-
remove the playlistBronze Age Collapse
- remove the playlistBronze Age Collapse











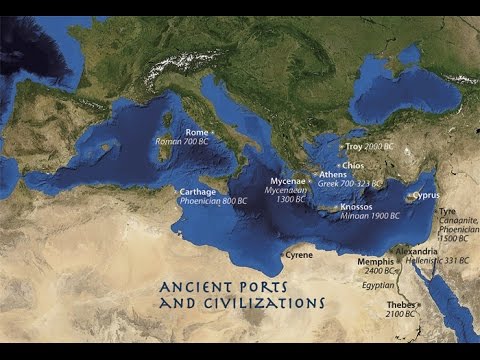

The Bronze Age collapse is a transition in the Aegean Region, Southwestern Asia and the Eastern Mediterranean from the Late Bronze Age to the Early Iron Age that historians such as M. Liverani, S. Richard, Robert Drews, Frank J. Yurco, Amos Nur, Manuel Robbins, Leonard R. Palmer, and others believe was violent, sudden and culturally disruptive. The palace economy of the Aegean Region and Anatolia which characterised the Late Bronze Age were replaced, after a hiatus, by the isolated village cultures of the Greek Dark Ages.
Between 1206 and 1150 BCE, the cultural collapse of the Mycenaean kingdoms, the Hittite Empire in Anatolia and Syria, and the New Kingdom of Egypt in Syria and Canaan interrupted trade routes and severely reduced literacy. In the first phase of this period, almost every city between Troy and Gaza was violently destroyed, and often left unoccupied thereafter: examples include Hattusa, Mycenae, and Ugarit.
The gradual end of the Dark Age that ensued saw the eventual rise of settled Syro-Hittite states in Cilicia and Syria, Aramaean kingdoms of the mid-10th century BCE in the Levant, and the eventual rise of the Neo-Assyrian Empire.
This article is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported License, which means that you can copy and modify it as long as the entire work (including additions) remains under this license.

The Bronze Age is a period characterized by the use of copper and its alloy bronze as the chief hard materials in the manufacture of some implements and weapons. Chronologically, it stands between the Stone Age and Iron Age. The term Stone Age implies the inability to smelt any ore, the term Bronze Age implies the inability to smelt iron ore and the term Iron Age implies the ability to manufacture artifacts in any of the three types of hard material. Their arrangement in the archaeological chronology reflects the difficulty of manufacture in the history of technology.
During the past few centuries of detailed, scientific study of the Bronze Age, it has become clear that on the whole, the use of copper or bronze was only the most stable and therefore the most diagnostic part of a cluster of features marking the period. In addition to the creation of bronze from raw materials and the widespread use of bronze tools and weapons, the period continued development of pictogramic or ideogramic symbols and proto-writing, and other features of urban civilization.
This article is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported License, which means that you can copy and modify it as long as the entire work (including additions) remains under this license.

In Greek mythology, the Trojan War was waged against the city of Troy by the Achaeans (Greeks) after Paris of Troy took Helen from her husband Menelaus king of Sparta. The war is one of the most important events in Greek mythology and has been narrated through many works of Greek literature, most notably through Homer's Iliad and the Odyssey. The Iliad relates a part of the last year of the siege of Troy; the Odyssey describes Odysseus's journey home. Other parts of the war are contained in a cycle of epic poems, which have survived through fragments. Episodes from the war provided material for Greek tragedy and other works of Greek literature, and for Roman poets including Virgil and Ovid.
The war originated from a quarrel between the goddesses Athena, Hera, and Aphrodite, after Eris, the goddess of strife and discord, gave them a golden apple, sometimes known as the Apple of Discord, marked "for the fairest". Zeus sent the goddesses to Paris, who judged that Aphrodite, as the "fairest", should receive the apple. In exchange, Aphrodite made Helen, the most beautiful of all women and wife of Menelaus, fall in love with Paris, who took her to Troy. Agamemnon, king of Mycenae and the brother of Helen's husband Menelaus, led an expedition of Achaean troops to Troy and besieged the city for ten years because of Paris' insult. After the deaths of many heroes, including the Achaeans Achilles and Ajax, and the Trojans Hector and Paris, the city fell to the ruse of the Trojan Horse. The Achaeans slaughtered the Trojans (except for some of the women and children whom they kept or sold as slaves) and desecrated the temples, thus earning the gods' wrath. Few of the Achaeans returned safely to their homes and many founded colonies in distant shores. The Romans later traced their origin to Aeneas, one of the Trojans, who was said to have led the surviving Trojans to modern day Italy.
This article is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported License, which means that you can copy and modify it as long as the entire work (including additions) remains under this license.
- Loading...

-
Bronze Age collapse
Bronze Age collapse -
Eric Cline | 1177 BC: The Year Civilization Collapsed
Eric Cline | 1177 BC: The Year Civilization CollapsedEric Cline | 1177 BC: The Year Civilization Collapsed
1177 BC: The Year Civilization Collapsed February 25, 2015 Dr. Eric H. Cline Professor of Classics and Anthropology Chair of the Department of Classical and Near Eastern Languages and Civilizations Director of the Capitol Archaeological Institute at The George Washington University, in Washington D.C. For more than three hundred years during the Late Bronze Age, from about 1500 BC to 1200 BC, the Mediterranean region played host to a complex international world in which Egyptians, Mycenaeans, Minoans, Hittites, Assyrians, Babylonians, Cypriots, and Canaanites all interacted, creating a cosmopolitan and globalized world-system such as has onl -
The End of Civilization (In the Bronze Age): Crash Course World History 211
The End of Civilization (In the Bronze Age): Crash Course World History 211The End of Civilization (In the Bronze Age): Crash Course World History 211
In which John Green teaches you about the Bronze Age civilization in what we today call the middle east, and how the vast, interconnected civilization that encompassed Egypt, The Levant, and Mesopotamia came to an end. What's that you say? There was no such civilization? Your word against ours. John will argue that through a complex network of trade and alliances, there was a loosely confederated and relatively continuous civilization in the region. Why it all fell apart was a mystery. Was it the invasion of the Sea People? An earthquake storm? Or just a general collapse, to which complex systems are prone? We'll look into a few of these pos -
09 The Collapse of the Bronze Age
09 The Collapse of the Bronze Age09 The Collapse of the Bronze Age
-
Epic Disaster of the Ancient World: Huge Ancient Civilization's Collapse Evidence of Destruction
Epic Disaster of the Ancient World: Huge Ancient Civilization's Collapse Evidence of DestructionEpic Disaster of the Ancient World: Huge Ancient Civilization's Collapse Evidence of Destruction
The Late Bronze Age collapse was a transition in the Aegean Region, Southwestern Asia and the Eastern Mediterranean from the Late Bronze Age to the Early Iron Age that historians believe was violent, sudden and culturally disruptive. The palace economy of the Aegean Region and Anatolia which characterised the Late Bronze Age was replaced, after a hiatus, by the isolated village cultures of the Greek Dark Ages. Between 1206 and 1150 BC, the cultural collapse of the Mycenaean kingdoms, the Hittite Empire in Anatolia and Syria, and the New Kingdom of Egypt in Syria and Canaan interrupted trade routes and severely reduced literacy. In the first -
HIST 180 Lecture 8: Collapse of the Late Bronze Age: 1200-1100 BCE
HIST 180 Lecture 8: Collapse of the Late Bronze Age: 1200-1100 BCEHIST 180 Lecture 8: Collapse of the Late Bronze Age: 1200-1100 BCE
Ethan Spanier, Visiting Assistant Professor at Whitman College. HIST 180, Spring 2011. -
Late Bronze Age collapse
Late Bronze Age collapseLate Bronze Age collapse
The Late Bronze Age collapse was a transition in the Aegean Region, Southwestern Asia and the Eastern Mediterranean from the Late Bronze Age to the Early Iron Age that historians, such as Amos Nur and Leonard R. Palmer, believe was violent, sudden and culturally disruptive. The palace economy of the Aegean Region and Anatolia which characterised the Late Bronze Age was replaced, after a hiatus, by the isolated village cultures of the Greek Dark Ages. Between 1206 and 1150 BCE, the cultural collapse of the Mycenaean kingdoms, the Hittite Empire in Anatolia and Syria, and the New Kingdom of Egypt in Syria and Canaan interrupted trade routes and -
In Search Of The Trojan War (6of6): The Fall Of Troy (BBC)
In Search Of The Trojan War (6of6): The Fall Of Troy (BBC)In Search Of The Trojan War (6of6): The Fall Of Troy (BBC)
The Trojan conflict and the Mediterranean late Bronze Age collapse. -
Sea Peoples
Sea PeoplesSea Peoples
During the late Bronze Age, civilization was progressing at an impressive rate in the Aegean and eastern Mediterranean regions. Kingdoms rose, order was established, and technology advanced. The Mycenaean and Minoans had intricate palaces in Greece and Crete, the Hittites dominated what is now Turkey. And the Canaanites controlled what would become the holy land -- Israel, Lebanon, and Jordan. But in the years surrounding 1200 B.C., all of the would change. Over the course of a single generation, all of those civilizations would be almost entirely wiped off the map, and those that did survive would be set back a thousand years, losing the abi -
1177 B C: The Year Civilization Collapsed by Eric H. Cline
1177 B C: The Year Civilization Collapsed by Eric H. Cline1177 B C: The Year Civilization Collapsed by Eric H. Cline
1177 B.C. The Year Civilization Collapsed Eric H. Cline Publication Date: April 2014 http://press.princeton.edu/titles/10185.html In 1177 B.C., marauding gro... -
Bronze Age Transformations of the Mediterranean World: A Perspective from the Countryside
Bronze Age Transformations of the Mediterranean World: A Perspective from the CountrysideBronze Age Transformations of the Mediterranean World: A Perspective from the Countryside
http://www.latrobe.edu.au/ Professor Steve Falconer studies the rise and collapse of urbanized societies in the Eastern Mediterranean and Near East, turning ... -
Ancient History Documentary: The Secrets of the Aegean Apocalypse
Ancient History Documentary: The Secrets of the Aegean ApocalypseAncient History Documentary: The Secrets of the Aegean Apocalypse
Ancient History Documentary: The Secrets of the Aegean Apocalypse This ancient history documentary, the Secrets of the Aegean Apocalypse, is about an ancient epic destruction that seems to have ended the Bronze Age. Around 1,200 BC, during the Bronze Age, an ancient Armageddon destroyed nearly every known civilization. Although it was predicted thousands of years ago, no one saw it coming. This was the disaster that was mentioned in Homer’s Iliad and Odyssey and in the Old Testament. What could have caused this epic destruction? One archaeologist has dedicated his life to following clues rediscovering the ancient pathways that lead up the -
Felix Höflmayer | Chronologies of Collapse: Climate Change
Felix Höflmayer | Chronologies of Collapse: Climate ChangeFelix Höflmayer | Chronologies of Collapse: Climate Change
Felix Höflmayer, Post-Doctoral Scholar, Oriental Institute -- University of Chicago presents the second lecture in our four-part series: Why Did Civilization... -
Ritual and Worship at Knossos (Minoan Bronze Age)
Ritual and Worship at Knossos (Minoan Bronze Age)Ritual and Worship at Knossos (Minoan Bronze Age)
This movie presents scenes of worship at Knossos and other sacred sites of the Minoan Bronze Age with the following themes: 1. Shrines, 2. Priestesses wieldi...
- Achaeans (Homer)
- Acre, Israel
- Acropolis of Athens
- Aegean Bronze Age
- Aegean Region
- Aegean Sea
- Akhenaten
- Akkadian Empire
- Alashiya
- Alasiya
- Ammurapi
- Amorites
- Anatolia
- Ancient Egypt
- Ancient Macedonians
- Ancient Near East
- Apennine culture
- Aramaeans
- Aramaic
- Arameans
- Armenians
- Arsenical bronze
- Ashdod
- Ashkelon
- Ashur-nasir-pal II
- Asia Minor
- Assyria
- Assyrians
- Athens
- Atlantic Bronze Age
- Ayios Dhimitrios
- Babylonia
- Basarabi culture
- Battle of Kadesh
- Beaker culture
- Beit Shemesh
- Bethel
- Book of Exodus
- Bronze Age
- Bronze Age Anatolia
- Bronze Age Britain
- Bronze Age Caucasus
- Bronze Age China
- Bronze Age collapse
- Bronze Age Europe
- Bronze Age India
- Bronze Age Levant
- Bronze Age sword
- Bronze Age writing
- Bulgaria
- Canaan
- Canaanite
- Canaanites
- Carthage
- Catacomb culture
- Caucasus
- Chalcolithic
- Chaldean people
- Chancellor Bay
- Chariot
- Cimmerians
- Code of Hammurabi
- Code of Ur-Nammu
- Colchians
- Copper
- Coțofeni culture
- Cuneiform
- Cyclopean
- Cyprus
- Debir
- Denyen
- Destruction layer
- Diyala valley
- Dorian Invasion
- Early Bronze Age
- Early Iron Age
- Earthquake storm
- Ebla
- Eblaites
- Eglon, Canaan
- Egypt
- Egyptians
- Ekrem Akurgal
- Elam
- Enheduanna
- Enkomi
- Fall of Nineveh
- Gaston Maspero
- Gaza
- Gojoseon
- Golden age
- Great Sphinx
- Greece
- Greek Dark Ages
- Greek Heroic Age
- Greek mythology
- Greeks
- Gudea
- Gutians
- Hallstatt culture
- Harvey Weiss
- Hattians
- Hattusa
- Hebrews
- Hekla 3 eruption
- Hesiod
- Hittite Empire
- Hittites
- Horemheb
- Hurrians
- Hyksos
- Indo-European
- Iran
- Iron Age
- Israel
- Jaffa
- Javelin
- Jiroft civilization
- Joseph Tainter
- Karaoglan (city)
- Kartvelian languages
- Kassites
- Kish tablet
- Kition
- Kokkinokremnos
- Kültepe texts
- Lachish
- Language Isolate
- Late Bronze Age
- Levant
- Libya
- Libyan
- Linear A
- Linear B
- Lukka lands
- Luwians
- Lycia
- Lydians
- Maryannu
- Medes
- Mediterranean Sea
- Merneptah
- Merneptah Stele
- Mesopotamia
- Metalsmith
- Middle Bronze Age
- Middle East
- Minoan civilization
- Minoan Crete
- Mitanni
- Moab
- Moses
- Mursili's eclipse
- Mushki
- Mycenae
- Mycenaean Greece
- Mycenaean period
- Narmer Palette
- Neo Assyrian Empire
- Neo-Assyrian Empire
- Neo-Hittite
- New Hittite Kingdom
- New Kingdom of Egypt
- Nordic Bronze Age
- Old Hittite Kingdom
- Old Kingdom
- Otomani culture
- Palace economy
- Palmer Drought Index
- Pecica culture
- Peloponnese
- Persian people
- Philistines
- Phoenicia
- Phoenician alphabet
- Phrygians
- Piracy
- Pontic languages
- Predynastic Egypt
- Prehistoric Cyprus
- Ramesses II
- Ramesses III
- Ramesses VI
- Refugees
- Romania
- Sarmatians
- Scythians
- Sea People
- Sea peoples
- Sea Peoples
- Semites
- Semitic
- Shasu
- Sherden
- Shutruk-Nahhunte
- Sinta, Cyprus
- Societal collapse
- Southwestern Asia
- Srubna culture
- Sukkot (place)
- Suppiluliuma II
- Suteans
- Synecdoche
- Syria
- Syro-Hittite states
- Tel Hazor
- Template Bronze Age
- Teresh
- Third Dynasty of Ur
- Thracians
- Tiglath-Pileser I
- Tiglath-Pileser III
- Tjeker
- Trade route
- Trojan War
- Troy
- Troy VIIa
- Tudhaliya IV
- Tumulus culture
- Tursha
- Twosret
- Ugarit
- Unetice culture
- Ur-Nanshe
- Urartians
- Urnfield culture
- Uruk period
- Via Maris
- Warka Vase
- Wietenberg culture
- Yenoam
- Achaea
- Acropolis of Athens
- Aegean Region
- Aegean Sea
- Akkadian Empire
- Anatolia
- Ashdod
- Ashkelon
- Beit Shemesh
- Bulgaria
- Carthage
- Caucasus
- Cyprus
- Ebla
- Egypt
- Elam
- Enkomi
- Gaston Maspero
- Gaza
- Greece
- Hattusa
- Iran
- Israel
- Jaffa
- Lachish
- Libya
- Lycia
- Medes
- Moab
- Mycenae
- Neo Assyrian Empire
- Peloponnese
- Phoenicia
- Romania
- Syria
- Tel Hazor
- Troy
- Ugarit
- Akhenaten
- Alashiya
- Ammurapi
- Arameans
- Armenians
- Catacomb culture
- Chancellor Bay
- Colchians
- Denyen
- Egyptians
- Ekrem Akurgal
- Enheduanna
- Gaston Maspero
- Greeks
- Harvey Weiss
- Hattians
- Hebrews
- Hesiod
- Hittites
- Horemheb
- Hyksos
- Joseph Tainter
- Lukka lands
- Lydians
- Medes
- Merneptah
- Moab
- Moses
- Mushki
- Nordic Bronze Age
- Persian people
- Philistines
- Phoenicia
- Phrygians
- Ramesses II
- Ramesses III
- Ramesses VI
- Sarmatians
- Scythians
- Sea Peoples
- Sea peoples
- Semitic
- Shasu
- Sherden
- Srubna culture
- Suppiluliuma II
- Tjeker
- Trojan War
- Tudhaliya IV
- Twosret
-
Bronze Age collapse
Bronze Age collapseBronze Age collapse
The Influence of Climatic Change on the Late Bronze Age Collapse and the Dark Ages. -
Eric Cline | 1177 BC: The Year Civilization Collapsed
Eric Cline | 1177 BC: The Year Civilization CollapsedEric Cline | 1177 BC: The Year Civilization Collapsed
1177 BC: The Year Civilization Collapsed February 25, 2015 Dr. Eric H. Cline Professor of Classics and Anthropology Chair of the Department of Classical and Near Eastern Languages and Civilizations Director of the Capitol Archaeological Institute at The George Washington University, in Washington D.C. For more than three hundred years during the Late Bronze Age, from about 1500 BC to 1200 BC, the Mediterranean region played host to a complex international world in which Egyptians, Mycenaeans, Minoans, Hittites, Assyrians, Babylonians, Cypriots, and Canaanites all interacted, creating a cosmopolitan and globalized world-system such as has onl -
The End of Civilization (In the Bronze Age): Crash Course World History 211
The End of Civilization (In the Bronze Age): Crash Course World History 211The End of Civilization (In the Bronze Age): Crash Course World History 211
In which John Green teaches you about the Bronze Age civilization in what we today call the middle east, and how the vast, interconnected civilization that encompassed Egypt, The Levant, and Mesopotamia came to an end. What's that you say? There was no such civilization? Your word against ours. John will argue that through a complex network of trade and alliances, there was a loosely confederated and relatively continuous civilization in the region. Why it all fell apart was a mystery. Was it the invasion of the Sea People? An earthquake storm? Or just a general collapse, to which complex systems are prone? We'll look into a few of these pos -
09 The Collapse of the Bronze Age
09 The Collapse of the Bronze Age09 The Collapse of the Bronze Age
-
Epic Disaster of the Ancient World: Huge Ancient Civilization's Collapse Evidence of Destruction
Epic Disaster of the Ancient World: Huge Ancient Civilization's Collapse Evidence of DestructionEpic Disaster of the Ancient World: Huge Ancient Civilization's Collapse Evidence of Destruction
The Late Bronze Age collapse was a transition in the Aegean Region, Southwestern Asia and the Eastern Mediterranean from the Late Bronze Age to the Early Iron Age that historians believe was violent, sudden and culturally disruptive. The palace economy of the Aegean Region and Anatolia which characterised the Late Bronze Age was replaced, after a hiatus, by the isolated village cultures of the Greek Dark Ages. Between 1206 and 1150 BC, the cultural collapse of the Mycenaean kingdoms, the Hittite Empire in Anatolia and Syria, and the New Kingdom of Egypt in Syria and Canaan interrupted trade routes and severely reduced literacy. In the first -
HIST 180 Lecture 8: Collapse of the Late Bronze Age: 1200-1100 BCE
HIST 180 Lecture 8: Collapse of the Late Bronze Age: 1200-1100 BCEHIST 180 Lecture 8: Collapse of the Late Bronze Age: 1200-1100 BCE
Ethan Spanier, Visiting Assistant Professor at Whitman College. HIST 180, Spring 2011. -
Late Bronze Age collapse
Late Bronze Age collapseLate Bronze Age collapse
The Late Bronze Age collapse was a transition in the Aegean Region, Southwestern Asia and the Eastern Mediterranean from the Late Bronze Age to the Early Iron Age that historians, such as Amos Nur and Leonard R. Palmer, believe was violent, sudden and culturally disruptive. The palace economy of the Aegean Region and Anatolia which characterised the Late Bronze Age was replaced, after a hiatus, by the isolated village cultures of the Greek Dark Ages. Between 1206 and 1150 BCE, the cultural collapse of the Mycenaean kingdoms, the Hittite Empire in Anatolia and Syria, and the New Kingdom of Egypt in Syria and Canaan interrupted trade routes and -
In Search Of The Trojan War (6of6): The Fall Of Troy (BBC)
In Search Of The Trojan War (6of6): The Fall Of Troy (BBC)In Search Of The Trojan War (6of6): The Fall Of Troy (BBC)
The Trojan conflict and the Mediterranean late Bronze Age collapse. -
Sea Peoples
Sea PeoplesSea Peoples
During the late Bronze Age, civilization was progressing at an impressive rate in the Aegean and eastern Mediterranean regions. Kingdoms rose, order was established, and technology advanced. The Mycenaean and Minoans had intricate palaces in Greece and Crete, the Hittites dominated what is now Turkey. And the Canaanites controlled what would become the holy land -- Israel, Lebanon, and Jordan. But in the years surrounding 1200 B.C., all of the would change. Over the course of a single generation, all of those civilizations would be almost entirely wiped off the map, and those that did survive would be set back a thousand years, losing the abi -
1177 B C: The Year Civilization Collapsed by Eric H. Cline
1177 B C: The Year Civilization Collapsed by Eric H. Cline1177 B C: The Year Civilization Collapsed by Eric H. Cline
1177 B.C. The Year Civilization Collapsed Eric H. Cline Publication Date: April 2014 http://press.princeton.edu/titles/10185.html In 1177 B.C., marauding gro... -
Bronze Age Transformations of the Mediterranean World: A Perspective from the Countryside
Bronze Age Transformations of the Mediterranean World: A Perspective from the CountrysideBronze Age Transformations of the Mediterranean World: A Perspective from the Countryside
http://www.latrobe.edu.au/ Professor Steve Falconer studies the rise and collapse of urbanized societies in the Eastern Mediterranean and Near East, turning ... -
Ancient History Documentary: The Secrets of the Aegean Apocalypse
Ancient History Documentary: The Secrets of the Aegean ApocalypseAncient History Documentary: The Secrets of the Aegean Apocalypse
Ancient History Documentary: The Secrets of the Aegean Apocalypse This ancient history documentary, the Secrets of the Aegean Apocalypse, is about an ancient epic destruction that seems to have ended the Bronze Age. Around 1,200 BC, during the Bronze Age, an ancient Armageddon destroyed nearly every known civilization. Although it was predicted thousands of years ago, no one saw it coming. This was the disaster that was mentioned in Homer’s Iliad and Odyssey and in the Old Testament. What could have caused this epic destruction? One archaeologist has dedicated his life to following clues rediscovering the ancient pathways that lead up the -
Felix Höflmayer | Chronologies of Collapse: Climate Change
Felix Höflmayer | Chronologies of Collapse: Climate ChangeFelix Höflmayer | Chronologies of Collapse: Climate Change
Felix Höflmayer, Post-Doctoral Scholar, Oriental Institute -- University of Chicago presents the second lecture in our four-part series: Why Did Civilization... -
Ritual and Worship at Knossos (Minoan Bronze Age)
Ritual and Worship at Knossos (Minoan Bronze Age)Ritual and Worship at Knossos (Minoan Bronze Age)
This movie presents scenes of worship at Knossos and other sacred sites of the Minoan Bronze Age with the following themes: 1. Shrines, 2. Priestesses wieldi... -
1177 B.C.: The Year Civilization Collapsed, Eric H. Cline - Book Trailer for Paperback
1177 B.C.: The Year Civilization Collapsed, Eric H. Cline - Book Trailer for Paperback1177 B.C.: The Year Civilization Collapsed, Eric H. Cline - Book Trailer for Paperback
In 1177 B.C., marauding groups known only as the “Sea Peoples” invaded Egypt. The pharaoh’s army and navy managed to defeat them, but the victory so weakened Egypt that it soon slid into decline, as did most of the surrounding civilizations. After centuries of brilliance, the civilized world of the Bronze Age came to an abrupt and cataclysmic end. Kingdoms fell like dominoes over the course of just a few decades. No more Minoans or Mycenaeans. No more Trojans, Hittites, or Babylonians. The thriving economy and cultures of the late second millennium B.C., which had stretched from Greece to Egypt and Mesopotamia, suddenly ceased to exist, along -
Forging a Bronze-Age Sword
Forging a Bronze-Age SwordForging a Bronze-Age Sword
How to craft a replica of an Irish bronze-age shortsword. This was a course run by http://bronzeagefoundry.com/. Follow Ancient Recitations for extra content on Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/AncientRecitations -
2. The Dark Ages
2. The Dark Ages2. The Dark Ages
Introduction to Ancient Greek History (CLCV 205) In this lecture, Professor Donald Kagan explores the earliest history of Greek civilization. He demonstrates... -
1177 B.C.: The Year Civilization Collapsed (Turning Points in Ancient History) — Download
1177 B.C.: The Year Civilization Collapsed (Turning Points in Ancient History) — Download1177 B.C.: The Year Civilization Collapsed (Turning Points in Ancient History) — Download
Download Here: http://tinyurl.com/ptt7umg In 1177 B.C., marauding groups known only as the "Sea Peoples" invaded Egypt. The pharaoh's army and navy managed to defeat them, but the victory so weakened Egypt that it soon slid into decline, as did most of the surrounding civilizations. After centuries of brilliance, the civilized world of the Bronze Age came to an abrupt and cataclysmic end. Kingdoms fell like dominoes over the course of just a few decades. No more Minoans or Mycenaeans. No more Trojans, Hittites, or Babylonians. The thriving economy and cultures of the late second millennium B.C., which had stretched from Greece to -
KS2 Prehistory – The Bronze Age
KS2 Prehistory – The Bronze AgeKS2 Prehistory – The Bronze Age
www.museumoflondon.org.uk/prehistory-resources How did people make tools from metal during the Bronze Age? This short video, introduced by children, demonstrates how a bronze axe is cast using Bronze Age technologies. -
[Documentary] China's Bronze Age - Shang Dynasty
[Documentary] China's Bronze Age - Shang Dynasty[Documentary] China's Bronze Age - Shang Dynasty
Playlist of documentaries about Chinese major dynasties: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=qXrkF5Nd4i8&list;=PLiVCagCDXANC6RPVc0NAzj3BcWHf5S1mK&spfreload;=10 -
THE HIDDEN PEARL Documentary History Of Arameans People
THE HIDDEN PEARL Documentary History Of Arameans PeopleTHE HIDDEN PEARL Documentary History Of Arameans People
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Aramean_people http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Aramean_Genocide The Arameans, or Aramaeans, (Aramaic: ܐܪ̈ܡܝܐ, ארמיא ; ʼaramáyé) were a Northwest Semitic semi-nomadic and pastoralist people who originated in what is now modern Syria (Biblical Aram) during the Late Bronze Age and the Iron Age. Large groups migrated to Mesopotamia where they intermingled with the native Akkadian (Assyrian and Babylonian) population. A large proportion of Syriac Christians in modern Syria still espouse an Aramean identity to this day, though few now speak the Western Aramaic language. The Arameans never had a unified nation; they were d -
Testing Middle Bronze Age Spears from Neil Burridge
Testing Middle Bronze Age Spears from Neil BurridgeTesting Middle Bronze Age Spears from Neil Burridge
Thrand and Eldgrim test Neil Burridge's Middle Bronze Age Spearheads mounted on proper shaped spear shafts. They test them on multiple layers of clothe and 1mm/20 gauge thick mild steel armour to see penetration into ballistic gelatin. They use Thrand's overarm throwing slide or thumb up and Christopher Matthew's underarm or thumb down lance technique as he proposed in his book A Storm of Spears: Understanding the Greek Hoplite at War to determine which was most likely used with these early Spears of antiquity. They also test the strength and edge of the hammered hardened bronze wile throwing and thrusting up close on a variety of mediums in -
1177 BC The Year Civilization Collapsed Turning Points in Ancient History
1177 BC The Year Civilization Collapsed Turning Points in Ancient History1177 BC The Year Civilization Collapsed Turning Points in Ancient History
1177 BC The Year Civilization Collapsed Turning Points in Ancient History Donwload Here http://youtube.channel.pdf.warlords.xyz/?book=0691140898&lokiuy;=t5xl.html In 1177 B.C., marauding groups known only as the "Sea Peoples" invaded Egypt. The pharaoh's army and navy managed to defeat them, but the victory so weakened Egypt that it soon slid into decline, as did most of the surrounding civilizations. After centuries of brilliance, the civilized world of the Bronze Age came to an abrupt and cataclysmic end. Kingdoms fell like dominoes over the course of just a few decades. No more Minoans or Mycenaeans. No more Trojans, Hittites, or B

Bronze Age collapse
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 44:07
- Updated: 23 Aug 2014
- author: archeo atlas
- published: 04 Jan 2014
- views: 1861
- author: archeo atlas

Eric Cline | 1177 BC: The Year Civilization Collapsed
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 52:19
- Updated: 06 Apr 2015
- published: 06 Apr 2015
- views: 3

The End of Civilization (In the Bronze Age): Crash Course World History 211
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 12:59
- Updated: 03 Oct 2014
- published: 03 Oct 2014
- views: 531943

09 The Collapse of the Bronze Age
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 30:13
- Updated: 21 Mar 2015
- published: 21 Mar 2015
- views: 0

Epic Disaster of the Ancient World: Huge Ancient Civilization's Collapse Evidence of Destruction
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 43:30
- Updated: 01 Jun 2015
- published: 01 Jun 2015
- views: 3

HIST 180 Lecture 8: Collapse of the Late Bronze Age: 1200-1100 BCE
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 50:28
- Updated: 04 Aug 2014
- author: Whitman College
- published: 11 Feb 2011
- views: 6372
- author: Whitman College

Late Bronze Age collapse
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 20:08
- Updated: 16 Nov 2014
- published: 16 Nov 2014
- views: 0

In Search Of The Trojan War (6of6): The Fall Of Troy (BBC)
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 57:37
- Updated: 07 Jul 2015
- published: 07 Jul 2015
- views: 10

Sea Peoples
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 1:54
- Updated: 16 Sep 2014
- published: 16 Sep 2014
- views: 392

1177 B C: The Year Civilization Collapsed by Eric H. Cline
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 1:01
- Updated: 03 Sep 2014
- author: Princeton University Press
- published: 08 Jan 2014
- views: 2691
- author: Princeton University Press

Bronze Age Transformations of the Mediterranean World: A Perspective from the Countryside
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 51:42
- Updated: 19 May 2014
- author: La Trobe University
- published: 06 Oct 2013
- views: 503
- author: La Trobe University

Ancient History Documentary: The Secrets of the Aegean Apocalypse
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 44:17
- Updated: 20 Apr 2015
- published: 20 Apr 2015
- views: 2

Felix Höflmayer | Chronologies of Collapse: Climate Change
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 49:27
- Updated: 22 Apr 2014
- author: The Oriental Institute
- published: 27 Dec 2013
- views: 786
- author: The Oriental Institute

Ritual and Worship at Knossos (Minoan Bronze Age)
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 9:28
- Updated: 01 Sep 2014
- author: Ladyofthe Labyrinth
- published: 13 May 2010
- views: 19227
- author: Ladyofthe Labyrinth

1177 B.C.: The Year Civilization Collapsed, Eric H. Cline - Book Trailer for Paperback
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 1:01
- Updated: 31 Aug 2015
- published: 31 Aug 2015
- views: 0

Forging a Bronze-Age Sword
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 15:00
- Updated: 28 Sep 2015
- published: 28 Sep 2015
- views: 3633

2. The Dark Ages
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 68:11
- Updated: 31 Aug 2014
- author: YaleCourses
- published: 21 Nov 2008
- views: 110611
- author: YaleCourses

1177 B.C.: The Year Civilization Collapsed (Turning Points in Ancient History) — Download
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 0:09
- Updated: 30 Jun 2015
- published: 30 Jun 2015
- views: 0

KS2 Prehistory – The Bronze Age
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 4:14
- Updated: 20 Feb 2015
- published: 20 Feb 2015
- views: 119
![[Documentary] China's Bronze Age - Shang Dynasty [Documentary] China's Bronze Age - Shang Dynasty](http://web.archive.org./web/20151023061515im_/http://i.ytimg.com/vi/VRQKp_vjVSY/0.jpg)
[Documentary] China's Bronze Age - Shang Dynasty
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 43:54
- Updated: 01 Mar 2015
- published: 01 Mar 2015
- views: 42

THE HIDDEN PEARL Documentary History Of Arameans People
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 197:55
- Updated: 18 Aug 2013
- published: 18 Aug 2013
- views: 18262

Testing Middle Bronze Age Spears from Neil Burridge
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 25:51
- Updated: 06 May 2015
- published: 06 May 2015
- views: 301

1177 BC The Year Civilization Collapsed Turning Points in Ancient History
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 0:46
- Updated: 19 Oct 2015
- published: 19 Oct 2015
- views: 0
- Playlist
- Chat
- Playlist
- Chat

Bronze Age collapse
- published: 04 Jan 2014
- views: 1861
-
author:
archeo atlas
Add Playlist for this Author

Eric Cline | 1177 BC: The Year Civilization Collapsed
- published: 06 Apr 2015
- views: 3

The End of Civilization (In the Bronze Age): Crash Course World History 211
- published: 03 Oct 2014
- views: 531943

09 The Collapse of the Bronze Age
- published: 21 Mar 2015
- views: 0

Epic Disaster of the Ancient World: Huge Ancient Civilization's Collapse Evidence of Destruction
- published: 01 Jun 2015
- views: 3

HIST 180 Lecture 8: Collapse of the Late Bronze Age: 1200-1100 BCE
- published: 11 Feb 2011
- views: 6372
-
author:
Whitman College
Add Playlist for this Author

Late Bronze Age collapse
- published: 16 Nov 2014
- views: 0

In Search Of The Trojan War (6of6): The Fall Of Troy (BBC)
- published: 07 Jul 2015
- views: 10

Sea Peoples
- published: 16 Sep 2014
- views: 392

1177 B C: The Year Civilization Collapsed by Eric H. Cline
- published: 08 Jan 2014
- views: 2691
-
author:
Princeton University Press
Add Playlist for this Author

Bronze Age Transformations of the Mediterranean World: A Perspective from the Countryside
- published: 06 Oct 2013
- views: 503
-
author:
La Trobe University
Add Playlist for this Author

Ancient History Documentary: The Secrets of the Aegean Apocalypse
- published: 20 Apr 2015
- views: 2

Felix Höflmayer | Chronologies of Collapse: Climate Change
- published: 27 Dec 2013
- views: 786
-
author:
The Oriental Institute
Add Playlist for this Author

Ritual and Worship at Knossos (Minoan Bronze Age)
- published: 13 May 2010
- views: 19227
-
author:
Ladyofthe Labyrinth
Add Playlist for this Author
Paranoia fuels mistaken identity killings in Israel
Edit Al Jazeera 22 Oct 2015Alien Engineering Around Strange Star?
Edit Huffington Post 22 Oct 2015US-Pakistan talks: Nukes, India, the Taliban, and China
Edit Al Jazeera 22 Oct 2015U.S. and Kurdish Commandos Said to Raid ISIS Prison in Northern Iraq
Edit New York Times 22 Oct 2015Science, Knowledge And Darkness
Edit National Public Radio 02 Sep 2015Six Clay Seals Discovered In Israel Linked To Era Of Kings David And Solomon>
Edit Huffington Post 20 Dec 2014The world’s biggest mysteries scientists still can’t solve
Edit The Australian 02 Sep 2014Lessons From The Last Time Civilization Collapsed
Edit National Public Radio 19 Aug 2014A Climate and Energy Roundup
Edit The New York Times 22 Oct 2013Exploring Solar, Efficiency, Gas and More with Amory Lovins and Joel Makower
Edit The New York Times 22 Oct 2013Did A Centuries-Long Drought Wipe Out Ancient Greece?
Edit Huffington Post 15 Aug 2013Ancient Greece Collapsed Because Of A 300-Year Drought
Edit Business Insider 15 Aug 2013Ancient history's mysteries part 2
Edit The Examiner 14 Jun 2013The Brief History of Civilized Man
Edit The Examiner 15 May 2013- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- Next page »






