It’s now being widely reported in Western mass media that Japan is abolishing its social sciences and humanities departments. I am not actually annoyed by these reports, because in this instance the Japanese media have done no better. Here’s the Yomiuri Shinbun attempting to explain:
The Yomiuri Shimbun conducted a survey among the presidents of all 86 national universities across the nation to ask about their faculty reform and abolition plans as of the end of July, and how they reacted to the education ministry’s notice. The Yomiuri received responses from 81 universities.
Of the 60 universities with humanities and social science faculties, 58 responded to the survey and 26 said they had plans to abolish such faculties or convert them to other fields.
Of the 26 universities, 17 plan to stop recruiting students for these departments, which contain at least 1,300 students.
Many universities plan to abolish “no-certificate” courses that do not require students to obtain a teaching certificate in their teacher training faculty and allocate their existing quota to newly established faculties.
There’s a lot of stuff making this report confusing, so here’s a full rundown.
Read the rest of this entry »
Posted: September 23rd, 2015 | Academic mumbo jumbo
暑雨後坐月 Resting in moonlight after summer rain
黃任 huáng rèn (18th c.)
雨洗月逾潔 Pure she waxes, washed by rain.
氣寒光転幽 The air is cool, the light turns dim.
露蛍不自夜 Fireflies stave off the eve.
風樹欲先秋 Drafts in woods herald the fall.
烹茗籟遥起 Distant rushes cool my tea.
払琴泉暗流 Darkness falls as I strum my qín.
清宵不成夢 Brisk the night, and without dreams.
心跡両虚舟 Mind and deed, both empty boats.
Posted: June 20th, 2015 | Odes
Soumission
Michel Houellebecq
Flammarion, 2015 (English translation)
This book is about the life of a French academic who cares about almost nothing except the 19th century writer Joris-Karl Huysmans, but who discovers that the spark he inherits from Huysmans is snuffed out by the reality of 21st century France. Although he ends up converting to Islam, and despite Houellebecq’s grumbling about Islam in public interviews, this book is not an analysis of Islam at all, and people looking for one will be disappointed. It contains elements of a political manifesto, but attributing some viewpoint to Houellebecq would eliminate the psychological crux of the narrative. Islam is neither the disease killing France nor the magic potion to cure the narrator. Islam is simply a reality happening in France. Whether it becomes a comfortable or uncomfortable reality, a Self or an Other, is the decision of the milquetoast narrator and millions like him.
Tens of thousands of intelligent French people have converted to Islam (far more than in England). So why a novel, rather than a biography of René Guénon? This is a question that unappreciative reviewers who zip through the book finding nothing unusual about it need to ask. Why is the narrator so normal—and why is he so abnormal? He keeps on talking about Huysmans. “Well,” says the putatively leftist reviewer, “he’s a Huysmans specialist. That’s his job.” But what is a job? The narrator François is propelled around the country by Huysmans; he wants the religious conviction that Huymans had. It’s more than just a job for him. Who cares? Well, this question itself is the problem. Is Huysmans not of the West, and is the narrator not of the West, and are we not of the West? How is it that Huysmans became a moldy old “object of study,” and the narrator an alienated professor, and the reader segregated from both of them? How did this strange “normal” way of relating to literature arise, and where did our commonalities go? Houellebecq wants us to be confused by the narrator’s alienation, as much as the narrator is confused himself. He does not want to give us a sociological study about some object of research; he wants us to feel that we need to examine ourselves, that something has gone wrong.
François is free from some of the illusions of his generation. He recognizes the illusory nature of money. Money is a means to get what you want; but what he wants is the consolation and intimacy of books. He recognizes, too, the illusion of free love, and is bemused by how women seem to brush past him, guided by something unwritten (et d’autant plus puissant qu’il demeurait implicite) to drift from person to person without lasting bonds. Throughout Houellebecq’s novels, modern society encourages voracious sexual appetites, so that the sexless are forced to participate as well. François is more mundane than sexless, but one gets a feeling that he ought to be able to rise above shallow relationships.
But he is penned in by some strange limits imposed by “libertine” society. Despite his ability to appreciate Huysman’s intimate portraits of the inner lives of men and women, he finds that he is unable to articulate his own inner life in conversation (car les conversations sur la vie intime ne font pas partie des sujets considérés comme admissibles dans la société des hommes). Pre-modern literature, by giving him a taste of truth, has ruined his life, since he cannot share that truth with others; at the very least, his girlfriends do not care, and he cannot conceive of a willing audience. Thus François becomes a prototypical Houellebecqian protagonist, locked into a sinecure and unable to form close personal relationships; “un pauvre type”.
A solitary existence, living in a world that was nothing but him and Huysmans, gave him some respite for a time. But now he is thrust into a world he does not want any part of: the 21st century liberal arts academy, its disconnect from the meaning of literature, and its endless, circular obsession with what is strangely called “identity”. Immediately, without even bothering to describe the narrator’s politics, Houellebecq gives us three conflicting images: a discussion of a university president practicing identity politics (gender studies) and a Ph.D. candidate’s thesis on the “identitarian” movement, right in the shadow of the Grand Mosque of Paris.
What is an identity? To some, it is a political battle cry. François feels no such thrills. He can write about his literary passion, but his writing can neither change the world nor reveal his authentic frustration, as in some of Houellebecq’s prior novels. Identity politics is not his thing; but he cannot escape the ground shaking beneath his feet. His Jewish girlfriend suddenly leaves for Israel. Neither the “identitarians” nor the Muslims represent the France she believes in. But what is that France? One English review has already commented on François’ self-pitying words, “There is no Israel for me,” but I also liked his girlfriend’s confused attempt to find a heritage she can claim: “J’aime la France! … J’aime, je sais pas… j’aime le fromage!” There is not only no Israel for François to flee to, there is no France for him either. There is only the after-image of Huysmans, transposed onto an unrecognizable cultural wasteland, where “identitarians” prowl after scraps.
To be fair, Houellebecq does not imagine the collapse of civilization. He imagines a peaceful Socialist-Muslim joint government that models itself after Chestertonian Distributism. This is, perhaps, a rather optimistic ideal of what the world like look like in 2022. The new, forward-looking government has solved many social problems by including Muslims in its governing alliance, and it feels like a sorte d’empire romain reconstitué. But as Oswald Spengler said, the Roman Empire only arose when the Republic had been defeated. They may cheer on the name of Chesterton, but the true king of France in 2022 is Spengler, constantly whispering his memento mori into the ear of the newly crowned Caesar (sorry for the mental image). At last the deus ex machina, a guy named Rediger, appears, accompanied by his nubile young wife Aisha, to convert the narrator to Islam; Rediger speaks precisely to François’s insecurities and worries, and proposes that, just like in Histoire d’O, Islam makes it possible for women to submit to men, and human beings to God.
Houellebecq is not actually arguing that this is the natural order of the world. In fact, by placing this argument into the context of François’s hedonism, he immediately problematizes it. The Histoire d’O-citing convert Islam that Houellebecq imagines in a half-sardonic, half-nihilistic tone clearly does not escape his criticism. It is not a French Islam, but an anti-French anti-Islam, based on a muddled confusion of both Middle Eastern and Western European traditions. But what is François supposed to do? No Christian or atheist has been able to offer him any hope. Only the East offers the faint glimmering of a road he can walk. Perhaps if he walks it long enough, his lie will begin to seem like truth.
The correct response to the end of the book is not despair, or excitement, but pathos. But those who skim the book looking for political arguments to use in their own little battles will naturally not only miss the point, but in fact do damage to whatever remaining value literature has to the Western European tradition. It is the darkest of ironies. Houellebecq’s character François loses faith in Huysmans, because he cannot hope to bring Huysmans to people around him. He burns his past; Islam is his only remaining path. Houellebecq writes a book about this, and the clickbait reviewers of the decayed “public sphere” deny him the ability to really connect with his readers, even as he lives. It is no wonder that Houellebecq has declared himself exasperated with having to promote his book, and as of this week has canceled all future interviews about it. But what of Europe?
Posted: May 26th, 2015 | Book Reviews
The first poem of the Book of Odes 詩経, translated by Ezra Pound. Pound originally wanted the Chinese to be included alongside his translation, but his publisher at the time didn’t care and this has never been done before this blog post. Pound also wanted a phonetic transliteration, but this is a lot of work because of the changes to Chinese over the centuries. I here include a rather butchered version of Pan Wuyun’s reconstructed phonology. You can compare with other translations on Matt’s blog.
關關雎鳩,
在河之洲。
窈窕淑女,
君子好逑。
|
Kroon kroon skha ku,
zuu’ gaal kju tju.
Quuw’ g-leew’ gljiwg na’,
klunsy’ hmhuu’ gu.
|
“Hid! Hid!” the fish-hawk saith,
by isle in Ho the fish-hawk saith:
“Dark and clear,
Dark and clear,
So shall be the prince’s fere.”
|
參差荇菜,
左右流之。
窈窕淑女,
寤寐求之。
|
Shuum skhraal graang’ shuus,
saal’ ghwu’ ru kju.
Quuw’ g-leew’ gljiwg na’,
ngaas mids gu kju.
|
Clear as the stream her modesty;
As neath dark boughs her secrecy,
reed against reed
tall on slight
as the stream moves left and right,
dark and clear,
dark and clear.
|
求之不得,
寤寐思服。
悠哉悠哉,
輾轉反側。
|
Gu kju pu tuug,
ngaas mids snu bug.
Luw stuu luw stuu,
ndens ton’ pan’ skrug.
|
To seek and not to find
as a dream in his mind,
think how her robe should be,
distantly, to toss and turn,
to toss and turn.
|
參差荇菜,
左右采之。
窈窕淑女,
琴瑟友之。
參差荇菜,
左右芼之。
窈窕淑女,
鐘鼓樂之。
|
Shuum skhraal graang’ shuus,
saal’ ghwu’ shuu’ kju.
Quuw’ g-leew’ gljiwg na’,
Grum sbrig ghwu’ kju.
Shuum skhraal graang’ shuus,
saal’ ghwu’ maaw kju.
Quuw’ g-leew’ gljiwg na’,
tjong khwaa’ nggraawgs kju.
|
High reed caught in ts’ai grass
so deep her secrecy;
lute sound in lute is caught,
touching, passing, left and right.
Bang the gong of her delight.
|
This is possibly the best translation ever made from the Book of Odes. It is far more wild than literal, but it has uncanny accuracy. A prince (klunsy’, Japanese kunshi) is to marry a “modest, retiring, virtuous, young lady,” as James Legge literally puts it. The word “lady” is straightforward, which is why Pound sought out “fere” instead. The two words describing her, quuw’ g-leew’ 窈窕, are less so. They are both written with the radical for “hole”, which is rarely seen in Japanese these days outside of the word 穴 “hole” itself and 空 “sky”. (Not actually true, thanks Leoboiko.) 窈 literally means “deep”, perhaps with a connotation of “concealed,” and 窕 means some sense of “refined”. Pound finds two wonderful yin-words to express the passiveness of the lady: “dark and clear.” While one may wonder where the second definition came from, the phrase 窈窕 was used much later by Tao Yuanming to refer to a mountain stream, so I think Pound has it spot on. He knows this so well that he repeats it twice.
In the second verse a lot of compromises are made. The word “stream” comes up twice where the text speaks only of flowing, “modesty” and “dark boughs” come lurching out of nowhere, and waterlilies become “reeds”. But this framework allows some of the repetition of the original to come through without sounding cloying to the modern ear. Finally the phrase “dark and clear” comes up again twice. The literal text is again referring to the lady, but in the next line it is made apparent that she is not yet meeting with anyone, but we are only hearing of the man being consumed with thoughts of her, both in waking and in dreaming. Pound uses the fuzzy impression of color and water, offering a dreamlike state, before translating the specific image of dreaming in the following verse.
In the third verse the word “distantly,” included in the ancient Chinese sense of 思, is worked in nicely. The translation falters a bit after this, though. The addition of the word “robe” does not really fit the poem; even this would have been a little too physical in ancient China. And there is no sense that the “reeds” are being gathered and picked by human hands, in preparation for a wedding celebration. Instead, the plants continue to bump around until the end of the poem. Still, it ends with a satisfying bang.
Posted: April 18th, 2015 | Odes
Earlier in this blog we heard from Nishibe Susumu and Watanabe Shōichi. Now it is time to break out the list of the man himself, Kure Tomofusa, from his book New Techniques for Readers 読書家の新技術 (1987). Kure-sensei sorted his recommendations into categories.
Politics
Carl Schmitt, The Concept of the Political
Carl Schmitt, Political Theology
Carl Schmitt, Theory of the Partisan
Yoshimoto Takaaki, Tentative Proposals on Mathieu (A recommendation offered without comment in New Techniques, but in 2012 Kure-sensei reread Yoshimoto’s complete works and discovered that he had been deceived by the difficult style of writing, and in fact there was nothing interesting about them. I’m guessing he would rescind his recommendation.)
D. H. Lawrence, Apocalypse and the Writings on Revelation (Recommended as a supplement to reading the Bible.)
Carl Schmitt, Essays on Political Philosophy
Engels, The Origin of the Family, Private Property and the State
Lenin, State and Revolution
Yoshimoto Takaaki, Communal Illusions (Read instead Kure-sensei’s commentary on this book.)
The rest of the suggestions are not nearly as interesting… Read the rest of this entry »
Posted: March 15th, 2015 | Books
Just want to wind things down with a proper conclusion. The Kogakkan study program is a truly excellent one featuring top quality classes on Shinto and a lot of hands-on experiences. The teachers are really friendly and open to further discussion, and my supervisor Tamada-san as well as the other supervisors and volunteers were wonderful people who I hope to keep in touch with in the future. I’d recommend the program to anyone stumbling across this blog.
Here’s my summary essay (more like a summary blurb…), which is based on a presentation I gave to the school president and many other dignitaries.
I think it is important to understand the uniqueness of what foreign students learn on the Ise and Japan Study Program. In particular, I would like to say a word about the lectures and tours offered to us by Shintogaku professors. Shintogaku is an approach to thinking about spiritual culture that exists only in Japan. The primary purpose of Shintogaku is to train students to become shrine priests. But Shintogaku professors, through writing books about shrines and educating the general public, also create a common standard for practices at shrines across the country. When Japanese people go to shrines, they know what to expect. In this way, even as shrines are non-sectarian and welcome freedom of belief, they can continue to maintain their traditions for future generations.
When foreigners want to read about Shinto, it is very rare for them to run into Shintogaku. It is far more common to encounter the personal opinions of priests, new religious leaders, or foreigners who have been to Japan. Even the authors of textbooks about world religions can be led astray by these opinions. Japanese people may be surprised by what foreigners read about Shinto in English. My experience on this program, and during my other trips to Japan, has shown that true quality in talking about Shinto is best obtained by reading, talking, and thinking about why shrines exist in the way that they do.
From the Kogakkan professors who participated on this study program, I learned that Shinto has a very deep and complex history. Shinto has a unique perspective on how to preserve traditions and spiritual culture. Religious studies and theology are ill equipped to confront the types of discussion that take place within Jinja Honcho. In the 21st century, culture clashes, based on misunderstanding of the culture of other countries, are resurfacing and are already the cause of serious international conflicts. This is an important time for foreigners interested in Japan to collaborate with Japanese Shintogaku professors in order for the world to gain a new and enlightening perspective on human diversity.
Posted: March 15th, 2015 | Kogakkan
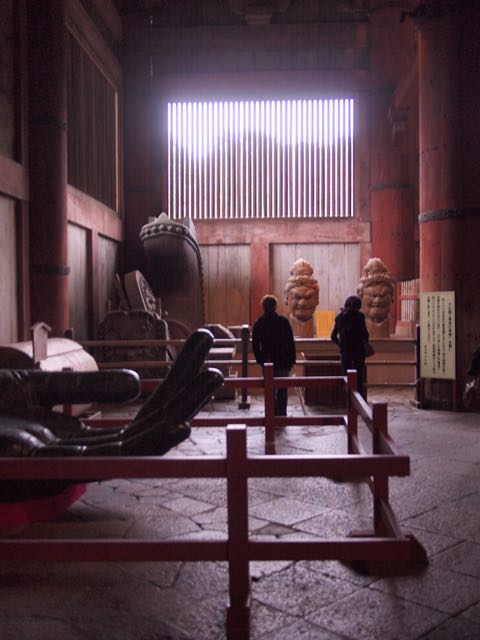
The past few days days have given us a little more free time, but actually the pace has been picking up as we begin work on our final presentations for Thursday. (I haven’t yet started work on mine.) Over the weekend we were given a free tour of Nara and Kyoto. I like this photo I took inside the hall of the Great Buddha.

I can only offer a few thoughts about the outing to the mature port town of Oominato we had yesterday. The people of Oominato were overjoyed to have foreigners visiting, and everyone stepped out of their homes and were watching us as we walked down the street surveying the town. They used to build ships here, but it seems that people do not order so many ships anymore. There is a very beautiful-looking, 120-year-old ryokan in this town, a relic of a time when people would arrive on boats on their way to the Jingu. The ryokan seems to be completely empty now, which makes me sad because it’s kept in great condition and is very clean. Here are some pictures. Consider it for your visit to Ise!
Today we all enjoyed a tea ceremony. I got to go inside a tea house used in the full-formal ceremony, and inside I felt like I should be acting a lot more formally. You get the instinct that you need to know where to move for each step of the ritual. We then went into a half-formal room and had tea served to all of us, but the servers really did know what they were doing the whole time, and it was quite impressive.
We all tried to whisk the tea ourselves, but no one seemed able to accomplish it in the same way the servers had done it. I tried to take some pictures but they came out blurry. Agh


Time to get working on my final presentation!
Posted: March 10th, 2015 | Kogakkan
After the lectures today we went to an old-fashioned used bookstore full of extremely good-quality works of history, literary criticism, and philosophy. Micchan bought the Heike monogatari, Michael bought a full set of Biographies of Japanese Swordsmen, and I found some nice books by Kure Tomofusa. The owner did not charge me full price for them, even though they were only priced at 400 yen each. I reflected on this a lot as we walked back to the dormitory, and I believe that the only reason he could have done this is because he didn’t care about the price at all, but was simply happy to see so many foreigners interested in Japanese literature. This is a type of interaction that I will never have over Amazon.

Without further ado, here are summaries of the three lectures!
Shimizu Kiyoshi
The gist of President Shimizu’s talk was that the Saiō symbolically brought the miyabi, or urban beauty, of the imperial capital to Ise. For a summary of his main point I will forward readers to Paula’s blog. I was much more interested in three tangents he went on:
(1) Why is the shikinen sengū necessary? He asked us to supply answers, and I gave him the standard answer that it’s because the kami like new, well-maintained buildings better than old buildings. He agreed, but then looked very expectantly to the room for another answer. He must have really expected more creativity from us! He then offered to us the possibility that the shikinen sengū teaches us a constant lesson about maintaining our mastery of difficult arts. The shikinen sengū creates something that is “newly old” (新しく古い). It therefore is a constant renewal and “revival” (甦り) of tradition. These days, the traditional crafts involved are so hard to come by that the implements for the shikinen sengū are often produced by “living national treasures”. But the renewal is about more than just the technology involved. The entire ritual must be constantly in the memory of the shrine priests, and the memory must be turned into action on a regular basis, once every 20 years.
(2) When Japan’s era name or nengō system was first introduced, said Professor Shimizu, they changed the name of the era whenever a good omen occurred, such as a great harvest or the appearance of a beautiful cloud. But by the later Heian period, the era was only changed when there was a bad omen, in order to ward off evil. The character of a nation changes with the times. Over the centuries, the Heian court became lax in its observation of the omens, and fell into depravity. Just like ancient Rome, the Heian aristocrats enjoyed endless parties as their political system began to decay around them. The Genji monogatari is a kind of high-water mark in the development of the classical court; a book that could not have been written in the Asuka or Nara periods, but which foreshadowed a decline.
(3) Ise is not the only religious institution in Japan that has been operated continuously since Asuka times. The Tōdaiji temple in Nara was built in in the early 8th century and has held a ceremony called shunie 修二会 nearly every year since 752. This year will mark the 1264th annual ceremony, which involves a traditional combination of Buddhist and Shinto rituals.
Sako Kazukiyo
Yamada Yoshio has been dubbed “the last national scholar,” but I believe we heard today from the last prewar scholar, Kogakkan’s director Sako Kazukiyo 佐古一洌. Unlike most of the other professors who spoke to us, Sako-sensei had no PowerPoint. Actually, his entire talk was a series of handwritten notes, and it quickly became evident he had never used a computer. He spoke in the highly educated and chauvinistic style of a prewar professor, which I found remarkably endearing, but also almost completely incomprehensible.
In place of an introduction, Sako-sensei shared with us some remarks about being old; he is 74, and as there are over 50,000 centenarians in Japan, he expects to live a bit longer. They are mostly women, though, so he amended this to say maybe he wouldn’t live that long. He said there was a method to beating senility named after the powers of 10. One must do the following every day: read one book, laugh 10 times, stretch 100 times, write 1000 characters (i.e. a letter to a friend), and walk 10,000 steps (一読、十笑、百吸、千字、万歩). To be honest this sounds like a great plan not just for old people but for people of every age.
Sako-sensei’s talk revolved around two points: (1) the Japanese spirit of magokoro, which I have written about in connection with the Genji monogatari, and (2) the Japanese tradition of matsuri, festivals. Matsuri is the expression of magokoro, and this is all that ever needs to happen in Japan. Unlike President Shimizu, Director Sako lives in a glorious, timeless state where the Japanese spirit and festivals are not subject to weathering and decay, but have simply always existed, and always will. He saw on television once that there are over 300,000 matsuri celebrated in Japan every year; therefore there are hundreds of matsuri taking place somewhere in the country every day. Contemplating this is clearly a great delight for him. He offered some words in praise of Minakata Kumagusu, who tried to stop the consolidation of shrines and save local chinjū-no-mori ecosystems back in the Meiji period.
The origin of these hundreds of thousands of matsuri was in desire for health, long life, marriage, safe childbirth, and worldly success. These are all expressed through magokoro, an honest heart. (Although he criticized the Chinese for encouraging selfish behavior in their philosophy, Sako-sensei’s definition of magokoro is rather Neo-Confucian, as I pointed out in my Genji paper.) Because women more often pray for the success of others, they have more pure hearts than balding old fools like Sako himself; this information came to him via his daughter. But regardless, Amaterasu commanded Lord Jimmu to create a country of people with pure and honest hearts, so it is the duty of every Japanese to avoid la négativité. In this one-hour talk, I am fairly certain that the only loan-word Sako-sensei employed was this one word “negatiibu“. The only thing he wrote on the board was the related phrase 神州清潔の民, “pure people of the divine country”.
Modernity was just a bothersome bit of foolishness to Sako-sensei, who whipped out a bit of English skills to quote Lincoln’s phrase “government of the people, by the people, for the people,” then replaced the Japanese word for “people,” jinmin 人民, with what he called its Edo period equivalent, ugō-no-shu 烏合の衆, making democracy the “government of the rabble, by the rabble, for the rabble.” The people of the Edo period had a better goal in mind: self-sufficiency, 自給自足. They were able to produce for themselves (自給), and they felt satisfied with what they had (自足). The complex world of democratic politics and technology is a mere distraction from the essentials of magokoro and matsuri.
Sako-sensei had saved the real tear-jerker for the end of his speech: a soaring anecdote about the end of the Pacific War. He was apparently completely unconcerned by the fact that the grandparents of his audience would have been fighting on the opposite side in that war; but in the end this didn’t matter anyway, because I am convinced that, since our Japanese friends were not listening to this talk, no one in the room understood a word he was saying at this point. The majority of his anecdote was a direct quotation of the way people spoke in 1945, which is basically Greek. So if my classmates are reading this and think I must be some kind of genius to have written down the whole anecdote, please rest assured that all I did was write down some misspelled names and dates and found the text he was quoting on the Internet.
On August 14, 1945, past 11 PM, after the Cabinet meeting on ending the war had adjourned, I [Hisatsune Sakomizu] entered the Prime Minister [antiwar navy admiral Suzuki Kantarō]’s office, and offered my thanks to him for taking on the challenges of that day.
We sat facing each other, and it naturally it was impossible to avoid crying. The Prime Minister sat across from me in pensive silence.
Unexpectedly, we heard a knock at the door. We turned to see Army Minister Anami [Korechika] enter with his sword equipped and his hat at his side. I stood and observed from the side.
The Army Minister walked directly to the Prime Minister’s desk and bowed respectfully.
“I said many things at today’s cabinet meeting, and I fear I must have caused some offense. I wish to humbly offer my apologies. My sole desire is for the protection of the national polity; I have no private motive. I beg your understanding of this.”
Seeing tears falling from Army Minister Anami’s face, I also began to cry. Then the Prime Minister, nodding in assent, rose to meet Army Minister Anami and said,
“I understand your intention, but Anami, the royal house will remain secure. No matter what happens, His Majesty will continue to personally and thoughtfully make offerings to the imperial ancestors every spring and autumn.”
Army Minister Anami said, “This I too believe.” He bowed deeply and departed.
After I saw him off at the door, the Prime Minister said, “Korechika came to say goodbye.”
I shall never forget that sight, as long as I shall live.
Anami Korechika committed seppuku later that night. But he died knowing that the matsuri would go on.
Kamo Masanori
Our last lecture of the day was from Kamo Masanori 加茂正典. He gave us the surprising news that the Saiō system was not the only link between the classical court and Ise. This was actually kind of comforting in a way, because I was wondering who actually was allowed inside Ise between 1300 and 1700. The Saiō didn’t come anymore, and the Emperor never visited… were the shrine priests and miko very lonely in there?
In fact there was another imperial messenger, called the Shiō 使王, who appeared even in the Nihon Shoki. Kamo-sensei seemed to have a poor sense of time and spent most of the hour explaining the divination system by which the Shiō was selected in the classical period. We heard that his main duty was to make offerings of silk and thread, but we did not get to hear about the rest of his job.
Unlike the Saiō system, the Shiō system continued throughout the Warring States and Edo periods, making it a hallmark 1150-year tradition that ended in… YUP, THAT’S RIGHT, 1871.
Posted: March 6th, 2015 | Kogakkan
At some point I’m going to have to write up all of the other things I’ve seen and done over the past four days. But for now, here’s a quick overview of the infrastructure that kept the sacred metropolis humming. Pictured here: the last remaining ryokan in Ise from before 1871, Asakichi 麻吉. Unlike the last onshi house, it is still operating, and is full of beautiful open spaces and antique calligraphy and porcelain, but it probably isn’t too popular with youngsters as it is quite cold in wintertime…
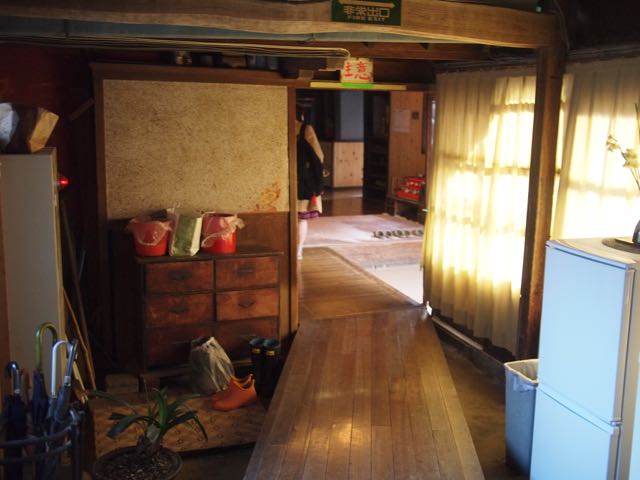

A constant influx of pilgrims and messengers to the Jingū meant a large population of employees and guests at the various onshi palaces and ryokan inns that had to be fed day in and day out, especially in Yamada, the Gekū area. With the rise of the onshi in the 1320s, a workshop and market area opened up in an area called Hatsukaichi (a name that means something like “Sunday Market”, from pre-medieval times). Hatsukaichi served not only the needs of the onshi, but also the Gekū itself, which needed to prepare food offerings for the kami every day. The merchants would sell their food to the Gekū in a building called the Korankan 子良館, which actually doubled as Japan’s first women’s college. Here, women were trained in ritual ceremony, which included the preparation of the sacred offerings. The Korankan was shut down alongside the onshi system in 1871.

The amount of work that needed to be done was quickly too much for the confined space of Hatsukaichi, and from the 1400s more serious, large-sale operations began in a separate area called Kawasaki 河崎, which was conveniently located on a river between Yamada and the ocean. By 1620, the crafts and trades in this are were so well-developed that merchants came from China to sell top-quality goods. The finished products would be floated down the waterways to the Korankan as well as various onshi estates. A Japanese economic historian summed up this area by saying, “Kawasaki is the throat of Yamada” 「河崎辺ハ山田の咽喉」.

For the first few hundred years, business was done using bartering and imported Chinese coins, since the Japanese government was not in a good state to produce its own currency. In the early 1600s, someone in Yamada came up with the idea of paper money, perhaps based on seeing Chinese banknotes. As a result, the Yamada Triad of elders took charge of printing Japan’s first paper money, Yamada Hagaki 山田羽書, which was produced continuously for over 200 years until the Japanese government declared a monopoly on money production, again in 1871. It featured different colors for different values of money, and anti-counterfeiting techniques. Like the onshi records, the Hagaki banknotes are mostly destroyed today, so we don’t know when exactly the system began. Chieda-sensei has spent the better part of a decade hunting down old ones. Pictured below is a one-momme note featuring Ebisu, god of prosperity.

Because it relied on business rather than patronage, Kawasaki survived after 1871 and many of its picturesque workshops are still standing, although they are slowly being demolished. The area is now oriented towards tourists and you can buy all sorts of cool antique stuff, rare prints, and old books. If you are looking to take a leisurely walk through Ise this is probably the best neighborhood to do it in.
Posted: March 5th, 2015 | Kogakkan
While we learned about and visited a large number of places over the past few days, I’m going to use this post to focus on the subject of onshi 御師. The existence of pilgrimage promoters called onshi had been hinted at in previous classes, and I was under the impression that these people were something like travel agents. This was also the impression of our tour guide for today, who labeled onshi estates as “hotels”. In fact, as the medievalist Okada Noboru 岡田登 explained to us this morning, the name onshi is shorthand for the mind-boggling distance between the ancien régime of 1867 and the New Japan of 1877. Onshi were the literal center of pre-modern worship at Ise, and a key aspect of Japanese feudalism. In an age where the Jingū was closed to everyone but the Emperor, the population of Japan, rich and poor, registered themselves with religious gentry called onshi in order to forward their prayers to Amaterasu. In a word, the onshi were Japan’s First Estate, and Ise was once a sprawling, aristocratic Vatican.
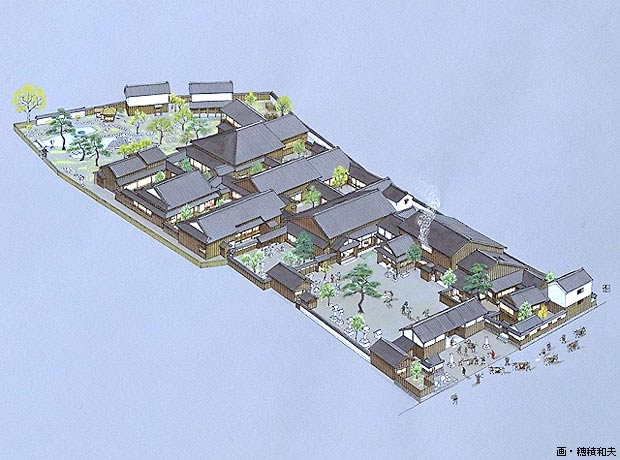
I stole this illustration from a corporate magazine called Obayashi Quarterly, I hope they don’t mind. Pictured here is the estate of an onshi named Mikkaichi Dayū Jirō 三日市大夫次郎, which means something like “Joe, Lord Wednesday Market”, certainly not a name I’d associate with nobility. Some of the onshi had strange names; one of them was called Lord Dragon. Mikkaichi Dayū’s parishioners amounted to 350,000 to 500,000 households, meaning that he likely had over a million people on his rolls who exchanged their “first rice” fees (初稲料 hatsuhoryō) for the right to have prayers forwarded to the Jingū, and the possibility of staying at his estate and witnessing a kagura sacred dance if they were ever able to save up the money for a pilgrimage. Here’s the shocking thing; the kagura dance was not performed at the Jingū itself, but was in a special building towards the back of this estate. Furthermore, the ofuda talismans that onshi sold to parishioners were not from the Jingū, but were produced completely by the onshi, in their capacity as shrine priests. In short, the onshi were religious institutions providing the public’s sole line of access to the Jingū.
Pictured: The original stamp used by a Gekū onshi to produce ofuda, along with several examples. The sticks that one finds inside ofuda would also have been supplied in-house.

Okada-sensei painted a rather dire portrait of the state of knowledge we have about onshi. He expounded at length on the fact that nothing was saved when the onshi system was abruptly abolished in 1869. A system that had received the support of 80-90% of the Japanese population suddenly vanished, and all the gorgeous estates had no means of upkeep. Like the suddenly disinherited samurai Shiba Ryōtarō describes in Clouds Above the Hill, the onshi had no choice but to move away and find new jobs, but where samurai families had houses scattered across the country, everything the onshi had done was centralized in Ise, which instantly transformed from the noble headquarters of an established religion to a backwater fishing village. Hundreds of years of detailed records, detailing up to 700 years of Shinto customs, were generally sold to paper mills where they were turned into tissues and toilet paper. In many cases we do not know how onshi families came into existence or how they became chosen by their patrons.
Many of the abandoned onshi estates were turned into rubble when the Americans bombed Ise in 1945, and others were demolished in the postwar years due to their extreme age. In 2015 there is only a single onshi estate still standing in Ise. This is the Estate of Maruoka Sō Dayū 丸岡宗大夫邸, which happens to have been built in 1866. It is currently owned by the 18th Maruoka Dayū, Maruoka Masayuki 丸岡正之, who works as a carpenter. Maruoka receives no money from the city or prefecture to pay for upkeep on the estate. He does not make enough money to keep it open, but has spent many years keeping it intact and opens it up for special occasions, such as when a group of foreigners are visiting. He says that his grandparents loved the old house very much and preserved it when many other houses were left to rot.
Pictured: Micchan stepping into a front room.

As I said, the onshi system lasted almost 700 years. (General Electric and Disney will be quite lucky to last that long.) It began as a replacement for the Saiō, when the Saikū was falling into disrepair and the Imperial household was no longer able to provide the Jingū with reliable funding. In 1181, Minamoto no Yoritomo, the founder of the shogunate system, came to Ise personally and petitioned a 4th rank Gekū priest (konnegi 権禰宜) named Watarai Mitsuchika 度会光親 to make a prayer on his behalf. It was the first time in the Jingū’s 700- to 1100-year history that a prayer was offered on behalf of someone other than the emperor, and it was the first time someone from outside the Imperial family had come to Ise for that purpose. As far as legitimizing his authority went, Minamoto no Yoritomo was both bold and clever.
He was also a trendsetter. As more estates in Japan fell into private hands, leading to the feudal or manor system (荘園 shōen), emerging landlords dedicated portions of their land to the Jingū specifically, in order to get the same divine favor that Minamoto had secured. This land was called mikuriya 御園 “sacred manors” or mizono 御厨 “sacred kitchens,” i.e., places where offerings were prepared. Similar to the medieval Church, the Jingū ended up inheriting and possessing large amounts of land in this way. The Gekū priests who made prayers in exchange for these offerings were called on’inorishi 御祈祷師, or “sacred prayer teachers,” later shortened to onshi. A similar system was already in place at Kumano, and later many shrines and Buddhist temples had such teachers, usually called oshi outside of Ise.
By 1383, the Ise onshi were serving parishioners in every part of the country, from Ezo (Hokkaido) to Kyushu. The onshi multiplied into the hundreds and they began purchasing parishes from each other and fighting over patrons. As we learned way back on day 1, the communities they supported, called Yamada and Uji, were basically at war with each other from 1400 to 1600, causing the only interruption of the shikinen sengū in Japanese history. Three classes of people served as onshi. First came the officiating priests called konnegi, who were usually called Dayū 大夫 after their aristocratic rank and often called ji’nin 神人 or “god people” in written documents. Lower level religious functionaries, also able to offer prayers, were called shin’yakujin 神役人. Finally, ordinary merchants, through some intervention that Okada-sensei did not describe, were able to become onshi at some point; perhaps this was how we got to Lord Wednesday Market above. [edit: Chieda-sensei clarified that the merchants, including Maruoka Dayū, purchased their titles.] All levels of onshi had to employ bureaucrats fluent in all the different dialects of pre-modern Japanese, in order to grant prayers and do business with people from across the country.
Uji-Yamada was at last pacified, and the onshi system officially regulated, with the rebirth of the shogunate in the 1590s, and the system reached its peak in the 18th century. Every onshi was at the head of an enormous nationwide network that had its luxurious headquarters in the sacred city of Ise but went all the way down to itinerant travelers bestowing ofuda as they did their rounds in rural villages, and selling goods such as astrological calendars from Ise or beauty products (usually made from mercury… oops). As noted above, up to 90% of Japan’s 30 million people were members of an onshi group in some way or another; those with no membership at all were considered in a vague way to be outside the reach of civilization.
In 1724, the Gekū peaked at 615 different onshi lords, and in 1777, the Naikū had a much smaller peak with 271 onshi. Following this, the groups slowly consolidated their power. The Maruoka Dayū estate that we visited today contained rare surviving testaments to this power. First, we have this hengaku 扁額, produced to memorialize a kagura dance conducted by the onshi and his parishioners in 1865.

It looks like a pretty ordinary engraving on wood… but when our tour guide Chieda-sensei saw it, he remarked, “pretty bold!” Why is it pretty bold? Because it reads “Great Jingū of Amaterasu Ōmikami” 天照皇太神宮, but in fact, this onshi was serving the Gekū, which honors Toyouke Ōmikami, god of agriculture and food preparation, and most certainly not Amaterasu. The ofuda stamps at the Maruoka Dayū estate seem to testify that as the Amaterasu cult picked up steam in the mid-1800s, the onshi around the Gekū simply began proclaiming that they were authorized to offer prayers to Amaterasu. But this is something it’s impossible to know for sure, because so many records were destroyed. Now, some more proofs of power.

On the left here is one of these newer ofuda; it appears to come from the “Great Jingū” (Gekū? Naikū? Both?), but was actually produced on site by the Maruoka Dayū. [edit: According to Chieda-sensei, he was not supposed to be able to do this, since he was only a merchant and not a priest. But Maruoka-san insisted that his ancestors made the ofuda themselves. Another mystery.]
Next to the ofuda is a very long list of people who gave money to the onshi in honor of the shikinen sengū (the money did not pay for the sengū itself, but apparently they simply solicited every time this happened). On the right is the reward provided to parishioners who came to Ise: a travel schedule for a deluxe package pilgrimage, with three days of meals and events surrounding the kagura dance. This may look like gross profiteering from a modern perspective, but in fact this onshi was performing a sacred duty for his parishioners. He was their link to the Jingū, as they were not allowed inside themselves. Only after the abolishment of the onshi system in 1871 were the gates opened and a kagura hall built inside the Jingū itself. By the way, if you go to Ise to see a kagura today, you will see it performed by beautiful young women. But the dance you would have seen at an onshi estate up until 1871 would have used older women, often in their 50s and 60s, with decades of practice.
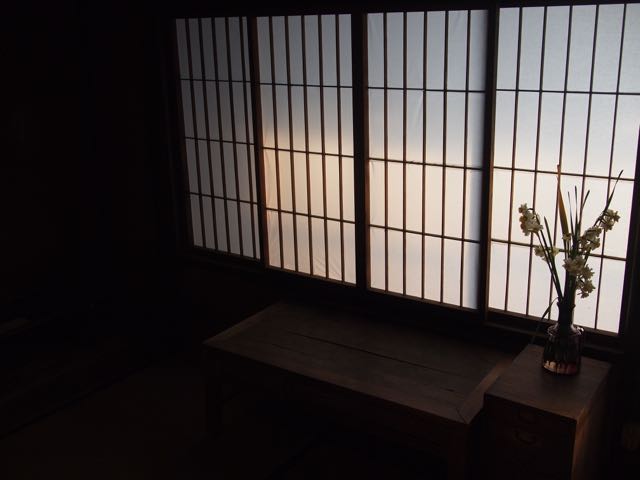

Ten luxurious gates of a style reserved for titled gentry are scattered here and there in the city of Ise, along with a few beautiful antique rooms comprising the partial remains of the Maruoka Dayū estate, and that is all that remains of the onshi system that once ruled this city. Once, Maruoka Dayū boasted a nationwide network, but now his heritage is hanging by a thread; the building seems ready to collapse, and the government will not pitch in for this last testament to 700 years of history. The friends of the owner have set up a Facebook page to encourage people to preserve the estate, and that’s about it.
Posted: March 4th, 2015 | Kogakkan














