- published: 13 May 2013
- views: 5624
-
remove the playlistPolyhedron
- remove the playlistPolyhedron
- published: 12 May 2012
- views: 24219
- published: 18 Mar 2012
- views: 19809
- published: 06 Mar 2014
- views: 5232
- published: 30 Jan 2012
- views: 6035
- published: 05 Jul 2013
- views: 5334
- published: 05 Nov 2012
- views: 3428
- published: 21 Nov 2012
- views: 6030
- published: 22 May 2014
- views: 8508

Polyhedron
In elementary geometry, a polyhedron (plural polyhedra or polyhedrons) is a solid in three dimensions with flat polygonal faces, straight edges and sharp corners or vertices. The word polyhedron comes from the Classical Greek πολύεδρον, as poly- (stem of πολύς, "many") + -hedron (form of ἕδρα, "base" or "seat").
Cubes and pyramids are examples of polyhedra.
A polyhedron is said to be convex if its surface (comprising its faces, edges and vertices) does not intersect itself and the line segment joining any two points of the polyhedron is contained in the interior or surface.
A polyhedron is a 3-dimensional example of the more general polytope in any number of dimensions.
Basis for definition
In elementary geometry, the faces are polygons – regions of planes – meeting in pairs along their edges which are straight-line segments, and with the edges meeting in vertex points. Treating a polyhedron as a solid bounded by flat faces and straight edges is not very precise, for example it is difficult to reconcile with star polyhedra. Grünbaum (1994, p. 43) observed, "The Original Sin in the theory of polyhedra goes back to Euclid, and through Kepler, Poinsot, Cauchy and many others ... [in that] at each stage ... the writers failed to define what are the 'polyhedra' ...." Many definitions of "polyhedron" have been given within particular contexts, some more rigorous than others. For example definitions based on the idea of a bounding surface rather than a solid are common. However such definitions are not always compatible in other mathematical contexts.
This article is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported License, which means that you can copy and modify it as long as the entire work (including additions) remains under this license.
- Loading...

-
 4:34
4:34Polyhedrons: Lesson (Basic Geometry Concepts)
Polyhedrons: Lesson (Basic Geometry Concepts)Polyhedrons: Lesson (Basic Geometry Concepts)
Discover more at www.ck12.org: http://www.ck12.org/geometry/Polyhedrons/ Here you'll learn what a polyhedron is and the parts of a polyhedron. You'll then use these parts in a formula called Euler's Theorem. This video provides the student with a walkthrough on polyhedrons. This is part of CK-12’s Basic Geometry: Surface Area and Volume. See more at: 1. Polyhedrons: http://www.ck12.org/geometry/Polyhedrons/ 2. Cross-Sections and Nets: http://www.ck12.org/geometry/Cross-Sections-and-Nets/ 3. Prisms: http://www.ck12.org/geometry/Prisms/ 4. Cylinders: http://www.ck12.org/geometry/Cylinders/ 5. Pyramids: http://www.ck12.org/geometry/Pyramids/ 6. Cones: http://www.ck12.org/geometry/Cones/ 7. Spheres: http://www.ck12.org/geometry/Spheres/ 8. Composite Solids: http://www.ck12.org/geometry/Composite-Solids/ 9. Area and Volume of Similar Solids: http://www.ck12.org/geometry/Area-and-Volume-of-Similar-Solids/ Watch the whole series of CK-12's Basic Geometry videos: https://www.youtube.com/playlist?list=PLhWx3LZhlpseSm7selpF8lEq_jtiOqpDX -
 7:09
7:09how to make a polyhedron
how to make a polyhedronhow to make a polyhedron
in this video you will learn how to make a polyhedron ball with detailed instructions. -
 5:34
5:34Little Jinder - Polyhedron (SUPRA1 Remix)
Little Jinder - Polyhedron (SUPRA1 Remix)Little Jinder - Polyhedron (SUPRA1 Remix)
SUPRA1 Remix! -
 12:39
12:39Modular Origami - Polyhedron
Modular Origami - PolyhedronModular Origami - Polyhedron
How to make a modular origami Difficulty level: ★★★☆☆ My paper:15.0cm×15.0cm / 7.5cm×15.0cm japanese paper Modular origami Modular origami or unit origami is a paperfolding technique which uses two or more sheets of paper to create a larger and more complex structure than would not be possible using single-piece origami techniques. Each individual sheet of paper is folded into a module, or unit, and then modules are assembled into an integrated flat shape or three-dimensional structure by inserting flaps into pockets created by the folding process. These insertions create tension or friction that holds the model together. From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia -
 6:28
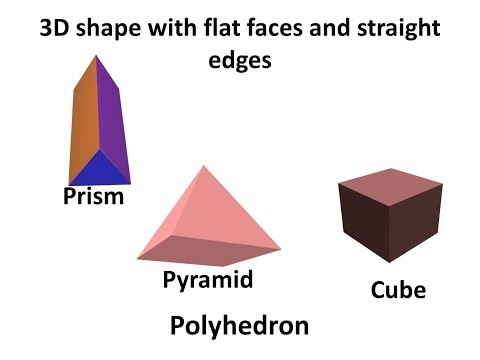
6:28Maths - What is a Polyhedron - Regular and Irregular polyhedron - English
Maths - What is a Polyhedron - Regular and Irregular polyhedron - EnglishMaths - What is a Polyhedron - Regular and Irregular polyhedron - English
Hello, BodhaGuru Learning proudly presents an animated video in English which 3D or solid shapes. It clears the concept of polyhedron and states the difference between polygon and polyhedron. It shows classification of polyhedron and explains about regular and irregular polyhedron. About us: We are a social enterprise working on a mission to make school learning interesting, relevant and affordable to every child on this planet. You can watch our FREE online videos at http://www.bodhaguru.com/watch and download our practice application/games - just visit http://www.bodhaguru.com/play If you like our videos, subscribe to our channel http://www.youtube.com/user/BodhaGuruLearning. Feel free to connect with us at http://www.facebook.com/BodhaGuru OR http://twitter.com/Bodhaguru Have fun, while you learn. Thanks for watching -- Team BodhaGuru -
 60:30
60:30Mod-01 Lec-05 Convex sets, dimension of a polyhedron, Faces, Example of a polytope.
Mod-01 Lec-05 Convex sets, dimension of a polyhedron, Faces, Example of a polytope.Mod-01 Lec-05 Convex sets, dimension of a polyhedron, Faces, Example of a polytope.
Linear programming and Extensions by Prof. Prabha Sharma, Department of Mathematics and Statistics, IIT Kanpur For more details on NPTEL visit http://nptel.iitm.ac.in -
 4:15
4:15Euler's Polyhedral Formula
Euler's Polyhedral FormulaEuler's Polyhedral Formula
Mathematics education video by Sam Kamperis, PhD Student in Mathematics Department of Mechanical Engineering and Mathematical Sciences Oxford Brookes University All animations made in Mathematica. Audio Recording: Pat Cheeseman Audio Editing: Anirudh Parthasarathy -
 1:26
1:26The Difference Between a Polyhedron & a Polygon : Math Questions
The Difference Between a Polyhedron & a Polygon : Math QuestionsThe Difference Between a Polyhedron & a Polygon : Math Questions
Subscribe Now: http://www.youtube.com/subscription_center?add_user=Ehow Watch More: http://www.youtube.com/Ehow A polyhedron and a polygon are two similar, yet different, shapes. Find out the difference between polyhedron and polygon with help from a high school mathematics tutor in this free video clip. Expert: Charlie Kasov Filmmaker: Victor Varnado Series Description: Though some more advanced mathematics topics may seem difficult at first, you will soon find out that everything has a purpose and you had nothing to worry about. Get tips on math and find out answers to all of your burning mathematics questions with help from a high school mathematics tutor in this free video series. -
 2:56
2:56Make polyhedron with M+!
Make polyhedron with M+!Make polyhedron with M+!
This video shows you how to make a dodecahedron or other types of polyhedra using an site called M+. With this fantastic kit, students create Platonic bodies, prisms and semi-regular polyhedrons. A total of 16 different types in any size! The parts can fixed together to form great polyhedrons for the classroom, or they can be disassembled for reuse. -
 4:46
4:46Mathematical Impressions: Goldberg Polyhedra
Mathematical Impressions: Goldberg PolyhedraMathematical Impressions: Goldberg Polyhedra
Because of their aesthetic appeal, organic feel and easily understood structure, Goldberg polyhedra have a surprising number of applications ranging from golf-ball dimple patterns to nuclear-particle detector arrays. http://www.simonsfoundation.org/multimedia/mathematical-impressions-goldberg-polyhedra/
-

Polyhedrons: Lesson (Basic Geometry Concepts)
Discover more at www.ck12.org: http://www.ck12.org/geometry/Polyhedrons/ Here you'll learn what a polyhedron is and the parts of a polyhedron. You'll then use these parts in a formula called Euler's Theorem. This video provides the student with a walkthrough on polyhedrons. This is part of CK-12’s Basic Geometry: Surface Area and Volume. See more at: 1. Polyhedrons: http://www.ck12.org/geometry/Polyhedrons/ 2. Cross-Sections and Nets: http://www.ck12.org/geometry/Cross-Sections-and-Nets/ 3. Prisms: http://www.ck12.org/geometry/Prisms/ 4. Cylinders: http://www.ck12.org/geometry/Cylinders/ 5. Pyramids: http://www.ck12.org/geometry/Pyramids/ 6. Cones: http://www.ck12.org/geometry/Cones/ 7. Spheres: http://www.ck12.org/geometry/Spheres/ 8. Composite Solids: http://www.ck12.org/geo...
published: 13 May 2013 -

how to make a polyhedron
in this video you will learn how to make a polyhedron ball with detailed instructions.
published: 12 May 2012 -

-

Modular Origami - Polyhedron
How to make a modular origami Difficulty level: ★★★☆☆ My paper:15.0cm×15.0cm / 7.5cm×15.0cm japanese paper Modular origami Modular origami or unit origami is a paperfolding technique which uses two or more sheets of paper to create a larger and more complex structure than would not be possible using single-piece origami techniques. Each individual sheet of paper is folded into a module, or unit, and then modules are assembled into an integrated flat shape or three-dimensional structure by inserting flaps into pockets created by the folding process. These insertions create tension or friction that holds the model together. From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
published: 18 Mar 2012 -

Maths - What is a Polyhedron - Regular and Irregular polyhedron - English
Hello, BodhaGuru Learning proudly presents an animated video in English which 3D or solid shapes. It clears the concept of polyhedron and states the difference between polygon and polyhedron. It shows classification of polyhedron and explains about regular and irregular polyhedron. About us: We are a social enterprise working on a mission to make school learning interesting, relevant and affordable to every child on this planet. You can watch our FREE online videos at http://www.bodhaguru.com/watch and download our practice application/games - just visit http://www.bodhaguru.com/play If you like our videos, subscribe to our channel http://www.youtube.com/user/BodhaGuruLearning. Feel free to connect with us at http://www.facebook.com/BodhaGuru OR http://twitter.com/Bodhaguru Have fun, ...
published: 06 Mar 2014 -
Mod-01 Lec-05 Convex sets, dimension of a polyhedron, Faces, Example of a polytope.
Linear programming and Extensions by Prof. Prabha Sharma, Department of Mathematics and Statistics, IIT Kanpur For more details on NPTEL visit http://nptel.iitm.ac.in
published: 30 Jan 2012 -

Euler's Polyhedral Formula
Mathematics education video by Sam Kamperis, PhD Student in Mathematics Department of Mechanical Engineering and Mathematical Sciences Oxford Brookes University All animations made in Mathematica. Audio Recording: Pat Cheeseman Audio Editing: Anirudh Parthasarathy
published: 05 Jul 2013 -

The Difference Between a Polyhedron & a Polygon : Math Questions
Subscribe Now: http://www.youtube.com/subscription_center?add_user=Ehow Watch More: http://www.youtube.com/Ehow A polyhedron and a polygon are two similar, yet different, shapes. Find out the difference between polyhedron and polygon with help from a high school mathematics tutor in this free video clip. Expert: Charlie Kasov Filmmaker: Victor Varnado Series Description: Though some more advanced mathematics topics may seem difficult at first, you will soon find out that everything has a purpose and you had nothing to worry about. Get tips on math and find out answers to all of your burning mathematics questions with help from a high school mathematics tutor in this free video series.
published: 05 Nov 2012 -

Make polyhedron with M+!
This video shows you how to make a dodecahedron or other types of polyhedra using an site called M+. With this fantastic kit, students create Platonic bodies, prisms and semi-regular polyhedrons. A total of 16 different types in any size! The parts can fixed together to form great polyhedrons for the classroom, or they can be disassembled for reuse.
published: 21 Nov 2012 -

Mathematical Impressions: Goldberg Polyhedra
Because of their aesthetic appeal, organic feel and easily understood structure, Goldberg polyhedra have a surprising number of applications ranging from golf-ball dimple patterns to nuclear-particle detector arrays. http://www.simonsfoundation.org/multimedia/mathematical-impressions-goldberg-polyhedra/
published: 22 May 2014
Polyhedrons: Lesson (Basic Geometry Concepts)
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 4:34
- Updated: 13 May 2013
- views: 5624
- published: 13 May 2013
- views: 5624
how to make a polyhedron
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 7:09
- Updated: 12 May 2012
- views: 24219
- published: 12 May 2012
- views: 24219
Little Jinder - Polyhedron (SUPRA1 Remix)
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 5:34
- Updated: 24 Jan 2009
- views: 229251
Modular Origami - Polyhedron
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 12:39
- Updated: 18 Mar 2012
- views: 19809
- published: 18 Mar 2012
- views: 19809
Maths - What is a Polyhedron - Regular and Irregular polyhedron - English
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 6:28
- Updated: 06 Mar 2014
- views: 5232
- published: 06 Mar 2014
- views: 5232
Mod-01 Lec-05 Convex sets, dimension of a polyhedron, Faces, Example of a polytope.
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 60:30
- Updated: 30 Jan 2012
- views: 6035
- published: 30 Jan 2012
- views: 6035
Euler's Polyhedral Formula
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 4:15
- Updated: 05 Jul 2013
- views: 5334
- published: 05 Jul 2013
- views: 5334
The Difference Between a Polyhedron & a Polygon : Math Questions
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 1:26
- Updated: 05 Nov 2012
- views: 3428
- published: 05 Nov 2012
- views: 3428
Make polyhedron with M+!
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 2:56
- Updated: 21 Nov 2012
- views: 6030
- published: 21 Nov 2012
- views: 6030
Mathematical Impressions: Goldberg Polyhedra
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 4:46
- Updated: 22 May 2014
- views: 8508
- published: 22 May 2014
- views: 8508
- Playlist
- Chat
- Playlist
- Chat

Polyhedrons: Lesson (Basic Geometry Concepts)
- Report rights infringement
- published: 13 May 2013
- views: 5624

how to make a polyhedron
- Report rights infringement
- published: 12 May 2012
- views: 24219

Little Jinder - Polyhedron (SUPRA1 Remix)
- Report rights infringement
- published: 24 Jan 2009
- views: 229251

Modular Origami - Polyhedron
- Report rights infringement
- published: 18 Mar 2012
- views: 19809

Maths - What is a Polyhedron - Regular and Irregular polyhedron - English
- Report rights infringement
- published: 06 Mar 2014
- views: 5232
Mod-01 Lec-05 Convex sets, dimension of a polyhedron, Faces, Example of a polytope.
- Report rights infringement
- published: 30 Jan 2012
- views: 6035

Euler's Polyhedral Formula
- Report rights infringement
- published: 05 Jul 2013
- views: 5334

The Difference Between a Polyhedron & a Polygon : Math Questions
- Report rights infringement
- published: 05 Nov 2012
- views: 3428

Make polyhedron with M+!
- Report rights infringement
- published: 21 Nov 2012
- views: 6030

Mathematical Impressions: Goldberg Polyhedra
- Report rights infringement
- published: 22 May 2014
- views: 8508
Chinese Company Unveils Plan To Build Reusable Space Plane
Edit WorldNews.com 05 Oct 2016NSA contractor arrested for alleged theft of top secret classified information
Edit The Guardian 05 Oct 2016Two Belgian police officers stabbed in Brussels
Edit Press TV 05 Oct 2016Smoking Damages Your DNA for Decades
Edit Mercola 05 Oct 2016National Gallery of Art's East Building review – a new view of America
Edit The Guardian 03 Oct 2016Kamehameha the Great
Edit Arkansas Online 11 Sep 2016Bulls Notebook: USFSM math instructor to present research (University of South Florida - Sarasota-Manatee)
Edit Public Technologies 26 Aug 2016Tight squeeze: The secrets behind Japan's coolest micro homes
Edit CNN 22 Aug 2016The 17 equations that changed the course of history
Edit The Independent 14 Aug 2016Journey back in time to King Kamehameha’s Hawaii
Edit Boston Herald 14 Aug 2016Finding a king on Hawaii's Big Island
Edit Stars and Stripes 12 Aug 2016Finding a king on Hawii's Big Island
Edit Stars and Stripes 11 Aug 2016Finding King Kamehameha: Charting a path to greatness
Edit The Miami Herald 08 Aug 2016500-year-old Albrecht Dürer engraving found in French flea market
Edit The Guardian 05 Aug 2016Biggest Little Self-Assembling Protein Nanostructures Created (DARPA - Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency)
Edit Public Technologies 22 Jul 2016Researchers improve catalyst efficiency for clean industries (The University of New Mexico)
Edit Public Technologies 07 Jul 2016Researchers improve catalyst efficiency for clean industries (Washington State University)
Edit Public Technologies 07 Jul 2016- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- Next page »








