- published: 21 May 2012
- views: 79330
-
remove the playlistComputed Tomography
-
remove the playlistLatest Videos
-
remove the playlistLongest Videos
- remove the playlistComputed Tomography
- remove the playlistLatest Videos
- remove the playlistLongest Videos
- published: 20 Dec 2010
- views: 129609
- published: 27 Dec 2012
- views: 85437
- published: 25 Jul 2008
- views: 319328
- published: 15 Nov 2015
- views: 1571
- published: 28 Apr 2015
- views: 8605
- published: 14 Mar 2014
- views: 10468
- published: 28 Jun 2013
- views: 41043
- published: 20 Feb 2012
- views: 4558

X-ray computed tomography, also Computed tomography (CT scan) or Computed axial tomography (CAT scan), can be used for medical imaging and industrial imaging methods employing tomography created by computer processing.Digital geometry processing is used to generate a three-dimensional image of the inside of an object from a large series of two-dimensional X-ray images taken around a single axis of rotation.
CT produces a volume of data that can be manipulated, through a process known as "windowing", in order to demonstrate various bodily structures based on their ability to block the X-ray beam. Although historically the images generated were in the axial or transverse plane, perpendicular to the long axis of the body, modern scanners allow this volume of data to be reformatted in various planes or even as volumetric (3D) representations of structures. Although most common in medicine, CT is also used in other fields, such as nondestructive materials testing. Another example is archaeological uses such as imaging the contents of sarcophagi.
This article is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported License, which means that you can copy and modify it as long as the entire work (including additions) remains under this license.
- Loading...

-
 12:17
12:17CT (Computed Tomography) Scans - A Level Physics
CT (Computed Tomography) Scans - A Level PhysicsCT (Computed Tomography) Scans - A Level Physics
A basic description of the mechanism of CT (computed tomography) scans for medical use in remote sensing. Part of the A Level Physics revision series. -
 26:39
26:39History of Computerized Tomography (CT Scanner)
History of Computerized Tomography (CT Scanner) -
 2:20
2:20CT (Computed Tomography) Scan: What to expect
CT (Computed Tomography) Scan: What to expectCT (Computed Tomography) Scan: What to expect
UW Medicine specialists give context to what patients experience during a CT scan. -
 1:01
1:01How CT Scan Machine Works
How CT Scan Machine WorksHow CT Scan Machine Works
Computed Tomography (CT) is a scanning technique that uses X-Rays to take highly detailed images of the body. A CT scan can give detailed information about many parts of the body, including the lungs, bones, soft tissues, heart and blood vessels. It can be used to diagnose and monitor many conditions. -
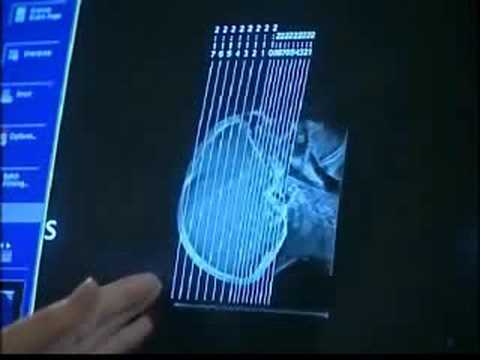 2:55
2:55CT scan - Imaging in medicine (3/13)
CT scan - Imaging in medicine (3/13)CT scan - Imaging in medicine (3/13)
TELL US WHAT YOU THINK and help us improve our Free Educational Resources https://www.surveymonkey.com/r/2015_YouTube_descr For more like this subscribe to the Open University channel https://www.youtube.com/channel/UCXsH4hSV_kEdAOsupMMm4Qw Free learning with The Open University http://www.open.edu/openlearn/subject/history-the-arts/history/history-science-technology-and-medicine/history-medicine --- Shows how a CT scan works, to see if a patient has a fracture of the skull. (Part 3 of 13) Playlist link - http://www.youtube.com/playlist?list=PL5F3E0D006EAC8E27 --- Study 'Imaging in medicine' with the OU http://www3.open.ac.uk/study/postgraduate/course/s809.htm Explore qualifications in Science with the OU http://www3.open.ac.uk/study/undergraduate/science/index.htm --- -
 12:30
12:30X-ray Inspection and Industrial Computed Tomography
X-ray Inspection and Industrial Computed TomographyX-ray Inspection and Industrial Computed Tomography
X-ray Inspection and Industrial Computed Tomography - Practical relevance - Basics and problems of X-ray inspection - Fundamentals of Computed Tomography - Filtered Back-Projection - Simple specimen and die cast sample in practice Responsible for this video: Prof. Dr.-Ing. Rainer Schwab, Hochschule Karlsruhe, University of Applied Sciences, Karlsruhe, Germany -
 59:00
59:00Basic Physics of CT.
Basic Physics of CT. -
 1:19
1:19Computed Tomography.swf
Computed Tomography.swfComputed Tomography.swf
How CT works -
 6:53
6:53CT Scan Physics - Basics Part1
CT Scan Physics - Basics Part1 -
 35:36
35:364.2 - Computed tomography - Image reconstruction/backprojection
4.2 - Computed tomography - Image reconstruction/backprojection4.2 - Computed tomography - Image reconstruction/backprojection
The second half of today's course covers the essentials of image reconstruction used for x-ray based imaging, here the example of computed tomography. -
 10:42
10:42Basic CT overview Part 1
Basic CT overview Part 1Basic CT overview Part 1
This is a basic overview of how to setup the control panel for scanning. This was done using a GE Lightspeed 16. Thanks to the students who helped me film it. -
 1:07
1:07X-ray easily explained: 12. What is Computed Tomography?
X-ray easily explained: 12. What is Computed Tomography?X-ray easily explained: 12. What is Computed Tomography?
What is Computed Tomography? A generally understandable explanation taken from the educational video "X-ray easily explained". To learn more about X-ray and medical radiation watch all chapters of "X-ray easily explained" or visit http://medicalradiation.com -
 7:32
7:32SPECT - Single Photon Emission Computed Tomography Part 1
SPECT - Single Photon Emission Computed Tomography Part 1SPECT - Single Photon Emission Computed Tomography Part 1
In this video we discuss SPECT, which stands for Single Photon Emission Computed Tomography, which is a useful form of medical imaging. -
 9:37
9:37SPECT - Single Photon Emission Computed Tomography Part 2
SPECT - Single Photon Emission Computed Tomography Part 2SPECT - Single Photon Emission Computed Tomography Part 2
In this video we discuss SPECT, which stands for Single Photon Emission Computed Tomography, which is a useful form of medical imaging.
- 3D ultrasound
- Abdominal x-ray
- Absorbed dose
- Allan McLeod Cormack
- Anaphylaxis
- Angiocardiography
- Angiography
- Aortography
- Appendicitis
- Arthrogram
- Atomic bomb
- Axis of rotation
- Background radiation
- Barium enema
- Base of the skull
- Bibcode
- Bone scintigraphy
- Breast MRI
- Breast thermography
- Breast ultrasound
- Bronchography
- Calcification
- Cancer
- Cardiac CT
- Cardiac PET
- Cesium iodide
- Chest radiograph
- Cholangiography
- Cholecystography
- Cholescintigraphy
- Colon cancer
- Computed tomography
- Confocal microscopy
- Contrast medium
- CT head
- Cystography
- Data General Nova
- Dental radiography
- Depth of field
- Diabetes mellitus
- Diffusion MRI
- DNA
- DNA repair
- Double strand breaks
- Echocardiography
- Echoencephalography
- Edge detection
- Effective dose
- Emergency physician
- Emergency ultrasound
- EMI
- Emphysema
- Epigenetic
- Fibrosis
- Fluoroscopy
- Focal plane
- Fracture (bone)
- Full-body CT scan
- Full-body scan
- Gallium 67 scan
- Gamma ray
- Geometry Processing
- Godfrey Hounsfield
- Gray (unit)
- Greek language
- Haemorrhage
- Hayes, Hillingdon
- High resolution CT
- Hounsfield scale
- Hounsfield units
- Human abdomen
- Human brain
- Human lung
- ICD-9-CM Volume 3
- Immunoscintigraphy
- Indium 111 WBC scan
- Infarction
- Injuries
- Intravenous
- Intravenous therapy
- Iodinated contrast
- Iodine
- Ion chamber
- Ionizing radiation
- Isotropy
- Johann Radon
- Laser
- Leukemia
- Linear algebra
- Lung cancer
- Lymphogram
- Mammography
- Massachusetts
- Mayo Clinic
- Medical imaging
- Medical radiography
- Medical test
- Medicine
- Medscape
- MRI
- Mutation
- Myelography
- Nephropathy
- Nuclear industry
- Nuclear medicine
- Octreotide scan
- OPS-301
- Optical imaging
- Optical tomography
- Orthopantomography
- PDP-11
- Perspex
- PET-CT
- Pfizer
- Photodiode
- Photomultiplier tube
- Pixel
- Positron
- Preventive medicine
- Projective geometry
- PubMed Identifier
- Pulmonary artery
- Pulmonary embolism
- Pyelogram
- Radiation
- Radiocontrast
- Radiodensity
- Radiographic testing
- Radiography
- Radiology
- Radon Transform
- Radon transform
- Renal failure
- Robert Ledley
- Ronald N. Bracewell
- Scintigraphy
- Scintimammography
- Screening (medicine)
- Sialography
- Sievert
- Skeletal survey
- SPECT of brain
- Stefan Kaczmarz
- The Beatles
- Tomography
- Tomosynthesis
- Transcranial doppler
- Tufts University
- Tumour
- Ultrasound scanning
- United Kingdom
- Venography
- Virtopsy
- Virtual colonoscopy
- Volume rendering
- Voxel
- Whole body imaging
- William Oldendorf
- Wilms' tumor
- Wimbledon, London
- World War II
- X-ray
- X-ray tube
- Xenon
-

CT (Computed Tomography) Scans - A Level Physics
A basic description of the mechanism of CT (computed tomography) scans for medical use in remote sensing. Part of the A Level Physics revision series. -

-

CT (Computed Tomography) Scan: What to expect
UW Medicine specialists give context to what patients experience during a CT scan. -

How CT Scan Machine Works
Computed Tomography (CT) is a scanning technique that uses X-Rays to take highly detailed images of the body. A CT scan can give detailed information about many parts of the body, including the lungs, bones, soft tissues, heart and blood vessels. It can be used to diagnose and monitor many conditions. -

CT scan - Imaging in medicine (3/13)
TELL US WHAT YOU THINK and help us improve our Free Educational Resources https://www.surveymonkey.com/r/2015_YouTube_descr For more like this subscribe to the Open University channel https://www.youtube.com/channel/UCXsH4hSV_kEdAOsupMMm4Qw Free learning with The Open University http://www.open.edu/openlearn/subject/history-the-arts/history/history-science-technology-and-medicine/history-medicine --- Shows how a CT scan works, to see if a patient has a fracture of the skull. (Part 3 of 13) Playlist link - http://www.youtube.com/playlist?list=PL5F3E0D006EAC8E27 --- Study 'Imaging in medicine' with the OU http://www3.open.ac.uk/study/postgraduate/course/s809.htm Explore qualifications in Science with the OU http://www3.open.ac.uk/study/undergraduate/science/index.htm --- -

X-ray Inspection and Industrial Computed Tomography
X-ray Inspection and Industrial Computed Tomography - Practical relevance - Basics and problems of X-ray inspection - Fundamentals of Computed Tomography - Filtered Back-Projection - Simple specimen and die cast sample in practice Responsible for this video: Prof. Dr.-Ing. Rainer Schwab, Hochschule Karlsruhe, University of Applied Sciences, Karlsruhe, Germany -

-

Computed Tomography.swf
How CT works -

-

4.2 - Computed tomography - Image reconstruction/backprojection
The second half of today's course covers the essentials of image reconstruction used for x-ray based imaging, here the example of computed tomography. -

Basic CT overview Part 1
This is a basic overview of how to setup the control panel for scanning. This was done using a GE Lightspeed 16. Thanks to the students who helped me film it. -

X-ray easily explained: 12. What is Computed Tomography?
What is Computed Tomography? A generally understandable explanation taken from the educational video "X-ray easily explained". To learn more about X-ray and medical radiation watch all chapters of "X-ray easily explained" or visit http://medicalradiation.com -

SPECT - Single Photon Emission Computed Tomography Part 1
In this video we discuss SPECT, which stands for Single Photon Emission Computed Tomography, which is a useful form of medical imaging. -

SPECT - Single Photon Emission Computed Tomography Part 2
In this video we discuss SPECT, which stands for Single Photon Emission Computed Tomography, which is a useful form of medical imaging. -

Cone Beam Computed Tomography (Vol. 1, Issue 1)
Dr. Parish Sedghizadeh discusses the benefits and increased utilization of Cone Beam CT scanning. Three-dimensional imaging is rapidly becoming the standard of care in dentistry, he explains, and its applications are increasing. Dr. Sedghizadeh also offers a refresher on pathology as well as a discussion on medical-legal liability in his video presentation. -

CT Scan of the Chest Explained Clearly
Understand Chest CT (Computed Tomography) scans with this clear explanation from Dr. Roger Seheult. Includes the difference between regular and high resolution CT scans. Speaker: Roger Seheult, MD Clinical and Exam Preparation Instructor Board Certified in Internal Medicine, Pulmonary Disease, Critical Care, and Sleep Medicine. MedCram: Medical topics explained clearly including: Asthma, COPD, Acute Renal Failure, Mechanical Ventilation, Oxygen Hemoglobin Dissociation Curve, Hypertension, Shock, Diabetic Ketoacidosis (DKA), Medical Acid Base, VQ Mismatch, Hyponatremia, Liver Function Tests, Pulmonary Function Tests (PFTs), Adrenal Gland, Pneumonia Treatment, any many others. New topics are often added weekly- please subscribe to help support MedCram and become notified when new vide... -

CT Scanner components inside the gantry
Computed tomography (CT) Scanner components inside the gantry: What are the major components inside the gantry of a CT scanner? This video showcases some of the major components inside the CT scanner. The major components are : -X-ray tube -Collimator -Detector -Data Acquisition system -Power unit -High voltage generator -Rotation control unit -Inverter -Oil tank -Cooling system website : http://www.iambiomed.com facebook : https://www.facebook.com/iambiomed Machine: Philips, 16 Slice CT Location: GuruNanak Hospital, Mumbai video by : Aditya Ekawade *This video is only for educational purpose. -

Computed Tomography (CT) Imaging
Introducing SVC's one year, fully online, post-graduate certification program in Computed Tomography (CT) Imaging, designed for licensed, registered ARRT technologists who want to advance their career with CT licensure. 16 credit program is offered fully online (preceptor work can be done at student's choice of facility) Taught by SVC's highly qualified and respected faculty May be completed in one year, part-time Open to all registered technologists in the areas of Radiography, Nuclear Medicine and/or Radiation Therapy Payment options available (including possible employee benefit options) -

CT Scan | Computerized Tomography | X-ray images | Manipal Hospitals
This animated video is an informative video that explains the working of Computerized Axial Tomography (CT scan) in an elaborate way. A CT scan is a painless diagnostic test that uses X-rays and computers to create cross-sectional images of bones and tissues inside the body. A doctor may recommend a CT scan to examine a blood clot, broken bones, cancerous tumours, infections, internal injuries and bleeding, and signs of heart and vascular disease. A CT scanner is a large square or round X-ray machine with a tunnel through the centre. The scanner has a ring called gantry that will rotate around the body of the patient and this gantry has an X-ray tube that will release X-ray beams. The X-ray detectors measure the amount of radiation observed by the body. The X-ray beams measure many views o... -

Industrial Computed Tomography with GE's phoenix|x-ray systems
Learn about industrial 3D computed tomography (CT) systems, how they work and how they help CT users to improve the health of industry. This movie introduces the GE Measurement & Control Site in Wunstorf, Germany which is part of GE's Inspection Technologies product line since 2007. This part of the business, well-known by its heritage brand phoenix|x-ray, develops X-ray inspection systems for 2D inspection as well as 3D computed tomography. The phoenix|x-ray story started in 1999; literally in a garage... Learn more at http://www.ge-mcs.com/en/phoenix-xray.html -

CTA - Computed Tomography Angiography
Clinnovo Research Labs Pvt Ltd is a clinical Innovation organization focused not only on clinical Research but also on the statastical Analysis(SAS) with strong emphasis on practical training and projects.We offer training program for freshers to enter into the professional field of clinical research,CDM, SAS or Imaging Trials as well to the professionals who are interested to achieve excellence at their professional world. http://www.clinnovo.com/home -

Lakeland Veterinary Imaging - Computed Tomography (CT)
What happens when I drop my pet off for a CT scan? This is an informational video for pet owners and veterinarians about Computed Tomography (CT) scans and pets as performed by Lakeland Veterinary Imaging. -

Iterative Reconstruction Methods in Computed Tomography.
Courtesy - AAPM Courtesy - Biomedical Imaging and Intervention Journal (biij).
CT (Computed Tomography) Scans - A Level Physics
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 12:17
- Updated: 21 May 2012
- views: 79330
- published: 21 May 2012
- views: 79330
History of Computerized Tomography (CT Scanner)
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 26:39
- Updated: 02 Dec 2013
- views: 73585
CT (Computed Tomography) Scan: What to expect
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 2:20
- Updated: 20 Dec 2010
- views: 129609
- published: 20 Dec 2010
- views: 129609
How CT Scan Machine Works
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 1:01
- Updated: 27 Dec 2012
- views: 85437
- published: 27 Dec 2012
- views: 85437
CT scan - Imaging in medicine (3/13)
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 2:55
- Updated: 25 Jul 2008
- views: 319328
- published: 25 Jul 2008
- views: 319328
X-ray Inspection and Industrial Computed Tomography
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 12:30
- Updated: 15 Nov 2015
- views: 1571
- published: 15 Nov 2015
- views: 1571
Basic Physics of CT.
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 59:00
- Updated: 28 Apr 2015
- views: 8605
- published: 28 Apr 2015
- views: 8605
Computed Tomography.swf
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 1:19
- Updated: 30 Jun 2011
- views: 2952
- published: 30 Jun 2011
- views: 2952
CT Scan Physics - Basics Part1
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 6:53
- Updated: 18 May 2008
- views: 55237
4.2 - Computed tomography - Image reconstruction/backprojection
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 35:36
- Updated: 14 Mar 2014
- views: 10468
- published: 14 Mar 2014
- views: 10468
Basic CT overview Part 1
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 10:42
- Updated: 28 Jun 2013
- views: 41043
- published: 28 Jun 2013
- views: 41043
X-ray easily explained: 12. What is Computed Tomography?
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 1:07
- Updated: 20 Feb 2012
- views: 4558
- published: 20 Feb 2012
- views: 4558
SPECT - Single Photon Emission Computed Tomography Part 1
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 7:32
- Updated: 25 Oct 2014
- views: 4161
- published: 25 Oct 2014
- views: 4161
SPECT - Single Photon Emission Computed Tomography Part 2
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 9:37
- Updated: 25 Oct 2014
- views: 1503
- published: 25 Oct 2014
- views: 1503
Cone Beam Computed Tomography (Vol. 1, Issue 1)
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 30:47
- Updated: 18 Jul 2014
- views: 11622
- published: 18 Jul 2014
- views: 11622
CT Scan of the Chest Explained Clearly
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 5:25
- Updated: 09 Mar 2013
- views: 31162
- published: 09 Mar 2013
- views: 31162
CT Scanner components inside the gantry
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 0:55
- Updated: 14 Jan 2015
- views: 2526
- published: 14 Jan 2015
- views: 2526
Computed Tomography (CT) Imaging
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 1:21
- Updated: 16 Jul 2014
- views: 827
- published: 16 Jul 2014
- views: 827
CT Scan | Computerized Tomography | X-ray images | Manipal Hospitals
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 2:50
- Updated: 21 May 2015
- views: 668
- published: 21 May 2015
- views: 668
Industrial Computed Tomography with GE's phoenix|x-ray systems
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 8:53
- Updated: 25 Mar 2014
- views: 6543
- published: 25 Mar 2014
- views: 6543
CTA - Computed Tomography Angiography
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 2:40
- Updated: 02 Mar 2013
- views: 1807
- published: 02 Mar 2013
- views: 1807
Lakeland Veterinary Imaging - Computed Tomography (CT)
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 6:37
- Updated: 20 Sep 2015
- views: 114
- published: 20 Sep 2015
- views: 114
Iterative Reconstruction Methods in Computed Tomography.
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 60:46
- Updated: 28 Apr 2015
- views: 1594
- published: 28 Apr 2015
- views: 1594
-

Download Computed Tomography: From Photon Statistics to Modern Cone-Beam CT PDF
http://j.mp/1PBNxbP -

Download Computed Tomography for Technologists: Exam Review (Point (Lippincott Williams & Wilkin PDF
http://j.mp/1WSsSWI -

Interpretation Basics of Cone Beam Computed Tomography
-

-

Computed tomography scan game strong
-

Computed tomography (CT) of MicroSD
-

Cone Beam Computed Tomography Oral and Maxillofacial Diagnosis and Applications
-

Cone Beam Computed Tomography in Orthodontics Indications, Insights, and Innovations
-

Cone Beam Computed Tomography From Capture to Reporting, An Issue of Dental Clinics of North America
-

Cone Beam Computed Tomography A Clinician's Guide to 3d Imaging
-

Computed Tomography for Technologists Exam Review Point Lippincott Williams & Wilkins
-

Computed Tomography Exam Secrets Study Guide CT Test Review for the Computed Tomography Exam
-

Atlas of Correlative Imaging Anatomy of the Normal Dog Ultrasound and Computed Tomography
-

CT scan (cat scan or computed tomography) - Diagnostic Imaging at St. Joseph's Health Care London
Demonstrating how a CT scan (abdominal scan) is completed for patients at St. Joseph's Health Care London. -

Download Mosby's Exam Review for Computed Tomography 2e PDF EPUB
Link: http://booksaa.com/0323065902 You can find here: http://www.amazon.com/gp/reader/0323065902/?tag=prevread-20#reader_0323065902 Follow Amazon: https://twitter.com/amazon Amazon Google+: https://plus.google.com/+amazon/ Amazon on Tumblr: http://amazon.tumblr.com/ Amazon Instagram: https://www.instagram.com/amazon/ Amazon on Pinterest: https://www.pinterest.com/amazon/ -

Download Mosby's Exam Review for Computed Tomography, 2e PDF
http://j.mp/1Ly7uWb -

-

Cone Beam CT Scanning in Auburn WA: Dr. Ben | Pacific Northwest Oral & Maxillofacial Surgeons
Cone Beam CT Scanning in Auburn WA: Dr. Ben | Pacific Northwest Oral & Maxillofacial Surgeons - https://www.pnwoms.com Dr. Ben attended college at Utah Valley University where he earned his bachelor’s degree in Biology. After receiving his undergraduate degree, he continued on to Temple University in Philadelphia to earn his Doctor of Medicine in Dentistry degree (DMD). Following dental school, Dr. Ben completed a residency in oral and maxillofacial surgery at Cook County Hospital in Chicago. While at his residency, Dr. Ben trained to be able to perform a variety of surgical procedures. His training was heavily focused on routine and complex extractions, wisdom tooth removal, the placement of dental implants, and the treatment of jaw misalignments and diseases. His training alongside prof... -

Computed tomography: Standard QA procedures
This video describes the basic quality assurance (QA) procedures for medical physicists involved in diagnostic radiology, and more precisely for computed tomography (CT). It describes the how-to of simple manipulations intending at measuring the performances of CT units. Following topics are described: -CTDIvol measurement and calculation (small and broad beams) -Primary beam collimation at isocenter -Hounsfield units in water -Manipulation of a Catphan® phantom -Manipulation of a QRM® phantom This video has been prepared in the frame of the EUTEMPE-RX course for medical physics experts (MPE). -

Computed Tomography for Technologists: Exam Review (Point (Lippincott)) by Lois Romans BA RT
Just visit : http://bit.ly/1LZGxL3 80n54y-2016 -

Mosbys Exam Review for Computed Tomography 2e
-

Computed Tomography (Arabic Narration)
Tomography,tomography,tomography definition,tomography scan,tomography breast,tomography journal,tomography machine,tomography definition psychology,tomography pronunciation,tomography etymology,tomography technologist -

3D Computed Tomography Virtual Intravascular Endoscopy
Intrigued by his book soon get and read his book here: http://bit.ly/24Qe7te
Download Computed Tomography: From Photon Statistics to Modern Cone-Beam CT PDF
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 0:32
- Updated: 28 Mar 2016
- views: 0
Download Computed Tomography for Technologists: Exam Review (Point (Lippincott Williams & Wilkin PDF
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 0:32
- Updated: 28 Mar 2016
- views: 0
Interpretation Basics of Cone Beam Computed Tomography
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 1:20
- Updated: 26 Mar 2016
- views: 0
- published: 26 Mar 2016
- views: 0
Atlas of Cardiovascular Computed Tomography by Matthew J. Budoff
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 0:17
- Updated: 24 Mar 2016
- views: 0
Computed tomography scan game strong
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 0:41
- Updated: 23 Mar 2016
- views: 2
- published: 23 Mar 2016
- views: 2
Computed tomography (CT) of MicroSD
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 0:41
- Updated: 23 Mar 2016
- views: 9
- published: 23 Mar 2016
- views: 9
Cone Beam Computed Tomography Oral and Maxillofacial Diagnosis and Applications
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 1:20
- Updated: 23 Mar 2016
- views: 0
- published: 23 Mar 2016
- views: 0
Cone Beam Computed Tomography in Orthodontics Indications, Insights, and Innovations
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 1:26
- Updated: 23 Mar 2016
- views: 0
- published: 23 Mar 2016
- views: 0
Cone Beam Computed Tomography From Capture to Reporting, An Issue of Dental Clinics of North America
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 1:17
- Updated: 23 Mar 2016
- views: 0
- published: 23 Mar 2016
- views: 0
Cone Beam Computed Tomography A Clinician's Guide to 3d Imaging
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 1:26
- Updated: 23 Mar 2016
- views: 0
- published: 23 Mar 2016
- views: 0
Computed Tomography for Technologists Exam Review Point Lippincott Williams & Wilkins
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 1:26
- Updated: 23 Mar 2016
- views: 0
- published: 23 Mar 2016
- views: 0
Computed Tomography Exam Secrets Study Guide CT Test Review for the Computed Tomography Exam
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 1:20
- Updated: 23 Mar 2016
- views: 0
- published: 23 Mar 2016
- views: 0
Atlas of Correlative Imaging Anatomy of the Normal Dog Ultrasound and Computed Tomography
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 1:26
- Updated: 22 Mar 2016
- views: 0
- published: 22 Mar 2016
- views: 0
CT scan (cat scan or computed tomography) - Diagnostic Imaging at St. Joseph's Health Care London
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 3:31
- Updated: 22 Mar 2016
- views: 1
- published: 22 Mar 2016
- views: 1
Download Mosby's Exam Review for Computed Tomography 2e PDF EPUB
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 0:00
- Updated: 22 Mar 2016
- views: 0
- published: 22 Mar 2016
- views: 0
Download Mosby's Exam Review for Computed Tomography, 2e PDF
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 0:32
- Updated: 20 Mar 2016
- views: 0
Computed Tomography by Euclid Seeram
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 0:26
- Updated: 17 Mar 2016
- views: 0
Cone Beam CT Scanning in Auburn WA: Dr. Ben | Pacific Northwest Oral & Maxillofacial Surgeons
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 2:15
- Updated: 14 Mar 2016
- views: 1
- published: 14 Mar 2016
- views: 1
Computed tomography: Standard QA procedures
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 11:40
- Updated: 13 Mar 2016
- views: 0
- published: 13 Mar 2016
- views: 0
Computed Tomography for Technologists: Exam Review (Point (Lippincott)) by Lois Romans BA RT
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 0:36
- Updated: 13 Mar 2016
- views: 0
Mosbys Exam Review for Computed Tomography 2e
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 0:44
- Updated: 09 Mar 2016
- views: 0
- published: 09 Mar 2016
- views: 0
Computed Tomography (Arabic Narration)
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 90:58
- Updated: 09 Mar 2016
- views: 6
- published: 09 Mar 2016
- views: 6
3D Computed Tomography Virtual Intravascular Endoscopy
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 0:24
- Updated: 09 Mar 2016
- views: 2
- published: 09 Mar 2016
- views: 2
-

Computed tomography - Image reconstruction backprojection
-

lecture 14 part 1 (Computer Tomography)
CT (Computer Tomography) -

Medical Equipment: Computed Tomography (Arabic Narration)
مجموعة محاضرات عن الأجهزة الطبية لطلاب الهندسة الحيوية الطبية. الشرح باللغة العربية مع الانجليزية كما تدرس في جامعة القاهرة. A lecture series on Medical Equipment for Biomedical Engineering undergraduate students with narration in Arabic as taught at Cairo University. Presentation available in .PPSX format is available for download in the Lectures section of this web site: http://www.k-space.org Presentation is free to use, share, and modify for your particular purposes -

Denoising, deconvolution and computed tomography using total variation penalty
Use of total variation penalty for signal and image denoising, deconvolution and image reconstruction in computed tomography Michael Zibulevsky, Technion - Israel Institute of Technology Help us caption & translate this video! http://amara.org/v/DQeS/ -

Assessment of the True Weld Toe Geometry using Micro-Computed Tomography.
The fatigue lives of steel arc welded joints are significantly lower than their corresponding parent material, primarily due to the stress-concentrating weld toe geometry, which consists of the weld bead and inherent flaws. The inherent flaws are known to dominate the early fatigue crack growth regimes and thus minimizing their severity and distribution is crucial to maximizing the fatigue strength of such joints. It is currently unknown whether or not alterations to the welding process influence the formation of inherent flaws, and research in the area has been limited by the inability of traditional surface profiling techniques to resolve the true weld toe geometry accurately. In this presentation, the capability of micro-computed tomography to provide data-rich 3D characterization o... -

Quality Digest TechnorazziLIVE: ZEISS Computed Tomography and CALYPSO Software
In the first half of this TechnorazziLIVE episode, the viewer can see the benefits of using CALYPSO as a common metrology software for both ZEISS CMMs and non-ZEISS machines. With CALYPSO software you will be able to increase your productivity while optimizing your measuring capabilities. -

Monday, X-ray Computed Tomography (CT) / Magnetic Resonance Imaging, Aristi Kourri
Please see the program and more educational materials at the Human Health Campus: https://nucleus.iaea.org/HHW/NuclearMedicine/Endocrinology/IAEATrainingCoursesandMeetings/Thyroid_and_Parathyroid_Diseases_Cyprus_2015/ The video recording of all the sessions of the seminar was made possible through the regional training course organized under the regional project RER6026, by the IAEA Department of Technical Cooperation, IAEA Nuclear Medicine and Diagnostic Imaging Section, the government of Cyprus, Limassol General Hospital and Bank of Cyprus Oncology Centre. -

CT Kidneys and Bladder - Five pathologic cases discussed
A board-certified radiologist discusses five patients with kidney and bladder pathology: Chronic UPJ obstruction, bladder stone, pyelonephritis, bladder cancer, and crossed-fused renal ectopia. Less than 24 minutes long. -

2014 Apr 30th, MEDCAC - Lung Cancer Screening with Low Dose Computed Tomography (Morning Session)
Effective January 1, 2009, CMS is allowed to add coverage of "additional preventive services" if certain statutory requirements are met. Per Section 1861(ddd) of the Social Security Act and implementing regulations at 42 CFR 410.64, CMS may cover "additional preventive services", if it determines through the national coverage determinations (NCD) process that the service is recommended with a grade A (strongly recommends) or grade B (recommends) rating by the United States Preventive Services Task Force (USPSTF) and that it also meets certain other requirements. CMS has accepted two formal complete requests to initiate a NCA on Lung Cancer Screening with Low Dose Computed Tomography (LDCT), which is recommended with a grade B by the USPSTF for certain persons at high risk for lung cancer ... -

CT Instrumentation
Introduction to the instrumentation of computed tomography including the axial reconstruction algorithm, collimation, pitch, and section width/interval. -

Quality Assurance in CT and MRI Scanning
This video describes the quality assurance techniques in CT and MRI scanning. This video explains the procedural techniques to maintain the quality control procedures of Computed Tomography and Magnetic Resonance Techniques. I would be grateful to get your valuable comments. -

2014 Apr 30th, MEDCAC - Lung Cancer Screening with Low Dose Computed Tomography (Afternoon Session)
Effective January 1, 2009, CMS is allowed to add coverage of "additional preventive services" if certain statutory requirements are met. Per Section 1861(ddd) of the Social Security Act and implementing regulations at 42 CFR 410.64, CMS may cover "additional preventive services", if it determines through the national coverage determinations (NCD) process that the service is recommended with a grade A (strongly recommends) or grade B (recommends) rating by the United States Preventive Services Task Force (USPSTF) and that it also meets certain other requirements. CMS has accepted two formal complete requests to initiate a NCA on Lung Cancer Screening with Low Dose Computed Tomography (LDCT), which is recommended with a grade B by the USPSTF for certain persons at high risk for lung cancer ... -

X-Ray μ-Computed Tomography for Plant Root Phenotyping
Increased interest in plant phenotyping has lead to a variety of sensors being applied in a range of growth environments. Environments vary from highly constrained laboratory growth rooms to natural field conditions, while sensors range from generic computer vision techniques to application-specific probes. At present the more generic technologies, those capable of providing rich descriptions of a wide range of objects, are limited to the more constrained environments. Only carefully designed sensors, providing a small number of measurements and measurement types, are truly reliable in the field. We believe that X-Ray CT has the potential to shift the balance between sensor generality and environmental complexity in root phenotyping. CT is a general 3D sensor providing data from which a l... -

Computed Tomography Principle Various Types & Advanced
-

Industrial Computed Tomography (CT) Scanning-How to Improve Your Quality
Industrial CT Scanning is the foremost inspection and part reconstruction technology available on the market today. How to Improve Your Quality and Increase Your Competitive Edge. Jesse Garant, President, Jess Garant & Associates -

CT Scanning Physics
Introduction to the radiation physics and acquisition geometry of computed tomography (CT). -

Forensic Anthropology 2011 : 05 : Computed Tomography Images
Part of the free online training on "Advances in Forensic Anthropology" at the NFSTC - http://projects.nfstc.org/tech_transition/anthropology/ -

CT windows, levels and densities
Lecture for medical students, physicians, 1st year radiology residents describing what we mean by windows and levels in CT, and why we need to use different levels.
Computed tomography - Image reconstruction backprojection
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 35:36
- Updated: 17 Mar 2015
- views: 285
- published: 17 Mar 2015
- views: 285
lecture 14 part 1 (Computer Tomography)
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 21:53
- Updated: 14 Jan 2012
- views: 9578
Medical Equipment: Computed Tomography (Arabic Narration)
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 90:58
- Updated: 04 Sep 2013
- views: 1459
- published: 04 Sep 2013
- views: 1459
Denoising, deconvolution and computed tomography using total variation penalty
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 31:48
- Updated: 12 Jun 2012
- views: 5263
- published: 12 Jun 2012
- views: 5263
Assessment of the True Weld Toe Geometry using Micro-Computed Tomography.
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 20:18
- Updated: 16 Dec 2014
- views: 475
- published: 16 Dec 2014
- views: 475
Quality Digest TechnorazziLIVE: ZEISS Computed Tomography and CALYPSO Software
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 54:12
- Updated: 13 Jan 2011
- views: 10064
- published: 13 Jan 2011
- views: 10064
Monday, X-ray Computed Tomography (CT) / Magnetic Resonance Imaging, Aristi Kourri
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 24:21
- Updated: 21 Jan 2016
- views: 10
- published: 21 Jan 2016
- views: 10
CT Kidneys and Bladder - Five pathologic cases discussed
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 23:40
- Updated: 19 May 2013
- views: 15708
- published: 19 May 2013
- views: 15708
2014 Apr 30th, MEDCAC - Lung Cancer Screening with Low Dose Computed Tomography (Morning Session)
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 251:13
- Updated: 01 May 2014
- views: 968
- published: 01 May 2014
- views: 968
CT Instrumentation
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 40:15
- Updated: 03 Feb 2015
- views: 198
- published: 03 Feb 2015
- views: 198
Quality Assurance in CT and MRI Scanning
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 40:34
- Updated: 12 Mar 2014
- views: 879
- published: 12 Mar 2014
- views: 879
2014 Apr 30th, MEDCAC - Lung Cancer Screening with Low Dose Computed Tomography (Afternoon Session)
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 133:51
- Updated: 01 May 2014
- views: 460
- published: 01 May 2014
- views: 460
X-Ray μ-Computed Tomography for Plant Root Phenotyping
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 23:37
- Updated: 06 Nov 2012
- views: 576
- published: 06 Nov 2012
- views: 576
Computed Tomography Principle Various Types & Advanced
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 49:39
- Updated: 25 Jan 2014
- views: 160
- published: 25 Jan 2014
- views: 160
Industrial Computed Tomography (CT) Scanning-How to Improve Your Quality
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 22:11
- Updated: 31 Oct 2011
- views: 510
- published: 31 Oct 2011
- views: 510
CT Scanning Physics
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 23:50
- Updated: 03 Feb 2015
- views: 370
- published: 03 Feb 2015
- views: 370
Forensic Anthropology 2011 : 05 : Computed Tomography Images
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 44:41
- Updated: 03 Oct 2012
- views: 406
- published: 03 Oct 2012
- views: 406
CT windows, levels and densities
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 22:28
- Updated: 02 Jul 2015
- views: 768
- published: 02 Jul 2015
- views: 768
- Playlist
- Chat
- Playlist
- Chat

CT (Computed Tomography) Scans - A Level Physics
- Report rights infringement
- published: 21 May 2012
- views: 79330

History of Computerized Tomography (CT Scanner)
- Report rights infringement
- published: 02 Dec 2013
- views: 73585

CT (Computed Tomography) Scan: What to expect
- Report rights infringement
- published: 20 Dec 2010
- views: 129609

How CT Scan Machine Works
- Report rights infringement
- published: 27 Dec 2012
- views: 85437

CT scan - Imaging in medicine (3/13)
- Report rights infringement
- published: 25 Jul 2008
- views: 319328

X-ray Inspection and Industrial Computed Tomography
- Report rights infringement
- published: 15 Nov 2015
- views: 1571

Basic Physics of CT.
- Report rights infringement
- published: 28 Apr 2015
- views: 8605

Computed Tomography.swf
- Report rights infringement
- published: 30 Jun 2011
- views: 2952

CT Scan Physics - Basics Part1
- Report rights infringement
- published: 18 May 2008
- views: 55237

4.2 - Computed tomography - Image reconstruction/backprojection
- Report rights infringement
- published: 14 Mar 2014
- views: 10468

Basic CT overview Part 1
- Report rights infringement
- published: 28 Jun 2013
- views: 41043

X-ray easily explained: 12. What is Computed Tomography?
- Report rights infringement
- published: 20 Feb 2012
- views: 4558

SPECT - Single Photon Emission Computed Tomography Part 1
- Report rights infringement
- published: 25 Oct 2014
- views: 4161

SPECT - Single Photon Emission Computed Tomography Part 2
- Report rights infringement
- published: 25 Oct 2014
- views: 1503
- Playlist
- Chat

Download Computed Tomography: From Photon Statistics to Modern Cone-Beam CT PDF
- Report rights infringement
- published: 28 Mar 2016
- views: 0

Download Computed Tomography for Technologists: Exam Review (Point (Lippincott Williams & Wilkin PDF
- Report rights infringement
- published: 28 Mar 2016
- views: 0

Interpretation Basics of Cone Beam Computed Tomography
- Report rights infringement
- published: 26 Mar 2016
- views: 0

Atlas of Cardiovascular Computed Tomography by Matthew J. Budoff
- Report rights infringement
- published: 24 Mar 2016
- views: 0

Computed tomography scan game strong
- Report rights infringement
- published: 23 Mar 2016
- views: 2

Computed tomography (CT) of MicroSD
- Report rights infringement
- published: 23 Mar 2016
- views: 9

Cone Beam Computed Tomography Oral and Maxillofacial Diagnosis and Applications
- Report rights infringement
- published: 23 Mar 2016
- views: 0

Cone Beam Computed Tomography in Orthodontics Indications, Insights, and Innovations
- Report rights infringement
- published: 23 Mar 2016
- views: 0

Cone Beam Computed Tomography From Capture to Reporting, An Issue of Dental Clinics of North America
- Report rights infringement
- published: 23 Mar 2016
- views: 0

Cone Beam Computed Tomography A Clinician's Guide to 3d Imaging
- Report rights infringement
- published: 23 Mar 2016
- views: 0

Computed Tomography for Technologists Exam Review Point Lippincott Williams & Wilkins
- Report rights infringement
- published: 23 Mar 2016
- views: 0

Computed Tomography Exam Secrets Study Guide CT Test Review for the Computed Tomography Exam
- Report rights infringement
- published: 23 Mar 2016
- views: 0

Atlas of Correlative Imaging Anatomy of the Normal Dog Ultrasound and Computed Tomography
- Report rights infringement
- published: 22 Mar 2016
- views: 0

CT scan (cat scan or computed tomography) - Diagnostic Imaging at St. Joseph's Health Care London
- Report rights infringement
- published: 22 Mar 2016
- views: 1
- Playlist
- Chat

Computed tomography - Image reconstruction backprojection
- Report rights infringement
- published: 17 Mar 2015
- views: 285

lecture 14 part 1 (Computer Tomography)
- Report rights infringement
- published: 14 Jan 2012
- views: 9578

Medical Equipment: Computed Tomography (Arabic Narration)
- Report rights infringement
- published: 04 Sep 2013
- views: 1459

Denoising, deconvolution and computed tomography using total variation penalty
- Report rights infringement
- published: 12 Jun 2012
- views: 5263

Assessment of the True Weld Toe Geometry using Micro-Computed Tomography.
- Report rights infringement
- published: 16 Dec 2014
- views: 475

Quality Digest TechnorazziLIVE: ZEISS Computed Tomography and CALYPSO Software
- Report rights infringement
- published: 13 Jan 2011
- views: 10064

Monday, X-ray Computed Tomography (CT) / Magnetic Resonance Imaging, Aristi Kourri
- Report rights infringement
- published: 21 Jan 2016
- views: 10

CT Kidneys and Bladder - Five pathologic cases discussed
- Report rights infringement
- published: 19 May 2013
- views: 15708

2014 Apr 30th, MEDCAC - Lung Cancer Screening with Low Dose Computed Tomography (Morning Session)
- Report rights infringement
- published: 01 May 2014
- views: 968

CT Instrumentation
- Report rights infringement
- published: 03 Feb 2015
- views: 198

Quality Assurance in CT and MRI Scanning
- Report rights infringement
- published: 12 Mar 2014
- views: 879

2014 Apr 30th, MEDCAC - Lung Cancer Screening with Low Dose Computed Tomography (Afternoon Session)
- Report rights infringement
- published: 01 May 2014
- views: 460

X-Ray μ-Computed Tomography for Plant Root Phenotyping
- Report rights infringement
- published: 06 Nov 2012
- views: 576

Computed Tomography Principle Various Types & Advanced
- Report rights infringement
- published: 25 Jan 2014
- views: 160
Kurdish Fighter Provides Realistic Assessment Of ISIS Strengths, Tactics, Rules Of Engagement
Edit WorldNews.com 29 Mar 2016Prosecutors Rarely Sanctioned For Judicial Misconduct Sending Innocents To Jail
Edit WorldNews.com 29 Mar 2016Act Of Kindness By Minneapolis Restaurant Owner Pays Off For Formerly Homeless Man
Edit WorldNews.com 29 Mar 2016Trump lambasts Nato as "obsolete" and demands reform or replacement
Edit The Independent 30 Mar 2016Hackers finding a way into your computer through remote access program
Edit WPTV 30 Mar 20167 Warning signs of malware infection (Choose Networks Inc)
Edit Public Technologies 30 Mar 2016Roshan Opens New Computer Classroom at Alawuddin Girls Orphanage
Edit Khaama Press 30 Mar 2016Defendant asks judge for computer to research his shooting spree
Edit New York Post 30 Mar 2016Lawrence Livermore buys IBM’s brain-like TrueNorth chip array
Edit San Francisco Chronicle 30 Mar 2016Minister of State for IT& Telecom Mrs. Anusha Rehman while Chairing 1st meeting of Cyber–Governance Policy committee meeting here in Islamabad today dated 29.3.2016 (Ministry of Information Technology and Telecommunication of the Islamic Republic of Pakistan)
Edit Public Technologies 30 Mar 2016Playstation VR could possible be compatible with PC, challenging Oculus Rift
Edit DNA India 30 Mar 2016Norman news in brief
Edit The Oklahoman 30 Mar 2016All vacant positions (DTU - Danmarks Tekniske Universitet)
Edit Public Technologies 30 Mar 2016Top computing awards show growing importance of cybersecurity
Edit Reuters 30 Mar 2016Reserve Bank tweaks marginal cost of lending rule
Edit DNA India 30 Mar 2016Scientists explain evolution of some of the largest dinosaurs (The University of Liverpool)
Edit Public Technologies 30 Mar 2016- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- Next page »







