










- Loading...

-
Atomic Number, Mass Number, and Net Charge
Atomic Number, Mass Number, and Net Charge -
Atomic Number and Mass Number | Chemistry | the virtual school
Atomic Number and Mass Number | Chemistry | the virtual schoolAtomic Number and Mass Number | Chemistry | the virtual school
How do we tell elements apart from each other? Find out in this video from the Properties of Matter chapter of the Virtual School GCSE Chemistry. This is par... -
How to Determine the ATOMIC NUMBER & MASS NUMBER - CLEAR & SIMPLE
How to Determine the ATOMIC NUMBER & MASS NUMBER - CLEAR & SIMPLEHow to Determine the ATOMIC NUMBER & MASS NUMBER - CLEAR & SIMPLE
-
Atomic number and Mass number of an atom - Science
Atomic number and Mass number of an atom - ScienceAtomic number and Mass number of an atom - Science
This is a science video for grade 8-9th students that explains Atomic Number and Mass Number of an atom and how they are linked to the electrons, protons and... -
Atomic Number - Isotopes
Atomic Number - IsotopesAtomic Number - Isotopes
Science Help at Brightstorm! http://brightstorm.com/science The meaning and uses of atomic numbers. -
CHEM 3.1.3 Atomic mass and Atomic Number
CHEM 3.1.3 Atomic mass and Atomic NumberCHEM 3.1.3 Atomic mass and Atomic Number
-
Atomic Numbers, Mass Numbers and Isotopes - Chemistry Tutorial
Atomic Numbers, Mass Numbers and Isotopes - Chemistry TutorialAtomic Numbers, Mass Numbers and Isotopes - Chemistry Tutorial
https://www.thechemistrysolution.com A chemistry tutorial designed to explain the definition and difference between atomic numbers and mass numbers as well a... -
Atomic Number, Atomic Mass and Mass Number
Atomic Number, Atomic Mass and Mass NumberAtomic Number, Atomic Mass and Mass Number
Check out us at:http://chemistry.tutorvista.com/inorganic-chemistry/atomic-mass-unit.html Atomic Mass Out of these the mass of electrons is infinitesimally s... -
Practice Problems: Net Charge, Mass Number, Atomic Number
Practice Problems: Net Charge, Mass Number, Atomic NumberPractice Problems: Net Charge, Mass Number, Atomic Number
Need help? Ask me your questions here: http://vespr.org/videos/5130b7d29d53443c3bd593d4 Practice and example problems to help you learn how to determine and ... -
What's the Difference between Mass Number and Atomic Mass?
What's the Difference between Mass Number and Atomic Mass?What's the Difference between Mass Number and Atomic Mass?
Need help? Ask me your questions here: http://vespr.org/videos/5130b7d19d53443c3bd5938d What's the difference between mass number and atomic mass? Mass numbe... -
GCSE Science Revision - Atomic Number and Mass Number
GCSE Science Revision - Atomic Number and Mass NumberGCSE Science Revision - Atomic Number and Mass Number
-
Atomic Number and Mass Number.mov
Atomic Number and Mass Number.movAtomic Number and Mass Number.mov
Lesson for Chemistry I, General Chemistry I, and Honors Chemistry I. How to interpret atomic numbers and mass numbers to calculate the number of neutrons in ... -
Effective atomic numbers
Effective atomic numbersEffective atomic numbers
-
How to Graph the Atomic Radii & Atomic Number : Chemistry and Physics Calculations
How to Graph the Atomic Radii & Atomic Number : Chemistry and Physics CalculationsHow to Graph the Atomic Radii & Atomic Number : Chemistry and Physics Calculations
Subscribe Now: http://www.youtube.com/subscription_center?add_user=ehoweducation Watch More: http://www.youtube.com/ehoweducation Graphing the atomic radii a...
- Atomic mass
- Atomic nucleus
- Atomic number
- Atomic theory
- Atomic weight
- Bohr model
- Charge number
- Chemical bonding
- Chemical element
- Chemistry
- Dmitri Mendeleev
- Electric charge
- Electron
- Electron shell
- Ernest Rutherford
- German language
- Hafnium
- Half-life
- Henry Moseley
- Iodine
- Island of stability
- Isotope
- Lanthanide
- Lanthanum
- Lutetium
- Mass defect
- Mass number
- Moseley's law
- Negligible
- Neutron
- Neutron number
- Periodic table
- Physics
- Proton
- Prout's hypothesis
- Quantum mechanics
- Rutherford model
- Tellurium
- Valence shell
- X-ray tube
-
Atomic Number, Mass Number, and Net Charge
Atomic Number, Mass Number, and Net ChargeAtomic Number, Mass Number, and Net Charge
Need help? Ask me your questions here: http://vespr.org/videos/5130b7d19d53443c3bd593b5 How do you calculate and determine atomic number, mass number, and ne... -
Atomic Number and Mass Number | Chemistry | the virtual school
Atomic Number and Mass Number | Chemistry | the virtual schoolAtomic Number and Mass Number | Chemistry | the virtual school
How do we tell elements apart from each other? Find out in this video from the Properties of Matter chapter of the Virtual School GCSE Chemistry. This is par... -
How to Determine the ATOMIC NUMBER & MASS NUMBER - CLEAR & SIMPLE
How to Determine the ATOMIC NUMBER & MASS NUMBER - CLEAR & SIMPLEHow to Determine the ATOMIC NUMBER & MASS NUMBER - CLEAR & SIMPLE
-
Atomic number and Mass number of an atom - Science
Atomic number and Mass number of an atom - ScienceAtomic number and Mass number of an atom - Science
This is a science video for grade 8-9th students that explains Atomic Number and Mass Number of an atom and how they are linked to the electrons, protons and... -
Atomic Number - Isotopes
Atomic Number - IsotopesAtomic Number - Isotopes
Science Help at Brightstorm! http://brightstorm.com/science The meaning and uses of atomic numbers. -
CHEM 3.1.3 Atomic mass and Atomic Number
CHEM 3.1.3 Atomic mass and Atomic NumberCHEM 3.1.3 Atomic mass and Atomic Number
-
Atomic Numbers, Mass Numbers and Isotopes - Chemistry Tutorial
Atomic Numbers, Mass Numbers and Isotopes - Chemistry TutorialAtomic Numbers, Mass Numbers and Isotopes - Chemistry Tutorial
https://www.thechemistrysolution.com A chemistry tutorial designed to explain the definition and difference between atomic numbers and mass numbers as well a... -
Atomic Number, Atomic Mass and Mass Number
Atomic Number, Atomic Mass and Mass NumberAtomic Number, Atomic Mass and Mass Number
Check out us at:http://chemistry.tutorvista.com/inorganic-chemistry/atomic-mass-unit.html Atomic Mass Out of these the mass of electrons is infinitesimally s... -
Practice Problems: Net Charge, Mass Number, Atomic Number
Practice Problems: Net Charge, Mass Number, Atomic NumberPractice Problems: Net Charge, Mass Number, Atomic Number
Need help? Ask me your questions here: http://vespr.org/videos/5130b7d29d53443c3bd593d4 Practice and example problems to help you learn how to determine and ... -
What's the Difference between Mass Number and Atomic Mass?
What's the Difference between Mass Number and Atomic Mass?What's the Difference between Mass Number and Atomic Mass?
Need help? Ask me your questions here: http://vespr.org/videos/5130b7d19d53443c3bd5938d What's the difference between mass number and atomic mass? Mass numbe... -
GCSE Science Revision - Atomic Number and Mass Number
GCSE Science Revision - Atomic Number and Mass NumberGCSE Science Revision - Atomic Number and Mass Number
-
Atomic Number and Mass Number.mov
Atomic Number and Mass Number.movAtomic Number and Mass Number.mov
Lesson for Chemistry I, General Chemistry I, and Honors Chemistry I. How to interpret atomic numbers and mass numbers to calculate the number of neutrons in ... -
Effective atomic numbers
Effective atomic numbersEffective atomic numbers
-
How to Graph the Atomic Radii & Atomic Number : Chemistry and Physics Calculations
How to Graph the Atomic Radii & Atomic Number : Chemistry and Physics CalculationsHow to Graph the Atomic Radii & Atomic Number : Chemistry and Physics Calculations
Subscribe Now: http://www.youtube.com/subscription_center?add_user=ehoweducation Watch More: http://www.youtube.com/ehoweducation Graphing the atomic radii a... -
2.1.5 Protons/neutrons/electrons in atoms/ions from mass/atomic number and charge IB Chemistry SL
2.1.5 Protons/neutrons/electrons in atoms/ions from mass/atomic number and charge IB Chemistry SL2.1.5 Protons/neutrons/electrons in atoms/ions from mass/atomic number and charge IB Chemistry SL
For atoms the atomic number (smaller of the two numbers) is the number of protons which equals the number of electrons. The larger number is the mass number,... -
QI - Atomic Number Wheelies
QI - Atomic Number WheeliesQI - Atomic Number Wheelies
from Series C, Episode 3 with Sean Lock, Jimmy Carr and Rory McGrath. -
2.1.3 Define the terms mass number (A), atomic number (Z) and isotopes of an element IB Chemistry SL
2.1.3 Define the terms mass number (A), atomic number (Z) and isotopes of an element IB Chemistry SL2.1.3 Define the terms mass number (A), atomic number (Z) and isotopes of an element IB Chemistry SL
Mass # = # of protons AND # of neutrons in an atom Atomic # = # of protons in an atom Isotopes of an element = Atoms of an element with the same atomic numbe... -
Atomic mass, mass number and isotopes
Atomic mass, mass number and isotopesAtomic mass, mass number and isotopes
http://www.sciencerevisionvideo.com In this video clip I will be looking at the relationships between the atomic mass of elements, their mass numbers, and wh... -
Attempts At: Atomic Number 78 - Trials Evolution Achievement Guide (Part 1)
Attempts At: Atomic Number 78 - Trials Evolution Achievement Guide (Part 1)Attempts At: Atomic Number 78 - Trials Evolution Achievement Guide (Part 1)
A new idea I got and thought you may like. Enjoy step one toward Atomic Number 78! Please suggest any ideas you have for any type of video. If you enjoyed, a... -
Atomic Structure Song
Atomic Structure SongAtomic Structure Song
Here is a song I created to help my 6th grade students study. I hope you enjoy. Positively charged protons (wow) In nucleus or heart of atoms Neutron particles no charge (wow) Share the space just like they own it You count protons in atoms, you see Atomic number is found indeed And they dance all night in atomic structure Protons and neutrons, nucleus or center Out in shells there they go, electrons are layered 'Cause they dance all night in atomic structure The shells are 2, 8, 18 And then it goes 32 I think it goes, Ooohhh Set up in the shells not rows (wow) Negatively charged electron Size of atoms by the cloud (the atoms by the clou -
ChemTutor: Atomic Number, Mass Number, Isotopes
ChemTutor: Atomic Number, Mass Number, IsotopesChemTutor: Atomic Number, Mass Number, Isotopes
A short lecture on how to determine the number of protons, nuetrons, and electrons using atomic numbers and mass numbers. I also explain the difference betwe... -
Nucleic Symbol - Atomic Notation - Atomic Number and Mass Number - www.whitwellhigh.com
Nucleic Symbol - Atomic Notation - Atomic Number and Mass Number - www.whitwellhigh.comNucleic Symbol - Atomic Notation - Atomic Number and Mass Number - www.whitwellhigh.com
Nucleic Symbol - Atomic Notation - Atomic Number and Mass Number | Chemistry Whitwell High School UTC - University of Tennessee at Chattanooga www.whitwellhi... -
Chemistry Structure of Atom part 11 (Atomic mass & atomic number) CBSE class 11 XI
Chemistry Structure of Atom part 11 (Atomic mass & atomic number) CBSE class 11 XIChemistry Structure of Atom part 11 (Atomic mass & atomic number) CBSE class 11 XI
Chemistry Structure of Atom part 11 (Atomic mass & atomic number) CBSE class 11 XI.

- Duration: 6:27
- Updated: 07 Aug 2013
- published: 21 Sep 2012
- views: 6591
- author: Tyler DeWitt

- Duration: 3:23
- Updated: 19 Aug 2013
- published: 31 Aug 2012
- views: 11023
- author: The Virtual School

- Duration: 10:15
- Updated: 17 Jan 2014
http://wn.com/How_to_Determine_the_ATOMIC_NUMBER_&_MASS_NUMBER_-_CLEAR_&_SIMPLE
- published: 17 Jan 2014
- views: 0

- Duration: 2:05
- Updated: 15 Apr 2013
- published: 08 Nov 2012
- views: 9115
- author: elearnin

- Duration: 4:47
- Updated: 19 Jul 2013
- published: 03 Sep 2010
- views: 29034
- author: Brightstorm

- Duration: 10:12
- Updated: 20 Jun 2013
http://wn.com/CHEM_3.1.3_Atomic_mass_and_Atomic_Number

- Duration: 11:24
- Updated: 16 Aug 2013
- published: 18 Nov 2012
- views: 2189
- author: TheChemistrySolution

- Duration: 6:21
- Updated: 18 Apr 2013
- published: 12 Mar 2013
- views: 194
- author: TutorVista

- Duration: 4:57
- Updated: 13 Aug 2013
- published: 29 Sep 2012
- views: 3265
- author: Tyler DeWitt

- Duration: 8:58
- Updated: 17 Aug 2013
- published: 03 Oct 2012
- views: 7746
- author: Tyler DeWitt

- Duration: 3:52
- Updated: 28 May 2013
http://wn.com/GCSE_Science_Revision_-_Atomic_Number_and_Mass_Number

- Duration: 6:12
- Updated: 15 Aug 2013
- published: 15 Feb 2010
- views: 21941
- author: Chem2Farr
- published: 03 Apr 2013
- views: 6

- Duration: 4:12
- Updated: 12 Jun 2013
- published: 28 Dec 2012
- views: 125
- author: eHowEducation

- Duration: 3:17
- Updated: 11 Jul 2013
- published: 04 Mar 2012
- views: 5269
- author: Richard Thornley

- Duration: 1:08
- Updated: 25 Jul 2013
- published: 15 Sep 2011
- views: 28089
- author: MrOggtheclever

- Duration: 2:04
- Updated: 15 Jun 2013
- published: 09 Sep 2011
- views: 8697
- author: Richard Thornley

- Duration: 5:14
- Updated: 29 Jul 2013
- published: 23 Jul 2012
- views: 1240
- author: ScienceRevisionVideo

- Duration: 9:58
- Updated: 11 Jul 2013
- published: 27 Mar 2013
- views: 173
- author: Shawnthebro

- Duration: 3:15
- Updated: 02 Sep 2013
- published: 02 Sep 2013
- views: 494

- Duration: 9:37
- Updated: 10 Jul 2013
- published: 13 Nov 2012
- views: 78
- author: TutorChem

- Duration: 9:55
- Updated: 04 Aug 2013
- published: 30 Mar 2010
- views: 6385
- author: Johnny Cantrell

- Duration: 11:30
- Updated: 15 Aug 2013
- published: 02 Dec 2012
- views: 1590
- author: ExamFearVideos

Atomic Number, Mass Number, and Net Charge
Need help? Ask me your questions here: http://vespr.org/videos/5130b7d19d53443c3bd593b5 How do you calculate and determine atomic number, mass number, and ne...- published: 21 Sep 2012
- views: 6591
- author: Tyler DeWitt

Atomic Number and Mass Number | Chemistry | the virtual school
How do we tell elements apart from each other? Find out in this video from the Properties of Matter chapter of the Virtual School GCSE Chemistry. This is par...- published: 31 Aug 2012
- views: 11023
- author: The Virtual School

Atomic number and Mass number of an atom - Science
This is a science video for grade 8-9th students that explains Atomic Number and Mass Number of an atom and how they are linked to the electrons, protons and...- published: 08 Nov 2012
- views: 9115
- author: elearnin

Atomic Number - Isotopes
Science Help at Brightstorm! http://brightstorm.com/science The meaning and uses of atomic numbers.- published: 03 Sep 2010
- views: 29034
- author: Brightstorm


Atomic Numbers, Mass Numbers and Isotopes - Chemistry Tutorial
https://www.thechemistrysolution.com A chemistry tutorial designed to explain the definition and difference between atomic numbers and mass numbers as well a...- published: 18 Nov 2012
- views: 2189
- author: TheChemistrySolution

Atomic Number, Atomic Mass and Mass Number
Check out us at:http://chemistry.tutorvista.com/inorganic-chemistry/atomic-mass-unit.html Atomic Mass Out of these the mass of electrons is infinitesimally s...- published: 12 Mar 2013
- views: 194
- author: TutorVista

Practice Problems: Net Charge, Mass Number, Atomic Number
Need help? Ask me your questions here: http://vespr.org/videos/5130b7d29d53443c3bd593d4 Practice and example problems to help you learn how to determine and ...- published: 29 Sep 2012
- views: 3265
- author: Tyler DeWitt

What's the Difference between Mass Number and Atomic Mass?
Need help? Ask me your questions here: http://vespr.org/videos/5130b7d19d53443c3bd5938d What's the difference between mass number and atomic mass? Mass numbe...- published: 03 Oct 2012
- views: 7746
- author: Tyler DeWitt

Atomic Number and Mass Number.mov
Lesson for Chemistry I, General Chemistry I, and Honors Chemistry I. How to interpret atomic numbers and mass numbers to calculate the number of neutrons in ...- published: 15 Feb 2010
- views: 21941
- author: Chem2Farr

How to Graph the Atomic Radii & Atomic Number : Chemistry and Physics Calculations
Subscribe Now: http://www.youtube.com/subscription_center?add_user=ehoweducation Watch More: http://www.youtube.com/ehoweducation Graphing the atomic radii a...- published: 28 Dec 2012
- views: 125
- author: eHowEducation

2.1.5 Protons/neutrons/electrons in atoms/ions from mass/atomic number and charge IB Chemistry SL
For atoms the atomic number (smaller of the two numbers) is the number of protons which equals the number of electrons. The larger number is the mass number,...- published: 04 Mar 2012
- views: 5269
- author: Richard Thornley

QI - Atomic Number Wheelies
from Series C, Episode 3 with Sean Lock, Jimmy Carr and Rory McGrath.- published: 15 Sep 2011
- views: 28089
- author: MrOggtheclever

2.1.3 Define the terms mass number (A), atomic number (Z) and isotopes of an element IB Chemistry SL
Mass # = # of protons AND # of neutrons in an atom Atomic # = # of protons in an atom Isotopes of an element = Atoms of an element with the same atomic numbe...- published: 09 Sep 2011
- views: 8697
- author: Richard Thornley

Atomic mass, mass number and isotopes
http://www.sciencerevisionvideo.com In this video clip I will be looking at the relationships between the atomic mass of elements, their mass numbers, and wh...- published: 23 Jul 2012
- views: 1240
- author: ScienceRevisionVideo

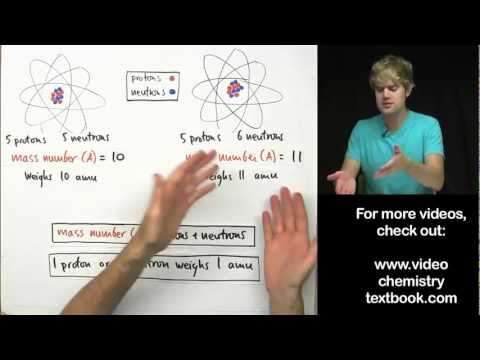
In chemistry and physics, the atomic number (also known as the proton number) is the number of protons found in the nucleus of an atom and therefore identical to the charge number of the nucleus. It is conventionally represented by the symbol Z. The atomic number uniquely identifies a chemical element. In an atom of neutral charge, the atomic number is also equal to the number of electrons.
The atomic number, Z, should not be confused with the mass number, A, which is the total number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus of an atom. The number of neutrons, N, is known as the neutron number of the atom; thus, A = Z + N. Since protons and neutrons have approximately the same mass (and the mass of the electrons is negligible for many purposes), and the mass defect is usually very small compared to the mass, the atomic mass of an atom is roughly equal to A.
Atoms having the same atomic number Z but different neutron number N, and hence different atomic mass, are known as isotopes. Most naturally occurring elements exist as a mixture of isotopes, and the average atomic mass of this mixture determines the element's atomic weight.
This article is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported License, which means that you can copy and modify it as long as the entire work (including additions) remains under this license.
![[u'Effective atomic numbers'][0].replace('](http://web.archive.org./web/20140903022055im_/http://i.ytimg.com/vi/xBwFbWnYF7U/0.jpg)
