- published: 20 Nov 2012
- views: 18069439
-
remove the playlistIncome Gap
-
remove the playlistLatest Videos
-
remove the playlistLongest Videos
- remove the playlistIncome Gap
- remove the playlistLatest Videos
- remove the playlistLongest Videos
- published: 14 Jul 2014
- views: 9560201
- published: 06 Dec 2015
- views: 225532
- published: 14 Sep 2015
- views: 223391
- published: 03 Apr 2013
- views: 713574
- published: 17 May 2012
- views: 209788
- published: 03 Oct 2014
- views: 125928
- published: 24 Jan 2014
- views: 30785
- published: 13 Sep 2013
- views: 23023
- published: 04 Dec 2013
- views: 14944

Economic inequality (also known as the gap between rich and poor, income inequality, wealth disparity, or wealth and income differences) comprises disparities in the distribution of economic assets (wealth) and income within or between populations or individuals. The term typically refers to inequality among individuals and groups within a society, but can also refer to inequality among countries. The issue of economic inequality is related to the ideas of equity, equality of outcome and equality of opportunity.
Observers differ on both the morality and utility of inequality, whether, and/or how much inequality is necessary in society and how it can be affected. It has been praised as necessary and beneficial, and attacked as a social problem.
Economic inequality varies between societies and historical periods; between economic structures or systems (for example, capitalism or socialism), ongoing or past wars, and differences in individuals' abilities to create wealth are all involved in the creation of economic inequality.
This article is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported License, which means that you can copy and modify it as long as the entire work (including additions) remains under this license.

Margaret Hilda Thatcher, Baroness Thatcher, LG, OM, PC, FRS, née Roberts (born 13 October 1925) is a British politician and the longest-serving (1979–1990) British prime minister of the 20th century, and the only woman ever to have held the post. A Soviet journalist nicknamed her the "Iron Lady", which later became associated with her uncompromising politics and leadership style. As prime minister, she implemented conservative policies that have come to be known as Thatcherism.
Originally a research chemist before becoming a barrister, Thatcher was elected Member of Parliament (MP) for Finchley in 1959. Edward Heath appointed her Secretary of State for Education and Science in his 1970 government. In 1975 Thatcher defeated Heath in the Conservative Party leadership election and became Leader of the Opposition, as well as the first woman to lead a major political party in the United Kingdom. She became prime minister after winning the 1979 general election.
After entering 10 Downing Street, Thatcher introduced a series of political and economic initiatives to reverse what she perceived as Britain's precipitous national decline. Her political philosophy and economic policies emphasised deregulation (particularly of the financial sector), flexible labour markets, the privatisation of state-owned companies, and reducing the power and influence of trade unions. Thatcher's popularity during her first years in office waned amid recession and high unemployment, until economic recovery and the 1982 Falklands War brought a resurgence of support, resulting in her re-election in 1983. Thatcher was re-elected for a third term in 1987, but her Community Charge (popularly referred to as "poll tax") was widely unpopular and her views on the European Community were not shared by others in her Cabinet. She resigned as Prime Minister and party leader in November 1990, after Michael Heseltine launched a challenge to her leadership.
This article is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported License, which means that you can copy and modify it as long as the entire work (including additions) remains under this license.
- Loading...

-
 6:24
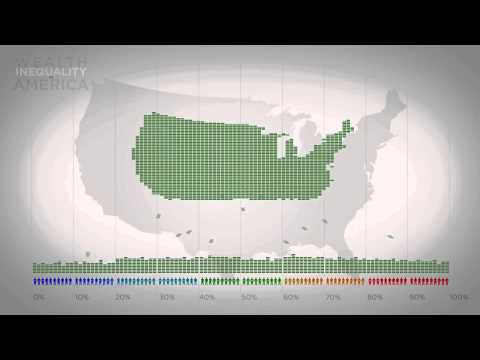
6:24Wealth Inequality in America
Wealth Inequality in AmericaWealth Inequality in America
Infographics on the distribution of wealth in America, highlighting both the inequality and the difference between our perception of inequality and the actual numbers. The reality is often not what we think it is. References: http://www.motherjones.com/politics/2011/02/income-inequality-in-america-chart-graph http://danariely.com/2010/09/30/wealth-inequality/ http://thinkprogress.org/economy/2011/10/03/334156/top-five-wealthiest-one-percent/ http://money.cnn.com/2012/04/19/news/economy/ceo-pay/index.htm -
 14:10
14:10Last Week Tonight with John Oliver: Wealth Gap (HBO)
Last Week Tonight with John Oliver: Wealth Gap (HBO)Last Week Tonight with John Oliver: Wealth Gap (HBO)
John Oliver discusses America's growing wealth gap and why it may be a problem in the future. Connect with Last Week Tonight online... Subscribe to the Last Week Tonight YouTube channel for more almost news as it almost happens: www.youtube.com/user/LastWeekTonight Find Last Week Tonight on Facebook like your mom would: http://Facebook.com/LastWeekTonight Follow us on Twitter for news about jokes and jokes about news: http://Twitter.com/LastWeekTonight Visit our official site for all that other stuff at once: http://www.hbo.com/lwt -
 10:16
10:16Income and Wealth Inequality: Crash Course Economics
Income and Wealth Inequality: Crash Course EconomicsIncome and Wealth Inequality: Crash Course Economics
Inequality is a big, big subject. There's racial inequality, gender inequality, and lots and lots of other kinds of inequality. This is Econ, so we're going to talk about wealth inequality and income inequality. There's no question that economic inequality is real. But there is disagreement as to whether income inequality is a problem, and what can or should be done about it. *** Crash Course is on Patreon! You can support us directly by signing up at http://www.patreon.com/crashcourse Thanks to the following Patrons for their generous monthly contributions that help keep Crash Course free for everyone forever: Mark, Eric Kitchen, Jessica Wode, Jeffrey Thompson, Steve Marshall, Moritz Schmidt, Robert Kunz, Tim Curwick, Jason A Saslow, SR Foxley, Elliot Beter, Jacob Ash, Christian, Jan Schmid, Jirat, Christy Huddleston, Daniel Baulig, Chris Peters, Anna-Ester Volozh, Ian Dundore, Caleb Weeks -- Want to find Crash Course elsewhere on the internet? Facebook - http://www.facebook.com/YouTubeCrashCourse Twitter - http://www.twitter.com/TheCrashCourse Tumblr - http://thecrashcourse.tumblr.com Support Crash Course on Patreon: http://patreon.com/crashcourse CC Kids: http://www.youtube.com/crashcoursekids -
 8:38
8:38Bernie Brief: Income Inequality | Ep. 1
Bernie Brief: Income Inequality | Ep. 1Bernie Brief: Income Inequality | Ep. 1
Bernie Sanders explains the one issue the billionaire class wants us to avoid -- and change. Read more about Income Inequality on our website: http://bernie.to/IncomeInequality --------- ★ Join the political revolution at www.berniesanders.com ★ Connect with Bernie: Facebook → https://www.facebook.com/berniesanders/ Twitter → https://twitter.com/berniesanders Instagram → https://www.instagram.com/berniesanders/ Tumblr → http://berniesanders.tumblr.com/ Snapchat → bernie.sanders ★ About Bernie: Bernie Sanders is a Democratic candidate for President of the United States. He is serving his second term in the U.S. Senate after winning re-election in 2012 with 71 percent of the vote. Sanders previously served as mayor of Vermont’s largest city for eight years before defeating an incumbent Republican to be the sole congressperson for the state in the U.S. House of Representatives. He lives in Burlington, Vermont with his wife Jane and has four children and seven grandchildren. Bernard “Bernie” Sanders was born in Brooklyn, New York, to immigrant parents and grew up in a small, rent-controlled apartment. His father came to the United States from Poland at the age of 17 without much money or a formal education. While attending the University of Chicago, a 20-year-old Sanders led students in a multi-week sit-in to oppose segregation in off-campus housing owned by the university as a Congress of Racial Equality (CORE) officer. In August of 1963, Sanders took an overnight bus as an organizer for the Student Nonviolent Coordinating Committee to hear Martin Luther King Jr.’s historic “I Have a Dream” speech firsthand at the March on Washington for Jobs and Freedom. After graduation, Bernie moved to Vermont where he worked as a carpenter and documentary filmmaker. In 1981, he was elected as mayor of Burlington as an Independent by a mere 10 votes, shocking the city’s political establishment by defeating a six-term, local machine mayor. In 1983, Bernie was re-elected by a 21 point margin with a record amount of voter turnout. Under his administration, the city made major strides in affordable housing, progressive taxation, environmental protection, child care, women’s rights, youth programs and the arts. In 1990, Sanders was elected to the House of Representatives as the first Independent in 40 years and joined the Democratic caucus. He was re-elected for eight terms, during which he voted against the deregulation of Wall Street, the Patriot Act, and the invasion of Iraq. In 2006, Sanders defeated the richest man in Vermont to win a seat in the U.S. Senate as an Independent. Known as a “practical and successful legislator,” Sanders served as chairman of the Committee on Veterans’ Affairs where he authored and passed the most significant veteran health care reform bill in recent history. While in the Senate, Sanders has fought tirelessly for working class Americans against the influence of big money in politics. In 2010, he gave an eight-and-a-half hour filibuster-like speech on the Senate floor in opposition to extending Bush-era tax breaks for the wealthy. In 2015, the Democratic leadership tapped Bernie to serve as the caucus’ ranking member of the Senate Budget Committee. Known for his consistency on the issues, Senator Sanders has supported the working class, women, communities of color, and the LGBT community throughout his career. He is an advocate for the environment, unions, and immigrants. He voted against Keystone XL, opposes the Trans-Pacific Partnership deal, wants to expand the Voting Rights Act, and pass the Equal Rights Amendment. To learn more about Bernie on the issues, click here: https://berniesanders.com/issues/ -
 3:51
3:51Global Wealth Inequality - What you never knew you never knew
Global Wealth Inequality - What you never knew you never knewGlobal Wealth Inequality - What you never knew you never knew
For more info go to www.therules.org Production Company: Grain Media (grainmedia.co.uk); Motion Graphics Artist: Nick Pittom (nickpittom.com); Music: Sup Doodle and Apple Juice Kid (AppleJuiceKid.com); References: http://www.therules.org/inequality-video-fact-sheet; Accompanying article in Al Jazeera: http://www.aljazeera.com/indepth/opinion/2013/04/201349124135226392.html -
 5:50
5:50A TED Talk on Income Inequality by Nick Hanauer
A TED Talk on Income Inequality by Nick HanauerA TED Talk on Income Inequality by Nick Hanauer
Further Discussion @ http://www.politicalyak.com/f13/nick-hanauers-ted-talk-101.html A talk on Income Inequality and the differences in taxation given by Nick Hanauer at a TED conference. Make sure you visit our website @ - http://www.politicalyak.com -! Make sure you like us on facebook - http://www.facebook.com/PoliticalYAK -! & finally follow our somewhat awesome tweets - http://www.twitter.com/politicalyak -! Enjoy! -
 3:11
3:11Thomas Sowell: The Income Gap Myth
Thomas Sowell: The Income Gap Myth -
 16:27
16:27This Is The Income Inequality Video CEOs Don’t Want Americans To See
This Is The Income Inequality Video CEOs Don’t Want Americans To SeeThis Is The Income Inequality Video CEOs Don’t Want Americans To See
“If Michael Norton’s research is to be believed, Americans don’t have the faintest clue how severe economic inequality has become—and if they only knew, they’d be appalled. Consider the Harvard Business School professor’s new study examining public opinion about executive compensation, co-authored with the Chulalongkorn University in Bangkok’s Sorapop Kiatpongsan. In the 1960s, the typical corporate chieftain in the U.S. earned 20 times as much as the average employee. Today, depending on whose estimate you choose, he makes anywhere from 272 to 354 times as much. According to the AFL-CIO, the average CEO takes home more than $12 million, while the average worker makes about $34,000. In their study, Norton and Kiatpongsan asked about 55,000 people around the globe, including 1,581 participants in the U.S., how much money they thought corporate CEOs made compared with unskilled factory workers."* The Young Turks host Cenk Uygur breaks it down. *Read more here from Jordan Weissmann / Slate: http://www.slate.com/articles/business/moneybox/2014/09/americans_have_no_idea_how_bad_inequality_is_new_harvard_business_school.html Help end the corrupting influence of money in politics: SUPPORT the 28th Amendment to #GetMoneyOut http://www.wolf-pac.com/petition?=tyt.... CLICK HERE to support Wolf PAC: http://www.wolf-pac.com/wolf_pac_memb... CLICK HERE to take action in your state: http://www.wolf-pac.com/states ********** Income Inequality, War Profiteering, Justice Scalia & Dinesh D'Souza - The Young Turks 10/2/2014 News & Politics http://www.youtube.com/playlist?list=PLTpcK80irdQh1EHmoPs65nk2ezs0hVhq_ ********** The Largest Online News Show in the World. Hosted by Cenk Uygur and Ana Kasparian. LIVE STREAMING weekdays 6-8pm ET. Young Turk (n), 1. Young progressive or insurgent member of an institution, movement, or political party. 2. Young person who rebels against authority or societal expectations. (American Heritage Dictionary) The Young Turks (Winner - Best Political Podcast & Best Political News Site of 2009) were the first original talk show on Sirius satellite radio and the first live, daily webcast on the internet. But that is not the revolution. We are a rare show that combines all of the news that people care about in one place. We are not afraid to talk about politics and entertainment and sports and pop culture. But that is not the revolution either. The real revolution is in daring to be honest with people. We don't patronize our viewers or lie to them. We have real conversations and deliver the news honestly. Download audio and video of the full two hour show on-demand + the members-only post game show by becoming a member at http://www.tytnetwork.com/subscribe/. Your membership supports the day to day operations and is vital for our continued success and growth. Join The Young Turks Network mailing list https://www.tytnetwork.com/newsletter/ or Support The Young Turks by Subscribing http://www.youtube.com/user/theyoungturks?sub_confirmation=1 Like Us on Facebook: http://www.facebook.com/TheYoungTurks Follow Us on Twitter: http://www.twitter.com/TheYoungTurks Support TYT for FREE by doing your Amazon shopping through this link (bookmark it!) http://www.amazon.com/?tag=theyoungturks-20 Get your TYT Merch: http://shoptyt.com ********** 'Your Country Is Just Not That Into You: How the Media, Wall Street, and Both Political Parties Keep on Screwing You—Even After You’ve Moved On' by Jimmy Dore. Buy it here: http://goo.gl/t7GnDA -
 2:13
2:13WHAT DOES INCOME INEQUALITY MEAN TO AMERICANS? - BBC NEWS
WHAT DOES INCOME INEQUALITY MEAN TO AMERICANS? - BBC NEWSWHAT DOES INCOME INEQUALITY MEAN TO AMERICANS? - BBC NEWS
Subscribe to BBC News www.youtube.com/bbcnews Subscribe http://www.youtube.com/bbcnews Check out our website: http://www.bbc.com/news Facebook: http://www.facebook.com/bbcworldnews Twitter: http://www.twitter.com/bbcworld Instagram: http://instagram.com/bbcnews As US president Obama prepares for his annual State of the Union speech on 28 January, income inequality is expected to be on the top of his agenda. The US has one of the highest income gaps in the developed world, and the gap is growing. The BBC's David Botti breaks down the numbers to see how the US compares to the rest of the world and how Americans are reacting to the income gap. -
 11:22
11:22Inequality for All: Robert Reich Warns Record Income Gap Is Undermining Our Democracy. (1 of 3)
Inequality for All: Robert Reich Warns Record Income Gap Is Undermining Our Democracy. (1 of 3)Inequality for All: Robert Reich Warns Record Income Gap Is Undermining Our Democracy. (1 of 3)
http://www.democracynow.org - Five years ago this weekend, the Wall Street giant Lehman Brothers collapsed triggering the worst financial crisis since the Great Depression. Today, the divide between the 1 percent and the 99 percent is as great as ever. According to one recent study, the top 1 percent has captured about 95 percent of the income gains since the recession ended. "Since the recovery, almost all of the gains have gone to the very, very top. People who are in the top 1 percent are doing even better than they did before the Great Recession, better than they have done since 1928," says former Labor Secretary Robert Reich. "Most Americans are on a downward escalator. Median wage in the United States, adjusted for inflation, keeps on dropping." Watch Part 2 of this interview: http://youtu.be/_dunMg95O5k Reich is the focus of the new film, "Inequality for All." In this interview, he also talks about Syria, the second anniversary of Occupy Wall Street on September 17, Obama's healthcare plan and Milton Friedman's connection to the Pinochet dictatorship in Chile. Democracy Now!, is an independent global news hour that airs weekdays on 1,200+ TV and radio stations Monday through Friday. Watch it live 8-9am ET at http://www.democracynow.org. FOLLOW DEMOCRACY NOW! ONLINE: Facebook: http://www.facebook.com/democracynow Twitter: @democracynow Subscribe on YouTube: http://www.youtube.com/democracynow Listen on SoundCloud: http://www.soundcloud.com/democracynow Daily Email News Digest: http://www.democracynow.org/subscribe Please consider supporting independent media by making a donation to Democracy Now! today, visit http://www.democracynow.org/donate/YT -
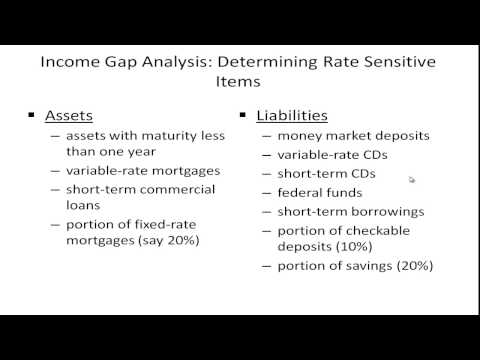 9:01
9:01Managing Interest Rate Risk - Income Gap Analysis
Managing Interest Rate Risk - Income Gap Analysis -
 48:27
48:27Obama: Income inequality is defining challenge for the U.S.
Obama: Income inequality is defining challenge for the U.S.Obama: Income inequality is defining challenge for the U.S.
Speaking at an event sponsored by the left-leaning think tank Center for American Progress, President Barack Obama said the income gap between America's rich and poor is a "defining challenge of our time."Income inequality has jeopardized the nation's middle class, he added.The president is also urging Washington to take steps to ensure that the economy benefits everyone. -
 7:37
7:37'Inequality for All': Documentary tracks American income gap
'Inequality for All': Documentary tracks American income gap'Inequality for All': Documentary tracks American income gap
This week marked the five-year anniversary of the collapse of Lehman Brothers investment bank, which triggered the largest financial crisis since the Great Depression, as well as the second anniversary of the Occupy Wall Street movement. Last year the gap between the wealthiest one percent of Americans and the rest of the country reached its widest point since the Gilded Age of the 1920s, according to global economists. The so called "One Percenters" earned 20 percent of American income last year. RT's Ameera David talks to Jacob Kornbluth, director of the "Inequality for All" documentary, about the growing income gap in this country. Find RT America in your area: http://rt.com/where-to-watch/ Or watch us online: http://rt.com/on-air/rt-america-air/ Like us on Facebook http://www.facebook.com/RTAmerica Follow us on Twitter http://twitter.com/RT_America -
 7:18
7:18Last Week Tonight with John Oliver: Wage Gap
Last Week Tonight with John Oliver: Wage GapLast Week Tonight with John Oliver: Wage Gap
John Oliver explores America's wage gap between men and women and proposes a possible solution. Note: Solution proposed is 100% sarcastic.
- Adam Smith
- Alberto Alesina
- Alcoholic beverage
- Amartya Sen
- Anthony Giddens
- Arthur Cecil Pigou
- Assets
- Austrian school
- Ben Bernanke
- Cambridge University
- Canada
- Canadian provinces
- Cancer
- Capability approach
- Capitalism
- Catch-22 (logic)
- Civic engagement
- Civil servants
- Classical liberals
- Cochin
- Competition
- Crime rate
- Cross-sectional data
- Cycle of poverty
- David Schmidtz
- Death
- Diminishing returns
- Dollars & Sense
- Economic
- Economic development
- Economic inequality
- Economic liberalism
- Economic mobility
- Economic theory
- Education
- Emmanuel Saez
- Epidemiology
- Equality of outcome
- Equity (economics)
- Equity (finance)
- Exercise
- Finance
- Food
- Free trade
- Gender Equity Index
- Gender income gap
- Gender inequality
- Gender role
- Gini coefficient
- Gini index
- Government
- Happiness
- Harvard
- Health care
- Healthcare
- Heart disease
- Henry Hazlitt
- High school
- Homicide
- House
- Housing inequality
- Incentive
- Income
- Income tax
- Index (economics)
- India
- Inequity aversion
- Informal sector
- Inheritance
- Innovation
- Invest
- Italy
- John Rawls
- Juliet Schor
- Kate Pickett
- Kuznets curve
- Labor economics
- Labor market
- Legal egalitarianism
- Leninism
- Libertarians
- Life expectancy
- London
- Ludwig von Mises
- Luxembourg
- Machine labor
- Marginal utility
- Market economy
- Market forces
- Marxism
- Means of production
- Meritocracy
- Milton Friedman
- Minimum wage
- Monetary policy
- Money supply
- NAIRU
- Nationalization
- Neoliberalism
- New York Times
- Nomenklatura
- Occupy movement
- OECD Publishing
- Panel data
- Paul Krugman
- Paul Ryan
- Pensions
- Peptic ulcer
- Peter Orszag
- Population health
- Poverty
- Premature aging
- Profit motive
- Progressive tax
- Psychosocial stress
- Public education
- Purchasing power
- Rafael Di Tella
- Ravi Batra
- Regulation
- Rheumatoid arthritis
- Richard G. Wilkinson
- Richard Lynn
- Risk
- Risk aversion
- Robert Alan Dahl
- Robert Barro
- Robert H. Frank
- Robert MacCulloch
- Robert Nozick
- Robert Putnam
- Robert Z. Lawrence
- Scientific American
- SES Gradient
- Simon Kuznets
- Slovakia
- Slums
- Social capital
- Social capital index
- Social cohesion
- Social justice
- Social liberalism
- Social status
- Social welfare
- Socialism
- Sovereign state
- Soviet Union
- Stress (medicine)
- Sub-Saharan Africa
- Subsidy
- Supply and demand
- Surplus value
- Tatu Vanhanen
- Tax evasion
- Tax rate
- The Economist
- Thomas Sowell
- Three Rivers Press
- Timothy Noah
- Tobacco smoking
- Trust (sociology)
- Type 2 diabetes
- U.S. state
- Unemployment
- Union membership
- Unionization
- United states
- United States
- Utility
- Wage
- Washington Post
- Wealth
- Wealth concentration
- Welfare state
- Whitehall Study
- World Bank
- Adam Smith
- Alberto Alesina
- Amartya Sen
- Arthur Cecil Pigou
- Ben Bernanke
- David Schmidtz
- Emmanuel Saez
- Henry Hazlitt
- John Rawls
- Juliet Schor
- Kate Pickett
- Ludwig von Mises
- Milton Friedman
- Paul Krugman
- Paul Ryan
- Rafael Di Tella
- Ravi Batra
- Richard Lynn
- Robert Barro
- Robert Nozick
- Simon Kuznets
- Tatu Vanhanen
- Thomas Sowell
- Timothy Noah
-

Wealth Inequality in America
Infographics on the distribution of wealth in America, highlighting both the inequality and the difference between our perception of inequality and the actual numbers. The reality is often not what we think it is. References: http://www.motherjones.com/politics/2011/02/income-inequality-in-america-chart-graph http://danariely.com/2010/09/30/wealth-inequality/ http://thinkprogress.org/economy/2011/10/03/334156/top-five-wealthiest-one-percent/ http://money.cnn.com/2012/04/19/news/economy/ceo-pay/index.htm -

Last Week Tonight with John Oliver: Wealth Gap (HBO)
John Oliver discusses America's growing wealth gap and why it may be a problem in the future. Connect with Last Week Tonight online... Subscribe to the Last Week Tonight YouTube channel for more almost news as it almost happens: www.youtube.com/user/LastWeekTonight Find Last Week Tonight on Facebook like your mom would: http://Facebook.com/LastWeekTonight Follow us on Twitter for news about jokes and jokes about news: http://Twitter.com/LastWeekTonight Visit our official site for all that other stuff at once: http://www.hbo.com/lwt -

Income and Wealth Inequality: Crash Course Economics
Inequality is a big, big subject. There's racial inequality, gender inequality, and lots and lots of other kinds of inequality. This is Econ, so we're going to talk about wealth inequality and income inequality. There's no question that economic inequality is real. But there is disagreement as to whether income inequality is a problem, and what can or should be done about it. *** Crash Course is on Patreon! You can support us directly by signing up at http://www.patreon.com/crashcourse Thanks to the following Patrons for their generous monthly contributions that help keep Crash Course free for everyone forever: Mark, Eric Kitchen, Jessica Wode, Jeffrey Thompson, Steve Marshall, Moritz Schmidt, Robert Kunz, Tim Curwick, Jason A Saslow, SR Foxley, Elliot Beter, Jacob Ash, Christian, Jan... -

Bernie Brief: Income Inequality | Ep. 1
Bernie Sanders explains the one issue the billionaire class wants us to avoid -- and change. Read more about Income Inequality on our website: http://bernie.to/IncomeInequality --------- ★ Join the political revolution at www.berniesanders.com ★ Connect with Bernie: Facebook → https://www.facebook.com/berniesanders/ Twitter → https://twitter.com/berniesanders Instagram → https://www.instagram.com/berniesanders/ Tumblr → http://berniesanders.tumblr.com/ Snapchat → bernie.sanders ★ About Bernie: Bernie Sanders is a Democratic candidate for President of the United States. He is serving his second term in the U.S. Senate after winning re-election in 2012 with 71 percent of the vote. Sanders previously served as mayor of Vermont’s largest city for eight years before defeating an incumbent ... -

Global Wealth Inequality - What you never knew you never knew
For more info go to www.therules.org Production Company: Grain Media (grainmedia.co.uk); Motion Graphics Artist: Nick Pittom (nickpittom.com); Music: Sup Doodle and Apple Juice Kid (AppleJuiceKid.com); References: http://www.therules.org/inequality-video-fact-sheet; Accompanying article in Al Jazeera: http://www.aljazeera.com/indepth/opinion/2013/04/201349124135226392.html -

A TED Talk on Income Inequality by Nick Hanauer
Further Discussion @ http://www.politicalyak.com/f13/nick-hanauers-ted-talk-101.html A talk on Income Inequality and the differences in taxation given by Nick Hanauer at a TED conference. Make sure you visit our website @ - http://www.politicalyak.com -! Make sure you like us on facebook - http://www.facebook.com/PoliticalYAK -! & finally follow our somewhat awesome tweets - http://www.twitter.com/politicalyak -! Enjoy! -

-

This Is The Income Inequality Video CEOs Don’t Want Americans To See
“If Michael Norton’s research is to be believed, Americans don’t have the faintest clue how severe economic inequality has become—and if they only knew, they’d be appalled. Consider the Harvard Business School professor’s new study examining public opinion about executive compensation, co-authored with the Chulalongkorn University in Bangkok’s Sorapop Kiatpongsan. In the 1960s, the typical corporate chieftain in the U.S. earned 20 times as much as the average employee. Today, depending on whose estimate you choose, he makes anywhere from 272 to 354 times as much. According to the AFL-CIO, the average CEO takes home more than $12 million, while the average worker makes about $34,000. In their study, Norton and Kiatpongsan asked about 55,000 people around the globe, including 1,581 partici... -

WHAT DOES INCOME INEQUALITY MEAN TO AMERICANS? - BBC NEWS
Subscribe to BBC News www.youtube.com/bbcnews Subscribe http://www.youtube.com/bbcnews Check out our website: http://www.bbc.com/news Facebook: http://www.facebook.com/bbcworldnews Twitter: http://www.twitter.com/bbcworld Instagram: http://instagram.com/bbcnews As US president Obama prepares for his annual State of the Union speech on 28 January, income inequality is expected to be on the top of his agenda. The US has one of the highest income gaps in the developed world, and the gap is growing. The BBC's David Botti breaks down the numbers to see how the US compares to the rest of the world and how Americans are reacting to the income gap. -

Inequality for All: Robert Reich Warns Record Income Gap Is Undermining Our Democracy. (1 of 3)
http://www.democracynow.org - Five years ago this weekend, the Wall Street giant Lehman Brothers collapsed triggering the worst financial crisis since the Great Depression. Today, the divide between the 1 percent and the 99 percent is as great as ever. According to one recent study, the top 1 percent has captured about 95 percent of the income gains since the recession ended. "Since the recovery, almost all of the gains have gone to the very, very top. People who are in the top 1 percent are doing even better than they did before the Great Recession, better than they have done since 1928," says former Labor Secretary Robert Reich. "Most Americans are on a downward escalator. Median wage in the United States, adjusted for inflation, keeps on dropping." Watch Part 2 of this interview: http... -

-

Obama: Income inequality is defining challenge for the U.S.
Speaking at an event sponsored by the left-leaning think tank Center for American Progress, President Barack Obama said the income gap between America's rich and poor is a "defining challenge of our time."Income inequality has jeopardized the nation's middle class, he added.The president is also urging Washington to take steps to ensure that the economy benefits everyone. -

'Inequality for All': Documentary tracks American income gap
This week marked the five-year anniversary of the collapse of Lehman Brothers investment bank, which triggered the largest financial crisis since the Great Depression, as well as the second anniversary of the Occupy Wall Street movement. Last year the gap between the wealthiest one percent of Americans and the rest of the country reached its widest point since the Gilded Age of the 1920s, according to global economists. The so called "One Percenters" earned 20 percent of American income last year. RT's Ameera David talks to Jacob Kornbluth, director of the "Inequality for All" documentary, about the growing income gap in this country. Find RT America in your area: http://rt.com/where-to-watch/ Or watch us online: http://rt.com/on-air/rt-america-air/ Like us on Facebook http://www.faceboo... -

Last Week Tonight with John Oliver: Wage Gap
John Oliver explores America's wage gap between men and women and proposes a possible solution. Note: Solution proposed is 100% sarcastic. -

SG Income Gap | ONE (SINGAPORE)
The wealth gap in Singapore is widening. More families are having problems making ends meet. Singapore has the world's highest per capita GDP. But income inequality here has risen sharply since 2000, posing a number of issues for the country. ONE (SINGAPORE) and the Wee Kim Wee Centre invited Mdm Halimah Yacob, Leong Sze Hian and Nicole Seah to discuss this issue and explore practical solutions. This resource page includes a number of related articles and videos. -

Startling Fact About Income Inequality in America
It’s no surprise that the rich tend to get richer while the poor tend to get poorer. But seeing the actual breakdown really drives the point home. Watch the video for the findings from a new study financed by the Russell Sage Foundation. What are your thoughts on this story? Comment below and share! Subscribe to The Rubin Report: http://www.youtube.com/subscription_center?add_user=RubinReport Follow Dave on Twitter: https://twitter.com/RubinReport Like Dave on Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/daverubin More Dave Rubin: http://daverubin.tv/ Host: Dave Rubin @RubinReport Guests: Gina Grad @GinaGrad Malcolm Fleschner @CultureShlock The Rubin Report is a comedy and current events panel show on The Young Turks Network hosted by Dave Rubin. Comedians, celebrities and media persona... -

Rockefeller Center - "Debating Income Inequality: What's the Problem? What's the Solution?"
"Debating Income Inequality: What's the Problem? What's the Solution?" N. Gregory Mankiw, Professor of Economics, Harvard University; The Brooks Family Lecturer Jared Bernstein, Senior Fellow at the Center on Budget and Policy Priorities Moderator: Charles Wheelan, Senior Lecturer and Policy Fellow, Rockefeller Center Monday, May 12, 2014 - Filene Auditorium, Moore Hall Presented by The Nelson A. Rockefeller Center for Public Policy and the Social Sciences and Co-sponsored with the Political Economy Project For other Rockefeller Center events please go to http://rockefeller.dartmouth.edu/events/programs.html -

Is there a growing income gap? If so, is it a problem?
Welcome to Ask a Libertarian 2012 with Reason's Nick Gillespie and Matt Welch. They are the authors of the book, The Declaration of Independents: How Libertarian Politics Can Fix What's Wrong With America, coming out in paperback later this month. Pre-order: http://www.amazon.com/The-Declaration-Independents-Libertarian-Politics/dp/16... On June 12, 2012 Gillespie and Welch used short, rapid-fire videos to answer dozens of reader questions submitted via email, Twitter, Facebook, and Reason.com. In this episode, they answer the question: "Is there a growing income gap? If so, is it a problem?" - Cason White Produced by Meredith Bragg, Jim Epstein, Josh Swain, and Tracy Oppenheimer with help from Katie Hooks. To watch answers from 2011's Ask a Libertarian series, go here: http://www.yo... -

Does globalization widen the income gap?
It's not at all clear, Thiel says, that income disparities are growing globally. -

Wealth Inequality in Canada
-

Margaret Thatcher Exposes Liberal Politics on Income Inequality
Margaret Thatcher explains how liberals would prefer the poor be poorer provided the rich were less rich rather than create more wealth for everyone. -

Richard Wilkinson: How economic inequality harms societies
http://www.ted.com We feel instinctively that societies with huge income gaps are somehow going wrong. Richard Wilkinson charts the hard data on economic inequality, and shows what gets worse when rich and poor are too far apart: real effects on health, lifespan, even such basic values as trust. TEDTalks is a daily video podcast of the best talks and performances from the TED Conference, where the world's leading thinkers and doers give the talk of their lives in 18 minutes. Featured speakers have included Al Gore on climate change, Philippe Starck on design, Jill Bolte Taylor on observing her own stroke, Nicholas Negroponte on One Laptop per Child, Jane Goodall on chimpanzees, Bill Gates on malaria and mosquitoes, Pattie Maes on the "Sixth Sense" wearable tech, and "Lost" producer JJ A... -

On rising income inequality (Singapore Summit 2014)
Prime Minister Lee Hsien Loong commenting on the issue of income inequality and the role government can play to manage the issue. PM Lee was speaking at the Singapore Summit 2014 Dialogue held on 20 September 2014.
Wealth Inequality in America
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 6:24
- Updated: 20 Nov 2012
- views: 18069439
- published: 20 Nov 2012
- views: 18069439
Last Week Tonight with John Oliver: Wealth Gap (HBO)
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 14:10
- Updated: 14 Jul 2014
- views: 9560201
- published: 14 Jul 2014
- views: 9560201
Income and Wealth Inequality: Crash Course Economics
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 10:16
- Updated: 06 Dec 2015
- views: 225532
- published: 06 Dec 2015
- views: 225532
Bernie Brief: Income Inequality | Ep. 1
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 8:38
- Updated: 14 Sep 2015
- views: 223391
- published: 14 Sep 2015
- views: 223391
Global Wealth Inequality - What you never knew you never knew
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 3:51
- Updated: 03 Apr 2013
- views: 713574
- published: 03 Apr 2013
- views: 713574
A TED Talk on Income Inequality by Nick Hanauer
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 5:50
- Updated: 17 May 2012
- views: 209788
- published: 17 May 2012
- views: 209788
Thomas Sowell: The Income Gap Myth
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 3:11
- Updated: 07 Nov 2012
- views: 11298
This Is The Income Inequality Video CEOs Don’t Want Americans To See
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 16:27
- Updated: 03 Oct 2014
- views: 125928
- published: 03 Oct 2014
- views: 125928
WHAT DOES INCOME INEQUALITY MEAN TO AMERICANS? - BBC NEWS
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 2:13
- Updated: 24 Jan 2014
- views: 30785
- published: 24 Jan 2014
- views: 30785
Inequality for All: Robert Reich Warns Record Income Gap Is Undermining Our Democracy. (1 of 3)
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 11:22
- Updated: 13 Sep 2013
- views: 23023
- published: 13 Sep 2013
- views: 23023
Managing Interest Rate Risk - Income Gap Analysis
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 9:01
- Updated: 16 Jul 2014
- views: 2123
Obama: Income inequality is defining challenge for the U.S.
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 48:27
- Updated: 04 Dec 2013
- views: 14944
- published: 04 Dec 2013
- views: 14944
'Inequality for All': Documentary tracks American income gap
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 7:37
- Updated: 20 Sep 2013
- views: 6195
- published: 20 Sep 2013
- views: 6195
Last Week Tonight with John Oliver: Wage Gap
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 7:18
- Updated: 25 Aug 2014
- views: 2315315
- published: 25 Aug 2014
- views: 2315315
SG Income Gap | ONE (SINGAPORE)
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 4:22
- Updated: 29 Jul 2013
- views: 800
- published: 29 Jul 2013
- views: 800
Startling Fact About Income Inequality in America
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 5:45
- Updated: 02 Aug 2014
- views: 11878
- published: 02 Aug 2014
- views: 11878
Rockefeller Center - "Debating Income Inequality: What's the Problem? What's the Solution?"
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 91:35
- Updated: 12 Jun 2014
- views: 5799
- published: 12 Jun 2014
- views: 5799
Is there a growing income gap? If so, is it a problem?
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 2:15
- Updated: 12 Jun 2012
- views: 3984
- published: 12 Jun 2012
- views: 3984
Does globalization widen the income gap?
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 5:17
- Updated: 24 Apr 2012
- views: 1707
- published: 24 Apr 2012
- views: 1707
Wealth Inequality in Canada
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 4:14
- Updated: 16 Dec 2014
- views: 172563
- published: 16 Dec 2014
- views: 172563
Margaret Thatcher Exposes Liberal Politics on Income Inequality
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 1:08
- Updated: 26 Jun 2012
- views: 15421
- published: 26 Jun 2012
- views: 15421
Richard Wilkinson: How economic inequality harms societies
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 16:55
- Updated: 24 Oct 2011
- views: 398356
- published: 24 Oct 2011
- views: 398356
On rising income inequality (Singapore Summit 2014)
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 3:30
- Updated: 20 Sep 2014
- views: 1877
- published: 20 Sep 2014
- views: 1877
-

Jay Weber 4/7/16 Income gap caused by liberal unionista policies. Toss the peasants a $15 bone.
Weber quotes a Forbes article stating that the biggest cities in America ( Weber inserts cities run by liberals ) have reverted back to Victorian Age Economies. He goes on to say in his own words that the Democrats / Unionista policies are what have led to this large gap in income inequality and now they want to toss the peasants a $15 bone. -

Congresswoman Barbara Lee: Economic mobility and racial justice are intertwined
It’s critical that we bridge not only the income gap, but the racial inequality gap. There’s still a lot of work to do to close these gaps. That’s why this discussion is so important. The report that you released, “The Color of Entrepreneurship,” shows that, in a more equal society, where there would be opportunities for all, we would have 1 million more businesses owned by people of color. We know that minority businesses hire people who are unemployed and need a good-paying jobs. I’m a former business owner myself. I owned a facilities-management company with 350-400 employees for 11 years. The difficulties I had then, in the ‘80s and ‘90s, to access capital, to make sure that my company had access to federal contracting opportunities, were tremendous. We had to work 10 times harder with... -

Robert Reich interview on Charlie Rose (1991)
Economist Robert Reich comments on the state of the U.S. economy and suggests what must be done to decrease the widening income gap and get the country out of its current recession. -

How to Avoid the Retirement Income Gap
-

Ben Shapiro: Obama goes to mosque, Hillary talks income inequality and the vaunted mailbag
Hillary Clinton Is A Flaming Garbage Heap. Chris Matthews loses his mind over Ted Cruz About Ben : In 2012, Shapiro became editor-at-large of Breitbart.com, a news and opinion website founded by Andrew Breitbart. In March 2016, Shapiro resigned from his position as editor-at-large of Breitbart.com following the website's lack of support for reporter Michelle Fields, in response to her alleged assault by Corey Lewandowski, Donald Trump's campaign manager. SUBCRIBE https://goo.gl/HFGpiR Follow on Website : DailyWire.com Copyright © 2016 Ben Shapiro Commentator (Show on Podcast) -

The Income Gap
-

Bernie Sanders slams income inequality in Vatican speech
► facebook : https://www.facebook.com/CFhack2014 ► Twitter : https://www.twitter.com/haythamplo -

Determine and Close Your Income Gap
This video provides a quick overview of the NYS Deferred Compensation Plan and reviews steps one and two in preparing for retirement — determining the income you will need in retirement and how you can increase your retirement income. Catch-up Provisions in the Plan are described. -

Hillary Clinton talks terrorism, economic growth, education and income inequality
Hillary Clinton saw something — and now she's saying something. The Democratic presidential front-runner, during a wide-ranging sitdown with the Daily News . On Tuesday, a draft statement from the Group of 20 finance officials warned that growing income inequality could harm economic growth, the first time the group . Rating agency S&P; recently came out with a report that details the effects of rising income inequality and offers a solution. Rising levels of income inequality in . Strengthening America's middle class President Obama's State of the Union address will focus heavily on America's growing wage gap. Ed Schultz and White . -

Narrowing the Income Inequality Gap
Speakers include Dr. Randy Albeda, Professor of Economics at UMASS Boston; Harris Gruman, Executive Director of the Service Employees International Union MA State Council; and Luc Schuster, Deputy Director of MassBudget. Senator Eldridge presents introductory remarks, while Sarah Cressy, CEO of the Assabet Valley Chamber, serves as moderator. The program covers the roots of income inequality, proposed wage and tax legislation to remedy income inequality, and the potential impact of the proposed legislation on the middle class and small businesses. Hosted by the Stow, Maynard, and Hudson Democratic Town Committees. Recorded at Stow Town Hall on March 30, 2016. -

-

Income Inequality and the Future of the American Dream: Differing Perspectives
Alan Auerbach, Ph.D., Professor of Economics and Law, and Director of the Burch Center for Tax Policy and Public Finance, University of California, Berkeley Yaron Brook, Ph.D., Executive Director, Ayn Rand Institute; Co-author, Equal Is Unfair: America's Misguided Fight Against Income Inequality Mary Cranston, Past Chair, Commonwealth Club Board of Governors; Retired Senior Partner and Past Chair, Pillsbury Winthrop Shaw Pittman Law Firm—Moderator It is argued by many that the American Dream is vanishing, and that the cause is rising income inequality. Are tax hikes and raising the minimum wage solutions to saving the American Dream? Or do they symbolize what free market advocate Yaron Brook calls “a war on success”? Join Dr. Brook and economist Dr. Alan Auerbach in a spirited discussi... -

The income inequality gap in soccer
Independent Women Forum’s Hadley Heath Manning discusses the income inequality between men and women soccer stars. -

Barton College economist John Bethune discusses income inequality
Dr. John Bethune, professor of business at Barton College, discusses the impact of various government policies on income inequality. Bethune offered these comments during an interview for Carolina Journal Radio Program No. 672. Video courtesy of CarolinaJournal.com. -

State of the Union 2016: Income Inequality
How does the U.S. stack up against peer countries in terms of income inequality? CPI research scholar Jonathan Fisher addresses this question at our 2016 State of the Union conference. Read the report: http://inequality.stanford.edu/sotu -

Joel Klein: Education key to ending income inequality
Joel Klein, a leading voice in the national conversation on education reform says its impossible to close the income gap without addressing shortcomings in our public education system. Klein sat down with Yahoo Finance Editor-in-Chief Aaron Task to discuss his thoughts on how to confront the challenges faced in public schools across the United States, which he also outlines in his newly-published memoir Lessons of Hope: How to Fix Our Schools. -

Why income inequality will dampen economic growth
Yahoo Finance's Aaron Task interviews S&P; chief economist Beth Ann Bovino about income inequality. -

How to Decrease the Income Inequality Gap
How to lessen the income inequality gap as well as some additional background information. -

Full Tim Income Trading Gaps - $1,000 Profit In Less Than 20 Minutes
http://LazyGapTrader.com/ Learn how to earn a full time income trading the morning gaps each and every day. In my course at http://LazyGapTrader.com/ you will learn the single best day trading strategy found in the markets today. You'll learn all about why gap trading provides a price method for finding price levels in stocks where there is a high probability for a price reaction allowing you to realize the profits that can change your life and provide a full time income from trading. -

19. Minimum Wage, Gender Wage Gap, Income Inequality, and More with Dr. Walter Block
The show notes page for this episode can be found at: http://www.wakeupcallpodcast.com/wages Dr. Walter Block, Professor of Economics at Loyola University New Orleans and author of Defending the Undefendable, joins Adam Camac and Daniel Laguros to discuss the minimum wage, the gender wage gap, income inequality, and other topics. -

Bernie Sanders - income inequality
Seattle 3/21/16 -

Income share held by top 10% in Korea hits 45%
한국 소득상위 10%가 전체소득의 45% 차지…아시아 최대 It seems the rich are getting richer in Korea. Korea is number one in Asia when it comes to the percentage of income held by the top 10 percent of earners, according to a new report. The country's income gap, however,... is not as great as that of other countries in the region. Kim Min-ji reports. Korea's highest paid people earn almost half of the nation's total income. According to the IMF,... the top ten percent of earners in the country held 45 percent of the nation's income as of 2013,... putting Korea at the top of the list among Asian countries. And the number has been moving steadily upward... from the 29 percent recorded in 1995. It's a significant jump, considering that other Asian countries saw their shares edge up between one and two percent on... -

Income Inequality
patreon.com/freedomtoons Income Inequality: This is kinda what it looks like when Americans complain about it Thanks to Pat Oberle for animating the lip syncing THANKS SO MUCH TO PATREON DONORS LESLEE FROST FRAN PODLASEK MUSIC: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=3qQQJ... Royalty Free Music - Dubstep - Sickdropz - FloidBeats #047 Beat for FotisEski
Jay Weber 4/7/16 Income gap caused by liberal unionista policies. Toss the peasants a $15 bone.
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 0:45
- Updated: 03 May 2016
- views: 3
- published: 03 May 2016
- views: 3
Congresswoman Barbara Lee: Economic mobility and racial justice are intertwined
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 6:36
- Updated: 01 May 2016
- views: 0
- published: 01 May 2016
- views: 0
Robert Reich interview on Charlie Rose (1991)
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 11:52
- Updated: 30 Apr 2016
- views: 6
- published: 30 Apr 2016
- views: 6
How to Avoid the Retirement Income Gap
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 3:24
- Updated: 25 Apr 2016
- views: 0
- published: 25 Apr 2016
- views: 0
Ben Shapiro: Obama goes to mosque, Hillary talks income inequality and the vaunted mailbag
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 60:12
- Updated: 24 Apr 2016
- views: 17
- published: 24 Apr 2016
- views: 17
The Income Gap
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 11:27
- Updated: 23 Apr 2016
- views: 20
- published: 23 Apr 2016
- views: 20
Bernie Sanders slams income inequality in Vatican speech
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 2:15
- Updated: 19 Apr 2016
- views: 8
- published: 19 Apr 2016
- views: 8
Determine and Close Your Income Gap
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 12:05
- Updated: 14 Apr 2016
- views: 24
- published: 14 Apr 2016
- views: 24
Hillary Clinton talks terrorism, economic growth, education and income inequality
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 128:39
- Updated: 11 Apr 2016
- views: 0
- published: 11 Apr 2016
- views: 0
Narrowing the Income Inequality Gap
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 114:46
- Updated: 10 Apr 2016
- views: 10
- published: 10 Apr 2016
- views: 10
MQ Video: Gender Income Inequality
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 5:16
- Updated: 09 Apr 2016
- views: 12
Income Inequality and the Future of the American Dream: Differing Perspectives
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 65:45
- Updated: 07 Apr 2016
- views: 0
- published: 07 Apr 2016
- views: 0
The income inequality gap in soccer
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 5:01
- Updated: 05 Apr 2016
- views: 180
- published: 05 Apr 2016
- views: 180
Barton College economist John Bethune discusses income inequality
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 1:25
- Updated: 01 Apr 2016
- views: 26
- published: 01 Apr 2016
- views: 26
State of the Union 2016: Income Inequality
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 12:43
- Updated: 31 Mar 2016
- views: 43
- published: 31 Mar 2016
- views: 43
Joel Klein: Education key to ending income inequality
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 2:19
- Updated: 30 Mar 2016
- views: 2
- published: 30 Mar 2016
- views: 2
Why income inequality will dampen economic growth
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 4:26
- Updated: 30 Mar 2016
- views: 10
- published: 30 Mar 2016
- views: 10
How to Decrease the Income Inequality Gap
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 2:06
- Updated: 30 Mar 2016
- views: 10
- published: 30 Mar 2016
- views: 10
Full Tim Income Trading Gaps - $1,000 Profit In Less Than 20 Minutes
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 4:25
- Updated: 25 Mar 2016
- views: 206
- published: 25 Mar 2016
- views: 206
19. Minimum Wage, Gender Wage Gap, Income Inequality, and More with Dr. Walter Block
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 50:14
- Updated: 23 Mar 2016
- views: 0
- published: 23 Mar 2016
- views: 0
Bernie Sanders - income inequality
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 0:56
- Updated: 22 Mar 2016
- views: 12
Income share held by top 10% in Korea hits 45%
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 1:46
- Updated: 16 Mar 2016
- views: 44
- published: 16 Mar 2016
- views: 44
Income Inequality
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 2:47
- Updated: 10 Mar 2016
- views: 901
- published: 10 Mar 2016
- views: 901
-

Obama's Powerful Speech On Income Inequality
The gap between America's rich and everyone else has grown to unprecedented levels at a time when upward social mobility has hit record lows. President Barack Obama's speech on the unraveling of the social compact addresses the frustration Americans have with Washington D.C.'s inability to act on important matters like this and explains how his administration plans to restore equality and mobility for future generations. The Daily Conversation https://www.youtube.com/TheDailyConversation Facebook http://www.facebook.com/thedailyconversation Google+ https://plus.google.com/100134925804523235350/posts Twitter http://www.twitter.com/thedailyconvo -

Income Inequality Impairs the American Dream of Upward Mobility
Income inequality has been on the rise for decades. In the last 30 years, the wages of the top 1% have grown by 154%, while the bottom 90% has seen growth of only 17%. As the rungs of the economic ladder move further and further apart, conventional wisdom says that it will become much more difficult to climb them. Opportunities for upward mobility-the American dream-will disappear as the deck becomes stacked against the middle class and the poor. But others see inequality as a positive, a sign of a dynamic and robust economy that, in the end, helps everyone. And contrary to public opinion, mobility has remained stable over the past few decades. If the American dream is dying, is it the result of income inequality? Or is disparity in income a red herring where more complex issues are at pla... -

Joseph Stiglitz: Income Inequality and American Democracy
Nobel Prize-winning economist Joseph Stiglitz is known for his incisive, often controversial, diagnoses of global economic problems. His latest work, The Great Divide, argues that inequality is the greatest threat facing America today, undermining all systems in our country, including our democracy itself. In this talk given to a sold-out crowd, Stiglitz explained how, by casting aside failed policies and principles, we can build a healthier, fairer economy–and strengthen our democracy. Thanks to Seattle Town Hall & University Bookstore -

Income Inequality: The Global Haves And Have-Nots In The 21st Century
Although inequality has recently become one of the current topics "de jour" in the economics profession, Branko Milanovic is certainly not a newbie to this area. Indeed, the World Bank economist and development specialist (currently a visiting presidential professor at CUNY's Graduate Center and a senior scholar at the Luxembourg Income Study Center), has been studying this particular field of economics since his days as a graduate student. One of his unique contributions has been to link this scholarship to prevailing financial conditions, providing substantial empirical evidence which illustrates how financial bubbles and the increasing financialisation of the global economy has played a key role in terms contributing to greater inequality. What kind of inequality are we talking about... -

Inequality for All: Robert Reich Warns Record Income Gap Is Undermining Our Democracy. (2 of 3)
http://www.democracynow.org - Five years ago this weekend, the Wall Street giant Lehman Brothers collapsed triggering the worst financial crisis since the Great Depression. Today, the divide between the 1 percent and the 99 percent is as great as ever. According to one recent study, the top 1 percent has captured about 95 percent of the income gains since the recession ended. "Since the recovery, almost all of the gains have gone to the very, very top. People who are in the top 1 percent are doing even better than they did before the Great Recession, better than they have done since 1928," says former Labor Secretary Robert Reich. "Most Americans are on a downward escalator. Median wage in the United States, adjusted for inflation, keeps on dropping." Watch Part 1 of this interview: http... -

Bridging the Income Gap - Living Income Guaranteed
What are the consequences to Income Inequality, how do corporations affect this problem and where do we the people stand in relation to this problem: how can we solve it? Discussing Living Income Guaranteed as an immediate solution to better the economy What is the Living Income Guaranteed? http://wp.me/P42l71-65 Living Income Guaranteed by Equal Life Foundation: http://livingincome.me/ Wordpress: http://livingincomeguaranteed.wordpress.com/ Facebook https://www.facebook.com/BasicIncomeGuaranteedByEqualLifeFoundation YouTube: http://www.youtube.com/biguaranteed Google+ https://plus.google.com/u/3/b/106743715342474012987/106743715342474012987/posts Twitter http://twitter.com/livingincome Watch our Live Google Hangouts: http://www.youtube.com/BIGuaranteed Equal Life Foundation:... -

Closing the Income Inequality Gap
A widening gap between haves and have-nots is shrinking the American middle class and making it tougher than ever to move up the economic ladder. The U.S. problem reflects a worldwide concentration of wealth. The top 1 percent control 48 percent of the world's assets, up from 44 percent in 2009. Disparate voices ranging from Pope Francis to IMF Director Christine Lagarde warn that the gulf between rich and poor diminishes hope and raises serious political and economic issues. Some companies are listening. Late last year, Walmart Stores pledged to end minimum-wage pay by raising the hourly rate of 500,000 workers. Other companies followed with similar increases for their lowest-paid workers. Will their announcements spur broader efforts to reduce income equality? What else can be done to li... -

Who Controls the U.S. Government and the Gap Between Rich and Poor: Noam Chomsky (1995)
Distribution of income in the United States has been the subject of study by scholars and institutions. Data from a number of sources indicate that income inequality has grown significantly since the early 1970s, after several decades of stability. While inequality has risen among most developed countries, and especially English-speaking ones, it is highest in the United States. Studies indicate the source of the widening gap (sometimes called the Great Divergence) has not been gender inequality, which has declined in the US over the last several decades, nor inequality between black and white Americans, which has stagnated during that time, nor has the gap between the poor and middle class been the major cause—though it has grown. Most of the growth has been between the middle class and ... -

Talking Point: Addressing Income Inequality - 28Aug2013
In Singapore, the top 10% earn 30% of all household income. The bottom 10%? 1.6%. Income inequality has been a fact of life since the 1980s, so what's behind the government's latest strategic shift to right the imbalance? Does it need to? -

Narrowing The Gap: How Cities Can Fight Income Inequality
Alan Berube, Senior Fellow and Deputy Director, Metropolitan Policy Program, Brookings Institution Bill Peduto, Mayor, Pittsburgh Blair Taylor, Chief Community Officer, Starbucks Moderator: Richard Florida, Co-Founder and Editor at Large, CityLab.com; Senior Editor, The Atlantic Presented by the Aspen Institute, The Atlantic, and Bloomberg Philanthropies, the second annual CityLab: Global Solutions to Urban Challenges will bring together 300 global city leaders — mayors, plus urban theorists, city planners, scholars, architects, and artists — for a series of conversations about urban ideas that are shaping the world's metro centers. The summit will further develop conversations started at last year’s CityLab on economic development; the environment and sustainability; cultural investment;... -

U.S. Income Gap reaches new record, Tea Party rally turns violent, Making the case for Obama
As unemployment continues to rise in the U.S., the average income of the wealthiest Americans increased five-fold from 2009 to over $500 million. Thom talks to a Pulitzer prize-winning journalist who says the government is to blame for the ridiculous income gap. Also, a Kentucky woman went to a rally for Rand Paul with a message, and left with a concussion after she was knocked to the ground and endured stomping on her head by Rand Paul campaign coordinator, Tim Profitt. And a new MoveOn.org ad paints a bleak picture of a future run by Republicans. Thom discusses if so-called "civil discourse" in the Tea Party is really all that civil. Plus, it may be too early to give up hope on President Obama. Thom talks to a Contributing Editor at Rolling Stone Magazine who makes the case for Obama. Fi... -

Income Inequality
How do we adequately remunerate highly skilled executives on a continent with massive wage gap and poverty? -

The Rising Income Gap and Inequality in Seattle
Conversations on Social Issues: he Rising Income Gap and Inequality in Seattle Speaker: SCC Faculty Jay McLean-Riggs -

Alan Schwartz and Tom Glocer: Growing Income Gap
“There’s this whole thing about the difference between aspirations and expectations. The aspirations of lower-income people and upper-income people are roughly the same, but you start to see this big widening of expectations as to, “that’s what I would love to be, but what are my shots?” Tom Glocer asks Alan Schwartz his thoughts on the causes and implications of the widening income gap in America, and how it is having profound effects on the social and economic landscape of the United States. -

Inequality for All
Bill Moyers talks with Economic analyst Robert Reich about the new film Inequality for All. Opening in theaters across the country next week, the film aims to be a game-changer in our national discussion of income inequality. -

Just the Facts: New Trends in Income Inequality
Contrary to popular belief, recent research suggests that executive pay isn't to blame for the wage divide. Rather, the gap between between high-paying firms and low-paying firms over the past 3 decades has been widening. The inequality resulting from between firm differences may have harmful effects on a range of social outcomes we value, from education to health to economic growth to democracy and more. -

Panel Discussion: Income Inequality in the 21st Century
In a panel discussion moderated by Dean Rich Lyons, Laura Tyson, professor of business administration and economics at the Haas School of Business, and Emmanuel Saez, economics professor and head of the Center for Equitable Growth at UC Berkeley, focus on income inequality, drawing from ideas central to Thomas Piketty's bestselling book Capital in the Twenty-First Century. This talk was part of the Dean's Speaker Series. (October 14, 2014) -

Florida Forward: Closing the Income Gap
Florida Forward panel discussion on “Closing the Income Gap.” The panelists are UCF economist Sean Snaith, Valencia economics Professor Jack Chambless, Organize Now Director Stephanie Porta, lawyer and commentator Tico Perez and former Orlando Police Chief Val Demings. -

Income Inequality: Non-Solutions to a Non-Problem
Tom discusses overlooked problems of income "redistribution." Subscribe to the Tom Woods Show: https://itunes.apple.com/us/podcast/the-tom-woods-show/id716825890?mt=2 http://www.TomWoods.com http://www.SupportingListeners.com http://www.RonPaulHomeschool.com http://www.TomWoodsHomeschool.com http://www.LibertyClassroom.com -

Encore Careers: Can Second Careers Bridge the Retirement Income Gap?
Encore Careers: Can Second Careers Bridge the Retirement Income Gap? As Washington grapples with enormous deficit challenges, the nation's 78 million Baby Boomers are approaching retirement age. This demographic wave colors much of the discussion about the nation's long-term finances. Top-down directives, like raising the Social Security eligibility age, get most of the attention. But could carrots work better than sticks? What if millions of Baby Boomers elected not to retire, and instead chose to change jobs, start small businesses, or find other ways to serve their communities? Encore careers that combine continued income and social purpose already are a real choice for millions of Americans. As that number grows in coming decades, this change in behavior touches an array of federal ...
Obama's Powerful Speech On Income Inequality
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 48:17
- Updated: 05 Dec 2013
- views: 55100
- published: 05 Dec 2013
- views: 55100
Income Inequality Impairs the American Dream of Upward Mobility
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 103:56
- Updated: 23 Oct 2014
- views: 38390
- published: 23 Oct 2014
- views: 38390
Joseph Stiglitz: Income Inequality and American Democracy
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 58:01
- Updated: 14 May 2015
- views: 2790
- published: 14 May 2015
- views: 2790
Income Inequality: The Global Haves And Have-Nots In The 21st Century
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 20:26
- Updated: 16 Nov 2015
- views: 2333
- published: 16 Nov 2015
- views: 2333
Inequality for All: Robert Reich Warns Record Income Gap Is Undermining Our Democracy. (2 of 3)
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 22:57
- Updated: 13 Sep 2013
- views: 13815
- published: 13 Sep 2013
- views: 13815
Bridging the Income Gap - Living Income Guaranteed
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 26:30
- Updated: 26 Jan 2014
- views: 181
- published: 26 Jan 2014
- views: 181
Closing the Income Inequality Gap
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 60:26
- Updated: 28 Apr 2015
- views: 579
- published: 28 Apr 2015
- views: 579
Who Controls the U.S. Government and the Gap Between Rich and Poor: Noam Chomsky (1995)
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 68:17
- Updated: 15 Aug 2013
- views: 34327
- published: 15 Aug 2013
- views: 34327
Talking Point: Addressing Income Inequality - 28Aug2013
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 50:55
- Updated: 28 Aug 2013
- views: 1172
- published: 28 Aug 2013
- views: 1172
Narrowing The Gap: How Cities Can Fight Income Inequality
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 28:01
- Updated: 20 Oct 2014
- views: 279
- published: 20 Oct 2014
- views: 279
U.S. Income Gap reaches new record, Tea Party rally turns violent, Making the case for Obama
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 56:57
- Updated: 27 Oct 2010
- views: 1519
- published: 27 Oct 2010
- views: 1519
Income Inequality
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 25:50
- Updated: 29 Jul 2014
- views: 41
- published: 29 Jul 2014
- views: 41
The Rising Income Gap and Inequality in Seattle
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 56:38
- Updated: 23 Feb 2016
- views: 29
- published: 23 Feb 2016
- views: 29
Alan Schwartz and Tom Glocer: Growing Income Gap
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 20:45
- Updated: 05 Aug 2015
- views: 30
- published: 05 Aug 2015
- views: 30
Inequality for All
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 56:47
- Updated: 20 Sep 2013
- views: 197644
- published: 20 Sep 2013
- views: 197644
Just the Facts: New Trends in Income Inequality
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 92:49
- Updated: 08 Mar 2016
- views: 40
- published: 08 Mar 2016
- views: 40
Panel Discussion: Income Inequality in the 21st Century
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 65:19
- Updated: 21 Oct 2014
- views: 2902
- published: 21 Oct 2014
- views: 2902
Florida Forward: Closing the Income Gap
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 89:51
- Updated: 16 Sep 2014
- views: 403
- published: 16 Sep 2014
- views: 403
Income Inequality: Non-Solutions to a Non-Problem
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 29:45
- Updated: 04 Dec 2014
- views: 3654
- published: 04 Dec 2014
- views: 3654
Encore Careers: Can Second Careers Bridge the Retirement Income Gap?
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 97:30
- Updated: 30 Mar 2012
- views: 626
- published: 30 Mar 2012
- views: 626
- Playlist
- Chat
- Playlist
- Chat

Wealth Inequality in America
- Report rights infringement
- published: 20 Nov 2012
- views: 18069439

Last Week Tonight with John Oliver: Wealth Gap (HBO)
- Report rights infringement
- published: 14 Jul 2014
- views: 9560201

Income and Wealth Inequality: Crash Course Economics
- Report rights infringement
- published: 06 Dec 2015
- views: 225532

Bernie Brief: Income Inequality | Ep. 1
- Report rights infringement
- published: 14 Sep 2015
- views: 223391

Global Wealth Inequality - What you never knew you never knew
- Report rights infringement
- published: 03 Apr 2013
- views: 713574

A TED Talk on Income Inequality by Nick Hanauer
- Report rights infringement
- published: 17 May 2012
- views: 209788

Thomas Sowell: The Income Gap Myth
- Report rights infringement
- published: 07 Nov 2012
- views: 11298

This Is The Income Inequality Video CEOs Don’t Want Americans To See
- Report rights infringement
- published: 03 Oct 2014
- views: 125928

WHAT DOES INCOME INEQUALITY MEAN TO AMERICANS? - BBC NEWS
- Report rights infringement
- published: 24 Jan 2014
- views: 30785

Inequality for All: Robert Reich Warns Record Income Gap Is Undermining Our Democracy. (1 of 3)
- Report rights infringement
- published: 13 Sep 2013
- views: 23023

Managing Interest Rate Risk - Income Gap Analysis
- Report rights infringement
- published: 16 Jul 2014
- views: 2123

Obama: Income inequality is defining challenge for the U.S.
- Report rights infringement
- published: 04 Dec 2013
- views: 14944

'Inequality for All': Documentary tracks American income gap
- Report rights infringement
- published: 20 Sep 2013
- views: 6195

Last Week Tonight with John Oliver: Wage Gap
- Report rights infringement
- published: 25 Aug 2014
- views: 2315315
- Playlist
- Chat

Jay Weber 4/7/16 Income gap caused by liberal unionista policies. Toss the peasants a $15 bone.
- Report rights infringement
- published: 03 May 2016
- views: 3

Congresswoman Barbara Lee: Economic mobility and racial justice are intertwined
- Report rights infringement
- published: 01 May 2016
- views: 0

Robert Reich interview on Charlie Rose (1991)
- Report rights infringement
- published: 30 Apr 2016
- views: 6

How to Avoid the Retirement Income Gap
- Report rights infringement
- published: 25 Apr 2016
- views: 0

Ben Shapiro: Obama goes to mosque, Hillary talks income inequality and the vaunted mailbag
- Report rights infringement
- published: 24 Apr 2016
- views: 17

The Income Gap
- Report rights infringement
- published: 23 Apr 2016
- views: 20

Bernie Sanders slams income inequality in Vatican speech
- Report rights infringement
- published: 19 Apr 2016
- views: 8

Determine and Close Your Income Gap
- Report rights infringement
- published: 14 Apr 2016
- views: 24

Hillary Clinton talks terrorism, economic growth, education and income inequality
- Report rights infringement
- published: 11 Apr 2016
- views: 0

Narrowing the Income Inequality Gap
- Report rights infringement
- published: 10 Apr 2016
- views: 10

MQ Video: Gender Income Inequality
- Report rights infringement
- published: 09 Apr 2016
- views: 12

Income Inequality and the Future of the American Dream: Differing Perspectives
- Report rights infringement
- published: 07 Apr 2016
- views: 0

The income inequality gap in soccer
- Report rights infringement
- published: 05 Apr 2016
- views: 180

Barton College economist John Bethune discusses income inequality
- Report rights infringement
- published: 01 Apr 2016
- views: 26
- Playlist
- Chat

Obama's Powerful Speech On Income Inequality
- Report rights infringement
- published: 05 Dec 2013
- views: 55100

Income Inequality Impairs the American Dream of Upward Mobility
- Report rights infringement
- published: 23 Oct 2014
- views: 38390

Joseph Stiglitz: Income Inequality and American Democracy
- Report rights infringement
- published: 14 May 2015
- views: 2790

Income Inequality: The Global Haves And Have-Nots In The 21st Century
- Report rights infringement
- published: 16 Nov 2015
- views: 2333

Inequality for All: Robert Reich Warns Record Income Gap Is Undermining Our Democracy. (2 of 3)
- Report rights infringement
- published: 13 Sep 2013
- views: 13815

Bridging the Income Gap - Living Income Guaranteed
- Report rights infringement
- published: 26 Jan 2014
- views: 181

Closing the Income Inequality Gap
- Report rights infringement
- published: 28 Apr 2015
- views: 579

Who Controls the U.S. Government and the Gap Between Rich and Poor: Noam Chomsky (1995)
- Report rights infringement
- published: 15 Aug 2013
- views: 34327

Talking Point: Addressing Income Inequality - 28Aug2013
- Report rights infringement
- published: 28 Aug 2013
- views: 1172

Narrowing The Gap: How Cities Can Fight Income Inequality
- Report rights infringement
- published: 20 Oct 2014
- views: 279

U.S. Income Gap reaches new record, Tea Party rally turns violent, Making the case for Obama
- Report rights infringement
- published: 27 Oct 2010
- views: 1519

Income Inequality
- Report rights infringement
- published: 29 Jul 2014
- views: 41

The Rising Income Gap and Inequality in Seattle
- Report rights infringement
- published: 23 Feb 2016
- views: 29

Alan Schwartz and Tom Glocer: Growing Income Gap
- Report rights infringement
- published: 05 Aug 2015
- views: 30
[VIDEO]: Angry Woman Confronts Man Using Food Stamps At Walmart
Edit WorldNews.com 03 May 2016Sanders And RI Live-Up To Perpetual Revolution, Will Other States Follow?
Edit WorldNews.com 03 May 2016Pakistan will get F-16s from elsewhere if funding not arranged, Aziz cautions US
Edit Dawn 03 May 2016Edward Snowden: ‘Governments can reduce our dignity to that of tagged animals’
Edit The Guardian 03 May 2016Things to know: the benefits of students taking a gap year
Edit Philadelphia Daily News 03 May 2016The Rising Longevity Gap Between Rich and Poor Americans
Edit Real Clear Politics 03 May 2016A social take on the economics of income inequality answers questions
Edit Deseret News 03 May 2016Rich-poor life expectancy gap rising again, research shows
Edit Belfast Telegraph 03 May 2016Lifespan gap 'widening between rich and poor'
Edit BBC News 03 May 2016How To Have A Successful Gap Year — Tips For Malia Obama And Other High School Grads
Edit National Public Radio 03 May 2016What's the real gender pay gap?
Edit Deseret News 03 May 2016Smart College Financial Choices
Edit ABC News 03 May 2016Taking a “gap year” before college is a British tradition that’s becoming a big trend in the US
Edit Quartz 03 May 2016The Economy Is Great. The Economy Is Terrible.
Edit The Atlantic 03 May 2016In Wealthier School Districts, Students Are Farther Apart
Edit The Atlantic 03 May 2016John Bel Edwards says no to another Louisiana sales tax hike
Edit The Times Picayune 03 May 2016- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- Next page »







