6:16

Cell Membranes and Cell Walls | Cell Biology
Cell Membranes and Cell Walls | Cell Biology
Segment from the program Cell Membranes: The Boundaries of Life. To purchase this program please visit www.greatpacificmedia.com
6:08

Cell Membrane - Cell Wall
Cell Membrane - Cell Wall
Free Science Help at Brightstorm! brightstorm.com The structure and composition of the cell membrane and of cell wall.
11:30

Chapter 7 Podcast 6: Cytoskeleton & Cell Wall
Chapter 7 Podcast 6: Cytoskeleton & Cell Wall
This podcast covers the structure & function of both the cytoskeleton and the cell wall of bacteria, fungi, and plants.
0:59

Cell wall and Plasma Membrane are Two Distinct Structures
Cell wall and Plasma Membrane are Two Distinct Structures
Check us out at www.tutorvista.com A cell wall is a tough, usually flexible but sometimes fairly rigid layer that surrounds some types of cells. It is located outside the cell membrane and provides these cells with structural support and protection, and also acts as a filtering mechanism. A major function of the cell wall is to act as a pressure vessel, preventing over-expansion when water enters the cell. They are found in plants, bacteria, fungi, algae, and some archaea. Animals and protozoa do not have cell walls. The materials in a cell wall vary between species, and in plants and fungi also differ between cell types and developmental stages. In plants, the strongest component of the complex cell wall is a carbohydrate called cellulose, which is a polymer of glucose. In bacteria, peptidoglycan forms the cell wall. Archaean cell walls have various compositions, and may be formed of glycoprotein S-layers, pseudopeptidoglycan, or polysaccharides. Fungi possess cell walls made of the glucosamine polymer chitin, and algae typically possess walls made of glycoproteins and polysaccharides. Unusually, diatoms have a cell wall composed of silicic acid. Often, other accessory molecules are found anchored to the cell wall. The plasma membrane consists of both lipids and proteins. The fundamental structure of the membrane is the phospholipid bilayer, which forms a stable barrier between two aqueous compartments. In the case of the plasma membrane, these compartments are the <b>...</b>
0:33

Cell Wall Deficient bacteria
Cell Wall Deficient bacteria
This micrographic clip was taken from a patient with fibromyalgia, bipolar disorder and multiple chronic illness symptoms. The sample shows emerging microbes from cells, after decay process begun--6 hours after initial sample was taken.
4:39

Plasma Membrane & Cell Wall
Plasma Membrane & Cell Wall
Mr Zhang Bergen County Academies Honors Biology Section 6 Plasma Membrane & Cell Wall
0:55

Plant Cell Wall
Plant Cell Wall
Simple 3D visualizations of Plant Cell Wall , or extra cellular matrix ECM
3:57

Cell Walls Baby (Ice Ice Baby Biology Remix) CELL WALL TUTORIAL
Cell Walls Baby (Ice Ice Baby Biology Remix) CELL WALL TUTORIAL
Music Video on Chapter 4 section 22 that I made for Biology Class. Basically the most entertaining Tutorial for cell walls ever. Cell Walls Baby!
1:12

Different Between Plant Cell and Animal Cell
Different Between Plant Cell and Animal Cell
Check us out at www.tutorvista.com Plant cells are eukaryotic cells that differ in several key respects from the cells of other eukaryotic organisms. Their distinctive features include: •A large central vacuole, a water-filled volume enclosed by a membrane known as the tonoplast maintains the cell's turgor, controls movement of molecules between the cytosol and sap, stores useful material and digests waste proteins and organelles. •A cell wall composed of cellulose and hemicellulose, pectin and in many cases lignin, and secreted by the protoplast on the outside of the cell membrane. This contrasts with the cell walls of fungi (which are made of chitin), and of bacteria, which are made of peptidoglycan. •Specialised cell-cell communication pathways known as plasmodesmata, pores in the primary cell wall through which the plasmalemma and endoplasmic reticulum of adjacent cells are continuous. •Plastids, notably the chloroplasts which contain chlorophyll and the biochemical systems for light harvesting and photosynthesis, but also amyloplasts specialized for starch storage, elaioplasts specialized for fat storage and chromoplasts specialized for synthesis and storage of pigments. As in mitochondria, which have a genome encoding 37 genes plastids have their own genomes of about 100-120 unique genes and probably arose as prokaryotic endosymbionts living in the cells of an early eukaryotic ancestor of the land plants and algae. •Unlike animal cells, plant cells are stationary <b>...</b>
7:23

ß-Lactams: Mechanisms of Action and Resistance
ß-Lactams: Mechanisms of Action and Resistance
Developed and produced by www.MechanismsinMedicine.com Animation Description This animation starts with the explanation of bacterial cell wall synthesis, the process targeted by ß-Lactams. Structurally, most bacteria consist of a cell membrane surrounded by a cell wall and, for some bacteria, an additional outer layer. Internal to the cell membrane is the cytoplasm which contains ribosomes, a nuclear region and in some cases granules and/or vesicles. Depending on the bacterial species, a number of different external structures may be found such as a capsule, flagella and pili. In gram negative bacteria, the gap between the cell membrane and the cell wall is known as the periplasmic space. Most gram positive bacteria do not possess a periplasmic space but have only periplasm where metabolic digestion occurs and new cell peptidoglycan is attached. Peptidoglycan, the most important component of the cell wall, is a polymer made of N-acetyl muramic acid alternating with N-acetyl glucosamine which are cross-linked by chains of four amino acids. The function of the bacterial cell wall is to maintain the characteristic shape of the organism and to prevent the bacterium from bursting when fluid flows into the organism by osmosis. Synthesis of peptidoglycan and ultimately the bacterial cell wall occurs in a number of stages. One of the first stages is the addition of 5 amino acids to N-acetyl muramic acid. Next, N-acetyl glucosamine is added to the N-acetyl muramic acid to form a <b>...</b>
3:09
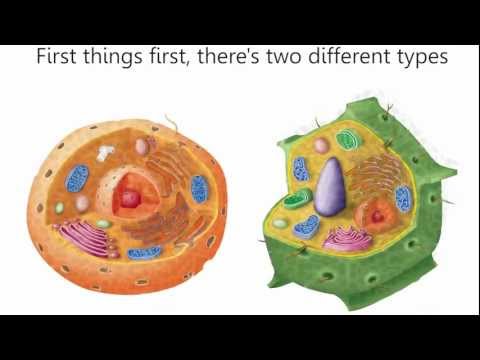
Cells Cells - Parts of the Cell Rap
Cells Cells - Parts of the Cell Rap
This rap was created for a 6th grade science classroom to teach about the different parts of a cell. With its catchy rhythm and rhymes, students of all learning styles and abilities will be able to learn about cells and their functions while having fun! "Cells, Cells" Original Rap by Ms. Quitmeyer Today's the day were gonna learn about the cell If I teach it okay, you'll know it very well So listen up 6th graders- -no room left for haters- lets talk about the building blocks of life- cells that make us. Chorus: Cells, cells they're made of organelles Try to pull a fast one, the cytoplasm gels The nucleus takes over controllin' everything The party don't stop 'till the membrane blocks the scene Inside the vacuole we can float around for hours Running round with chloroplasts, lovin' sunlight showers Cells, cells, they're made of organelles First things first, there's two different types- animal and plant cells that make up all life. The little things that make up microscopic cells, The main structures- yeah, we call them organelles. Now let's break it down and get some information- How do cells work? It's a crazy combination! -Chorus- The cell membrane is the border patrol, Who can cross over? The membrane lets 'em know The gooey stuff inside, is called the cytoplasm It holds the organelles- don't worry, plasm-has 'em! In the middle of the cell you'll find the big brain, The nucleus surrounded by nuclear membrane Don't forget the vacuole filled up with water It's a basic <b>...</b>
3:34

Cells From Other Cells Song
Cells From Other Cells Song
Cell Theory/ Part of a Cell Song. Here is a video I created for my 6th grade science students to help them study.I hope you enjoy. Hook saw small rooms Or pores, or Cells that look dividing Inside all Cells Organelles float in Cytoplasm In all Plant Cells The outside is a Wall Around the Cell Is like a skin the Cellular Membrane Its job is to Let particles go out, in, out, in Chloroplasts help plants to capture energy For Photosynthesis Chorus Looking inside Cells They are the things that make up life Cell Theory's amazing Cells from other Cells All living things The whole world's made from basic Cells Cell Theory's amazing Cells from other Cells The Nucleus Is like the major control center Nuclear Membrane Has pores to only let in some things Inside's the Chromatin Genetic instructions Nucleolus is a structure Where Ribosomes are made Protein is sent to the Endoplasmic Reticulum The Golgi Bodies package The material And send it around Chorus Mitocondria Is a rod shaped powerhouse of the cell It produces energy For functions to carry out Then there's Vacuoles Storage for food and H2O And then Lysosomes That break food pieces down All Living things Are composed of cells The basic unit Cells from other Cells Chorus Looking inside Cells They are the things that make up life Cell Theory's amazing Cells from other Cells All living things The whole world's made from basic Cells Cell Theory's amazing Cells from other Cells Yeah!
3:53

Raw Foods - All About Juicing
Raw Foods - All About Juicing
Learn Guitar FREE on iPhone & iPad: bit.ly In this video, Mahalo expert Kristina Jackson conveys her broad knowledge of juicing. What Can Be Juiced? --------------------------------------------------------------------- * Vegetables * Leafy greens * Root vegetables * Fruits Different Types of Juicers --------------------------------------------------------------------- A centrifugal juicer is the most common type that you see in stores. It spins at high speeds. During the spinning motion, the vegetables that you push down the chute are ground to a pulp. The juice then pours out another spout.A juice press is manually operated, so no electricity is needed. Pressing causes the least oxidation of the juicing methods, and produces a pulp-free juice, since the juice is strained through cheese cloth. This type of juicer juices fruits (especially soft ones) better than other types.c A twin-gear juicer has two gears that press the juice out of the produce. It is very similar to two gears in an automobile transmission that mesh together. The produce is pushed (with some force) into the two gears, which first shreds, and then squeezes the produce. These machines are best for juicing vegetables since they rely on the fibrous cell wall to push the pulp through. As a bonus, these machines will also juice wheatgrass. cA masticating juicer grinds fruits and vegetables and squeezes out the juice. It works at low speeds with no spinning action, so it tends to be more efficient. This kind <b>...</b>
2:25

fantastic vesicle traffic
fantastic vesicle traffic
The miracle of life relies in its cells. The root hair is one of the fastest growing cells in the plant. To allow this rapid growth, continuous delivery of membrane and cell wall material to the growing tip of the hair cell is required. A component part of this material is protein, which is synthesized by ribosomes along the Endoplasmic Reticulum, modified in the Golgi apparatus and packaged into vesicles. The vesicles are finally delivered to the plasma membrane by motor proteins along the cytoskeleton. How do vesicles find their target membranes? The specificity of target recognition is mediated by the interaction of v-SNARE proteins on the vesicle surface with t-SNARE proteins on the target membrane. Among others, small G-proteins regulate this process. One group of small G-proteins is the so-called RabGTPases. To visualize the distribution of such RabGTPase proteins within the cell, they are tagged with the Green Fluorescent Protein. The video shows the germination of Arabidopsis thaliana seeds, zooming in on the root hairs, which display movement of fluorescent vesicles through the cytoplasm, and finally one can see an animation of myosin VI motor proteins dragging the fluorescently marked vesicles along actin filaments. This video is part of the videocontest at www.chlorofilms.org
3:48

Cytokinesis Animal Plant | Biology | Genetics
Cytokinesis Animal Plant | Biology | Genetics
To purchase this DVD please visit www.greatpacificmedia.com Segment from the program Cellular Reproduction: Mitosis, Cytokinesis, and the Cell Cycle DVD Description Our Mitosis DVD starts by introducing the cell cycle and briefly describing the process of binary fusion in prokaryotic cells before going on to a detailed look at the eukaryotic cell cycle from the G1, S and G2 phases of interphase through the prophase, metaphase, anaphase and telophase phases of mitosis. The difference between cytokinesis in animal and plant cells is then illustrated. The program concludes by explaining why an understanding of cellular division is critical to: conquering cancer, cloning organs, and perhaps even reversing aging.

























![The chemical compound silicon dioxide, also known as silica (from the Latin silex), is an oxide of silicon with a chemical formula of SiO2 and has been known for its hardness since antiquity. Silica is most commonly found in nature as sand or quartz, as well as in the cell walls of diatoms. Silica is the most abundant mineral in the Earth's crust.[1][2] Silica is manufactured in several forms including fused quartz, crystal, fumed silica (or pyrogenic silica, trademarked Aerosil or Cab-O-Sil), c The chemical compound silicon dioxide, also known as silica (from the Latin silex), is an oxide of silicon with a chemical formula of SiO2 and has been known for its hardness since antiquity. Silica is most commonly found in nature as sand or quartz, as well as in the cell walls of diatoms. Silica is the most abundant mineral in the Earth's crust.[1][2] Silica is manufactured in several forms including fused quartz, crystal, fumed silica (or pyrogenic silica, trademarked Aerosil or Cab-O-Sil), c](http://web.archive.org./web/20120419134544im_/http://cdn0.wn.com/pd/a8/e9/d1630cddae572cb8ad29dde5d568_small.jpg)




