- published: 26 Feb 2013
- views: 221695
-
remove the playlistTheorem
- remove the playlistTheorem
- published: 24 Sep 2013
- views: 667706
- published: 09 Aug 2010
- views: 708248
- published: 02 Jun 2012
- views: 232969
- published: 25 Nov 2013
- views: 14350
- published: 27 Jan 2014
- views: 2849877
- published: 25 Sep 2015
- views: 317199
- published: 30 Apr 2015
- views: 146945
- published: 09 Jul 2014
- views: 391723
- published: 23 Sep 2015
- views: 23317

In mathematics, a theorem is a statement that has been proven on the basis of previously established statements, such as other theorems, and previously accepted statements, such as axioms. The derivation of a theorem is often interpreted as a proof of the truth of the resulting expression, but different deductive systems can yield other interpretations, depending on the meanings of the derivation rules. The proof of a mathematical theorem is a logical argument demonstrating that the conclusions are a necessary consequence of the hypotheses, in the sense that if the hypotheses are true then the conclusions must also be true, without any further assumptions. The concept of a theorem is therefore fundamentally deductive, in contrast to the notion of a scientific theory, which is empirical.
This article is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported License, which means that you can copy and modify it as long as the entire work (including additions) remains under this license.
- Loading...

-
 13:22
13:22Algebra - Pythagorean Theorem
Algebra - Pythagorean TheoremAlgebra - Pythagorean Theorem
Sure, technically it's a Geometry topic, but why not learn about it in Algebra? Don't be lured into a false sense of security, there may be problems on this video that you may not be able to do! Check out my tie. YAY MATH! Visit yaymath.org Videos copyright (c) Yay Math -
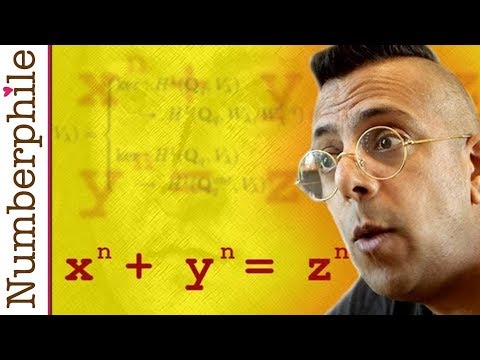 9:31
9:31Fermat's Last Theorem - Numberphile
Fermat's Last Theorem - NumberphileFermat's Last Theorem - Numberphile
Simon Singh on Fermat's Last Theorem. Simpsons book: http://amzn.to/1fKe4Yo Fermat book: http://amzn.to/1jWqMTa EXTRA FOOTAGE: http://youtu.be/FXbsIbRVios FERMAT IN SIMPSONS:http://youtu.be/ReOQ300AcSU Buy Numberphile papers on Ebay (including from this video): http://bit.ly/brownpapers Wiles' proof: http://bit.ly/FermatProof Website: http://www.numberphile.com/ Numberphile on Facebook: http://www.facebook.com/numberphile Numberphile tweets: https://twitter.com/numberphile Google Plus: http://bit.ly/numberGplus Tumblr: http://numberphile.tumblr.com Videos by Brady Haran A run-down of Brady's channels: http://bit.ly/bradychannels Simon Singh's website: http://simonsingh.net/ -
 10:46
10:46The Pythagorean theorem intro | Right triangles and trigonometry | Geometry | Khan Academy
The Pythagorean theorem intro | Right triangles and trigonometry | Geometry | Khan AcademyThe Pythagorean theorem intro | Right triangles and trigonometry | Geometry | Khan Academy
Introduction to the Pythagorean Theorem Practice this lesson yourself on KhanAcademy.org right now: https://www.khanacademy.org/math/geometry/right_triangles_topic/pyth_theor/e/pythagorean_theorem_1?utm_source=YT&utm;_medium=Desc&utm;_campaign=Geometry Watch the next lesson: https://www.khanacademy.org/math/geometry/right_triangles_topic/pyth_theor/v/pythagorean-theorem-1?utm_source=YT&utm;_medium=Desc&utm;_campaign=Geometry Missed the previous lesson? https://www.khanacademy.org/math/geometry/right_triangles_topic/pyth_theor/v/pythagorean-theorem?utm_source=YT&utm;_medium=Desc&utm;_campaign=Geometry Geometry on Khan Academy: We are surrounded by space. And that space contains lots of things. And these things have shapes. In geometry we are concerned with the nature of these shapes, how we define them, and what they teach us about the world at large--from math to architecture to biology to astronomy (and everything in between). Learning geometry is about more than just taking your medicine ("It's good for you!"), it's at the core of everything that exists--including you. Having said all that, some of the specific topics we'll cover include angles, intersecting lines, right triangles, perimeter, area, volume, circles, triangles, quadrilaterals, analytic geometry, and geometric constructions. Wow. That's a lot. To summarize: it's difficult to imagine any area of math that is more widely used than geometry. About Khan Academy: Khan Academy offers practice exercises, instructional videos, and a personalized learning dashboard that empower learners to study at their own pace in and outside of the classroom. We tackle math, science, computer programming, history, art history, economics, and more. Our math missions guide learners from kindergarten to calculus using state-of-the-art, adaptive technology that identifies strengths and learning gaps. We've also partnered with institutions like NASA, The Museum of Modern Art, The California Academy of Sciences, and MIT to offer specialized content. For free. For everyone. Forever. #YouCanLearnAnything Subscribe to Khan Academy’s Geometry channel: https://www.youtube.com/channel/UCD3OtKxPRUFw8kzYlhJXa1Q?sub_confirmation=1 Subscribe to Khan Academy: https://www.youtube.com/subscription_center?add_user=khanacademy -
 8:43
8:43Theorem - Ring
Theorem - Ring -
 20:02
20:02Circle Theorems - GCSE Maths Higher
Circle Theorems - GCSE Maths HigherCircle Theorems - GCSE Maths Higher
This video is a tutorial on Circle Theorems. Please make yourself a revision card while watching this and attempt my examples. Straight away then move to my video on Circle Theorems 2 - Exam Questions 14. This video is for students attempting the Higher paper AQA Unit 3 Maths GCSE, who have previously sat the foundation paper. Explanations are aimed at being as simple as possible and so students who previously did the Foundation paper can access. They would also be useful for students who have always sat the higher paper. www.hegartymaths.com http://www.hegartymaths.com/ -
 13:42
13:42Triangle Congruence Theorems - SSS, SAS, ASA, AAS
Triangle Congruence Theorems - SSS, SAS, ASA, AASTriangle Congruence Theorems - SSS, SAS, ASA, AAS
Definition and examples for the four triangle congruence postulates and theorems -
 2:27
2:27The Zero Theorem - Official Trailer (2014)
The Zero Theorem - Official Trailer (2014)The Zero Theorem - Official Trailer (2014)
Subscribe to Voltage Pictures for all our latest releases: http://bit.ly/1kjjbOy Visit the official site: http://www.thezerotheorem-movie.com Like on Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/TheZeroTheorem Follow on Twitter: http://www.twitter.com/TheZeroTheorem_ Purchase the soundtrack: http://bit.ly/1kgDM8u An eccentric and reclusive computer genius plagued with existential angst works on a mysterious project aimed at discovering the purpose of existence - or the lack thereof -once and for all. However, it is only once he experiences the power of love and desire that he is able to understand his very reason for being. Director: Terry Gilliam Writer: Pat Rushin Cast: Christoph Waltz, David Thewlis, Melanie thierry, Lucas Hedges, Ben Whishaw, Peter Stormare, and Tilda Swinton. -
 9:31
9:31Fold and Cut Theorem - Numberphile
Fold and Cut Theorem - NumberphileFold and Cut Theorem - Numberphile
Lynda free trial (try the typography stuff!!): http://www.lynda.com/numberphile Katie Steckles discusses the Fold and Cut Theorem - from A to Z. Katie: http://www.katiesteckles.co.uk More on the topic: http://erikdemaine.org/foldcut/ NUMBERPHILE Website: http://www.numberphile.com/ Numberphile on Facebook: http://www.facebook.com/numberphile Numberphile tweets: https://twitter.com/numberphile Numberphile is supported by the Mathematical Sciences Research Institute (MSRI): http://bit.ly/MSRINumberphile Videos by Brady Haran Support us on Patreon: http://www.patreon.com/numberphile Brady's videos subreddit: http://www.reddit.com/r/BradyHaran/ A run-down of Brady's channels: http://www.bradyharan.com Sign up for (occasional) emails: http://eepurl.com/YdjL9 -
 20:07
20:07The Futurama Theorem
The Futurama TheoremThe Futurama Theorem
The Futurama episode The Prisoner of Benda features a machine that allows two people to switch minds. The problem is that two bodies can only switch minds once. Fry and Co. goes wild on the mind switching machine and have to resort to some serious math to get back into their own bodies. Our mission in this video is to give a crystal clear explanation of the Futurama theorem. As an added bonus there is also some Stargate mind switching action towards the end of the video. (added 15 August 2015) We just posted a follow up video: https://youtu.be/w0mxdo5ur_A Enjoy! Burkard Polster and Giuseppe Geracitano -
 15:26
15:26Fundamental Theorem of Algebra - Numberphile
Fundamental Theorem of Algebra - NumberphileFundamental Theorem of Algebra - Numberphile
Part one on odd polynomials: http://youtu.be/8l-La9HEUIU A nice extra bit about complex numbers: http://youtu.be/-IJuqR6nz_Q Professor David Eisenbud is an algebraic geometer (and director of the Mathematical Sciences Research Institute at Berkeley) Hello Internet: http://www.hellointernet.fm Website: http://www.numberphile.com/ Numberphile on Facebook: http://www.facebook.com/numberphile Numberphile tweets: https://twitter.com/numberphile Google Plus: http://bit.ly/numberGplus Tumblr: http://numberphile.tumblr.com Numberphile is supported by the Mathematical Sciences Research Institute (MSRI): http://bit.ly/MSRINumberphile Videos by Brady Haran Brown papers: http://bit.ly/brownpapers A run-down of Brady's channels: http://bit.ly/bradychannels -
 4:54
4:54Theorem - Latin girl
Theorem - Latin girlTheorem - Latin girl
Olivier Jean Alphonse -
 9:53
9:53The most beautiful idea in physics - Noether's Theorem
The most beautiful idea in physics - Noether's TheoremThe most beautiful idea in physics - Noether's Theorem
Homework: -What do you think of this idea? Have you heard of it before? -Maybe you’ve heard about things like super symmetry in physics- try find out how that’s related. -If you know some calculus and classical physics, try and find a proof of this theorem. -Try come up with strange systems with strange symmetries- then see if you can figure out what’s conserved. The proof and maths of Noether's theorem: There are two ways to approach Noether's theorem that I know of. The most common is through Lagrangian mechanics- where the proof is surprisingly simple but unfortunately quite opaque (see http://math.ucr.edu/home/baez/noether.html) . The other way, and the way I allude to in this video, is using hamiltonian mechanics. I find this way a bit easier to understand and it involves the generators of the transforms more. A great resource for this is the last lecture in this course: http://www.physics.usu.edu/torre/6010_Fall_2010/Lectures.html but it requires multivariable calculus and a little knowledge of Hamiltonian mechanics. -
 14:37
14:37The Mean Value Theorem
The Mean Value TheoremThe Mean Value Theorem
Need a LIVE tutor to help answer a question? Check out the people at http://www.tutor.com/signup?AdDist=1&ExAdId;=90fddaff-89aa-4a4f-91da-90841e168246&TDC;_OfferCode=e2bf363b-0cb8-4635-98c3-2b5211d0847a&subject;=math&grade;=undefined for a FREE 30 minute session! The Mean Value Theorem - In this video, I explain the MVT and then I find values of c in a certain interval for a particular function. For more free math videos, visit http://PatrickJMT.com -
 7:37
7:37Squeeze theorem (sandwich theorem) | Limits | Differential Calculus | Khan Academy
Squeeze theorem (sandwich theorem) | Limits | Differential Calculus | Khan AcademySqueeze theorem (sandwich theorem) | Limits | Differential Calculus | Khan Academy
Watch the next lesson: https://www.khanacademy.org/math/differential-calculus/limits_topic/squeeze_theorem/v/proof-lim-sin-x-x?utm_source=YT&utm;_medium=Desc&utm;_campaign=DifferentialCalculus Missed the previous lesson? https://www.khanacademy.org/math/differential-calculus/limits_topic/squeeze_theorem/v/squeeze-theorem-exercise-example?utm_source=YT&utm;_medium=Desc&utm;_campaign=DifferentialCalculus Differential calculus on Khan Academy: Limit introduction, squeeze theorem, and epsilon-delta definition of limits. About Khan Academy: Khan Academy offers practice exercises, instructional videos, and a personalized learning dashboard that empower learners to study at their own pace in and outside of the classroom. We tackle math, science, computer programming, history, art history, economics, and more. Our math missions guide learners from kindergarten to calculus using state-of-the-art, adaptive technology that identifies strengths and learning gaps. We've also partnered with institutions like NASA, The Museum of Modern Art, The California Academy of Sciences, and MIT to offer specialized content. For free. For everyone. Forever. #YouCanLearnAnything Subscribe to KhanAcademy’s Differential Calculus channel: https://www.youtube.com/channel/UCNLzjGl1HBdZrHXo4Vae3iA?sub_confirmation=1 Subscribe to KhanAcademy: https://www.youtube.com/subscription_center?add_user=khanacademy
- Alan Ross Anderson
- Alan Turing
- Alexander Bain
- Alfred Tarski
- Alfréd Rényi
- Alonzo Church
- Ambiguity
- Antinomy
- Aphorism
- Archimedes
- Argument
- Argumentation theory
- Aristotle
- Augustus De Morgan
- Averroes
- Avicenna
- Axiology
- Axiom
- Axiomatic system
- Bayes' rule
- Belief
- Benson Mates
- Bertrand Russell
- Bias
- Boolean function
- Boolean logic
- Cantor's theorem
- Category Logic
- Chrysippus
- Church–Turing thesis
- Class (set theory)
- Classical logic
- Cogency
- Collatz conjecture
- Combinatorics
- Completeness
- Computability theory
- Computable function
- Conjecture
- Consistency
- Converse (logic)
- Corollary
- Countable set
- Cramer's rule
- Credibility
- Critical thinking
- David Hilbert
- Decidability (logic)
- Decision problem
- Deductive
- Deductive reasoning
- Deductive system
- Definition
- Degree of truth
- Deontic logic
- Description
- Description logic
- Dialetheism
- Division algorithm
- Domain of a function
- Doron Zeilberger
- Douglas Hofstadter
- Doxastic logic
- Duns Scotus
- Effective method
- Empirical
- Empty set
- Entailment
- Entscheidungsproblem
- Enumeration
- Epistemology
- Erdős number
- Eric W. Weisstein
- Ernst Schröder
- Ernst Zermelo
- Euler's identity
- Evidence
- Exhaustive search
- Experiment
- Explanation
- Explanatory power
- Exponential function
- Extensionality
- Fact
- Fallacy
- Falsifiable
- Fictionalism
- Finitary relation
- Finite model theory
- Finite set
- Finitism
- First-order logic
- Formal language
- Formal proof
- Formal system
- Formation rule
- Formula
- Four color theorem
- Fractal
- Fuzzy finite element
- Fuzzy logic
- Fuzzy rule
- Fuzzy set
- Fuzzy set operations
- Georg Cantor
- George Boole
- George Boolos
- Gerhard Gentzen
- Giuseppe Peano
- Googol
- Gottlob Frege
- Group theory
- Gödel, Escher, Bach
- Harnack's principle
- Haskell Curry
- Heyting arithmetic
- Hilary Putnam
- History of logic
- House style
- Hypothesis
- Inductive reasoning
- Inference
- Informal logic
- Inquiry
- Intuitionism
- Intuitionistic logic
- Jon Barwise
- Kepler conjecture
- Kurt Gödel
- Lambda calculus
- Law of cosines
- Law of large numbers
- Laws of science
- Lemma (mathematics)
- Leopold Löwenheim
- Linear logic
- List of fallacies
- List of logicians
- List of paradoxes
- List of theorems
- Logic
- Logical atomism
- Logical connective
- Logical consequence
- Logical form
- Logical truth
- Logically
- Logicism
- Ludwig Wittgenstein
- Mandelbrot set
- Mathematical logic
- Mathematical proof
- Mathematics
- MathWorld
- Mertens conjecture
- Metalogic
- Metamath
- Metamathematics
- Metatheorem
- Modal logic
- Modal operator
- Model theory
- Name
- Natural deduction
- Natural number
- Nominalism
- Non-classical logic
- Non-standard model
- Nonsense
- Number theory
- Ontology
- Ontology language
- Opinion
- Ordered pair
- Outline of logic
- Paraconsistent logic
- Paradox
- Parsimony
- Paul Bernays
- Paul Erdős
- Paul Halmos
- Peter Geach
- Philosophical logic
- Philosophy
- Philosophy of logic
- Pigeonhole principle
- Plane (mathematics)
- Platonic realism
- Portal Logic
- Possible world
- Power set
- Pragmatism
- Predicate logic
- Premise
- Presupposition
- Principle
- Probability
- Probability theory
- Proof theory
- Propaganda
- Proposition
- Prudence
- Pythagorean theorem
- Q.E.D.
- Quantification
- Range (mathematics)
- Raymond Smullyan
- Reason
- Recursion
- Recursive set
- Reference
- Relevance
- Relevance logic
- Rhetoric
- Riemann hypothesis
- Rigour
- Rudolf Carnap
- Rule of inference
- Rules of inference
- Satisfiability
- Saul Kripke
- Second-order logic
- Semantics
- Set (mathematics)
- Set theory
- Soundness
- Square of opposition
- Statement (logic)
- Stephen Cole Kleene
- Strict implication
- Structural rule
- Subset
- Substitution (logic)
- Substructural logic
- Syllogism
- Symbol (formal)
- Syntax (logic)
- Talk Theorem
- Tautology (logic)
- Template Logic
- Template talk Logic
- Temporal logic
- Teorema (film)
- Term logic
- Term rewriting
- Theorem
- Theory
- Thoralf Skolem
- Toy theorem
- Transformation rule
- Truth
- Truth table
- Truth value
- Type theory
- Uncountable set
- Vagueness
- Validity
- Venn diagram
- Well formed formula
- Well-formed formula
- William of Ockham
- WP NPOVD
- Zorn's lemma
- Alan Ross Anderson
- Alan Turing
- Alexander Bain
- Alfred Tarski
- Alfréd Rényi
- Alonzo Church
- Archimedes
- Aristotle
- Augustus De Morgan
- Averroes
- Avicenna
- Benson Mates
- Bertrand Russell
- Chrysippus
- David Hilbert
- Doron Zeilberger
- Douglas Hofstadter
- Duns Scotus
- Ernst Schröder
- Ernst Zermelo
- Georg Cantor
- George Boole
- George Boolos
- Gerhard Gentzen
- Giuseppe Peano
- Gottlob Frege
- Haskell Curry
- Hilary Putnam
- Jon Barwise
- Kurt Gödel
- Leopold Löwenheim
- Ludwig Wittgenstein
- Paul Bernays
- Paul Erdős
- Paul Halmos
- Peter Geach
- Raymond Smullyan
- Rudolf Carnap
- Saul Kripke
- Stephen Cole Kleene
- Thoralf Skolem
- William of Ockham
Theorem
ALBUMS
- THX: Experiments in Synchronicity released: 2002
- Ion released: 1999
- Nano released: 1996
THX: Experiments in Synchronicity
Released 2002- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Socius
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Recoil
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Break in at Apt 205
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Minor Explosions
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Mitochondria
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Unherluferlick
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Day From Hell
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Canis
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Too Distant Images
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Devil of Rotations
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Interstate
Ion
Released 1999- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Debris
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Embed
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Cinder
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Shift
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Fallout
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Igneous
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Emerge
Nano
Released 1996- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Nebulus
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Graviti
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Stasis
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Terrabella
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Steem
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Emulsion
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Dilate
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Radii
- add to main playlist Play in Full Screen Aslan
-

Algebra - Pythagorean Theorem
Sure, technically it's a Geometry topic, but why not learn about it in Algebra? Don't be lured into a false sense of security, there may be problems on this video that you may not be able to do! Check out my tie. YAY MATH! Visit yaymath.org Videos copyright (c) Yay Math -
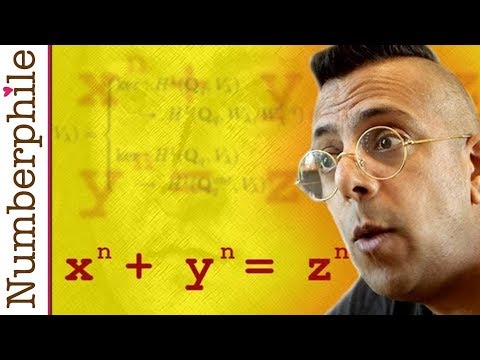
Fermat's Last Theorem - Numberphile
Simon Singh on Fermat's Last Theorem. Simpsons book: http://amzn.to/1fKe4Yo Fermat book: http://amzn.to/1jWqMTa EXTRA FOOTAGE: http://youtu.be/FXbsIbRVios FERMAT IN SIMPSONS:http://youtu.be/ReOQ300AcSU Buy Numberphile papers on Ebay (including from this video): http://bit.ly/brownpapers Wiles' proof: http://bit.ly/FermatProof Website: http://www.numberphile.com/ Numberphile on Facebook: http://www.facebook.com/numberphile Numberphile tweets: https://twitter.com/numberphile Google Plus: http://bit.ly/numberGplus Tumblr: http://numberphile.tumblr.com Videos by Brady Haran A run-down of Brady's channels: http://bit.ly/bradychannels Simon Singh's website: http://simonsingh.net/ -

The Pythagorean theorem intro | Right triangles and trigonometry | Geometry | Khan Academy
Introduction to the Pythagorean Theorem Practice this lesson yourself on KhanAcademy.org right now: https://www.khanacademy.org/math/geometry/right_triangles_topic/pyth_theor/e/pythagorean_theorem_1?utm_source=YT&utm;_medium=Desc&utm;_campaign=Geometry Watch the next lesson: https://www.khanacademy.org/math/geometry/right_triangles_topic/pyth_theor/v/pythagorean-theorem-1?utm_source=YT&utm;_medium=Desc&utm;_campaign=Geometry Missed the previous lesson? https://www.khanacademy.org/math/geometry/right_triangles_topic/pyth_theor/v/pythagorean-theorem?utm_source=YT&utm;_medium=Desc&utm;_campaign=Geometry Geometry on Khan Academy: We are surrounded by space. And that space contains lots of things. And these things have shapes. In geometry we are concerned with the nature of these shapes, how we... -

-

Circle Theorems - GCSE Maths Higher
This video is a tutorial on Circle Theorems. Please make yourself a revision card while watching this and attempt my examples. Straight away then move to my video on Circle Theorems 2 - Exam Questions 14. This video is for students attempting the Higher paper AQA Unit 3 Maths GCSE, who have previously sat the foundation paper. Explanations are aimed at being as simple as possible and so students who previously did the Foundation paper can access. They would also be useful for students who have always sat the higher paper. www.hegartymaths.com http://www.hegartymaths.com/ -

Triangle Congruence Theorems - SSS, SAS, ASA, AAS
Definition and examples for the four triangle congruence postulates and theorems -

The Zero Theorem - Official Trailer (2014)
Subscribe to Voltage Pictures for all our latest releases: http://bit.ly/1kjjbOy Visit the official site: http://www.thezerotheorem-movie.com Like on Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/TheZeroTheorem Follow on Twitter: http://www.twitter.com/TheZeroTheorem_ Purchase the soundtrack: http://bit.ly/1kgDM8u An eccentric and reclusive computer genius plagued with existential angst works on a mysterious project aimed at discovering the purpose of existence - or the lack thereof -once and for all. However, it is only once he experiences the power of love and desire that he is able to understand his very reason for being. Director: Terry Gilliam Writer: Pat Rushin Cast: Christoph Waltz, David Thewlis, Melanie thierry, Lucas Hedges, Ben Whishaw, Peter Stormare, and Tilda Swinton. -

Fold and Cut Theorem - Numberphile
Lynda free trial (try the typography stuff!!): http://www.lynda.com/numberphile Katie Steckles discusses the Fold and Cut Theorem - from A to Z. Katie: http://www.katiesteckles.co.uk More on the topic: http://erikdemaine.org/foldcut/ NUMBERPHILE Website: http://www.numberphile.com/ Numberphile on Facebook: http://www.facebook.com/numberphile Numberphile tweets: https://twitter.com/numberphile Numberphile is supported by the Mathematical Sciences Research Institute (MSRI): http://bit.ly/MSRINumberphile Videos by Brady Haran Support us on Patreon: http://www.patreon.com/numberphile Brady's videos subreddit: http://www.reddit.com/r/BradyHaran/ A run-down of Brady's channels: http://www.bradyharan.com Sign up for (occasional) emails: http://eepurl.com/YdjL9 -

The Futurama Theorem
The Futurama episode The Prisoner of Benda features a machine that allows two people to switch minds. The problem is that two bodies can only switch minds once. Fry and Co. goes wild on the mind switching machine and have to resort to some serious math to get back into their own bodies. Our mission in this video is to give a crystal clear explanation of the Futurama theorem. As an added bonus there is also some Stargate mind switching action towards the end of the video. (added 15 August 2015) We just posted a follow up video: https://youtu.be/w0mxdo5ur_A Enjoy! Burkard Polster and Giuseppe Geracitano -

Fundamental Theorem of Algebra - Numberphile
Part one on odd polynomials: http://youtu.be/8l-La9HEUIU A nice extra bit about complex numbers: http://youtu.be/-IJuqR6nz_Q Professor David Eisenbud is an algebraic geometer (and director of the Mathematical Sciences Research Institute at Berkeley) Hello Internet: http://www.hellointernet.fm Website: http://www.numberphile.com/ Numberphile on Facebook: http://www.facebook.com/numberphile Numberphile tweets: https://twitter.com/numberphile Google Plus: http://bit.ly/numberGplus Tumblr: http://numberphile.tumblr.com Numberphile is supported by the Mathematical Sciences Research Institute (MSRI): http://bit.ly/MSRINumberphile Videos by Brady Haran Brown papers: http://bit.ly/brownpapers A run-down of Brady's channels: http://bit.ly/bradychannels -

Theorem - Latin girl
Olivier Jean Alphonse -

The most beautiful idea in physics - Noether's Theorem
Homework: -What do you think of this idea? Have you heard of it before? -Maybe you’ve heard about things like super symmetry in physics- try find out how that’s related. -If you know some calculus and classical physics, try and find a proof of this theorem. -Try come up with strange systems with strange symmetries- then see if you can figure out what’s conserved. The proof and maths of Noether's theorem: There are two ways to approach Noether's theorem that I know of. The most common is through Lagrangian mechanics- where the proof is surprisingly simple but unfortunately quite opaque (see http://math.ucr.edu/home/baez/noether.html) . The other way, and the way I allude to in this video, is using hamiltonian mechanics. I find this way a bit easier to understand and it involves the ge... -

The Mean Value Theorem
Need a LIVE tutor to help answer a question? Check out the people at http://www.tutor.com/signup?AdDist=1&ExAdId;=90fddaff-89aa-4a4f-91da-90841e168246&TDC;_OfferCode=e2bf363b-0cb8-4635-98c3-2b5211d0847a&subject;=math&grade;=undefined for a FREE 30 minute session! The Mean Value Theorem - In this video, I explain the MVT and then I find values of c in a certain interval for a particular function. For more free math videos, visit http://PatrickJMT.com -

Squeeze theorem (sandwich theorem) | Limits | Differential Calculus | Khan Academy
Watch the next lesson: https://www.khanacademy.org/math/differential-calculus/limits_topic/squeeze_theorem/v/proof-lim-sin-x-x?utm_source=YT&utm;_medium=Desc&utm;_campaign=DifferentialCalculus Missed the previous lesson? https://www.khanacademy.org/math/differential-calculus/limits_topic/squeeze_theorem/v/squeeze-theorem-exercise-example?utm_source=YT&utm;_medium=Desc&utm;_campaign=DifferentialCalculus Differential calculus on Khan Academy: Limit introduction, squeeze theorem, and epsilon-delta definition of limits. About Khan Academy: Khan Academy offers practice exercises, instructional videos, and a personalized learning dashboard that empower learners to study at their own pace in and outside of the classroom. We tackle math, science, computer programming, history, art history, economi... -

Binomial theorem | Polynomial and rational functions | Algebra II | Khan Academy
Practice this lesson yourself on KhanAcademy.org right now: https://www.khanacademy.org/math/algebra2/polynomial_and_rational/binomial_theorem/e/binomial-theorem?utm_source=YT&utm;_medium=Desc&utm;_campaign=AlgebraII Watch the next lesson: https://www.khanacademy.org/math/algebra2/polynomial_and_rational/binomial_theorem/v/pascals-triangle-binomial-theorem?utm_source=YT&utm;_medium=Desc&utm;_campaign=AlgebraII Missed the previous lesson? https://www.khanacademy.org/math/algebra2/polynomial_and_rational/polynomial-end-behavior/v/polynomial-end-behavior-exercise-example?utm_source=YT&utm;_medium=Desc&utm;_campaign=AlgebraII Algebra II on Khan Academy: Your studies in algebra 1 have built a solid foundation from which you can explore linear equations, inequalities, and functions. In algebra 2 ... -

Theorem (1968) - Pier Paolo Pasolini (Trailer) | BFI
Theorem (1968) - Pier Paolo Pasolini (Trailer) | BFI. Subscribe: http://bit.ly/subscribetotheBFI Pier Paolo Pasolini's playful satire, starring Terence Stamp at the peak of his beauty. In cinemas 12 April Book tickets: http://bit.ly/13P9ula Watch more on the BFI Player: http://player.bfi.org.uk/ Follow us on Twitter: https://twitter.com/BFI Like us on Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/BritishFilmInstitute Follow us on Google+: https://plus.google.com/+britishfilminstitute/ -

Fundamental theorem of calculus
More free lessons at: http://www.khanacademy.org/video?v=C7ducZoLKgw -

The Squeeze Theorem for Limits, Example 1
Buy my book!: '1001 Calculus Problems for Dummies' - you can get it on my website: http://patrickjmt.com/ The Squeeze Theorem for Limits - I discuss the idea of the Squeeze Theorem as well as showing two examples illustrating the Squeeze Theorem! For more free math videos, check out http://PatrickJMT.com -

Intermediate Value Theorem
SORRY ABOUT MY TERRIBLE ARITHMETIC! ntermediate Value Theorem - The idea of the Intermediate Value Theorem is discussed. I then do two examples using the IVT to justify that two specific functions have roots. -

Fundamental theorem of algebra | Polynomial and rational functions | Algebra II | Khan Academy
Practice this lesson yourself on KhanAcademy.org right now: https://www.khanacademy.org/math/algebra2/polynomial_and_rational/fundamental-theorem-of-algebra/e/the-fundamental-theorem-of-algebra?utm_source=YT&utm;_medium=Desc&utm;_campaign=AlgebraII Watch the next lesson: https://www.khanacademy.org/math/algebra2/polynomial_and_rational/fundamental-theorem-of-algebra/v/fundamental-theorem-algebra-quadratic?utm_source=YT&utm;_medium=Desc&utm;_campaign=AlgebraII Missed the previous lesson? https://www.khanacademy.org/math/algebra2/polynomial_and_rational/advanced-structure-in-expression/v/structure-in-exponential-expression?utm_source=YT&utm;_medium=Desc&utm;_campaign=AlgebraII Algebra II on Khan Academy: Your studies in algebra 1 have built a solid foundation from which you can explore linear... -

Pythagorean Theorem
You will learn about "Pythagorean Theorem" in this video. To implement the Pythagorean Theorem, a triangle has to be a right-angled triangle. The longest side of a right-angled triangle is always opposite to the 90-degree angle. It is called the hypotenuse. The other 2 adjacent sides are called the legs of the triangle. Pythagorean theorem states that the square of the hypotenuse of a right angled triangle is equal to the sum of the squares of the other 2 sides. If one side = AB, other side = BC and the hypotenuse = AC, then according to Pythagorean theorem, AB^2 + BC^2 = AC^2 Let us understand this with the help of an example. Consider this triangle in which the length of AB = 3 m and the length of BC is 4 m. We need to find the length of AC. By Pythagorean theorem, AB^2 + BC^2 = AC^2 ... -

Introduction to the Central Limit Theorem
I discuss the central limit theorem, a very important concept in the world of statistics. I illustrate the concept by sampling from two different distributions, and for both distributions plot the sampling distribution of the sample mean for various sample sizes. I also discuss why the central limit theorem is important in statistics, and work through a probability calculation. (For the most part this is a non-technical treatment, and simply illustrates the important implications of the central limit theorem.) -

Squeeze theorem or sandwich theorem | Limits | Differential Calculus | Khan Academy
Practice this lesson yourself on KhanAcademy.org right now: https://www.khanacademy.org/math/differential-calculus/limits_topic/squeeze_theorem/e/squeeze-theorem?utm_source=YT&utm;_medium=Desc&utm;_campaign=DifferentialCalculus Watch the next lesson: https://www.khanacademy.org/math/differential-calculus/limits_topic/squeeze_theorem/v/squeeze-theorem-exercise-example?utm_source=YT&utm;_medium=Desc&utm;_campaign=DifferentialCalculus Missed the previous lesson? https://www.khanacademy.org/math/differential-calculus/limits_topic/limits-infinity/v/limits-infinity-algebra ?utm_source=YT&utm;_medium=Desc&utm;_campaign=DifferentialCalculus Differential calculus on Khan Academy: Limit introduction, squeeze theorem, and epsilon-delta definition of limits. About Khan Academy: Khan Academy offers pra...
Algebra - Pythagorean Theorem
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 13:22
- Updated: 26 Feb 2013
- views: 221695
- published: 26 Feb 2013
- views: 221695
Fermat's Last Theorem - Numberphile
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 9:31
- Updated: 24 Sep 2013
- views: 667706
- published: 24 Sep 2013
- views: 667706
The Pythagorean theorem intro | Right triangles and trigonometry | Geometry | Khan Academy
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 10:46
- Updated: 09 Aug 2010
- views: 708248
- published: 09 Aug 2010
- views: 708248
Theorem - Ring
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 8:43
- Updated: 07 Feb 2009
- views: 27133
Circle Theorems - GCSE Maths Higher
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 20:02
- Updated: 02 Jun 2012
- views: 232969
- published: 02 Jun 2012
- views: 232969
Triangle Congruence Theorems - SSS, SAS, ASA, AAS
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 13:42
- Updated: 25 Nov 2013
- views: 14350
- published: 25 Nov 2013
- views: 14350
The Zero Theorem - Official Trailer (2014)
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 2:27
- Updated: 27 Jan 2014
- views: 2849877
- published: 27 Jan 2014
- views: 2849877
Fold and Cut Theorem - Numberphile
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 9:31
- Updated: 25 Sep 2015
- views: 317199
- published: 25 Sep 2015
- views: 317199
The Futurama Theorem
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 20:07
- Updated: 30 Apr 2015
- views: 146945
- published: 30 Apr 2015
- views: 146945
Fundamental Theorem of Algebra - Numberphile
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 15:26
- Updated: 09 Jul 2014
- views: 391723
- published: 09 Jul 2014
- views: 391723
Theorem - Latin girl
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 4:54
- Updated: 04 Feb 2009
- views: 266841
The most beautiful idea in physics - Noether's Theorem
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 9:53
- Updated: 23 Sep 2015
- views: 23317
- published: 23 Sep 2015
- views: 23317
The Mean Value Theorem
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 14:37
- Updated: 08 Dec 2008
- views: 478324
- published: 08 Dec 2008
- views: 478324
Squeeze theorem (sandwich theorem) | Limits | Differential Calculus | Khan Academy
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 7:37
- Updated: 25 Jun 2008
- views: 593207
- published: 25 Jun 2008
- views: 593207
Binomial theorem | Polynomial and rational functions | Algebra II | Khan Academy
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 13:15
- Updated: 27 Mar 2014
- views: 190630
- published: 27 Mar 2014
- views: 190630
Theorem (1968) - Pier Paolo Pasolini (Trailer) | BFI
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 1:28
- Updated: 11 Mar 2013
- views: 74218
- published: 11 Mar 2013
- views: 74218
Fundamental theorem of calculus
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 8:03
- Updated: 04 Feb 2013
- views: 333661
- published: 04 Feb 2013
- views: 333661
The Squeeze Theorem for Limits, Example 1
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 7:13
- Updated: 12 Aug 2008
- views: 394356
- published: 12 Aug 2008
- views: 394356
Intermediate Value Theorem
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 7:54
- Updated: 12 Aug 2008
- views: 412394
- published: 12 Aug 2008
- views: 412394
Fundamental theorem of algebra | Polynomial and rational functions | Algebra II | Khan Academy
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 5:34
- Updated: 26 Mar 2014
- views: 64542
- published: 26 Mar 2014
- views: 64542
Pythagorean Theorem
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 6:16
- Updated: 11 Apr 2015
- views: 20215
- published: 11 Apr 2015
- views: 20215
Introduction to the Central Limit Theorem
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 13:14
- Updated: 29 Dec 2012
- views: 107463
- published: 29 Dec 2012
- views: 107463
Squeeze theorem or sandwich theorem | Limits | Differential Calculus | Khan Academy
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 7:11
- Updated: 30 Dec 2013
- views: 109085
- published: 30 Dec 2013
- views: 109085
- Playlist
- Chat
- Playlist
- Chat

Algebra - Pythagorean Theorem
- Report rights infringement
- published: 26 Feb 2013
- views: 221695
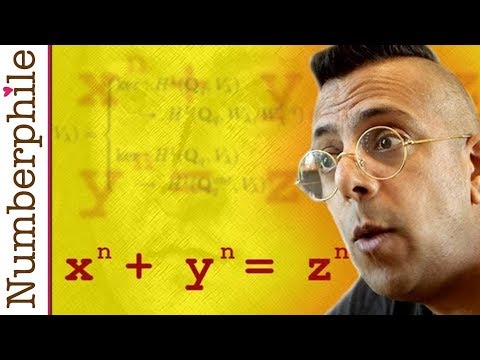
Fermat's Last Theorem - Numberphile
- Report rights infringement
- published: 24 Sep 2013
- views: 667706

The Pythagorean theorem intro | Right triangles and trigonometry | Geometry | Khan Academy
- Report rights infringement
- published: 09 Aug 2010
- views: 708248


Circle Theorems - GCSE Maths Higher
- Report rights infringement
- published: 02 Jun 2012
- views: 232969

Triangle Congruence Theorems - SSS, SAS, ASA, AAS
- Report rights infringement
- published: 25 Nov 2013
- views: 14350

The Zero Theorem - Official Trailer (2014)
- Report rights infringement
- published: 27 Jan 2014
- views: 2849877

Fold and Cut Theorem - Numberphile
- Report rights infringement
- published: 25 Sep 2015
- views: 317199

The Futurama Theorem
- Report rights infringement
- published: 30 Apr 2015
- views: 146945

Fundamental Theorem of Algebra - Numberphile
- Report rights infringement
- published: 09 Jul 2014
- views: 391723

Theorem - Latin girl
- Report rights infringement
- published: 04 Feb 2009
- views: 266841

The most beautiful idea in physics - Noether's Theorem
- Report rights infringement
- published: 23 Sep 2015
- views: 23317

The Mean Value Theorem
- Report rights infringement
- published: 08 Dec 2008
- views: 478324

Squeeze theorem (sandwich theorem) | Limits | Differential Calculus | Khan Academy
- Report rights infringement
- published: 25 Jun 2008
- views: 593207
-
Lyrics list:text lyricsplay full screenplay karaoke
Deep State And The Reality Behind Super Tuesday And November Election
Edit WorldNews.com 03 Mar 2016Teacher Resigns After Student Steals, Distributes Nude Photos From Unlocked, Unattended Cell
Edit WorldNews.com 03 Mar 2016Oscar Pistorius Murder Conviction Appeal Denied by South African Court
Edit WorldNews.com 03 Mar 2016Secret U.S. Expeditionary Force Captures, Questioning Top ISIS Militant In Iraq Raid
Edit WorldNews.com 02 Mar 2016Report: Trump Off-The-Record Audio Remarks Could Derail His Campaign If Revealed
Edit WorldNews.com 02 Mar 2016Whole Foods Market experts forecast top 10 food trends for 2016
Edit Yahoo Daily News 02 Mar 20165D Black Holes Could Break Relativity
Edit Yahoo Daily News 29 Feb 2016Oscar Hangover Special: Why “Spotlight” Is a Terrible Film
Edit CounterPunch 29 Feb 2016Change of Senate guards boost for lobbyists, not reform
Edit Sydney Morning Herald 28 Feb 2016The last-leg sprint
Edit The Hindu 28 Feb 2016Hoffarth: ‘Utley Rule’ slides past ‘bona fide’ reality
Edit LA Daily News 26 Feb 2016Infinite Jest at 20: 20 things you need to know
Edit The Guardian 26 Feb 2016Last-minute exam help is just a click away
Edit The Times of India 25 Feb 2016How to build a time machine
Edit CNN 25 Feb 2016The problem with NSW's new Biodiversity Act
Edit Sydney Morning Herald 24 Feb 2016Sir Christopher Zeeman obituary
Edit The Guardian 24 Feb 2016Comment: How to build a time machine (Newcastle University)
Edit Public Technologies 24 Feb 2016New theorem helps reveal tuberculosis’ secret (Rice University)
Edit Public Technologies 22 Feb 2016- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- Next page »







