2:18

Hanja (漢字 한자) Part 1
The first lesson to Hanja (한자) or the Chinese characters previously used :) ...
published: 08 Jul 2010
Author: shinjeongsuh
Hanja (漢字 한자) Part 1
The first lesson to Hanja (한자) or the Chinese characters previously used :) No negative comments plz :) WEBSITE: teamkorean.webs.com
6:37

Korean Alphabet Script. Hangul Hanja History and Origin
www.koreanovernight.com Korean Alphabet Script. Hangul Hanja History and Origin...
published: 23 Nov 2008
Author: koreancrashcourse
Korean Alphabet Script. Hangul Hanja History and Origin
www.koreanovernight.com Korean Alphabet Script. Hangul Hanja History and Origin
1:56

Hanja
Answering a question about the use of Hanja, or the Chinse script, in Korea....
published: 16 Nov 2011
Author: theqirangervlog
Hanja
Answering a question about the use of Hanja, or the Chinse script, in Korea.
8:25
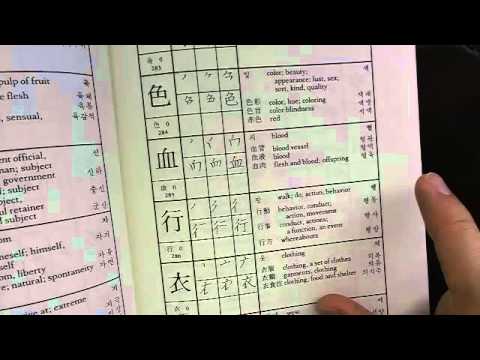
Korean Characters 한자 (Hanja)
Showing A Guide to Korean Characters with a few examples of indigenous and Chinese reading...
published: 08 Jul 2012
Author: Tommy McDonald
Korean Characters 한자 (Hanja)
Showing A Guide to Korean Characters with a few examples of indigenous and Chinese readings and their comparisons with Japanese
1:59

06. chloe knows her hanja (aug. 24, 2008)
chloe knows her hanja (video taken on sunday, aug. 24, 2008). chloe knows more hanja than ...
published: 25 Aug 2008
Author: handlchoi
06. chloe knows her hanja (aug. 24, 2008)
chloe knows her hanja (video taken on sunday, aug. 24, 2008). chloe knows more hanja than mommy and daddy......
1:03

learn hanja 1 lesson: 鵑 두견이 cuckoo
I downloaded this video illegally. They will kill me for posting such wonderful videos. If...
published: 30 Jun 2008
Author: Ilovemengzi
learn hanja 1 lesson: 鵑 두견이 cuckoo
I downloaded this video illegally. They will kill me for posting such wonderful videos. If you would liek to buy it you would have to pay 1000 €.
3:31

Hanja - esmalte vermelho
Eu seco o esmalte vermelho das minhas mãos Espero do telefone uma ligaç&atil...;
published: 31 Jan 2012
Author: singeranallu
Hanja - esmalte vermelho
Eu seco o esmalte vermelho das minhas mãos Espero do telefone uma ligação Eu espero mais de mim do que correr atrás Porque já sei que você não quer mais Eu seco os sentimentos do meu coração Mesmo querendo sim eu vou dizer que não Mesmo sabendo que eu não preciso tanto de você Há coisas que são dificeis de esquecer Eu não vou chorar não vou mais tentar Eu não vou sofrer Vou voltar a viver E aos poucos vou Me acostumar A não ficar feliz Quando te ver Vou encontrar alguem que me faça feliz Como você nunca quis fazer.
4:32

How to input Korean hanja(kanji)
How to input Korean Hanja(Kanji) Easier. Few days after I saw a video uploaded by zacu00, ...
published: 30 Aug 2009
Author: asatmissile
How to input Korean hanja(kanji)
How to input Korean Hanja(Kanji) Easier. Few days after I saw a video uploaded by zacu00, I try making this video...
8:17

Përrallë me Tupan - Zet'hanja & Mafia
Musafir special: Florent Boshnjaku...
published: 31 May 2012
Author: ValaMalaTV
Përrallë me Tupan - Zet'hanja & Mafia
Musafir special: Florent Boshnjaku
3:48

Hanja - Separation
Cantando uma das minhas músicas: Separation. O vídeo tem a letra ea tradu&cc...;
published: 03 Apr 2011
Author: singeranallu
Hanja - Separation
Cantando uma das minhas músicas: Separation. O vídeo tem a letra ea tradução
9:01

DOBRENJI ne hanja te kretes
...
published: 03 Sep 2010
Author: skrapalliu
DOBRENJI ne hanja te kretes
3:00

Twinkle (SMTOWN LA Taeyeon focus) [Vietsub + Hanja]
cr: flying petals / kimtaeyeon.co.kr FIXED AUDIO :)...
published: 30 May 2012
Author: Gevy Lee
Twinkle (SMTOWN LA Taeyeon focus) [Vietsub + Hanja]
cr: flying petals / kimtaeyeon.co.kr FIXED AUDIO :)
4:50

Bodo super action movie clip-****RWIKA HANJA ****
dubbed of Magnificient seven.... after 4:30 subtiles in bodo..!..enjoy !!!!...
published: 22 Jun 2011
Author: detsung69
Bodo super action movie clip-****RWIKA HANJA ****
dubbed of Magnificient seven.... after 4:30 subtiles in bodo..!..enjoy !!!!
6:39

Wi Nwngswr Laimwn Bwiswni Jwhwlao Hanja!
...
published: 30 Jul 2009
Author: Charanjit82
Wi Nwngswr Laimwn Bwiswni Jwhwlao Hanja!
Youtube results:
1:33

Hanja Book Introduction 한자책 소개
My introduction of the "Living Korean" series of textbooks. book.naver.com...
published: 08 Jun 2008
Author: austinfd
Hanja Book Introduction 한자책 소개
My introduction of the "Living Korean" series of textbooks. book.naver.com
9:31

dobrenji ne hanja te KRETES
...
published: 25 Feb 2012
Author: kriskrapalliu
dobrenji ne hanja te KRETES
2:26

Second Life - Hanja by ZiggyZ Beam
Hey all here is another video of SL Hope you all enjoy it. ziggyz-production.webs.com...
published: 01 Feb 2009
Author: Zaneer Zareen
Second Life - Hanja by ZiggyZ Beam
Hey all here is another video of SL Hope you all enjoy it. ziggyz-production.webs.com
1:18

[G-STAR 2010] 'Magic Cheonjamun Hanja Battle' to enjoy at mart
A card battle game developed by pure domestic technology appears at Amusement Game Booth o...
published: 20 Nov 2010
Author: avingusa
[G-STAR 2010] 'Magic Cheonjamun Hanja Battle' to enjoy at mart
A card battle game developed by pure domestic technology appears at Amusement Game Booth of global game exhibition 'G-STAR2010' on November 18th-21th at BEXCO, Busan











![Can't stop loving you, Taeyeon [Vietsub + Hanja] Can't stop loving you, Taeyeon [Vietsub + Hanja]](http://web.archive.org./web/20121014082133im_/http://i.ytimg.com/vi/mSot_6QYMyA/0.jpg)






![The Taedong River (Hangul:대동강/Hanja:大同江) is a large river in North Korea. It rises in the Rangrim Mountains of the country's north. It then flows southwest into Korea Bay at Namp'o.[1] In between, it runs through the country's capital, Pyongyang. Along the river are landmarks such as the Juche Tower and Kim Il-sung Square. The Taedong River (Hangul:대동강/Hanja:大同江) is a large river in North Korea. It rises in the Rangrim Mountains of the country's north. It then flows southwest into Korea Bay at Namp'o.[1] In between, it runs through the country's capital, Pyongyang. Along the river are landmarks such as the Juche Tower and Kim Il-sung Square.](http://web.archive.org./web/20121014082133im_/http://cdn2.wn.com/pd/ee/fc/ff1dcd4c75612efbc4588c501720_small.jpg)

![Kang Gangnyeongjeon (Hangul: 강녕전; Hanja: 康寧殿), also called Gangnyeongjeon Hall, is a building used as the king's main sleeping and living quarters [3] The building contains the king's bed chamber and was first constructed in 1359 the fourth year of King Taejo Kang Gangnyeongjeon (Hangul: 강녕전; Hanja: 康寧殿), also called Gangnyeongjeon Hall, is a building used as the king's main sleeping and living quarters [3] The building contains the king's bed chamber and was first constructed in 1359 the fourth year of King Taejo](http://web.archive.org./web/20121014082133im_/http://cdn2.wn.com/pd/52/28/484d350510d5c2f42ff25cec2582_small.jpg)












