RLUK's Unique and Distinctive Collections workstrand and OCLC Research's Mobilizing Unique Materials theme. The report provides institutional leaders, curators, special collections staff, and archivists both evidence and inspi... -

County Down Tourist Guide, Kingdom of Mourne, Northern Ireland
Husband and Wife Bobby and Carol take us on a tour through County Down in Northern Ireland which is the Kingdom of Mourne and home of the Mourne mountains. This makes it the ideal place for walks, outdoor activities and sports. They introduce us to bouldering, which is rock climbing along the river. The scenery is what people back to the Kingdom of Mourne every year! The then head over to the seaweed baths in Newcastle before heading to Carlingford Lough to unwind! -

Lets Conquer: Ireland | Crusader Kings 2 | Part 6 Becoming King
This is the lets conquer series in which I begin my journey to take over all of Ireland! Starting from 1066. Today we expand the kingdom yes, kingdom! We put pressure on our rivals, and finally crown ourselves high king of all Ireland. Will everyone fall into line and accept my right to rule? Follow me on Twitter? https://twitter.com/FTMoment -

Sacred places of ancient United Kingdom and Ireland
Stone circles, passage tombs... If you like Stonehenge, here's more of them. Song credit: Therion, "Clavicula Nox".
The Difference between the United Kingdom, Great Britain and England Explained
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 5:15
- Updated: 30 Jan 2011
- views: 8482072
Crusader Kings 2 - Irish Campaign - Part 7: The Kingdom Of Ireland
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 36:46
- Updated: 25 May 2013
- views: 1294
- published: 25 May 2013
- views: 1294
History of United Kingdom and Ireland - Timelapse (301BC - 2016)
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 9:46
- Updated: 02 Mar 2016
- views: 94
- published: 02 Mar 2016
- views: 94
How To Draw Map Of United Kingdom And Ireland
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 1:36
- Updated: 16 Mar 2013
- views: 8903
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland | ArtArsDJ HomeStudio
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 10:21
- Updated: 12 Jun 2014
- views: 32233
- published: 12 Jun 2014
- views: 32233
Learn English in the United Kingdom and Ireland with Kaplan
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 5:43
- Updated: 24 Aug 2011
- views: 9522
- published: 24 Aug 2011
- views: 9522
History of the United Kingdom and Ireland Flags | ASL - American Sign Language
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 5:16
- Updated: 20 Apr 2015
- views: 771
- published: 20 Apr 2015
- views: 771
Power Grid: Northern Europe/United Kingdom & Ireland Overview - Spiel 2012
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 5:08
- Updated: 26 Oct 2012
- views: 892
- published: 26 Oct 2012
- views: 892
Wild Atlantic Way - Kerry - Ireland's Spectacular Kingdom
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 4:58
- Updated: 24 May 2014
- views: 10545
- published: 24 May 2014
- views: 10545
United Kingdom vs. Great Britain vs. Ireland
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 2:32
- Updated: 22 Jul 2013
- views: 2754
- published: 22 Jul 2013
- views: 2754
United Kingdom and Ireland Regional 5v5 Cup
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 37:12
- Updated: 20 Jan 2014
- views: 326
- published: 20 Jan 2014
- views: 326
Let's Play Crusader Kings II - Kingdom of Ireland & Empire of Britannia - Part 1
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 16:10
- Updated: 18 Apr 2013
- views: 3397
- published: 18 Apr 2013
- views: 3397
Let's Play Crusader Kings II - Kingdom of Ireland & Empire of Britannia - Part 2
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 23:09
- Updated: 18 Apr 2013
- views: 546
- published: 18 Apr 2013
- views: 546
Let's Play Crusader Kings II - Kingdom of Ireland & Empire of Britannia - Part 14
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 20:40
- Updated: 29 Jul 2013
- views: 162
- published: 29 Jul 2013
- views: 162
Let's Play Crusader Kings II - Kingdom of Ireland & Empire of Britannia - Part 45
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 15:29
- Updated: 17 Aug 2014
- views: 238
- published: 17 Aug 2014
- views: 238
Let's Play Crusader Kings II - Kingdom of Ireland & Empire of Britannia - Part 50
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 15:11
- Updated: 09 Apr 2015
- views: 147
- published: 09 Apr 2015
- views: 147
Let's Play Medieval 2: Total War | The Kingdom of Ireland #1 | Thus the Irish march to war
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 23:10
- Updated: 14 Dec 2015
- views: 68
- published: 14 Dec 2015
- views: 68
The United Kingdom of Great Britain & Northern Ireland - A History of Origins
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 5:03
- Updated: 05 May 2015
- views: 322
- published: 05 May 2015
- views: 322
Conor McGregor steals Jose Aldo's UFC Belt during Dublin Press Conference
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 1:12
- Updated: 31 Mar 2015
- views: 49365
- published: 31 Mar 2015
- views: 49365
Survey of Special Collections and Archives in the United Kingdom and Ireland
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 7:28
- Updated: 19 Aug 2013
- views: 278
- published: 19 Aug 2013
- views: 278
County Down Tourist Guide, Kingdom of Mourne, Northern Ireland
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 5:47
- Updated: 17 Sep 2010
- views: 3804
- published: 17 Sep 2010
- views: 3804
Lets Conquer: Ireland | Crusader Kings 2 | Part 6 Becoming King
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 25:21
- Updated: 22 May 2013
- views: 1361
- published: 22 May 2013
- views: 1361
Sacred places of ancient United Kingdom and Ireland
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 8:49
- Updated: 04 Aug 2015
- views: 89
- published: 04 Aug 2015
- views: 89
-

Ireland (Europe) Vacation Travel Video Guide
✱ 3.113 Hotels in Ireland - Lowest Price Guarantee ► http://goo.gl/2zYMsN Travel video about destination Ireland. Ireland is one of Europe’s most green and mysterious islands and everyone who visits this isolated island in the Atlantic Ocean is given a very warm welcome. Dublin is the capital of the Irish Republic and it is a city of musicians, poets and dreamers, as well as being a financial centre. Its many old buildings indicate its long and dramatic past. It was founded by the Vikings within a wonderful valley where the River Liffey flows into the Atlantic Ocean. After the Vikings, the Normans conquered the city and ruled over it for seven hundred years and under King Henry The Eighth Dublin became the capital of what was then a British colony. South west of Dublin is Kildare, the hea... -

20 things to do in Belfast Travel Guide
Belfast is the capital city and largest city in Northern Ireland. This destination hasn't always been popular with visitors due to a conflict known as The Troubles; however, in recent years Belfast has experienced a resurgence and it's slowly starting to make a name for itself. We gave ourselves a few days to explore the city, and the result is the following video showcasing 20 things to do in Belfast: 1) Titanic Belfast 2) SS Nomadic 3) St George's Market 4) Ulster Fry Breakfast 5) Queen's University Belfast 6) Botanic Gardens 7) Belfast Castle 8) Cellar Restaurant 9) Cave Hill 10) Belfast Giants Ice Hockey Game 11) Boxty 12) Ulster Museum 13) Visit the Murals 14) Belfast City Hall 15) Octopus's Garden Vintage Store 16) Belfast Black Stout 17) Victoria Square Dome 18) St. Anne's Cathe... -

Ireland trip 2015
Ireland trip 2015, Ireland tourism & Vacations 2015, Ireland travel guide Travel Videos HD, World Travel Guide http://www.youtube.com/subscription_center?add_user=World1Tube Ireland is an island in north-western Europe which has been divided politically since 1920. Most of the island is made up of Ireland (Irish: Éire, also known as Poblacht na hÉireann = the Republic of Ireland). The remainder is Northern Ireland, which is part of the United Kingdom. See in Ireland ============ Blarney Castle - Located in County Cork This historic castle is known for its "Blarney Stone." Tradition is that if the Blarney Stone is kissed, one will be blessed with great eloquence, better known as "the gift of the gab." One kisses the stone by lying back and being held by an employee of the castle. Photogr... -

Dublin Vacation Travel Video Guide
Travel video about destination Dublin in Ireland. Dublin is the capital of the Irish Republic and is a city of musicians, poets and dreamers. Its Georgian buildings, whisky distilleries and historic castles are tangible and colorful reminders of bygone times. Numerous well preserved buildings, cafes, churches and idyllic canals also add to the captivating atmosphere of this fun loving city. One of the city's main landmarks is a splendid structure, Halfpenny Bridge, which derived its name due to a toll that was once extracted from those who crossed it. Dublin Castle is one of the city's oldest buildings. It has seen much transformation and is a combination of several building styles. After the Vikings, the Normans conquered the city and ruled over it for 700 years and under King Henry VI... -

Ireland Travel Guide, Tourism, Vacation HD
Ireland Travel Guide, Tourism, Vacation HD World Travel https://www.youtube.com/user/World1Tube Dublin, Galway, Killarney http://youtu.be/58JcEHZCws8 As you discover Ireland on this guided tour, delve deep into the magic of the Emerald Isle from Galway—an enchanting city on Ireland's western coast—to its bustling capital of Dublin. From enchanting, verdant landscapes to time-honored Celtic customs and traditions, watch Ireland come alive through the eyes of our travelers: Delve deeply into the magic of the Emerald Isle—from lush, verdant landscapes to enriching Old World cities replete with legend and song. Watch our video to learn more: Explore the famed Blarney Castle in Cork Witness glassblowing in Waterford Enjoy a Home-Hosted Lunch in Cobh Day by Day Itinerary As you ... -

Ireland Vacation Travel Video Guide • Great Destinations
Ireland, the Emerald Island. The hills, covered with lush, emerald green grass are full of mystical stone buildings from prehistoric times, Celtic monuments and medieval forts and monasteries. The island is the home of legends, music, poetry and dance. The capital of the Republic of Ireland, Dublin, has many sights worth take a look, for example the Trinity College, Christchurch and the St. Patrick Cathedral, the Parliament, and the National Gallery. The Georgian houses in the vicinity of Merrion Square, with their colorful doors and bronze knockers are the nicest in the city. One cannot skip the Jameson whiskey factory, the Guinness Brewery, and the pubs of the Temple Bar district, where live music is played every evening. Dublin is the city of G. B. Shaw, Oscar Wilde, Yeats, Swift and Ja... -

Ireland Vacation Travel Video Guide
Travel video about destination Ireland. Ireland is one of Europe’s most green and mysterious islands and everyone who visits this isolated island in the Atlantic Ocean is given a very warm welcome.Dublin is the capital of the Irish Republic and it is a city of musicians, poets and dreamers, as well as being a financial centre. Its many old buildings indicate its long and dramatic past. It was founded by the Vikings within a wonderful valley where the River Liffey flows into the Atlantic Ocean. South west of Dublin is Kildare, the heart of Ireland’s horse racing. In 1902 the Irish national stud, Tully House, was founded there. Rich and eccentric Scottish brewery heir, Colonel William Hall-Walker, had the idea of a creating unique horse breeding scheme that would be based upon astrological c... -

Ireland Travel Video Guide
Ireland Travel Video Guide, The island of Ireland historically consists of 32 counties, of which six, collectively known as Northern Ireland, have remained as part of the United Kingdom since the rest of Ireland gained independence in 1922. The name "Ireland" applies to the island as a whole, but in English is also the official name of the independent state (i.e., the 26 counties which are not part of the United Kingdom), since 1921. Celtic tribes settled on the island in the 4th century B.C. Invasions by Norsemen that began in the late 8th century were finally ended when King Brian Boru defeated the Danes in 1014. Norman invasions began in the early 12th century and set in place Though a relatively poor country for much of the 20th century, Ireland joined the European Community in 1973... -

Liverpool Vacation Travel Guide | Expedia
Get to know Liverpool, England, where the River Mersey meets the Irish Sea. This charming city is filled with maritime history, Beatlemania, and places of worship. Begin your English adventures at the Three Graces, which include the Royal Liver Building, Cunard Building, and Port of Liverpool Building. These iconic and architecturally magnificent structures sit in Pier Head, overlooking the River Mersey. View the buildings in all their glory at the nearby Museum of Liverpool. Then head to U-Boat Story to explore a previously sunken German submarine, followed by a trip to the Merseyside Maritime Museum, where you’ll learn boatloads of information about ships of the past, from the Titanic to the Lusitania. As long as you’re in Liverpool, explore the fabulous four’s old stomping grounds. T... -

Sheila O'Connell, Ireland tour guide
Sheila O'Connell, Ireland tour guide - Sheila O'Connell, Ireland trip leader Travel Videos HD, World Travel Guide http://www.youtube.com/subscription_center?add_user=World1Tube Ireland is an island in north-western Europe which has been divided politically since 1920. Most of the island is made up of Ireland (Irish: Éire, also known as Poblacht na hÉireann = the Republic of Ireland). The remainder is Northern Ireland, which is part of the United Kingdom. See in Ireland ============= Blarney Castle - Located in County Cork This historic castle is known for its "Blarney Stone." Tradition is that if the Blarney Stone is kissed, one will be blessed with great eloquence, better known as "the gift of the gab." One kisses the stone by lying back and being held by an employee of the castle. Ph... -

London (United Kingdom) Vacation Travel Video Guide
✱ 2180 Hotels in London - Lowest Price Guarantee ► http://goo.gl/tuEtwR Travel video about destination London in England. London is an exciting and pulsating metropolis of the new millennium, a melting pot of both people and culture and a fascinating city of diverse contrasts. The City Of London contains the Tower, an historic landmark with a remarkable history. A mighty medieval fortress with 13 towers that throughout its 900 years, has served many functions and from the Middle Ages, it was a heavily fortified prison. After the medieval St. Paul's Cathedral was destroyed by a devastating fire in 1666, Christopher Wren was ordered to re-build it with a dome. During the 36 years of its construction, its design was frequently altered until finally a wonderful masterpiece of church archite... -

Ireland Travel Video Guide, Meet a Local Travel Series
Meet the locals as the Overlander travels around Ireland - Complete Program See the beauty and hospitality of Ireland, through the eyes of it's people. Stories include: In Dublin I interviewed Niamh Ni Mhir who works for Hostel World,a local IT business that rode the Celtic Tiger to become the biggest Hostel booking website online Niamh explains how Ireland has changed since my last visit, in the early 1990 s and also tells us what it is she likes about living in Dublin. I interview Kathleen Moran about the Kilkenny Craft Centre and how Kilkenny established itself as Ireland's craft capital. In Belfast I interviewed Sean McKernan, a photographer who in 1983 set up a photo exhibition called Belfast Exposed, featuring a lot of images from the height of the troubles. On the Aran Island... -

Travel Britain and Ireland with Tour the World TV
Tour the World is the new Aussie travel show that joins real tour groups travelling to the world's most exciting destinations. In this episode we're off to blighty for an incredible tour through England and Scotland with Evergreen Tours. We drop in on the amazing Edinburgh Military Tattoo, catch up with Her Maj at the Royal Yacht Britannia, taste test haggis -- Scotland's national dish, and shop up a storm on London's Regent and Oxford Streets! Toodle-pip! To read our blogs from this tour please visit http://thebigbus.com.au/united-kingdom. This episode of Tour the World was produced by Late Night Media Productions, under a co-production agreement with Peppercorn Productions - publisher of The Big Bus tour and travel guide. Copyright © Late Night Media Productions. -

10 Best Places to Visit the United Kingdom - Video Travel Guide
Best Places to Visit in United Kingdom, Places to Visit in United Kingdom, United Kingdom Best Places to Visit, Tourist attractions in United Kingdom, United Kingdom Travel Video, List of Places in the United Kingdom : 1. London 2. Scottish Highlands 3. Stonehenge 4. Edinburgh 5. York 6. Cornwall 7. Chester 8. Snowdonia 9. Lake District 10. Cambridge Copyright: Video created by Omegatours.vn Omega Tours Co., LTD Add: 176 Tran Phu Str - Hai Chau Dist - Da Nang City, Vietnam Website: http://Omegatours.vn Disclaimer: All audio in this video, We was used free audio in Youtube Library. Photo Credit: Updating.... -

Visit Dublin - Top 10 places to see in the city
http://www.vidtur.com/dublin-attractions/ Watch vidtur's travel guides to learn more about Dublin and plan your perfect holiday in the Irish Capitol. Get a glimps of the notable tourists attractions such as Kilmainham Jail, Dublin Castle and learn about Dublin's night life at the popular Tempel Bar area. -

A Tourist's Guide to Dublin, Ireland
We fly into Dublin for a rapid-fire tour of Temple Bar, the Guinness Factory and the craic! visit www.theredquest.com for details of my travel books. -

City Hall - Belfast, Northern Ireland, United Kingdom
http://tripwow.tripadvisor.com/tripwow/ta-00a0-6678-a31d?ytv2=1 - Created at TripWow by TravelPod Attractions (a TripAdvisor™ company) City Hall Belfast This beautiful, neoclassical building serves as the seat of the city's government. Read more at: http://www.travelpod.com/ad/City_Hall-Belfast Travel blogs from City Hall: - "... The only things our bus tour guide talked about were politics and religion We saw the major sites of Belfast, including the City Hall, the shipyards where the Titanic was built, Queen's University, the Shankill, and the leaning Albert Clock ..." - "... Aside from the great history lesson and cab tour, we wandered about the city seeing the city hall, an open air market, and a nice little shopping district ..." - "... After lunch, we headed to the Belfast City Hal... -

United Kingdom holiday destinations - UK nature & cities
United Kingdom holiday destinations - UK nature & cities Travel Guide: http://www.quality4-u.com/united-kingdom-travel-guide-ebook.html You may also be interested in: http://www.quality4-u.com/russia-travel-guide-ebook.html http://www.quality4-u.com/france-travel-guide-ebook.html http://www.quality4-u.com/spain-travel-guide-ebook.html Video created with Royalty-free images! The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland (the United Kingdom or the UK) is a constitutional monarchy comprising much of the British Isles. This Union is more than 300 years old and comprises four constituent nations: England, Scotland, Wales, and Northern Ireland. It occupies all of the island of Great Britain, the north-eastern portion of the island of Ireland and most of the remaining British Isle... -

Fermanagh County Tourist guide, Northern Ireland
Irvine and his son take you on a guided tour of County Fermanagh in Northern Ireland which is known for its tranquility, beauty and the nicest Loughs in Ireland. Their first stop is a pottery shop in Enniskillen before going fishing for trout in Lough Erne. They then head to a monks retreat on an island in the Lake. After seeing this video there is nobody who would not want to travel here! -

Ireland Travel Guide - Travel Around The World | Charming Travel
Ireland Travel Guide - Travel Around The World | Charming Travel The beauty of Ireland is perfectly represented during a tour of Torr Head. This eastern headland is covered with a green carpet of plants, bushes, and trees, and stunning views of the Irish Sea and Antrim County’s lush countryside. There’s a lot of history behind this area; for centuries, Torr Head acted as a watchpoint for Lloyd’s of London, marking the comings and goings of transatlantic shipping. Your Torr Head sightseeing will take you around narrow, winding roads, past small fishing villages and clifftop lookout points. Make sure you bring your camera—on a clear day you can see straight across the North Channel to the Mull of Kintyre, located some 10 miles away in Scotland. Warmest greeting from Vietnam Charming T... -

Cork City Guide | Discover Ireland
Let Gerry Malone be your personal tour guide of Cork as he takes us through some famous sights of the city. Cork is a vibrant city described by Lonely Planet in 2009 as a must see with plenty to see and do such as wander its small streets, shop in Patrick Street or the English market or use it as a base to see the South West of Ireland. -

A tour of the British Isles in accents
The person doing the voice is Andrew Jack who is a dialect coach. Visit his website at http://www.andrewjack.com/. Original audio here: http://www.bbc.co.uk/programmes/p01slnp5
Ireland (Europe) Vacation Travel Video Guide
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 51:36
- Updated: 14 Aug 2013
- views: 165558
- published: 14 Aug 2013
- views: 165558
20 things to do in Belfast Travel Guide
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 12:44
- Updated: 26 Dec 2015
- views: 3325
- published: 26 Dec 2015
- views: 3325
Ireland trip 2015
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 7:08
- Updated: 10 Feb 2015
- views: 17660
- published: 10 Feb 2015
- views: 17660
Dublin Vacation Travel Video Guide
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 25:35
- Updated: 13 Aug 2013
- views: 11069
- published: 13 Aug 2013
- views: 11069
Ireland Travel Guide, Tourism, Vacation HD
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 2:48
- Updated: 31 Dec 2013
- views: 23287
- published: 31 Dec 2013
- views: 23287
Ireland Vacation Travel Video Guide • Great Destinations
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 66:40
- Updated: 10 Apr 2015
- views: 5503
- published: 10 Apr 2015
- views: 5503
Ireland Vacation Travel Video Guide
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 25:34
- Updated: 13 Aug 2013
- views: 3169
- published: 13 Aug 2013
- views: 3169
Ireland Travel Video Guide
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 0:35
- Updated: 05 May 2014
- views: 147
- published: 05 May 2014
- views: 147
Liverpool Vacation Travel Guide | Expedia
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 7:57
- Updated: 07 Jul 2015
- views: 33975
- published: 07 Jul 2015
- views: 33975
Sheila O'Connell, Ireland tour guide
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 3:01
- Updated: 10 Mar 2015
- views: 295
- published: 10 Mar 2015
- views: 295
London (United Kingdom) Vacation Travel Video Guide
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 25:35
- Updated: 13 Aug 2013
- views: 533732
- published: 13 Aug 2013
- views: 533732
Ireland Travel Video Guide, Meet a Local Travel Series
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 50:39
- Updated: 12 Jan 2012
- views: 9350
- published: 12 Jan 2012
- views: 9350
Travel Britain and Ireland with Tour the World TV
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 20:47
- Updated: 25 Mar 2014
- views: 291
- published: 25 Mar 2014
- views: 291
10 Best Places to Visit the United Kingdom - Video Travel Guide
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 3:46
- Updated: 24 Nov 2014
- views: 12119
- published: 24 Nov 2014
- views: 12119
Visit Dublin - Top 10 places to see in the city
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 6:23
- Updated: 23 Dec 2012
- views: 351200
- published: 23 Dec 2012
- views: 351200
A Tourist's Guide to Dublin, Ireland
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 10:13
- Updated: 07 Aug 2015
- views: 433
- published: 07 Aug 2015
- views: 433
City Hall - Belfast, Northern Ireland, United Kingdom
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 2:24
- Updated: 24 May 2011
- views: 153
- published: 24 May 2011
- views: 153
United Kingdom holiday destinations - UK nature & cities
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 1:25
- Updated: 10 Oct 2014
- views: 169
- published: 10 Oct 2014
- views: 169
Fermanagh County Tourist guide, Northern Ireland
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 6:11
- Updated: 17 Sep 2010
- views: 1216
- published: 17 Sep 2010
- views: 1216
Ireland Travel Guide - Travel Around The World | Charming Travel
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 22:25
- Updated: 16 Mar 2016
- views: 3
- published: 16 Mar 2016
- views: 3
Cork City Guide | Discover Ireland
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 3:27
- Updated: 06 Jul 2010
- views: 18478
- published: 06 Jul 2010
- views: 18478
A tour of the British Isles in accents
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 1:25
- Updated: 02 Apr 2014
- views: 1820374
- published: 02 Apr 2014
- views: 1820374
- Playlist
- Chat
- Playlist
- Chat

The Difference between the United Kingdom, Great Britain and England Explained
- Report rights infringement
- published: 30 Jan 2011
- views: 8482072

Crusader Kings 2 - Irish Campaign - Part 7: The Kingdom Of Ireland
- Report rights infringement
- published: 25 May 2013
- views: 1294

History of United Kingdom and Ireland - Timelapse (301BC - 2016)
- Report rights infringement
- published: 02 Mar 2016
- views: 94

How To Draw Map Of United Kingdom And Ireland
- Report rights infringement
- published: 16 Mar 2013
- views: 8903

The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland | ArtArsDJ HomeStudio
- Report rights infringement
- published: 12 Jun 2014
- views: 32233

Learn English in the United Kingdom and Ireland with Kaplan
- Report rights infringement
- published: 24 Aug 2011
- views: 9522

History of the United Kingdom and Ireland Flags | ASL - American Sign Language
- Report rights infringement
- published: 20 Apr 2015
- views: 771

Power Grid: Northern Europe/United Kingdom & Ireland Overview - Spiel 2012
- Report rights infringement
- published: 26 Oct 2012
- views: 892

Wild Atlantic Way - Kerry - Ireland's Spectacular Kingdom
- Report rights infringement
- published: 24 May 2014
- views: 10545

United Kingdom vs. Great Britain vs. Ireland
- Report rights infringement
- published: 22 Jul 2013
- views: 2754

United Kingdom and Ireland Regional 5v5 Cup
- Report rights infringement
- published: 20 Jan 2014
- views: 326

Let's Play Crusader Kings II - Kingdom of Ireland & Empire of Britannia - Part 1
- Report rights infringement
- published: 18 Apr 2013
- views: 3397

Let's Play Crusader Kings II - Kingdom of Ireland & Empire of Britannia - Part 2
- Report rights infringement
- published: 18 Apr 2013
- views: 546

Let's Play Crusader Kings II - Kingdom of Ireland & Empire of Britannia - Part 14
- Report rights infringement
- published: 29 Jul 2013
- views: 162
- Playlist
- Chat

Ireland (Europe) Vacation Travel Video Guide
- Report rights infringement
- published: 14 Aug 2013
- views: 165558

20 things to do in Belfast Travel Guide
- Report rights infringement
- published: 26 Dec 2015
- views: 3325

Ireland trip 2015
- Report rights infringement
- published: 10 Feb 2015
- views: 17660

Dublin Vacation Travel Video Guide
- Report rights infringement
- published: 13 Aug 2013
- views: 11069

Ireland Travel Guide, Tourism, Vacation HD
- Report rights infringement
- published: 31 Dec 2013
- views: 23287

Ireland Vacation Travel Video Guide • Great Destinations
- Report rights infringement
- published: 10 Apr 2015
- views: 5503

Ireland Vacation Travel Video Guide
- Report rights infringement
- published: 13 Aug 2013
- views: 3169

Ireland Travel Video Guide
- Report rights infringement
- published: 05 May 2014
- views: 147

Liverpool Vacation Travel Guide | Expedia
- Report rights infringement
- published: 07 Jul 2015
- views: 33975

Sheila O'Connell, Ireland tour guide
- Report rights infringement
- published: 10 Mar 2015
- views: 295

London (United Kingdom) Vacation Travel Video Guide
- Report rights infringement
- published: 13 Aug 2013
- views: 533732

Ireland Travel Video Guide, Meet a Local Travel Series
- Report rights infringement
- published: 12 Jan 2012
- views: 9350

Travel Britain and Ireland with Tour the World TV
- Report rights infringement
- published: 25 Mar 2014
- views: 291

10 Best Places to Visit the United Kingdom - Video Travel Guide
- Report rights infringement
- published: 24 Nov 2014
- views: 12119


