- published: 16 Feb 2013
- views: 34936
-
remove the playlistW3c
- remove the playlistW3c
- published: 16 Nov 2011
- views: 2909
- published: 26 Apr 2014
- views: 2089
- published: 31 Aug 2012
- views: 1983
- published: 14 Mar 2010
- views: 22590
- published: 22 Sep 2014
- views: 2951
The World Wide Web Consortium (W3C) is the main international standards organization for the World Wide Web (abbreviated WWW or W3).
Founded by Tim Berners-Lee at MIT and currently headed by him, the consortium is made up of member organizations which maintain full-time staff for the purpose of working together in the development of standards for the World Wide Web. As of 29 March 2012, the World Wide Web Consortium (W3C) has 351 members.
W3C also engages in education and outreach, develops software and serves as an open forum for discussion about the Web.
The World Wide Web Consortium (W3C) was founded by Tim Berners-Lee after he left the European Organization for Nuclear Research (CERN) in October, 1994. It was founded at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology Laboratory for Computer Science (MIT/LCS) with support from the European Commission and the Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency (DARPA), which had pioneered the Internet and its predecessor ARPANET.
W3C was created to ensure compatibility and agreement among industry members in the adoption of new standards. Prior to its creation, incompatible versions of HTML were offered by different vendors, increasing the potential for inconsistency between web pages. The consortium was created to get all those vendors to agree on a set of core principles and components which would be supported by everyone.[citation needed]
This article is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported License, which means that you can copy and modify it as long as the entire work (including additions) remains under this license.
- Loading...

-
 7:11
7:11HTML5 and CSS3 Beginner Tutorial 10 - W3C and Validating your code
HTML5 and CSS3 Beginner Tutorial 10 - W3C and Validating your codeHTML5 and CSS3 Beginner Tutorial 10 - W3C and Validating your code
In this video I show you guys how to make your code meet up with W3C standards. I explain who the W3C are and how to validate your code to find any errors in your HTML. Here is the link to the online validator I used: http://validator.w3.org Social links: ------------------------------------------------------------- Add me on twitter: http://www.twitter.com/QuentinWatt facebook group: https://www.facebook.com/quentin.watt ------------------------------------------------------------- -
 5:53
5:53W3C: The World Wide Web Consortium
W3C: The World Wide Web ConsortiumW3C: The World Wide Web Consortium
Interviews with W3C staff and consortium members at the Third W3C Web and Television Workshop, September 2011, Hollywood, CA. -
 1:34
1:34What is the W3C Standard?
What is the W3C Standard? -
 2:43
2:43O que é a W3C?
O que é a W3C? -
 13:04
13:04Curso de HTML - Capítulo 10: ¿Qué es el W3C?
Curso de HTML - Capítulo 10: ¿Qué es el W3C? -
 5:15
5:15How to validate website's HTML code (W3C HTML Validator)
How to validate website's HTML code (W3C HTML Validator)How to validate website's HTML code (W3C HTML Validator)
This is a tutorial about validating your website's HTML code. I use the W3C HTML Validator. Just watch the video and follow the steps I show you. Please add a comment about what I could have done better. Thanks for watching and... have fun!!! HTML Validator by W3C (www.w3.org). -
 4:34
4:34W3C Tutorial on WordPress
W3C Tutorial on WordPress -
 5:25
5:25W3C-Consorcio internacional para páginas web. Validación gratis
W3C-Consorcio internacional para páginas web. Validación gratisW3C-Consorcio internacional para páginas web. Validación gratis
www.ms2progress.org Video corto, solamente introductorio al tema del W3C. Explico qué es, por qué es importante, y cómo puede hacer la validación. Si tienen dudas después de ver el video o validar sus páginas, pueden dejar sus preguntas aquí o escribirme en facebook o twitter, y con gusto oriento a cualquier personas interesada en mejorar su sitio web. Facebook: ms2progress Twitter: @ms2progress. -
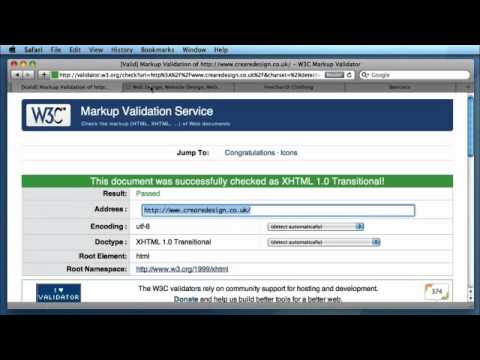 6:29
6:29W3C HTML Validator - Introduction & Compliance Benefits
W3C HTML Validator - Introduction & Compliance BenefitsW3C HTML Validator - Introduction & Compliance Benefits
The advantages of making websites W3C compliant. After an introduction to the W3C HTML Markup Validator, we talk about the benefits of going that extra mile. Find the supporting post at http://www.crearedesign.co.uk/blog/videos/w3c-html-validator.html -
 9:53
9:53Hak5 - Spoofing the W3C Geolocation API
Hak5 - Spoofing the W3C Geolocation APIHak5 - Spoofing the W3C Geolocation API
Spoofing the W3C Geolocation API -
 8:32
8:32HTML W3C Tutorial Pt 1
HTML W3C Tutorial Pt 1HTML W3C Tutorial Pt 1
Here I'll teach you everything there is to know about html w3c. This part 1 of a 3 video set, that will show you every html tag and how they work. -
 25:40
25:40News from the W3C webperf-landia with Ilya Grigorik
News from the W3C webperf-landia with Ilya GrigorikNews from the W3C webperf-landia with Ilya Grigorik
Requests getting lost at sea or need better and more careful handling? Error Logging and Beacon APIs will help. Wondering about the network weather? Network Information API is a work in progress. Finally, trying to chart a faster navigation course? Resource Hints should help... We'll take a quick tour of the latest perf-related specs, their use cases, and implementation status. Ilya Grigorik is a web performance engineer and developer advocate at Google, where his focus is on making the web fast and driving adoption of performance best practices. -
 1:45
1:45El W3C
El W3CEl W3C
Curso de HTML 5 -
 1:11
1:11Welcome to W3C | W3Cx on edX
Welcome to W3C | W3Cx on edXWelcome to W3C | W3Cx on edX
Take this course for free on edX: https://www.edx.org/course/learn-html5-w3c-w3cx-html5-1x# Learn HTML5 and core Web technologies directly from the organization creating them! Learn to code Web pages and Web sites the right way.
- Amaya (web browser)
- Arena (web browser)
- Argo (web browser)
- ARPANET
- Austria
- Belgium
- Brazil
- C-HTML
- Canonical XML
- CERN
- CERN httpd
- Compete.com
- Consortium
- CSAIL
- CURIE
- ERCIM
- European Commission
- Finland
- GRDDL
- Greece
- HTML
- HTML5
- India
- InkML
- INRIA
- Internet
- Internet forum
- Internet Society
- Italy
- Jeffrey Jaffe
- Keio University
- Libwww
- Line Mode Browser
- MathML
- MIT
- Morocco
- Netherlands
- Novell
- P3P
- RDF Schema
- SCXML
- SKOS
- SMIL Timesheets
- SOAP
- SOAP (protocol)
- Sophia Antipolis
- SPARQL
- Stata Center
- SVG Working Group
- SXBL
- Template Cleanup doc
- Tim Berners-Lee
- Timed Text
- VoiceXML
- W3C Geolocation API
- W3C MMI
- W3C recommendation
- W3C XML Schema
- WebOnt
- Wikipedia Cleanup
- World Wide Web
- WWWC (AM)
- XAdES
- XBL
- XForms
- XFrames
- XHTML
- XHTML+MathML+SVG
- XHTML+RDFa
- XHTML+SMIL
- XHTML+Voice
- XInclude
- XLink
- XML
- XML Base
- XML Encryption
- XML Events
- XML Information Set
- XML namespace
- XML Schema (W3C)
- XML Signature
- XMLHttpRequest
- XPath
- XPath 1.0
- XPath 2.0
- XPointer
- XProc
- XQuery
- XSL Transformations
- XSL-FO
- XSLT
- XSLT elements
-

HTML5 and CSS3 Beginner Tutorial 10 - W3C and Validating your code
In this video I show you guys how to make your code meet up with W3C standards. I explain who the W3C are and how to validate your code to find any errors in your HTML. Here is the link to the online validator I used: http://validator.w3.org Social links: ------------------------------------------------------------- Add me on twitter: http://www.twitter.com/QuentinWatt facebook group: https://www.facebook.com/quentin.watt ------------------------------------------------------------- -

W3C: The World Wide Web Consortium
Interviews with W3C staff and consortium members at the Third W3C Web and Television Workshop, September 2011, Hollywood, CA. -

-

-

-

How to validate website's HTML code (W3C HTML Validator)
This is a tutorial about validating your website's HTML code. I use the W3C HTML Validator. Just watch the video and follow the steps I show you. Please add a comment about what I could have done better. Thanks for watching and... have fun!!! HTML Validator by W3C (www.w3.org). -

-

W3C-Consorcio internacional para páginas web. Validación gratis
www.ms2progress.org Video corto, solamente introductorio al tema del W3C. Explico qué es, por qué es importante, y cómo puede hacer la validación. Si tienen dudas después de ver el video o validar sus páginas, pueden dejar sus preguntas aquí o escribirme en facebook o twitter, y con gusto oriento a cualquier personas interesada en mejorar su sitio web. Facebook: ms2progress Twitter: @ms2progress. -

W3C HTML Validator - Introduction & Compliance Benefits
The advantages of making websites W3C compliant. After an introduction to the W3C HTML Markup Validator, we talk about the benefits of going that extra mile. Find the supporting post at http://www.crearedesign.co.uk/blog/videos/w3c-html-validator.html -

Hak5 - Spoofing the W3C Geolocation API
Spoofing the W3C Geolocation API -

HTML W3C Tutorial Pt 1
Here I'll teach you everything there is to know about html w3c. This part 1 of a 3 video set, that will show you every html tag and how they work. -

News from the W3C webperf-landia with Ilya Grigorik
Requests getting lost at sea or need better and more careful handling? Error Logging and Beacon APIs will help. Wondering about the network weather? Network Information API is a work in progress. Finally, trying to chart a faster navigation course? Resource Hints should help... We'll take a quick tour of the latest perf-related specs, their use cases, and implementation status. Ilya Grigorik is a web performance engineer and developer advocate at Google, where his focus is on making the web fast and driving adoption of performance best practices. -

El W3C
Curso de HTML 5 -

Welcome to W3C | W3Cx on edX
Take this course for free on edX: https://www.edx.org/course/learn-html5-w3c-w3cx-html5-1x# Learn HTML5 and core Web technologies directly from the organization creating them! Learn to code Web pages and Web sites the right way. -

W3C Standards and Implementors Panel
Representatives of the W3C working groups on CSS and SVG discuss the W3C graphic specifications, current work and future plans. Q & A session at The Graphical Web Conference 2014 (http://www.graphicalweb.org/) held at The University of Winchester, August 27th-30th 2014. Video produced by John Wilson (@snoop2003) of Winchester University Journalism School. -

Cómo hacer una Página Web desde cero 12 - Validación w3c @JoseCodFacilito
¡¡ SUSCRIBETE !! http://goo.gl/ZPioOq Para completar el proceso de desarrollo, veremos como validar nuestros archivos HTML5 con http://validator.w3.org/ donde se marcan los estandaras a los que conviene ajustarse para tener un codigo sin error de sintaxis. Aquí tienes todos los links de este curso basico de desarrollo web desde cero Cómo hacer una Página Web desde cero 00 - Introducción https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=uZpxbPSFkwA&index;=1&list;=PLraIUviMMM3eC5Gmk-cLwgpd5jUYJ2ilF Cómo hacer una Página Web desde cero 01 - Dominio y Hosting https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=udQXLYATzh4&index;=2&list;=PLraIUviMMM3eC5Gmk-cLwgpd5jUYJ2ilF Descargar gratis FileZilla - FTP - Cómo hacer una Página Web desde cero 02 - https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=25mSkK-XAcs&index;=3&list;=PLraIUviMMM3eC5Gmk-cLw... -

DOCTYPE y el validador de la W3C
Todo el contenido está producido por http://lineadecodigo.com Para más información en http://lineadecodigo.com/html/indicando-el-tipo-de-documento-html/ Conoce los diferentes tipos de documentos HTML que se pueden crear así como sus DOCTYPE asociados. Aprende a utilizar el validador de la W3C para chequear el contenido de tus ficheros. -

-

EB118 – Manu Sporney: W3C, Making Payments A Web Standard
Support the show, consider donating: 1MRWvkHvzpZKVAbpx4eqVPwgkV6vQgjZbK (http://bit.ly/23BZ59I) A typical online transaction today isn't very different from how it was done 25 years ago at the dawn of the Internet. In fact, online payments haven't changed much at all. When we want to pay for something online, we copy very sensitive credit card information into a form on a website and trust that website to capture it securely and make proper use of it. If this seems like an old and antiquated way to pay, that's because it is, and it costs billions of dollars per year in security and fraud prevention. The World Wide Web Consortium wants to standardize the way we pay online, making it more secure, and hopefully a better experience for users. Manu Sporney is a computer scientists and Standa... -

How to use the W3C Validation Service
The W3C Validation Service is an online tool to know what the errors of your webpages are so you can fix them to end with an accessible webpage -

01 08 Web standards and the W3C
-

A Walkthrough the W3C Markup Validation Service
A Walkthrough the W3C Markup Validation Service -

Choosing the Right W3C Standard
Phil Archer
HTML5 and CSS3 Beginner Tutorial 10 - W3C and Validating your code
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 7:11
- Updated: 16 Feb 2013
- views: 34936
- published: 16 Feb 2013
- views: 34936
W3C: The World Wide Web Consortium
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 5:53
- Updated: 16 Nov 2011
- views: 2909
- published: 16 Nov 2011
- views: 2909
What is the W3C Standard?
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 1:34
- Updated: 02 Feb 2009
- views: 5291
O que é a W3C?
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 2:43
- Updated: 30 Sep 2014
- views: 712
Curso de HTML - Capítulo 10: ¿Qué es el W3C?
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 13:04
- Updated: 29 May 2013
- views: 1157
How to validate website's HTML code (W3C HTML Validator)
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 5:15
- Updated: 26 Apr 2014
- views: 2089
- published: 26 Apr 2014
- views: 2089
W3C Tutorial on WordPress
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 4:34
- Updated: 06 Mar 2012
- views: 2477
W3C-Consorcio internacional para páginas web. Validación gratis
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 5:25
- Updated: 31 Aug 2012
- views: 1983
- published: 31 Aug 2012
- views: 1983
W3C HTML Validator - Introduction & Compliance Benefits
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 6:29
- Updated: 06 Dec 2010
- views: 3790
Hak5 - Spoofing the W3C Geolocation API
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 9:53
- Updated: 03 Aug 2011
- views: 9940
HTML W3C Tutorial Pt 1
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 8:32
- Updated: 14 Mar 2010
- views: 22590
- published: 14 Mar 2010
- views: 22590
News from the W3C webperf-landia with Ilya Grigorik
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 25:40
- Updated: 22 Sep 2014
- views: 2951
- published: 22 Sep 2014
- views: 2951
El W3C
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 1:45
- Updated: 27 Jun 2012
- views: 391
Welcome to W3C | W3Cx on edX
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 1:11
- Updated: 31 Mar 2015
- views: 2539
- published: 31 Mar 2015
- views: 2539
W3C Standards and Implementors Panel
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 63:03
- Updated: 05 Sep 2014
- views: 225
- published: 05 Sep 2014
- views: 225
Cómo hacer una Página Web desde cero 12 - Validación w3c @JoseCodFacilito
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 10:15
- Updated: 25 Dec 2013
- views: 2439
- published: 25 Dec 2013
- views: 2439
DOCTYPE y el validador de la W3C
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 7:25
- Updated: 25 Dec 2012
- views: 442
- published: 25 Dec 2012
- views: 442
Como validar HTML na W3C
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 5:41
- Updated: 06 Nov 2014
- views: 408
EB118 – Manu Sporney: W3C, Making Payments A Web Standard
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 78:28
- Updated: 17 Feb 2016
- views: 48
- published: 17 Feb 2016
- views: 48
How to use the W3C Validation Service
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 7:15
- Updated: 12 Dec 2009
- views: 5393
- published: 12 Dec 2009
- views: 5393
01 08 Web standards and the W3C
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 3:47
- Updated: 04 Jun 2015
- views: 80
- published: 04 Jun 2015
- views: 80
A Walkthrough the W3C Markup Validation Service
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 4:37
- Updated: 18 Oct 2011
- views: 826
Choosing the Right W3C Standard
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 12:28
- Updated: 25 Oct 2011
- views: 150
- Playlist
- Chat
- Playlist
- Chat

HTML5 and CSS3 Beginner Tutorial 10 - W3C and Validating your code
- Report rights infringement
- published: 16 Feb 2013
- views: 34936

W3C: The World Wide Web Consortium
- Report rights infringement
- published: 16 Nov 2011
- views: 2909

What is the W3C Standard?
- Report rights infringement
- published: 02 Feb 2009
- views: 5291

O que é a W3C?
- Report rights infringement
- published: 30 Sep 2014
- views: 712


How to validate website's HTML code (W3C HTML Validator)
- Report rights infringement
- published: 26 Apr 2014
- views: 2089

W3C Tutorial on WordPress
- Report rights infringement
- published: 06 Mar 2012
- views: 2477

W3C-Consorcio internacional para páginas web. Validación gratis
- Report rights infringement
- published: 31 Aug 2012
- views: 1983

W3C HTML Validator - Introduction & Compliance Benefits
- Report rights infringement
- published: 06 Dec 2010
- views: 3790

Hak5 - Spoofing the W3C Geolocation API
- Report rights infringement
- published: 03 Aug 2011
- views: 9940

HTML W3C Tutorial Pt 1
- Report rights infringement
- published: 14 Mar 2010
- views: 22590

News from the W3C webperf-landia with Ilya Grigorik
- Report rights infringement
- published: 22 Sep 2014
- views: 2951

Welcome to W3C | W3Cx on edX
- Report rights infringement
- published: 31 Mar 2015
- views: 2539
-
Lyrics list:text lyricsplay full screenplay karaoke
North Korea ship impounded in Philippines as part of fresh sanctions
Edit CNN 05 Mar 2016Saudi calls on Syria’s Assad to step down before transitional government
Edit Press TV 06 Mar 2016Karachi Citizens Must Exercise Restraint And Avoid Confrontation On Mustafa Kamal's Press Conference
Edit WorldNews.com 05 Mar 2016Cruz projected winner in Kansas
Edit Otago Daily Times 06 Mar 2016Health 2.0 And Mad*Pow Announce Final Agenda For HxRefactored Design & Developer-focused Conference on April 5-6th Will Discuss How to Improve the Healthcare Experience
Edit PR Newswire 23 Feb 2016Edit About.com 22 Feb 2016
Edit About.com 22 Feb 2016
Edit About.com 22 Feb 2016
HTML Quick and Dirty
Edit About.com 22 Feb 2016Edit About.com 22 Feb 2016
Edit About.com 22 Feb 2016
Hyphenation in CSS3
Edit About.com 22 Feb 2016Teach Yourself Javascript in 24 Hours (4th edition) Book Review
Edit About.com 22 Feb 2016Adobe Dreamweaver CS5.5
Edit About.com 22 Feb 2016Is there a 3d Canvas Context?
Edit About.com 22 Feb 2016What is XLink
Edit About.com 22 Feb 2016What is an XML Schema
Edit About.com 22 Feb 2016- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- Next page »







