- published: 29 Oct 2012
- views: 387205
- published: 18 Mar 2015
- views: 50693
- published: 14 Sep 2015
- views: 16834
- published: 01 Oct 2015
- views: 15207
- published: 15 Apr 2016
- views: 10789
- published: 30 Apr 2016
- views: 3618
- published: 28 Aug 2013
- views: 58811
- published: 29 Apr 2016
- views: 127
- published: 12 Nov 2012
- views: 407178
- published: 18 Dec 2012
- views: 304484

Ecology (from Greek: οἶκος, "house"; -λογία, "study of") is the scientific study of the relations that living organisms have with respect to each other and their natural environment. Variables of interest to ecologists include the composition, distribution, amount (biomass), number, and changing states of organisms within and among ecosystems. Ecosystems are hierarchical systems that are organized into a graded series of regularly interacting and semi-independent parts (e.g., species) that aggregate into higher orders of complex integrated wholes (e.g., communities). Ecosystems are sustained by the biodiversity within them. Biodiversity is the full-scale of life and its processes, including genes, species and ecosystems forming lineages that integrate into a complex and regenerative spatial arrangement of types, forms, and interactions. Ecosystems create biophysical feedback mechanisms between living (biotic) and nonliving (abiotic) components of the planet. These feedback loops regulate and sustain local communities, continental climate systems, and global biogeochemical cycles.
This article is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported License, which means that you can copy and modify it as long as the entire work (including additions) remains under this license.
News is the communication of selected information on current events which is presented by print, broadcast, Internet, or word of mouth to a third-party or mass audience.
One theory claims that the English word "news" developed in the 14th century as a special use of the plural form of "new". In Middle English, the equivalent word was newes, like the French nouvelles and the German neues. Similar developments are found in the Slavic languages – the Czech and Slovak noviny (from nový, "new"), the cognate Polish nowiny and Russian novosti – and in the Celtic languages: the Welsh newyddion (from newydd) and the Cornish nowodhow (from nowydh).
Before the invention of newspapers in the early 17th century, official government bulletins and edicts were circulated at times in some centralized empires.
The first documented use of an organized courier service for the diffusion of written documents is in Egypt, where Pharaohs used couriers for the diffusion of their decrees in the territory of the State (2400 BC). This practice almost certainly has roots in the much older practice of oral messaging and may have been built on a pre-existing infrastructure.
This article is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported License, which means that you can copy and modify it as long as the entire work (including additions) remains under this license.
- Loading...

-
 10:26
10:26Ecology - Rules for Living on Earth: Crash Course Biology #40
Ecology - Rules for Living on Earth: Crash Course Biology #40Ecology - Rules for Living on Earth: Crash Course Biology #40
Hank introduces us to ecology - the study of the rules of engagement for all of us earthlings - which seeks to explain why the world looks and acts the way it does. The world is crammed with things, both animate and not, that have been interacting with each other all the time, every day, since life on this planet began, and these interactions depend mostly on just two things... Learn what they are as Crash Course Biology takes its final voyage outside the body and into the entire world. Stay tuned in the coming weeks for a new Crash Course in ECOLOGY! Crash Course Biology is now available on DVD! http://dft.ba/-8bCC Like CrashCourse: http://www.facebook.com/YouTubeCrashCourse Follow CrashCourse: http://www.twitter.com/TheCrashCourse Table of Contents 1) Ecological Hierarchy 02:01:2 a) Population 02:12 b) Community 02:26:1 c) Ecosystem 02:50 d) Biome 03:22:1 e) Biosphere 03:51 2) Key Ecological Factors 04:07 a) Temperature 05:06:1 b) Water 05:37 3) Biome Type 06:03:1 References/Image Licenses: http://dft.ba/-2qQ3 crash course, biology, ecology, hank green, science, organism, interaction, molecule, environment, hierarchy, Earth, ecological, population, community, predation, cooperation, competition, ecosystem, soil, water, air, temperature, energy, materials, physical environment, biome, technique, adaptation, condition, evolution, biosphere, biotic, abiotic, predator, animal, plant, food, shelter, moisture, sunlight, elevation, category, chemistry, enzyme, photosynthesis, physiognomy, biodiversity, tropical rainforest, tundra, desert, grassland, taiga, human impact Support CrashCourse on Subbable: http://subbable.com/crashcourse -
 4:47
4:47Introduction to Ecology
Introduction to EcologyIntroduction to Ecology
Learn about the biosphere, ecosystems, communities, populations, organisms, habitats, niches, generalists, specialists, biotic and abiotic factors in this video! -
 11:14
11:14Ecosystem Ecology
Ecosystem EcologyEcosystem Ecology
007 - Ecosystem Ecology In this video Paul Andersen explains how ecosystems function. He begins with a description of how life on the planet is ordered from large to small in biomes, ecosystems, communities, population, and individuals. He describes the major terrestrial and aquatic biomes on the planet. He then describes interactions at the ecosystem level with food food webs. He also explains the importance of niche, keystone species, and the edge effect. Do you speak another language? Help me translate my videos: http://www.bozemanscience.com/translations/ Music Attribution Intro Title: I4dsong_loop_main.wav Artist: CosmicD Link to sound: http://www.freesound.org/people/CosmicD/sounds/72556/ Creative Commons Atribution License Outro Title: String Theory Artist: Herman Jolly http://sunsetvalley.bandcamp.com/track/string-theory All of the images are licensed under creative commons and public domain licensing: Daderot. Kelp Forest Tank, Monterey Bay Aquarium, Monterey County, California, USA., April 20, 2012. Daderot. https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Kelp_Forest_-_MBA_-_DSC06945.JPG. “Ecological Niche.” Wikipedia, the Free Encyclopedia, May 17, 2015. https://en.wikipedia.org/w/index.php?title=Ecological_niche&oldid;=662726986. “File:PrecipitationTempBiomes.jpg.” Wikipedia, the Free Encyclopedia, December 23, 2013. https://en.wikipedia.org/w/index.php?title=File:PrecipitationTempBiomes.jpg&oldid;=587430172. “Generalist and Specialist Species.” Wikipedia, the Free Encyclopedia, January 28, 2015. https://en.wikipedia.org/w/index.php?title=Generalist_and_specialist_species&oldid;=644599063. “Generalist and Specialist Species.” Wikipedia, the Free Encyclopedia, January 28, 2015. https://en.wikipedia.org/w/index.php?title=Generalist_and_specialist_species&oldid;=644599063. “Google Image Result for https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/7/76/Edge_Effect.jpg.” Accessed September 8, 2015. http://www.google.com/imgres?imgurl=https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/7/76/Edge_Effect.jpg&imgrefurl;=https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Edge_effects&h;=2112&w;=2816&tbnid;=1l-bJ0vXrAqrpM:&tbnh;=160&tbnw;=213&usg;=__AUxYLJdRU0uacd52R_eDgKAk0f0=&docid;=CKdWtQVgMZ5r7M&sa;=X&ved;=0CCIQ9QEwAGoVChMIneyxtdfnxwIVAy-ICh2FUg9k. “Greater Yellowstone Ecosystem.” Wikipedia, the Free Encyclopedia, March 22, 2015. https://en.wikipedia.org/w/index.php?title=Greater_Yellowstone_Ecosystem&oldid;=653036516. Joshfn. English: Primary Succession Is the Process Characterized by Soil and Organisms Becoming Established in an Area Lacking Topsoil and Vegetation., May 19, 2014. Own work. https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:AP_Biology_-_Primary_Succession_Drawing.svg. KennyOMG. English: View of the Pahalgam Valley, June 4, 2011. Own work. https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Pahalgam_Valley.jpg. Lab", This image has been created during “DensityDesign Integrated Course Final Synthesis Studio” at Polytechnic University of Milan, organized by DensityDesign Research Lab Image is released under CC-BY-SA licence Attribution goes to "Roberta Rosina, DensityDesign Research. English: “A Food Web Consists of All the Food Chains in a Single Ecosystem” [Cit. National Geographic Education], December 1, 2014. Own work. https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Food_Web.svg. “Lake.” Wikipedia, the Free Encyclopedia, September 1, 2015. https://en.wikipedia.org/w/index.php?title=Lake&oldid;=678968456. “Ocean.” Wikipedia, the Free Encyclopedia, September 7, 2015. https://en.wikipedia.org/w/index.php?title=Ocean&oldid;=679853061. “Old Faithful.” Wikipedia, the Free Encyclopedia, August 23, 2015. https://en.wikipedia.org/w/index.php?title=Old_Faithful&oldid;=677486601. “Sea Urchin.” Wikipedia, the Free Encyclopedia, August 24, 2015. https://en.wikipedia.org/w/index.php?title=Sea_urchin&oldid;=677556207. “The Blue Marble.” Wikipedia, the Free Encyclopedia, August 30, 2015. https://en.wikipedia.org/w/index.php?title=The_Blue_Marble&oldid;=678648703. USA, Ed Bierman from Redwood City. Pam My Best Dive Buddy -- Look at the Kelp Forest, Why I Dive California, November 6, 2004. Dive buddy in deep green kelp forest. https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Diver_in_kelp_forest.jpg. “Wikipedia:Featured pictures/Places/Landscapes.” Wikipedia, the Free Encyclopedia, July 28, 2015. https://en.wikipedia.org/w/index.php?title=Wikipedia:Featured_pictures/Places/Landscapes&oldid;=673421165. -
 12:10
12:10Population Ecology
Population EcologyPopulation Ecology
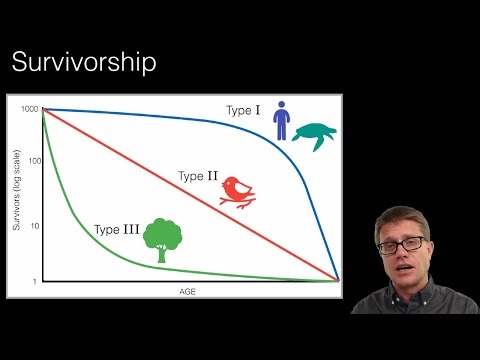
Logistic Growth Video - https://youtu.be/rXlyYFXyfIM 012 - Population Ecology In this video Paul Andersen explains how population ecology studies the density, distribution, size, sex ration, and age structure of populations. Intrinsic growth rate and exponential growth calculations are included along with a discussion of logistic growth. K-selected and r-selected species are explained along with survivorship curves. Do you speak another language? Help me translate my videos: http://www.bozemanscience.com/translations/ Music Attribution Intro Title: I4dsong_loop_main.wav Artist: CosmicD Link to sound: http://www.freesound.org/people/CosmicD/sounds/72556/ Creative Commons Atribution License Outro Title: String Theory Artist: Herman Jolly http://sunsetvalley.bandcamp.com/track/string-theory All of the images are licensed under creative commons and public domain licensing: Agriculture, U. S. Department of. Whooping Crane in Flight in Texas. USDA Photo by John Noll., March 18, 2011. Flickr: 20110214-USDA-JN-0001. https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Whooping_Crane_in_flight_in_Texas.jpg. “Bird on Branch - Free Animals Icons.” Flaticon. Accessed September 15, 2015. www.flaticon.com/free-icon/bird-on-branch_61289. “Canada Lynx.” Wikipedia, the Free Encyclopedia, July 25, 2015. https://en.wikipedia.org/w/index.php?title=Canada_lynx&oldid;=672981991. Headquarters, U. S. Fish and Wildlife Service. Adult Whooping Crane (Grus Americana) with Chick., February 23, 2012. Adult Whooping Crane and Chick. https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Adult_Whooping_Crane_and_Chick_(6923604379).jpg. Husthwaite, Ray. English: Survivorship Curves, 23 April 09. Own work (Original text: I created this work entirely by myself.). https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Survivorship_Curves.jpg. Karine, Gill-Weir. “The Whooping Cranes: Survivors Against All Odds,” n.d. http://www.prairiefirenewspaper.com/2010/09/the-whooping-cranes-survivors-against-all-odds. Robertson, D. Gordon E. English: Snowshoe Hare (Lepus Americanus), White Morph, Shirleys Bay, Ottawa, Ontario, Canada, January 21, 2013. Own work. https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Snowshoe_Hare,_Shirleys_Bay.jpg. Sasata. English: The Whooping Crane, Grus Americana at the Calgary Zoo., September 11, 2010. Own work. https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Grus_americana_Sasata.jpg. “Standing Up Man - Free People Icons.” Flaticon. Accessed September 15, 2015. www.flaticon.com/free-icon/standing-up-man-_10522. “Tree Silhouette - Free Nature Icons.” Flaticon. Accessed September 15, 2015. www.flaticon.com/free-icon/tree-silhouette_46564. “Turtle Shape - Free Animals Icons.” Flaticon. Accessed September 15, 2015. www.flaticon.com/free-icon/turtle-shape_47331. -
 24:11
24:11Tyto Ecology | BUILDING OUR OWN ECOSYSTEM
Tyto Ecology | BUILDING OUR OWN ECOSYSTEMTyto Ecology | BUILDING OUR OWN ECOSYSTEM
This game came out of nowhere to be pretty cool. In Tyto Ecology we have a choice of three biomes to build an ecodome in. The best thing is the game progresses when you're offline so you can check in down the line and see if your ecosystem has flourished or capitulated! Buy Tyto Ecology on Steam here : http://store.steampowered.com/app/453750/ ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- ★ Subscribe : http://bit.ly/13OT2RF ★ Twitch : http://www.twitch.tv/bestinslot I stream every Tuesday and Saturday from 7-10PM GMT/UK Time ★ Patreon : https://www.patreon.com/bestinslot?ty=h ★ Facebook : http://on.fb.me/17FhW3J ★ Twitter : https://twitter.com/BestInSlotYT ★ Merchandise : https://www.districtlines.com/BESTINSLOT -
 26:47
26:47Tyto Ecology | EVERYTHING'S DYING (Week 3)
Tyto Ecology | EVERYTHING'S DYING (Week 3)Tyto Ecology | EVERYTHING'S DYING (Week 3)
After two months of survival for my beloved biomes, things start to turn south pretty quickly. BUT ON THE PLUS SIDE WE HAVE BEEEEEEEEEEES Buy Tyto Ecology on Steam here : http://store.steampowered.com/app/453750/ Tyto Ecology playthrough playlist : https://www.youtube.com/playlist?list=PLU0V6ITiWqjh1ke_VZ3OEIrc8AYgZMl2M ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- ★ Subscribe : http://bit.ly/13OT2RF ★ Twitch : http://www.twitch.tv/bestinslot I stream every Tuesday and Saturday from 7-10PM GMT/UK Time ★ Patreon : https://www.patreon.com/bestinslot?ty=h ★ Facebook : http://on.fb.me/17FhW3J ★ Twitter : https://twitter.com/BestInSlotYT ★ Merchandise : https://www.districtlines.com/BESTINSLOT Music: TheFatRat - Monody (feat. Laura Brehm) https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=B7xai5u_tnk -
 15:01
15:01Biology - The Science of Life - Ecology - Organisms in Their Environment
Biology - The Science of Life - Ecology - Organisms in Their EnvironmentBiology - The Science of Life - Ecology - Organisms in Their Environment
This fifteen-minute program examines the interactions between organisms in their environments. The program addresses two important questions posed by core-curriculum standards. The first is, "What are ecosystems and how do organisms interact in them?" The second is, "How do matter and energy flow in the environment?" The concepts of ecosystem, population, niche, food chain, food web, energy pyramid, and the carbon cycle are all explained in this program. -
 22:14
22:14NATURAL SELECTION BY WRESTLING WITH TREES || TYTO: ECOLOGY - Episode #6
NATURAL SELECTION BY WRESTLING WITH TREES || TYTO: ECOLOGY - Episode #6NATURAL SELECTION BY WRESTLING WITH TREES || TYTO: ECOLOGY - Episode #6
• Join the Pixel Biology Community! • http://goo.gl/Xro8bE • TYTO: ECOLOGY Playlist • https://goo.gl/o8HdQ1 • World Zoo Season 2 Playlist || https://goo.gl/CVNgQ9 • • Zoo Crafting: Season Three Playlist • https://goo.gl/1laAUu • Thank you so much to the amazing Violinaria aka April for giving us this awesome game!! Check her out • https://www.youtube.com/user/TheViolinaria There is a fine-tuned balance to eco-systems: consumers, producers, predators... and, of course, piles and piles of adorable mushrooms that rain down from the sky as Seri goes mad with the power of controlling her own biodomes! Join us as we dive into TYTO: ECOLOGY and discuss the cycle of ecosystems, environmental science, and just how adorable the little herbivores right before our equally adorable predators make their contribution to the food chain! Lots of babble about Seri's passionate love of teaching ecology ahead - ONWARD TO SCIENCE! _______________________________________________ Twitter • • https://twitter.com/Seriiiously Facebook • • https://goo.gl/GsymoK Instagram • • https://instagram.com/seriiiously Etsy Shop • • https://www.etsy.com/shop/ByTheLeaf _______________________________________________ • Seri is a biologist-in-training with an intense passion for plants and filling her house to the brim with finches, potted plants, and biology "specimens" that look oddly like snail shells, mossy, and twigs covering every available surface. She is also big into spreading her love of the natural world through the entertaining medium of story-telling through video games! Jump on in and see what our amazing, animal-loving, plant-studying community is all about! And remember, stay curious! -
 4:07
4:07Ecology Introduction
Ecology IntroductionEcology Introduction
Population, community and ecosystem -
 11:53
11:53Population Ecology: The Texas Mosquito Mystery - Crash Course Ecology #2
Population Ecology: The Texas Mosquito Mystery - Crash Course Ecology #2Population Ecology: The Texas Mosquito Mystery - Crash Course Ecology #2
Population ecology is the study of groups within a species that interact mostly with each other, and it examines how they live together in one geographic area to understand why these populations are different in one time and place than they are in another. How is that in any way useful to anyone ever? Hank uses the example a of West Nile virus outbreak in Texas to show you in this episode of Crash Course: Ecology. Like Crash Course? http://www.facebook.com/YouTubeCrashCourse Follow Crash Course! http://www.twitter.com/TheCrashCourse Table of Contents 1) Density & Dispersion 02:03 2) Population Growth 03:07 3) Limiting Factors 03:45 a) Density Dependent 06:16 b) Density Independent 07:11 4) Exponential & Logistical Growth 08:04 5) How to Calculate Growth Rate 09:33 References: http://www.latimes.com/news/nation/nationnow/la-na-nn-west-nile-virus-20120817,0,2506584.story http://www.dshs.state.tx.us/idcu/disease/arboviral/westnile/information/general/myths/ http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Mosquito http://www.nature.com/scitable/knowledge/library/population-limiting-factors-17059572 Campbell Biology 9th ed. Support CrashCourse on Subbable: http://subbable.com/crashcourse -
 10:10
10:10Ecosystem Ecology: Links in the Chain - Crash Course Ecology #7
Ecosystem Ecology: Links in the Chain - Crash Course Ecology #7Ecosystem Ecology: Links in the Chain - Crash Course Ecology #7
Hank brings us to the next level of ecological study with ecosystem ecology, which looks at how energy, nutrients, and materials are getting shuffled around within an ecosystem (a collection of living and nonliving things interacting in a specific place), and which basically comes down to who is eating who. Like Crash Course! http://www.facebook.com/YouTubeCrashCourse Follow Crash Course! http://www.twitter.com/TheCrashCourse Table of Contents 1) Defining Ecosystems 0:49:1 2) Trophic Structure 4:44:1 a) Primary Producers 5:27 b) Primary Consumers 5:41 c) Secondary Consumers 5:49:1 d) Tertiary Consumers 5:58:2 e) Detrivores 6:08:1 3) Bioaccumulation 8:47 References and image licenses for this episode in the Google doc here: http://dft.ba/-3f2M Support CrashCourse on Subbable: http://subbable.com/crashcourse -
 1:25
1:25Ecology is...
Ecology is...Ecology is...
https://www.facebook.com/lukfilms http://www.lukfilms.pl -
 13:51
13:51Greg Asner: Ecology from the air
Greg Asner: Ecology from the airGreg Asner: Ecology from the air
What are our forests really made of? From the air, ecologist Greg Asner uses a spectrometer and high-powered lasers to map nature in meticulous kaleidoscopic 3D detail -- what he calls "a very high-tech accounting system" of carbon. In this fascinating talk, Asner gives a clear message: To save our ecosystems, we need more data, gathered in new ways. TEDTalks is a daily video podcast of the best talks and performances from the TED Conference, where the world's leading thinkers and doers give the talk of their lives in 18 minutes (or less). Look for talks on Technology, Entertainment and Design -- plus science, business, global issues, the arts and much more. Find closed captions and translated subtitles in many languages at http://www.ted.com/translate Follow TED news on Twitter: http://www.twitter.com/tednews Like TED on Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/TED Subscribe to our channel: http://www.youtube.com/user/TEDtalksDirector -
 11:30
11:30Community Ecology: Feel the Love - Crash Course Ecology #4
Community Ecology: Feel the Love - Crash Course Ecology #4Community Ecology: Feel the Love - Crash Course Ecology #4
Interactions between species are what define ecological communities, and community ecology studies these interactions anywhere they take place. Although interspecies interactions are mostly competitive, competition is pretty dangerous, so a lot of interactions are actually about side-stepping direct competition and instead finding ways to divvy up resources to let species get along. Feel the love? Like CrashCourse! http://www.facebook.com/YouTubeCrashCourse Follow CrashCourse! http://www.twitter.com/TheCrashCourse Table of Contents 1) Competitive Exclusion Principle 2:02 2) Fundamental vs. Realized Niche 3:48 3) Eco-lography / Resource Partitioning 5:25 4) Character Displacement 7:29 5) Mutualism 9:15 6) Commensalism 9:55 References for this episode can be found in the Google document here: http://dft.ba/-2YuA crashcourse, ecology, biology, competition, evolution, survival, habitat, species, interaction, communities, community ecology, resource, animal, limiting factors, competitive exclusion principle, success, paramecium, competitive advantage, extinction, food, prey, diversity, life, adaptation, niche, security, stability, fundamental niche, realized niche, conflict, nature, natural order, robert macarthur, warbler, ecologist, yale, resource partitioning, observation, zone, hunting, foraging, coexist, organism, selection, character displacement, peter grant, rosemary grant, galapagos finches, trait, mutualism, commensalism, mycorrhizae, termite, obligate mutualism, barnacle Support CrashCourse on Subbable: http://subbable.com/crashcourse
- Abiotic
- Abundance (ecology)
- Acoustic ecology
- Adaptation
- Adaptations
- Aerenchyma
- Africa
- Agriculture
- Agroecology
- Algae
- Alpha diversity
- Alpine climate
- Ammonia
- Amoeba
- Anaerobic bacteria
- Anatomy
- Anemophily
- Animal
- Animal migration
- Anoxic waters
- Ant
- Antarctica
- Apartheid
- Aphid
- Applied science
- Aquatic ecology
- Aquatic ecosystem
- Arachnid
- Archaea
- Arctic Ocean
- Aristotle
- Asia
- Astrobiology
- Atlantic Ocean
- Atmosphere of Earth
- Atom
- Autotrophs
- Bacteria
- Balance of nature
- Basic science
- Beaver
- Bee
- Behavioral ecology
- Beta diversity
- Bibcode
- Biochemistry
- Biocoenosis
- Biocomplexity
- Biodiversity
- Biogeochemical cycle
- Biogeochemistry
- Biogeography
- Bioinformatics
- Biological dispersal
- Biological system
- Biology
- Biomass
- Biomass (ecology)
- Biome
- Biomechanics
- Biomes
- Biomolecular
- Biomolecule
- Biophysics
- Bioregionalism
- Biosphere
- Biostatistics
- Biotic component
- Biotope
- Bioturbation
- Birds of paradise
- Boreal ecosystem
- Botany
- Brackish
- C4 carbon fixation
- Calcium carbonate
- Carbohydrate
- Carbohydrates
- Carbon
- Carbon cycle
- Carbon dioxide
- Carl Linnaeus
- Carnivorous
- Carrying capacity
- Category Biology
- Category Nature
- Cell (biology)
- Cell biology
- Cell signalling
- Cell theory
- Chameleons
- Charles Darwin
- Chemical biology
- Chemical ecology
- Chemosynthesis
- Chesapeake Bay
- Chronobiology
- Circulatory system
- Climate
- Cline (biology)
- Clones
- Coevolution
- Columbia Basin
- Commensalism
- Community (ecology)
- Community ecology
- Community health
- Complex systems
- Complexity
- Concept map
- Conservation biology
- Consumer
- Continent
- Continental climate
- Coral
- Coral reef
- Corals
- Courtship
- Crocodile
- Cultural ecology
- Cyanobacteria
- Decomposers
- Decomposition
- Demographics
- Detritivore
- Detrivore
- Devonian period
- Display (zoology)
- Dynamic equilibrium
- Earth
- Earth Day
- Earth science
- Ecoacoustics
- Ecohydrology
- Ecological economics
- Ecological health
- Ecological network
- Ecological niche
- Ecological theory
- Ecology
- Ecology movement
- Ecology of contexts
- Ecoregion
- Ecosphere
- Ecosystem
- Ecosystem diversity
- Ecosystem ecology
- Ecosystem model
- Ecosystem services
- Ecosystems
- Ecotones
- Ecotope
- Edward O. Wilson
- Emergence
- Emergy
- Emigration
- Endemism
- Energy
- Energy budget
- Enthalpy
- Environmentalism
- Epidemiology
- Epigenetics
- Ernst Haeckel
- Erosion
- Estuarine
- Ethology
- Euclidean space
- Eugenius Warming
- Eukaryote
- Europe
- Eusocialism
- Evolution
- Evolutionary biology
- Evolutionary Biology
- Evolutionary ecology
- Exergy
- Extinction
- Fauna
- Fecundity
- Feedback
- Feedback loop
- Ferric
- Field study
- Fig wasp
- Fire ecology
- First Nations
- Fisheries
- Fitness (biology)
- Flora
- Fluid pressure
- Food chain
- Food web
- Forest farming
- Forest gardening
- Forestry
- Frederic Clements
- Freshwater ecosystem
- Fungi
- Fungus
- Fungus-growing ants
- Future of the Earth
- G. Evelyn Hutchinson
- Gaia hypothesis
- Gene
- Gene flow
- Genetic diversity
- Genetic drift
- Genetic mutation
- Genetics
- Genomics
- Geology
- Geomorphic
- George Perkins Marsh
- German language
- Germination
- Gilbert White
- Global warming
- Glossary of ecology
- Gravitropism
- Greek language
- Greenhouse gas
- Group selection
- Guild (ecology)
- Habitat
- Habitat conservation
- Habitats
- Hadean
- Henry Gleason
- Herbivores
- Heredity
- Herodotos
- Heterotrophs
- Heuristic
- Hippocrates
- Histology
- History of ecology
- History of the Earth
- Holism
- Holistic
- Homeorhesis
- Homeostasis
- Homeotherms
- Hot desert
- Human biology
- Human ecology
- Human society
- Hydrogen
- Hydrogen sulfide
- Hydrothermal vents
- Immigration
- Immunology
- Indian Ocean
- Industrial ecology
- Inflorescence
- Information ecology
- Insect ecology
- Integrative level
- Interdisciplinary
- Invasive species
- Island biogeography
- James Hutton
- Jan Christian Smuts
- John Avise
- JSTOR
- Juvenile (organism)
- Kelp
- Keystone species
- Kin selection
- Kinji Imanishi
- Knowledge ecology
- Landscape
- Landscape ecology
- Landscape limnology
- Leaf
- Leafhopper
- Leech
- Lichens
- Life
- Life history theory
- Linnaean taxonomy
- Lipids
- List of ecologists
- Logistic function
- LTER
- Macroevolution
- Macromolecule
- Manganese
- Marine biology
- Matrix (mathematics)
- Matter
- Meat ant
- Meiosis
- Metabolism
- Metaphysics
- Metapopulation
- Meteorology
- Methane
- Methanogen
- Microbiology
- Microbiome
- Microevolution
- Microorganisms
- Mikkelson
- Minerals
- Mites
- Mitosis
- Molecular Biology
- Molecular biology
- Molecular ecology
- Molecular genetics
- Molecule
- Monogamous
- Montane ecology
- Mosaic (ecology)
- Motile
- Mutation
- Mutualism (biology)
- Mutualisms
- Mycology
- N-dimensional space
- Naked mole rat
- Nanobiotechnology
- Natural capital
- Natural environment
- Natural history
- Natural landscape
- Natural resource
- Natural sciences
- Natural selection
- Nature
- Negative feedback
- Nematodes
- Neuroscience
- New Hampshire
- Niche construction
- Nitrate
- Nitrogen
- Nitrogen fixation
- Non-linear
- North America
- Nucleic Acids
- Null hypothesis
- Nutrient cycle
- Nutrients
- Nutrition
- Ocean
- Old-growth forests
- Oligocene
- Omnivores
- Organ (anatomy)
- Organelle
- Organic compounds
- Organism
- Organisms
- Organs
- Orogeny
- Orographic lift
- Osmotic pressure
- Outgassing
- Outline of biology
- Outline of ecology
- Oxidizing
- Oxygen
- Pacific Ocean
- Palaeoecology
- Paleoecology
- Paleontology
- Panarchy
- Parasitism
- Parasitology
- Parts-per notation
- Pathology
- Pedodiversity
- Pedogenesis
- Pedosphere
- Permafrost
- Pharmacology
- Phenology
- Phenomena
- Phenotype
- Phenotypic trait
- Phosphorus
- Photosynthesis
- Phylogenetics
- Phylogeography
- Physiological
- Physiology
- Phytoplankton
- Pinus halepensis
- Plant
- Plantesamfund
- Plate tectonics
- Poikilotherms
- Polar desert
- Pollination
- Pond
- Population
- Population densities
- Population Ecology
- Population ecology
- Population growth
- Populations
- Portal Biology
- Portal Ecology
- Portal Environment
- Portal Science
- Predation
- Predator
- Primary consumers
- Primary producers
- Primary production
- Prokaryote
- Promiscuous
- Proteins
- Protist
- Public ecology
- PubMed Central
- PubMed Identifier
- Quantum biology
- R K selection
- Radiant energy
- Rain shadow
- Random
- Range (biology)
- Reducing
- Reduction potential
- Reductionistic
- Resilience (ecology)
- Resource (biology)
- Restoration ecology
- Reverse ecology
- Riparian forest
- Robert MacArthur
- Salamander
- Sandpiper
- Science
- Scientific law
- Scientific modelling
- Sea otters
- Sea urchins
- Self-organization
- Seral community
- Seral development
- Serotiny
- Silica
- Simple sugars
- Slime moulds
- Social ecology
- Social insects
- Social spider
- Soil
- Soil ecology
- Soils
- Solar energy
- Solar radiation
- Solar System
- South America
- Southern Ocean
- Space
- Spatial ecology
- Speciation
- Species
- Species diversity
- Sperm
- Statistical model
- Statistics
- Steller's Sea Cow
- Succession(ecology)
- Suitors
- Sulfate
- Sulfur
- Superorganism
- Symbiosis
- Systematics
- Systems biology
- Taiga
- Taxonomy
- Taylor's law
- Technoecosystems
- Tectonic plates
- Temperature
- Template Biology nav
- Template Nature nav
- Template Ref book
- Termite
- Theophrastus
- Theoretical ecology
- Thermodynamics
- Time
- Tissue (biology)
- Toxicology
- Trade winds
- Trait (biology)
- Transportation
- Tree swallow
- Trophic cascade
- Trophic dynamics
- Trophic level
- Trophic species
- Trophism
- Tropical rainforest
- Tundra
- Turbulent forces
- Umwelt
- Universe
- Urban ecology
- Virus
- Vladimir Vernadsky
- Wasp
- Water column
- Wavelength
- Weather
- Weevils
- Westerlies
- Wetland
- Wikipedia Link rot
- Wilderness
- Woburn Abbey
- World
- Yucca moth
- Zoology
- Zooplankton
-

Ecology - Rules for Living on Earth: Crash Course Biology #40
Hank introduces us to ecology - the study of the rules of engagement for all of us earthlings - which seeks to explain why the world looks and acts the way it does. The world is crammed with things, both animate and not, that have been interacting with each other all the time, every day, since life on this planet began, and these interactions depend mostly on just two things... Learn what they are as Crash Course Biology takes its final voyage outside the body and into the entire world. Stay tuned in the coming weeks for a new Crash Course in ECOLOGY! Crash Course Biology is now available on DVD! http://dft.ba/-8bCC Like CrashCourse: http://www.facebook.com/YouTubeCrashCourse Follow CrashCourse: http://www.twitter.com/TheCrashCourse Table of Contents 1) Ecological Hierarchy 02:01:2 ... -

Introduction to Ecology
Learn about the biosphere, ecosystems, communities, populations, organisms, habitats, niches, generalists, specialists, biotic and abiotic factors in this video! -

Ecosystem Ecology
007 - Ecosystem Ecology In this video Paul Andersen explains how ecosystems function. He begins with a description of how life on the planet is ordered from large to small in biomes, ecosystems, communities, population, and individuals. He describes the major terrestrial and aquatic biomes on the planet. He then describes interactions at the ecosystem level with food food webs. He also explains the importance of niche, keystone species, and the edge effect. Do you speak another language? Help me translate my videos: http://www.bozemanscience.com/translations/ Music Attribution Intro Title: I4dsong_loop_main.wav Artist: CosmicD Link to sound: http://www.freesound.org/people/CosmicD/sounds/72556/ Creative Commons Atribution License Outro Title: String Theory Artist: Herman Jolly h... -

Population Ecology
Logistic Growth Video - https://youtu.be/rXlyYFXyfIM 012 - Population Ecology In this video Paul Andersen explains how population ecology studies the density, distribution, size, sex ration, and age structure of populations. Intrinsic growth rate and exponential growth calculations are included along with a discussion of logistic growth. K-selected and r-selected species are explained along with survivorship curves. Do you speak another language? Help me translate my videos: http://www.bozemanscience.com/translations/ Music Attribution Intro Title: I4dsong_loop_main.wav Artist: CosmicD Link to sound: http://www.freesound.org/people/CosmicD/sounds/72556/ Creative Commons Atribution License Outro Title: String Theory Artist: Herman Jolly http://sunsetvalley.bandcamp.com/track/strin... -

Tyto Ecology | BUILDING OUR OWN ECOSYSTEM
This game came out of nowhere to be pretty cool. In Tyto Ecology we have a choice of three biomes to build an ecodome in. The best thing is the game progresses when you're offline so you can check in down the line and see if your ecosystem has flourished or capitulated! Buy Tyto Ecology on Steam here : http://store.steampowered.com/app/453750/ ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- ★ Subscribe : http://bit.ly/13OT2RF ★ Twitch : http://www.twitch.tv/bestinslot I stream every Tuesday and Saturday from 7-10PM GMT/UK Time ★ Patreon : https://www.patreon.com/bestinslot?ty=h ★ Facebook : http://on.fb.me/17FhW3J ★ Twitter : https://twitter.com/BestInSlotYT ★ Merchandise : https://www.districtlines.com/BESTINSLOT -

Tyto Ecology | EVERYTHING'S DYING (Week 3)
After two months of survival for my beloved biomes, things start to turn south pretty quickly. BUT ON THE PLUS SIDE WE HAVE BEEEEEEEEEEES Buy Tyto Ecology on Steam here : http://store.steampowered.com/app/453750/ Tyto Ecology playthrough playlist : https://www.youtube.com/playlist?list=PLU0V6ITiWqjh1ke_VZ3OEIrc8AYgZMl2M ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- ★ Subscribe : http://bit.ly/13OT2RF ★ Twitch : http://www.twitch.tv/bestinslot I stream every Tuesday and Saturday from 7-10PM GMT/UK Time ★ Patreon : https://www.patreon.com/bestinslot?ty=h ★ Facebook : http://on.fb.me/17FhW3J ★ Twitter : https://twitter.com/BestInSlotYT ★ Merchandise : https://www.districtlines.com/BESTINSLOT Music: TheFatRat - Monody (feat. Laur... -

Biology - The Science of Life - Ecology - Organisms in Their Environment
This fifteen-minute program examines the interactions between organisms in their environments. The program addresses two important questions posed by core-curriculum standards. The first is, "What are ecosystems and how do organisms interact in them?" The second is, "How do matter and energy flow in the environment?" The concepts of ecosystem, population, niche, food chain, food web, energy pyramid, and the carbon cycle are all explained in this program. -

NATURAL SELECTION BY WRESTLING WITH TREES || TYTO: ECOLOGY - Episode #6
• Join the Pixel Biology Community! • http://goo.gl/Xro8bE • TYTO: ECOLOGY Playlist • https://goo.gl/o8HdQ1 • World Zoo Season 2 Playlist || https://goo.gl/CVNgQ9 • • Zoo Crafting: Season Three Playlist • https://goo.gl/1laAUu • Thank you so much to the amazing Violinaria aka April for giving us this awesome game!! Check her out • https://www.youtube.com/user/TheViolinaria There is a fine-tuned balance to eco-systems: consumers, producers, predators... and, of course, piles and piles of adorable mushrooms that rain down from the sky as Seri goes mad with the power of controlling her own biodomes! Join us as we dive into TYTO: ECOLOGY and discuss the cycle of ecosystems, environmental science, and just how adorable the little herbivores right before our equally adorable predators make ... -

Ecology Introduction
Population, community and ecosystem -

Population Ecology: The Texas Mosquito Mystery - Crash Course Ecology #2
Population ecology is the study of groups within a species that interact mostly with each other, and it examines how they live together in one geographic area to understand why these populations are different in one time and place than they are in another. How is that in any way useful to anyone ever? Hank uses the example a of West Nile virus outbreak in Texas to show you in this episode of Crash Course: Ecology. Like Crash Course? http://www.facebook.com/YouTubeCrashCourse Follow Crash Course! http://www.twitter.com/TheCrashCourse Table of Contents 1) Density & Dispersion 02:03 2) Population Growth 03:07 3) Limiting Factors 03:45 a) Density Dependent 06:16 b) Density Independent 07:11 4) Exponential & Logistical Growth 08:04 5) How to Calculate Growth Rate 09:33 References: http://... -

Ecosystem Ecology: Links in the Chain - Crash Course Ecology #7
Hank brings us to the next level of ecological study with ecosystem ecology, which looks at how energy, nutrients, and materials are getting shuffled around within an ecosystem (a collection of living and nonliving things interacting in a specific place), and which basically comes down to who is eating who. Like Crash Course! http://www.facebook.com/YouTubeCrashCourse Follow Crash Course! http://www.twitter.com/TheCrashCourse Table of Contents 1) Defining Ecosystems 0:49:1 2) Trophic Structure 4:44:1 a) Primary Producers 5:27 b) Primary Consumers 5:41 c) Secondary Consumers 5:49:1 d) Tertiary Consumers 5:58:2 e) Detrivores 6:08:1 3) Bioaccumulation 8:47 References and image licenses for this episode in the Google doc here: http://dft.ba/-3f2M Support CrashCourse on Subbable: http://s... -

Ecology is...
https://www.facebook.com/lukfilms http://www.lukfilms.pl -

Greg Asner: Ecology from the air
What are our forests really made of? From the air, ecologist Greg Asner uses a spectrometer and high-powered lasers to map nature in meticulous kaleidoscopic 3D detail -- what he calls "a very high-tech accounting system" of carbon. In this fascinating talk, Asner gives a clear message: To save our ecosystems, we need more data, gathered in new ways. TEDTalks is a daily video podcast of the best talks and performances from the TED Conference, where the world's leading thinkers and doers give the talk of their lives in 18 minutes (or less). Look for talks on Technology, Entertainment and Design -- plus science, business, global issues, the arts and much more. Find closed captions and translated subtitles in many languages at http://www.ted.com/translate Follow TED news on Twitter: http://... -

Community Ecology: Feel the Love - Crash Course Ecology #4
Interactions between species are what define ecological communities, and community ecology studies these interactions anywhere they take place. Although interspecies interactions are mostly competitive, competition is pretty dangerous, so a lot of interactions are actually about side-stepping direct competition and instead finding ways to divvy up resources to let species get along. Feel the love? Like CrashCourse! http://www.facebook.com/YouTubeCrashCourse Follow CrashCourse! http://www.twitter.com/TheCrashCourse Table of Contents 1) Competitive Exclusion Principle 2:02 2) Fundamental vs. Realized Niche 3:48 3) Eco-lography / Resource Partitioning 5:25 4) Character Displacement 7:29 5) Mutualism 9:15 6) Commensalism 9:55 References for this episode can be found in the Google docume... -

Ecology Song
Here is a song I created to help my 6th grade students study. I hope you enjoy. All the life we have seen Interactions we study The air, sand, water in a stream Abiotic that we see Now trees, animals, you know They’re all biotic if it grows Organisms we’ve been told All same species, young and old Population-same kind in place Community-(pop’s) populations in same space Ecosystems so you know Nonliving and all that grows Animals fighting for it all their life They are struggling so they don’t die That’s how an organism stays alive Producers and consumers Webs and chains, decomposers Competition for space and food they fight Predation it is to take a life And then there’s symbiosis all three kinds Mutualism, parasitism Third in chain, commensalism Adaptations they will thrive All that ... -

UPSC CSE (IAS): High Yield Series: Introduction to Environment and Ecology Part 1.1
This video deals with introduction to Environment and Ecology (EnE), includes all the major topics in EnE, terminologies, graphical representation of major biomes (where x-axis is mean annual precipitation and y-axis is mean annual temperature), list of abiotic factors, diffrent response of various organisms to these abiotic factors, definition of adaptation, its various examples and finally it culminates with explaining in detail the population pyramids. In this video, Dr. Roman deals with major topics like ecology, ecosystem structure and function, primary ecological succession, population interaction, secondary succession, biodiversity, IUCN Red Data book, biomes, Indian biomes, Interaction (Mutualism, Predation, Parasitism, Commensalism, Amensalism, Energy flow (Rule of 10% and how e... -

FIRST FOX OF THE GRASSLANDS || TYTO: ECOLOGY - Episode #5
• Join the Pixel Biology Community! • http://goo.gl/Xro8bE • TYTO: ECOLOGY Playlist • https://goo.gl/o8HdQ1 • World Zoo Season 2 Playlist || https://goo.gl/CVNgQ9 • • Zoo Crafting: Season Three Playlist • https://goo.gl/1laAUu • Thank you so much to the amazing Violinaria aka April for giving us this awesome game!! Check her out • https://www.youtube.com/user/TheViolinaria There is a fine-tuned balance to eco-systems: consumers, producers, predators... and, of course, piles and piles of adorable mushrooms that rain down from the sky as Seri goes mad with the power of controlling her own biodomes! Join us as we dive into TYTO: ECOLOGY and discuss the cycle of ecosystems, environmental science, and just how adorable the little herbivores right before our equally adorable predators make ... -

The History of Life on Earth - Crash Course Ecology #1
With a solid understanding of biology on the small scale under our belts, it's time for the long view - for the next twelve weeks, we'll be learning how the living things that we've studied interact with and influence each other and their environments. Life is powerful, and in order to understand how living systems work, you first have to understand how they originated, developed and diversified over the past 4.5 billion years of Earth's history. Hang on to your hats as Hank tells us the epic drama that is the history of life on Earth. Like CrashCourse on Facebook! http://www.facebook.com/YouTubeCrashCourse Follow CrashCourse on Twitter: http://www.twitter.com/TheCrashCourse Table of Contents 1) Archaean & Proterozoic Eons 01:53 a) Protobionts 03:54 b) Prokaryotes 04:18 c) Eukaryotes 06:... -

Conservation and Restoration Ecology: Crash Course Ecology #12
Hank wraps up the Crash Course on ecology by taking a look at the growing fields of conservation biology and restoration ecology, which use all the kung fu moves we've learned about in the past eleven weeks and apply them to protecting ecosystems and to cleaning up the messes that we've already made. Like Crash Course: http://www.facebook.com/YouTubeCrashCourse Follow Crash Course: http://www.twitter.com/TheCrashCourse Table of Contents 1) Types of Diversity 3:00 2) Conservation Biology 4:12 A) Small Population Conservation 4:26 B) Declining Population Conservation 5:50 3) Restoration Ecology 7:06 A) Structural Restoration 7:30 B) Bioremediation 7:48 C) Biological Augmentation 8:03 References and image licenses for this episode can be found in the Google document here: http://... -

Ecology Part 1 - Basic Ecology
Mr. Judd covers ecology, abiotic factors, biotic factors, niche, habitat, population, community, ecosystem, biome, biosphere, decomposers, autotrophs, heterotrophs, symbiosis, mutualism, parasitism, commensalism, and competition. -

Population ecology part 1 population growth and growth rate
For more information, log on to- http://shomusbiology.weebly.com/ Download the study materials here- http://shomusbiology.weebly.com/bio-materials.html Population growth is the change in a population over time, and can be quantified as the change in the number of individuals of any species in a population using "per unit time" for measurement. In biology, the term population growth is likely to refer to any known organism, but this article deals mostly with the application of the term to human populations in demography. Population growth rates might have declined, but in 2013 every 60 minutes there are another 8,000 people in the world: about 75 million every year.[1] In demography, population growth is used informally for the more specific term population growth rate (see below), and is... -

Pollution: Crash Course Ecology #11
Hank talks about the last major way humans are impacting the environment in this penultimate episode of Crash Course Ecology. Pollution takes many forms - from the simplest piece of litter to the more complex endocrine distruptors - and ultimately, humans are responsible for it all. Like Crash Course: http://www.facebook.com/YouTubeCrashCourse Follow Crash Course: http://www.twitter.com/TheCrashCourse T*mbl Crash Course: http://thecrashcourse.tumblr.com Table of Contents 1) Natural Compounds 01:12:1 a) Carbon 01:35 b) Nitrogen and Phosphorous 02:11:2 c) Cyanide 04:05 d) Mercury 05:15 e) Sulfur & Nitrogen Dioxide 05:58 2) Synthetic Compounds 06:51 a) Endocrine Disruptors 07:09 References for this episode can be found in the Google document here: http://dft.ba/-3wpP Support CrashCour... -

Ecological Succession: Change is Good - Crash Course Ecology #6
In the world of ecology, the only constant is change - but change can be good. Today Hank explains ecological succession and how ecological communities change over time to become beautiful, biodiverse mosaics. Like Crash Course on Facebook! http://www.facebook.com/YouTubeCrashCourse Follow Crash Course on Twitter! http://www.twitter.com/TheCrashCourse Table of Contents 1. Primary Succession 1:56:1 2. Secondary Succession 3:36 3. Climax Community Model 5:11 4. Intermediate Disturbance Hypothesis 7:25:1 References and image licenses for this episode can be found in the Google document here: http://dft.ba/-381q Support CrashCourse on Subbable: http://subbable.com/crashcourse
Ecology - Rules for Living on Earth: Crash Course Biology #40
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 10:26
- Updated: 29 Oct 2012
- views: 387205
- published: 29 Oct 2012
- views: 387205
Introduction to Ecology
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 4:47
- Updated: 18 Mar 2015
- views: 50693
- published: 18 Mar 2015
- views: 50693
Ecosystem Ecology
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 11:14
- Updated: 14 Sep 2015
- views: 16834
- published: 14 Sep 2015
- views: 16834
Population Ecology
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 12:10
- Updated: 01 Oct 2015
- views: 15207
- published: 01 Oct 2015
- views: 15207
Tyto Ecology | BUILDING OUR OWN ECOSYSTEM
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 24:11
- Updated: 15 Apr 2016
- views: 10789
- published: 15 Apr 2016
- views: 10789
Tyto Ecology | EVERYTHING'S DYING (Week 3)
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 26:47
- Updated: 30 Apr 2016
- views: 3618
- published: 30 Apr 2016
- views: 3618
Biology - The Science of Life - Ecology - Organisms in Their Environment
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 15:01
- Updated: 28 Aug 2013
- views: 58811
- published: 28 Aug 2013
- views: 58811
NATURAL SELECTION BY WRESTLING WITH TREES || TYTO: ECOLOGY - Episode #6
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 22:14
- Updated: 29 Apr 2016
- views: 127
- published: 29 Apr 2016
- views: 127
Ecology Introduction
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 4:07
- Updated: 05 Apr 2011
- views: 201955
Population Ecology: The Texas Mosquito Mystery - Crash Course Ecology #2
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 11:53
- Updated: 12 Nov 2012
- views: 407178
- published: 12 Nov 2012
- views: 407178
Ecosystem Ecology: Links in the Chain - Crash Course Ecology #7
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 10:10
- Updated: 18 Dec 2012
- views: 304484
- published: 18 Dec 2012
- views: 304484
Ecology is...
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 1:25
- Updated: 06 Jul 2009
- views: 135765
Greg Asner: Ecology from the air
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 13:51
- Updated: 19 Nov 2013
- views: 41143
- published: 19 Nov 2013
- views: 41143
Community Ecology: Feel the Love - Crash Course Ecology #4
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 11:30
- Updated: 26 Nov 2012
- views: 286495
- published: 26 Nov 2012
- views: 286495
Ecology Song
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 3:58
- Updated: 01 Sep 2014
- views: 49519
- published: 01 Sep 2014
- views: 49519
UPSC CSE (IAS): High Yield Series: Introduction to Environment and Ecology Part 1.1
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 20:30
- Updated: 06 Aug 2014
- views: 143934
- published: 06 Aug 2014
- views: 143934
FIRST FOX OF THE GRASSLANDS || TYTO: ECOLOGY - Episode #5
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 25:35
- Updated: 26 Apr 2016
- views: 760
- published: 26 Apr 2016
- views: 760
The History of Life on Earth - Crash Course Ecology #1
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 13:37
- Updated: 05 Nov 2012
- views: 713356
- published: 05 Nov 2012
- views: 713356
Conservation and Restoration Ecology: Crash Course Ecology #12
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 10:13
- Updated: 22 Jan 2013
- views: 150705
- published: 22 Jan 2013
- views: 150705
Ecology Part 1 - Basic Ecology
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 6:29
- Updated: 03 Jan 2013
- views: 16886
- published: 03 Jan 2013
- views: 16886
Population ecology part 1 population growth and growth rate
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 21:30
- Updated: 13 Nov 2013
- views: 9369
- published: 13 Nov 2013
- views: 9369
Pollution: Crash Course Ecology #11
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 9:22
- Updated: 14 Jan 2013
- views: 191603
- published: 14 Jan 2013
- views: 191603
Ecological Succession: Change is Good - Crash Course Ecology #6
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 10:02
- Updated: 11 Dec 2012
- views: 265886
- published: 11 Dec 2012
- views: 265886
-

Sky News Live
SUBSCRIBE to our YouTube channel for more great videos: http://www.youtube.com/skynews Follow us on Twitter: https://twitter.com/skynews and https://twitter.com/skynewsbreak Like us on Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/skynews For more great content go to http://news.sky.com and download our apps: iPad https://itunes.apple.com/gb/app/Sky-News-for-iPad/id422583124 iPhone https://itunes.apple.com/gb/app/sky-news/id316391924?mt=8 Android https://play.google.com/store/apps/details?id=com.bskyb.skynews.android&hl;=en_GB -

The Queen vs The President: "Boom" - BBC News
The Queen and Prince Harry have responded to Barack and Michelle Obama's Invictus Games challenge in a video posted on the Kensington Palace Twitter account. Subscribe to BBC News HERE http://bit.ly/1rbfUog Check out our website: http://www.bbc.com/news Facebook: http://www.facebook.com/bbcnews Twitter: http://www.twitter.com/bbcworld Instagram: http://instagram.com/bbcnews -

Khabardar Aftab Iqbal 28 April 2016 - خبردارآفتاب اقبال - Express News
Watch Khabardar Aftab Iqbal 28 April 2016 - خبردارآفتاب اقبال - Express News The famous journalist and TV anchor Aftab Iqbal has left Geo TV and Khabarnak, an Urdu and Punjabi comedy TV show. Now he can be seen on Express News with a new program Khabardaar. Aftab Iqbal is considered to be one of the top columnist. Lets see what new Aftab Iqbal brings with this show.. Watch , Enjoy and Subscribe to our channel for more. -

Facebook: US tops list of countries wanting access to your data (CNET News)
Watch more CNET News: http://bit.ly/1LGPOmk Social network's latest report on government requests shows a big leap in filings around the globe, and the US is in the lead. Subscribe to CNET: http://bit.ly/17qqqCs Watch more CNET videos: http://www.cnet.com/video Follow CNET on Twitter: http://twitter.com/CNET Follow CNET on Facebook: http://www.facebook.com/cnet -

36 Hours Later - Nintendo's E3, Zelda, & NX News Aftermath Discussion
It's been 36 hours since Nintendo dropped some bombs, and we decided to revisit the news, this time with Derrick in tow. We talk more about Nintendo's E3 plans, as well as NX, Zelda NX, and Zelda Wii U all coming next year. • If you want to listen to our first discussion: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=E8Lt-6JHh3Y • Support us on Patreon: https://www.patreon.com/GameXplain ...Facebook: http://www.facebook.com/gamexplain ...Twitter: http://twitter.com/GameXplain ...Instagram: https://www.instagram.com/gamexplain_official ...Ash's Twitter: https://twitter.com/AshPaulsen ...Derrick's Twitter: https://twitter.com/bitnerdgx ...Andre's Twitter https://twitter.com/andresegers -

Norway helicopter crash: 13 people missing - BBC News
A helicopter carrying at least 13 people has crashed in Norway near the city of Bergen. Local police say the aircraft which was carrying oil workers, crashed onto a small rocky island. No survivors have yet been found. We spoke to o Kyrre Styve from the Vestnytt newspaper who is near the scene. Subscribe to BBC News HERE http://bit.ly/1rbfUog Check out our website: http://www.bbc.com/news Facebook: http://www.facebook.com/bbcnews Twitter: http://www.twitter.com/bbcworld Instagram: http://instagram.com/bbcnews -

Netflix Orders The Punisher Series - IGN News
The Punisher -- as introduced in Daredevil: Season 2 -- is getting his own Netflix spinoff series. Read more here: http://www.ign.com/articles/2016/04/29/netflix-orders-the-punisher-series Subscribe to the IGN News Channel https://www.youtube.com/user/ignnews?sub_confirmation=1 ---------------------------------- Follow IGN for more! ---------------------------------- IGN OFFICIAL APP: http://www.ign.com/mobile FACEBOOK: https://www.facebook.com/ign TWITTER: https://twitter.com/ign INSTAGRAM: https://instagram.com/igndotcom/?hl=en WEBSITE: http://www.ign.com/ GOOGLE+: https://plus.google.com/+IGN -

Inside the Bernie Sanders campaign with the official photographer - BBC News
The Bernie Sanders campaign may be down this week, but ask any of his supporters and they'll tell you the Vermont Senator is far from out. Despite winning just one of the five states in Tuesday's primaries (Rhode Island), his largely young and fervently passionate backers say his message against economic inequality will resonate long after this race is over. Arun Chaudhary served as President Barack Obama's official videographer, and has been filming Mr Sanders and his supporters. The BBC caught up with him in New York for a behind-the-scenes look at capturing the campaign. Filmed by Ian Cartwright. Edited by Bill McKenna. Produced by Suzanne Kianpour. Subscribe to BBC News HERE http://bit.ly/1rbfUog Check out our website: http://www.bbc.com/news Facebook: http://www.facebook.com/bbc... -

Man Builds Homemade Hover Bike| ABC News
YouTuber and inventor Colin Furze debuts his fully-functioning DIY hover bike. SUBSCRIBE to ABC NEWS: https://www.youtube.com/ABCNews/ Watch More on http://abcnews.go.com/ LIKE ABC News on FACEBOOK https://www.facebook.com/abcnews FOLLOW ABC News on TWITTER: https://twitter.com/abc GOOD MORNING AMERICA'S HOMEPAGE: https://gma.yahoo.com/ -

Iron Man Director Discusses Potential Marvel Return - IGN News
Jungle Book helmer Jon Favreau - who directed the first two Iron Man movies - says a great superhero story would tempt him back Read more here: http://www.ign.com/articles/2016/04/29/iron-man-director-jon-favreau-discusses-potential-marvel-return ---------------------------------- Follow IGN for more! ---------------------------------- IGN OFFICIAL APP: http://www.ign.com/mobile FACEBOOK: https://www.facebook.com/ign TWITTER: https://twitter.com/ign INSTAGRAM: https://instagram.com/igndotcom/?hl=en WEBSITE: http://www.ign.com/ GOOGLE+: https://plus.google.com/+IGN -

Nintenday - Nintendo's Huge NX News Day Explained
E-Mail : tylermcvicker@yahoo.com Patreon : https://www.patreon.com/valvenewsnetwork Nintendo Network ID : valvenewsnetwor Today on Nintendo News Network, we discuss and explain the large amount of news released by Nintendo in a few different events yesterday. A lot of the information talked about has unfortunitly been squed through the internet's reations, and I am going to try to explain everything that happend. The NX, the new Zelda U, E3 2016, many people are wondering what Nintendo is doing, and hopefully we can find out. Sources : https://twitter.com/mochi_wsj https://www.nintendo.co.uk/News/2016/April/Nintendo-provides-updates-on-mobile-NX-and-The-Legend-of-Zelda-along-with-annual-earnings-1102529.html https://www.nintendo.co.jp/ir/pdf/2016/160428e.pdf https://www.nintendo.co.jp/i... -

04282016 年代新聞面對面 ERA FACE NEWS
-

The TED CRUZ PORN Nobody Asked For - Weekly Weird News
A recent episode of the Maury show revealed to the world a female Ted Cruz lookalike, and she's taking her 15 minutes to its logical next step: porn. --- Ted Cruz Porn: http://www.huffingtonpost.com/entry/ted-cruz-lookalike-porn_us_571aa703e4b0d4d3f7237467 30 yr old high school basketball player: http://windsorstar.com/news/local-news/border-officials-arrest-man-who-was-attending-windsor-high-school-as-a-teen High School names: http://kxan.com/2016/03/28/community-divided-over-changing-name-of-robert-e-lee-elementary/ Monopoly video: https://www.facebook.com/monopoly/videos/10153525225001517/ --- Visit our subreddit: http://reddit.com/r/etcshow Follow us on Twitter: http://twitter.com/EliotETC http://twitter.com/Rickyftw http://twitter.com/MachinimaETC -

Norway: Helicopter crashes near Bergen - BBC News
A helicopter has crashed near the Norwegian city of Bergen with at least 14 people on board, and there are reports of people in the sea. Rescue officials told local media that the helicopter had been "totally destroyed". Photos from the scene showed thick smoke coming from an area of rocky islets. Norwegian paper Aftonbladet reports that the helicopter was heading to the Brage oil field from Bergen. Subscribe to BBC News HERE http://bit.ly/1rbfUog Check out our website: http://www.bbc.com/news Facebook: http://www.facebook.com/bbcnews Twitter: http://www.twitter.com/bbcworld Instagram: http://instagram.com/bbcnews -

Wonder Kid Lakshmi Srija speech at TRS Plenary | Khammam | V6 News
Wonder Kid Lakshmi Srija speech at TRS Plenary meet held in Khammam. V6 IOS App ► https://goo.gl/EfEqlJ Download V6 Android App ► http://bit.ly/V6NewsAPP Subscribe at http://goo.gl/t2pFrq Visit our Website ► http://V6news.tv Twitter ► https://twitter.com/V6News Facebook ► http://www.facebook.com/V6News.tv Google+ ► https://plus.google.com/109903438943940210337 V6 News, Official YouTube V6 News Channel owned by VIL Media Pvt Ltd. V6 News, a 24 hour Telugu News Broadcaster, dedicated to report news across Telangana and other parts of the world through live reports, breaking news, sports updates, weather reports, entertainment, business trends, exclusive interviews, and current affairs. The channel airs programs like 'Teenmaar News,Telangana Yatra,Telangana Shakam,Rangeela,Top News,Taara,... -

CNN Student News - 04/29/16
The complicated war in Syria, a dive to the Marianas Trench, a proposed U.S. national mammal, and the most common noun in English are all part of today's show. -

Mads Mikkelsen Reveals Star Wars Rogue One Character
The Casino Royale and Hannibal star talks about his upcoming roles in Doctor Strange and Star Wars: Rogue One SUBSCRIBE to our YouTube channel for more videos: http://www.youtube.com/skynews Follow us on Twitter: https://twitter.com/skynews and https://twitter.com/skynewsbreak Like us on Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/skynews For more content go to http://news.sky.com and download our apps: iPad https://itunes.apple.com/gb/app/Sky-News-for-iPad/id422583124 iPhone https://itunes.apple.com/gb/app/sky-news/id316391924?mt=8 Android https://play.google.com/store/apps/details?id=com.bskyb.skynews.android&hl;=en_GB -

-

Top 10 Live News Reporting Fails
Watching the news is how many keep up with what is happening out there in the world, so it's too bad one cannot always rely on top notch reporting. These are the top 10 news reporting fails. Subscribe: http://bit.ly/1IPtQdq CHECK OUT MY MAIN CHANNEL- http://bit.ly/1Q7kPWb FOLLOW ME ON SOCIAL MEDIA INSTAGRAM- http://instagram.com/landonproductions FACEBOOK- https://www.facebook.com/pages/Landonproduction/268626033166262?ref=hl TWITTER- https://twitter.com/LandonYoutube VIDEO EDITED BY: Jesse O'Riordan: www.spacehouse.org -

What Will the Nintendo NX Be? (Nerdist News w/ Jessica Chobot)
We’ve heard rumors about the new Nintendo console, but we finally got a release date! But what should we expect? What will it do? Jessica figures it out on today's Nerdist News! Are you pumped to see what Nintendo has in store? Let us know in the comments below! Subscribe for more Nerdist News: http://nerdi.st/subscribe Watch the last episode at: http://nerdist.com/?p=395592 More on this story: http://nerdi.st/1TeCaZK More Nintendo: http://nerdist.com/tag/nintendo Watch more Nerdist News: http://bit.ly/1qvVVhV Follow Us: Facebook: https://facebook.com/nerdist Nerdist News https://twitter.com/NerdistNews Twitter https://twitter.com/Nerdist Instagram https://instagram.com/nerdist/ Jessica Chobot https://twitter.com/JessicaChobot Dan Casey https://twitter.com/osteoferocious Ma... -

Nerdist News LIVE! with Jessica Chobot (Open Beta Week)
Give us YOUR feedback on Nerdist News LIVE right here: https://www.surveymonkey.com/r/6NGKXYN Have you ever wondered how we choose which story to cover for Nerdist News? Which news gets cut or breaks at the very last second? How Jessica Chobot gets into the hosting zone? Well now, you get to join us behind the scenes of the Nerdist newsroom. Join our motley crew to talk down the day’s episode with Nerdist hosts, staff, and guests. Follow us! Nerdist - https://twitter.com/nerdist Jessica Chobot - https://twitter.com/JessicaChobot -

Wallace: Cruz taking big gamble to 'win one news cycle'
'Fox News Sunday' anchor weighs in on Republican presidential candidate's decision to name Carly Fiorina as running mate -

Jeremy Corbyn: No crisis in Labour after Livingstone's suspension - BBC News
Labour leader Jeremy Corbyn tells the BBC's deputy political editor John Pienaar there is "no crisis" over anti-Semitism in the Labour Party. He said any racism "will be rooted out" adding: "We have dealt with any case brought to my attention of any degree of intolerance in the party. The number of cases is very very small indeed." Subscribe to BBC News HERE http://bit.ly/1rbfUog Check out our website: http://www.bbc.com/news Facebook: http://www.facebook.com/bbcnews Twitter: http://www.twitter.com/bbcworld Instagram: http://instagram.com/bbcnews
Sky News Live
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 0:00
- Updated: 10 Aug 2015
- views: 21444896
- published: 10 Aug 2015
- views: 21444896
The Queen vs The President: "Boom" - BBC News
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 0:37
- Updated: 29 Apr 2016
- views: 98
- published: 29 Apr 2016
- views: 98
Khabardar Aftab Iqbal 28 April 2016 - خبردارآفتاب اقبال - Express News
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 36:17
- Updated: 28 Apr 2016
- views: 172
- published: 28 Apr 2016
- views: 172
Facebook: US tops list of countries wanting access to your data (CNET News)
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 1:32
- Updated: 29 Apr 2016
- views: 413
- published: 29 Apr 2016
- views: 413
36 Hours Later - Nintendo's E3, Zelda, & NX News Aftermath Discussion
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 30:06
- Updated: 28 Apr 2016
- views: 25863
- published: 28 Apr 2016
- views: 25863
Norway helicopter crash: 13 people missing - BBC News
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 3:04
- Updated: 29 Apr 2016
- views: 100
- published: 29 Apr 2016
- views: 100
Netflix Orders The Punisher Series - IGN News
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 0:46
- Updated: 29 Apr 2016
- views: 3699
- published: 29 Apr 2016
- views: 3699
Inside the Bernie Sanders campaign with the official photographer - BBC News
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 2:04
- Updated: 29 Apr 2016
- views: 400
- published: 29 Apr 2016
- views: 400
Man Builds Homemade Hover Bike| ABC News
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 3:03
- Updated: 29 Apr 2016
- views: 176
- published: 29 Apr 2016
- views: 176
Iron Man Director Discusses Potential Marvel Return - IGN News
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 1:22
- Updated: 29 Apr 2016
- views: 720
- published: 29 Apr 2016
- views: 720
Nintenday - Nintendo's Huge NX News Day Explained
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 8:27
- Updated: 28 Apr 2016
- views: 4634
- published: 28 Apr 2016
- views: 4634
04282016 年代新聞面對面 ERA FACE NEWS
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 89:30
- Updated: 28 Apr 2016
- views: 169
- published: 28 Apr 2016
- views: 169
The TED CRUZ PORN Nobody Asked For - Weekly Weird News
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 33:36
- Updated: 29 Apr 2016
- views: 14918
- published: 29 Apr 2016
- views: 14918
Norway: Helicopter crashes near Bergen - BBC News
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 0:47
- Updated: 29 Apr 2016
- views: 91
- published: 29 Apr 2016
- views: 91
Wonder Kid Lakshmi Srija speech at TRS Plenary | Khammam | V6 News
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 5:08
- Updated: 27 Apr 2016
- views: 301
- published: 27 Apr 2016
- views: 301
CNN Student News - 04/29/16
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 10:01
- Updated: 28 Apr 2016
- views: 390
- published: 28 Apr 2016
- views: 390
Mads Mikkelsen Reveals Star Wars Rogue One Character
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 5:41
- Updated: 28 Apr 2016
- views: 220
- published: 28 Apr 2016
- views: 220
More bad news for the American economy
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 2:43
- Updated: 29 Apr 2016
- views: 1
Top 10 Live News Reporting Fails
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 8:48
- Updated: 22 Jan 2016
- views: 5324976
- published: 22 Jan 2016
- views: 5324976
What Will the Nintendo NX Be? (Nerdist News w/ Jessica Chobot)
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 6:28
- Updated: 27 Apr 2016
- views: 2120
- published: 27 Apr 2016
- views: 2120
Nerdist News LIVE! with Jessica Chobot (Open Beta Week)
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 24:17
- Updated: 30 Apr 2016
- views: 1685
- published: 30 Apr 2016
- views: 1685
Wallace: Cruz taking big gamble to 'win one news cycle'
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 5:08
- Updated: 28 Apr 2016
- views: 480
- published: 28 Apr 2016
- views: 480
Jeremy Corbyn: No crisis in Labour after Livingstone's suspension - BBC News
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 2:30
- Updated: 28 Apr 2016
- views: 333
- published: 28 Apr 2016
- views: 333
- Playlist
- Chat
- Playlist
- Chat

Ecology - Rules for Living on Earth: Crash Course Biology #40
- Report rights infringement
- published: 29 Oct 2012
- views: 387205

Introduction to Ecology
- Report rights infringement
- published: 18 Mar 2015
- views: 50693

Ecosystem Ecology
- Report rights infringement
- published: 14 Sep 2015
- views: 16834

Population Ecology
- Report rights infringement
- published: 01 Oct 2015
- views: 15207

Tyto Ecology | BUILDING OUR OWN ECOSYSTEM
- Report rights infringement
- published: 15 Apr 2016
- views: 10789

Tyto Ecology | EVERYTHING'S DYING (Week 3)
- Report rights infringement
- published: 30 Apr 2016
- views: 3618

Biology - The Science of Life - Ecology - Organisms in Their Environment
- Report rights infringement
- published: 28 Aug 2013
- views: 58811

NATURAL SELECTION BY WRESTLING WITH TREES || TYTO: ECOLOGY - Episode #6
- Report rights infringement
- published: 29 Apr 2016
- views: 127

Ecology Introduction
- Report rights infringement
- published: 05 Apr 2011
- views: 201955

Population Ecology: The Texas Mosquito Mystery - Crash Course Ecology #2
- Report rights infringement
- published: 12 Nov 2012
- views: 407178

Ecosystem Ecology: Links in the Chain - Crash Course Ecology #7
- Report rights infringement
- published: 18 Dec 2012
- views: 304484

Ecology is...
- Report rights infringement
- published: 06 Jul 2009
- views: 135765

Greg Asner: Ecology from the air
- Report rights infringement
- published: 19 Nov 2013
- views: 41143

Community Ecology: Feel the Love - Crash Course Ecology #4
- Report rights infringement
- published: 26 Nov 2012
- views: 286495
- Playlist
- Chat

Sky News Live
- Report rights infringement
- published: 10 Aug 2015
- views: 21444896

The Queen vs The President: "Boom" - BBC News
- Report rights infringement
- published: 29 Apr 2016
- views: 98

Khabardar Aftab Iqbal 28 April 2016 - خبردارآفتاب اقبال - Express News
- Report rights infringement
- published: 28 Apr 2016
- views: 172

Facebook: US tops list of countries wanting access to your data (CNET News)
- Report rights infringement
- published: 29 Apr 2016
- views: 413

36 Hours Later - Nintendo's E3, Zelda, & NX News Aftermath Discussion
- Report rights infringement
- published: 28 Apr 2016
- views: 25863

Norway helicopter crash: 13 people missing - BBC News
- Report rights infringement
- published: 29 Apr 2016
- views: 100

Netflix Orders The Punisher Series - IGN News
- Report rights infringement
- published: 29 Apr 2016
- views: 3699

Inside the Bernie Sanders campaign with the official photographer - BBC News
- Report rights infringement
- published: 29 Apr 2016
- views: 400

Man Builds Homemade Hover Bike| ABC News
- Report rights infringement
- published: 29 Apr 2016
- views: 176

Iron Man Director Discusses Potential Marvel Return - IGN News
- Report rights infringement
- published: 29 Apr 2016
- views: 720

Nintenday - Nintendo's Huge NX News Day Explained
- Report rights infringement
- published: 28 Apr 2016
- views: 4634

04282016 年代新聞面對面 ERA FACE NEWS
- Report rights infringement
- published: 28 Apr 2016
- views: 169

The TED CRUZ PORN Nobody Asked For - Weekly Weird News
- Report rights infringement
- published: 29 Apr 2016
- views: 14918

Norway: Helicopter crashes near Bergen - BBC News
- Report rights infringement
- published: 29 Apr 2016
- views: 91
Gerson Galvez: Peruvian drug lord deported from Colombia
Edit BBC News 02 May 2016Dark Energy Has Not Changed In Billions Of Years
Edit IFL Science 01 May 2016Bowe Bergdahl's defense wins battle over classified documents
Edit CNN 01 May 2016Anti-immigrant party says Muslims not welcome in Germany
Edit Dawn 01 May 2016US once again forced to turn to Russia for help on Syria
Edit Deseret News 01 May 2016ABC News Sunday (WA) 1/5/2016
Edit Australian Broadcasting Corporation 02 May 2016‘Well-maintained’ and ‘rejuvenated’ lakes fare no better
Edit The Hindu 02 May 2016Join the News at candidate forum
Edit Clarion Ledger 02 May 2016Click to watch SLBC news 29th April 2016
Edit SLBC 02 May 2016ONE News and Stuff in video collaboration
Edit Scoop 02 May 2016Fight Breaks Out Between Fox News Host, HuffPost Reporter at White House Correspondents Dinner
Edit Breitbart 02 May 2016Vector Network News for the week ending 1 May 2016 (Vector Limited)
Edit Public Technologies 02 May 2016Company News Company News for May 2
Edit Richmond Times Dispatch 02 May 2016Marine Who Was Target Of Violent Assault Gets Bad News
Edit Opposing Views 02 May 2016Chennai floods a result of urban governance collapse, says expert
Edit The Hindu 02 May 2016- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- Next page »







