Iraq, known in Classical Antiquity as Mesopotamia, was home to the oldest civilizations in the world, with a cultural history of over 10,000 years, hence its common epithet, the Cradle of Civilization. Mesopotamia, as part of the larger Fertile Crescent, was a significant part of the Ancient Near East throughout the Bronze Age and the Iron Age. Successively ruled by the Assyrian, Medo-Persian, Seleucid and Parthian empires during the Iron Age and Classical Antiquity, Iraq was conquered by the Rashidun Caliphate and became a center of the Islamic Golden Age during the medieval Abbasid Caliphate. After a series of invasions and conquest by the Mongols and Turkmens, Iraq fell under Ottoman rule in the 16th century, intermittently falling under Mamluk and Safavid control.
Ottoman rule ended with World War I, and Iraq came to be administered by the British Empire until the establishment of the Kingdom of Iraq in 1932. The Republic of Iraq was established in 1958 following a coup d'état. The Republic was controlled by Saddam Hussein from 1979 to 2003, into which period falls into the war with Iran and the Gulf War. Saddam was deposed following the 2003 US-led invasion of the country. Following the invasion, the situation deteriorated to the extent that in 2006-2007, Iraq was on the brink of civil war. However, conditions improved following a surge in U.S. troops in 2007-2008, and the war was declared formally over in December 2011.
This article is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported License, which means that you can copy and modify it as long as the entire work (including additions) remains under this license.

Iraq (/ɪˈræk/ or ![]() i/ɪˈrɑːk/; Arabic: العراق al-‘Irāq); officially the Republic of Iraq (Arabic:
i/ɪˈrɑːk/; Arabic: العراق al-‘Irāq); officially the Republic of Iraq (Arabic: ![]() جمهورية العراق (help·info) Jumhūriyyat al-‘Irāq), is a country in Western Asia spanning most of the northwestern end of the Zagros mountain range, the eastern part of the Syrian Desert and the northern part of the Arabian Desert.
جمهورية العراق (help·info) Jumhūriyyat al-‘Irāq), is a country in Western Asia spanning most of the northwestern end of the Zagros mountain range, the eastern part of the Syrian Desert and the northern part of the Arabian Desert.
Iraq borders Syria to the northwest, Turkey to the north, Iran to the east, Jordan to the southwest and Kuwait and Saudi Arabia to the south. Iraq has a narrow section of coastline measuring 58 km (36 mi) on the northern Persian Gulf. The capital city, Baghdad is in the center-east of the country.
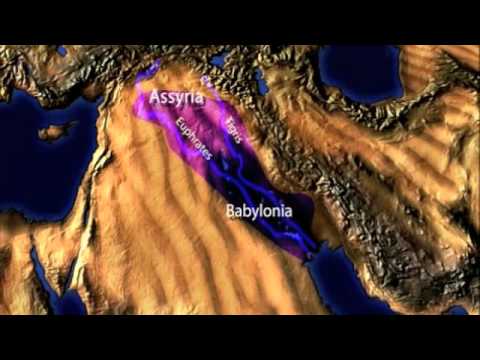
Two major rivers, the Tigris and Euphrates, run through the center of Iraq, flowing from northwest to southeast. These provide Iraq with agriculturally capable land and contrast with the steppe and desert landscape that covers most of Western Asia.
Historically, Iraq was the center of the Abbasid Arabic Islamic Empire. Iraq has been known to the west by the Greek toponym 'Mesopotamia' (Land between the rivers) and has been home to continuous successive civilizations since the 6th millennium BC. The region between the Tigris and Euphrates rivers is often referred to as the cradle of civilization and the birthplace of writing, law and the wheel. At different periods in its history, Iraq was the center of the indigenous Akkadian, Sumerian, Assyrian, Babylonian, and Abbasid empires. It was also part of the Achaemenid, Hellenistic, Parthian, Sassanid, Roman, Rashidun, Umayyad, Mongol, Safavid, Afsharid, and Ottoman empires, and under British control as a League of Nations mandate.
This article is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported License, which means that you can copy and modify it as long as the entire work (including additions) remains under this license.
Radio Stations - Baghdad
SEARCH FOR RADIOS
- Loading...

-
Iraq, the Cradle Of Civilization - Documentary
Iraq, the Cradle Of Civilization - Documentary -
Iraq, the Cradle Of Civilization - Documentary
Iraq, the Cradle Of Civilization - DocumentaryIraq, the Cradle Of Civilization - Documentary
National Geographic Documentary 2015 National Geographic Documentary 2015 National Geographic Documentary 2015 National Geographic, National Geographic Docum... Documentaries Iraq - the Cradle Of Civilization - Documentary History Channel Full Length Documentary the Cradle Of Civilization Documentaries the Cradle Of ... Iraq, the Cradle Of Civilization - Documentary After thousands of years as a hunter/gatherer, man built the first cities 5000 years ago on the banks of the ... Documentary | Iraq, the Cradle Of Civilization | History Documentary documentaries documentary documentaries 2014 youtube documentaries History Documentary d... -
Iraq Explained -- ISIS, Syria and War
Iraq Explained -- ISIS, Syria and WarIraq Explained -- ISIS, Syria and War
The current crisis in Iraq explained in under 5 minutes. There is war in Iraq? Again? And the US and Iran are talking about working together? And who is this ISIS Terrorist group that is all over the news? And Religion? Oh dear... When exactly has the world gone mad again? It is not possible to explain a complicated topic like this without simplification. We are very aware that this video is not painting a full picture of the situation. But we hope that it may lay the foundation on which you can try to do your own research and understand how horribly Fu**ed up the whole situation is. We did have to produce the video super fast -- thanks -
Documentary Iraq a history of colonialism - 1 of 5
Documentary Iraq a history of colonialism - 1 of 5Documentary Iraq a history of colonialism - 1 of 5
Wednesday, 19 March 2008 This video documentary, on the anniversary of the invasion of Iraq, illustrates the west's history of colonialism in Iraq. Charting ... -
The Kings: From Babylon to Baghdad 1
The Kings: From Babylon to Baghdad 1The Kings: From Babylon to Baghdad 1
The Kings: From Babylon to Baghdad 1 -
Iran - Iraq War | 3 Minute History
Iran - Iraq War | 3 Minute HistoryIran - Iraq War | 3 Minute History
And here's some modern stuff. -
History of Iraq (Mesopotamia) Part 1 تأريخ العراق
History of Iraq (Mesopotamia) Part 1 تأريخ العراقHistory of Iraq (Mesopotamia) Part 1 تأريخ العراق
History of Iraq. -
A brief history of ISIS and the current crisis in Iraq
A brief history of ISIS and the current crisis in IraqA brief history of ISIS and the current crisis in Iraq
For starters: they used to be called Al Qaeda in Iraq. But they were too extreme for even Al Qaeda. Ezra Klein explains in three minutes. Warning: this video... -
Lecture 16 A Short History of Iraq
Lecture 16 A Short History of IraqLecture 16 A Short History of Iraq
Up to the time of the Second Gulf War. -
History of Iraq 1956-1979
History of Iraq 1956-1979History of Iraq 1956-1979
History of Iraq. -
Mr. Peabody and Sherman Travel WayBack to 1953 - A History of Iraq
Mr. Peabody and Sherman Travel WayBack to 1953 - A History of IraqMr. Peabody and Sherman Travel WayBack to 1953 - A History of Iraq
SCRIPT © 2008 by Matthew Hahn. All rights reserved. Mr. Peabody and Sherman visit NYC on 9/11. Based on a webcomic series I wrote in 2005. Neither created by... -
Iran's Revolutions: Crash Course World History 226
Iran's Revolutions: Crash Course World History 226Iran's Revolutions: Crash Course World History 226
In which John Green teaches you about Iran's Revolutions. Yes, revolutions plural. What was the1979 Iranian Revolution about? It turns out, Iran has a pretty long history of unrest in order to put power in the hands of the people, and the most recent revolution in 1979 was, at least at first, not necessarily about creating an Islamic state. It certainly turned out to be about that, but it was initially just about people who wanted to get rid of an oppressive regime. Listen up as John teaches you about Iran's long history of revolution. Citation 1: Caryl, Christian. Strange Rebels: 1979 and the Birth of the 21st Century. New York, Basic Books -
ISIS Is About to Destroy Biblical History In Iraq! Baghdadi Has $2 Billion War Chest!
ISIS Is About to Destroy Biblical History In Iraq! Baghdadi Has $2 Billion War Chest!ISIS Is About to Destroy Biblical History In Iraq! Baghdadi Has $2 Billion War Chest!
As reported in The Guardian, a windfall of intelligence just before Mosul fell revealed that al-Baghdadi had accumulated a $2 billion war chest, in part by s... -
Jeremy Corbyn speaking at biggest protest in UK history against Iraq war
Jeremy Corbyn speaking at biggest protest in UK history against Iraq warJeremy Corbyn speaking at biggest protest in UK history against Iraq war
On 15 February 2003, two million people on the streets of London, in the biggest process ever in UK history, said not in our name to the Iraq war. Jeremy Corbyn gave this speech to the huge rally in Hyde Park.
- 14 July Revolution
- 17 July Revolution
- 3rd Division (Iraq)
- 612 BC
- 727 BC
- 745 BC
- 911 BC
- Abbasid Caliphate
- Abdul Rahman Arif
- Abdul Salam Arif
- Abdul-Karim Qassem
- Abu Musab Al Zarqawi
- Achaemenid Assyria
- Achaemenid Empire
- Adad-nirari II
- Adiabene
- Ahmed Hasan al-Bakr
- Ahmed Hassan al-Bakr
- Akkadian Empire
- Akkadian language
- Al Askari Mosque
- Al Qaeda in Iraq
- Al-Faw Peninsula
- Al-Hirah
- Al-Wathbah uprising
- Alexander the Great
- Amida (Mesopotamia)
- Amorites
- Ancient Near East
- Anglo-Iraqi War
- Arab
- Arab Federation
- Arab League
- Arabia
- Arabic literature
- Arabic poetry
- Assur
- Assyria
- Assyrian people
- Asuristan
- Ba'ath Party
- Babylon
- Babylonia
- Baghdad
- Baghdad Pact
- Barbed wire
- Basra
- Black Sheep Turkmen
- Bronze Age
- Byzantine Empire
- Cabinet of Iraq
- Caliphate
- Category Iraq
- Central Bank of Iraq
- Central Powers
- Chalcolithic
- Chaldea
- Chaldean dynasty
- Chemical weapons
- Christianity in Iraq
- City-state
- Civil war
- Civil war in Iraq
- Civilization
- Classical Antiquity
- Classical antiquity
- Common Era
- Constitution of Iraq
- Ctesiphon
- Culture of Iraq
- Cyrus the Great
- Demographics of Iraq
- Dependent territory
- Desert Storm
- Districts of Iraq
- Diyarbakır
- Early Bronze Age
- Earthenware
- Economic sanctions
- Economy of Iraq
- Education in Iraq
- Elam
- Elections in Iraq
- English language
- Eridu
- Euphrates
- Faisal I of Iraq
- Fertile Crescent
- Foreign aid to Iraq
- Geography of Iraq
- Georgia (country)
- Germany
- Gilgamesh
- Golden Square (Iraq)
- Gulf War
- Gutian period
- Hadrian
- Hammurabi
- Hamrin Mountains
- Hans Blix
- Hashemite
- Health in Iraq
- Hebrew Bible
- Hellenistic Greece
- History of Abkhazia
- History of Armenia
- History of Asia
- History of Baghdad
- History of Bahrain
- History of Bhutan
- History of Brunei
- History of Burma
- History of Cambodia
- History of Cyprus
- History of Egypt
- History of Hong Kong
- History of India
- History of Indonesia
- History of Iran
- History of Iraq
- History of Israel
- History of Japan
- History of Jordan
- History of Kuwait
- History of Laos
- History of Lebanon
- History of Macau
- History of Malaysia
- History of Mongolia
- History of Nepal
- History of Oman
- History of Pakistan
- History of Palestine
- History of Qatar
- History of Russia
- History of Singapore
- History of Sri Lanka
- History of Syria
- History of Thailand
- History of Turkey
- History of Vietnam
- History of Yemen
- Human wave attacks
- Hussein of Jordan
- Invasion of Kuwait
- Iran
- Iran-Iraq war
- Iranian Revolution
- Iran–Iraq War
- Iraq
- Iraq Insurgency
- Iraq Liberation Act
- Iraq Stock Exchange
- Iraq War
- Iraqi Air Force
- Iraqi Arabic
- Iraqi Armed Forces
- Iraqi Army
- Iraqi cuisine
- Iraqi diaspora
- Iraqi Dinar
- Iraqi insurgency
- Iraqi Kurdistan
- Iraqi Navy
- Iraqi no-fly zones
- Iraqi people
- Iraqi Police
- Iraqi Turkmen
- Irbil
- Iron Age
- Isin
- Islam in Iraq
- Islamic Golden Age
- Jami' al-tawarikh
- Jay Garner
- Jemdet Nasr period
- Jerusalem
- John Negroponte
- Judea
- Khalid ibn al-Walid
- Khanaqin
- Khosrow I
- Khosrow II
- Kingdom of Iraq
- Kurd
- Kurdish language
- Kurdish people
- Kuwait
- L. Paul Bremer
- Lake Habbaniyah
- Lake Hammar
- Lake Milh
- Lake Tharthar
- Lakhmid
- Languages of Iraq
- Larsa
- Law of Iraq
- Lower Mesopotamia
- Mamluk
- Mamluk rule in Iraq
- Mandaeans
- Mandaeism
- Mandate of Syria
- Mari, Syria
- Marsh Arabs
- Medes
- Media of Iraq
- Medo-Persian Empire
- Mesopotamia
- Mesopotamian Marshes
- Military campaign
- Minorities in Iraq
- Monarchy
- Mosul
- Music of Iraq
- Muslim world
- Muslims
- Mustafa Barzani
- Mustard gas
- Nabopolassar
- Nebuchadnezzar II
- Neo-Assyrian Empire
- Neolithic
- Neolithic Revolution
- Nineveh
- Nisibis
- No-man's land
- Nuri as-Said
- Oil for food program
- Oil reserves in Iraq
- Old Babylonian
- Oman
- Osama bin Laden
- Osroene
- Ottoman Empire
- Ottoman Iraq
- Parthian Empire
- Pashalik
- Persian Gulf
- Plebiscite
- Politics of Iraq
- Portal Iraq
- Pottery Neolithic
- President of Iraq
- Prime minister
- Prisoner of war
- Provinces of Iraq
- Rashid Ali
- Rashidun Caliphate
- Regime change
- Religion in Iraq
- Republic
- Republic of Iraq
- Roads in Iraq
- Roman Empire
- Routledge
- Sa`d ibn Abī Waqqās
- Saddam Hussein
- Safavid dynasty
- Samarra
- Sargon of Akkad
- Sassanid dynasty
- Seleucid
- Seleucid Empire
- Shahanshah
- Shamshi-Adad I
- Shatt al-Arab
- Shia
- Shia Islam
- Siege of Kut
- Six Day War
- Solomon
- South Azeri language
- Soviet Union
- Sport in Iraq
- Sprachbund
- State (polity)
- Sumer
- Sumerian language
- Sumerian renaissance
- Sunni Triangle
- Syria
- Syrian Desert
- Talk History of Iraq
- Template Cleanup doc
- Template Iraq topics
- Temple in Jerusalem
- Territorial dispute
- Third Dynasty of Ur
- Tiglath-Pileser III
- Tigris
- Tikrit
- Tim Cross
- Trajan
- Transport in Iraq
- Trench warfare
- Troops
- Turkey
- Ubaid period
- Umm Qasr
- UN Resolution 661
- UN Resolution 687
- UN Security Council
- United Kingdom
- United Nations
- United States
- United States Senate
- UNSCOM
- Ur III period
- Ur-III
- Uruk period
- Vilayets
- Washington, D.C.
- Wheel
- White Sheep Turkmen
- Wikipedia Cleanup
- World War I
- World War II
- Yazdegerd III
- Zagros Mountains
- 14 July Revolution
- 17 July Revolution
- Achaemenid Empire
- Akkadian Empire
- Arab League
- Assur
- Babylon
- Baghdad
- Basra
- Central Bank of Iraq
- Ctesiphon
- Diyarbakır
- Elam
- Eridu
- Geography of Iraq
- Germany
- Hamrin Mountains
- Iran
- Iraq
- Iraqi Kurdistan
- Isin
- Jemdet Nasr period
- Jerusalem
- Judea
- Khanaqin
- Kuwait
- Larsa
- Medes
- Mesopotamian Marshes
- Mosul
- Nineveh
- Oman
- Parthian Empire
- Persian Gulf
- Safavid dynasty
- Samarra
- Soviet Union
- Syria
- Syrian Desert
- Temple in Jerusalem
- Tigris
- Tikrit
- Turkey
- Umm Qasr
- United Kingdom
- United States
- Zagros Mountains
- Abdul Rahman Arif
- Abdul Salam Arif
- Abu Musab Al Zarqawi
- Alexander the Great
- Assyrian people
- Chaldea
- Civil war in Iraq
- Civilization
- Cyrus the Great
- Faisal I of Iraq
- Gilgamesh
- Hadrian
- Hammurabi
- Hans Blix
- Hashemite
- Hussein of Jordan
- Iraqi people
- Jay Garner
- John Negroponte
- Kurdish people
- Mamluk
- Mandaeans
- Marsh Arabs
- Medes
- Mustafa Barzani
- Nabopolassar
- Nebuchadnezzar II
- Osama bin Laden
- Rashidun Caliphate
- Saddam Hussein
- Sargon of Akkad
- Solomon
- Tim Cross
- Trajan
- World War I
- Yazdegerd III
-
Iraq, the Cradle Of Civilization - Documentary
Iraq, the Cradle Of Civilization - DocumentaryIraq, the Cradle Of Civilization - Documentary
After thousands of years as a hunter/gatherer, man built the first cities 5,000 years ago on the banks of the Euphrates in Southern Iraq. Civilization began. City life transformed the human race with the glorious cultures of Mesopotamia such as Ur, and Babylon. -
Iraq, the Cradle Of Civilization - Documentary
Iraq, the Cradle Of Civilization - DocumentaryIraq, the Cradle Of Civilization - Documentary
National Geographic Documentary 2015 National Geographic Documentary 2015 National Geographic Documentary 2015 National Geographic, National Geographic Docum... Documentaries Iraq - the Cradle Of Civilization - Documentary History Channel Full Length Documentary the Cradle Of Civilization Documentaries the Cradle Of ... Iraq, the Cradle Of Civilization - Documentary After thousands of years as a hunter/gatherer, man built the first cities 5000 years ago on the banks of the ... Documentary | Iraq, the Cradle Of Civilization | History Documentary documentaries documentary documentaries 2014 youtube documentaries History Documentary d... -
Iraq Explained -- ISIS, Syria and War
Iraq Explained -- ISIS, Syria and WarIraq Explained -- ISIS, Syria and War
The current crisis in Iraq explained in under 5 minutes. There is war in Iraq? Again? And the US and Iran are talking about working together? And who is this ISIS Terrorist group that is all over the news? And Religion? Oh dear... When exactly has the world gone mad again? It is not possible to explain a complicated topic like this without simplification. We are very aware that this video is not painting a full picture of the situation. But we hope that it may lay the foundation on which you can try to do your own research and understand how horribly Fu**ed up the whole situation is. We did have to produce the video super fast -- thanks -
Documentary Iraq a history of colonialism - 1 of 5
Documentary Iraq a history of colonialism - 1 of 5Documentary Iraq a history of colonialism - 1 of 5
Wednesday, 19 March 2008 This video documentary, on the anniversary of the invasion of Iraq, illustrates the west's history of colonialism in Iraq. Charting ... -
The Kings: From Babylon to Baghdad 1
The Kings: From Babylon to Baghdad 1The Kings: From Babylon to Baghdad 1
The Kings: From Babylon to Baghdad 1 -
Iran - Iraq War | 3 Minute History
Iran - Iraq War | 3 Minute HistoryIran - Iraq War | 3 Minute History
And here's some modern stuff. -
History of Iraq (Mesopotamia) Part 1 تأريخ العراق
History of Iraq (Mesopotamia) Part 1 تأريخ العراقHistory of Iraq (Mesopotamia) Part 1 تأريخ العراق
History of Iraq. -
A brief history of ISIS and the current crisis in Iraq
A brief history of ISIS and the current crisis in IraqA brief history of ISIS and the current crisis in Iraq
For starters: they used to be called Al Qaeda in Iraq. But they were too extreme for even Al Qaeda. Ezra Klein explains in three minutes. Warning: this video... -
Lecture 16 A Short History of Iraq
Lecture 16 A Short History of IraqLecture 16 A Short History of Iraq
Up to the time of the Second Gulf War. -
History of Iraq 1956-1979
History of Iraq 1956-1979History of Iraq 1956-1979
History of Iraq. -
Mr. Peabody and Sherman Travel WayBack to 1953 - A History of Iraq
Mr. Peabody and Sherman Travel WayBack to 1953 - A History of IraqMr. Peabody and Sherman Travel WayBack to 1953 - A History of Iraq
SCRIPT © 2008 by Matthew Hahn. All rights reserved. Mr. Peabody and Sherman visit NYC on 9/11. Based on a webcomic series I wrote in 2005. Neither created by... -
Iran's Revolutions: Crash Course World History 226
Iran's Revolutions: Crash Course World History 226Iran's Revolutions: Crash Course World History 226
In which John Green teaches you about Iran's Revolutions. Yes, revolutions plural. What was the1979 Iranian Revolution about? It turns out, Iran has a pretty long history of unrest in order to put power in the hands of the people, and the most recent revolution in 1979 was, at least at first, not necessarily about creating an Islamic state. It certainly turned out to be about that, but it was initially just about people who wanted to get rid of an oppressive regime. Listen up as John teaches you about Iran's long history of revolution. Citation 1: Caryl, Christian. Strange Rebels: 1979 and the Birth of the 21st Century. New York, Basic Books -
ISIS Is About to Destroy Biblical History In Iraq! Baghdadi Has $2 Billion War Chest!
ISIS Is About to Destroy Biblical History In Iraq! Baghdadi Has $2 Billion War Chest!ISIS Is About to Destroy Biblical History In Iraq! Baghdadi Has $2 Billion War Chest!
As reported in The Guardian, a windfall of intelligence just before Mosul fell revealed that al-Baghdadi had accumulated a $2 billion war chest, in part by s... -
Jeremy Corbyn speaking at biggest protest in UK history against Iraq war
Jeremy Corbyn speaking at biggest protest in UK history against Iraq warJeremy Corbyn speaking at biggest protest in UK history against Iraq war
On 15 February 2003, two million people on the streets of London, in the biggest process ever in UK history, said not in our name to the Iraq war. Jeremy Corbyn gave this speech to the huge rally in Hyde Park. -
Killing Them For 93 years (A brief history of Iraq)
Killing Them For 93 years (A brief history of Iraq)Killing Them For 93 years (A brief history of Iraq)
Short 10 minute interview mainly on the history of Iraq. -
August Alhf Modern History of Iraq WW I to 2003
August Alhf Modern History of Iraq WW I to 2003August Alhf Modern History of Iraq WW I to 2003
August Alhf talks about his time in Iraq in 1956 - 58 before and after the revolution, the History of Iraq from World War 1 and his slides of Baghdad and aro... -
Iraq War History Lesson | Jesse Ventura Off The Grid - Ora TV
Iraq War History Lesson | Jesse Ventura Off The Grid - Ora TVIraq War History Lesson | Jesse Ventura Off The Grid - Ora TV
"Those who cannot learn from history are doomed to repeat it." That seems like a pretty good slogan for the Iraq War, doesn't it? Today on #OffTheGrid, Jesse Ventura takes us on a trip down memory lane to follow the trail of money, oil and blood that led the United States from 9/11 into Iraq. How were George W. Bush, Dick Cheney and Donald Rumsfeld able to fool the United States citizens into supporting a war built on lies? The Governor breaks it all down right now. Got your own question for Jesse? Ask him at http://www.ora.tv/offthegrid/askjesse. Message Jesse at ora.tv/offthegrid/askjesse. www.ora.tv SUBSCRIBE to Jesse Ventura's channel: -
Iraq the Cradle Of Civilization - History Documentary
Iraq the Cradle Of Civilization - History DocumentaryIraq the Cradle Of Civilization - History Documentary
The Cradle Of Civilization - History Documentary Subscribe https://www.youtube.com/channel/UCIMXQrzdaDRdJnLCmpPCztw 4 cradles of civilization africa cradle of civilization africa the cradle of civilization american civilization history ancient civilization documentary ancient civilization history ancient civilization of the world ancient civilization of world ancient cultures of the world ancient western civilization beheadings in iraq breaking news on iraq british army in iraq capital of iraq christians in iraq civ 5 cradle of civilization civ v dlc civilizace 4 civilizati civilization 5 cradle of civilization civilization and climate civil -
Ancient Babylon documentary
Ancient Babylon documentaryAncient Babylon documentary
The region now known as Iraq has always been, in many ways, world history's ground zero. From this rich territory sprang the earliest cities and empires, ear... -
The invasion to ISIS: a brief history of violence in Iraq
The invasion to ISIS: a brief history of violence in IraqThe invasion to ISIS: a brief history of violence in Iraq
Learn how the 2003 invasion of Iraq, by the US and its allies, led to sectarian violence, terror and sowed the seeds of the Islamic State. Our International Editor, Lindsey Hilsum, recounts her experiences of Iraq during the first months of conflict and explains how ISIS has grown from the remnants of a defeated Al-Qaeda group and gained a stronghold in the heart of Iraq and Syria. -
Religious History of Iraq (Beyond Belief, 8/9/14)
Religious History of Iraq (Beyond Belief, 8/9/14)Religious History of Iraq (Beyond Belief, 8/9/14)
*** Today life for religious minorities in Northern Iraq is perilous as the militant Islamist group, Islamic State, continues to attack a range of diverse groups across the country in its pursuit of establishing a new Caliphate. But in this programme Ernie Rea and guests explore how up until the 20th century Iraq was known as a harmonious melting pot of religious and ethnic diversity. How true is that assessment? What has happened to change that? Is there any way for Iraq to step back from the brink? And could a Caliphate ever be part of the solution? Joining Ernie Rea to discuss the current situation in Iraq from a religious perspective are -
Babilon great history of iraq
Babilon great history of iraqBabilon great history of iraq
Babilon great history of iraq -
Welcome to Baghdad: How Iraq Used to Be in the 1950s
Welcome to Baghdad: How Iraq Used to Be in the 1950sWelcome to Baghdad: How Iraq Used to Be in the 1950s
Fascinating insight in to Iraq in the 1950s. The country is steeped in a rich history and culture. The very beginnings of civilisation started here and where man began cultivating the land and where writing was conceived. It even used to be a tourist hot spot. Watch another video about Iraq in the 1950s here: http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=LkcoQ1EJ_hU This film is actually a shortened version of our Ageless Iraq reels 1 & 2 which you can see here: Reel 1: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=YY-V-Bl7GU8 Reel 2: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Q9YC89Btock ___ Specially interested in War? - Check out our ‚War Archive': http://bit.ly/1jHBjmY Inter

- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 50:06
- Updated: 08 Feb 2014
- published: 08 Feb 2014
- views: 90073

- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 66:35
- Updated: 13 Feb 2015
- published: 13 Feb 2015
- views: 35

- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 4:36
- Updated: 19 Jun 2014
- published: 19 Jun 2014
- views: 1523417

- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 9:59
- Updated: 20 Aug 2014
- author: IslamicFront
- published: 05 Aug 2008
- views: 35247
- author: IslamicFront
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 42:49
- Updated: 09 Oct 2012
- published: 09 Oct 2012
- views: 261726

- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 4:07
- Updated: 30 Jan 2015
- published: 30 Jan 2015
- views: 1011


- published: 25 Jun 2014
- views: 84125
- author: Vox

- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 106:03
- Updated: 01 Apr 2015
- published: 01 Apr 2015
- views: 12

- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 4:19
- Updated: 01 Sep 2014
- author: grouchobeer
- published: 28 Nov 2008
- views: 365524
- author: grouchobeer

- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 13:41
- Updated: 26 Feb 2015
- published: 26 Feb 2015
- views: 591334

- published: 07 Jul 2014
- views: 20264
- author: DAHBOO77

- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 5:40
- Updated: 20 Aug 2015
- published: 20 Aug 2015
- views: 92

- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 10:13
- Updated: 23 Jun 2013
- author: surreyfilms
- published: 21 Jul 2007
- views: 2912
- author: surreyfilms

- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 40:36
- Updated: 18 Sep 2013
- author: eahawaii1902
- published: 17 Sep 2013
- views: 554
- author: eahawaii1902

- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 10:21
- Updated: 23 Sep 2014
- published: 23 Sep 2014
- views: 254

- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 50:06
- Updated: 17 Mar 2015
- published: 17 Mar 2015
- views: 12

- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 48:03
- Updated: 29 Aug 2014
- author: MrHistoryofart
- published: 25 Feb 2014
- views: 2572
- author: MrHistoryofart

- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 6:13
- Updated: 30 Mar 2015
- published: 30 Mar 2015
- views: 84

- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 27:36
- Updated: 14 Mar 2015
- published: 14 Mar 2015
- views: 5

- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 8:43
- Updated: 18 Apr 2015
- published: 18 Apr 2015
- views: 74

- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 3:46
- Updated: 08 Aug 2014
- published: 08 Aug 2014
- views: 172184
- Playlist
- Chat

Iraq, the Cradle Of Civilization - Documentary
- published: 08 Feb 2014
- views: 90073

Iraq, the Cradle Of Civilization - Documentary
- published: 13 Feb 2015
- views: 35

Iraq Explained -- ISIS, Syria and War
- published: 19 Jun 2014
- views: 1523417

Documentary Iraq a history of colonialism - 1 of 5
- published: 05 Aug 2008
- views: 35247
- author: IslamicFront

A brief history of ISIS and the current crisis in Iraq
- published: 25 Jun 2014
- views: 84125
- author: Vox

Mr. Peabody and Sherman Travel WayBack to 1953 - A History of Iraq
- published: 28 Nov 2008
- views: 365524
- author: grouchobeer

Iran's Revolutions: Crash Course World History 226
- published: 26 Feb 2015
- views: 591334

ISIS Is About to Destroy Biblical History In Iraq! Baghdadi Has $2 Billion War Chest!
- published: 07 Jul 2014
- views: 20264
- author: DAHBOO77

Jeremy Corbyn speaking at biggest protest in UK history against Iraq war
- published: 20 Aug 2015
- views: 92
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- Next page »





