- published: 13 Mar 2012
- views: 180228
-
remove the playlistGaba
- remove the playlistGaba
- published: 23 Feb 2014
- views: 17816
- published: 29 Nov 2015
- views: 1836269
- published: 21 Jan 2016
- views: 2377843
- published: 21 Feb 2014
- views: 661835
- published: 10 Jun 2015
- views: 690419
- published: 17 Feb 2014
- views: 15219
- published: 16 Aug 2014
- views: 1672224
- published: 18 Mar 2016
- views: 4823
- published: 16 Mar 2016
- views: 4313
- published: 03 Dec 2014
- views: 22951
Gaba may refer to:
This article is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported License, which means that you can copy and modify it as long as the entire work (including additions) remains under this license.
- Loading...

-
 9:52
9:52The GABA receptor | How does it work?
The GABA receptor | How does it work?The GABA receptor | How does it work?
Help us caption and translate this video on Amara.org: http://www.amara.org/en/v/B5Eg/ A short video on how benzodiazepines, barbiturates, BZ agonists like zolpidem, and how antagonists like flumazenil work. The focus is on the GABA receptor and an explanation of CNS depression. View the rest of my posted videos below: (1) Pharmacokinetics Core concepts: http://youtu.be/CMRZqdrkCZw ---- DRUG ABSORPTION Videos: (2) Drug Absorption Overview: http://youtu.be/eya9jR3v7i8 (3) Bioavailability: http://youtu.be/rv2Rpdi7OHM --------- DRUG DISTRIBUTION Videos: (4) Drug Distribution Overview: http://youtu.be/DH2WGUd7MBs (5) Volume of Distribution: http://youtu.be/B63sqUfvFQQ ------------------ DRUG METABOLISM Videos: (6) First Pass Metabolism: http://youtu.be/5AB8WkCbz4k (7) Phase I Metabolism: http://youtu.be/GGLddVpVg9M (8) Phase II Metabolism: http://youtu.be/iIWAUo05GFE (9) First Order and Zero Order Kinetics: http://youtu.be/XEotDfKhNTw (10) Drug Half-life: http://youtu.be/eTqPsqnbwoc (11) First-order elimination rate constant: http://youtu.be/De9999Jj-5Q ------------------------------------------ DRUG ELIMINATION / EXCRETION (12) Drug Clearance: [not yet posted] (13) Practice problems: [not yet posted] (13) Dosage Regimens: [not yet posted] --------------------------------------------------------------------- Factors That Affect Drug Metabolism: (14) Enzyme Induction: http://youtu.be/Dtbkc8F_ff0 (15) Competitive Inhibition Overview: http://youtu.be/iNIxMuHuL3w (16) Competitive Inhibition of Statins: http://youtu.be/Lt1-mjMFniE (17) Acetaminophen toxicity (Clinical Correlate): [Not yet posted] (18) Pharmacogenomics Overview: http://youtu.be/3vZxbX5P9TU (19) Slow Acetylators - Pharmacogenomics: [not yet posted] Help us caption & translate this video! http://amara.org/v/B5Eg/ -
 23:00
23:00Yo Gabba Gabba Español Latino - Familia
Yo Gabba Gabba Español Latino - FamiliaYo Gabba Gabba Español Latino - Familia
-
 4:57
4:57NOW Foods GABA Honest Review
NOW Foods GABA Honest ReviewNOW Foods GABA Honest Review
GABA is a confusing supplement. On the one hand it saves people's sanity. On the other hand people don't feel a thing. Learn more here: http://dominatedepression.com/now-foods-gaba-review/ 0:20 - What is GABA? 1:02 - Valium and Other Benzodiazepines Mimic GABA 1:48 - Blood-Brain Barrier Conflicting Research 2:55 - GABA Might Be a Little More Complex 3:15 - Should You Try Other Amino Acids First? 4:18 - My Honest Experience With GABA's Effects Like Dominate Depression on Facebook: http://www.facebook.com/DominateDepression -
 3:58
3:58Daaru Party (Full Song) | Millind Gaba | Latest Punjabi Songs 2015 | Speed Records
Daaru Party (Full Song) | Millind Gaba | Latest Punjabi Songs 2015 | Speed RecordsDaaru Party (Full Song) | Millind Gaba | Latest Punjabi Songs 2015 | Speed Records
Speed Records & Dinesh Presents Millind Gaba's Daaru Party FULL VIDEO Song Saavn :- http://www.saavn.com/s/album/punjabi/Daaru-Party-2015/1jz-EPKTN-8_ Song - Daaru Party Singer Music & Lyrics : Millind Gaba #MusicMG DOP : Ashish Rai Director : Shabby Singh & Kamaljot Singh Editor : Sunil Arora Production : Kuldeep Production House Art Director : Karma Mastered By : B-Sanj A Sunil Sethi Project Label - Speed Records Available on Wynk Music - http://www.wynk.in/music/ALBUM/Daaru_Party/srch_venus_SR1790.html Vodafone Subscribers for Caller Tune Direct Dial 5376920335 Airtel Subscribers Direct Dial 5432115136270 to Set as Hello tune (Toll Free) Idea Subscribers for Dialer Tone Direct Dial 567896920335 Airtel Hellotune - https://www.airtelhellotunes.in/single/index/vcode/009151300006270 iTunes: https://goo.gl/BzvZ1T Spotify: https://goo.gl/ce4Ivi Google Play: https://goo.gl/Q1pktD Deezer: http://goo.gl/ksZ0go Amazon: https://goo.gl/aIaEzM Facebook - https://www.facebook.com/MillindGabaofficial Twitter - https://twitter.com/themillind Digitally Powered by One Digital Entertainment [https://www.facebook.com/onedigitalentertainment] Click to Subscribe - http://bit.ly/SpeedRecords Facebook - https://www.facebook.com/SpeedRecords Twitter - https://twitter.com/Speed_Records Instagram - https://instagram.com/Speed_Records -
 4:54
4:54Yaar Mod Do Full Video Song | Guru Randhawa, Millind Gaba | T-Series
Yaar Mod Do Full Video Song | Guru Randhawa, Millind Gaba | T-SeriesYaar Mod Do Full Video Song | Guru Randhawa, Millind Gaba | T-Series
Presenting latest video song of Guru Randhawa, Millind Gaba "Yaar Mod Do". There is nothing on this earth more to be prized than true friendship . Click to SHARE on FACEBOOK - http://bit.ly/YaarModDo Click to TWEET - http://bit.ly/TweetYaarModDo Song: YAAR MOD DO Singer: GURU RANDHAWA,MILLIND GABA Music: MILLIND GABA Lyrics: GURU RANDHAWA,MILLIND GABA Music Label: T-SERIES Mastered By : B Sanj DOP : Ashish Rai Editor : Sunil Arora | Kamajot Singh Production : Kuldeep Project Coordination : Sunil Sethi, Jassi Singh, S Mukhtiar Publicity Design : Pankaj Sharma Direction and Screenplay : Shabby Singh Buy it on iTunes - https://geo.itunes.apple.com/in/album/yaar-mod-do-single/id1077187136?ls=1&app;=itunes Listen it on Hungama - http://www.hungama.com/#/music/song-yaar-mod-do/17241737 For Caller Tunes : Yaar Mod Do - http://bit.ly/1SyKk3x Yaar Mod Do - Ek Wari O Rabba - http://bit.ly/1P7s5jw Yaar Mod Do - Jeb Wich Cass - http://bit.ly/1lxXpMg Yaar Mod Do - Wo Bhi Si Sama - http://bit.ly/1UdiIP3 Enjoy and stay connected with us!! Subscribe to T-Series Channel for unlimited entertainment http://www.youtube.com/user/tseries?sub_confirmation=1 Circle us on G+ http://www.google.com/+tseriesmusic Like us on Facebook http://www.facebook.com/tseriesmusic Follow us on http://www.twitter.com/tseries Follow us on http://www.instagram.com/tseries.official Find us on http://pinterest.com/tseries ---------------------------------------------- Operator Codes : 1. Yaar Mod Do Vodafone Subscribers Dial 5377229461 Airtel Subscribers Dial 5432115233174 Idea Subscribers Dial 567897229461 Tata DoCoMo Subscribers dial 5432117229461 Aircel Subscribers sms DT 5574557 To 53000 BSNL (South / East) Subscribers sms BT 7229461 To 56700 BSNL (North / West) Subscribers sms BT 5574557 To 56700 Virgin Subscribers sms TT 7229461 To 58475 MTS Subscribers sms CT 5575315 to 55777 Telenor Subscribers dial 50015575455 MTNL Subscribers sms PT 7229461 To 56789 2.Yaar Mod Do - Ek Wari O Rabba Vodafone Subscribers Dial 5377229448 Airtel Subscribers Dial 5432115233243 Idea Subscribers Dial 567897229448 Tata DoCoMo Subscribers dial 5432117229448 Aircel Subscribers sms DT 5574554 To 53000 BSNL (South / East) Subscribers sms BT 7229448 To 56700 BSNL (North / West) Subscribers sms BT 5574554 To 56700 Virgin Subscribers sms TT 7229448 To 58475 MTS Subscribers sms CT 5575312 to 55777 Telenor Subscribers dial 50015575452 MTNL Subscribers sms PT 7229448 To 56789 3.Yaar Mod Do - Jeb Wich Cass Vodafone Subscribers Dial 5377229457 Airtel Subscribers Dial 5432115233143 Idea Subscribers Dial 567897229457 Tata DoCoMo Subscribers dial 5432117229457 Aircel Subscribers sms DT 5574555 To 53000 BSNL (South / East) Subscribers sms BT 7229457 To 56700 BSNL (North / West) Subscribers sms BT 5574555 To 56700 Virgin Subscribers sms TT 7229457 To 58475 MTS Subscribers sms CT 5575313 to 55777 Telenor Subscribers dial 50015575453 MTNL Subscribers sms PT 7229457 To 56789 4.Yaar Mod Do - Wo Bhi Si Sama Vodafone Subscribers Dial 5377229467 Airtel Subscribers Dial 5432115233194 Idea Subscribers Dial 567897229467 Tata DoCoMo Subscribers dial 5432117229467 Aircel Subscribers sms DT 5574556 To 53000 BSNL (South / East) Subscribers sms BT 7229467 To 56700 BSNL (North / West) Subscribers sms BT 5574556 To 56700 Virgin Subscribers sms TT 7229467 To 58475 MTS Subscribers sms CT 5575314 to 55777 Telenor Subscribers dial 50015575454 MTNL Subscribers sms PT 7229467 To 56789 -
 3:32
3:32Thodi Jinni Peeti Hai | Dilbagh Singh | Millind Gaba | Official Song
Thodi Jinni Peeti Hai | Dilbagh Singh | Millind Gaba | Official SongThodi Jinni Peeti Hai | Dilbagh Singh | Millind Gaba | Official Song
Presenting latest groovy dance number featuring Dilbagh Singh & Millind Gaba. Download the song on itune https://itunes.apple.com/in/album/thodi-jinni-peeti-hai-single/id855175065 Singer: Dilbagh Singh Music: Milind Gaba Producer: House of Cheers Director: Colossus For more updates Follow us on Facebook: http://www.facebook.com/Saregama Follow us on Twitter: http://twitter.com/Saregamaindia Follow us on Twitter: http://twitter.com/Saregamaindia -
 3:12
3:12Chura Liya Cover feat Millind Gaba MusicMG
Chura Liya Cover feat Millind Gaba MusicMGChura Liya Cover feat Millind Gaba MusicMG
Chura Liya Cover Performed by Millind Gaba Vocals , Rap and Additional Lyrics : Millind Gaba Music Production and arrangement : Millind Gaba Mixed and Mastered at 43 Digital Recording Studio , New Subscribe My Channel :) Join Me https://twitter.com/themillind https://www.facebook.com/MillindGabao... Instagram/millindgaba For Info and Inquiries Contact Artist By Nature Mr.Sunil Sethi : +919910084100 Mr.Sumit Arora :+919811179580 -
 6:13
6:13Explain GABA and Natural Ways to Increase It
Explain GABA and Natural Ways to Increase ItExplain GABA and Natural Ways to Increase It
GABA is a neurotransmitter. Neurotransmitters are chemicals that are produced in the brain that allow the nerve cells to communicate with each other. They have a lot to do with regulating the mood and the different systems of the body. There are two types of neurotransmitters - those that excite things and those that inhibit, or slow down, things. GABA falls into the category of relaxation, or inhibitory, neurotransmitters. So what is GABA, what does it do? GABA is responsible for regulating the body's internal rhythm and repsonible for relaxation and mental focus. If you have a GABA deficiency, then you might experience things in the body like: -- Arrhythmias, abnormal rhythms of the heart -- Over-excitation, in general with your moods -- Insomnia -- Anxiety There are some ways that you can naturally increase your GABA production. First, let's talk about some food things you do. You know I'm a food-as-medicine doctor! Green tea is a great way to increase the production of GABA. If you are tea drinker, load up on some green teas! There's lots of different types green teas - oolong green tea (which also helps with weight loss), rose green tea, hot green tea, cold green tea. I recommend brewing your own green tea. Of course there are a lot of commercial green teas on the market but the most beneficial green tea is the one your brew and prepare yourself. It has the most nutritional value. The second thing you can do is actually take the supplement L-Theanine? L-Theanine is an amino acid that stimulates GABA production in the brain as well. So you can go to your local vitamin shop, or you can order online (one of my favorite sites it www.iherb.com) and you can take the L-Theanine. I do recommend that if you take L-Theanine, that you see your integrative medicine doctor, or holistic doctor, first and make sure there are no other contradictory indication of why you should not take it. The third thing you can do is eat complex carbohydrates. Of course "carbohydrates" in our society has become a dirty word but carbohydrates are not bad. After we eat the carbohydrates, we stimulate the production of this relaxing neurotransmitter and it makes us want to be laid back, relaxed, and go to sleep. So yes, you can eat carbohydrates, but here is the pitfall. We say, "Oh I'm stressed out. I'm going to go eat some pasta."You want to think about what healthy complex carbohydrates you can eat. Beans, lentils, garbanzos, even bananas - these are carbohydrates that are good for you, rather than going to pasta or bread and eating those out of moderation. So that's where we fall into the pitfall of carbohydrates. Carbohydrates are not totally bad for you, they can create a state of relaxation for you, if you do them in moderation and eat the healthy ones. There are a couple of other foods that you can think about snacking on to help release GABA in the brain - bananas, walnuts, almonds, broccoli (so go ahead and make that broccoli and brown rice casserole), lentils, oats and other whole grains that are healthy like quinoa and brown rice. All of these things increase GABA in the brain and there are also know to increase serotonin in the brain, too. They promote relaxation, promote an elevate (a good) mood, and they are good for you. -
 3:45
3:454MenDown Full Video - Millind Gaba | Latest Punjabi Songs | Speed Records
4MenDown Full Video - Millind Gaba | Latest Punjabi Songs | Speed Records4MenDown Full Video - Millind Gaba | Latest Punjabi Songs | Speed Records
Click to Share on Facebook - http://bit.ly/4MenDown Speed Records & Sunil Sethi Presents Song - 4MenDown Artist - Millind Gaba [https://www.facebook.com/MillindGabaofficial] Lyrics - Millind Gaba [https://twitter.com/themillind] Music - Millind Gaba Editor - Baljinder Muhar Film By - Navraj Raja Label - Speed Records Airtel Hello Tunes – https://www.airtelhellotunes.in/single/index/vcode/009141100006194 Digital Partner - One Digital Entertainment [https://www.facebook.com/onedigitalentertainment] Click to Subscribe - http://bit.ly/SpeedRecords Facebook - https://www.facebook.com/SpeedRecords Twitter - https://twitter.com/Speed_Records Instagram - https://instagram.com/Speed_Records -
 2:54
2:54BILLO Video Song | MIKA SINGH | Millind Gaba | New Song 2016 | T-Series
BILLO Video Song | MIKA SINGH | Millind Gaba | New Song 2016 | T-SeriesBILLO Video Song | MIKA SINGH | Millind Gaba | New Song 2016 | T-Series
King Mika Singh is back again with his new Video Song BILLO. Click to SHARE on FB - http://bit.ly/BilloVideoSong Click to TWEET - http://bit.ly/TweetBillo T-SERIES presents BILLO Video Song in the voice of Mika Singh, music composition by Millind Gaba (MUSIC MG) in the lyrics of Raj Hans. SONG - BILLO SINGER - MIKA SINGH MUSIC - MUSIC MG, BABA HONEY LYRICS - RAJ HANS DIRECTOR : DAVID ZENNIE CHOREOGRAPHER - JESSICA SHARMA PROGRAMMED, MIXED, MASTERED AND RECORDED AT MS STUDIO MUSIC LABEL - T-SERIES Buy it on iTunes - https://geo.itunes.apple.com/in/album/billo-single/id1094594481?ls=1&app;=itunes Listen it on Hungama - http://www.hungama.com/#/music/album-billo-songs/17597206 For Caller Tunes : Billo http://bit.ly/1MqOl3m Billo - Dil Mein Hai http://bit.ly/1S7vQ8w Billo - Tere Thumke Pe http://bit.ly/1Xzr3y8 Billo - Rap Part http://bit.ly/1Wv1mym Enjoy and stay connected with us!! Subscribe to T-Series Channel for unlimited entertainment http://www.youtube.com/user/tseries?sub_confirmation=1 Circle us on G+ http://www.google.com/+tseriesmusic Like us on Facebook http://www.facebook.com/tseriesmusic Follow us on http://www.twitter.com/tseries Follow us on http://www.instagram.com/tseries.official Find us on http://pinterest.com/tseries ---------------------------------------------------- Set "Billo" as your caller tune - sms BLLO1 To 54646 Set "Billo - Dil Mein Hai" as your caller tune - sms BLLO2 To 54646 Set "Billo - Tere Thumke Pe" as your caller tune - sms BLLO3 To 54646 Set "Billo - Rap Part" as your caller tune - sms BLLO4 To 54646 ________________________________ OPERATOR CODES : 1.Billo Vodafone Subscribers Dial 5377536684 Airtel Subscribers Dial 5432115360893 Reliance Subscribers SMS CT 64279979 to 51234 Idea Subscribers Dial 567897536684 Tata DoCoMo Subscribers dial 5432117536684 Aircel Subscribers sms DT 5914440 To 53000 BSNL (South / East) Subscribers sms BT 7536684 To 56700 BSNL (North / West) Subscribers sms BT 5914440 To 56700 Virgin Subscribers sms TT 7536684 To 58475 MTS Subscribers sms CT 5915214 to 55777 Videocon Subscribers dial 54321100460504 Telenor Subscribers dial 50015914839 MTNL Subscribers sms PT 7536684 To 56789 2.Billo - Dil Mein Hai Vodafone Subscribers Dial 5377536711 Airtel Subscribers Dial 5432115360913 Reliance Subscribers SMS CT 64279980 to 51234 Idea Subscribers Dial 567897536711 Tata DoCoMo Subscribers dial 5432117536711 Aircel Subscribers sms DT 5914441 To 53000 BSNL (South / East) Subscribers sms BT 7536711 To 56700 BSNL (North / West) Subscribers sms BT 5914441 To 56700 Virgin Subscribers sms TT 7536711 To 58475 MTS Subscribers sms CT 5915215 to 55777 Videocon Subscribers dial 54321100460505 Telenor Subscribers dial 50015914840 MTNL Subscribers sms PT 7536711 To 56789 3. Billo - Tere Thumke Pe Vodafone Subscribers Dial 5377536683 Airtel Subscribers Dial 5432115359653 Reliance Subscribers SMS CT 64279982 to 51234 Idea Subscribers Dial 567897536683 Tata DoCoMo Subscribers dial 5432117536683 Aircel Subscribers sms DT 5914443 To 53000 BSNL (South / East) Subscribers sms BT 7536683 To 56700 BSNL (North / West) Subscribers sms BT 5914443 To 56700 Virgin Subscribers sms TT 7536683 To 58475 MTS Subscribers sms CT 5915217 to 55777 Videocon Subscribers dial 54321100460506 Telenor Subscribers dial 50015914842 MTNL Subscribers sms PT 7536683 To 56789 4.Billo - Rap Part Vodafone Subscribers Dial 5377536678 Airtel Subscribers Dial 5432115360567 Reliance Subscribers SMS CT 64279981 to 51234 Idea Subscribers Dial 567897536678 Tata DoCoMo Subscribers dial 5432117536678 Aircel Subscribers sms DT 5914442 To 53000 BSNL (South / East) Subscribers sms BT 7536678 To 56700 BSNL (North / West) Subscribers sms BT 5914442 To 56700 Virgin Subscribers sms TT 7536678 To 58475 MTS Subscribers sms CT 5915216 to 55777 Videocon Subscribers dial 54321100460507 Telenor Subscribers dial 50015914841 MTNL Subscribers sms PT 7536678 To 56789 -
 3:11
3:11Jatti De Nain | New Punjabi Songs 2016 | Roshan Prince ft. Millind Gaba | Surbhi Mahendru
Jatti De Nain | New Punjabi Songs 2016 | Roshan Prince ft. Millind Gaba | Surbhi MahendruJatti De Nain | New Punjabi Songs 2016 | Roshan Prince ft. Millind Gaba | Surbhi Mahendru
Check out the Official Video of 'Jatti De Nain' by Roshan Prince featuring Millind Gaba and Surbhi Mahendru Exclusively on Times Music! The Punjabi song has been directed by Parmod Sharma Rana. Credits: Singer - Roshan Prince https://www.facebook.com/theroshanprince/ http://instagram.com/theroshanprince Artist - Roshan Prince ft Millind Gaba and Surbhi Mahendru Female Lead Surbhi Mahendru https://m.facebook.com/profile.php?id=1573063022917790&tsid;=0.8909779849927872&source;=typeahead Music- Millind Gaba https://www.facebook.com/MillindGabaofficial/ Writer- Happy Raikoti https://www.facebook.com/HappyRaikotiOfficial/ Projected & Video Director - Parmod Sharma Rana https://m.facebook.com/iParmodsharmarana/?ref=bookmarks Video Editor - Ashu Kathpal and Sarabjeet Sohal Poster design- Aman Kalsi (https://m.facebook.com/Aman-Kalsi-1571643013083769/) Cinematographer - Shelly Dhiman Choreographer - John Jonny Makeup & Hair by - Ishaan Malhotra & Vicky Abrime Costumes by - PSR Designs Art Director - Karm Singh Creative Director - Raja Sharma Associate Director - Surbhi Mahendru Production By - Antrix & Roshan Caller Tunes Codes for New Punjabi Songs 2016 below: Jatti De Nain Vodafone Users For Caller Tunes Dial 5377459855 (Rs 0.30/Min) Airtel Users For Hello Tunes Dial 5432115338793 (Toll Free) Idea Users For Dialer Tones Dial 567897459855 (Toll Free) For More Updates: Like us on: www.facebook.com/TimesMusic Follow us on: www.twitter.com/TimesMusicHub Join our Circle: www.google.com/+TimesMusic -
 30:46
30:46EMP Neurociencias: GABA
EMP Neurociencias: GABAEMP Neurociencias: GABA
Después del Glutamato, el Ácido Gama Amino Butírico o GABA es de los neurotransmisores más abundantes y con una mayor función en el cerebro, en este video explicamos la fisiología y la farmacología relacionada con este neurotransmisor. Las imágenes fueron obtenidas de wikipedia. Para más información del tema les sugerimos revisar el libro de Neuroquímica Básica de Siegel, así como el Kandel de Neurociencias. -
 5:19
5:19Anxiety, Stress and the Benefits of GABA
Anxiety, Stress and the Benefits of GABAAnxiety, Stress and the Benefits of GABA
The benefits of GABA are astounding. I abused alcohol for years and GABA helped me treat the underlying anxiety that was a contributing factor in my addiction and helped me stop drinking on my own. Plus, GABA (also known as gamma-aminobutyric acid) is a great natural alternative treatment for depression and anxiety and an amazing way to improve your mental health. ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- Track included "Ulyses" (by Jahzzar): http://freemusicarchive.org/music/jahzzar/kuddelmuddel/ulyses_master_2 http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/4.0/legalcode -
 3:25
3:25Swag Babe - Official Music Video - Mehak Malhotra Ft. Milind Gaba
Swag Babe - Official Music Video - Mehak Malhotra Ft. Milind GabaSwag Babe - Official Music Video - Mehak Malhotra Ft. Milind Gaba
Presenting to you the full video of "Swag Babe" by Mehak Malhotra ft. Milind Gaba. Song: Swag Babe Singers: Mehak Malhotra Ft. Milind Gaba Music Director: Milind Gaba Lyricist: Milind Gaba Director: Gsk (Gursharan Singh Kohli) Music Label : T-Series https://www.facebook.com/fanclubmehak Enjoy & stay connected with us!! FOR LATEST UPDATES: ---------------------------------------- SUBSCRIBE US Here: http://bitly.com/SJIuwJ "If you like the Video, Don't forget to Share and leave your comments" Visit Our Channel For More Videos: http://www.youtube.com/Popchartbusters Operator Codes - 1 - Swagbabe Vodafone Subscribers Dial 5376187335 Airtel Subscribers Dial 5432114727390 Idea Subscribers Dial 567896187335 Tata DoCoMo Subscribers dial 5432116187335 Aircel Subscribers sms DT 2471248 To 53000 BSNL (South / East) Subscribers sms BT 6187335 To 56700 BSNL (North / West) Subscribers sms BT 2471248 To 56700 Virgin Subscribers sms TT 6187335 To 58475 MTS Subscribers sms CT 87562072 to 55777 Uninor Subscribers sms ACT CT 0881786 to 51234 MTNL Subscribers sms PT 6187335 To 56789 2 - Swagbabe - Introducing Mehak Malhotra Vodafone Subscribers Dial 5376187338 Airtel Subscribers Dial 5432114727385 Idea Subscribers Dial 567896187338 Tata DoCoMo Subscribers dial 5432116187338 Aircel Subscribers sms DT 2471243 To 53000 BSNL (South / East) Subscribers sms BT 6187338 To 56700 BSNL (North / West) Subscribers sms BT 2471243 To 56700 Virgin Subscribers sms TT 6187338 To 58475 MTS Subscribers sms CT 87562073 to 55777 Uninor Subscribers sms ACT CT 0881781 to 51234 MTNL Subscribers sms PT 6187338 To 56789 3 - Swagbabe - Laal Mirha - Rap Vodafone Subscribers Dial 5376187360 Airtel Subscribers Dial 5432114727386 Idea Subscribers Dial 567896187360 Tata DoCoMo Subscribers dial 5432116187360 Aircel Subscribers sms DT 2471244 To 53000 BSNL (South / East) Subscribers sms BT 6187360 To 56700 BSNL (North / West) Subscribers sms BT 2471244 To 56700 Virgin Subscribers sms TT 6187360 To 58475 MTS Subscribers sms CT 87562074 to 55777 Uninor Subscribers sms ACT CT 0881782 to 51234 MTNL Subscribers sms PT 6187360 To 56789 4)Swagbabe - Magar Agar - Rap Vodafone Subscribers Dial 5376187361 Airtel Subscribers Dial 5432114727387 Idea Subscribers Dial 567896187361 Tata DoCoMo Subscribers dial 5432116187361 Aircel Subscribers sms DT 2471245 To 53000 BSNL (South / East) Subscribers sms BT 6187361 To 56700 BSNL (North / West) Subscribers sms BT 2471245 To 56700 Virgin Subscribers sms TT 6187361 To 58475 MTS Subscribers sms CT 87562075 to 55777 Uninor Subscribers sms ACT CT 0881783 to 51234 MTNL Subscribers sms PT 6187361 To 56789
'Gaba' is featured as a movie character in the following productions:
I Want to Join the Police (2010)
Actors: Elzbieta Jarosik (actress), Grzegorz Przybyl (actor), Agnieszka Mania (director), Aneta Awtoniuk (actress), Agnieszka Mania (writer), Maria Andrzejewska (actress), Gabriel Kaczmarek (composer), Marta Kedziora (actress),
Genres: Drama, Short,Vlci bouda (1987)
Actors: Vera Chytilová (writer), Jirí Brozek (editor), Vera Chytilová (director), Jan Kacer (actor), Jirí Krampol (actor), Miroslav Machácek (actor), Nina Divísková (actress), Michael Kocáb (composer), Sárka Hejnová (costume designer), Jan Bidlas (actor), Frantisek Stanek (actor), Daniela Fischerová (writer), Jitka Zelenková (actress), Tomás Palatý (actor), Roman Fiser (actor),
Genres: Adventure, Drama, Horror, Sci-Fi, Thriller,Lampás malého plavcíka (1984)
Actors: Hana Talpová (actress), Maros Kramár (actor), Jozef Zachar (director), Svetozár Stúr (composer), Pavol Mikulík (actor), Ján Melkovic (actor), Ján Gresso (actor), Anita Hrossová (costume designer), Ján Klimo (actor), Marie Logojdová (actress), Vladimír Zimmer (actor), Judita Durdiaková (actress), Milan Drotár (actor), Ján Barto (actor), Adam Kerdo (actor),
Genres: ,Mladá léta (1953)
Actors: Josef Príhoda (actor), Vladimír Repa (actor), Radovan Lukavský (actor), Frantisek Kreuzmann (actor), Karel Höger (actor), Jirí Dohnal (actor), Eduard Kohout (actor), Eman Fiala (actor), Frantisek Filipovský (actor), Svatopluk Benes (actor), Eduard Cupák (actor), Josef Hlinomaz (actor), Alois Dvorský (actor), Raoul Schránil (actor), Václav Krska (actor),
Genres: ,-

The GABA receptor | How does it work?
Help us caption and translate this video on Amara.org: http://www.amara.org/en/v/B5Eg/ A short video on how benzodiazepines, barbiturates, BZ agonists like zolpidem, and how antagonists like flumazenil work. The focus is on the GABA receptor and an explanation of CNS depression. View the rest of my posted videos below: (1) Pharmacokinetics Core concepts: http://youtu.be/CMRZqdrkCZw ---- DRUG ABSORPTION Videos: (2) Drug Absorption Overview: http://youtu.be/eya9jR3v7i8 (3) Bioavailability: http://youtu.be/rv2Rpdi7OHM --------- DRUG DISTRIBUTION Videos: (4) Drug Distribution Overview: http://youtu.be/DH2WGUd7MBs (5) Volume of Distribution: http://youtu.be/B63sqUfvFQQ ------------------ DRUG METABOLISM Videos: (6) First Pass Metabolism: http://youtu.be/5AB8WkCbz4k (7) Phase I Metabolism: htt... -

Yo Gabba Gabba Español Latino - Familia
-

NOW Foods GABA Honest Review
GABA is a confusing supplement. On the one hand it saves people's sanity. On the other hand people don't feel a thing. Learn more here: http://dominatedepression.com/now-foods-gaba-review/ 0:20 - What is GABA? 1:02 - Valium and Other Benzodiazepines Mimic GABA 1:48 - Blood-Brain Barrier Conflicting Research 2:55 - GABA Might Be a Little More Complex 3:15 - Should You Try Other Amino Acids First? 4:18 - My Honest Experience With GABA's Effects Like Dominate Depression on Facebook: http://www.facebook.com/DominateDepression -

Daaru Party (Full Song) | Millind Gaba | Latest Punjabi Songs 2015 | Speed Records
Speed Records & Dinesh Presents Millind Gaba's Daaru Party FULL VIDEO Song Saavn :- http://www.saavn.com/s/album/punjabi/Daaru-Party-2015/1jz-EPKTN-8_ Song - Daaru Party Singer Music & Lyrics : Millind Gaba #MusicMG DOP : Ashish Rai Director : Shabby Singh & Kamaljot Singh Editor : Sunil Arora Production : Kuldeep Production House Art Director : Karma Mastered By : B-Sanj A Sunil Sethi Project Label - Speed Records Available on Wynk Music - http://www.wynk.in/music/ALBUM/Daaru_Party/srch_venus_SR1790.html Vodafone Subscribers for Caller Tune Direct Dial 5376920335 Airtel Subscribers Direct Dial 5432115136270 to Set as Hello tune (Toll Free) Idea Subscribers for Dialer Tone Direct Dial 567896920335 Airtel Hellotune - https://www.airtelhellotunes.in/single/index/vcode/009151300006270 ... -

Yaar Mod Do Full Video Song | Guru Randhawa, Millind Gaba | T-Series
Presenting latest video song of Guru Randhawa, Millind Gaba "Yaar Mod Do". There is nothing on this earth more to be prized than true friendship . Click to SHARE on FACEBOOK - http://bit.ly/YaarModDo Click to TWEET - http://bit.ly/TweetYaarModDo Song: YAAR MOD DO Singer: GURU RANDHAWA,MILLIND GABA Music: MILLIND GABA Lyrics: GURU RANDHAWA,MILLIND GABA Music Label: T-SERIES Mastered By : B Sanj DOP : Ashish Rai Editor : Sunil Arora | Kamajot Singh Production : Kuldeep Project Coordination : Sunil Sethi, Jassi Singh, S Mukhtiar Publicity Design : Pankaj Sharma Direction and Screenplay : Shabby Singh Buy it on iTunes - https://geo.itunes.apple.com/in/album/yaar-mod-do-single/id1077187136?ls=1&app;=itunes Listen it on Hungama - http://www.hungama.com/#/music/song-yaar-mod-do/17241737 ... -

Thodi Jinni Peeti Hai | Dilbagh Singh | Millind Gaba | Official Song
Presenting latest groovy dance number featuring Dilbagh Singh & Millind Gaba. Download the song on itune https://itunes.apple.com/in/album/thodi-jinni-peeti-hai-single/id855175065 Singer: Dilbagh Singh Music: Milind Gaba Producer: House of Cheers Director: Colossus For more updates Follow us on Facebook: http://www.facebook.com/Saregama Follow us on Twitter: http://twitter.com/Saregamaindia Follow us on Twitter: http://twitter.com/Saregamaindia -

Chura Liya Cover feat Millind Gaba MusicMG
Chura Liya Cover Performed by Millind Gaba Vocals , Rap and Additional Lyrics : Millind Gaba Music Production and arrangement : Millind Gaba Mixed and Mastered at 43 Digital Recording Studio , New Subscribe My Channel :) Join Me https://twitter.com/themillind https://www.facebook.com/MillindGabao... Instagram/millindgaba For Info and Inquiries Contact Artist By Nature Mr.Sunil Sethi : +919910084100 Mr.Sumit Arora :+919811179580 -

Explain GABA and Natural Ways to Increase It
GABA is a neurotransmitter. Neurotransmitters are chemicals that are produced in the brain that allow the nerve cells to communicate with each other. They have a lot to do with regulating the mood and the different systems of the body. There are two types of neurotransmitters - those that excite things and those that inhibit, or slow down, things. GABA falls into the category of relaxation, or inhibitory, neurotransmitters. So what is GABA, what does it do? GABA is responsible for regulating the body's internal rhythm and repsonible for relaxation and mental focus. If you have a GABA deficiency, then you might experience things in the body like: -- Arrhythmias, abnormal rhythms of the heart -- Over-excitation, in general with your moods -- Insomnia -- Anxiety There are some ways that you ... -

4MenDown Full Video - Millind Gaba | Latest Punjabi Songs | Speed Records
Click to Share on Facebook - http://bit.ly/4MenDown Speed Records & Sunil Sethi Presents Song - 4MenDown Artist - Millind Gaba [https://www.facebook.com/MillindGabaofficial] Lyrics - Millind Gaba [https://twitter.com/themillind] Music - Millind Gaba Editor - Baljinder Muhar Film By - Navraj Raja Label - Speed Records Airtel Hello Tunes – https://www.airtelhellotunes.in/single/index/vcode/009141100006194 Digital Partner - One Digital Entertainment [https://www.facebook.com/onedigitalentertainment] Click to Subscribe - http://bit.ly/SpeedRecords Facebook - https://www.facebook.com/SpeedRecords Twitter - https://twitter.com/Speed_Records Instagram - https://instagram.com/Speed_Records -

BILLO Video Song | MIKA SINGH | Millind Gaba | New Song 2016 | T-Series
King Mika Singh is back again with his new Video Song BILLO. Click to SHARE on FB - http://bit.ly/BilloVideoSong Click to TWEET - http://bit.ly/TweetBillo T-SERIES presents BILLO Video Song in the voice of Mika Singh, music composition by Millind Gaba (MUSIC MG) in the lyrics of Raj Hans. SONG - BILLO SINGER - MIKA SINGH MUSIC - MUSIC MG, BABA HONEY LYRICS - RAJ HANS DIRECTOR : DAVID ZENNIE CHOREOGRAPHER - JESSICA SHARMA PROGRAMMED, MIXED, MASTERED AND RECORDED AT MS STUDIO MUSIC LABEL - T-SERIES Buy it on iTunes - https://geo.itunes.apple.com/in/album/billo-single/id1094594481?ls=1&app;=itunes Listen it on Hungama - http://www.hungama.com/#/music/album-billo-songs/17597206 For Caller Tunes : Billo http://bit.ly/1MqOl3m Billo - Dil Mein Hai http://bit.ly/1S7vQ8w Billo - Tere Thumke P... -

Jatti De Nain | New Punjabi Songs 2016 | Roshan Prince ft. Millind Gaba | Surbhi Mahendru
Check out the Official Video of 'Jatti De Nain' by Roshan Prince featuring Millind Gaba and Surbhi Mahendru Exclusively on Times Music! The Punjabi song has been directed by Parmod Sharma Rana. Credits: Singer - Roshan Prince https://www.facebook.com/theroshanprince/ http://instagram.com/theroshanprince Artist - Roshan Prince ft Millind Gaba and Surbhi Mahendru Female Lead Surbhi Mahendru https://m.facebook.com/profile.php?id=1573063022917790&tsid;=0.8909779849927872&source;=typeahead Music- Millind Gaba https://www.facebook.com/MillindGabaofficial/ Writer- Happy Raikoti https://www.facebook.com/HappyRaikotiOfficial/ Projected & Video Director - Parmod Sharma Rana https://m.facebook.com/iParmodsharmarana/?ref=bookmarks Video Editor - Ashu Kathpal and Sarabjeet Sohal Poster design- Aman Ka... -

EMP Neurociencias: GABA
Después del Glutamato, el Ácido Gama Amino Butírico o GABA es de los neurotransmisores más abundantes y con una mayor función en el cerebro, en este video explicamos la fisiología y la farmacología relacionada con este neurotransmisor. Las imágenes fueron obtenidas de wikipedia. Para más información del tema les sugerimos revisar el libro de Neuroquímica Básica de Siegel, así como el Kandel de Neurociencias. -

Anxiety, Stress and the Benefits of GABA
The benefits of GABA are astounding. I abused alcohol for years and GABA helped me treat the underlying anxiety that was a contributing factor in my addiction and helped me stop drinking on my own. Plus, GABA (also known as gamma-aminobutyric acid) is a great natural alternative treatment for depression and anxiety and an amazing way to improve your mental health. ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- Track included "Ulyses" (by Jahzzar): http://freemusicarchive.org/music/jahzzar/kuddelmuddel/ulyses_master_2 http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/4.0/legalcode -

Swag Babe - Official Music Video - Mehak Malhotra Ft. Milind Gaba
Presenting to you the full video of "Swag Babe" by Mehak Malhotra ft. Milind Gaba. Song: Swag Babe Singers: Mehak Malhotra Ft. Milind Gaba Music Director: Milind Gaba Lyricist: Milind Gaba Director: Gsk (Gursharan Singh Kohli) Music Label : T-Series https://www.facebook.com/fanclubmehak Enjoy & stay connected with us!! FOR LATEST UPDATES: ---------------------------------------- SUBSCRIBE US Here: http://bitly.com/SJIuwJ "If you like the Video, Don't forget to Share and leave your comments" Visit Our Channel For More Videos: http://www.youtube.com/Popchartbusters Operator Codes - 1 - Swagbabe Vodafone Subscribers Dial 5376187335 Airtel Subscribers Dial 5432114727390 Idea Subscribers Dial 567896187335 Tata DoCoMo Subscribers dial 5432116187335 Aircel Subscribers sms DT 2471248 T... -

GABA Neurotransmitters, Anxiety, and the Dangers of Benzodiazepines
Dr. Von Stieff explains the dangers of what benzodiazepines do and how these GABA drugs, like Xanax and diazepam, can lead to prescription addiction and even cause alcoholics to relapse. Learn how benzodiazepine effects on GABA neurotransmitters can actually incite anxiety. -

-

neurotransmitter gaba
gaba,neurotransmitter epsp ipsp -

GABA to Combat Stress and Anxiety, My Experience
I originally started taking this when I wanted something to stop the anxiety associated with Wellbutrin. GABA is an over the counter drug that for me has worked wonders to allieve stress, as well as help me focus in school. Disclaimer: I'm simply here to explain my experience. I'm not a medical professional, nor do I recommend this drug without your doctor's concent. -

GABA Neurotransmitters and Glutamate
Dr. Von Stieff teaches the fascinating role that glutamate and GABA neurotransmitters play in feelings, perceptions, and prescription addiction, addictions to prescription anxiety medications that can result in a paradoxical effect. That's right: That anxiety medication you're taking may actually end up causing you more anxiety. Buy the entire Brain in Balance book here: http://www.amazon.com/exec/obidos/ASIN/0983951802 -

-

GABA - 5HTP Replicator (Relaxation and Mood Improvement) - Binaural Beats + Isochronic Tones
PLEASE SHARE AND SUBSCRIBE Downloads Here: http://samadhientrainment.com/products/2/ Binaural and Isochronic frequencies that target specific neurotransmitter receptors in the brain, giving a brainwave entrainment effect that is similar to the effect that drugs have on the brain. Binaural beats, or binaural tones, are auditory processing artifacts, or apparent sounds, caused by specific physical stimuli. This effect was discovered in 1839 by Heinrich Wilhelm Dove and earned greater public awareness in the late 20th century based on claims coming from the alternative medicine community that binaural beats could help induce relaxation, meditation, creativity and other desirable mental states. The effect on the brainwaves depends on the difference in frequencies of each tone: for example, ... -

"DILRUBA" Feat. MILLIND GABA ( Film by ShaBby's Prodction )
"DILRUBA" Feat. MILLIND GABA ( Film by ShaBby's Prodction ) PRESENTED BY SHABBY SINGH ShaBby's Production :https://www.facebook.com/shabbyproduction Millind Gaba : https://www.facebook.com/MillindGabao... Sparkplug :https://www.facebook.com/pages/SprkPl... CREDITS Music production : Millind Gaba Beatbox : SparkPlug DIRECTOR : Shabby Singh -

The GABA receptor | How does it work?
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 9:52
- Updated: 13 Mar 2012
- views: 180228
- published: 13 Mar 2012
- views: 180228
Yo Gabba Gabba Español Latino - Familia
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 23:00
- Updated: 23 Jun 2014
- views: 6643830
- published: 23 Jun 2014
- views: 6643830
NOW Foods GABA Honest Review
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 4:57
- Updated: 23 Feb 2014
- views: 17816
- published: 23 Feb 2014
- views: 17816
Daaru Party (Full Song) | Millind Gaba | Latest Punjabi Songs 2015 | Speed Records
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 3:58
- Updated: 29 Nov 2015
- views: 1836269
- published: 29 Nov 2015
- views: 1836269
Yaar Mod Do Full Video Song | Guru Randhawa, Millind Gaba | T-Series
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 4:54
- Updated: 21 Jan 2016
- views: 2377843
- published: 21 Jan 2016
- views: 2377843
Thodi Jinni Peeti Hai | Dilbagh Singh | Millind Gaba | Official Song
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 3:32
- Updated: 21 Feb 2014
- views: 661835
- published: 21 Feb 2014
- views: 661835
Chura Liya Cover feat Millind Gaba MusicMG
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 3:12
- Updated: 10 Jun 2015
- views: 690419
- published: 10 Jun 2015
- views: 690419
Explain GABA and Natural Ways to Increase It
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 6:13
- Updated: 17 Feb 2014
- views: 15219
- published: 17 Feb 2014
- views: 15219
4MenDown Full Video - Millind Gaba | Latest Punjabi Songs | Speed Records
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 3:45
- Updated: 16 Aug 2014
- views: 1672224
- published: 16 Aug 2014
- views: 1672224
BILLO Video Song | MIKA SINGH | Millind Gaba | New Song 2016 | T-Series
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 2:54
- Updated: 18 Mar 2016
- views: 4823
- published: 18 Mar 2016
- views: 4823
Jatti De Nain | New Punjabi Songs 2016 | Roshan Prince ft. Millind Gaba | Surbhi Mahendru
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 3:11
- Updated: 16 Mar 2016
- views: 4313
- published: 16 Mar 2016
- views: 4313
EMP Neurociencias: GABA
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 30:46
- Updated: 03 Dec 2014
- views: 22951
- published: 03 Dec 2014
- views: 22951
Anxiety, Stress and the Benefits of GABA
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 5:19
- Updated: 03 Jan 2015
- views: 4097
- published: 03 Jan 2015
- views: 4097
Swag Babe - Official Music Video - Mehak Malhotra Ft. Milind Gaba
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 3:25
- Updated: 08 Apr 2015
- views: 1478680
- published: 08 Apr 2015
- views: 1478680
GABA Neurotransmitters, Anxiety, and the Dangers of Benzodiazepines
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 4:17
- Updated: 07 May 2013
- views: 65337
- published: 07 May 2013
- views: 65337
How The Neurotransmitter GABA Works For Anxiety In The Brain
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 8:41
- Updated: 07 Dec 2015
- views: 282
neurotransmitter gaba
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 1:24
- Updated: 07 May 2008
- views: 165027
- published: 07 May 2008
- views: 165027
GABA to Combat Stress and Anxiety, My Experience
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 5:02
- Updated: 19 Sep 2011
- views: 33932
- published: 19 Sep 2011
- views: 33932
GABA Neurotransmitters and Glutamate
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 2:43
- Updated: 29 Aug 2012
- views: 23974
- published: 29 Aug 2012
- views: 23974
Quick Facts on GABA
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 2:07
- Updated: 26 Apr 2012
- views: 17534
GABA - 5HTP Replicator (Relaxation and Mood Improvement) - Binaural Beats + Isochronic Tones
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 30:01
- Updated: 07 Feb 2014
- views: 21781
- published: 07 Feb 2014
- views: 21781
"DILRUBA" Feat. MILLIND GABA ( Film by ShaBby's Prodction )
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 3:52
- Updated: 16 Sep 2013
- views: 438893
- published: 16 Sep 2013
- views: 438893
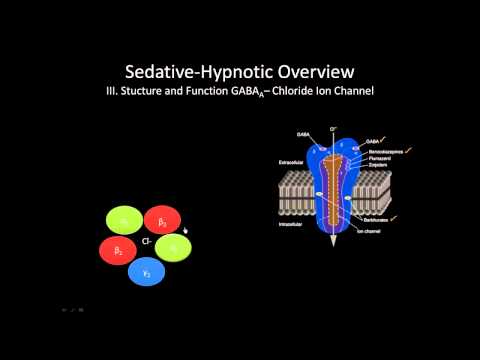
GABA Receptor - Structure and Mechanism of Action
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 6:11
- Updated: 21 Jun 2015
- views: 18922
- Playlist
- Chat
- Playlist
- Chat

The GABA receptor | How does it work?
- Report rights infringement
- published: 13 Mar 2012
- views: 180228

Yo Gabba Gabba Español Latino - Familia
- Report rights infringement
- published: 23 Jun 2014
- views: 6643830

NOW Foods GABA Honest Review
- Report rights infringement
- published: 23 Feb 2014
- views: 17816

Daaru Party (Full Song) | Millind Gaba | Latest Punjabi Songs 2015 | Speed Records
- Report rights infringement
- published: 29 Nov 2015
- views: 1836269

Yaar Mod Do Full Video Song | Guru Randhawa, Millind Gaba | T-Series
- Report rights infringement
- published: 21 Jan 2016
- views: 2377843

Thodi Jinni Peeti Hai | Dilbagh Singh | Millind Gaba | Official Song
- Report rights infringement
- published: 21 Feb 2014
- views: 661835

Chura Liya Cover feat Millind Gaba MusicMG
- Report rights infringement
- published: 10 Jun 2015
- views: 690419

Explain GABA and Natural Ways to Increase It
- Report rights infringement
- published: 17 Feb 2014
- views: 15219

4MenDown Full Video - Millind Gaba | Latest Punjabi Songs | Speed Records
- Report rights infringement
- published: 16 Aug 2014
- views: 1672224

BILLO Video Song | MIKA SINGH | Millind Gaba | New Song 2016 | T-Series
- Report rights infringement
- published: 18 Mar 2016
- views: 4823

Jatti De Nain | New Punjabi Songs 2016 | Roshan Prince ft. Millind Gaba | Surbhi Mahendru
- Report rights infringement
- published: 16 Mar 2016
- views: 4313

EMP Neurociencias: GABA
- Report rights infringement
- published: 03 Dec 2014
- views: 22951

Anxiety, Stress and the Benefits of GABA
- Report rights infringement
- published: 03 Jan 2015
- views: 4097

Swag Babe - Official Music Video - Mehak Malhotra Ft. Milind Gaba
- Report rights infringement
- published: 08 Apr 2015
- views: 1478680
-
Lyrics list:text lyricsplay full screenplay karaoke
Cynthia Lee Fontaine on her "Drag Race" elimination and battle with cancer
Edit The Examiner 22 Mar 2016Islamic State issues statement promising ‘dark days’ ahead
Edit Indian Express 23 Mar 2016FBI's New Unlocking Method May Resolve Terrorist's iPhone 5C, But Scares Apple
Edit WorldNews.com 23 Mar 2016Australian Police Arrest 16-Year-Old Student Suspected Of Raising Funds For Islamic State
Edit WorldNews.com 23 Mar 2016Wed, 23 Mar, 2016, 08:30 - English - Diamyd® in combination with etanercept and vitamin D shows safety in a first preliminary interim report (Diamyd Medical AB)
Edit Public Technologies 23 Mar 2016Paramount Chief Paul Gaba Saquee raises more than200,000,000 for educational purpose
Edit SLBC 21 Mar 2016Understanding the data: In the battle over the conclusions of a major research reproducibility study, a VCU professor weighs in (Virginia Commonwealth University)
Edit Public Technologies 21 Mar 2016March 2, 2016 Announcements (University of Louisville)
Edit Public Technologies 17 Mar 2016Transporter for GABA receptors holds key to autism (University of Tokyo)
Edit Public Technologies 16 Mar 2016Understanding obesity from the inside out (Baylor College of Medicine)
Edit Public Technologies 16 Mar 2016Salute to World Sleep Day
Edit Toronto Sun 16 Mar 2016GABA knockout by a novel inducible genetic system [Neuroscience]>
Edit PNAS 15 Mar 2016SCCL: All-Time Semifinal Results & Scorers (CONCACAF - Confederation of North, Central American and Caribbean Association Football)
Edit Public Technologies 15 Mar 2016Catalyst Pharmaceuticals Announces Fourth Quarter and Year-End 2015 Financial Results (Catalyst Pharmaceutical Partners Inc)
Edit Public Technologies 15 Mar 2016- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- Next page »







