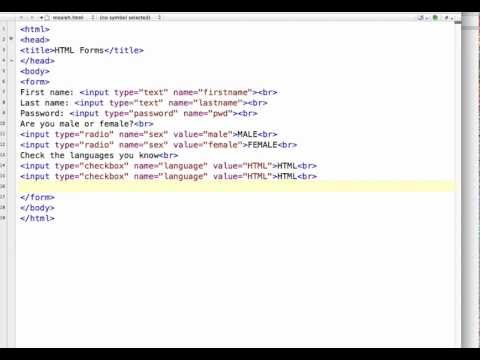
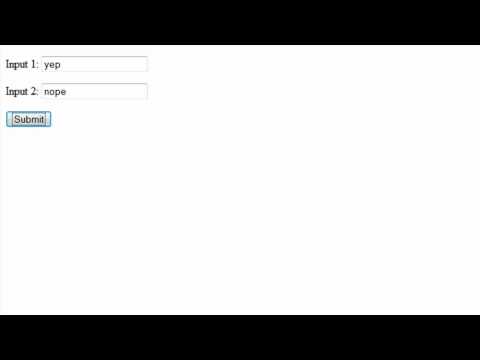


A webform on a web page allows a user to enter data that is sent to a server for processing. Webforms resemble paper or database forms because internet users fill out the forms using checkboxes, radio buttons, or text fields. For example, webforms can be used to enter shipping or credit card data to order a product or can be used to retrieve data (e.g., searching on a search engine).
In addition to functioning as input templates for new information, webforms can also be used to query and display existing data in a similar manner to mail merge forms, with the same advantages. The decoupling of message structure and underlying data allow both to vary independently. The use of webforms for this purpose avoids the problems associated with explicitly creating separate web pages for each record in a database.
Webforms are defined in formal programming languages such as HTML, Perl, PHP, Java, Javascript or .NET (including ASP.NET). The implementations of these languages often automatically invoke user interface idioms, such as grids and themes, minimizing programming time, costs and risks.
This article is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported License, which means that you can copy and modify it as long as the entire work (including additions) remains under this license.

HyperText Markup Language (HTML) is the main markup language for web pages. HTML elements are the basic building-blocks of webpages.
HTML is written in the form of HTML elements consisting of tags enclosed in angle brackets (like <html>), within the web page content. HTML tags most commonly come in pairs like <h1> and </h1>, although some tags, known as empty elements, are unpaired, for example <img>. The first tag in a pair is the start tag, the second tag is the end tag (they are also called opening tags and closing tags). In between these tags web designers can add text, tags, comments and other types of text-based content.
The purpose of a web browser is to read HTML documents and compose them into visible or audible web pages. The browser does not display the HTML tags, but uses the tags to interpret the content of the page.
HTML elements form the building blocks of all websites. HTML allows images and objects to be embedded and can be used to create interactive forms. It provides a means to create structured documents by denoting structural semantics for text such as headings, paragraphs, lists, links, quotes and other items. It can embed scripts in languages such as JavaScript which affect the behavior of HTML webpages.
This article is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported License, which means that you can copy and modify it as long as the entire work (including additions) remains under this license.
Form is the shape, visual appearance, or configuration of an object.
Form may also refer to:
This article is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported License, which means that you can copy and modify it as long as the entire work (including additions) remains under this license.
- Loading...

-
How to create an html form
How to create an html form -
HTML and CSS - Using CSS to Layout a Form
HTML and CSS - Using CSS to Layout a FormHTML and CSS - Using CSS to Layout a Form
Demonstrates how to layout a form using CSS in place of html tables. -
How to create a registration form in HTML
How to create a registration form in HTMLHow to create a registration form in HTML
This video will show you how to create a registration form in HTML with input elements. For more HTML videos please visit http://www.findsourcecode.com. -
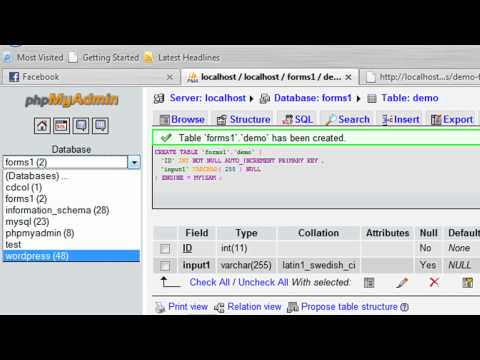
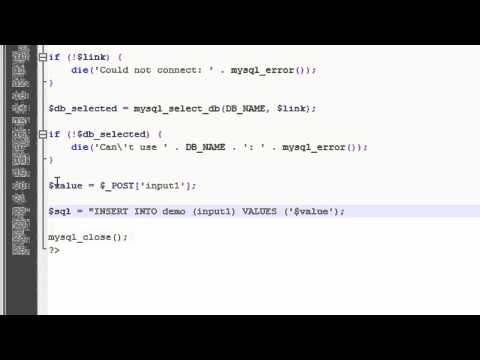
How to Create an HTML Form That Stores Data in a MySQL Database Using PHP Part 1 of 4
How to Create an HTML Form That Stores Data in a MySQL Database Using PHP Part 1 of 4How to Create an HTML Form That Stores Data in a MySQL Database Using PHP Part 1 of 4
For more video tutorials, go to http://www.johnmorrisonline.com/training/ Learn how to create a PHP form that will store data in a MySQL database. In this 4-... -
How to Create an HTML Form That Stores Data in a MySQL Database Using PHP Part 2 of 4
How to Create an HTML Form That Stores Data in a MySQL Database Using PHP Part 2 of 4How to Create an HTML Form That Stores Data in a MySQL Database Using PHP Part 2 of 4
For more video tutorials, go to http://www.johnmorrisonline.com/training/ Learn how to create a PHP form that will store data in a MySQL database. In this 4-... -
How to Create an HTML Form That Stores Data in a MySQL Database Using PHP Part 3 of 4
How to Create an HTML Form That Stores Data in a MySQL Database Using PHP Part 3 of 4How to Create an HTML Form That Stores Data in a MySQL Database Using PHP Part 3 of 4
For more video tutorials, go to http://www.johnmorrisonline.com/training/ Learn how to create a PHP form that will store data in a MySQL database. In this 4-... -
How to Create an HTML Form That Stores Data in a MySQL Database Using PHP Part 4 of 4
How to Create an HTML Form That Stores Data in a MySQL Database Using PHP Part 4 of 4How to Create an HTML Form That Stores Data in a MySQL Database Using PHP Part 4 of 4
For more video tutorials, go to http://www.johnmorrisonline.com/training/ Learn how to create a PHP form that will store data in a MySQL database. In this 4-... -
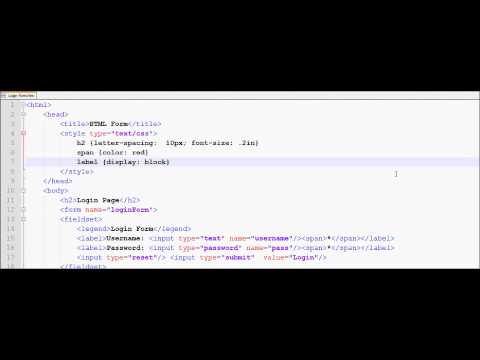
HTML Tutorial 33 - HTML Login Form and CSS
HTML Tutorial 33 - HTML Login Form and CSSHTML Tutorial 33 - HTML Login Form and CSS
Working with HTML Form Elements and also using CSS. -
Html Form Oluşturma
Html Form OluşturmaHtml Form Oluşturma
www.phphocam.com Html Form Oluşturma Dersi -
HTML Form and PHP Action Handler Tutorial
HTML Form and PHP Action Handler TutorialHTML Form and PHP Action Handler Tutorial
Create a simple HTML form with JavaScript validation and then print the submitted values using PHP. -
2. Style Custom HTML Form Fields Tutorial Programming Process
2. Style Custom HTML Form Fields Tutorial Programming Process2. Style Custom HTML Form Fields Tutorial Programming Process
Script Reference: http://www.developphp.com/view.php?tid=1232 In this 2 part custom HTML form field video lesson we will be demonstrating how to design in th... -
Basic Contact Form HTML and CSS
Basic Contact Form HTML and CSSBasic Contact Form HTML and CSS
In this video I show how to create a simple Contact Form in HTML and CSS. We will be moving on to scripting this Form and making it functional. -
Web applications with Java - Tutorial 02 - Servlet + Basic HTML Form
Web applications with Java - Tutorial 02 - Servlet + Basic HTML FormWeb applications with Java - Tutorial 02 - Servlet + Basic HTML Form
In this tutorial I will show how to create a simple HTML Form that will send information to the server. I will also create a Java HTTP Servlet to access that... -
HTML Forms - Part 1
HTML Forms - Part 1HTML Forms - Part 1
In this tutorial, I will be teaching you about forms. Forms are used to take information. As an example, you will most likely have to fill out a form when yo...
- Active Server Pages
- Adobe ColdFusion
- Apache HTTP Server
- ASCII
- ASP.NET
- Authentication
- Balloon help
- Bluehost
- Button (computing)
- C++
- CAPTCHA
- Check box
- Combo box
- Data query
- Data validation
- Database
- De facto standard
- Doteasy
- Drop-down list
- Dynamic HTML
- E-mail attachment
- FastCGI
- File select
- Form (document)
- Form (web)
- Grid (page layout)
- Grid view
- HTML
- HTML element
- HTTP
- HTTP cookie
- Input template
- Javascript
- JavaScript
- JavaScript library
- JavaServer Pages
- Login
- Mail merge
- MIME type
- Mod perl
- Mozilla Firefox
- Multipart form-data
- MySQL
- Newline
- Percent-encoding
- Perl
- Perl module
- PHP
- POST (HTTP)
- Postback
- Radio button
- Radio buttons
- Reset button
- Ruby on Rails
- Scripting language
- Search engine
- Server (computing)
- Software developer
- Spammer
- Spell checker
- Table (HTML)
- Talk Form (web)
- Text box
- Theme (computing)
- Tree view
- Visual Basic
- W3C
- Web applications
- Web browser
- Web development
- Web host
- Web page
- Web server
- Web site
- XForms
- XHTML
-
How to create an html form
How to create an html formHow to create an html form
In this video I will teach you how to create an form using html. This form can be used as any type of form you like, such as contact form, newsletter form, etc. -
HTML and CSS - Using CSS to Layout a Form
HTML and CSS - Using CSS to Layout a FormHTML and CSS - Using CSS to Layout a Form
Demonstrates how to layout a form using CSS in place of html tables. -
How to create a registration form in HTML
How to create a registration form in HTMLHow to create a registration form in HTML
This video will show you how to create a registration form in HTML with input elements. For more HTML videos please visit http://www.findsourcecode.com. -
How to Create an HTML Form That Stores Data in a MySQL Database Using PHP Part 1 of 4
How to Create an HTML Form That Stores Data in a MySQL Database Using PHP Part 1 of 4How to Create an HTML Form That Stores Data in a MySQL Database Using PHP Part 1 of 4
For more video tutorials, go to http://www.johnmorrisonline.com/training/ Learn how to create a PHP form that will store data in a MySQL database. In this 4-... -
How to Create an HTML Form That Stores Data in a MySQL Database Using PHP Part 2 of 4
How to Create an HTML Form That Stores Data in a MySQL Database Using PHP Part 2 of 4How to Create an HTML Form That Stores Data in a MySQL Database Using PHP Part 2 of 4
For more video tutorials, go to http://www.johnmorrisonline.com/training/ Learn how to create a PHP form that will store data in a MySQL database. In this 4-... -
How to Create an HTML Form That Stores Data in a MySQL Database Using PHP Part 3 of 4
How to Create an HTML Form That Stores Data in a MySQL Database Using PHP Part 3 of 4How to Create an HTML Form That Stores Data in a MySQL Database Using PHP Part 3 of 4
For more video tutorials, go to http://www.johnmorrisonline.com/training/ Learn how to create a PHP form that will store data in a MySQL database. In this 4-... -
How to Create an HTML Form That Stores Data in a MySQL Database Using PHP Part 4 of 4
How to Create an HTML Form That Stores Data in a MySQL Database Using PHP Part 4 of 4How to Create an HTML Form That Stores Data in a MySQL Database Using PHP Part 4 of 4
For more video tutorials, go to http://www.johnmorrisonline.com/training/ Learn how to create a PHP form that will store data in a MySQL database. In this 4-... -
HTML Tutorial 33 - HTML Login Form and CSS
HTML Tutorial 33 - HTML Login Form and CSSHTML Tutorial 33 - HTML Login Form and CSS
Working with HTML Form Elements and also using CSS. -
Html Form Oluşturma
Html Form OluşturmaHtml Form Oluşturma
www.phphocam.com Html Form Oluşturma Dersi -
HTML Form and PHP Action Handler Tutorial
HTML Form and PHP Action Handler TutorialHTML Form and PHP Action Handler Tutorial
Create a simple HTML form with JavaScript validation and then print the submitted values using PHP. -
2. Style Custom HTML Form Fields Tutorial Programming Process
2. Style Custom HTML Form Fields Tutorial Programming Process2. Style Custom HTML Form Fields Tutorial Programming Process
Script Reference: http://www.developphp.com/view.php?tid=1232 In this 2 part custom HTML form field video lesson we will be demonstrating how to design in th... -
Basic Contact Form HTML and CSS
Basic Contact Form HTML and CSSBasic Contact Form HTML and CSS
In this video I show how to create a simple Contact Form in HTML and CSS. We will be moving on to scripting this Form and making it functional. -
Web applications with Java - Tutorial 02 - Servlet + Basic HTML Form
Web applications with Java - Tutorial 02 - Servlet + Basic HTML FormWeb applications with Java - Tutorial 02 - Servlet + Basic HTML Form
In this tutorial I will show how to create a simple HTML Form that will send information to the server. I will also create a Java HTTP Servlet to access that... -
HTML Forms - Part 1
HTML Forms - Part 1HTML Forms - Part 1
In this tutorial, I will be teaching you about forms. Forms are used to take information. As an example, you will most likely have to fill out a form when yo... -
PHP Basics: HTML Forms & PHP Form Handling
PHP Basics: HTML Forms & PHP Form HandlingPHP Basics: HTML Forms & PHP Form Handling
In this video I discuss the very basics of HTML form handling. I discuss the inputs of an HTML form, and a couple of different types. With this I discuss the... -
HTML Tutorials: HTML Forms - User Registration Form
HTML Tutorials: HTML Forms - User Registration FormHTML Tutorials: HTML Forms - User Registration Form
Welcome to easy online jobs' video tutorials. In this video, we learn how to make html user registration form. HTML Forms are used to select different kinds ... -
How to Make a HTML Contact Form with PHP
How to Make a HTML Contact Form with PHPHow to Make a HTML Contact Form with PHP
Need a contact form for your website? I've got you covered! This quick 10 minute video will get you going in no time! In the tutorial, I will teach you two t... -
How to Build an Advanced HTML Form Using PHP and MySQL
How to Build an Advanced HTML Form Using PHP and MySQLHow to Build an Advanced HTML Form Using PHP and MySQL
Get the entire course for free here: http://www.johnmorrisonline.com/course/php-forms-101/ In this lesson, you'll learn how to build a kick ass form processi... -
PHP: HTML Mail Form Coding / PHP Mail Send Scripting Tutorial
PHP: HTML Mail Form Coding / PHP Mail Send Scripting TutorialPHP: HTML Mail Form Coding / PHP Mail Send Scripting Tutorial
In this lesson we go over how to code a basic mail form in HTML. We then show how to create the corresponding php file used to send mail to any email address... -
JavaScript Tutorial - Dynamic Select Year List Script HTML Form Elements
JavaScript Tutorial - Dynamic Select Year List Script HTML Form ElementsJavaScript Tutorial - Dynamic Select Year List Script HTML Form Elements
Lesson Code: http://www.developphp.com/view.php?tid=1328 PHP Version: http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=_vEyFYj09GE Learn to program dynamic year select lists i... -
PHP Tutorial: Passing Form Data Using PHP and HTML
PHP Tutorial: Passing Form Data Using PHP and HTMLPHP Tutorial: Passing Form Data Using PHP and HTML
https://academy.learntoprogram.tv/course/learn-php-mysql-for-beginners/?src=yt -- Redeem coupon code YOUTUBE at checkout to receive 50% off the full course! ... -
Understand HTML Form and types -- HTML Form in hindi (part 1/9) [ html in hindi]
Understand HTML Form and types -- HTML Form in hindi (part 1/9) [ html in hindi]Understand HTML Form and types -- HTML Form in hindi (part 1/9) [ html in hindi]
Subscribe me and Feel free to ask and comment below this video. Website : http://www.vishacademy.com http://www.youtube.com/VishAcademy facebook: http://www.... -
PHP Tutorial Parse Multiple Select HTML Form Fields - DevelopPHP dot com
PHP Tutorial Parse Multiple Select HTML Form Fields - DevelopPHP dot comPHP Tutorial Parse Multiple Select HTML Form Fields - DevelopPHP dot com
Script: http://www.developphp.com/view.php?tid=1225 Adam teaches how to use PHP to parse multiple selection form fields in your HTML or HTML5 forms. The resu...

- Duration: 16:28
- Updated: 30 Jul 2013
- published: 19 Aug 2011
- views: 2740
- author: noobiesites

- Duration: 8:25
- Updated: 02 Jul 2013
- published: 26 Dec 2012
- views: 824
- author: profgustin

- Duration: 7:33
- Updated: 03 Sep 2014
- published: 07 Feb 2013
- views: 22685
- author: Find Source Code

- Duration: 10:00
- Updated: 06 Sep 2014
- published: 11 Oct 2010
- views: 190129
- author: John Morris

- Duration: 9:59
- Updated: 19 Aug 2014
- published: 11 Oct 2010
- views: 62432
- author: John Morris

- Duration: 10:00
- Updated: 31 Aug 2014
- published: 11 Oct 2010
- views: 46532
- author: John Morris

- Duration: 9:59
- Updated: 01 Sep 2014
- published: 11 Oct 2010
- views: 38086
- author: John Morris

- Duration: 21:26
- Updated: 30 Aug 2014
- published: 22 Feb 2012
- views: 15464
- author: ssby79

- Duration: 13:49
- Updated: 15 Dec 2011
- published: 15 Dec 2011
- views: 5289

- Duration: 13:29
- Updated: 14 Mar 2012
- published: 14 Mar 2012
- views: 665

- Duration: 19:35
- Updated: 17 Aug 2013
- published: 04 Feb 2012
- views: 13477
- author: Adam Khoury

- Duration: 14:57
- Updated: 05 Aug 2013
- published: 11 Jul 2011
- views: 10949
- author: jaffe75

- Duration: 9:56
- Updated: 03 Sep 2014
- published: 30 Dec 2008
- views: 94927
- author: camigonz

- Duration: 7:18
- Updated: 11 Jul 2013
- published: 13 Apr 2008
- views: 17428
- author: Asib

- Duration: 13:30
- Updated: 08 Aug 2013
- published: 28 Mar 2011
- views: 16479
- author: SlothScripts

- Duration: 2:24
- Updated: 26 Aug 2014
- published: 07 Jun 2012
- views: 8041
- author: Sooraj Mohan

- Duration: 11:22
- Updated: 05 Sep 2014
- published: 26 May 2012
- views: 37302
- author: DoctorTechnology

- Duration: 54:57
- Updated: 04 Sep 2014
- published: 02 Mar 2014
- views: 7823
- author: John Morris

- Duration: 24:50
- Updated: 09 Aug 2014
- published: 12 Mar 2012
- views: 29173
- author: pfltuts

- Duration: 4:21
- Updated: 25 Aug 2014
- published: 14 Apr 2013
- views: 5558
- author: Adam Khoury

- Duration: 9:01
- Updated: 17 Aug 2014
- published: 07 Nov 2012
- views: 8672
- author: LearnToProgram: Your Technical Learning Resource
![Understand HTML Form and types -- HTML Form in hindi (part 1/9) [ html in hindi] Understand HTML Form and types -- HTML Form in hindi (part 1/9) [ html in hindi]](http://web.archive.org./web/20141212083124im_/http://i.ytimg.com/vi/u7bqJIPxj-I/0.jpg)
- Duration: 9:29
- Updated: 19 Nov 2012
- published: 13 Oct 2012
- views: 317
- author: VishAcademy

- Duration: 8:20
- Updated: 06 Aug 2013
- published: 11 Jan 2012
- views: 12459
- author: Adam Khoury
-
PHP Programming Part 5: HTML Forms and PHP Programming
PHP Programming Part 5: HTML Forms and PHP ProgrammingPHP Programming Part 5: HTML Forms and PHP Programming
-
How Build a Simple HTML Form Using PHP and MySQL
How Build a Simple HTML Form Using PHP and MySQLHow Build a Simple HTML Form Using PHP and MySQL
Get the entire course for free here: http://www.johnmorrisonline.com/course/php-forms-101/ In this lesson, you'll discover how to build an PHP form that stor... -
PHP+HTML Contact form tutorial
PHP+HTML Contact form tutorialPHP+HTML Contact form tutorial
NEW Contact Form Tutorial here = http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=j7lnU8hJRjo **** Hey all, had a few people asking about a PHP based contact form so here... -
HTML Form Basics
HTML Form BasicsHTML Form Basics
Demonstrates how to create a form and use some of the basic form elements such as text boxes, select lists, checkboxes, radio buttons and textarea. Also expl... -
13. User Profile Photo File Upload HTML Form Tutorial PHP Parse Script MySQL
13. User Profile Photo File Upload HTML Form Tutorial PHP Parse Script MySQL13. User Profile Photo File Upload HTML Form Tutorial PHP Parse Script MySQL
Lesson Code: http://www.developphp.com/view.php?tid=1304 Learn to allow your users to change their profile photo and begin building your file upload applicat... -
Styling a Simple Form with CSS in Dreamweaver
Styling a Simple Form with CSS in DreamweaverStyling a Simple Form with CSS in Dreamweaver
We will go ahead and create a form and then style it using CSS. Learn how to hand code a simple form and then hand code all of the CSS code you need to creat... -
Form Generator PHP Generator MySQL Generator (FPMG) - Generate HTML Forms, PHP & MySQL Code!
Form Generator PHP Generator MySQL Generator (FPMG) - Generate HTML Forms, PHP & MySQL Code!Form Generator PHP Generator MySQL Generator (FPMG) - Generate HTML Forms, PHP & MySQL Code!
http://www.fpmgonline.com FPMG is the Best, Online, Free Form Generator, PHP Generator & MySQL Generator ever built. It is a very powerful tool to increase w... -
How To Create An Html Form With SQL Database Via PHP, And Custom Downloadable RTF Files
How To Create An Html Form With SQL Database Via PHP, And Custom Downloadable RTF FilesHow To Create An Html Form With SQL Database Via PHP, And Custom Downloadable RTF Files
You can learn wit this video How To Create An Html Form With SQL Database Via PHP, And Custom Downloadable RTF Files. Please watch the interested tutorial vi... -
IMN Instant Money Network HTML Form Code Generator Tutorial
IMN Instant Money Network HTML Form Code Generator TutorialIMN Instant Money Network HTML Form Code Generator Tutorial
IMN Instant Money Network HTML Form Code Generator Tutorial The HTML code generator creates custom lead capture form code to be used off-site on another web ... -
15 - Insert HTML Form Data Into Database Using PHP - Tutorial in Urdu
15 - Insert HTML Form Data Into Database Using PHP - Tutorial in Urdu15 - Insert HTML Form Data Into Database Using PHP - Tutorial in Urdu
In This Tutorial i am going to teach you "How to Save Form Submitted Data into MySQL Database Using PHP" You Can Find Exercise Files in Our Facebook Group : ... -
Send Emails with a Web Form: PHP Scripting
Send Emails with a Web Form: PHP ScriptingSend Emails with a Web Form: PHP Scripting
Check this video out at Hi-Res here: http://www.tutvid.com/tutorials/dreamweaver/tutorials/phpFormHandler.php Files are Located here: http://www.tutvid.com/r... -
Tạo Form với HTML và CSS
Tạo Form với HTML và CSSTạo Form với HTML và CSS
Form là cửa ngõ của một trang web, là công cụ duy nhất giúp bạn với người đọc tương tác với nhau cho dù có bằng email, diễn đàn, comments ... thì đều là một ... -
Creating HTML form to submit info to database using PHP
Creating HTML form to submit info to database using PHPCreating HTML form to submit info to database using PHP
-
HTML Dersleri 5 - Form (input-textarea) ve List Kodları
HTML Dersleri 5 - Form (input-textarea) ve List KodlarıHTML Dersleri 5 - Form (input-textarea) ve List Kodları
Bu dersimizde, form ve list kodlarını inceledik, kullanımlarını anlattık, küçük püf noktaları verdik ve almanca film altyazısı yaptık. Kullanılan kodları şuradan: http://www.buraktokak.com/?p=235 Diğer derslere şuradan: www.buraktokak.com Ulaşabilirsiniz. -
HTML-Forms-Sample-Form.Part 2
HTML-Forms-Sample-Form.Part 2HTML-Forms-Sample-Form.Part 2
Video about first homework-sample form, in telerik academy. -
Validate HTML Form Data with JavaScript
Validate HTML Form Data with JavaScriptValidate HTML Form Data with JavaScript
Learn how to validate form data with Javascript. Tutorial by Carmen Branje. -
(9) JavaScript: Form Validation
(9) JavaScript: Form Validation(9) JavaScript: Form Validation
In this screencast, you will get to know about the different ways you can validate input from HTML forms in JavaScript. Although some of the validation types... -
#20 Learn Html - Form Part 3
#20 Learn Html - Form Part 3#20 Learn Html - Form Part 3
شرج اجزاء ال Form الحزء الثالث و بعض حقول الادخال -
j2ee003-Html Form and Input Items
j2ee003-Html Form and Input Itemsj2ee003-Html Form and Input Items
j2ee003-Html Form and Input Items -
Html, form elemanları
Html, form elemanlarıHtml, form elemanları
html form elemanları http://www.yilmazarslanturk.com/makaleGoster/html-form-elemanlari.html

- Duration: 61:07
- Updated: 03 Sep 2014
http://wn.com/PHP_Programming_Part_5_HTML_Forms_and_PHP_Programming

- Duration: 32:18
- Updated: 30 Aug 2014
- published: 02 Mar 2014
- views: 6765
- author: John Morris

- Duration: 30:12
- Updated: 01 Sep 2014
- published: 26 Jan 2011
- views: 31968
- author: Harry Finn

- Duration: 26:01
- Updated: 28 Apr 2014
- published: 23 Dec 2012
- views: 1698
- author: profgustin

- Duration: 21:23
- Updated: 16 Aug 2014
- published: 12 Feb 2013
- views: 31236
- author: Adam Khoury

- Duration: 22:12
- Updated: 28 Aug 2014
- published: 21 Apr 2010
- views: 74088
- author: tutvid

- Duration: 23:20
- Updated: 03 Aug 2014
- published: 25 Dec 2012
- views: 10091
- author: FPMGOnline

- Duration: 27:56
- Updated: 06 Jul 2014
- published: 07 May 2014
- views: 164
- author: Tutorial Video

- Duration: 45:57
- Updated: 03 Jan 2014
- published: 18 Sep 2013
- views: 96
- author: Ernest ODell

- Duration: 24:59
- Updated: 21 May 2014
- published: 16 May 2014
- views: 168
- author: XiTCLUB

- Duration: 26:27
- Updated: 03 Sep 2014
- published: 13 Jan 2008
- views: 392619
- author: tutvid

- Duration: 23:18
- Updated: 22 Jul 2014
- published: 03 Mar 2013
- views: 7017
- author: Izwebz Page

- Duration: 45:54
- Updated: 25 Nov 2013
http://wn.com/Creating_HTML_form_to_submit_info_to_database_using_PHP
- published: 25 Nov 2013
- views: 48

- Duration: 23:44
- Updated: 30 Mar 2013
- published: 30 Mar 2013
- views: 9

- Duration: 27:21
- Updated: 09 Mar 2014
- published: 15 Jan 2014
- views: 370
- author: Nikolay Dimov

- Duration: 32:07
- Updated: 01 May 2014
- published: 10 Nov 2013
- views: 62
- author: Carmen Branje

- Duration: 45:54
- Updated: 04 Aug 2014
- published: 19 Apr 2014
- views: 570
- author: CCSIT-KFU

- Duration: 23:01
- Updated: 20 Sep 2014
- published: 20 Sep 2014
- views: 41

- Duration: 25:15
- Updated: 04 Feb 2013
- published: 04 Feb 2013
- views: 235

- Duration: 22:36
- Updated: 15 Oct 2011
- published: 15 Oct 2011
- views: 110
-
Photshop Template Naughty HTML Coder
Photshop Template Naughty HTML CoderPhotshop Template Naughty HTML Coder
http://bit.ly/1lkj9b6 A naughty HTML coder in action html tutorial ,tutorial for html ,tutorial of html ,tutorial on html ,tutorial in html ,html 5 tutorial ,tutorial on html pdf ,pdf on html tutorial ,html pdf tutorial ,pdf html tutorial ,pdf of html tutorial ,pdf for html tutorial ,pdf to html tutorial ,html tutorial in pdf ,html tutorial pdf ,html tutorial example ,html tutorial in pdf format ,html tutorial pdf format ,html css tutorial ,html tutorial css ,css tutorial html ,html css tutorial ,css html tutorial ,html and css tutorial ,css and html tutorial ,html tutorial with examples ,video html tutorial ,html tutorial video ,ht -
Bài 10 - Thẻ Form
Bài 10 - Thẻ FormBài 10 - Thẻ Form
Trong HTML, các thẻ form giúp chúng ta tạo ra các biểu mẫu ( form ) giúp người dùng nhập nội dung và chuyển dữ liệu đến web server. Một form có thể chứa những phần tử đề người sử dụng nhập vào như trường dữ liệu , menu thả xuống, nút radio, nút xác nhận... Form được xem là ứng dụng quan trọng trong ngôn ngữ lập trình PHP có tác dụng giúp cập nhật thông tin một cách linh hoạt và dễ dàng quản lý chung nhờ vào sự kết hợp chặt chẽ với cơ sở dữ liệu. Ở đây chúng ta chỉ tìm hiều về cách tạo form trong HTML, còn việc xử lý form ( xử lý dữ liệu được gửi đi ) là thuộc về mảng PHP. -
How to Create a Registration Form in HTML
How to Create a Registration Form in HTMLHow to Create a Registration Form in HTML
Visit and follow our blog: http://www.howtodopc.wordpress.com. Plus us on Google+: https://plus.google.com/u/0/b/113201504131435597310/113201504131435597310/posts. Follow us on Twitter: https://www.twitter.com/HowtodoVids. Like us on Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/HowtodoTutorials. In this tutorial, you will learn how to create a registration form in HTML. Carefully understand the following step-by-step guide to learn:- 1. Inside the body tag, comes the form coding. 2. When you have inserted the form code, save the file. 3. After giving the name to the file, make sure that you type .html at the end. 4. Open the saved file. Now the regist -
Web API on Web Form using AngularJS, HTML AND Javascript Part II
Web API on Web Form using AngularJS, HTML AND Javascript Part IIWeb API on Web Form using AngularJS, HTML AND Javascript Part II
Description -
Web API on Web Form using AngularJS, HTML AND Javascript Part III
Web API on Web Form using AngularJS, HTML AND Javascript Part IIIWeb API on Web Form using AngularJS, HTML AND Javascript Part III
In this video tutorial, I am will be talking about how to integrate WEB API into the ASP.NET web form and I will be creating a little AngularJS demo app to consume the web api service from the client side. -
Web API on Web Form using AngularJS, HTML AND Javascript Part I
Web API on Web Form using AngularJS, HTML AND Javascript Part IWeb API on Web Form using AngularJS, HTML AND Javascript Part I
Description -
CMSC331 Project 1 Demo Video
CMSC331 Project 1 Demo VideoCMSC331 Project 1 Demo Video
Demonstration of the working html form interacting with the customer request database. -
Part4 - Html And Form
Part4 - Html And FormPart4 - Html And Form
Uploaded with Free Video Converter from Freemake http://www.freemake.com/free_video_converter/ -
html form
html formhtml form
HTML Table Form Create -
HTML Form Etiketleri
HTML Form EtiketleriHTML Form Etiketleri
Güncel Eğitimler İçin Abone Olmayı Unutmayın.! Web Sitemiz : http://www.egitimsaati.com/ Youtube : https://www.youtube.com/user/EgitimSaatiOfficial Google+ : https://plus.google.com/+EgitimSaatiOfficial Facebook : https://www.facebook.com/EgitimSaatiOfficial Twitter : https://twitter.com/EgitimSaatiHD Türkiye'nin Ücretsiz Eğitim Sitesi -
How To Learn Instant Form Pro Review-Best Form Creation Software For Marketers
How To Learn Instant Form Pro Review-Best Form Creation Software For MarketersHow To Learn Instant Form Pro Review-Best Form Creation Software For Marketers
Click The Link Below For More Information: http://x.vu/instantformproguides Instant Form Pro Review-Best Form Creation Software For Marketers Instant Form Pro from Joel Comm of Info Media, Inc. is an absolutely incredible software! After seeing all of the features of this software I was blown away with all that it offered. This form program gives you complete and total control over the forms you build, and it allows you to build world class surveys so you can gather that extremely important customer data. With just a few clicks of a mouse you can be on your way to having professional forms that can help really improve your bottom line. Under -
HTML 5 Form Elements
HTML 5 Form ElementsHTML 5 Form Elements
This will discuss some of the newer HTML5 form element types -
Jak ustawić kursor w polu formularza HTML.How to set up cursor on specify HTML form field
Jak ustawić kursor w polu formularza HTML.How to set up cursor on specify HTML form fieldJak ustawić kursor w polu formularza HTML.How to set up cursor on specify HTML form field
Czasami chcemy ustawić pozycję kursora w określonym polu formularza HTML, przy pomocy zmiennej body onload możemy tego dokonać. Wystarczy dla wpisu input w form dodać zmienną id a następnie dodać kod w sekcji body: body onload="document.getElementById*'form1'*.focus**" Uwaga w związku z ograniczeniami Youtube co do opisu filmu nawiasy zostały zastąpione * Powodzenia. Pełny kod strony: https://www.dropbox.com/s/q2zja37to16e06c/start.html?dl=0 W taki właśnie sposób ustawiamy kursor w odpowiednim polu formularza :). If you would like to set up cursor on specify field in html form use: body onload="document.getElementById*'form1'*.focus* -
[HTML] Show_Hide Form Elements Using JavaScript [HD].mp4
[HTML] Show_Hide Form Elements Using JavaScript [HD].mp4[HTML] Show_Hide Form Elements Using JavaScript [HD].mp4
[HTML] Show_Hide Form Elements Using JavaScript [HD].mp4 -
10 HTML Form Submit button urdu / hindi
10 HTML Form Submit button urdu / hindi10 HTML Form Submit button urdu / hindi
-
9 HTML Form reset button urdu / hindi
9 HTML Form reset button urdu / hindi9 HTML Form reset button urdu / hindi
-
6 HTML Form Radio Button urdu / hindi
6 HTML Form Radio Button urdu / hindi6 HTML Form Radio Button urdu / hindi
-
8 HTML Form Drop Down List urdu / hindi
8 HTML Form Drop Down List urdu / hindi8 HTML Form Drop Down List urdu / hindi
-
7 HTML Form Checkbox urdu / hindi
7 HTML Form Checkbox urdu / hindi7 HTML Form Checkbox urdu / hindi
-
5 HTML Form password field urdu / hindi
5 HTML Form password field urdu / hindi5 HTML Form password field urdu / hindi
-
3 HTML Form text field single line urdu / hindi
3 HTML Form text field single line urdu / hindi3 HTML Form text field single line urdu / hindi
1 to 10 video -
2 HTML Form tags & parameters urdu / hindi
2 HTML Form tags & parameters urdu / hindi2 HTML Form tags & parameters urdu / hindi
this video 1 to 10 -
1 HTML Form intro urdu /hindi
1 HTML Form intro urdu /hindi1 HTML Form intro urdu /hindi
gift 4 all HTML is 1 to 10 video

- Duration: 0:29
- Updated: 27 Nov 2014
- published: 27 Nov 2014
- views: 301

- Duration: 1:20
- Updated: 26 Nov 2014
- published: 26 Nov 2014
- views: 0

- Duration: 3:00
- Updated: 26 Nov 2014
- published: 26 Nov 2014
- views: 3

- Duration: 10:02
- Updated: 26 Nov 2014
- published: 26 Nov 2014
- views: 8

- Duration: 10:02
- Updated: 26 Nov 2014
- published: 26 Nov 2014
- views: 12

- Duration: 10:01
- Updated: 26 Nov 2014
- published: 26 Nov 2014
- views: 21

- Duration: 3:37
- Updated: 26 Nov 2014
- published: 26 Nov 2014
- views: 4

- Duration: 10:17
- Updated: 23 Nov 2014
- published: 23 Nov 2014
- views: 3
- published: 22 Nov 2014
- views: 9

- Duration: 59:40
- Updated: 21 Nov 2014
- published: 21 Nov 2014
- views: 2

- Duration: 1:56
- Updated: 20 Nov 2014
- published: 20 Nov 2014
- views: 297

- Duration: 23:01
- Updated: 19 Nov 2014
- published: 19 Nov 2014
- views: 0

- Duration: 3:48
- Updated: 18 Nov 2014
- published: 18 Nov 2014
- views: 24
![[HTML] Show_Hide Form Elements Using JavaScript [HD].mp4 [HTML] Show_Hide Form Elements Using JavaScript [HD].mp4](http://web.archive.org./web/20141212083124im_/http://i.ytimg.com/vi/_82Xgnn78lk/0.jpg)
- Duration: 10:29
- Updated: 17 Nov 2014
- published: 17 Nov 2014
- views: 1

- Duration: 5:57
- Updated: 17 Nov 2014
http://wn.com/10_HTML_Form_Submit_button_urdu_hindi
- published: 17 Nov 2014
- views: 2

- Duration: 3:59
- Updated: 17 Nov 2014
http://wn.com/9_HTML_Form_reset_button_urdu_hindi
- published: 17 Nov 2014
- views: 0

- Duration: 3:25
- Updated: 17 Nov 2014
http://wn.com/6_HTML_Form_Radio_Button_urdu_hindi
- published: 17 Nov 2014
- views: 0

- Duration: 5:34
- Updated: 17 Nov 2014
http://wn.com/8_HTML_Form_Drop_Down_List_urdu_hindi
- published: 17 Nov 2014
- views: 2

- Duration: 4:47
- Updated: 17 Nov 2014
http://wn.com/7_HTML_Form_Checkbox_urdu_hindi
- published: 17 Nov 2014
- views: 2

- Duration: 2:02
- Updated: 17 Nov 2014
http://wn.com/5_HTML_Form_password_field_urdu_hindi
- published: 17 Nov 2014
- views: 2

- Duration: 4:01
- Updated: 17 Nov 2014
- published: 17 Nov 2014
- views: 1

- Duration: 4:31
- Updated: 17 Nov 2014
- published: 17 Nov 2014
- views: 2

- Duration: 3:48
- Updated: 17 Nov 2014
- published: 17 Nov 2014
- views: 1
- Playlist
- Chat

How to create an html form
In this video I will teach you how to create an form using html. This form can be used as any type of form you like, such as contact form, newsletter form, etc.- published: 19 Aug 2011
- views: 2740
- author: noobiesites

HTML and CSS - Using CSS to Layout a Form
Demonstrates how to layout a form using CSS in place of html tables.- published: 26 Dec 2012
- views: 824
- author: profgustin

How to create a registration form in HTML
This video will show you how to create a registration form in HTML with input elements. For more HTML videos please visit http://www.findsourcecode.com.- published: 07 Feb 2013
- views: 22685
- author: Find Source Code

How to Create an HTML Form That Stores Data in a MySQL Database Using PHP Part 1 of 4
For more video tutorials, go to http://www.johnmorrisonline.com/training/ Learn how to create a PHP form that will store data in a MySQL database. In this 4-...- published: 11 Oct 2010
- views: 190129
- author: John Morris

How to Create an HTML Form That Stores Data in a MySQL Database Using PHP Part 2 of 4
For more video tutorials, go to http://www.johnmorrisonline.com/training/ Learn how to create a PHP form that will store data in a MySQL database. In this 4-...- published: 11 Oct 2010
- views: 62432
- author: John Morris

How to Create an HTML Form That Stores Data in a MySQL Database Using PHP Part 3 of 4
For more video tutorials, go to http://www.johnmorrisonline.com/training/ Learn how to create a PHP form that will store data in a MySQL database. In this 4-...- published: 11 Oct 2010
- views: 46532
- author: John Morris

How to Create an HTML Form That Stores Data in a MySQL Database Using PHP Part 4 of 4
For more video tutorials, go to http://www.johnmorrisonline.com/training/ Learn how to create a PHP form that will store data in a MySQL database. In this 4-...- published: 11 Oct 2010
- views: 38086
- author: John Morris

HTML Tutorial 33 - HTML Login Form and CSS
Working with HTML Form Elements and also using CSS.- published: 22 Feb 2012
- views: 15464
- author: ssby79

HTML Form and PHP Action Handler Tutorial
Create a simple HTML form with JavaScript validation and then print the submitted values using PHP.- published: 14 Mar 2012
- views: 665

2. Style Custom HTML Form Fields Tutorial Programming Process
Script Reference: http://www.developphp.com/view.php?tid=1232 In this 2 part custom HTML form field video lesson we will be demonstrating how to design in th...- published: 04 Feb 2012
- views: 13477
- author: Adam Khoury

Basic Contact Form HTML and CSS
In this video I show how to create a simple Contact Form in HTML and CSS. We will be moving on to scripting this Form and making it functional.- published: 11 Jul 2011
- views: 10949
- author: jaffe75

Web applications with Java - Tutorial 02 - Servlet + Basic HTML Form
In this tutorial I will show how to create a simple HTML Form that will send information to the server. I will also create a Java HTTP Servlet to access that...- published: 30 Dec 2008
- views: 94927
- author: camigonz

HTML Forms - Part 1
In this tutorial, I will be teaching you about forms. Forms are used to take information. As an example, you will most likely have to fill out a form when yo...- published: 13 Apr 2008
- views: 17428
- author: Asib

PHP Basics: HTML Forms & PHP Form Handling
In this video I discuss the very basics of HTML form handling. I discuss the inputs of an HTML form, and a couple of different types. With this I discuss the...- published: 28 Mar 2011
- views: 16479
- author: SlothScripts

HTML Tutorials: HTML Forms - User Registration Form
Welcome to easy online jobs' video tutorials. In this video, we learn how to make html user registration form. HTML Forms are used to select different kinds ...- published: 07 Jun 2012
- views: 8041
- author: Sooraj Mohan

How to Make a HTML Contact Form with PHP
Need a contact form for your website? I've got you covered! This quick 10 minute video will get you going in no time! In the tutorial, I will teach you two t...- published: 26 May 2012
- views: 37302
- author: DoctorTechnology

How to Build an Advanced HTML Form Using PHP and MySQL
Get the entire course for free here: http://www.johnmorrisonline.com/course/php-forms-101/ In this lesson, you'll learn how to build a kick ass form processi...- published: 02 Mar 2014
- views: 7823
- author: John Morris
- Playlist
- Chat

PHP Programming Part 5: HTML Forms and PHP Programming
- published: 06 Jun 2012
- views: 58331
- author: Eli the Computer Guy

How Build a Simple HTML Form Using PHP and MySQL
Get the entire course for free here: http://www.johnmorrisonline.com/course/php-forms-101/ In this lesson, you'll discover how to build an PHP form that stor...- published: 02 Mar 2014
- views: 6765
- author: John Morris

PHP+HTML Contact form tutorial
NEW Contact Form Tutorial here = http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=j7lnU8hJRjo **** Hey all, had a few people asking about a PHP based contact form so here...- published: 26 Jan 2011
- views: 31968
- author: Harry Finn

HTML Form Basics
Demonstrates how to create a form and use some of the basic form elements such as text boxes, select lists, checkboxes, radio buttons and textarea. Also expl...- published: 23 Dec 2012
- views: 1698
- author: profgustin

13. User Profile Photo File Upload HTML Form Tutorial PHP Parse Script MySQL
Lesson Code: http://www.developphp.com/view.php?tid=1304 Learn to allow your users to change their profile photo and begin building your file upload applicat...- published: 12 Feb 2013
- views: 31236
- author: Adam Khoury

Styling a Simple Form with CSS in Dreamweaver
We will go ahead and create a form and then style it using CSS. Learn how to hand code a simple form and then hand code all of the CSS code you need to creat...- published: 21 Apr 2010
- views: 74088
- author: tutvid

Form Generator PHP Generator MySQL Generator (FPMG) - Generate HTML Forms, PHP & MySQL Code!
http://www.fpmgonline.com FPMG is the Best, Online, Free Form Generator, PHP Generator & MySQL Generator ever built. It is a very powerful tool to increase w...- published: 25 Dec 2012
- views: 10091
- author: FPMGOnline

How To Create An Html Form With SQL Database Via PHP, And Custom Downloadable RTF Files
You can learn wit this video How To Create An Html Form With SQL Database Via PHP, And Custom Downloadable RTF Files. Please watch the interested tutorial vi...- published: 07 May 2014
- views: 164
- author: Tutorial Video

IMN Instant Money Network HTML Form Code Generator Tutorial
IMN Instant Money Network HTML Form Code Generator Tutorial The HTML code generator creates custom lead capture form code to be used off-site on another web ...- published: 18 Sep 2013
- views: 96
- author: Ernest ODell

15 - Insert HTML Form Data Into Database Using PHP - Tutorial in Urdu
In This Tutorial i am going to teach you "How to Save Form Submitted Data into MySQL Database Using PHP" You Can Find Exercise Files in Our Facebook Group : ...- published: 16 May 2014
- views: 168
- author: XiTCLUB

Send Emails with a Web Form: PHP Scripting
Check this video out at Hi-Res here: http://www.tutvid.com/tutorials/dreamweaver/tutorials/phpFormHandler.php Files are Located here: http://www.tutvid.com/r...- published: 13 Jan 2008
- views: 392619
- author: tutvid

Tạo Form với HTML và CSS
Form là cửa ngõ của một trang web, là công cụ duy nhất giúp bạn với người đọc tương tác với nhau cho dù có bằng email, diễn đàn, comments ... thì đều là một ...- published: 03 Mar 2013
- views: 7017
- author: Izwebz Page

HTML Dersleri 5 - Form (input-textarea) ve List Kodları
Bu dersimizde, form ve list kodlarını inceledik, kullanımlarını anlattık, küçük püf noktaları verdik ve almanca film altyazısı yaptık. Kullanılan kodları şuradan: http://www.buraktokak.com/?p=235 Diğer derslere şuradan: www.buraktokak.com Ulaşabilirsiniz.- published: 30 Mar 2013
- views: 9

HTML-Forms-Sample-Form.Part 2
Video about first homework-sample form, in telerik academy.- published: 15 Jan 2014
- views: 370
- author: Nikolay Dimov

Validate HTML Form Data with JavaScript
Learn how to validate form data with Javascript. Tutorial by Carmen Branje.- published: 10 Nov 2013
- views: 62
- author: Carmen Branje

(9) JavaScript: Form Validation
In this screencast, you will get to know about the different ways you can validate input from HTML forms in JavaScript. Although some of the validation types...- published: 19 Apr 2014
- views: 570
- author: CCSIT-KFU
- Playlist
- Chat

Photshop Template Naughty HTML Coder
http://bit.ly/1lkj9b6 A naughty HTML coder in action html tutorial ,tutorial for html ,tutorial of html ,tutorial on html ,tutorial in html ,html 5 tutorial ,tutorial on html pdf ,pdf on html tutorial ,html pdf tutorial ,pdf html tutorial ,pdf of html tutorial ,pdf for html tutorial ,pdf to html tutorial ,html tutorial in pdf ,html tutorial pdf ,html tutorial example ,html tutorial in pdf format ,html tutorial pdf format ,html css tutorial ,html tutorial css ,css tutorial html ,html css tutorial ,css html tutorial ,html and css tutorial ,css and html tutorial ,html tutorial with examples ,video html tutorial ,html tutorial video ,html video tutorial ,html canvas tutorial ,html tutorial download ,download html tutorial ,html tutorial beginners ,html for beginners tutorial ,html tutorial for beginners ,html beginners tutorial ,free tutorial on html ,html tutorial free ,free tutorial for html ,html free tutorial ,free tutorial html ,free html tutorial ,html 5 canvas tutorial ,html beginner tutorial ,beginner html tutorial ,html tutorial for beginner ,html 5 tutorial pdf ,psd html tutorial ,from psd to html tutorial ,psd to html tutorial ,free download html tutorial ,free html tutorial download ,basic html tutorial ,html tutorial basic ,html basic tutorial ,java html tutorial ,html java tutorial ,download html tutorial pdf ,html tutorial pdf download ,html tutorial download pdf ,html 5 game tutorial ,html 5 tutorial video ,html 5 video tutorial ,form tutorial html ,html tutorial form ,html form tutorial ,tutorial html form ,form html tutorial ,html website tutorial ,html tutorial website ,html code tutorial- published: 27 Nov 2014
- views: 301

Bài 10 - Thẻ Form
Trong HTML, các thẻ form giúp chúng ta tạo ra các biểu mẫu ( form ) giúp người dùng nhập nội dung và chuyển dữ liệu đến web server. Một form có thể chứa những phần tử đề người sử dụng nhập vào như trường dữ liệu , menu thả xuống, nút radio, nút xác nhận... Form được xem là ứng dụng quan trọng trong ngôn ngữ lập trình PHP có tác dụng giúp cập nhật thông tin một cách linh hoạt và dễ dàng quản lý chung nhờ vào sự kết hợp chặt chẽ với cơ sở dữ liệu. Ở đây chúng ta chỉ tìm hiều về cách tạo form trong HTML, còn việc xử lý form ( xử lý dữ liệu được gửi đi ) là thuộc về mảng PHP.- published: 26 Nov 2014
- views: 0

How to Create a Registration Form in HTML
Visit and follow our blog: http://www.howtodopc.wordpress.com. Plus us on Google+: https://plus.google.com/u/0/b/113201504131435597310/113201504131435597310/posts. Follow us on Twitter: https://www.twitter.com/HowtodoVids. Like us on Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/HowtodoTutorials. In this tutorial, you will learn how to create a registration form in HTML. Carefully understand the following step-by-step guide to learn:- 1. Inside the body tag, comes the form coding. 2. When you have inserted the form code, save the file. 3. After giving the name to the file, make sure that you type .html at the end. 4. Open the saved file. Now the registration form will be appeared in your default web browser. 5. Click on the "X" button located at the right side of the "UserID" text field to clear the UserID. 6. Click on the eye-looking icon located at the right side of the "Password" text filed to see the password. 7. Click on the "Clear" button to clear "UserID" and "Password". Thanks for watching! Please like, comment and the most important subscribe for our more how-to-do videos.- published: 26 Nov 2014
- views: 3

Web API on Web Form using AngularJS, HTML AND Javascript Part III
In this video tutorial, I am will be talking about how to integrate WEB API into the ASP.NET web form and I will be creating a little AngularJS demo app to consume the web api service from the client side.- published: 26 Nov 2014
- views: 12

CMSC331 Project 1 Demo Video
Demonstration of the working html form interacting with the customer request database.- published: 26 Nov 2014
- views: 4

Part4 - Html And Form
Uploaded with Free Video Converter from Freemake http://www.freemake.com/free_video_converter/- published: 23 Nov 2014
- views: 3

HTML Form Etiketleri
Güncel Eğitimler İçin Abone Olmayı Unutmayın.! Web Sitemiz : http://www.egitimsaati.com/ Youtube : https://www.youtube.com/user/EgitimSaatiOfficial Google+ : https://plus.google.com/+EgitimSaatiOfficial Facebook : https://www.facebook.com/EgitimSaatiOfficial Twitter : https://twitter.com/EgitimSaatiHD Türkiye'nin Ücretsiz Eğitim Sitesi- published: 21 Nov 2014
- views: 2

How To Learn Instant Form Pro Review-Best Form Creation Software For Marketers
Click The Link Below For More Information: http://x.vu/instantformproguides Instant Form Pro Review-Best Form Creation Software For Marketers Instant Form Pro from Joel Comm of Info Media, Inc. is an absolutely incredible software! After seeing all of the features of this software I was blown away with all that it offered. This form program gives you complete and total control over the forms you build, and it allows you to build world class surveys so you can gather that extremely important customer data. With just a few clicks of a mouse you can be on your way to having professional forms that can help really improve your bottom line. Understanding more about your customers really is huge, and it gives you that edge over the competition. If you know your customers hot buttons, than you can convert more sales, which means more cash, plain and simple. I can’t stress enough how simple this software is to use. If you can type and point and click a mouse you can setup forms that would normally take quite a bit of time to setup. Further these forms and surveys when complete are every bit as good as the ones you see on some of the largest and most well known websites on the Internet. This is the type of software that gives your website the edge. Professionalism can make a big difference in your customers minds simply because it gives you the appeal of looking like a bigger company than you are. If your site functions and has features like a major player online, than they will lump you into that same category. Instant Form Pro makes this all possible for you. http://x.vu/instantformproguides With just a simple click of a mouse in a check box you can have features for these survey forms turned on that would take a long time to setup if done the old way. For example you can turn on form Spam protection through CAPTCHA with a simple click! This is a program that would cost you multiple man hours to get it setup, or it would cost you several hours and the headache of setting it up. All of the features you need to create professional forms are directly at your fingertips with Instant Form Pro. This software is also coded in Ajax so you see the changes made to the form or survey as you actually make the changes. This is another hot feature that basically eliminates the need to click an update button to see changes; as you edit or change some of the wording it appears automatically. Ok, so this software does a lot of awesome things and most importantly it helps you get information and feedback from your customers which can be worth a lot of money to you. You owe it to yourself to check out Instant Form Pro today, and get the full story of just how powerful this software is. Click The Link Below For More Information: http://x.vu/instantformproguides best free password manager payday loans austin tx work cited page maker html form in form payday loans vancouver wa payday loans with debit card poor credit payday loans legitimate payday loans online payday loans atlanta ga form within a form free html form builder monthly installment payday loans free online password manager payday loans odessa tx ai software free download auto fill form software automated web form filler legit bad credit loans legit payday loan sites online html form builder web form builder software no debit card loans online form creator free buy online from usa buy online in usa free form builder software free php form builder html form within form instant debit card loans legitimate bad credit loans payday loans austin texas php web form builder bad credit loans ohio creating a web form- published: 20 Nov 2014
- views: 297

Jak ustawić kursor w polu formularza HTML.How to set up cursor on specify HTML form field
Czasami chcemy ustawić pozycję kursora w określonym polu formularza HTML, przy pomocy zmiennej body onload możemy tego dokonać. Wystarczy dla wpisu input w form dodać zmienną id a następnie dodać kod w sekcji body: body onload="document.getElementById*'form1'*.focus**" Uwaga w związku z ograniczeniami Youtube co do opisu filmu nawiasy zostały zastąpione * Powodzenia. Pełny kod strony: https://www.dropbox.com/s/q2zja37to16e06c/start.html?dl=0 W taki właśnie sposób ustawiamy kursor w odpowiednim polu formularza :). If you would like to set up cursor on specify field in html form use: body onload="document.getElementById*'form1'*.focus**"- published: 18 Nov 2014
- views: 24

[HTML] Show_Hide Form Elements Using JavaScript [HD].mp4
[HTML] Show_Hide Form Elements Using JavaScript [HD].mp4- published: 17 Nov 2014
- views: 1
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- Next page »
![[u'html form'][0].replace('](http://web.archive.org./web/20141212083124im_/http://i.ytimg.com/vi/L84543gmKBU/0.jpg)



