
- Order:
- Duration: 3:21
- Published: 03 Oct 2009
- Uploaded: 01 Sep 2011
- Author: rodolfo1114









![[ Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors ] ~ 2nd Half [ Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors ] ~ 2nd Half](http://web.archive.org./web/20110907164704im_/http://i.ytimg.com/vi/k2ewX6ctcHM/0.jpg)
![[ Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors ] ~ 1st Half [ Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors ] ~ 1st Half](http://web.archive.org./web/20110907164704im_/http://i.ytimg.com/vi/H5QpgkLUapI/0.jpg)

![Sintax - Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitor [CLIP] Sintax - Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitor [CLIP]](http://web.archive.org./web/20110907164704im_/http://i.ytimg.com/vi/JWOParc7Ltk/0.jpg)








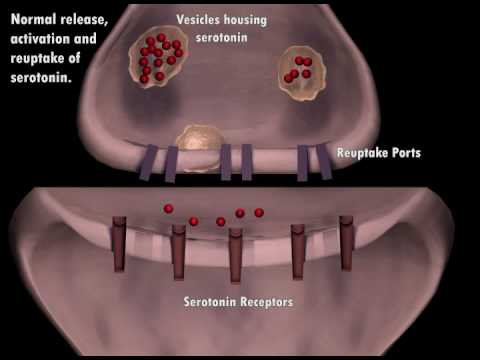













A serotonin reuptake inhibitor (SRI) is a type of drug which acts as a reuptake inhibitor for the neurotransmitter serotonin (5-hydroxytryptamine (5-HT)) by blocking the action of the serotonin transporter (SERT). This in turn leads to increased extracellular concentrations of serotonin and therefore an increase in serotonergic neurotransmission.
SRIs are not synonymous with selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs), as the latter term is usually used to describe the class of antidepressants of the same name, and, because SRIs, unlike SSRIs, can be either selective or nonselective in their action. For example, cocaine, which nonselectively inhibits the reuptake of serotonin, norepinephrine, and dopamine, can obviously be called an SRI, but not an SSRI.
It should be noted, however, that many of these effects are dependent on whether the administration of the SRI is acute or chronic. As an example, acute ingestion typically does not result in a mood lift, and chronic administration usually does not result in any sort of psychedelia whatsoever. Additionally, many of these properties are also dependent on whether the SRI in question is capable of crossing the blood-brain-barrier (BBB). Those that do not will only produce peripheral effects.
; Street Drugs
Category:Monoamine reuptake inhibitors Category:Drugs acting on the nervous system
This text is licensed under the Creative Commons CC-BY-SA License. This text was originally published on Wikipedia and was developed by the Wikipedia community.
