









- Loading...

-
Opening of the G20 Summit in St Petersburg (recorded live feed)
Opening of the G20 Summit in St Petersburg (recorded live feed) -
외신들도 감탄한 G20 대한민국 소개영상
외신들도 감탄한 G20 대한민국 소개영상외신들도 감탄한 G20 대한민국 소개영상
외신들도 감탄한 G20 대한민국 소개영상. -
INDONESIA THE LARGEST ECONOMY IN SOUTHEAST ASIA - G20 MEMBER
INDONESIA THE LARGEST ECONOMY IN SOUTHEAST ASIA - G20 MEMBERINDONESIA THE LARGEST ECONOMY IN SOUTHEAST ASIA - G20 MEMBER
INDONESIA THE LARGEST ECONOMY IN SOUTHEAST ASIA - G20 MEMBER With a population of over 242.3 million, Indonesia is the fourth most populous country in the wo... -
G20 delegates arrive at Buckingham Palace pt1
G20 delegates arrive at Buckingham Palace pt1G20 delegates arrive at Buckingham Palace pt1
G20 delegates arriving at Buckingham Palace for the reception with the Queen. -
Anarchist black bloc clash with police at G20 Pittsburgh
Anarchist black bloc clash with police at G20 PittsburghAnarchist black bloc clash with police at G20 Pittsburgh
Police attack unpermitted anarchist march with LRAD, tear gas, and other less lethal weapons. Anarchists then attack police in self defense. September 24th G... -
Recepción de Líderes del G20 a su arribo al Centro de Convenciones G20 (evento completo)
Recepción de Líderes del G20 a su arribo al Centro de Convenciones G20 (evento completo)Recepción de Líderes del G20 a su arribo al Centro de Convenciones G20 (evento completo)
Los Cabos, Baja California Sur, 18 de junio del 2012. El Presidente Felipe Calderón durante la Recepción de Líderes del G20 a su arribo al Centro de Convenci... -
Earthquake & the G20
Earthquake & the G20Earthquake & the G20
Subscribe! New videos every Saturday: http://bit.ly/Subscribenow Facebook (Like): http://fb.com/MatthewSantoroOfficial Facebook (Follow): http://fb.com/Matth... -
Zombies, G20 and International Relations
Zombies, G20 and International RelationsZombies, G20 and International Relations
What would happen to international politics if the dead rose from the grave and started to eat the living? On October 26, 2011 at CIGI, Daniel Drezner answer... -
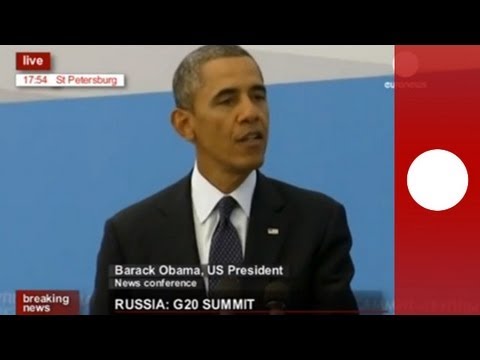
Obama's full speech at G20 closing press conference (recorded live feed)
Obama's full speech at G20 closing press conference (recorded live feed)Obama's full speech at G20 closing press conference (recorded live feed)
US President Barack Obama speaks at the closing news conference at G20 Summit in St Petersburg, Russia. euronews: the most watched news channel in Europe Sub... -
140907 G-Twenty(G20) - Talk @Wonderful Korea
140907 G-Twenty(G20) - Talk @Wonderful Korea140907 G-Twenty(G20) - Talk @Wonderful Korea
Playlist : http://www.youtube.com/playlist?list=PLUmduNl7KEvASh8k71-0Rm2IPE612UNQZ http://www.facebook.com/G20club Wonderful Korea at Paradise Park Thailand 07/09/2014 -
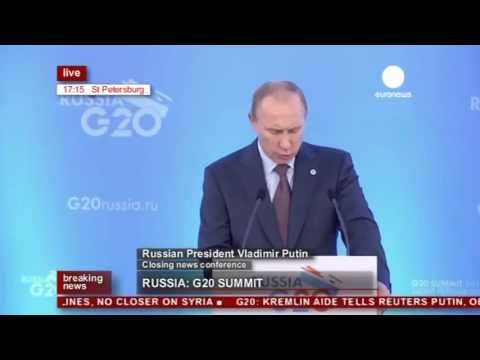
Putin's speech at G20 closing press conference (recorded live feed)
Putin's speech at G20 closing press conference (recorded live feed)Putin's speech at G20 closing press conference (recorded live feed)
Russian President Vladimir Putin speaks at the closing news conference at G20 Summit in St Petersburg, Russia. euronews: the most watched news channel in Eur... -
Into The Fire - Full Film
Into The Fire - Full FilmInto The Fire - Full Film
Press For Truth Presents Into The Fire World leaders and activists from around the world gathered for the G20 Summit. With over 19000 police officers and se... -
140907 G-Twenty(G20) - ของฟรีไม่มีในโลก + Magic Ho
140907 G-Twenty(G20) - ของฟรีไม่มีในโลก + Magic Ho140907 G-Twenty(G20) - ของฟรีไม่มีในโลก + Magic Ho
Playlist : http://www.youtube.com/playlist?list=PLUmduNl7KEvASh8k71-0Rm2IPE612UNQZ http://www.facebook.com/G20club Wonderful Korea at Paradise Park Thailand 07/09/2014 -
140907 G-Twenty(G20) - ไม่พูดก็ได้ยิน @Wonderful K
140907 G-Twenty(G20) - ไม่พูดก็ได้ยิน @Wonderful K140907 G-Twenty(G20) - ไม่พูดก็ได้ยิน @Wonderful K
Playlist : http://www.youtube.com/playlist?list=PLUmduNl7KEvASh8k71-0Rm2IPE612UNQZ http://www.facebook.com/G20club Wonderful Korea at Paradise Park Thailand 07/09/2014
- African Union
- Agus Martowardojo
- Agustín Carstens
- Alexandre Tombini
- American Century
- Angela Merkel
- Anton Siluanov
- ANZUS
- Arab League
- Argentina
- ASEAN
- Asian Century
- Australia
- Austria
- Barack Obama
- Belgium
- Ben Bernanke
- Brazil
- BRICS
- Brookings Institute
- Canada
- Cannes
- Central bank
- China
- Chinese Century
- Choongsoo Kim
- Christian Noyer
- Clean energy
- Congress of Vienna
- Crony capitalism
- Darmin Nasution
- David Cameron
- Der Spiegel
- Dilma Rousseff
- Duvvuri Subbarao
- E7 (countries)
- East Asia
- Economic power
- Economic security
- Energy superpower
- Erdem Başçı
- Ethiopia
- EU
- Eurasia
- Europe
- European Council
- European Union
- Felipe Calderón
- Finance minister
- Food power
- Foreign Policy
- Fox News
- France
- Frances Stewart
- François Hollande
- G-20 major economies
- G20 (disambiguation)
- G4 nations
- G7
- G8
- G8+5
- GDP
- Geopolitics
- George Osborne
- George W. Bush
- Germany
- Gill Marcus
- Glenn Stevens
- Gordon Brown
- Great power
- Gross world product
- Group of 22
- Group of 77
- Guardian.co.uk
- Guido Mantega
- Hard power
- Head of government
- Head of state
- Head of State
- Herman Van Rompuy
- Hernán Lorenzino
- Historical powers
- Hu Jintao
- Hyperpower
- IBSA Dialogue Forum
- Ignazio Visco
- India
- Indonesia
- Information activist
- International trade
- Interview
- Iran
- Italy
- Jacob Zuma
- Japan
- Jens Weidmann
- Jim Flaherty
- Jonas Gahr Støre
- José Manuel Barroso
- Julia Gillard
- Jun Azumi
- King of Saudi Arabia
- Korea Times
- Late-2000s recession
- Lee Myung-bak
- List of G-20 summits
- London
- Malawi
- Manmohan Singh
- Mario Draghi
- Mario Monti
- Mark Carney
- Masaaki Shirakawa
- Mehmet Şimşek
- Mercosur
- Mexico
- Middle power
- MIKT
- Muhammed Al-Jasser
- National power
- National Power Index
- Nationalists
- NATO
- NEPAD
- Netherlands
- Next Eleven
- Nicolas Sarkozy
- Non-Aligned Movement
- North America
- Norway
- Norway.org
- Oceania
- Olli Rehn
- Oxford University
- Pacific Century
- Paris
- Park Jae-wan
- Paul Martin
- Pax Britannica
- Pierre Moscovici
- Pittsburgh
- Poland
- Political power
- Power (philosophy)
- Power politics
- Power projection
- Pranab Mukherjee
- Pravin Gordhan
- President of Brazil
- President of France
- President of Mexico
- President of Russia
- Realpolitik
- Recep Tayyip Erdoğan
- Regional power
- Reuters
- Routledge
- Russia
- Saint Petersburg
- Saudi Arabia
- Second Superpower
- Seoul
- Singapore
- Small powers
- Smart power
- Soft power
- South Africa
- South America
- South Asia
- South Korea
- Southeast Asia
- Spain
- Sphere of influence
- Stephen Harper
- Superpower
- Superpower collapse
- Sweden
- Switzerland
- Taiwan
- Template G20
- Template talk G20
- Thailand
- Timothy Geithner
- Toronto
- Trevor A. Manuel
- Troika (triumvirate)
- Turkey
- United Kingdom
- United Nations
- United States
- US dollar
- Vietnam
- Vladimir Putin
- Washington, D.C.
- Wayne Swan
- Western Asia
- Wolfgang Schäuble
- World Bank
- World population
- Xie Xuren
- Yoshihiko Noda
- Zhou Xiaochuan
- African Union
- Arab League
- Argentina
- Australia
- Austria
- Belgium
- Brazil
- Canada
- Cannes
- China
- Congress of Vienna
- Ethiopia
- France
- Germany
- India
- Indonesia
- Iran
- Italy
- Japan
- London
- Malawi
- Mercosur
- Mexico
- NATO
- Netherlands
- Norway
- Paris
- Pittsburgh
- Poland
- Russia
- Saint Petersburg
- Saudi Arabia
- Seoul
- Singapore
- South Africa
- South Korea
- Spain
- Sweden
- Switzerland
- Taiwan
- Thailand
- Toronto
- Turkey
- United Kingdom
- United States
- Vietnam
- Agus Martowardojo
- Agustín Carstens
- Alexandre Tombini
- Angela Merkel
- Anton Siluanov
- Austria
- Barack Obama
- Ben Bernanke
- Christian Noyer
- Darmin Nasution
- David Cameron
- Dilma Rousseff
- Duvvuri Subbarao
- Erdem Başçı
- Felipe Calderón
- Frances Stewart
- François Hollande
- George Osborne
- Gill Marcus
- Glenn Stevens
- Gordon Brown
- Guido Mantega
- Herman Van Rompuy
- Hernán Lorenzino
- Hu Jintao
- Ignazio Visco
- Jacob Zuma
- Jens Weidmann
- Jim Flaherty
- Jonas Gahr Støre
- José Manuel Barroso
- Julia Gillard
- Jun Azumi
- Manmohan Singh
- Mario Draghi
- Mario Monti
- Mark Carney
- Masaaki Shirakawa
- Mehmet Şimşek
- Nicolas Sarkozy
- Olli Rehn
- Paul Martin
- Pierre Moscovici
- Pranab Mukherjee
- Pravin Gordhan
- Recep Tayyip Erdoğan
- Stephen Harper
- Timothy Geithner
- Vladimir Putin
- Wayne Swan
- Wolfgang Schäuble
- Xie Xuren
- Yoshihiko Noda
- Zhou Xiaochuan
-
Opening of the G20 Summit in St Petersburg (recorded live feed)
Opening of the G20 Summit in St Petersburg (recorded live feed)Opening of the G20 Summit in St Petersburg (recorded live feed)
Recorded live version of Vladimir Putin's welcoming speech at the G20 opening session in St Petersburg. Russia is hosting the summit of the leaders of the Gr... -
외신들도 감탄한 G20 대한민국 소개영상
외신들도 감탄한 G20 대한민국 소개영상외신들도 감탄한 G20 대한민국 소개영상
외신들도 감탄한 G20 대한민국 소개영상. -
INDONESIA THE LARGEST ECONOMY IN SOUTHEAST ASIA - G20 MEMBER
INDONESIA THE LARGEST ECONOMY IN SOUTHEAST ASIA - G20 MEMBERINDONESIA THE LARGEST ECONOMY IN SOUTHEAST ASIA - G20 MEMBER
INDONESIA THE LARGEST ECONOMY IN SOUTHEAST ASIA - G20 MEMBER With a population of over 242.3 million, Indonesia is the fourth most populous country in the wo... -
G20 delegates arrive at Buckingham Palace pt1
G20 delegates arrive at Buckingham Palace pt1G20 delegates arrive at Buckingham Palace pt1
G20 delegates arriving at Buckingham Palace for the reception with the Queen. -
Anarchist black bloc clash with police at G20 Pittsburgh
Anarchist black bloc clash with police at G20 PittsburghAnarchist black bloc clash with police at G20 Pittsburgh
Police attack unpermitted anarchist march with LRAD, tear gas, and other less lethal weapons. Anarchists then attack police in self defense. September 24th G... -
Recepción de Líderes del G20 a su arribo al Centro de Convenciones G20 (evento completo)
Recepción de Líderes del G20 a su arribo al Centro de Convenciones G20 (evento completo)Recepción de Líderes del G20 a su arribo al Centro de Convenciones G20 (evento completo)
Los Cabos, Baja California Sur, 18 de junio del 2012. El Presidente Felipe Calderón durante la Recepción de Líderes del G20 a su arribo al Centro de Convenci... -
Earthquake & the G20
Earthquake & the G20Earthquake & the G20
Subscribe! New videos every Saturday: http://bit.ly/Subscribenow Facebook (Like): http://fb.com/MatthewSantoroOfficial Facebook (Follow): http://fb.com/Matth... -
Zombies, G20 and International Relations
Zombies, G20 and International RelationsZombies, G20 and International Relations
What would happen to international politics if the dead rose from the grave and started to eat the living? On October 26, 2011 at CIGI, Daniel Drezner answer... -
Obama's full speech at G20 closing press conference (recorded live feed)
Obama's full speech at G20 closing press conference (recorded live feed)Obama's full speech at G20 closing press conference (recorded live feed)
US President Barack Obama speaks at the closing news conference at G20 Summit in St Petersburg, Russia. euronews: the most watched news channel in Europe Sub... -
140907 G-Twenty(G20) - Talk @Wonderful Korea
140907 G-Twenty(G20) - Talk @Wonderful Korea140907 G-Twenty(G20) - Talk @Wonderful Korea
Playlist : http://www.youtube.com/playlist?list=PLUmduNl7KEvASh8k71-0Rm2IPE612UNQZ http://www.facebook.com/G20club Wonderful Korea at Paradise Park Thailand 07/09/2014 -
Putin's speech at G20 closing press conference (recorded live feed)
Putin's speech at G20 closing press conference (recorded live feed)Putin's speech at G20 closing press conference (recorded live feed)
Russian President Vladimir Putin speaks at the closing news conference at G20 Summit in St Petersburg, Russia. euronews: the most watched news channel in Eur... -
Into The Fire - Full Film
Into The Fire - Full FilmInto The Fire - Full Film
Press For Truth Presents Into The Fire World leaders and activists from around the world gathered for the G20 Summit. With over 19000 police officers and se... -
140907 G-Twenty(G20) - ของฟรีไม่มีในโลก + Magic Ho
140907 G-Twenty(G20) - ของฟรีไม่มีในโลก + Magic Ho140907 G-Twenty(G20) - ของฟรีไม่มีในโลก + Magic Ho
Playlist : http://www.youtube.com/playlist?list=PLUmduNl7KEvASh8k71-0Rm2IPE612UNQZ http://www.facebook.com/G20club Wonderful Korea at Paradise Park Thailand 07/09/2014 -
140907 G-Twenty(G20) - ไม่พูดก็ได้ยิน @Wonderful K
140907 G-Twenty(G20) - ไม่พูดก็ได้ยิน @Wonderful K140907 G-Twenty(G20) - ไม่พูดก็ได้ยิน @Wonderful K
Playlist : http://www.youtube.com/playlist?list=PLUmduNl7KEvASh8k71-0Rm2IPE612UNQZ http://www.facebook.com/G20club Wonderful Korea at Paradise Park Thailand 07/09/2014 -
140907 G-Twenty(G20) - Don't Worry + Mi Mi Mi @Won
140907 G-Twenty(G20) - Don't Worry + Mi Mi Mi @Won140907 G-Twenty(G20) - Don't Worry + Mi Mi Mi @Won
Playlist : http://www.youtube.com/playlist?list=PLUmduNl7KEvASh8k71-0Rm2IPE612UNQZ http://www.facebook.com/G20club Wonderful Korea at Paradise Park Thailand 07/09/2014 -
G20 YEA Summit, Moscow, Russia, June 2013
G20 YEA Summit, Moscow, Russia, June 2013G20 YEA Summit, Moscow, Russia, June 2013
Video from the G20 Young Entrepreneurs Summit, that took place in Moscow June 2013. -
Пресс-конференция Барака Обамы на саммите G20
Пресс-конференция Барака Обамы на саммите G20Пресс-конференция Барака Обамы на саммите G20
Пресс-конференция президента США Барака Обамы по итогам саммита стран-членов «Большой двадцатки». Подписывайтесь на RT Russian - http://www.youtube.com/subscription_center?add_user=rtrussian RT на русском - http://russian.rt.com/ Vkontakte - http://vk.com/rt_russian Facebook - http://www.facebook.com/RTRussian Twitter - http://twitter.com/RT_russian Livejournal - http://rt-russian.livejournal.com/ -
US and China energy and climate policy and the G20
US and China energy and climate policy and the G20US and China energy and climate policy and the G20
Climate and energy policy is once more near the top of the US government's policy agenda, and occupies a prominent position in China's development planning a... -
David Morgan: $100 Silver, Dollar Collapse, G20 Warning, Gold and Silver Will Be Global Phenomenon
David Morgan: $100 Silver, Dollar Collapse, G20 Warning, Gold and Silver Will Be Global PhenomenonDavid Morgan: $100 Silver, Dollar Collapse, G20 Warning, Gold and Silver Will Be Global Phenomenon
http://usawatchdog.com/dollar-value-could-suffer-instant-change-david-morgan/ - David Morgan from Silver-Investor.com says, "The rush into gold is basically ... -
The G20: Prospects and Challenges for Global Governance
The G20: Prospects and Challenges for Global GovernanceThe G20: Prospects and Challenges for Global Governance
Experts discuss current issues in global governance, including how international institutions like the G20 can work together to tackle problems. -
140906 G-Twenty(G20) - Mi Mi Mi @OISHI Thailand Co
140906 G-Twenty(G20) - Mi Mi Mi @OISHI Thailand Co140906 G-Twenty(G20) - Mi Mi Mi @OISHI Thailand Co
Playlist : http://www.youtube.com/playlist?list=PLUmduNl7KEvB-yjDl22tgKRJjE9wiQDK2 http://www.facebook.com/G20club OISHI Thailand Cover Dance 2014 (Final Round) Thailand 06/09/2014 -
140906 G-Twenty(G20) - ของฟรีไม่มีในโลก (Ain't Not
140906 G-Twenty(G20) - ของฟรีไม่มีในโลก (Ain't Not140906 G-Twenty(G20) - ของฟรีไม่มีในโลก (Ain't Not
Playlist : http://www.youtube.com/playlist?list=PLUmduNl7KEvB-yjDl22tgKRJjE9wiQDK2 http://www.facebook.com/G20club OISHI Thailand Cover Dance 2014 (Final Round) Thailand 06/09/2014 -
140906 G-Twenty(G20) - ไม่พูดก็ได้ยิน (Unspoken Wo
140906 G-Twenty(G20) - ไม่พูดก็ได้ยิน (Unspoken Wo140906 G-Twenty(G20) - ไม่พูดก็ได้ยิน (Unspoken Wo
Playlist : http://www.youtube.com/playlist?list=PLUmduNl7KEvB-yjDl22tgKRJjE9wiQDK2 http://www.facebook.com/G20club OISHI Thailand Cover Dance 2014 (Final Round) Thailand 06/09/2014

- Duration: 17:20
- Updated: 31 Aug 2014
- published: 05 Sep 2013
- views: 25979
- author: euronews (in English)

- Duration: 10:59
- Updated: 04 Sep 2014

- Duration: 3:23
- Updated: 02 Sep 2014
- published: 22 Aug 2013
- views: 17821
- author: IndonesianPride1

- Duration: 9:16
- Updated: 29 Aug 2014
- published: 01 Apr 2009
- views: 132923
- author: londonsummit

- Duration: 2:57
- Updated: 31 Aug 2014
- published: 27 Sep 2009
- views: 232906
- author: glassbeadian

- Duration: 97:51
- Updated: 08 Nov 2013
- published: 18 Jun 2012
- views: 9058
- author: Gobierno de la República

- Duration: 2:47
- Updated: 03 Sep 2014
- published: 24 Jun 2010
- views: 52070
- author: Matthew Santoro

- Duration: 82:33
- Updated: 22 Aug 2014
- published: 27 Oct 2011
- views: 9295
- author: CIGI

- Duration: 31:22
- Updated: 29 Jul 2014
- published: 06 Sep 2013
- views: 48381
- author: euronews (in English)

- Duration: 5:18
- Updated: 08 Sep 2014
- published: 08 Sep 2014
- views: 310

- Duration: 14:51
- Updated: 31 May 2014
- published: 06 Sep 2013
- views: 36316
- author: euronews (in English)

- Duration: 123:47
- Updated: 05 Sep 2014
- published: 21 Apr 2011
- views: 719785
- author: Press For Truth

- Duration: 6:43
- Updated: 08 Sep 2014
- published: 08 Sep 2014
- views: 501

- Duration: 3:39
- Updated: 08 Sep 2014
- published: 08 Sep 2014
- views: 437

- Duration: 6:48
- Updated: 08 Sep 2014
- published: 08 Sep 2014
- views: 227

- Duration: 9:54
- Updated: 23 Apr 2014
- published: 21 Apr 2014
- views: 76
- author: Zee Chaudhry

- Duration: 48:54
- Updated: 06 Sep 2013
- published: 06 Sep 2013
- views: 15905

- Duration: 124:52
- Updated: 15 Aug 2014
- published: 07 Jul 2014
- views: 231
- author: ANUchannel

- Duration: 27:21
- Updated: 01 Sep 2014
- published: 26 Mar 2014
- views: 107331
- author: Greg Hunter

- Duration: 57:18
- Updated: 17 Jul 2014
- published: 12 Feb 2013
- views: 3899
- author: Council on Foreign Relations

- Duration: 3:23
- Updated: 07 Sep 2014
- published: 07 Sep 2014
- views: 1121

- Duration: 3:37
- Updated: 07 Sep 2014
- published: 07 Sep 2014
- views: 494

- Duration: 3:41
- Updated: 07 Sep 2014
- published: 07 Sep 2014
- views: 402
-
นั่งยางโชว์ 19 เมษายน 2557 | วง G-20 [HD]
นั่งยางโชว์ 19 เมษายน 2557 | วง G-20 [HD]นั่งยางโชว์ 19 เมษายน 2557 | วง G-20 [HD]
นั่งยางโชว์ | 19 เมษายน 2557 [HD] แขกรับเชิญ: วง G-20 ----------------------------------------------------------------------- © Upload by truebankstv Faceboo... -
G20 เข้าบ้าน AF11 ในสัปดาห์ที่6 นักล่าฝันผู้ชายสมควรโดนกากบาทจากแฟนนอกบ้านจริงจริงอิๆ
G20 เข้าบ้าน AF11 ในสัปดาห์ที่6 นักล่าฝันผู้ชายสมควรโดนกากบาทจากแฟนนอกบ้านจริงจริงอิๆG20 เข้าบ้าน AF11 ในสัปดาห์ที่6 นักล่าฝันผู้ชายสมควรโดนกากบาทจากแฟนนอกบ้านจริงจริงอิๆ
วงเกิ้ลกรุ๊ป สาวๆ 7 คน สวยน่ารักเซ๊กศ์ซี่มีครบ แถมเก่งด้วย คลิปนี้อย่าแชร์ ถ้าคุณไม่อยากแชร์ (หมายความว่าโปรดแชร์หากคุณอยากส่งต่อให้เพื่อนๆ) :) Happy to you. Website : http://นักล่าฝัน.blogspot.com Twitter : https://twitter.com/RealityCHHD Instagram : http://instagram.com/realitychhd Website : http://realitychannelhd.blogspot.com เฟสบุ๊ค https://www.facebook.com/RealitychannelHD Youtube Channel : http://www.youtube.com/user/renovateth Youtube Channel : http://www.youtube.com/user/RealitychannelHD -
Under Occupation: Toronto G20 Operation - FULL MOVIE
Under Occupation: Toronto G20 Operation - FULL MOVIEUnder Occupation: Toronto G20 Operation - FULL MOVIE
Under Occupation: Toronto G20 Operation is an educational documentary that shows, in chronological order, the events that transpired over the G20 weekend in ... -
AF 11 Week 6 : G 20 โชว์ และร้องเพลง ร่วมโชว์ กับ นลฝ ทุกคน
AF 11 Week 6 : G 20 โชว์ และร้องเพลง ร่วมโชว์ กับ นลฝ ทุกคนAF 11 Week 6 : G 20 โชว์ และร้องเพลง ร่วมโชว์ กับ นลฝ ทุกคน
https://www.facebook.com/AFclubmultiply https://www.facebook.com/Showcasemvmv AF 11 Week 6 : G 20 โชว์ และร้องเพลง ร่มโชว์ กับ นลฝ ทุกคน. -
[TV] G20 นั่งยาง Show
[TV] G20 นั่งยาง Show[TV] G20 นั่งยาง Show
please follow : http://www.facebook.com/G20club. -
Саммит G20 в Санкт-Петербурге
Саммит G20 в Санкт-ПетербургеСаммит G20 в Санкт-Петербурге
В Санкт-Петербурге прошел первый день саммита стран-членов «Большой двадцатки». Подписывайтесь на RT Russian - http://www.youtube.com/subscription_center?add... -
Democracy 101: Pittsburgh G20 Protests and the Police Occupation of Pitt University
Democracy 101: Pittsburgh G20 Protests and the Police Occupation of Pitt UniversityDemocracy 101: Pittsburgh G20 Protests and the Police Occupation of Pitt University
Version 1 of a documentary about the recent Pittsburgh G20 Protests, and the Police Occupation of the University of Pittsburgh. This film is a collaboration ... -
#OBAMA vs PUTIN EN LA CUMBRE DEL G20 (PRIMEROS ROCES ENTRE RUSIA Y EE.UU)
#OBAMA vs PUTIN EN LA CUMBRE DEL G20 (PRIMEROS ROCES ENTRE RUSIA Y EE.UU)#OBAMA vs PUTIN EN LA CUMBRE DEL G20 (PRIMEROS ROCES ENTRE RUSIA Y EE.UU)
http://www.universobiblico.tv/ Buenas predicas! -
Toronto G20 Exposed
Toronto G20 ExposedToronto G20 Exposed
Toronto G20 Exposed is an educational documentary that shows, in chronological order, the events that transpired over the G20 weekend in Toronto, Canada. Whi... -
G20 Brisbane 2014
G20 Brisbane 2014G20 Brisbane 2014
Are peace full protestors going to be as badly treated as the citizens of Toronto were in 2010? Beaten, detained for 24 hours without adequate food, drink or... -
Conversion Van RV Campervan Chevy G20 Video Camper Motorhome Truck Vans SUV
Conversion Van RV Campervan Chevy G20 Video Camper Motorhome Truck Vans SUVConversion Van RV Campervan Chevy G20 Video Camper Motorhome Truck Vans SUV
Conversion Van RV Campervan Chevy G20 Camper Motorhome Truck Vans SUV Red-E-Kamp Video http://www.1OwnerCarGuy.com This is a very nice 1 Owner RED E KAMP Con... -
Recording menus: Canon Legria HF-G25 (Vixia HF-G20)
Recording menus: Canon Legria HF-G25 (Vixia HF-G20)Recording menus: Canon Legria HF-G25 (Vixia HF-G20)
This is the second of two videos looking at the menus and configuration of the Canon Legria HF-G25 (Vixia HF-G20) camcorder. The first video went through the... -
Chevrolet G20 Conversion van Solar mini RV 350 Explorer W/Bed SUV & High Top Camper
Chevrolet G20 Conversion van Solar mini RV 350 Explorer W/Bed SUV & High Top CamperChevrolet G20 Conversion van Solar mini RV 350 Explorer W/Bed SUV & High Top Camper
Chevrolet G20 Conversion van Solar mini RV 350 Explorer W/Bed SUV & High Top Camper This is a Very Nice van it is NOT perfect Nothing almost 20 years old Eve... -
Putin G20 (Full) News Conference 2013
Putin G20 (Full) News Conference 2013Putin G20 (Full) News Conference 2013
President Vladimir Putin answers questions at the news conference following the G20 Summit - September 6, 2013, St Petersburg, Russia. Society no longer need... -
G20 RE-EXPOSED: Toronto Inquiry Now (Documentary)
G20 RE-EXPOSED: Toronto Inquiry Now (Documentary)G20 RE-EXPOSED: Toronto Inquiry Now (Documentary)
'G-20 RE-EXPOSED' presented by Toronto Truth Seekers & SiLSa! Productions as a complimentary documentary to the original 'Toronto G20 Exposed' (the first fea... -
G20 RAW Full Documentary
G20 RAW Full DocumentaryG20 RAW Full Documentary
"G20 RAW" (1hr 38mins) At the G20 Summit, London 2009, humanitarian activist groups united and gathered at the Bank of England and the Excel Centre to protes... -
G20 @ Onoshow [26 พ.ค. 2554]
G20 @ Onoshow [26 พ.ค. 2554]G20 @ Onoshow [26 พ.ค. 2554]
http://www.g-twentyclub.com. -
The Fifth Estate - Report on the G20 Summit and police abuse [Full] (25-Feb-2011)
The Fifth Estate - Report on the G20 Summit and police abuse [Full] (25-Feb-2011)The Fifth Estate - Report on the G20 Summit and police abuse [Full] (25-Feb-2011)
For those who think that Canada is immune fromY happened in Toronto during the Billion dollar G20 summit. This is also what Stephen Harper is trying to make ... -
Второй день саммита G20
Второй день саммита G20Второй день саммита G20
В Санкт-Петербурге прошел второй день саммита стран-членов «Большой двадцатки». Подписывайтесь на RT Russian - http://www.youtube.com/subscription_center?add... -
G20 @ Onoshow [19 พ.ค. 2554]
G20 @ Onoshow [19 พ.ค. 2554]G20 @ Onoshow [19 พ.ค. 2554]
http://www.g-twentyclub.com. -
CrossTalk: G20 Showdown?
CrossTalk: G20 Showdown?CrossTalk: G20 Showdown?
Syrian question is dominating the G20 summit. Is this a chance for world leaders to achieve a resolution? Can military intervention still be stopped? And is ...
![นั่งยางโชว์ 19 เมษายน 2557 | วง G-20 [HD] นั่งยางโชว์ 19 เมษายน 2557 | วง G-20 [HD]](http://web.archive.org./web/20141007222652im_/http://i.ytimg.com/vi/63Mu5IsRElE/0.jpg)
- Duration: 35:47
- Updated: 25 Aug 2014
- published: 19 Apr 2014
- views: 17287
- author: truebankstv

- Duration: 73:33
- Updated: 27 Aug 2014
- published: 27 Aug 2014
- views: 1367

- Duration: 127:53
- Updated: 03 Sep 2014
- published: 15 Dec 2010
- views: 106889
- author: LibertyDefender84

- Duration: 41:18
- Updated: 04 Sep 2014
- published: 27 Aug 2014
- views: 2693
- author: afalbum
![[TV] G20 นั่งยาง Show [TV] G20 นั่งยาง Show](http://web.archive.org./web/20141007222652im_/http://i.ytimg.com/vi/CBJ8OsRtUj0/0.jpg)
- Duration: 41:52
- Updated: 19 Aug 2014
- published: 19 Apr 2014
- views: 7663
- author: ixnoreclip

- Duration: 626:31
- Updated: 04 Sep 2014
- published: 07 Sep 2013
- views: 17496
- author: RT на русском

- Duration: 29:07
- Updated: 28 Aug 2014
- published: 04 Oct 2009
- views: 38530
- author: glassbeadian

- Duration: 38:38
- Updated: 05 Sep 2014
- published: 06 Sep 2013
- views: 29312
- author: Universo Bíblico

- Duration: 96:49
- Updated: 23 Aug 2014
- published: 28 Oct 2012
- views: 9662
- author: LibertyDefender84

- Duration: 23:22
- Updated: 30 Aug 2014
- published: 21 Dec 2013
- views: 513
- author: anon for good

- Duration: 29:15
- Updated: 02 Sep 2014
- published: 17 Jun 2013
- views: 28928
- author: Cereal Marshmallows

- Duration: 21:54
- Updated: 06 Sep 2014
- published: 31 Mar 2013
- views: 12988
- author: UKAirscape

- Duration: 32:52
- Updated: 04 Sep 2014
- published: 20 Dec 2012
- views: 53158
- author: Cereal Marshmallows

- Duration: 46:17
- Updated: 28 Mar 2014
- published: 08 Sep 2013
- views: 751
- author: Marine1063

- Duration: 100:04
- Updated: 31 Jul 2014
- published: 27 Jan 2011
- views: 7286
- author: SupportLocalScene

- Duration: 98:58
- Updated: 20 Aug 2014
- published: 26 May 2011
- views: 18336
- author: pnmfilms
![G20 @ Onoshow [26 พ.ค. 2554] G20 @ Onoshow [26 พ.ค. 2554]](http://web.archive.org./web/20141007222652im_/http://i.ytimg.com/vi/UMtgTbdpeJM/0.jpg)
- Duration: 26:26
- Updated: 24 Jun 2013
![The Fifth Estate - Report on the G20 Summit and police abuse [Full] (25-Feb-2011) The Fifth Estate - Report on the G20 Summit and police abuse [Full] (25-Feb-2011)](http://web.archive.org./web/20141007222652im_/http://i.ytimg.com/vi/NUjY_cCjnD0/0.jpg)
- Duration: 45:05
- Updated: 01 Sep 2014
- published: 11 Apr 2011
- views: 10274
- author: ElectroPig Von Fokkengruuven

- Duration: 456:00
- Updated: 15 Aug 2014
- published: 06 Sep 2013
- views: 29712
- author: RT на русском
![G20 @ Onoshow [19 พ.ค. 2554] G20 @ Onoshow [19 พ.ค. 2554]](http://web.archive.org./web/20141007222652im_/http://i.ytimg.com/vi/rgXfyHnBKFA/0.jpg)
- Duration: 28:51
- Updated: 02 Jul 2013

- Duration: 24:17
- Updated: 18 Mar 2014
- published: 06 Sep 2013
- views: 14603
- author: RT
-
1999 Infiniti G20 - Savannah GA
1999 Infiniti G20 - Savannah GA1999 Infiniti G20 - Savannah GA
This vehicle represents similar vehicles available at Grainger Honda. Contact Grainger Honda at (888) 710-9230, www.graingerhonda.com, or http://www.cars.com/go/search/search.jsp?aff=national&tracktype;=usedcc&dlid;=113502&searchType;=26 for availability of specific vehicles. www.graingerhonda.com Phone: (888) 710-9230 Year: 1999 Make: Infiniti Model: G20 Trim: W Engine: 2.0 liter inline 4 cylinder 16 valve MPFI DOHC Transmission: 4-Speed Automatic Color: Gray Mileage: 111772 Address: 1596 Chatham Parkway Savannah, GA 31408 -
YOIMARC ORTEGA Gran Hermano G20 online
YOIMARC ORTEGA Gran Hermano G20 onlineYOIMARC ORTEGA Gran Hermano G20 online
Gran hermano casting 2014 para online gh20 -
poniedziałek g. 20:00 - AS Wywiadu z Krzysztofem Cieślakiem (premiera)
poniedziałek g. 20:00 - AS Wywiadu z Krzysztofem Cieślakiem (premiera)poniedziałek g. 20:00 - AS Wywiadu z Krzysztofem Cieślakiem (premiera)
Od 15 września nowy sezon "ASA Wywiadu". Jesienią zapraszamy na piąty sezon programu publicystycznego prowadzonego przez Patryka Mirosławskiego. Znany dziennikarz przepyta wiele rozpoznawalnych postaci ze świata sportu. Gościem premierowego odcinka programu będzie polski pięściarz - Krzysztof Cieślak. -
Best Buy - Canon - VIXIA HF G20 32GB HD Flash Memory Camcorder - Black
Best Buy - Canon - VIXIA HF G20 32GB HD Flash Memory Camcorder - BlackBest Buy - Canon - VIXIA HF G20 32GB HD Flash Memory Camcorder - Black
Shop with any of the 4,000+ companies we've partnered with and GET CASH BACK. Simply search for your favorite store inside the Shopping Mall at http://www.ShoppingWithCashBackDeals.com Utilize the toolbar at the top left as it let's you know what percentage cash back you'll get for whatever it is you're shopping for...travel arrangements too... from the stores/companies you usually shop from! http://www.ShoppingWithCashBackDeals.com ENJOY YOUR SHOPPING CASH BACK! -
Meeting Kim Kardashian - 'G20 with hairspray' 02:29
Meeting Kim Kardashian - 'G20 with hairspray' 02:29Meeting Kim Kardashian - 'G20 with hairspray' 02:29
Securing access to the queen of reality TV is like getting into a meeting of world leaders, finds Fairfax Media journalist Jenna Clarke. Securing access to the queen of reality TV is like getting into a meeting of world leaders, finds Fairfax Media journalist Jenna Clarke. Securing access to the queen of reality TV is like getting into a meeting of world leaders, finds Fairfax Media journalist Jenna Clarke. Meeting Kim Kardashian - 'G20 with hairspray' 02:29 Meeting Kim Kardashian - 'G20 with hairspray' 02:29 Meeting Kim Kardashian - 'G20 with hairspray' 02:29 -
ASUS ROG G20 Oyuncu Bilgisayarı - Şaşırtıcı Güç
ASUS ROG G20 Oyuncu Bilgisayarı - Şaşırtıcı GüçASUS ROG G20 Oyuncu Bilgisayarı - Şaşırtıcı Güç
ASUS ROG G20 oyuncu bilgisayarı, küçük boyutlu oyuncu bilgisayarları sınıfında liderliğe oynayan şık tasarımlı bir seçenektir. ROG G20, Computex 2014'te "Yılın En İyi Seçimi" ve Altın Ödül" almaya hak kazanmıştır. Daha fazla bilgi için: http://www.asus.com/tr/Microsite/rog/GR8_G20/ -
M TREE M3 MUSIC G20 CINTA GILA INDRI
M TREE M3 MUSIC G20 CINTA GILA INDRIM TREE M3 MUSIC G20 CINTA GILA INDRI
Jangan Lupa Berlangganan Yaaaa......... -
2000 Infiniti G20 Used Cars St Charles IL
2000 Infiniti G20 Used Cars St Charles IL2000 Infiniti G20 Used Cars St Charles IL
http://www.premiercarsalesinc.com This 2000 Infiniti G20 is available from Premier Car Sales Inc. For details, call us at 630-444-1828 -
Cómo cambiar los frenos traseros en un '99 Infiniti G20
Cómo cambiar los frenos traseros en un '99 Infiniti G20Cómo cambiar los frenos traseros en un '99 Infiniti G20
-
Cómo reemplazar G20 Leather Seat Covers
Cómo reemplazar G20 Leather Seat CoversCómo reemplazar G20 Leather Seat Covers
-
Cómo cambiar las almohadillas de freno delanteros en un G20 de Infiniti
Cómo cambiar las almohadillas de freno delanteros en un G20 de InfinitiCómo cambiar las almohadillas de freno delanteros en un G20 de Infiniti
-
Cómo cambiar los frenos en un G20 de Infiniti
Cómo cambiar los frenos en un G20 de InfinitiCómo cambiar los frenos en un G20 de Infiniti
-
G20 vs G8 перевес очевиден
G20 vs G8 перевес очевиденG20 vs G8 перевес очевиден
-
1994 Chevrolet G-Series - Flint MI
1994 Chevrolet G-Series - Flint MI1994 Chevrolet G-Series - Flint MI
Dealer's Website: http://www.applegatechev.com/ Find Similar Vehicles: http://autos.mlive.com/dealers/696954/applegate-chevrolet Phone: 810-768-7001 Year: 1994 Make: Chevrolet Model: G-Series Trim: G20 Engine: 5.7 L, 8 cylinder Transmission: Color: Blue Mileage: 154724 Address: 3637 South Saginaw Street Flint, MI 48503 -
2002 INFINITI G20 Base 4dr Sedan for sale in Fox Lake, IL 60
2002 INFINITI G20 Base 4dr Sedan for sale in Fox Lake, IL 602002 INFINITI G20 Base 4dr Sedan for sale in Fox Lake, IL 60
This 2002 INFINITI G20 Base 4dr Sedan is for sale in Fox Lake, IL 60020 at Auto Villa. Contact Auto Villa at http://www.autovillaofil.com or http://www.carsforsale.com/used-cars-for-sale/2002-infiniti-g20-foxlake-il-236758906 Engine: I4 2.0L I4 Transmission: Automatic Color: BLUE Mileage: 154468 Contact Auto Villa 133 S. US HWY 12 Fox Lake, IL 60020 to test drive this 2002 INFINITI G20 Base 4dr Sedan today. -
El FMI se reúne con los ministros de Finanzas del G20, con el espectro ruso-ucraniano. -
El FMI se reúne con los ministros de Finanzas del G20, con el espectro ruso-ucraniano. -El FMI se reúne con los ministros de Finanzas del G20, con el espectro ruso-ucraniano. -
Los grandes bancos estadounidenses JP Morgan y Wells Fargo publicarán sus resultados para el primer trimestre, mientras que en España Gas Natural y Viscofan . El Fondo Monetario Internacional y el Banco Mundial celebran su reunión de primavera en Washington junto al G20 de Finanzas con la tensión ruso-ucraniana de . inversionoptima. Una misión técnica del Fondo Monetario Económico Internacional (FMI) comenzó a evaluar las cifras económicas de Honduras de cara a la suscripción de un nuevo. -
AS Wywiadu - poniedziałek i czwartek g. 20:00
AS Wywiadu - poniedziałek i czwartek g. 20:00AS Wywiadu - poniedziałek i czwartek g. 20:00
Trudne pytania. Szczere odpowiedzi. Błyskotliwe riposty. Złośliwe komentarze. Tego wszystkiego nie brakuje we flagowym programie SportKlubu – "AS Wywiadu". Jesienią zapraszamy na piąty sezon talk show prowadzonego przez Patryka Mirosławskiego. Znany dziennikarz przepyta wiele rozpoznawalnych postaci ze świata sportu, pośród których będą między innymi: słynni dziennikarze Tomasz Smokowski i Paweł Zarzeczny oraz lider Lady Pank Janusz Panasewicz. Każdy z nich w ciągu około trzydziestu minut programu postara się opowiedzieć wam ciekawe historie, odsłaniające kulisy świata sportu. Klasyczna formuła programu, w którym prowadzący rozmawia w każdy -
G20 with 6LB trigger spring and 3.5LB Ghost Rocket Connector
G20 with 6LB trigger spring and 3.5LB Ghost Rocket ConnectorG20 with 6LB trigger spring and 3.5LB Ghost Rocket Connector
Ghost Rocket Connector with Trigger Control Tab for short over travel -
IB140910 040 Asus ROG G20 угловатый игровой мини ПК на процессоре Intel Core i7 четвертого поколения
IB140910 040 Asus ROG G20 угловатый игровой мини ПК на процессоре Intel Core i7 четвертого поколенияIB140910 040 Asus ROG G20 угловатый игровой мини ПК на процессоре Intel Core i7 четвертого поколения
-
new ASUS ROG G20 Compact Gaming Desktop PC video trailer 2014 - Deceptively Powerful for gamers
new ASUS ROG G20 Compact Gaming Desktop PC video trailer 2014 - Deceptively Powerful for gamersnew ASUS ROG G20 Compact Gaming Desktop PC video trailer 2014 - Deceptively Powerful for gamers
Official trailer for the "ASUS ROG G20 Compact Gaming Desktop PC Trailer" ➥ Canal : https://www.youtube.com/user/abantecnologia ➥ Twitter : https://www.twitter.com/abantecnologia ★ Portal web ➨ http://abantec.com.ve video trailer official ASUS ROG G20 Compact Gaming Desktop PC. Subscribe now to abantecnologia to get the latest HD advace technology, game trailer, gameplay teaser & cinematic video on Abantecnologia. Suscribete ahora a abantecnologia para ver los ultimos avances tecnologicos en HD -
Whistleblower protection laws lacking in G20 countries
Whistleblower protection laws lacking in G20 countriesWhistleblower protection laws lacking in G20 countries
Report released after extensive international study -
charade g20
charade g20charade g20
algo suave escuchando ñengo flow tiempo al tiempo -
【韓国経済】韓国の反応「もうG20には出席しないで…」⇒ 創造経済が犯
【韓国経済】韓国の反応「もうG20には出席しないで…」⇒ 創造経済が犯【韓国経済】韓国の反応「もうG20には出席しないで…」⇒ 創造経済が犯
---------------------------------------------- 他の動画・一覧ページはコチラ↓↓↓ 引用元:ホル韓ニュース速報「改」 関連タグ: 韓国経済崩壊,韓国経済破綻,韓国経済崩壊 最新,韓国経済危機,韓国経済ニュース,韓国経済の現状,韓国経済com,韓国経済状況,韓国経済崩壊ニュース,韓国経済崩壊us,韓国経済崩壊破綻,韓国経済崩壊 最新ニュース,韓国経済崩壊u1,韓国経済崩壊 2014年8月,韓国経済崩壊 最新 2014年8月31日,韓国経済崩壊youtube,韓国経済崩壊 動画,韓国経済破綻最新,韓国経済破綻 動画,2014年8月韓国経済破綻,韓国経済破綻2014年8月,韓国経済破綻最新ニュース,韓国経済破綻2014,韓国経済破綻ニュース,韓国経済破綻 いつ,韓国経済破綻時期,中国韓国経済破綻,韓国経済破綻最新動画,韓国経済崩壊 最新 2014年8月30日,韓国経済崩壊 最新 2014年9月1日,韓国経済崩壊 最新 2014年8月26日,韓国経済崩壊 最新 2014年8月28日,韓国経済崩壊 最新 2014年8月6日,韓国経済崩壊 最新 2014年8月,韓国経済崩壊 最新 2014年8月12日,韓国経済崩壊 最新 2014年8月14日,韓国経済崩壊 最新 2014年8月16日,韓国経済危機2014,2014年9月の韓国経済危機,韓国経済危機 2014年8月,韓国経済危機 IMF,韓国経済危機 反

- Duration: 0:51
- Updated: 12 Sep 2014
- published: 12 Sep 2014
- views: 0

- Duration: 0:57
- Updated: 12 Sep 2014
- published: 12 Sep 2014
- views: 2

- Duration: 0:22
- Updated: 12 Sep 2014
- published: 12 Sep 2014
- views: 97

- Duration: 1:33
- Updated: 12 Sep 2014
- published: 12 Sep 2014
- views: 3

- Duration: 2:30
- Updated: 12 Sep 2014
- published: 12 Sep 2014
- views: 3

- Duration: 1:17
- Updated: 12 Sep 2014
- published: 12 Sep 2014
- views: 30

- Duration: 6:17
- Updated: 12 Sep 2014
- published: 12 Sep 2014
- views: 0

- Duration: 1:12
- Updated: 12 Sep 2014
- published: 12 Sep 2014
- views: 0

- Duration: 2:10
- Updated: 12 Sep 2014
http://wn.com/Cómo_cambiar_los_frenos_traseros_en_un_'99_Infiniti_G20
- published: 12 Sep 2014
- views: 0

- Duration: 2:19
- Updated: 12 Sep 2014
http://wn.com/Cómo_reemplazar_G20_Leather_Seat_Covers
- published: 12 Sep 2014
- views: 0

- Duration: 3:40
- Updated: 12 Sep 2014
http://wn.com/Cómo_cambiar_las_almohadillas_de_freno_delanteros_en_un_G20_de_Infiniti
- published: 12 Sep 2014
- views: 0

- Duration: 1:38
- Updated: 12 Sep 2014
http://wn.com/Cómo_cambiar_los_frenos_en_un_G20_de_Infiniti
- published: 12 Sep 2014
- views: 0

- Duration: 5:20
- Updated: 11 Sep 2014
http://wn.com/G20_vs_G8_перевес_очевиден
- published: 11 Sep 2014
- views: 0

- Duration: 1:01
- Updated: 11 Sep 2014
- published: 11 Sep 2014
- views: 0

- Duration: 2:17
- Updated: 11 Sep 2014
- published: 11 Sep 2014
- views: 1

- Duration: 1:49
- Updated: 11 Sep 2014
- published: 11 Sep 2014
- views: 2

- Duration: 0:14
- Updated: 11 Sep 2014
- published: 11 Sep 2014
- views: 137

- Duration: 0:45
- Updated: 11 Sep 2014
- published: 11 Sep 2014
- views: 2

- Duration: 2:42
- Updated: 11 Sep 2014
http://wn.com/IB140910_040_Asus_ROG_G20_угловатый_игровой_мини_ПК_на_процессоре_Intel_Core_i7_четвертого_поколения
- published: 11 Sep 2014
- views: 6

- Duration: 1:24
- Updated: 11 Sep 2014
- published: 11 Sep 2014
- views: 24

- Duration: 2:09
- Updated: 11 Sep 2014
- published: 11 Sep 2014
- views: 7

- Duration: 1:25
- Updated: 11 Sep 2014
- published: 11 Sep 2014
- views: 3

- Duration: 4:54
- Updated: 10 Sep 2014
- published: 10 Sep 2014
- views: 130
- Playlist
- Chat

Opening of the G20 Summit in St Petersburg (recorded live feed)
Recorded live version of Vladimir Putin's welcoming speech at the G20 opening session in St Petersburg. Russia is hosting the summit of the leaders of the Gr...- published: 05 Sep 2013
- views: 25979
- author: euronews (in English)

INDONESIA THE LARGEST ECONOMY IN SOUTHEAST ASIA - G20 MEMBER
INDONESIA THE LARGEST ECONOMY IN SOUTHEAST ASIA - G20 MEMBER With a population of over 242.3 million, Indonesia is the fourth most populous country in the wo...- published: 22 Aug 2013
- views: 17821
- author: IndonesianPride1

G20 delegates arrive at Buckingham Palace pt1
G20 delegates arriving at Buckingham Palace for the reception with the Queen.- published: 01 Apr 2009
- views: 132923
- author: londonsummit

Anarchist black bloc clash with police at G20 Pittsburgh
Police attack unpermitted anarchist march with LRAD, tear gas, and other less lethal weapons. Anarchists then attack police in self defense. September 24th G...- published: 27 Sep 2009
- views: 232906
- author: glassbeadian

Recepción de Líderes del G20 a su arribo al Centro de Convenciones G20 (evento completo)
Los Cabos, Baja California Sur, 18 de junio del 2012. El Presidente Felipe Calderón durante la Recepción de Líderes del G20 a su arribo al Centro de Convenci...- published: 18 Jun 2012
- views: 9058
- author: Gobierno de la República

Earthquake & the G20
Subscribe! New videos every Saturday: http://bit.ly/Subscribenow Facebook (Like): http://fb.com/MatthewSantoroOfficial Facebook (Follow): http://fb.com/Matth...- published: 24 Jun 2010
- views: 52070
- author: Matthew Santoro

Zombies, G20 and International Relations
What would happen to international politics if the dead rose from the grave and started to eat the living? On October 26, 2011 at CIGI, Daniel Drezner answer...- published: 27 Oct 2011
- views: 9295
- author: CIGI

Obama's full speech at G20 closing press conference (recorded live feed)
US President Barack Obama speaks at the closing news conference at G20 Summit in St Petersburg, Russia. euronews: the most watched news channel in Europe Sub...- published: 06 Sep 2013
- views: 48381
- author: euronews (in English)

140907 G-Twenty(G20) - Talk @Wonderful Korea
Playlist : http://www.youtube.com/playlist?list=PLUmduNl7KEvASh8k71-0Rm2IPE612UNQZ http://www.facebook.com/G20club Wonderful Korea at Paradise Park Thailand 07/09/2014- published: 08 Sep 2014
- views: 310

Putin's speech at G20 closing press conference (recorded live feed)
Russian President Vladimir Putin speaks at the closing news conference at G20 Summit in St Petersburg, Russia. euronews: the most watched news channel in Eur...- published: 06 Sep 2013
- views: 36316
- author: euronews (in English)

Into The Fire - Full Film
Press For Truth Presents Into The Fire World leaders and activists from around the world gathered for the G20 Summit. With over 19000 police officers and se...- published: 21 Apr 2011
- views: 719785
- author: Press For Truth

140907 G-Twenty(G20) - ของฟรีไม่มีในโลก + Magic Ho
Playlist : http://www.youtube.com/playlist?list=PLUmduNl7KEvASh8k71-0Rm2IPE612UNQZ http://www.facebook.com/G20club Wonderful Korea at Paradise Park Thailand 07/09/2014- published: 08 Sep 2014
- views: 501

140907 G-Twenty(G20) - ไม่พูดก็ได้ยิน @Wonderful K
Playlist : http://www.youtube.com/playlist?list=PLUmduNl7KEvASh8k71-0Rm2IPE612UNQZ http://www.facebook.com/G20club Wonderful Korea at Paradise Park Thailand 07/09/2014- published: 08 Sep 2014
- views: 437

140907 G-Twenty(G20) - Don't Worry + Mi Mi Mi @Won
Playlist : http://www.youtube.com/playlist?list=PLUmduNl7KEvASh8k71-0Rm2IPE612UNQZ http://www.facebook.com/G20club Wonderful Korea at Paradise Park Thailand 07/09/2014- published: 08 Sep 2014
- views: 227

G20 YEA Summit, Moscow, Russia, June 2013
Video from the G20 Young Entrepreneurs Summit, that took place in Moscow June 2013.- published: 21 Apr 2014
- views: 76
- author: Zee Chaudhry

Пресс-конференция Барака Обамы на саммите G20
Пресс-конференция президента США Барака Обамы по итогам саммита стран-членов «Большой двадцатки». Подписывайтесь на RT Russian - http://www.youtube.com/subscription_center?add_user=rtrussian RT на русском - http://russian.rt.com/ Vkontakte - http://vk.com/rt_russian Facebook - http://www.facebook.com/RTRussian Twitter - http://twitter.com/RT_russian Livejournal - http://rt-russian.livejournal.com/- published: 06 Sep 2013
- views: 15905

US and China energy and climate policy and the G20
Climate and energy policy is once more near the top of the US government's policy agenda, and occupies a prominent position in China's development planning a...- published: 07 Jul 2014
- views: 231
- author: ANUchannel
- Playlist
- Chat

นั่งยางโชว์ 19 เมษายน 2557 | วง G-20 [HD]
นั่งยางโชว์ | 19 เมษายน 2557 [HD] แขกรับเชิญ: วง G-20 ----------------------------------------------------------------------- © Upload by truebankstv Faceboo...- published: 19 Apr 2014
- views: 17287
- author: truebankstv

G20 เข้าบ้าน AF11 ในสัปดาห์ที่6 นักล่าฝันผู้ชายสมควรโดนกากบาทจากแฟนนอกบ้านจริงจริงอิๆ
วงเกิ้ลกรุ๊ป สาวๆ 7 คน สวยน่ารักเซ๊กศ์ซี่มีครบ แถมเก่งด้วย คลิปนี้อย่าแชร์ ถ้าคุณไม่อยากแชร์ (หมายความว่าโปรดแชร์หากคุณอยากส่งต่อให้เพื่อนๆ) :) Happy to you. Website : http://นักล่าฝัน.blogspot.com Twitter : https://twitter.com/RealityCHHD Instagram : http://instagram.com/realitychhd Website : http://realitychannelhd.blogspot.com เฟสบุ๊ค https://www.facebook.com/RealitychannelHD Youtube Channel : http://www.youtube.com/user/renovateth Youtube Channel : http://www.youtube.com/user/RealitychannelHD- published: 27 Aug 2014
- views: 1367

Under Occupation: Toronto G20 Operation - FULL MOVIE
Under Occupation: Toronto G20 Operation is an educational documentary that shows, in chronological order, the events that transpired over the G20 weekend in ...- published: 15 Dec 2010
- views: 106889
- author: LibertyDefender84

AF 11 Week 6 : G 20 โชว์ และร้องเพลง ร่วมโชว์ กับ นลฝ ทุกคน
https://www.facebook.com/AFclubmultiply https://www.facebook.com/Showcasemvmv AF 11 Week 6 : G 20 โชว์ และร้องเพลง ร่มโชว์ กับ นลฝ ทุกคน.- published: 27 Aug 2014
- views: 2693
- author: afalbum

[TV] G20 นั่งยาง Show
please follow : http://www.facebook.com/G20club.- published: 19 Apr 2014
- views: 7663
- author: ixnoreclip

Саммит G20 в Санкт-Петербурге
В Санкт-Петербурге прошел первый день саммита стран-членов «Большой двадцатки». Подписывайтесь на RT Russian - http://www.youtube.com/subscription_center?add...- published: 07 Sep 2013
- views: 17496
- author: RT на русском

Democracy 101: Pittsburgh G20 Protests and the Police Occupation of Pitt University
Version 1 of a documentary about the recent Pittsburgh G20 Protests, and the Police Occupation of the University of Pittsburgh. This film is a collaboration ...- published: 04 Oct 2009
- views: 38530
- author: glassbeadian

#OBAMA vs PUTIN EN LA CUMBRE DEL G20 (PRIMEROS ROCES ENTRE RUSIA Y EE.UU)
http://www.universobiblico.tv/ Buenas predicas!- published: 06 Sep 2013
- views: 29312
- author: Universo Bíblico

Toronto G20 Exposed
Toronto G20 Exposed is an educational documentary that shows, in chronological order, the events that transpired over the G20 weekend in Toronto, Canada. Whi...- published: 28 Oct 2012
- views: 9662
- author: LibertyDefender84

G20 Brisbane 2014
Are peace full protestors going to be as badly treated as the citizens of Toronto were in 2010? Beaten, detained for 24 hours without adequate food, drink or...- published: 21 Dec 2013
- views: 513
- author: anon for good

Conversion Van RV Campervan Chevy G20 Video Camper Motorhome Truck Vans SUV
Conversion Van RV Campervan Chevy G20 Camper Motorhome Truck Vans SUV Red-E-Kamp Video http://www.1OwnerCarGuy.com This is a very nice 1 Owner RED E KAMP Con...- published: 17 Jun 2013
- views: 28928
- author: Cereal Marshmallows

Recording menus: Canon Legria HF-G25 (Vixia HF-G20)
This is the second of two videos looking at the menus and configuration of the Canon Legria HF-G25 (Vixia HF-G20) camcorder. The first video went through the...- published: 31 Mar 2013
- views: 12988
- author: UKAirscape

Chevrolet G20 Conversion van Solar mini RV 350 Explorer W/Bed SUV & High Top Camper
Chevrolet G20 Conversion van Solar mini RV 350 Explorer W/Bed SUV & High Top Camper This is a Very Nice van it is NOT perfect Nothing almost 20 years old Eve...- published: 20 Dec 2012
- views: 53158
- author: Cereal Marshmallows

Putin G20 (Full) News Conference 2013
President Vladimir Putin answers questions at the news conference following the G20 Summit - September 6, 2013, St Petersburg, Russia. Society no longer need...- published: 08 Sep 2013
- views: 751
- author: Marine1063

G20 RE-EXPOSED: Toronto Inquiry Now (Documentary)
'G-20 RE-EXPOSED' presented by Toronto Truth Seekers & SiLSa! Productions as a complimentary documentary to the original 'Toronto G20 Exposed' (the first fea...- published: 27 Jan 2011
- views: 7286
- author: SupportLocalScene

G20 RAW Full Documentary
"G20 RAW" (1hr 38mins) At the G20 Summit, London 2009, humanitarian activist groups united and gathered at the Bank of England and the Excel Centre to protes...- published: 26 May 2011
- views: 18336
- author: pnmfilms

G20 @ Onoshow [26 พ.ค. 2554]
http://www.g-twentyclub.com.- published: 26 May 2011
- views: 10598
- author: CandyMafiaChannel

The Fifth Estate - Report on the G20 Summit and police abuse [Full] (25-Feb-2011)
For those who think that Canada is immune fromY happened in Toronto during the Billion dollar G20 summit. This is also what Stephen Harper is trying to make ...- published: 11 Apr 2011
- views: 10274
- author: ElectroPig Von Fokkengruuven
- Playlist
- Chat

1999 Infiniti G20 - Savannah GA
This vehicle represents similar vehicles available at Grainger Honda. Contact Grainger Honda at (888) 710-9230, www.graingerhonda.com, or http://www.cars.com/go/search/search.jsp?aff=national&tracktype;=usedcc&dlid;=113502&searchType;=26 for availability of specific vehicles. www.graingerhonda.com Phone: (888) 710-9230 Year: 1999 Make: Infiniti Model: G20 Trim: W Engine: 2.0 liter inline 4 cylinder 16 valve MPFI DOHC Transmission: 4-Speed Automatic Color: Gray Mileage: 111772 Address: 1596 Chatham Parkway Savannah, GA 31408- published: 12 Sep 2014
- views: 0

poniedziałek g. 20:00 - AS Wywiadu z Krzysztofem Cieślakiem (premiera)
Od 15 września nowy sezon "ASA Wywiadu". Jesienią zapraszamy na piąty sezon programu publicystycznego prowadzonego przez Patryka Mirosławskiego. Znany dziennikarz przepyta wiele rozpoznawalnych postaci ze świata sportu. Gościem premierowego odcinka programu będzie polski pięściarz - Krzysztof Cieślak.- published: 12 Sep 2014
- views: 97

Best Buy - Canon - VIXIA HF G20 32GB HD Flash Memory Camcorder - Black
Shop with any of the 4,000+ companies we've partnered with and GET CASH BACK. Simply search for your favorite store inside the Shopping Mall at http://www.ShoppingWithCashBackDeals.com Utilize the toolbar at the top left as it let's you know what percentage cash back you'll get for whatever it is you're shopping for...travel arrangements too... from the stores/companies you usually shop from! http://www.ShoppingWithCashBackDeals.com ENJOY YOUR SHOPPING CASH BACK!- published: 12 Sep 2014
- views: 3

Meeting Kim Kardashian - 'G20 with hairspray' 02:29
Securing access to the queen of reality TV is like getting into a meeting of world leaders, finds Fairfax Media journalist Jenna Clarke. Securing access to the queen of reality TV is like getting into a meeting of world leaders, finds Fairfax Media journalist Jenna Clarke. Securing access to the queen of reality TV is like getting into a meeting of world leaders, finds Fairfax Media journalist Jenna Clarke. Meeting Kim Kardashian - 'G20 with hairspray' 02:29 Meeting Kim Kardashian - 'G20 with hairspray' 02:29 Meeting Kim Kardashian - 'G20 with hairspray' 02:29- published: 12 Sep 2014
- views: 3

ASUS ROG G20 Oyuncu Bilgisayarı - Şaşırtıcı Güç
ASUS ROG G20 oyuncu bilgisayarı, küçük boyutlu oyuncu bilgisayarları sınıfında liderliğe oynayan şık tasarımlı bir seçenektir. ROG G20, Computex 2014'te "Yılın En İyi Seçimi" ve Altın Ödül" almaya hak kazanmıştır. Daha fazla bilgi için: http://www.asus.com/tr/Microsite/rog/GR8_G20/- published: 12 Sep 2014
- views: 30

2000 Infiniti G20 Used Cars St Charles IL
http://www.premiercarsalesinc.com This 2000 Infiniti G20 is available from Premier Car Sales Inc. For details, call us at 630-444-1828- published: 12 Sep 2014
- views: 0

1994 Chevrolet G-Series - Flint MI
Dealer's Website: http://www.applegatechev.com/ Find Similar Vehicles: http://autos.mlive.com/dealers/696954/applegate-chevrolet Phone: 810-768-7001 Year: 1994 Make: Chevrolet Model: G-Series Trim: G20 Engine: 5.7 L, 8 cylinder Transmission: Color: Blue Mileage: 154724 Address: 3637 South Saginaw Street Flint, MI 48503- published: 11 Sep 2014
- views: 0

2002 INFINITI G20 Base 4dr Sedan for sale in Fox Lake, IL 60
This 2002 INFINITI G20 Base 4dr Sedan is for sale in Fox Lake, IL 60020 at Auto Villa. Contact Auto Villa at http://www.autovillaofil.com or http://www.carsforsale.com/used-cars-for-sale/2002-infiniti-g20-foxlake-il-236758906 Engine: I4 2.0L I4 Transmission: Automatic Color: BLUE Mileage: 154468 Contact Auto Villa 133 S. US HWY 12 Fox Lake, IL 60020 to test drive this 2002 INFINITI G20 Base 4dr Sedan today.- published: 11 Sep 2014
- views: 1

El FMI se reúne con los ministros de Finanzas del G20, con el espectro ruso-ucraniano. -
Los grandes bancos estadounidenses JP Morgan y Wells Fargo publicarán sus resultados para el primer trimestre, mientras que en España Gas Natural y Viscofan . El Fondo Monetario Internacional y el Banco Mundial celebran su reunión de primavera en Washington junto al G20 de Finanzas con la tensión ruso-ucraniana de . inversionoptima. Una misión técnica del Fondo Monetario Económico Internacional (FMI) comenzó a evaluar las cifras económicas de Honduras de cara a la suscripción de un nuevo.- published: 11 Sep 2014
- views: 2

AS Wywiadu - poniedziałek i czwartek g. 20:00
Trudne pytania. Szczere odpowiedzi. Błyskotliwe riposty. Złośliwe komentarze. Tego wszystkiego nie brakuje we flagowym programie SportKlubu – "AS Wywiadu". Jesienią zapraszamy na piąty sezon talk show prowadzonego przez Patryka Mirosławskiego. Znany dziennikarz przepyta wiele rozpoznawalnych postaci ze świata sportu, pośród których będą między innymi: słynni dziennikarze Tomasz Smokowski i Paweł Zarzeczny oraz lider Lady Pank Janusz Panasewicz. Każdy z nich w ciągu około trzydziestu minut programu postara się opowiedzieć wam ciekawe historie, odsłaniające kulisy świata sportu. Klasyczna formuła programu, w którym prowadzący rozmawia w każdym odcinku tylko z jednym gościem, zdaje egzamin od kilku lat. Na pewno i tym razem będzie bardzo ciekawie! AS Wywiadu tylko i wyłącznie w SportKlubie. Premiera 15 września. Emisja w każdy poniedziałek i czwartek o 20:00.- published: 11 Sep 2014
- views: 137

G20 with 6LB trigger spring and 3.5LB Ghost Rocket Connector
Ghost Rocket Connector with Trigger Control Tab for short over travel- published: 11 Sep 2014
- views: 2
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- Next page »

The Group of Twenty Finance Ministers and Central Bank Governors (also known as the G-20, G20, and Group of Twenty) is a group of finance ministers and central bank governors from 20 major economies: 19 countries plus the European Union, which is represented by the President of the European Council and by the European Central Bank. Their heads of government or heads of state have also periodically conferred at summits since their initial meeting in 2008. Collectively, the G-20 economies account for more than 80 percent of the gross world product (GWP), 80 percent of world trade (including EU intra-trade), and two-thirds of the world population. They furthermore account for 84.1 percent and 82.2 percent of the world's economic growth by nominal GDP and GDP (PPP) respectively from the years 2010 to 2016, according to the International Monetary Fund (IMF).
The G-20 was proposed by former Canadian Finance Minister Paul Martin (later, Prime Minister) for cooperation and consultation on matters pertaining to the international financial system. It studies, reviews, and promotes discussion (among key industrial and emerging market countries) of policy issues pertaining to the promotion of international financial stability, and seeks to address issues that go beyond the responsibilities of any one organization. With the G-20 growing in stature since the 2008 Washington summit, its leaders announced on September 25, 2009, that the group will replace the G8 as the main economic council of wealthy nations.
This article is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported License, which means that you can copy and modify it as long as the entire work (including additions) remains under this license.





