









![Xenakis' Iannis Xenakis: Eonta (1963-64) [1/2]](http://web.archive.org./web/20150112110512im_/http://i.ytimg.com/vi/vbU69HObLeg/0.jpg)

The orthography of the Greek language ultimately has its roots in the adoption of the Greek alphabet in the 9th century BC. Some time prior to that, one early form of Greek, Mycenaean, was written in Linear B, although there was a lapse of several centuries (the Greek Dark Ages) between the time Mycenaean stopped being written and the time when the Greek alphabet came into use.
Early Greek writing in the Greek alphabet was phonemic, and different in each dialect. Since the adoption of the Ionic variant for Attic in 403 BC, however, Greek orthography has been largely conservative and historical.
Given the phonetic development of Greek, especially in the Hellenistic period, certain modern vowel phonemes have multiple orthographic realizations:
This affects not only lexical items but also inflectional affixes, so correct orthography requires mastery of formal grammar (as in French), e.g. η καλή /i kaˈli/ 'the good one (fem. sing.)' vs. οι καλοί /i kaˈli/ 'the good ones (masc. pl.)'; καλώ /kaˈlo/ 'I call' vs. καλό /kaˈlo/ 'good (neut. sing.)'.
This article is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported License, which means that you can copy and modify it as long as the entire work (including additions) remains under this license.

Iannis Xenakis (Greek pronunciation: [ˈʝanis kseˈnakis], Greek: Γιάννης Ξενάκης) (May 29, 1922 – February 4, 2001) was a Greek composer, music theorist, and architect-engineer. After 1947, he fled Greece, becoming a naturalized citizen of France. He is commonly recognized as one of the most important post-war avant-garde composers. Xenakis pioneered the use of mathematical models in music such as applications of set theory, stochastic processes and game theory and was also an important influence on the development of electronic music. He integrated music with architecture, designing music for pre-existing spaces, and designing spaces to be integrated with specific music compositions and performances.
Among his most important works are Metastaseis (1953–4) for orchestra, which introduced independent parts for every musician of the orchestra; percussion works such as Psappha (1975) and Pléïades (1979); compositions that introduced spatialization by dispersing musicians among the audience, such as Terretektorh (1966); electronic works created using Xenakis's UPIC system; and the massive multimedia performances Xenakis called polytopes. Among the numerous theoretical writings he authored, the book Formalized Music: Thought and Mathematics in Composition (1971) is regarded as one of his most important. As an architect, Xenakis is primarily known for his early work under Le Corbusier: the Sainte Marie de La Tourette, on which the two architects collaborated, and the Philips Pavilion at Expo 58, which Xenakis designed alone.
This article is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported License, which means that you can copy and modify it as long as the entire work (including additions) remains under this license.
- Loading...

-
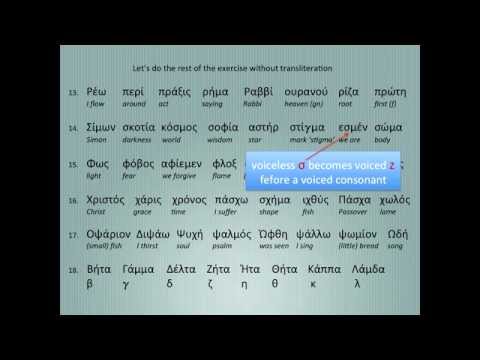
GREEK PRONUNCIATION 2 (Phonetics)
GREEK PRONUNCIATION 2 (Phonetics) -
Orthography Makes Sense!
Orthography Makes Sense!Orthography Makes Sense!
Fifth graders reflect on a year of word investigations. They speak honestly about what they have learned and how they feel it has made a difference. -
How to Pronounce Orthography
How to Pronounce OrthographyHow to Pronounce Orthography
Learn how to say Orthography correctly with EmmaSaying's "how do you pronounce" free tutorials. Definition of orthography (oxford dictionary): noun (plural o... -
Part 1: On Kurdish orthography-The Arabic script vs the Latin alphabet debate
Part 1: On Kurdish orthography-The Arabic script vs the Latin alphabet debatePart 1: On Kurdish orthography-The Arabic script vs the Latin alphabet debate
by Zana Muhammad, University of Suleimani, Kurdistan-Iraq. -
Part 2: On Kurdish orthography-The Arabic script vs the Latin alphabet debate
Part 2: On Kurdish orthography-The Arabic script vs the Latin alphabet debatePart 2: On Kurdish orthography-The Arabic script vs the Latin alphabet debate
by Zana Muhammad, University of Suleimani, Kurdistan-Iraq. -
Part 3: On Kurdish orthography-The Arabic script vs the Latin alphabet debate
Part 3: On Kurdish orthography-The Arabic script vs the Latin alphabet debatePart 3: On Kurdish orthography-The Arabic script vs the Latin alphabet debate
by Zana Muhammad, University of Suleimani, Kurdistan-Iraq. -
How to Pronounce Orthographical
How to Pronounce OrthographicalHow to Pronounce Orthographical
Learn how to say Orthographical correctly with emmasaying's "how do you pronounce" free tutorials. Definition of orthography (oxford dictionary): noun (plura... -
How to Pronounce Orthographic
How to Pronounce OrthographicHow to Pronounce Orthographic
Learn how to say Orthographic correctly with EmmaSaying's "how do you pronounce" free tutorials. Definition of orthography (oxford dictionary): noun (plural ... -
Grave accent
Grave accentGrave accent
The grave accent ( ` ) (/ˈɡreɪv/ or UK /ˈɡrɑːv/) is a diacritical mark used in many written languages, including Breton, Catalan, Corsican, Dutch, French, Greek (until 1982; see polytonic orthography), Haitian Creole, Italian, Macedonian, Mohawk, Norwegian, Occitan, Portuguese, Ligurian, Scottish Gaelic, Vietnamese, Welsh, Romansh and Yoruba. This video is targeted to blind users. Attribution: Article text available under CC-BY-SA Creative Commons image source in video -
How to Pronounce Orthographically
How to Pronounce OrthographicallyHow to Pronounce Orthographically
Learn how to say Orthographically correctly with EmmaSaying's "how do you pronounce" free tutorials. Definition of orthography (oxford dictionary): noun (plu... -
How to Pronounce Orthographies
How to Pronounce OrthographiesHow to Pronounce Orthographies
Learn how to say Orthographies correctly with EmmaSaying's "how do you pronounce" free tutorials. Definition of orthography (oxford dictionary): noun (plural... -
Iannis Xenakis: Eonta (1963-64) [1/2]
Iannis Xenakis: Eonta (1963-64) [1/2]Iannis Xenakis: Eonta (1963-64) [1/2]
Xenakis' "Eonta" (1963-64) for piano, 2 trumpets and 3 tenor trombones. Eonta (beings) is so entitled as a homage to the ancient Greek philosopher and poet P... -
Iannis Xenakis - Eonta (1964)
Iannis Xenakis - Eonta (1964)Iannis Xenakis - Eonta (1964)
(Unknown perfomer) Eonta (beings) is so entitled as a homage to the ancient Greek philosopher and poet Parmenides. The original printed form of the title wor... -
Nu (letter)
Nu (letter)Nu (letter)
Nu /nuː/ (uppercase Ν lowercase ν, also transcribed Ny; modern Greek: Νι [ni] Ni), is the 13th letter of the Greek alphabet. In the system of Greek numerals it has a value of 50. It is derived from the Phoenician letter nun . Its Latin equivalent is N, though the lowercase resembles the Roman lowercase v. The name of the letter is written νῦ in Ancient Greek and traditional Modern Greek polytonic orthography, while in Modern Greek it is written νι [ni]. This video is targeted to blind users. Attribution: Article text available under CC-BY-SA Creative Commons image source in video
- Acute accent
- Alpha
- Ancient Greek
- Ancient Greek accent
- Attic Greek
- Beta
- Byzantine literature
- Chalkidiki Greek
- Chi (letter)
- Close vowel
- Cretan Greek
- Cypriot Greek
- Cypriot syllabary
- Delta (letter)
- Demotic Greek
- Diacritic
- Digamma
- Diphthong
- Epsilon
- Eta
- Feminine gender
- French language
- Front vowel
- Gamma
- Graeco-Armenian
- Graeco-Aryan
- Grammatical number
- Greek alphabet
- Greek Dark Ages
- Greek diacritics
- Greek exonyms
- Greek grammar
- Greek language
- Greek ligatures
- Greek literature
- Greek morphemes
- Greek numerals
- Greek orthography
- Greek Wikipedia
- Greek words for love
- Greeklish
- Griko language
- Hebrew language
- Heta
- History of Greek
- Ionic Greek
- Iota
- Iota adscript
- Iota subscript
- Iotacism
- Kappa
- Katharevousa
- Koine Greek
- Koppa (letter)
- Lambda
- Latin language
- Linear B
- Lowercase
- Masculine gender
- Medieval Greek
- Mid vowel
- Misthi, Cappadocia
- Modern Greek
- Modern Greek grammar
- Monophthong
- Moses
- Mu (letter)
- Mycenaean Greek
- Mycenaean language
- Neuter gender
- Nu (letter)
- Omega
- Omicron
- Orthography
- Palatalization
- Phi
- Phoneme
- Phonemic orthography
- Pi (letter)
- Plural
- Pontic Greek
- Pre-Greek substrate
- Proto-Greek language
- Psi (letter)
- Rho
- Sampi
- San (letter)
- Septuagint
- Sigma
- Silent letter
- Spanish language
- Spelling
- Stigma (letter)
- Tau
- Theta
- Tsakonian language
- Umlaut (diacritic)
- Upsilon
- Velar consonant
- Velar nasal
- Voiced alveolar stop
- Voiced bilabial stop
- Voiced velar stop
- Vulgate
- Xi (letter)
- Yevanic language
- Zeta
- Βικιλεξικό
-
GREEK PRONUNCIATION 2 (Phonetics)
GREEK PRONUNCIATION 2 (Phonetics)GREEK PRONUNCIATION 2 (Phonetics)
Greek alphabet, sounds, and listening and reading exercises according to the historical Greek pronunciation (HGP). Music by songwriter Panos Zachariou. See a... -
Orthography Makes Sense!
Orthography Makes Sense!Orthography Makes Sense!
Fifth graders reflect on a year of word investigations. They speak honestly about what they have learned and how they feel it has made a difference. -
How to Pronounce Orthography
How to Pronounce OrthographyHow to Pronounce Orthography
Learn how to say Orthography correctly with EmmaSaying's "how do you pronounce" free tutorials. Definition of orthography (oxford dictionary): noun (plural o... -
Part 1: On Kurdish orthography-The Arabic script vs the Latin alphabet debate
Part 1: On Kurdish orthography-The Arabic script vs the Latin alphabet debatePart 1: On Kurdish orthography-The Arabic script vs the Latin alphabet debate
by Zana Muhammad, University of Suleimani, Kurdistan-Iraq. -
Part 2: On Kurdish orthography-The Arabic script vs the Latin alphabet debate
Part 2: On Kurdish orthography-The Arabic script vs the Latin alphabet debatePart 2: On Kurdish orthography-The Arabic script vs the Latin alphabet debate
by Zana Muhammad, University of Suleimani, Kurdistan-Iraq. -
Part 3: On Kurdish orthography-The Arabic script vs the Latin alphabet debate
Part 3: On Kurdish orthography-The Arabic script vs the Latin alphabet debatePart 3: On Kurdish orthography-The Arabic script vs the Latin alphabet debate
by Zana Muhammad, University of Suleimani, Kurdistan-Iraq. -
How to Pronounce Orthographical
How to Pronounce OrthographicalHow to Pronounce Orthographical
Learn how to say Orthographical correctly with emmasaying's "how do you pronounce" free tutorials. Definition of orthography (oxford dictionary): noun (plura... -
How to Pronounce Orthographic
How to Pronounce OrthographicHow to Pronounce Orthographic
Learn how to say Orthographic correctly with EmmaSaying's "how do you pronounce" free tutorials. Definition of orthography (oxford dictionary): noun (plural ... -
Grave accent
Grave accentGrave accent
The grave accent ( ` ) (/ˈɡreɪv/ or UK /ˈɡrɑːv/) is a diacritical mark used in many written languages, including Breton, Catalan, Corsican, Dutch, French, Greek (until 1982; see polytonic orthography), Haitian Creole, Italian, Macedonian, Mohawk, Norwegian, Occitan, Portuguese, Ligurian, Scottish Gaelic, Vietnamese, Welsh, Romansh and Yoruba. This video is targeted to blind users. Attribution: Article text available under CC-BY-SA Creative Commons image source in video -
How to Pronounce Orthographically
How to Pronounce OrthographicallyHow to Pronounce Orthographically
Learn how to say Orthographically correctly with EmmaSaying's "how do you pronounce" free tutorials. Definition of orthography (oxford dictionary): noun (plu... -
How to Pronounce Orthographies
How to Pronounce OrthographiesHow to Pronounce Orthographies
Learn how to say Orthographies correctly with EmmaSaying's "how do you pronounce" free tutorials. Definition of orthography (oxford dictionary): noun (plural... -
Iannis Xenakis: Eonta (1963-64) [1/2]
Iannis Xenakis: Eonta (1963-64) [1/2]Iannis Xenakis: Eonta (1963-64) [1/2]
Xenakis' "Eonta" (1963-64) for piano, 2 trumpets and 3 tenor trombones. Eonta (beings) is so entitled as a homage to the ancient Greek philosopher and poet P... -
Iannis Xenakis - Eonta (1964)
Iannis Xenakis - Eonta (1964)Iannis Xenakis - Eonta (1964)
(Unknown perfomer) Eonta (beings) is so entitled as a homage to the ancient Greek philosopher and poet Parmenides. The original printed form of the title wor... -
Nu (letter)
Nu (letter)Nu (letter)
Nu /nuː/ (uppercase Ν lowercase ν, also transcribed Ny; modern Greek: Νι [ni] Ni), is the 13th letter of the Greek alphabet. In the system of Greek numerals it has a value of 50. It is derived from the Phoenician letter nun . Its Latin equivalent is N, though the lowercase resembles the Roman lowercase v. The name of the letter is written νῦ in Ancient Greek and traditional Modern Greek polytonic orthography, while in Modern Greek it is written νι [ni]. This video is targeted to blind users. Attribution: Article text available under CC-BY-SA Creative Commons image source in video -
Dyslexia SW no sound
Dyslexia SW no soundDyslexia SW no sound
Software about dictation,orthography,spelling for the greek language.Dyslexia. Deafness. Λογισμικό "ασκήσεις ορθογραφίας για παιδιά του δημοτικού".Δυσλεξία -... -
A Psalm fragment in early Middle Arabic
A Psalm fragment in early Middle ArabicA Psalm fragment in early Middle Arabic
This is a fragment of Psalm LXXVIII (LXXVII according to the Septuagint) in Middle Arabic - thus a mixture of Classical and Spoken Arabic - which was found i... -
TRANSIT TV TEACHER - Lesson #419: "Another Word for Proper Spelling" - Justin Vyor Los Angeles
TRANSIT TV TEACHER - Lesson #419: "Another Word for Proper Spelling" - Justin Vyor Los AngelesTRANSIT TV TEACHER - Lesson #419: "Another Word for Proper Spelling" - Justin Vyor Los Angeles
Orthography is the art of spelling words properly. It comes from the Greek words 'orthos' meaning “right or true” and 'graphein' meaning “to write” -
The"Aramean" Identity ? (Truth and Facts)
The"Aramean" Identity ? (Truth and Facts)The"Aramean" Identity ? (Truth and Facts)
The True History and Facts! The word Aššūrāyu is an adjective derived from the geographical and divine name Aššur with the gentilic suffix -āyu. This name wa... -
The Mark Of The Beast 666 - Patrick Bukassa
The Mark Of The Beast 666 - Patrick BukassaThe Mark Of The Beast 666 - Patrick Bukassa
Played and Inspired by Patrick Bukassa (Copyright): The Number of the Beast is a concept from the Book of Revelation of the New Testament of the Christian Bi... -
How to Pronounce Rhotacized
How to Pronounce RhotacizedHow to Pronounce Rhotacized
Learn how to say Rhotacized correctly with EmmaSaying's "how do you pronounce" free tutorials. Definition of rhotacization (oxford dictionary): noun [mass no... -
Garmarna - Herr Mannelig (Lyrics, translation & explanation / Letra, traducción y explicación)
Garmarna - Herr Mannelig (Lyrics, translation & explanation / Letra, traducción y explicación)Garmarna - Herr Mannelig (Lyrics, translation & explanation / Letra, traducción y explicación)
Frecuent comments and responses / Comentarios frecuentes y respuestas Q: What's this language? / ¿Qué idioma es? A: This is swedish, with old pronouncing, th... -
Eastern vs. Western Armenian
Eastern vs. Western ArmenianEastern vs. Western Armenian
There exists a division in the Armenian language. Like many languages of the world, geography and the events of history have shaped this language, dividing i... -
Learn English Idioms Firing on all Cylinders!!!
Learn English Idioms Firing on all Cylinders!!!Learn English Idioms Firing on all Cylinders!!!
Learn English Idioms Hilarious comedy sketch Hello. Welcome Do you want to learn English with a native speaker?... I am sure you do! Many more videos will be...

- Duration: 24:05
- Updated: 04 Sep 2014
- published: 13 Mar 2013
- views: 12018
- author: Philemon Zachariou

- Duration: 5:39
- Updated: 15 Jun 2014
- published: 04 Jun 2014
- views: 256
- author: Mary Beth Steven

- Duration: 0:21
- Updated: 03 Sep 2014
- published: 03 Jan 2013
- views: 134
- author: Emma Saying

- Duration: 10:00
- Updated: 08 Mar 2014
- published: 02 Sep 2011
- views: 803
- author: sbscmes

- Duration: 10:01
- Updated: 15 Feb 2014
- published: 02 Sep 2011
- views: 290
- author: sbscmes

- Duration: 10:01
- Updated: 22 Jan 2014
- published: 02 Sep 2011
- views: 348
- author: sbscmes

- Duration: 0:21
- Updated: 29 Aug 2014
- published: 03 Jan 2013
- views: 7
- author: Emma Saying

- Duration: 0:21
- Updated: 03 Sep 2014
- published: 03 Jan 2013
- views: 39
- author: Emma Saying

- Duration: 15:45
- Updated: 04 Oct 2014
- published: 04 Oct 2014
- views: 3

- Duration: 0:20
- Updated: 03 Sep 2014
- published: 03 Jan 2013
- views: 18
- author: Emma Saying

- Duration: 0:21
- Updated: 03 Sep 2014
- published: 03 Jan 2013
- views: 12
- author: Emma Saying
![Iannis Xenakis: Eonta (1963-64) [1/2] Iannis Xenakis: Eonta (1963-64) [1/2]](http://web.archive.org./web/20150112110512im_/http://i.ytimg.com/vi/vbU69HObLeg/0.jpg)
- Duration: 10:46
- Updated: 11 Jul 2014
- published: 10 Apr 2010
- views: 6587
- author: Michael Nelson

- Duration: 20:04
- Updated: 01 Sep 2014
- published: 18 Jul 2014
- views: 569
- author: Sihyeon Choe

- Duration: 2:08
- Updated: 15 Nov 2014
- published: 15 Nov 2014
- views: 0

- Duration: 1:39
- Updated: 28 Jun 2010
- published: 30 Sep 2009
- views: 289
- author: Spyros Zygouris

- Duration: 2:26
- Updated: 04 Jul 2013
- published: 14 Feb 2013
- views: 178
- author: AncientSemitic

- Duration: 3:30
- Updated: 16 Dec 2014
- published: 16 Dec 2014
- views: 1

- Duration: 8:21
- Updated: 26 Jun 2014
- published: 14 Jun 2013
- views: 2429
- author: Assur History

- Duration: 10:42
- Updated: 24 Apr 2014
- published: 02 Apr 2011
- views: 1101
- author: Patrick Bukassa

- Duration: 0:16
- Updated: 03 Sep 2014
- published: 29 Jul 2013
- views: 58
- author: Emma Saying

- Duration: 6:23
- Updated: 03 Sep 2014
- published: 13 Apr 2008
- views: 679757
- author: davealcarin

- Duration: 5:00
- Updated: 18 Aug 2014
- published: 11 Jun 2009
- views: 19439
- author: MedaghGuitarist

- Duration: 1:30
- Updated: 13 Jun 2014
- published: 10 Oct 2011
- views: 8255
- author: Learn English Idioms
- Playlist
- Chat

GREEK PRONUNCIATION 2 (Phonetics)
Greek alphabet, sounds, and listening and reading exercises according to the historical Greek pronunciation (HGP). Music by songwriter Panos Zachariou. See a...- published: 13 Mar 2013
- views: 12018
- author: Philemon Zachariou

Orthography Makes Sense!
Fifth graders reflect on a year of word investigations. They speak honestly about what they have learned and how they feel it has made a difference.- published: 04 Jun 2014
- views: 256
- author: Mary Beth Steven

How to Pronounce Orthography
Learn how to say Orthography correctly with EmmaSaying's "how do you pronounce" free tutorials. Definition of orthography (oxford dictionary): noun (plural o...- published: 03 Jan 2013
- views: 134
- author: Emma Saying

Part 1: On Kurdish orthography-The Arabic script vs the Latin alphabet debate
by Zana Muhammad, University of Suleimani, Kurdistan-Iraq.- published: 02 Sep 2011
- views: 803
- author: sbscmes

Part 2: On Kurdish orthography-The Arabic script vs the Latin alphabet debate
by Zana Muhammad, University of Suleimani, Kurdistan-Iraq.- published: 02 Sep 2011
- views: 290
- author: sbscmes

Part 3: On Kurdish orthography-The Arabic script vs the Latin alphabet debate
by Zana Muhammad, University of Suleimani, Kurdistan-Iraq.- published: 02 Sep 2011
- views: 348
- author: sbscmes

How to Pronounce Orthographical
Learn how to say Orthographical correctly with emmasaying's "how do you pronounce" free tutorials. Definition of orthography (oxford dictionary): noun (plura...- published: 03 Jan 2013
- views: 7
- author: Emma Saying

How to Pronounce Orthographic
Learn how to say Orthographic correctly with EmmaSaying's "how do you pronounce" free tutorials. Definition of orthography (oxford dictionary): noun (plural ...- published: 03 Jan 2013
- views: 39
- author: Emma Saying

Grave accent
The grave accent ( ` ) (/ˈɡreɪv/ or UK /ˈɡrɑːv/) is a diacritical mark used in many written languages, including Breton, Catalan, Corsican, Dutch, French, Greek (until 1982; see polytonic orthography), Haitian Creole, Italian, Macedonian, Mohawk, Norwegian, Occitan, Portuguese, Ligurian, Scottish Gaelic, Vietnamese, Welsh, Romansh and Yoruba. This video is targeted to blind users. Attribution: Article text available under CC-BY-SA Creative Commons image source in video- published: 04 Oct 2014
- views: 3

How to Pronounce Orthographically
Learn how to say Orthographically correctly with EmmaSaying's "how do you pronounce" free tutorials. Definition of orthography (oxford dictionary): noun (plu...- published: 03 Jan 2013
- views: 18
- author: Emma Saying

How to Pronounce Orthographies
Learn how to say Orthographies correctly with EmmaSaying's "how do you pronounce" free tutorials. Definition of orthography (oxford dictionary): noun (plural...- published: 03 Jan 2013
- views: 12
- author: Emma Saying

Iannis Xenakis: Eonta (1963-64) [1/2]
Xenakis' "Eonta" (1963-64) for piano, 2 trumpets and 3 tenor trombones. Eonta (beings) is so entitled as a homage to the ancient Greek philosopher and poet P...- published: 10 Apr 2010
- views: 6587
- author: Michael Nelson

Iannis Xenakis - Eonta (1964)
(Unknown perfomer) Eonta (beings) is so entitled as a homage to the ancient Greek philosopher and poet Parmenides. The original printed form of the title wor...- published: 18 Jul 2014
- views: 569
- author: Sihyeon Choe

Nu (letter)
Nu /nuː/ (uppercase Ν lowercase ν, also transcribed Ny; modern Greek: Νι [ni] Ni), is the 13th letter of the Greek alphabet. In the system of Greek numerals it has a value of 50. It is derived from the Phoenician letter nun . Its Latin equivalent is N, though the lowercase resembles the Roman lowercase v. The name of the letter is written νῦ in Ancient Greek and traditional Modern Greek polytonic orthography, while in Modern Greek it is written νι [ni]. This video is targeted to blind users. Attribution: Article text available under CC-BY-SA Creative Commons image source in video- published: 15 Nov 2014
- views: 0

Dyslexia SW no sound
Software about dictation,orthography,spelling for the greek language.Dyslexia. Deafness. Λογισμικό "ασκήσεις ορθογραφίας για παιδιά του δημοτικού".Δυσλεξία -...- published: 30 Sep 2009
- views: 289
- author: Spyros Zygouris

A Psalm fragment in early Middle Arabic
This is a fragment of Psalm LXXVIII (LXXVII according to the Septuagint) in Middle Arabic - thus a mixture of Classical and Spoken Arabic - which was found i...- published: 14 Feb 2013
- views: 178
- author: AncientSemitic

TRANSIT TV TEACHER - Lesson #419: "Another Word for Proper Spelling" - Justin Vyor Los Angeles
Orthography is the art of spelling words properly. It comes from the Greek words 'orthos' meaning “right or true” and 'graphein' meaning “to write”- published: 16 Dec 2014
- views: 1

The"Aramean" Identity ? (Truth and Facts)
The True History and Facts! The word Aššūrāyu is an adjective derived from the geographical and divine name Aššur with the gentilic suffix -āyu. This name wa...- published: 14 Jun 2013
- views: 2429
- author: Assur History
