
Correlogram
In the analysis of data, a correlogram is an image of correlation statistics. For example, in time series analysis, a correlogram, also known as an autocorrelation plot, is a plot of the sample autocorrelations  versus
versus 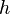 (the time lags).
(the time lags).
If cross-correlation is used, the result is called a cross-correlogram. The correlogram is a commonly used tool for checking randomness in a data set. This randomness is ascertained by computing autocorrelations for data values at varying time lags. If random, such autocorrelations should be near zero for any and all time-lag separations. If non-random, then one or more of the autocorrelations will be significantly non-zero.
In addition, correlograms are used in the model identification stage for Box–Jenkins autoregressive moving average time series models. Autocorrelations should be near-zero for randomness; if the analyst does not check for randomness, then the validity of many of the statistical conclusions becomes suspect. The correlogram is an excellent way of checking for such randomness.
Podcasts:

