- published: 15 Jul 2016
- views: 29008
-
remove the playlistLaw Of France
-
remove the playlistLatest Videos
- remove the playlistLaw Of France
- remove the playlistLatest Videos
Please tell us which country and city you'd like to see the weather in.
- published: 15 Jul 2016
- views: 524912
- published: 14 Jul 2016
- views: 386566
- published: 15 Jul 2016
- views: 17855
- published: 15 Jul 2016
- views: 463
- published: 14 Jul 2016
- views: 5400
- published: 14 Jul 2016
- views: 101
- published: 15 Jul 2016
- views: 176
- published: 15 Jul 2016
- views: 10150

Law of France
In academic terms, French law can be divided into two main categories: private law ("droit privé") and public law ("droit public"). This differs from the traditional Common Law conception in which the main distinction is between Criminal law and Civil Law.
Private Law governs relationships between individuals. It includes, in particular:
Public law defines the structure and the workings of the government as well as relationships between the State and individuals. It includes, in particular:
Together, these two distinctions form the backbone of legal studies in France, such that it has become a classical distinction
This article is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported License, which means that you can copy and modify it as long as the entire work (including additions) remains under this license.

France
France (French: [fʁɑ̃s]), officially the French Republic (French: République française [ʁepyblik fʁɑ̃sɛz]), is a sovereign state comprising territory in western Europe and several overseas regions and territories. The European part of France, called metropolitan France, extends from the Mediterranean Sea to the English Channel and the North Sea, and from the Rhine to the Atlantic Ocean. France spans 643,801 square kilometres (248,573 sq mi) and has a total population of 66.6 million. It is a unitary semi-presidential republic with the capital in Paris, the country's largest city and main cultural and commercial centre. The Constitution of France establishes the state as secular and democratic, with its sovereignty derived from the people.
During the Iron Age, what is now Metropolitan France was inhabited by the Gauls, a Celtic people. The Gauls were conquered in 51 BC by the Roman Empire, which held Gaul until 486. The Gallo-Romans faced raids and migration from the Germanic Franks, who dominated the region for hundreds of years, eventually creating the medieval Kingdom of France. France emerged as a major European power in the Late Middle Ages, with its victory in the Hundred Years' War (1337 to 1453) strengthening French state-building and paving the way for a future centralized absolute monarchy. During the Renaissance, France experienced a vast cultural development and established the beginning of a global colonial empire. The 16th century was dominated by religious civil wars between Catholics and Protestants (Huguenots).
This article is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported License, which means that you can copy and modify it as long as the entire work (including additions) remains under this license.
Radio Stations - Paris
SEARCH FOR RADIOS
- Loading...

-
 3:28
3:28France on Alert After Bastille Day Attack in Nice
France on Alert After Bastille Day Attack in NiceFrance on Alert After Bastille Day Attack in Nice
July 15 -- France again was put on a terror footing as a truck drove into a late-night crowd in Nice on the country’s Mediterranean coast, killing at least 70 people as the nation celebrated its Bastille Day holiday. The Paris prosecutor’s office called it a terrorist attack. Bloomberg's Ramy Inocencio has the latest developments on "Trending Business." -
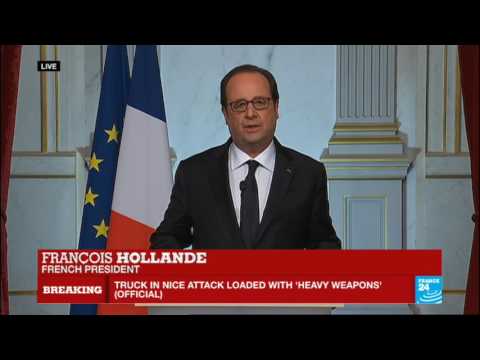 5:58
5:58Nice attack - French President François Hollande addresses nation: "France is horrified"
Nice attack - French President François Hollande addresses nation: "France is horrified"Nice attack - French President François Hollande addresses nation: "France is horrified"
Nice attack: French President François Hollande addresses nation on terror attack -
 1:00
1:00France: Truck ploughs into crowd in Nice during Bastille Day celebrations, several dead
France: Truck ploughs into crowd in Nice during Bastille Day celebrations, several deadFrance: Truck ploughs into crowd in Nice during Bastille Day celebrations, several dead
France: Truck ploughs into crowd in Nice during the Bastille Day celebrations, several people are reported dead. -
 0:00
0:00FRANCE Nice Terror Attack in France - Truck Plows Into Crowd
FRANCE Nice Terror Attack in France - Truck Plows Into Crowd -
 3:10
3:10Security expert on Bastille Day attack in Nice, France
Security expert on Bastille Day attack in Nice, FranceSecurity expert on Bastille Day attack in Nice, France
Former CSIS Assistant Director Ray Boisvert weighs in on the attack in Nice, France. Click here for the full story: http://www.cbc.ca/1.3679807 »»» Subscribe to The National to watch more videos here: https://www.youtube.com/user/CBCTheNational?sub_confirmation=1 Voice Your Opinion & Connect With Us Online: The National Updates on Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/thenational The National Updates on Twitter: https://twitter.com/CBCTheNational The National Updates on Google+: https://plus.google.com/+CBCTheNational »»» »»» »»» »»» »»» The National is CBC Television's flagship news program. Airing seven days a week, the show delivers news, feature documentaries and analysis from some of Canada's leading journalists. -
 0:57
0:57Breaking News: Several Injured In Nice, France
Breaking News: Several Injured In Nice, FranceBreaking News: Several Injured In Nice, France
AFP: several people have been reported injured after a vehicle crashed into a crowd of people celebrating Bastille Day in Nice, France -
 1:00
1:0014 Juillet 2016 - La Patrouille de France survole Paris
14 Juillet 2016 - La Patrouille de France survole Paris14 Juillet 2016 - La Patrouille de France survole Paris
Huit Alphajet de la Patrouille de France, en formation Tour Eiffel, survolent Paris en ce jour de Fête Nationale. Retrouvez-nous sur Facebook : https://www.facebook.com/tv5mondeofficiel/?fref=ts Suivez-nous sur Twitter : @TV5MONDE Sur Instagram : https://www.instagram.com/tv5monde/ En vidéo à la demande sur TV5MONDEPLUS : http://www.tv5mondeplus.com/ Notre site info : http://information.tv5monde.com/ -
 16:49
16:49Défense en France : Un budget à la hauteur des défis ? (partie 1)
Défense en France : Un budget à la hauteur des défis ? (partie 1)Défense en France : Un budget à la hauteur des défis ? (partie 1)
Abonnez-vous à notre chaîne sur YouTube : http://f24.my/youtube En DIRECT - Suivez FRANCE 24 ici : http://f24.my/YTliveFR Ce 14 juillet, 3 239 militaires français ont paradé sur les Champs-Élysées. Un défilé mettant à l'honneur l'Australie et la Nouvelle-Zélande mais aussi les troupes françaises mobilisées ces derniers mois pour assurer la sécurité du pays. La France, comme l'affirment ses dirigeants, est en guerre contre un ennemi invisible, le terrorisme. Une guerre menée dans l'hexagone mais aussi sur de nombreux terrains à l'étranger. Quels défis pour cette armée? Une émission préparée par Elise Duffau, Anthony Saint-Léger et Gaëlle Essoo. Notre site : http://www.france24.com/fr/ Rejoignez nous sur Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/FRANCE24.videos Suivez nous sur Twitter : https://twitter.com/F24videos -
 3:17
3:17Terror in France: At Least 77 Killed in Nice
Terror in France: At Least 77 Killed in NiceTerror in France: At Least 77 Killed in Nice
July 15 -- France again was put on a terror footing as a truck drove into a late-night crowd in Nice on the country’s Mediterranean coast, killing at least 70 people as the nation celebrated its Bastille Day holiday. The Paris prosecutor’s office called it a terrorist attack. Bloomberg's Rosalind Chin has the latest developments on "Trending Business." -
 8:30
8:30BREAKING: Dozens Killed In Truck Attack In France
BREAKING: Dozens Killed In Truck Attack In FranceBREAKING: Dozens Killed In Truck Attack In France
A truck attack in Nice, France has killed dozens of people on Bastille Day. Cenk Uygur and Ana Kasparian, hosts of The Young Turks, break it down. Tell us what you think in the comment section below. “(CNN)At least 77 people were killed Thursday night when a large truck plowed through a crowd celebrating Bastille Day in Nice, France, tweeted regional President Christian Estrosi. The driver pointed his tractor-trailer into the crowd and accelerated, mowing bodies over, witnesses said. Police shot the driver to death, authorities said. Nobody has claimed responsibility Here are the latest developments in the tragedy: • The attack in Nice, France, began when an occupant of the truck shot into the crowd and then drove for 2 kilometers along the pavement of the Boulevard des Anglais, the main street in Nice, regional President Christian Estrosi told CNN affiliate BFM-TV. He said police later found firearms, explosives and grenades in the truck.” Read more here: http://www.cnn.com/2016/07/14/europe/nice-france-truck/ Hosts: Cenk Uygur, Ana Kasparian Cast: Cenk Uygur, Ana Kasparian *** The Largest Online News Show in the World. Hosted by Cenk Uygur and Ana Kasparian. LIVE STREAMING weekdays 6-8pm ET. http://www.tytnetwork.com/live Young Turk (n), 1. Young progressive or insurgent member of an institution, movement, or political party. 2. Young person who rebels against authority or societal expectations. (American Heritage Dictionary) Download audio and video of the full two hour show on-demand + the members-only post game show by becoming a member at http://www.tytnetwork.com/join/. Your membership supports the day to day operations and is vital for our continued success and growth. Get The Young Turks Mobile App Today! Download the iOS version here: https://itunes.apple.com/us/app/the-young-turks/id412793195
-

France on Alert After Bastille Day Attack in Nice
July 15 -- France again was put on a terror footing as a truck drove into a late-night crowd in Nice on the country’s Mediterranean coast, killing at least 70 people as the nation celebrated its Bastille Day holiday. The Paris prosecutor’s office called it a terrorist attack. Bloomberg's Ramy Inocencio has the latest developments on "Trending Business." -

Nice attack - French President François Hollande addresses nation: "France is horrified"
Nice attack: French President François Hollande addresses nation on terror attack -

France: Truck ploughs into crowd in Nice during Bastille Day celebrations, several dead
France: Truck ploughs into crowd in Nice during the Bastille Day celebrations, several people are reported dead. -

-

Security expert on Bastille Day attack in Nice, France
Former CSIS Assistant Director Ray Boisvert weighs in on the attack in Nice, France. Click here for the full story: http://www.cbc.ca/1.3679807 »»» Subscribe to The National to watch more videos here: https://www.youtube.com/user/CBCTheNational?sub_confirmation=1 Voice Your Opinion & Connect With Us Online: The National Updates on Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/thenational The National Updates on Twitter: https://twitter.com/CBCTheNational The National Updates on Google+: https://plus.google.com/+CBCTheNational »»» »»» »»» »»» »»» The National is CBC Television's flagship news program. Airing seven days a week, the show delivers news, feature documentaries and analysis from some of Canada's leading journalists. -

Breaking News: Several Injured In Nice, France
AFP: several people have been reported injured after a vehicle crashed into a crowd of people celebrating Bastille Day in Nice, France -

14 Juillet 2016 - La Patrouille de France survole Paris
Huit Alphajet de la Patrouille de France, en formation Tour Eiffel, survolent Paris en ce jour de Fête Nationale. Retrouvez-nous sur Facebook : https://www.facebook.com/tv5mondeofficiel/?fref=ts Suivez-nous sur Twitter : @TV5MONDE Sur Instagram : https://www.instagram.com/tv5monde/ En vidéo à la demande sur TV5MONDEPLUS : http://www.tv5mondeplus.com/ Notre site info : http://information.tv5monde.com/ -

Défense en France : Un budget à la hauteur des défis ? (partie 1)
Abonnez-vous à notre chaîne sur YouTube : http://f24.my/youtube En DIRECT - Suivez FRANCE 24 ici : http://f24.my/YTliveFR Ce 14 juillet, 3 239 militaires français ont paradé sur les Champs-Élysées. Un défilé mettant à l'honneur l'Australie et la Nouvelle-Zélande mais aussi les troupes françaises mobilisées ces derniers mois pour assurer la sécurité du pays. La France, comme l'affirment ses dirigeants, est en guerre contre un ennemi invisible, le terrorisme. Une guerre menée dans l'hexagone mais aussi sur de nombreux terrains à l'étranger. Quels défis pour cette armée? Une émission préparée par Elise Duffau, Anthony Saint-Léger et Gaëlle Essoo. Notre site : http://www.france24.com/fr/ Rejoignez nous sur Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/FRANCE24.videos Suivez nous sur Twitter : https://... -

Terror in France: At Least 77 Killed in Nice
July 15 -- France again was put on a terror footing as a truck drove into a late-night crowd in Nice on the country’s Mediterranean coast, killing at least 70 people as the nation celebrated its Bastille Day holiday. The Paris prosecutor’s office called it a terrorist attack. Bloomberg's Rosalind Chin has the latest developments on "Trending Business." -

BREAKING: Dozens Killed In Truck Attack In France
A truck attack in Nice, France has killed dozens of people on Bastille Day. Cenk Uygur and Ana Kasparian, hosts of The Young Turks, break it down. Tell us what you think in the comment section below. “(CNN)At least 77 people were killed Thursday night when a large truck plowed through a crowd celebrating Bastille Day in Nice, France, tweeted regional President Christian Estrosi. The driver pointed his tractor-trailer into the crowd and accelerated, mowing bodies over, witnesses said. Police shot the driver to death, authorities said. Nobody has claimed responsibility Here are the latest developments in the tragedy: • The attack in Nice, France, began when an occupant of the truck shot into the crowd and then drove for 2 kilometers along the pavement of the Boulevard des Anglais, the mai...
France on Alert After Bastille Day Attack in Nice
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 3:28
- Updated: 15 Jul 2016
- views: 29008
- published: 15 Jul 2016
- views: 29008
Nice attack - French President François Hollande addresses nation: "France is horrified"
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 5:58
- Updated: 15 Jul 2016
- views: 524912
- published: 15 Jul 2016
- views: 524912
France: Truck ploughs into crowd in Nice during Bastille Day celebrations, several dead
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 1:00
- Updated: 14 Jul 2016
- views: 386566
- published: 14 Jul 2016
- views: 386566
FRANCE Nice Terror Attack in France - Truck Plows Into Crowd
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 0:00
- Updated: 13 Jul 2016
- views: 5922
Security expert on Bastille Day attack in Nice, France
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 3:10
- Updated: 15 Jul 2016
- views: 17855
- published: 15 Jul 2016
- views: 17855
Breaking News: Several Injured In Nice, France
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 0:57
- Updated: 15 Jul 2016
- views: 463
- published: 15 Jul 2016
- views: 463
14 Juillet 2016 - La Patrouille de France survole Paris
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 1:00
- Updated: 14 Jul 2016
- views: 5400
- published: 14 Jul 2016
- views: 5400
Défense en France : Un budget à la hauteur des défis ? (partie 1)
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 16:49
- Updated: 14 Jul 2016
- views: 101
- published: 14 Jul 2016
- views: 101
Terror in France: At Least 77 Killed in Nice
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 3:17
- Updated: 15 Jul 2016
- views: 176
- published: 15 Jul 2016
- views: 176
BREAKING: Dozens Killed In Truck Attack In France
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 8:30
- Updated: 15 Jul 2016
- views: 10150
- published: 15 Jul 2016
- views: 10150
-

Faada Freddy at Chateau De Grimaud, Grimaud, France 2016 July - live concert
Faada Freddy at Chateau De Grimaud, Grimaud, France 2016 July - live full concert Visit Here Go To : http://v.ht/vpOo Get Ticket On : http://v.ht/Ticket_Music Date/Start Time : 2016 July LIVE Faada Freddy 2016 July Live concert Faada Freddy 2016 Live concert Faada Freddy at Chateau De Grimaud, Grimaud, France Live at Chateau De Grimaud, Grimaud, France concert Faada Freddy 2016 Faada Freddy live concert 2016 at Chateau De Grimaud, Grimaud, France 2016 ========================================= Simply download our app - connect to a location and enjoy! - Connect to over 30 locations worldwide with Total Premium Click and connect to a location of your choice Start enjoying an unrestricted - secure and anonymous internet ========================================= Millions of bestsellers a... -

Maitre Gim's at Arènes de Bayonne, Bayonne, France 2016 July - live concert
Maitre Gim's at Arènes de Bayonne, Bayonne, France 2016 July - live full concert Visit Here Go To : http://v.ht/zLoI Get Ticket On : http://v.ht/Ticket_Music Date/Start Time : 2016 July LIVE Maitre Gim's 2016 July Live concert Maitre Gim's 2016 Live concert Maitre Gim's at Arènes de Bayonne, Bayonne, France Live at Arènes de Bayonne, Bayonne, France concert Maitre Gim's 2016 Maitre Gim's live concert 2016 at Arènes de Bayonne, Bayonne, France 2016 ========================================= Simply download our app - connect to a location and enjoy! - Connect to over 30 locations worldwide with Total Premium Click and connect to a location of your choice Start enjoying an unrestricted - secure and anonymous internet ========================================= Millions of bestsellers and n... -

Marc Ribot at New Morning, Paris, France July 20 2016 - live concert
Marc Ribot at New Morning, Paris, France July 20 2016 - live full concert Visit Here Go To : http://v.ht/DCRs Get Ticket On : http://v.ht/Ticket_Music Date/Start Time : July 20 2016 LIVE Marc Ribot July 20 2016 Live concert Marc Ribot 2016 Live concert Marc Ribot at New Morning, Paris, France Live at New Morning, Paris, France concert Marc Ribot 2016 Marc Ribot live concert 2016 at New Morning, Paris, France 2016 ========================================= Simply download our app - connect to a location and enjoy! - Connect to over 30 locations worldwide with Total Premium Click and connect to a location of your choice Start enjoying an unrestricted - secure and anonymous internet ========================================= Millions of bestsellers and new releases No limits - play - watc... -

Bastille Day Attack aftermath - remembering (France) - ITV News - 18th July 2016
40,000 people remember on the promenade in Nice. Government leaders get jeered, more on the man who committed this crime and a city in mourning for such terrible loss. Emma Murphy and Rohit Kachroo report (introduced by Nina Hossain). -

France Truck Attack - BLOODLESS Truck Towed
The title of this Liveleak footage is "BLOODY TRUCK TOWED". Talk about being FALSE. Not one single drop of blood to be seen anywhere. And this truck supposedly hit 300 people and it's front end is very badly damaged. To all you morons who think this event was real WHERE IS THE BLOOD? http://www.liveleak.com/view?i=f1c_1468664625 Please Share on FACEBOOK: http://bit.ly/1SDK41r Donate: http://bit.ly/1rtfS0i -

John McCain Blames Obama For Terror Attack In Nice, France
Sen. John McCain (R-AZ) again placed some blame on President Obama for a terrorist attack, this time for the deadly truck attack in Nice, France, last week. McCain said on Friday that Obama's policies gave rise to the Islamic State, which the senator argued is responsible for the attack... Read More At: http://talkingpointsmemo.com/livewire/john-mccain-obama-nice-attack Clip from The Kyle Kulinski Show, which airs live on Blog Talk Radio and Secular Talk Radio Monday - Friday 4:00 - 5:30 PM Eastern time zone. Check out our website - and become a member - at: http://www.SecularTalkRadio.com Listen to the Live Show or On Demand archive at: http://www.blogtalkradio.com/kylekulinski Follow on Twitter: http://www.twitter.com/kylekulinski Like on Facebook: http://www.facebook.com/Secul... -

Finland v France - Live - FIBA U20 European Championship 2016
Watch Finland v France at the FIBA U20 European Championship 2016. ► Subscribe: http://fiba.com/subYT Also visit the official FIBA website (http://www.fiba.com) and follow us on our social media platforms to never miss a beat. Facebook: http://facebook.com/FIBA Twitter: http://twitter.com/FIBA Google+: http://google.com/+FIBA Instagram: http://instagr.am/FIBA Sina Weibo: http://weibo.com/FIBAofficial Vine: http://vine.co/FIBA -

Riding With Peter Sagan & Oleg Tinkov – Tour De France Rest Day Ride With Tinkoff
Matt caught up (OK, he just held on...) with the Tinkoff team for their rest day ride on the second rest day of the 2016 Tour de France. Subscribe to GCN: http://gcn.eu/SubscribeToGCN Get exclusive GCN gear in the GCN store! http://gcn.eu/BuyGCNKit_ Sign up to the GCN newsletter: http://gcn.eu/gcnnewsletter With Peter Sagan dominant at this year's race, Tinkoff have had a busy couple of weeks. What better place to unwind, then, than in the shadow of Mont Blanc? Matt rode with them on their rest day ride – although he didn't content the €50 prime sprint. Can you guess who won that one? Watch more on GCN... Tour de France playlist ▶︎ http://gcn.eu/gcntourdefrance2016 Riding with Peter Sagan at the 2015 Vuelta ▶︎ http://gcn.eu/29S776J Buy NEW GCN cycling kit, casual wear and accessories ... -

France : An armed man intruded a hotel in Bollene
An armed man intruded a hotel in Bollene. Watch this special segment and get to know more here. Zee News always stay ahead in bringing current affairs from all the valley of National interest, Politics, Entertainment, Sports and International happenings. We take you to the depth of every matter by providing every small detail and makes you familiar with all the happening around you. Zee News is the highly popular Hindi News channel of India’s largest television network ZMCL. The channel, which has a huge following in India and abroad, has won several prestigious national and international awards. Among its popular programs are - Dr. Subhash Chandra Show: https://goo.gl/fCugXC Daily News and Analysis: https://goo.gl/B8eVsD Manthan: https://goo.gl/6q0wUN Fast n Facts: https://go... -

Tour de France 2016: Chris Froome Sees the Home Stretch
As the race reaches its second rest day before the final push to Paris, two-time Tour de France winner and current leader Chris Froome looks comfortable heading into the last five stages. WSJ's Niki Blasina reports from Bern, Switzerland. Photo: Niki Blasina. Subscribe to the WSJ channel here: http://bit.ly/14Q81Xy More from the Wall Street Journal: Visit WSJ.com: http://www.wsj.com Follow WSJ on Facebook: http://www.facebook.com/wsjvideo Follow WSJ on Google+: https://plus.google.com/+wsj/posts Follow WSJ on Twitter: https://twitter.com/WSJvideo Follow WSJ on Instagram: http://instagram.com/wsj Follow WSJ on Pinterest: http://www.pinterest.com/wsj/
Faada Freddy at Chateau De Grimaud, Grimaud, France 2016 July - live concert
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 0:00
- Updated: 20 Jul 2016
- views: 63
- published: 20 Jul 2016
- views: 63
Maitre Gim's at Arènes de Bayonne, Bayonne, France 2016 July - live concert
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 0:00
- Updated: 20 Jul 2016
- views: 96
- published: 20 Jul 2016
- views: 96
Marc Ribot at New Morning, Paris, France July 20 2016 - live concert
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 0:00
- Updated: 20 Jul 2016
- views: 86
- published: 20 Jul 2016
- views: 86
Bastille Day Attack aftermath - remembering (France) - ITV News - 18th July 2016
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 5:02
- Updated: 20 Jul 2016
- views: 3
- published: 20 Jul 2016
- views: 3
France Truck Attack - BLOODLESS Truck Towed
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 3:42
- Updated: 19 Jul 2016
- views: 2437
- published: 19 Jul 2016
- views: 2437
John McCain Blames Obama For Terror Attack In Nice, France
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 5:32
- Updated: 19 Jul 2016
- views: 2727
- published: 19 Jul 2016
- views: 2727
Finland v France - Live - FIBA U20 European Championship 2016
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 0:00
- Updated: 18 Jul 2016
- views: 153
- published: 18 Jul 2016
- views: 153
Riding With Peter Sagan & Oleg Tinkov – Tour De France Rest Day Ride With Tinkoff
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 5:17
- Updated: 19 Jul 2016
- views: 3255
- published: 19 Jul 2016
- views: 3255
France : An armed man intruded a hotel in Bollene
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 0:46
- Updated: 19 Jul 2016
- views: 839
- published: 19 Jul 2016
- views: 839
Tour de France 2016: Chris Froome Sees the Home Stretch
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 1:38
- Updated: 19 Jul 2016
- views: 1097
- published: 19 Jul 2016
- views: 1097
- Playlist
- Chat
- Playlist
- Chat

France on Alert After Bastille Day Attack in Nice
- Report rights infringement
- published: 15 Jul 2016
- views: 29008

Nice attack - French President François Hollande addresses nation: "France is horrified"
- Report rights infringement
- published: 15 Jul 2016
- views: 524912

France: Truck ploughs into crowd in Nice during Bastille Day celebrations, several dead
- Report rights infringement
- published: 14 Jul 2016
- views: 386566


Security expert on Bastille Day attack in Nice, France
- Report rights infringement
- published: 15 Jul 2016
- views: 17855

Breaking News: Several Injured In Nice, France
- Report rights infringement
- published: 15 Jul 2016
- views: 463

14 Juillet 2016 - La Patrouille de France survole Paris
- Report rights infringement
- published: 14 Jul 2016
- views: 5400

Défense en France : Un budget à la hauteur des défis ? (partie 1)
- Report rights infringement
- published: 14 Jul 2016
- views: 101

Terror in France: At Least 77 Killed in Nice
- Report rights infringement
- published: 15 Jul 2016
- views: 176

BREAKING: Dozens Killed In Truck Attack In France
- Report rights infringement
- published: 15 Jul 2016
- views: 10150
- Playlist
- Chat

Faada Freddy at Chateau De Grimaud, Grimaud, France 2016 July - live concert
- Report rights infringement
- published: 20 Jul 2016
- views: 63

Maitre Gim's at Arènes de Bayonne, Bayonne, France 2016 July - live concert
- Report rights infringement
- published: 20 Jul 2016
- views: 96

Marc Ribot at New Morning, Paris, France July 20 2016 - live concert
- Report rights infringement
- published: 20 Jul 2016
- views: 86

Bastille Day Attack aftermath - remembering (France) - ITV News - 18th July 2016
- Report rights infringement
- published: 20 Jul 2016
- views: 3

France Truck Attack - BLOODLESS Truck Towed
- Report rights infringement
- published: 19 Jul 2016
- views: 2437

John McCain Blames Obama For Terror Attack In Nice, France
- Report rights infringement
- published: 19 Jul 2016
- views: 2727

Finland v France - Live - FIBA U20 European Championship 2016
- Report rights infringement
- published: 18 Jul 2016
- views: 153

Riding With Peter Sagan & Oleg Tinkov – Tour De France Rest Day Ride With Tinkoff
- Report rights infringement
- published: 19 Jul 2016
- views: 3255

France : An armed man intruded a hotel in Bollene
- Report rights infringement
- published: 19 Jul 2016
- views: 839

Tour de France 2016: Chris Froome Sees the Home Stretch
- Report rights infringement
- published: 19 Jul 2016
- views: 1097
Michelle Obama’s “I Wake up Every Morning in A House Built by Slaves” Is Only Partially Right
Edit WorldNews.com 28 Jul 2016North Korea says U.S. has crossed red line, relations now on war footing
Edit Baltimore Sun 28 Jul 2016Rep. Duckworth to Trump: I didn't serve my country 'so you could invite Russia to ...
Edit Politico 29 Jul 2016[VIDEO]: Mysterious Fireball Soars Over Western U.S. Skies
Edit WorldNews.com 28 Jul 2016Military Offensive in Manbij Yields ISIS Data Windfall
Edit WorldNews.com 28 Jul 2016Live updates: Church attacker urges all Muslims to destroy France in new video
Edit ITV 29 Jul 2016Air France strike enters second day, 30,000 passengers affected
Edit Indian Express 29 Jul 2016Chinese tourists shun western Europe in wake of terror attacks as travel to France drops ...
Edit Topix 29 Jul 2016Islamic State releases new video of France church attacker
Edit Reuters 29 Jul 2016From 'Liar' To 'Dear Boris': Boris Johnson Eases Way In France
Edit NDTV 29 Jul 2016Islamic State news agency releases video showing French attacker urging all Muslims to destroy France
Edit ITV 29 Jul 2016France had been hunting second church attacker after tipoff
Edit China Daily 29 Jul 2016Announcing the new president of the National Research Council of Canada (Embassy of Canada in France)
Edit Public Technologies 29 Jul 2016Recent attacks in Western Europe are scaring away Chinese tourists
Edit Business Insider 29 Jul 2016In a massive attempt to stop the spread of terror, French media are no longer publishing photos of terrorists
Edit Quartz 29 Jul 2016- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- Next page »







