-
remove the playlistProvinces Of Italy
- remove the playlistProvinces Of Italy




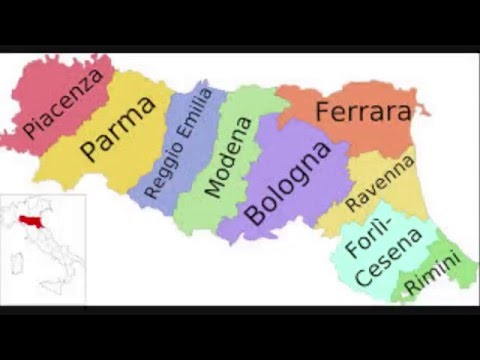








In Italy, a province (provincia) is an administrative division of intermediate level between a municipality (comune) and a region (regione).
A province is composed of many municipalities (comune), and usually several provinces form a region. The region of Aosta Valley is the only exception being the province coincident with the region.
The three main functions devolved to provinces are:
There are 110 provinces in Italy. Lombardy has the most provinces, with 12. The number of provinces in Italy has been steadily growing in recent years, as many new ones are carved out of older ones.
Each province is headed by a President assisted by a legislative body, the Provincial Council, and an executive body, the Provincial Executive. President and members of Council are elected together by resident citizens: the coalition of the elected President (who needs an absolute majority in the first or second round of voting) gains the three fifths of the Council's seats. The Executive is chaired by the President who appoint others members, called assessori.
This article is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported License, which means that you can copy and modify it as long as the entire work (including additions) remains under this license.

Italy ![]() i/ˈɪtəli/ (Italian: Italia [iˈtaːlja]), officially the Italian Republic or the Republic of Italy (Italian: Repubblica italiana), is a unitary parliamentary republic in south-central Europe. To the north, it borders France, Switzerland, Austria and Slovenia along the Alps. To the south, it consists of the entirety of the Italian Peninsula, Sicily, Sardinia–the two largest islands in the Mediterranean Sea–and many other smaller islands. The independent states of San Marino and the Vatican City are enclaves within Italy, while Campione d'Italia is an Italian exclave in Switzerland. The territory of Italy covers some 301,338 km2 (116,347 sq mi) and is influenced by a temperate seasonal climate. With 60.6 million inhabitants, it is the fifth most populous country in Europe, and the 23rd most populous in the world.
i/ˈɪtəli/ (Italian: Italia [iˈtaːlja]), officially the Italian Republic or the Republic of Italy (Italian: Repubblica italiana), is a unitary parliamentary republic in south-central Europe. To the north, it borders France, Switzerland, Austria and Slovenia along the Alps. To the south, it consists of the entirety of the Italian Peninsula, Sicily, Sardinia–the two largest islands in the Mediterranean Sea–and many other smaller islands. The independent states of San Marino and the Vatican City are enclaves within Italy, while Campione d'Italia is an Italian exclave in Switzerland. The territory of Italy covers some 301,338 km2 (116,347 sq mi) and is influenced by a temperate seasonal climate. With 60.6 million inhabitants, it is the fifth most populous country in Europe, and the 23rd most populous in the world.
Rome, the capital of Italy, was for centuries a political and religious centre of Western civilisation as the capital of the Roman Empire and site of the Holy See. After the decline of the Roman Empire, Italy endured numerous invasions by foreign peoples, from Germanic tribes such as the Lombards and Ostrogoths, to the Byzantines and later, the Normans, among others. Centuries later, Italy became the birthplace of Maritime republics and the Renaissance, an immensely fruitful intellectual movement that would prove to be integral in shaping the subsequent course of European thought.
This article is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported License, which means that you can copy and modify it as long as the entire work (including additions) remains under this license.
Radio Stations - Roma
SEARCH FOR RADIOS
- Loading...

-
Tuscan countryhouse in province of Arezzo, Italy
Tuscan countryhouse in province of Arezzo, Italy -
Visual Management - 3D Topicscape - Provinces of Italy
Visual Management - 3D Topicscape - Provinces of ItalyVisual Management - 3D Topicscape - Provinces of Italy
example of 3D knowledge mapping with Topicscape solution. -
Mindjet MindManager - Italy - Provinces - mindmapping diagram
Mindjet MindManager - Italy - Provinces - mindmapping diagramMindjet MindManager - Italy - Provinces - mindmapping diagram
example of use - Mindjet MindManager - visual knowledge base as mindmapping diagram. -
Capitals : 22 regions of France, 20 regions of Italy, 12 provinces of the Netherlands ...
Capitals : 22 regions of France, 20 regions of Italy, 12 provinces of the Netherlands ...Capitals : 22 regions of France, 20 regions of Italy, 12 provinces of the Netherlands ...
22 regiony Francji, 20 regionów Włoch, 12 prowincji Holandii i 10 prowincji Belgii + Region Stołeczny w losowej kolejności ( 22 regions of France, 20 regions of Italy, 12 provinces of the Netherlands and 10 provinces of Belgium + Capital Region in random order ) Capitals in random order ( translation to English ) : 1. Lazio - Rome 2. Provence-Alpes-Côte d'Azur - Marseille 3. Burgundy - Dijon 4. Marche - Ancona 5. Tuscany - Florence 6. Flemish Brabant - Leuven 7. South Holland - The Hague 8. East Flanders - Ghent 9. Umbria - Perugia 10. Hainaut - Mons 11. Molise - Campobasso 12. West Flanders - Bruges 13. Nord-Pas-de-Calais - Lille 14. Drenthe -
Italian provinces by area
Italian provinces by areaItalian provinces by area
This time it might be a little cool because this is not the U.S. and this is Italy. There's not even a wikipedia page for this. -
EXTREME WEATHER STRIKES ITALIAN NORTHERN PROVINCES
EXTREME WEATHER STRIKES ITALIAN NORTHERN PROVINCESEXTREME WEATHER STRIKES ITALIAN NORTHERN PROVINCES
EXTREME WEATHER STRIKES ITALIAN NORTHERN PROVINCES 1. ws pan floodwaters to bridge 2. gv building pan to floodwaters nearby 3. cu floodwaters 4. ms men clearing fallen trees from river 5. gv wrecked boats in floodwater 6. ms floodwaters and floating debris 7. gv partly submerged wall, people looking on, pan to floodwaters 8. ms surging water 9. ws floodwaters, pan to people looking at damage 10. gv wrecked bridge, pan to men talking 11. mcu dynamite taken from box 12. ms men setting dynamite 13. gv dynamite exploding 14. ms tracking shot, floodwaters and uprooted trees 15. ms man carried across flooded street to vehicle 16. ws flooded street, -
Italy during WW1
Italy during WW1Italy during WW1
A map simulation showing the London Pact, the battles between Italy and Austria-Hungary, and the aftermath of WW1 for Italy. Red - Italy Orange - Occupied by... -
Sirmione - Lake Garda - Italy
Sirmione - Lake Garda - ItalySirmione - Lake Garda - Italy
Sirmione is a comune in the province of Brescia, in Lombardy (northern Italy). It is bounded by the comunes of Desenzano del Garda and Peschiera del Garda in... -
Trentino Region - Italy
Trentino Region - ItalyTrentino Region - Italy
Trentino-Alto Adige/Südtirol[3] (Italian: Trentino-Alto Adige, pronounced [trenˈtiːno ˈalto ˈaːdidʒe]; German: Trentino-Südtirol;[4] Ladin: 'Trentin-Südtirol... -
Via Portici, Bolzano, Trentino-Alto Adige, South Tyrol, Italy, Europe
Via Portici, Bolzano, Trentino-Alto Adige, South Tyrol, Italy, EuropeVia Portici, Bolzano, Trentino-Alto Adige, South Tyrol, Italy, Europe
Trentino-Alto Adige/Südtirol is an autonomous region in Northern Italy. Since the 1970s most legislative and administrative competencies have been transferre... -
Europa Universalis 4 Let's Play as austria part 45. We take the provinces in Italy.
Europa Universalis 4 Let's Play as austria part 45. We take the provinces in Italy.Europa Universalis 4 Let's Play as austria part 45. We take the provinces in Italy.
This is part 45 of the Let’s Play series as Austria in EU4 Common Sense patch 1.12. We beat Spain in the race to get more territory in Italy. Twitchchannel: http://www.twitch.tv/flyingdutchy91 Please subscribe to my channel and give me a like when you like my video's. Achievements in this let's play: * The pen is mightier then the sword * A kaiser not just in name * Guarantor of peace * Neither Holy, nor German * City of Cities * One family to rule all * Bleed them dry --- Accomplished * Black Jack I will be streaming all my video's on twitch.tv click the link in my banner to get to my channel and follow the action live! I've got a str -
Mr. Kincaid WHAP Unification of Italy
Mr. Kincaid WHAP Unification of ItalyMr. Kincaid WHAP Unification of Italy
I. Italy in the early 1800s 1. Austria ruled the provinces of Venetia and Lombardy 2. Spanish ruled the Kingdom of the Two Sicilies. 3. Papal States controlled by the Church 4. Nationalism called for unification II. Movement for Unity A. 1832 Guiseppe Mazzini 1. Organized group called Young Italy 2. People over 40 were excluded 3. 1848: revolts broke out in Italy 4. Mazzini headed a republican government in Rome in 1849 5. 1848 rebellions failed forcing nationalist leaders into exile B. Kingdom of Piedmont-Sardinia 1. King Victor Emanuel II granted a liberal constitution in 1848 2. Camillo di Cavour named prime minister in 1852 3. Cavou -
Statue Of A King Of Italy
Statue Of A King Of ItalyStatue Of A King Of Italy
In front of the duomo, will will also notice that there is a statue. This is the statue of one of the ancient kings of Italy. This is because Italy used to be a monarchy right after the provinces of Italy united. -
F4 Tornado crosses Highway A4 in Italy
F4 Tornado crosses Highway A4 in ItalyF4 Tornado crosses Highway A4 in Italy
8th July 2015. The dramatic images taken with a dashcam, of the destructive F4 Tornado meanwhile it passes very close to the highway A4. Millions of damages in the territory between the provinces of Padua and Venice. One person dead and more than 90 injured. Original video + Newsarticle (in Italian): http://www.meteoweb.eu/2015/07/il-tor... Location on Street View: https://goo.gl/maps/zKueX https://www.facebook.com/CaughtOnDashcamsOrCCTV
- Alessandra Giudici
- Alessandro Ciriani
- Alessandro Pastacci
- Alessandro Repetto
- Alpes Maritimes
- Andrea Barducci
- Andrea Pieroni
- Angelo Vaccarezza
- Aniello Cimitile
- Antonello Iannarilli
- Antonino Saitta
- Antonio Del Corvo
- Antonio Pepe
- Antonio Pettinari
- Aosta Valley
- Armando Cusani
- Assessor (Italy)
- Attilio Schneck
- Augusto Rollandin
- Austrian Empire
- Barbara Degani
- Basilicata
- Beatrice Draghetti
- Benghazi Province
- Briançon
- Bruno Pilia
- Cabinet of Italy
- Calabria
- Campania
- Claudio Casadio
- Comune
- Corte d'Assise
- Cosimo Sibilia
- Daniele Bosone
- Daniele Molgora
- Daniele Nava
- Dario Allevi
- Derna Province
- Diego Sozzani
- Districts of Albania
- Districts of Austria
- Districts of Moldova
- Districts of Turkey
- Domenico Zinzi
- Edmondo Cirielli
- Elections in Italy
- Emilia-Romagna
- Emilio Sabattini
- Enrico Gherghetta
- Ettore Pirovano
- Eugenio d'Orsi
- Fabio Melilli
- Fabrizio Cesetti
- Fedele Sanciu
- Federica Fratoni
- Feliciano Polli
- Fiume
- Francesco De Nisi
- Francesco Schittulli
- Francesco Ventola
- Fulvio Tocco
- Gazzetta Ufficiale
- Gianna Gancia
- Gianpaolo Bottacin
- Giorgio Kutufà
- Giorgio Napolitano
- Giovanni Avanti
- Giovanni Florido
- Giovanni Miozzi
- Girolamo Turano
- Giuseppe Federico
- Giuseppe Monaco
- Giuseppe Raffa
- Graziano Milia
- Great Britain
- Guerino Testa
- Guido Podestà
- Hautes Alpes
- ISO 3166-2 IT
- Italian capitulation
- Italian Libya
- Italian Republic
- Italian Senate
- Italian Unification
- Italy
- Judiciary of Italy
- Lamberto Gestri
- Lazio
- Left Ecology Freedom
- Lega Nord
- Leonardo Carioni
- Leonardo Marras
- Leonardo Muraro
- Liguria
- Lombardy
- Lorenzo Dellai
- Luigi Cesaro
- Luigi Mazzuto
- Luigi Sappa
- Luis Durnwalder
- Mantova
- Marcella Zappaterra
- Marcello Meroi
- Marche
- Marino Fiasella
- Mario Monti
- Mario Oliverio
- Massimiliano Salini
- Massimo Bulbi
- Massimo Ferrarese
- Massimo Nobili
- Massimo Sertori
- Massimo Trespidi
- Misurata Province
- Molise
- Nanni Ricevuto
- Nazi Germany
- Nicola Bono
- Nicola Zingaretti
- Osvaldo Angeli
- Paolo Filippi
- Papal States
- Parliament of Italy
- Piedmont
- Piero Celani
- Piero Lacorazza
- Pietro Fontanini
- Pietro Foroni
- Politics of Abruzzo
- Politics of Apulia
- Politics of Calabria
- Politics of Campania
- Politics of Italy
- Politics of Lazio
- Politics of Liguria
- Politics of Lombardy
- Politics of Marche
- Politics of Molise
- Politics of Piedmont
- Politics of Sardinia
- Politics of Sicily
- Politics of Tuscany
- Politics of Umbria
- Politics of Veneto
- Polizia di Stato
- Portal Politics
- Prefetto
- President of Italy
- Province
- Province of Ancona
- Province of Aosta
- Province of Arezzo
- Province of Asti
- Province of Avellino
- Province of Bari
- Province of Belluno
- Province of Bergamo
- Province of Biella
- Province of Bologna
- Province of Bolzano
- Province of Brescia
- Province of Brindisi
- Province of Cagliari
- Province of Caserta
- Province of Catania
- Province of Cattaro
- Province of Chieti
- Province of Como
- Province of Cosenza
- Province of Cremona
- Province of Crotone
- Province of Cuneo
- Province of Enna
- Province of Fermo
- Province of Ferrara
- Province of Florence
- Province of Foggia
- Province of Genoa
- Province of Gorizia
- Province of Grosseto
- Province of Imperia
- Province of Isernia
- Province of Kotor
- Province of L'Aquila
- Province of Latina
- Province of Lecce
- Province of Lecco
- Province of Livorno
- Province of Lodi
- Province of Lubiana
- Province of Lucca
- Province of Macerata
- Province of Mantova
- Province of Mantua
- Province of Matera
- Province of Messina
- Province of Milan
- Province of Modena
- Province of Naples
- Province of Novara
- Province of Nuoro
- Province of Oristano
- Province of Padova
- Province of Padua
- Province of Palermo
- Province of Parma
- Province of Pavia
- Province of Perugia
- Province of Pescara
- Province of Piacenza
- Province of Pisa
- Province of Pistoia
- Province of Potenza
- Province of Prato
- Province of Pula
- Province of Ragusa
- Province of Ravenna
- Province of Rieti
- Province of Rijeka
- Province of Rimini
- Province of Rome
- Province of Rovigo
- Province of Salerno
- Province of Sassari
- Province of Savona
- Province of Siena
- Province of Sondrio
- Province of Spalato
- Province of Split
- Province of Syracuse
- Province of Taranto
- Province of Teramo
- Province of Terni
- Province of Trapani
- Province of Trento
- Province of Treviso
- Province of Trieste
- Province of Turin
- Province of Udine
- Province of Varese
- Province of Venezia
- Province of Venice
- Province of Vercelli
- Province of Verona
- Province of Vicenza
- Province of Viterbo
- Province of Zadar
- Provinces of Belgium
- Provinces of Italy
- Provinces of Spain
- Provincial police
- Puglia
- Pula
- Raions of Ukraine
- Referendums in Italy
- Regierungsbezirk
- Regions of Italy
- Roberto Deriu
- Roberto Simonetti
- Roberto Vasai
- Rome
- Rosario De Matteis
- Royal charter
- Salvatore Cherchi
- Sardinia
- Savoie
- Sicily
- Simone Bezzini
- Slovenia
- Sonia Masini
- South Tyrol
- Stanislao Zurlo
- Stefano Baccelli
- Stefano Vitali
- Tiziana Virgili
- Trentino
- Trentino Alto Adige
- Tripoli Province
- Tuscany
- Umbria
- Union for Trentino
- Union Valdôtaine
- USA
- Valle d'Aosta
- Valter Catarra
- Veneto
- Vincenzo Bernazzoli
- Wanda Ferro
- West Asia
- World War I
- World War II
- Yugoslavia
- Zadar
- Alpes Maritimes
- Austrian Empire
- Basilicata
- Briançon
- Great Britain
- Hautes Alpes
- Italy
- Lazio
- Molise
- Nazi Germany
- Papal States
- Province of Ancona
- Province of Arezzo
- Province of Asti
- Province of Avellino
- Province of Bari
- Province of Belluno
- Province of Bergamo
- Province of Biella
- Province of Bologna
- Province of Brescia
- Province of Brindisi
- Province of Cagliari
- Province of Caserta
- Province of Catania
- Province of Chieti
- Province of Como
- Province of Cosenza
- Province of Cremona
- Province of Crotone
- Province of Cuneo
- Province of Enna
- Province of Fermo
- Province of Ferrara
- Province of Florence
- Province of Foggia
- Province of Genoa
- Province of Gorizia
- Province of Grosseto
- Province of Imperia
- Province of Isernia
- Province of Latina
- Province of Lecce
- Province of Lecco
- Province of Livorno
- Province of Lodi
- Province of Lucca
- Province of Macerata
- Province of Mantua
- Province of Matera
- Province of Messina
- Province of Milan
- Province of Modena
- Province of Naples
- Province of Novara
- Province of Nuoro
- Province of Oristano
- Province of Padua
- Province of Palermo
- Province of Parma
- Province of Pavia
- Province of Perugia
- Province of Pescara
- Province of Piacenza
- Province of Pisa
- Province of Pistoia
- Province of Potenza
- Province of Prato
- Province of Ragusa
- Province of Ravenna
- Province of Rieti
- Province of Rimini
- Province of Rome
- Province of Rovigo
- Province of Salerno
- Province of Sassari
- Province of Savona
- Province of Siena
- Province of Sondrio
- Province of Syracuse
- Province of Taranto
- Province of Teramo
- Province of Terni
- Province of Trapani
- Province of Treviso
- Province of Trieste
- Province of Turin
- Province of Udine
- Province of Varese
- Province of Venice
- Province of Vercelli
- Province of Verona
- Province of Vicenza
- Province of Viterbo
- Pula
- Rome
- Sardinia
- Savoie
- Sicily
- Slovenia
- South Tyrol
- Trentino
- Yugoslavia
- Zadar
-
Tuscan countryhouse in province of Arezzo, Italy
Tuscan countryhouse in province of Arezzo, ItalyTuscan countryhouse in province of Arezzo, Italy
The estate (59 hectares) is located on Chianti hills between the provinces of Siena, Florence and Arezzio. Located at the end of a stone road of Etruscan ori... -
Visual Management - 3D Topicscape - Provinces of Italy
Visual Management - 3D Topicscape - Provinces of ItalyVisual Management - 3D Topicscape - Provinces of Italy
example of 3D knowledge mapping with Topicscape solution. -
Mindjet MindManager - Italy - Provinces - mindmapping diagram
Mindjet MindManager - Italy - Provinces - mindmapping diagramMindjet MindManager - Italy - Provinces - mindmapping diagram
example of use - Mindjet MindManager - visual knowledge base as mindmapping diagram. -
Capitals : 22 regions of France, 20 regions of Italy, 12 provinces of the Netherlands ...
Capitals : 22 regions of France, 20 regions of Italy, 12 provinces of the Netherlands ...Capitals : 22 regions of France, 20 regions of Italy, 12 provinces of the Netherlands ...
22 regiony Francji, 20 regionów Włoch, 12 prowincji Holandii i 10 prowincji Belgii + Region Stołeczny w losowej kolejności ( 22 regions of France, 20 regions of Italy, 12 provinces of the Netherlands and 10 provinces of Belgium + Capital Region in random order ) Capitals in random order ( translation to English ) : 1. Lazio - Rome 2. Provence-Alpes-Côte d'Azur - Marseille 3. Burgundy - Dijon 4. Marche - Ancona 5. Tuscany - Florence 6. Flemish Brabant - Leuven 7. South Holland - The Hague 8. East Flanders - Ghent 9. Umbria - Perugia 10. Hainaut - Mons 11. Molise - Campobasso 12. West Flanders - Bruges 13. Nord-Pas-de-Calais - Lille 14. Drenthe -
Italian provinces by area
Italian provinces by areaItalian provinces by area
This time it might be a little cool because this is not the U.S. and this is Italy. There's not even a wikipedia page for this. -
EXTREME WEATHER STRIKES ITALIAN NORTHERN PROVINCES
EXTREME WEATHER STRIKES ITALIAN NORTHERN PROVINCESEXTREME WEATHER STRIKES ITALIAN NORTHERN PROVINCES
EXTREME WEATHER STRIKES ITALIAN NORTHERN PROVINCES 1. ws pan floodwaters to bridge 2. gv building pan to floodwaters nearby 3. cu floodwaters 4. ms men clearing fallen trees from river 5. gv wrecked boats in floodwater 6. ms floodwaters and floating debris 7. gv partly submerged wall, people looking on, pan to floodwaters 8. ms surging water 9. ws floodwaters, pan to people looking at damage 10. gv wrecked bridge, pan to men talking 11. mcu dynamite taken from box 12. ms men setting dynamite 13. gv dynamite exploding 14. ms tracking shot, floodwaters and uprooted trees 15. ms man carried across flooded street to vehicle 16. ws flooded street, -
Italy during WW1
Italy during WW1Italy during WW1
A map simulation showing the London Pact, the battles between Italy and Austria-Hungary, and the aftermath of WW1 for Italy. Red - Italy Orange - Occupied by... -
Sirmione - Lake Garda - Italy
Sirmione - Lake Garda - ItalySirmione - Lake Garda - Italy
Sirmione is a comune in the province of Brescia, in Lombardy (northern Italy). It is bounded by the comunes of Desenzano del Garda and Peschiera del Garda in... -
Trentino Region - Italy
Trentino Region - ItalyTrentino Region - Italy
Trentino-Alto Adige/Südtirol[3] (Italian: Trentino-Alto Adige, pronounced [trenˈtiːno ˈalto ˈaːdidʒe]; German: Trentino-Südtirol;[4] Ladin: 'Trentin-Südtirol... -
Via Portici, Bolzano, Trentino-Alto Adige, South Tyrol, Italy, Europe
Via Portici, Bolzano, Trentino-Alto Adige, South Tyrol, Italy, EuropeVia Portici, Bolzano, Trentino-Alto Adige, South Tyrol, Italy, Europe
Trentino-Alto Adige/Südtirol is an autonomous region in Northern Italy. Since the 1970s most legislative and administrative competencies have been transferre... -
Europa Universalis 4 Let's Play as austria part 45. We take the provinces in Italy.
Europa Universalis 4 Let's Play as austria part 45. We take the provinces in Italy.Europa Universalis 4 Let's Play as austria part 45. We take the provinces in Italy.
This is part 45 of the Let’s Play series as Austria in EU4 Common Sense patch 1.12. We beat Spain in the race to get more territory in Italy. Twitchchannel: http://www.twitch.tv/flyingdutchy91 Please subscribe to my channel and give me a like when you like my video's. Achievements in this let's play: * The pen is mightier then the sword * A kaiser not just in name * Guarantor of peace * Neither Holy, nor German * City of Cities * One family to rule all * Bleed them dry --- Accomplished * Black Jack I will be streaming all my video's on twitch.tv click the link in my banner to get to my channel and follow the action live! I've got a str -
Mr. Kincaid WHAP Unification of Italy
Mr. Kincaid WHAP Unification of ItalyMr. Kincaid WHAP Unification of Italy
I. Italy in the early 1800s 1. Austria ruled the provinces of Venetia and Lombardy 2. Spanish ruled the Kingdom of the Two Sicilies. 3. Papal States controlled by the Church 4. Nationalism called for unification II. Movement for Unity A. 1832 Guiseppe Mazzini 1. Organized group called Young Italy 2. People over 40 were excluded 3. 1848: revolts broke out in Italy 4. Mazzini headed a republican government in Rome in 1849 5. 1848 rebellions failed forcing nationalist leaders into exile B. Kingdom of Piedmont-Sardinia 1. King Victor Emanuel II granted a liberal constitution in 1848 2. Camillo di Cavour named prime minister in 1852 3. Cavou -
Statue Of A King Of Italy
Statue Of A King Of ItalyStatue Of A King Of Italy
In front of the duomo, will will also notice that there is a statue. This is the statue of one of the ancient kings of Italy. This is because Italy used to be a monarchy right after the provinces of Italy united. -
F4 Tornado crosses Highway A4 in Italy
F4 Tornado crosses Highway A4 in ItalyF4 Tornado crosses Highway A4 in Italy
8th July 2015. The dramatic images taken with a dashcam, of the destructive F4 Tornado meanwhile it passes very close to the highway A4. Millions of damages in the territory between the provinces of Padua and Venice. One person dead and more than 90 injured. Original video + Newsarticle (in Italian): http://www.meteoweb.eu/2015/07/il-tor... Location on Street View: https://goo.gl/maps/zKueX https://www.facebook.com/CaughtOnDashcamsOrCCTV -
Aosta Valley - Italy
Aosta Valley - ItalyAosta Valley - Italy
The Aosta Valley is a mountainous semi-autonomous region in northwestern Italy. It is bordered by Rhône-Alpes, France to the west, Valais, Switzerland to the north and the region of Piedmont to the south and east. With an area of 3,263 km2 (1,260 sq mi) and a population of about 126,933, it is the smallest, least populous, and least densely populated region of Italy. It is the only Italian region which has no provinces (the province of Aosta was dissolved in 1945). Provincial administrative functions are provided by the regional government.The region is divided into 74 comuni (communes). Italian and French are both official, though the nati -
Abruzzo beautiful region -- italy
Abruzzo beautiful region -- italyAbruzzo beautiful region -- italy
Abruzzo (pronounced [aˈbruttso]) is a region in Italy, its western border lying less than 50 miles (80 km) due east of Rome. Abruzzo borders the region of Ma... -
Abruzzo
AbruzzoAbruzzo
Abruzzo (pronounced [aˈbruttso]) is a region of Italy, and is divided into the four provinces of L'Aquila, Teramo, Pescara, and Chieti. Geographically, Abruzzo is divided into a mountainous area to the west, which includes the Gran Sasso d'Italia, and a coastal area to the east with beaches on the Adriatic sea. Abruzzo is considered to be part of Southern Italy, although geographically it is more central. Abruzzo is known as "the greenest region in Europe" as one third of its territory, the largest in Europe, is set aside as national parks and protected nature reserves: there are three national parks, one regional park, and 38 protected natu -
Intercultural Communication: Italian Culture
Intercultural Communication: Italian CultureIntercultural Communication: Italian Culture
1. Bellamy, Richard. Modern Italian Social Theory: Ideology and Politics from Pareto to the Present. Stanford, California: Stanford University Press. 1987. Print. 2. Hendrix, John. History and Culture in Italy. Lanham, Maryland: Univserity Press of America. 2003. Print. 3. Bergami, Roberto, and Biagio Aulino. "Teaching and Learning Italian Abroad: A Comparative Pilot Study of Italian-Canadian, Italian-Australian and Italian Adolescent Speech." International Journal of Learning 16.8 (2009): 595-614. Print. 4. Caprara, Gian. "Personality and Politics: Values, Traits, and Political Choice." Political Psychology. (2012): Vol. 31-33. Pri -
Sutri, Lazio, Italy
Sutri, Lazio, ItalySutri, Lazio, Italy
SEE MY TRAVEL WEBPAGES: http://www.motorhomefulltime.com/ https://www.facebook.com/motorhomefulltime Sutri is located around 50 kilometres north of Rome and about 30 kilometres south of Viterbo on the Italian SR2 route which once was the Via Cassia, which linked Rome with the provinces to the north of the capital. Approaching from a distance it cannot be missed as it is located at the top of a hill. As with many walled Italian towns there are parking spaces outside of the city walls, one of which I used to spend the night in my motorhome before making this film the following morning. The whole comune of Sutri has only around 5,000 inhab -
Republic of Rome - Chapter 1 - Part 1.wmv
Republic of Rome - Chapter 1 - Part 1.wmvRepublic of Rome - Chapter 1 - Part 1.wmv
280-279 BC "Uniting the provinces Italy" With the conclusion of the Samnite Wars, Rome had consolidated its position as master of central Italy. The Republic... -
Dolomites, Italy
Dolomites, ItalyDolomites, Italy
The Dolomites (Italian. Dolomiti) is a mountain range in the Southern Limestone Alps, located in the North-East of Italy on the territory of the provinces of Bolzano-Bozen - South Tyrol, Trento and Belluno. Extends from the valley of the river Adige in the West to the valley of the Piave river on the East, North and South of the border-lined river valleys Pusteria and the Brenta. Dolomites special by the fact that deposits of colored stones, forming peaks and steep slopes, under the rays of the sun have creamy-pink attention the origin of the array is obliged to coral reefs, which are formed on the bottom of an ancient shallow sea. Approximat -
Roman Province Africa ROMAN EMPIRE | HISTORY of ROME
Roman Province Africa ROMAN EMPIRE | HISTORY of ROMERoman Province Africa ROMAN EMPIRE | HISTORY of ROME
The Roman province of Africa Proconsularis was established after the Romans defeated Carthage in the Third Punic War. It roughly comprised the territory of present-day northern Tunisia, the northeast of modern-day Algeria, and the small Mediterranean Sea coast of modern-day western Libya along the Syrtis Minor. It was the richest province in the western part of the empire. The Arabs later named roughly the same region as the original province Ifriqiya, a rendering of Africa, from the Latin language. The African provinces were amongst the wealthiest regions in the Empire (rivaled only by Egypt, Syria and Italy itself) and as a consequence pe -
EUROPA UNIVERSALIS 4 (IV) Let's Play - Savoy/Italy - HARD+AI BONUS - #14 "Integrating New Provinces"
EUROPA UNIVERSALIS 4 (IV) Let's Play - Savoy/Italy - HARD+AI BONUS - #14 "Integrating New Provinces"EUROPA UNIVERSALIS 4 (IV) Let's Play - Savoy/Italy - HARD+AI BONUS - #14 "Integrating New Provinces"
HARD DIFFICULTY and AI BONUSES! Europa Universalis 4 Let's Play with Random Lucky Nations. EU4 Grand Campaign 1444 Start. Link to Hotfix: http://forum.paradoxplaza.com/forum/showthread.php?714668-1.1.2-Hotfix-checksum-408b-NOT-FOR-PROBLEM-REPORTS!&s;=97962386635cf21a1164bc88897cfc41 -------------------------- Notes on this Video -------------------------- Last Napoli attack at Modena. Peace with Milan, 100% war score. Mission to integrate Cremona. Coring of Parma at Cremona begins. Claims made on Modena and Pisa. Want to watch more content like this? Check out my channel: http://www.youtube.com/user/MacsenGaming Some of my Playli

Tuscan countryhouse in province of Arezzo, Italy
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 2:07
- Updated: 14 Jul 2014
- author: Milan | Lake Como | Tuscany Sotheby's International Realty
- published: 14 Jul 2014
- views: 32
- author: Milan | Lake Como | Tuscany Sotheby's International Realty

Visual Management - 3D Topicscape - Provinces of Italy
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 0:56
- Updated: 08 Mar 2014
- author: Wojciech Korsak
- published: 26 Feb 2014
- views: 32
- author: Wojciech Korsak

Mindjet MindManager - Italy - Provinces - mindmapping diagram
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 1:08
- Updated: 28 Jan 2014
- author: Wojciech Korsak
- published: 08 Sep 2013
- views: 41
- author: Wojciech Korsak

Capitals : 22 regions of France, 20 regions of Italy, 12 provinces of the Netherlands ...
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 2:18
- Updated: 01 Oct 2014
- published: 01 Oct 2014
- views: 0

Italian provinces by area
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 1:56
- Updated: 03 Oct 2015
- published: 03 Oct 2015
- views: 9

EXTREME WEATHER STRIKES ITALIAN NORTHERN PROVINCES
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 1:55
- Updated: 31 Mar 2015
- published: 31 Mar 2015
- views: 495

Italy during WW1
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 2:59
- Updated: 05 Jul 2014
- author: KingCreateur
- published: 30 Aug 2012
- views: 3471
- author: KingCreateur

Sirmione - Lake Garda - Italy
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 3:00
- Updated: 19 Jul 2014
- author: TravelServiceEurope
- published: 24 Mar 2012
- views: 6664
- author: TravelServiceEurope

Trentino Region - Italy
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 2:02
- Updated: 02 Jul 2014
- author: THEWORLDOFTRAVEL
- published: 23 Oct 2010
- views: 5594
- author: THEWORLDOFTRAVEL

Via Portici, Bolzano, Trentino-Alto Adige, South Tyrol, Italy, Europe
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 0:21
- Updated: 15 May 2014
- author: Pietro Pecco
- published: 30 Sep 2011
- views: 229
- author: Pietro Pecco

Europa Universalis 4 Let's Play as austria part 45. We take the provinces in Italy.
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 26:13
- Updated: 21 Jun 2015
- published: 21 Jun 2015
- views: 28

Mr. Kincaid WHAP Unification of Italy
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 4:33
- Updated: 06 Mar 2015
- published: 06 Mar 2015
- views: 0

Statue Of A King Of Italy
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 0:26
- Updated: 20 Jun 2014
- published: 20 Jun 2014
- views: 1

F4 Tornado crosses Highway A4 in Italy
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 1:50
- Updated: 10 Jul 2015
- published: 10 Jul 2015
- views: 87

Aosta Valley - Italy
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 1:50
- Updated: 23 Sep 2014
- published: 23 Sep 2014
- views: 17

Abruzzo beautiful region -- italy
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 2:06
- Updated: 31 Aug 2014
- author: THEWORLDOFTRAVEL
- published: 18 Oct 2010
- views: 3564
- author: THEWORLDOFTRAVEL

Abruzzo
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 7:55
- Updated: 18 Sep 2015
- published: 18 Sep 2015
- views: 6

Intercultural Communication: Italian Culture
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 10:09
- Updated: 13 Nov 2013
- published: 13 Nov 2013
- views: 4970

Sutri, Lazio, Italy
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 14:53
- Updated: 23 Jul 2015
- published: 23 Jul 2015
- views: 44

Republic of Rome - Chapter 1 - Part 1.wmv
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 9:56
- Updated: 04 Sep 2014
- author: Jp Willemse
- published: 16 Feb 2010
- views: 11438
- author: Jp Willemse

Dolomites, Italy
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 3:19
- Updated: 05 Oct 2014
- published: 05 Oct 2014
- views: 0

Roman Province Africa ROMAN EMPIRE | HISTORY of ROME
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 40:45
- Updated: 23 May 2015
- published: 23 May 2015
- views: 0

EUROPA UNIVERSALIS 4 (IV) Let's Play - Savoy/Italy - HARD+AI BONUS - #14 "Integrating New Provinces"
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 31:05
- Updated: 25 Aug 2013
- published: 25 Aug 2013
- views: 51
- Playlist
- Chat
- Playlist
- Chat

Tuscan countryhouse in province of Arezzo, Italy
- published: 14 Jul 2014
- views: 32
-
author:
Milan | Lake Como | Tuscany Sotheby\'s International Realty
Add Playlist for this Author

Visual Management - 3D Topicscape - Provinces of Italy
- published: 26 Feb 2014
- views: 32
-
author:
Wojciech Korsak
Add Playlist for this Author

Mindjet MindManager - Italy - Provinces - mindmapping diagram
- published: 08 Sep 2013
- views: 41
-
author:
Wojciech Korsak
Add Playlist for this Author

Capitals : 22 regions of France, 20 regions of Italy, 12 provinces of the Netherlands ...
- published: 01 Oct 2014
- views: 0

Italian provinces by area
- published: 03 Oct 2015
- views: 9

EXTREME WEATHER STRIKES ITALIAN NORTHERN PROVINCES
- published: 31 Mar 2015
- views: 495

Italy during WW1
- published: 30 Aug 2012
- views: 3471
-
author:
KingCreateur
Add Playlist for this Author

Sirmione - Lake Garda - Italy
- published: 24 Mar 2012
- views: 6664
-
author:
TravelServiceEurope
Add Playlist for this Author

Trentino Region - Italy
- published: 23 Oct 2010
- views: 5594
-
author:
THEWORLDOFTRAVEL
Add Playlist for this Author

Via Portici, Bolzano, Trentino-Alto Adige, South Tyrol, Italy, Europe
- published: 30 Sep 2011
- views: 229
-
author:
Pietro Pecco
Add Playlist for this Author

Europa Universalis 4 Let's Play as austria part 45. We take the provinces in Italy.
- published: 21 Jun 2015
- views: 28

Mr. Kincaid WHAP Unification of Italy
- published: 06 Mar 2015
- views: 0

Statue Of A King Of Italy
- published: 20 Jun 2014
- views: 1

F4 Tornado crosses Highway A4 in Italy
- published: 10 Jul 2015
- views: 87

