- go to the top
- About WN
- Contact
- Feedback
- Privacy Policy
- © 2012 World News Inc., all Rights Reserved
-
Adam Smith

Adam Smith (baptised 16 June 1723 – died 17 July 1790 ) was a Scottish moral philosopher and a pioneer of political economics. One of the key figures of the Scottish Enlightenment, Smith is the author of The Theory of Moral Sentiments and An Inquiry into the Nature and Causes of the Wealth of Nations. The latter, usually abbreviated as The Wealth of Nations, is considered his magnum opus and the first modern work of economics. Smith is widely cited as the father of modern economics and capitalism.
http://wn.com/Adam_Smith -
Alan Dershowitz

Alan Morton Dershowitz (born September 1, 1938) is an American lawyer, jurist, political commentator,and Mid East Analyst. He is the Felix Frankfurter Professor of Law at Harvard Law School. Dershowitz is known for his career as an attorney in several high-profile law cases and as a commentator on the Arab–Israeli conflict. He has spent most of his career at Harvard University, where, at the age of 28, he became the youngest full professor of law in its history.
http://wn.com/Alan_Dershowitz -
Alan Turing

Alan Mathison Turing, OBE, FRS ( ; 23 June 1912 – 7 June 1954), was an English mathematician, logician, cryptanalyst and computer scientist. He was highly influential in the development of computer science and providing a formalization of the concept of the algorithm and computation with the Turing machine, playing a significant role in the creation of the modern computer.
http://wn.com/Alan_Turing -
Amy Goodman

Amy Goodman (born April 13, 1957) is an American progressive broadcast journalist, syndicated columnist, investigative reporter and author. Goodman is the principal host of Democracy Now!, an independent global news program broadcast daily on radio, television and the internet.
http://wn.com/Amy_Goodman -
Antoine Danchin

Antoine Danchin PhD DSc is a French geneticist known for his research in several fields of biology, from the structure and function of adenylate cyclase, to modelisation of learning in the nervous system and the early development of genomics and bioinformatics. He is the Chairman of the startup AMAbiotics [http://www.amabiotics.com/], specialised in metabolic bioremediation and synthetic biology [http://synbio.ku.dk/augustworkshop2010/]. He was the director of the Department Genomes and Genetics at the Institut Pasteur in Paris where he headed the Genetics of Bacterial Genomes Unit.
http://wn.com/Antoine_Danchin -
Augusto Pinochet

Augusto José Ramón Pinochet Ugarte (25 November 1915 – 10 December 2006) was a Chilean army general and president who assumed power in a coup d'état on 11 September 1973. Among his titles, he was the Commander-in-Chief of the Chilean army from 1973 to 1998, president of the Government Junta of Chile from 1973 to 1974 and President of the Republic from 1974 until transferring power to a democratically elected president in 1990.
http://wn.com/Augusto_Pinochet -
B.F. Skinner
http://wn.com/BF_Skinner -
Bertrand Russell

Bertrand Arthur William Russell, 3rd Earl Russell, OM, FRS (18 May 1872 – 2 February 1970) was a British philosopher, logician, mathematician, historian, socialist, pacifist, and social critic. He spent most of his life in England; he was born in Wales where he also died, aged 97.
http://wn.com/Bertrand_Russell -
C. West Churchman
Charles West Churchman (29 August 1913 – 21 March 2004 Bolinas, California.) was an American philosopher and systems scientist, who was Professor at the School of Business Administration and Professor of Peace and Conflict Studies at the University of California, Berkeley. He was internationally known for his pioneering work in operations research, system analysis and ethics.
http://wn.com/C_West_Churchman -
Carolus Linnaeus
http://wn.com/Carolus_Linnaeus -
Christopher Hitchens

Christopher Eric Hitchens (born 13 April 1949) is an English-American author and journalist (or Sage writer) whose books, essays, and journalistic career span more than four decades. He has been a columnist and literary critic at The Atlantic, Vanity Fair, Slate, World Affairs, The Nation, Free Inquiry, and became the William S. Hertz media fellow at the Hoover Institution in September 2008. He is a staple of talk shows and lecture circuits and in 2005 he was voted the world's fifth top public intellectual in a Prospect/Foreign Policy poll.
http://wn.com/Christopher_Hitchens -
David Pesetsky
David Michael Pesetsky (born 1957) is Ferrari P. Ward Professor of Modern Languages and Linguistics at MIT. He has published numerous articles and books within the framework of transformational grammar.
http://wn.com/David_Pesetsky -
Derek Bickerton
Derek Bickerton (born March 25, 1926) is a linguist and Professor Emeritus at the University of Hawaii, Manoa. Based on his work in creole languages in Guyana and Hawaii, he has proposed that the features of creole languages provide powerful insights into the development of language both by individuals and as a feature of the human species. He is the originator and main proponent of the language bioprogram hypothesis according to which the similarity of creoles is due to their being formed from a prior pidgin by children who all share a universal human innate grammar capacity.
http://wn.com/Derek_Bickerton -
Donald Knuth

Donald Ervin Knuth () (born January 10, 1938) is a computer scientist and Professor Emeritus of the Art of Computer Programming at Stanford University.
http://wn.com/Donald_Knuth -
Dwight Macdonald
Dwight Macdonald (24 March 1906 - 19 December 1982) was an American writer, editor, film critic, social critic, philosopher, and political radical.
http://wn.com/Dwight_Macdonald -
Edward Manukyan
Edward Manukyan (Armenian: Էդվարդ Մանուկյան, Russian: Эдвард Манукян) (born July 27, 1981) is an Armenian-born composer residing in Southern California, United States. His main works are orchestral and chamber compositions, which lean heavily upon elements of Armenian national folklore.
http://wn.com/Edward_Manukyan -
Edward Said

Edward Wadie Saïd ( , ; 1 November 1935 – 25 September 2003) was a Palestinian-American literary theorist and advocate for Palestinian rights. He was University Professor of English and Comparative Literature at Columbia University and a founding figure in postcolonialism. Robert Fisk described him as the Palestinians' "most powerful political voice."
http://wn.com/Edward_Said -
Elizabeth Bates
Elizabeth Bates (July 26, 1947 – December 13, 2003) was a Professor of psychology and cognitive science at the University of California, San Diego. She was an internationally-renowned expert and leading researcher in child language acquisition, psycholinguistics, and the neurological bases of language, and she authored 10 books and over 200 peer-reviewed articles and book chapters on these subjects. Bates was well-known for her assertion that linguistic knowledge is distributed throughout the brain and is subserved by general cognitive and neurological processes.
http://wn.com/Elizabeth_Bates -
Erich Fromm
Erich SeligmannFunk, Rainer. Erich Fromm: His Life and Ideas. Translators Ian Portman, Manuela Kunkel. New York: Continuum International Publishing Group, 2003. ISBN 0-8264-1519-9, ISBN 978-0-8264-1519-6. P. 13:"For a second name he was given that of his grandfather on his father's side–Seligmann Pinchas Fromm, although the registry office in Frankfurt does not record him as Erich Pinchas Fromm, but as Erich Seligmann Fromm. Also his parents addressed his mail to 'Erich S. Fromm.'" Fromm (March 23, 1900 – March 18, 1980) was a German social psychologist, psychoanalyst, humanistic philosopher, and democratic socialist. He was associated with what became known as the Frankfurt School of critical theory.
http://wn.com/Erich_Fromm -
Gennaro Chierchia
Gennaro Chierchia is Haas Foundation's professor of linguistics at Harvard University, and "one of the world's leading formal semanticists" according to the Harvard Gazette. Prior to appointment to Harvard's faculty, Chierchia was linguistics professor in the psychology department of the University of Milan-Bicocca.
http://wn.com/Gennaro_Chierchia -
George Lakoff

:"Lakoff" and "Professor Lakoff" redirect here. For the sociolinguist (his former wife), see Robin Lakoff.
http://wn.com/George_Lakoff -
George Orwell

Eric Arthur Blair (25 June 1903 – 21 January 1950), better known by his pen name George Orwell, was a British author and journalist. His work is marked by keen intelligence and wit, a profound awareness of social injustice, an intense, revolutionary opposition to totalitarianism, a passion for clarity in language and a belief in democratic socialism.
http://wn.com/George_Orwell -
Gilbert Harman
Gilbert Harman (born 1938) is a contemporary American philosopher, teaching at Princeton University, who has published widely on ethics, epistemology, metaphysics and the philosophies of language and mind. He was educated at Swarthmore College and Harvard University, where he earned his Ph.D. in Philosophy. He currently holds the James S. McDonnell Distinguished University Professorship in Philosophy. His daughter, Elizabeth Harman, is also a philosopher and a member of the philosophy department and the center for human values at Princeton University.
http://wn.com/Gilbert_Harman -
Hilary Putnam

Hilary Whitehall Putnam (born July 31, 1926) is an American philosopher who has been a central figure in analytic philosophy since the 1960s, especially in philosophy of mind, philosophy of language, and philosophy of science. He is known for his willingness to apply an equal degree of scrutiny to his own philosophical positions as to those of others, subjecting each position to rigorous analysis until he exposes its flaws. As a result, he has acquired a reputation for frequently changing his own position. Putnam is currently Cogan University Professor Emeritus at Harvard University.
http://wn.com/Hilary_Putnam -
Howard Lasnik
Howard Lasnik (born July 3, 1945) is a Distinguished University Professor in the Department of Linguistics at the University of Maryland.
http://wn.com/Howard_Lasnik -
Hugo Chavez
http://wn.com/Hugo_Chavez -
Immanuel Kant

Immanuel Kant () (22 April 1724 – 12 February 1804) was an 18th-century German philosopher from the Prussian city of Königsberg. Kant was the last influential philosopher of modern Europe in the classic sequence of the theory of knowledge during the Enlightenment beginning with thinkers John Locke, George Berkeley, and David Hume.
http://wn.com/Immanuel_Kant -
Jacques Mehler
Born in Barcelona (Spain) in 1936, Jacques Mehler is an influential cognitive psychologist specializing in language acquisition.
http://wn.com/Jacques_Mehler -
Jean Piaget
Jean Piaget (; (9 August 1896 – 16 September 1980) was a Swiss developmental psychologist known for his epistemological studies with children. His theory of cognitive development and epistemological view are together called "genetic epistemology".
http://wn.com/Jean_Piaget -
Jennifer Abbott

Jennifer Abbott (born c. 1965) is a Canadian director, cinematographer and editor, best known as a documentary maker. Her first feature documentary, A Cow at My Table (1998), explores contemporary Western attitudes to livestock and meat production. More recently, she served as co-director and editor of the widely acclaimed documentary, The Corporation (2003), which critically examines large corporations in the modern world. That film won numerous international film awards, including a Genie for best documentary, an audience award from the Sundance Film Festival, and a Top Ten Films of the Year designation from the Toronto International Film Festival. Her previous work includes the experimental short Skinned, and as editor for (1999). She is also the editor of the book ''Making Video 'In': The Contested Ground of Alternative Video on the West Coast''. She has taught at the Emily Carr Institute of Art & Design in Vancouver. She lives on Galiano Island in British Columbia, Canada.
http://wn.com/Jennifer_Abbott -
Jerry Fodor

Jerry Alan Fodor (born 1935) is an American philosopher and cognitive scientist. He holds the position of State of New Jersey Professor of Philosophy at Rutgers University and is the author of many works in the fields of philosophy of mind and cognitive science, in which he has laid the groundwork for the modularity of mind and the language of thought hypotheses, among other ideas. He is known for his provocative and sometimes polemical style of argumentation.
http://wn.com/Jerry_Fodor -
Joel Bakan

Joel Conrad Bakan (born 1959) is a Canadian lawyer and writer.
http://wn.com/Joel_Bakan -
John Dewey

John Dewey (October 20, 1859 – June 1, 1952) was an American philosopher, psychologist and educational reformer whose ideas have been influential in education and social reform. Dewey, along with Charles Sanders Peirce and William James, is recognized as one of the founders of the philosophy of pragmatism and of functional psychology. He was a major representative of the progressive and progressive populist philosophies of schooling during the first half of the 20th century in the USA.
http://wn.com/John_Dewey -
Julian C. Boyd
Julian Charles Boyd (December 25, 1931 – April 5, 2005) was an American linguist, reputed for his expertise on modality in English, as well as for his pedagogical excellence at the University of California, Berkeley, where he spent most of his academic career.
http://wn.com/Julian_C_Boyd -
Karl Marx

Karl Heinrich Marx (May 5, 1818 – March 14, 1883) was a German philosopher, political economist, historian, political theorist, sociologist, communist, and revolutionary, whose ideas played a significant role in the development of modern communism and socialism. Marx summarized his approach in the first line of chapter one of The Communist Manifesto, published in 1848: "The history of all hitherto existing society is the history of class struggles."
http://wn.com/Karl_Marx -
Ludwig Wittgenstein

Ludwig Josef Johann Wittgenstein (; 26 April 1889 – 29 April 1951) was an Austrian philosopher who held the professorship of philosophy at the University of Cambridge from 1939 until 1947.
http://wn.com/Ludwig_Wittgenstein -
Marc Hauser

Marc D. Hauser (born 25 October 1959) is an American evolutionary biologist and a researcher in primate behavior and animal cognition who teaches at the Psychology Department at Harvard University. In August 2010, Harvard found him solely responsible for eight counts of unspecified scientific misconduct.
http://wn.com/Marc_Hauser -
Mark Achbar
Mark Achbar is a Canadian filmmaker, best known for directing The Corporation and .
http://wn.com/Mark_Achbar -
Michael Albert

Michael Albert (born April 8, 1947) is an American activist, speaker, and writer. He is co-editor of ZNet, and co-editor and co-founder of Z Magazine. He also co-founded South End Press and has written numerous books and articles. He developed along with Robin Hahnel the economic vision called participatory economics.
http://wn.com/Michael_Albert -
Michel Foucault
Michel Foucault (), born Paul-Michel Foucault (15 October 1926 – 25 June 1984), was a French philosopher, sociologist, and historian. He held a chair at the prestigious Collège de France with the title "History of Systems of Thought," and also taught at the University at Buffalo and the University of California, Berkeley.
http://wn.com/Michel_Foucault -
Mikhail Bakunin

Mikhail Alexandrovich Bakunin ( - 1 July 1876) (; ) was a well-known Russian revolutionary and theorist of collectivist anarchism.
http://wn.com/Mikhail_Bakunin -
Morris Halle
Morris Halle, born Pinkowitz (Latvian: Moriss Pinkovics), is a Latvian-American Jewish linguist and an Institute Professor and professor emeritus of linguistics at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology. He is best known for his pioneering work in generative phonology, having written "On Accent and Juncture in English" in 1956 with Noam Chomsky and Fred Lukoff and The Sound Pattern of English in 1968 with Chomsky.
http://wn.com/Morris_Halle -
Nehru
http://wn.com/Nehru -
Nelson Goodman
Henry Nelson Goodman (7 August 1906, Somerville, Massachusetts – 25 November 1998, Needham, Massachusetts) was an American philosopher, known for his work on counterfactuals, mereology, the problem of induction, irrealism and aesthetics.
http://wn.com/Nelson_Goodman -
Niall McLaren
Niall (Jock) McLaren is an Australian psychiatrist, author and theoretician. His work opposes the mainstream view in psychiatry to the extent that he argues modern psychiatry has no scientific basis whatsoever. However, he insists that he is not “anti-psychiatry,” but a committed scientist following his duty of criticizing the prevailing models in his field in order to improve it.
http://wn.com/Niall_McLaren -
Niels Kaj Jerne

Niels Kaj Jerne, FRS (December 23, 1911 – October 7, 1994) was a Danish (English-born) immunologist. He was awarded the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine in 1984. The citation read "For theories concerning the specificity in development and control of the immune system and the discovery of the principle for production of monoclonal antibodies"[http://nobelprize.org/medicine/laureates/1984/]. He shared the prize with Georges J. F. Köhler and César Milstein.
http://wn.com/Niels_Kaj_Jerne -
Norman Finkelstein

Norman Gary Finkelstein (born December 8, 1953) is an American political scientist and author whose primary fields of research are the Israeli-Palestinian conflict and the politics of the Holocaust. He is a graduate of Binghamton University and received his Ph.D in Political Science from Princeton University. He has held faculty positions at Brooklyn College, Rutgers University, Hunter College, New York University, and, most recently, DePaul University, where he was an assistant professor from 2001 to 2007.
http://wn.com/Norman_Finkelstein -
Olivier Azam
Olivier Azam (born 21 October 1974 in Tarbes), is a French rugby union footballer, currently playing in the Guinness Premiership for Gloucester Rugby. He plays at hooker and can also cover prop. Olivier Azam also has 10 caps for France.
http://wn.com/Olivier_Azam -
Palestinian people

The Palestinian people, (, ash-sha`b al-filasTīni) also referred to as Palestinians or Palestinian Arabs (, al-filasTīnīyyūn; , al-`Arab al-filasTīnīyyūn), are an Arabic-speaking nation of Levantine people with family origins in Palestine. In the areas of Israel, the West Bank, the Gaza Strip, as of 2004, Arabs constitute 49% of all inhabitants, some of whom are internally displaced. The remainder, comprise what is known as the Palestinian diaspora, of whom more than half are stateless refugees, lacking citizenship in any country. Of the diaspora, about 1.9 million live in neighboring Jordan, one and a half million between Syria and Lebanon, a quarter million in Saudi Arabia, while Chile's half a million are the largest concentration outside the Arab world.
http://wn.com/Palestinian_people -
Peking University

Peking University (), colloquially known in Chinese as Beida (北大, Běidà), is a major research university located in Beijing, China, and a member of the C9 League. It is the first formally established modern national university of China. It was founded as Imperial Capital University in 1898 as a replacement of the ancient Guozijian (國子監 guózǐjiàn). By 1920 it had become a center for progressive thought. Today, many national and international rankings frequently place Peking University as one of the best universities in China. In addition to its academics, Peking University is especially renowned for the beauty of its traditional Chinese architecture at its campus grounds.
http://wn.com/Peking_University -
Peter Ludlow
Peter Ludlow (January 16, 1957), who also writes under the name Urizenus Sklar, is a professor of philosophy at Northwestern University. Before moving to Northwestern, Ludlow taught at University of Toronto, the University of Michigan, State University of New York at Stony Brook and was Visiting Professor of Philosophy at Syracuse University and Cornell University. He has done much interdisciplinary work on the interface of linguistics and philosophy. His dissertation at Columbia University was on intensional transitive verbs, such as "seek" and "worship". Among his influential early articles were "Implicit Comparison Classes" (Linguistics and Philosophy, 1989), in which he argued for the syntactic reality of comparison class variables in adjectival constructions, and his paper with the semanticist Richard Larson, "Interpreted Logical Forms", in which he advocated a sententialist view of propositional attitude verbs (a view that has been criticized by Scott Soames in Chapter 7 of his book Beyond Rigidity). His first book, Semantics, Tense, and Time, was devoted to arguing that presentism, a metaphysical thesis that denies the reality of past and future events, is consistent with the intuitive truth of much of our tensed discourse. In recent years, he has been developing a view of linguistic meaning according to which meaning shifts are much more common than intuition suggests, and applying the view to controversies in epistemology.
http://wn.com/Peter_Ludlow -
Peter Wintonick
Peter Wintonick (born 1953, Trenton, Canada) is an independent documentary filmmaker based in Montreal. A winner of the 2006 Governor General's Award in Visual and Media Arts, former Thinker in Residence for the Premier of South Australia, prolific award winning filmmaker, he is one of Canada's best known international documentarians. He currently runs Necessary Illusions Productions along with his partner Francis Miquet. Wintonick is one of the founders of DocAgora, an event inserted into various film festivals showcasing cutting-edge digital strategies.
http://wn.com/Peter_Wintonick -
Ray Jackendoff
Ray Jackendoff (born January 23, 1945) is an American linguist. He is professor of philosophy, Seth Merrin Chair in the Humanities and, with Daniel Dennett, Co-director of the Center for Cognitive Studies at Tufts University. He has always straddled the boundary between generative linguistics and cognitive linguistics, committed as he is both to the existence of an innate Universal Grammar (an important thesis of generative linguistics) and to giving an account of language that meshes well with the current understanding of the human mind and cognition (the main purpose of cognitive linguistics).
http://wn.com/Ray_Jackendoff -
René Descartes

René Descartes (; 31 March 1596 – 11 February 1650) (Latinized form: Renatus Cartesius; adjectival form: "Cartesian"), was a French philosopher, mathematician, physicist, and writer who spent most of his adult life in the Dutch Republic. He has been dubbed the "Father of Modern Philosophy," and much subsequent Western philosophy is a response to his writings, which are studied closely to this day. In particular, his Meditations on First Philosophy continues to be a standard text at most university philosophy departments. Descartes' influence in mathematics is also apparent; the Cartesian coordinate system—allowing geometric shapes to be expressed in algebraic equations—was named after him. He is credited as the father of analytical geometry. Descartes was also one of the key figures in the Scientific Revolution.
http://wn.com/René_Descartes -
Richard Perle
:This is about the conservative official and lobbyist; for the liberal author, see Rick Perlstein.
http://wn.com/Richard_Perle -
Robert Fisk

Robert Fisk (born 12 July 1946) is an English writer and journalist from Maidstone, Kent.
http://wn.com/Robert_Fisk -
Rudolf Carnap
Rudolf Carnap (May 18, 1891 – September 14, 1970) was an influential German-born philosopher who was active in Europe before 1935 and in the United States thereafter. He was a leading member of the Vienna Circle and a prominent advocate of logical positivism.
http://wn.com/Rudolf_Carnap -
Rudolf Rocker

Johann Rudolf Rocker (March 25, 1873– September 10, 1958) was an anarcho-syndicalist writer and activist. A self-professed anarchist without adjectives, Rocker believed that anarchist schools of thought represented "only different methods of economy" and that the first objective for anarchists was "to secure the personal and social freedom of men".
http://wn.com/Rudolf_Rocker -
Spanish Civil War

The Spanish Civil War was a major conflict that devastated Spain from 17 July 1936 to 1 April 1939. It began after an attempted ''coup d'état by a group of Spanish Army generals against the government of the Second Spanish Republic, then under the leadership of president Manuel Azaña. The nationalist coup was supported by the conservative Spanish Confederation of the Autonomous Right (Confederación Española de Derechas Autónomas, or C.E.D.A), monarchists known as Carlist groups, and the Fascist Falange (Falange Española de las J.O.N.S.''). Following the partially successful coup, Spain was left divided as supporters of the existing Republican government fought the forces of the new Nationalist government for control of the country. The war ended with the victory of the Nationalists, the overthrow of the Republican government, and the founding of an authoritarian state led by General Francisco Franco. In the aftermath of the civil war, all right-wing parties were fused into the state party of the Franco regime.
http://wn.com/Spanish_Civil_War -
Srebrenica massacre

The Srebrenica massacre, also known as the Srebrenica genocide, refers to the July 1995 killing of more than 8,000 Bosniak men and boys, as well as the ethnic cleansing of another 25,000–30,000 refugees, in and around the town of Srebrenica in Bosnia and Herzegovina, by units of the Army of Republika Srpska (VRS) under the command of General Ratko Mladić during the Bosnian War. A paramilitary unit from Serbia known as the Scorpions, officially part of the Serbian Interior Ministry until 1991, participated in the massacre. It is alleged that foreign volunteers including the Greek Volunteer Guard also participated.
http://wn.com/Srebrenica_massacre -
Stanislas Dehaene
Stanislas Dehaene is a professor at the Collège de France, author, and (since 1989) director of INSERM [http://www.unicog.org/ Unit 562, "Cognitive Neuroimaging,"]. He has worked on a number of topics, including numerical cognition, the neural basis of reading and the neural correlates of consciousness.
http://wn.com/Stanislas_Dehaene -
Steven Pinker
Steven Arthur Pinker (born September 18, 1954) is a Canadian-American experimental psychologist, cognitive scientist, linguist and author of popular science. He is a Harvard College Professor and Johnstone Family Professor in the Department of Psychology at Harvard University and is known for his wide-ranging advocacy of evolutionary psychology and the computational theory of mind.
http://wn.com/Steven_Pinker -
Sut Jhally

Satvinder "Sut" Jhally(),() (born 29 May 1955) is a professor of Communication at the University of Massachusetts Amherst and is a cultural studies scholar in the area of advertising, media, and consumption. He is the producer of several documentaries on media literacy topics and the founder and executive director of the [http://www.mediaed.org Media Education Foundation],
http://wn.com/Sut_Jhally -
Tanya Reinhart

Tanya Reinhart (; July 1943 – March 17, 2007) was an Israeli linguist who wrote frequently on the Israeli-Palestinian conflict. She contributed columns to the Israeli newspaper Yediot Aharonot and longer articles to the CounterPunch, Znet, and Israeli Indymedia websites.
http://wn.com/Tanya_Reinhart -
Theodore Kaczynski
http://wn.com/Theodore_Kaczynski -
Tony Kaye (director)
Tony Kaye (born 1952, London, United Kingdom) is a director of films, music videos, advertisements and documentaries.
http://wn.com/Tony_Kaye_(director) -
Walter Lippmann

Walter Lippmann (23 September 1889 – 14 December 1974) was an American intellectual, writer, reporter, and political commentator who gained notoriety for the introduction of the concept of Cold War for the first time in the world. Lippmann was twice awarded (1958 and 1962) a Pulitzer Prize for his syndicated newspaper column, “Today and Tomorrow”.
http://wn.com/Walter_Lippmann -
Wilhelm von Humboldt

Friedrich Wilhelm Christian Karl Ferdinand Freiherr von Humboldt (22 June 1767 – 8 April 1835) was a German philosopher, government functionary, diplomat, and founder of Humboldt Universität. He is especially remembered as a linguist who made important contributions to the philosophy of language and to the theory and practice of education. In particular, he is widely recognized as having been the architect of the Prussian education system which was used as a model for education systems in countries such as the United States and Japan.
http://wn.com/Wilhelm_von_Humboldt -
William Chomsky
William Chomsky (1896–1977) was an American scholar of Hebrew, born in Ukraine, who was a professor at Gratz College. He was made faculty president of Gratz in 1932, a position that he held for thirty seven years. He also taught at Dropsie College, a graduate school of Jewish and Semitic studies from 1955 until 1977. He was a renowned specialist of the history of the Hebrew grammatical tradition, before and after David Kimhi (1160–1235). His obituary (New York Times, 22 July 1977) describes him as "one of the world's foremost Hebrew grammarians."
http://wn.com/William_Chomsky -
Zellig Harris
Zellig Sabbettai Harris (October 23, 1909 – May 22, 1992) was a renowned American linguist, mathematical syntactician, and methodologist of science. Originally a Semiticist, he is best known for his work in structural linguistics and discourse analysis and for the discovery of transformational structure in language. These developments from the first 10 years of his career were published within the first 25. His contributions in the subsequent 35 years of his career include sublanguage grammar, operator grammar, and a theory of linguistic information.
http://wn.com/Zellig_Harris
-
Bude

Bude () is a small seaside resort town in North Cornwall, England, at the mouth of the River Neet [also known locally as the River Strat]. Bude is twinned with Ergué-Gabéric in Brittany, France. It is suggested that the modern name is a shortened form of Bude Haven and that this in turn was a corruption of the name Bede Haven meaning "Harbour of the holy men" suggesting Bude might have been a landing place for early Christians.
http://wn.com/Bude -
Bush (Beer)
http://wn.com/Bush_(Beer) -
Bush Tower

Bush Tower, also called the Bush Terminal International Exhibit Building is an historic thirty-story skyscraper located just east of Times Square at 130-132 West 42nd Street between Broadway and Sixth Avenue in Midtown Manhattan, New York City. It was built in 1916-18 for Irving T. Bush's Bush Terminal Company, owners of Bush Terminal in Sunset Park, Brooklyn. Bush Tower's unique original purpose as commercial display space and social space, its notable design that combined narrowness, height, and Neo-Gothic architecture, and its role in the evolution of Times Square and of New York skyscrapers after the 1916 Zoning Resolution all qualify it as an exceptional structure.
http://wn.com/Bush_Tower -
Cornwall

Cornwall (; ) is a ceremonial county and unitary authority of England, United Kingdom, forming the tip of the south-western peninsula of Great Britain. It is bordered to the north and west by the Atlantic Ocean, to the south by the English Channel, and to the east by the county of Devon, over the River Tamar. Taken with the Isles of Scilly, Cornwall has a population of , and covers an area of . The administrative centre and only city is Truro.
http://wn.com/Cornwall -
Shepherds Bush
http://wn.com/Shepherds_Bush
- Bush
- Bush (band)
- Bush (Beer)
- Bush (brand)
- Bush (Canadian band)
- Bush House, London
- Bush Mechanics
- Bush Tower
- Bush, Illinois
- Bush, Louisiana
- Bushcraft
- Cornwall
- galago
- Pubic hair
- Shepherds Bush
- Shrub
- The Bush
- The Bush (Alaska)
- The Mirror of the Signs
- The Sound of Winter
- All My Life
- The Afterlife
- All Night Doctors
- Baby Come Home
- Red Light
- She's a Stallion
- I Believe in You
- Stand Up
- The Heart of the Matter
- Be Still My Love
- Everything Zen
- Little Things
- Comedown
- Glycerine
- Machinehead
- Swallowed
- Greedy Fly
- Warm Machine
- The Chemicals Between Us
- Letting the Cables Sleep
- Everything Zen (The Lhasa Fever mix)
- Swallowed (Goldie/Toasted Both Sides Please mix)
- Mouth (The Stingray mix)
- Warm Machine
- Jesus Online
- The Chemicals Between Us
- English Fire
- Spacetravel
- 40 Miles From the Sun
- Prizefighter
- The Disease of the Dancing Cats
- Altered States
- Dead Meat
- Letting the Cables Sleep
- Mindchanger
- Solutions
- Headful of Ghosts
- The People That We Love
- Superman
- Fugitive
- Hurricane
- Inflatable
- Reasons
- Land of the Living
- My Engine Is With You
- Out of This World
- Float
- Everything Zen
- Swim
- Bomb
- Little Things
- Comedown
- Body
- Machinehead
- Testosterone
- Monkey
- Glycerine
- Alien
- X-Girlfriend
- Personal Holloway
- Greedy Fly
- Swallowed
- Insect Kin
- Cold Contagious
- A Tendency to Start Fires
- Mouth
- Straight No Chaser
- History
- Synapse
- Communicator
- Bonedriven
- Distant Voices / [unknown]
- Backstage Girl
- Yonge St. Patty
- Got to Leave the City
- I Miss You
- The Grand Commander
- Cross Country Man
- I Can Hear You Calling
- Messin' Around With Boxes
- Livin' Life
- Turn Down
- Drink Your Wine
- Try (live)
- Lookin' (live)
- Wicked Woman (live)
- Cross Country Man (live)

- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 3:45
- Published: 09 Sep 2011
- Uploaded: 29 Feb 2012
- Author: earMUSICofficial


- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 4:19
- Published: 01 Jun 2008
- Uploaded: 29 Feb 2012
- Author: lalalovesyou03

- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 2:54
- Published: 06 May 2006
- Uploaded: 29 Feb 2012
- Author: bigrich0861

- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 3:38
- Published: 10 Feb 2010
- Uploaded: 29 Feb 2012
- Author: setzerlock


- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 4:32
- Published: 02 Dec 2011
- Uploaded: 29 Feb 2012
- Author: earMUSICofficial

- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 3:32
- Published: 22 Jul 2011
- Uploaded: 01 Mar 2012
- Author: BushOfficial

- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 3:56
- Published: 14 Dec 2011
- Uploaded: 01 Mar 2012
- Author: BushOfficial
- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 12:08
- Published: 29 Sep 2011
- Uploaded: 29 Feb 2012
- Author: RussiaToday

- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 6:33
- Published: 09 Dec 2011
- Uploaded: 29 Feb 2012
- Author: mathiasnielsen66

- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 11:26
- Published: 08 Dec 2011
- Uploaded: 27 Feb 2012
- Author: vibesinthesky

- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 10:19
- Published: 26 Aug 2007
- Uploaded: 01 Mar 2012
- Author: Leaderofwhat

- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 6:55
- Published: 10 Dec 2006
- Uploaded: 29 Feb 2012
- Author: Mystwalkers

- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 5:02
- Published: 19 Jan 2012
- Uploaded: 29 Feb 2012
- Author: KateBushMusic

- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 4:27
- Published: 07 Dec 2007
- Uploaded: 29 Feb 2012
- Author: dawnrun911

- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 5:26
- Published: 22 Feb 2008
- Uploaded: 01 Mar 2012
- Author: novembrrain



- Order: Reorder
- Duration: 3:46
- Published: 30 Dec 2010
- Uploaded: 01 Mar 2012
- Author: KateBushMusic
 Creative Commons
Creative Commons Creative Commons / Dual Freq
Creative Commons / Dual Freq Creative Commons / Abesty
Creative Commons / Abesty US Navy / Mass Communication Specialist Seaman Benjamin E. Kelly
US Navy / Mass Communication Specialist Seaman Benjamin E. Kelly US Navy / Mass Communication Specialist Seaman Brian Read Castillo
US Navy / Mass Communication Specialist Seaman Brian Read Castillo Creative Commons / Glen Fergus
Creative Commons / Glen Fergus Creative Commons / JJ Harrison
Creative Commons / JJ Harrison AP / Dennis Cook, FIle
AP / Dennis Cook, FIle UN / Isaac Billy
UN / Isaac Billy UN / Isaac Billy
UN / Isaac Billy UN / Isaac Billy
UN / Isaac Billy Creative Commons / TCY
Creative Commons / TCY AP / Rogelio V. Solis
AP / Rogelio V. Solis Creative Commons / Killerscene
Creative Commons / Killerscene Creative Commons / Cyron Ray Macey
Creative Commons / Cyron Ray Macey US Navy / Mass Communication Specialist 2nd Class Timothy Walter
US Navy / Mass Communication Specialist 2nd Class Timothy Walter US Navy / Mass Communication Specialist 2nd Class Timothy Walter
US Navy / Mass Communication Specialist 2nd Class Timothy Walter Creative Commons / Adam.J.W.C.
Creative Commons / Adam.J.W.C. Creative Commons / J Bar
Creative Commons / J Bar Creative Commons / Jasabella
Creative Commons / Jasabella Creative Commons / J Bar
Creative Commons / J Bar Creative Commons / JROBBO
Creative Commons / JROBBO Creative Commons / J Bar
Creative Commons / J Bar US Navy / Mass Communication Specialist 2nd Class Brian M. Brooks
US Navy / Mass Communication Specialist 2nd Class Brian M. Brooks US Navy / Mass Communication Specialist 2nd Class Timothy Walter
US Navy / Mass Communication Specialist 2nd Class Timothy Walter US Navy / Mass Communication Specialist 2nd Class Rafael Martie
US Navy / Mass Communication Specialist 2nd Class Rafael Martie US Navy / Mass Communication Specialist 2nd Class Rafael Martie
US Navy / Mass Communication Specialist 2nd Class Rafael Martie US Navy / Mass Communication Specialist 2nd Class Eric S. Garst
US Navy / Mass Communication Specialist 2nd Class Eric S. Garst US Navy / Mass Communication Specialist 2nd Class Rafael Martie
US Navy / Mass Communication Specialist 2nd Class Rafael Martie US Navy / Mass Communication Specialist MC1 Lynn Friant
US Navy / Mass Communication Specialist MC1 Lynn Friant
Bush may refer to:
Nouns
Places
Brand names and companies
Media and entertainment
Sport
Vessels
, two destroyers in the United States Navy
See also
ar:بوش (توضيح) bg:Буш ca:Bush cs:Bush (příjmení) de:Bush es:Bush fr:Bush ko:부시 hy:Բուշ (այլ կիրառումներ) is:Bush it:Bush he:בוש hu:Bush (egyértelműsítő lap) nl:Bush ja:ブッシュ no:Bush pl:Bush pt:Bush ro:Bush ru:Буш simple:Bush sk:Bush fi:Bush sv:Bush tr:Bush uk:Буш zh:布什
This text is licensed under the Creative Commons CC-BY-SA License. This text was originally published on Wikipedia and was developed by the Wikipedia community.
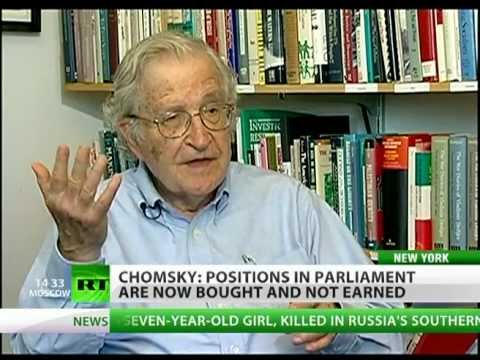
Avram Noam Chomsky (; born December 7, 1928) is an American linguist, philosopher, cognitive scientist, historian, and activist. He is an Institute Professor and Professor (Emeritus) in the Department of Linguistics & Philosophy at MIT, where he has worked for over 50 years. Chomsky has been described as the "father of modern linguistics" and a major figure of analytic philosophy. His work has influenced fields such as computer science, mathematics, and psychology.
Chomsky is credited as the creator or co-creator of the Chomsky hierarchy, the universal grammar theory, and the Chomsky–Schützenberger theorem.
Ideologically identifying with anarchism and libertarian socialism, Chomsky is known for his critiques of U.S. foreign policy and contemporary capitalism, and he has been described as a prominent cultural figure. His media criticism has included ''Manufacturing Consent: The Political Economy of the Mass Media'' (1988), co-written with Edward S. Herman, an analysis articulating the propaganda model theory for examining the media.
According to the Arts and Humanities Citation Index in 1992, Chomsky was cited as a source more often than any other living scholar from 1980 to 1992, and was the eighth most cited source overall. Chomsky is the author of over 100 books.
Life and career
Chomsky was born on the morning of December 7, 1928, to Jewish parents in the affluent East Oak Lane neighborhood of Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, the son of noted professor of Hebrew at Gratz College and IWW (Industrial Workers of the World) member William Chomsky (1896–1977), a native of Ukraine. His mother, Elsie Chomsky (née Simonofsky)—a native of what is present-day Belarus—grew up in the United States and, unlike her husband, spoke "ordinary New York English". Chomsky's parents' first language was Yiddish, but Chomsky said it was "taboo" in his family to speak it. Although Chomsky's mother was part of the radical activism in the 1930s, he was influenced largely by his uncle who, having never passed 4th grade, owned a newsstand that acted as an "intellectual center [where] professors of this and that argu[ed] all night". Chomsky was influenced also by being a part of a Hebrew-based, Zionist organization, as well as by hanging around anarchist bookstores.He describes his family as living in a sort of "Jewish ghetto", split into a "Yiddish side" and "Hebrew side", with his family aligning with the latter and bringing him up "immersed in Hebrew culture and literature", though he means more a "cultural ghetto than a physical one". Chomsky also describes tensions he experienced with Irish Catholics and German Catholics and anti-semitism in the mid-1930s. He recalls "beer parties" celebrating the fall of Paris to the Nazis. In a discussion of the irony of his staying in the 1980s in a Jesuit House in Central America, Chomsky explained that during his childhood, "We were the only Jewish family around. I grew up with a visceral fear of Catholics. They're the people who beat you up on your way to school. So I knew when they came out of that building down the street, which was the Jesuit school, they were raving anti-Semites. So childhood memories took a long time to overcome."
Chomsky remembers the first article he wrote was at age 10 while a student at Oak Lane Country Day School about the threat of the spread of fascism, following the fall of Barcelona in the Spanish Civil War. From the age of 12 or 13, he identified more fully with anarchist politics.
A graduate of Central High School of Philadelphia, Chomsky began studying philosophy and linguistics at the University of Pennsylvania in 1945, taking classes with philosophers such as C. West Churchman and Nelson Goodman and linguist Zellig Harris. Harris's teaching included his discovery of transformations as a mathematical analysis of language structure (mappings from one subset to another in the set of sentences). Chomsky referred to the morphophonemic rules in his 1951 master's thesis—''The Morphophonemics of Modern Hebrew''—as transformations in the sense of Carnap's 1938 notion of rules of transformation (vs. rules of formation), and subsequently reinterpreted the notion of grammatical transformations in a very different way from Harris, as operations on the productions of a context-free grammar (derived from Post production systems). Harris's political views were instrumental in shaping those of Chomsky. Chomsky earned a BA in 1949 and an MA in 1951.
In 1949, he married linguist Carol Schatz. They remained married for 59 years until her death from cancer in December 2008. The couple had two daughters, Aviva (b. 1957) and Diane (b. 1960), and a son, Harry (b. 1967). With his wife Carol, Chomsky spent time in 1953 living in HaZore'a, a kibbutz in Israel. Asked in an interview whether the stay was "a disappointment" Chomsky replied, "No, I loved it"; however, he "couldn't stand the ideological atmosphere" and "fervent nationalism" in the early 1950s at the kibbutz, with Stalin being defended by many of the left-leaning kibbutz members who chose to paint a rosy image of future possibilities and contemporary realities in the USSR. Chomsky notes seeing many positive elements in the commune-like living of the kibbutz, in which parents and children lived together in separate houses, and when asked whether there were "lessons that we have learned from the history of the kibbutz", responded, that in "some respects, the kibbutzim came closer to the anarchist ideal than any other attempt that lasted for more than a very brief moment before destruction, or that was on anything like a similar scale. In these respects, I think they were extremely attractive and successful; apart from personal accident, I probably would have lived there myself – for how long, it's hard to guess."
Chomsky received his PhD in linguistics from the University of Pennsylvania in 1955. He conducted part of his doctoral research during four years at Harvard University as a Harvard Junior Fellow. In his doctoral thesis, he began to develop some of his linguistic ideas, elaborating on them in his 1957 book ''Syntactic Structures'', one of his best-known works in linguistics.
Chomsky joined the staff of MIT in 1955 and in 1961 was appointed full professor in the Department of Modern Languages and Linguistics (now the Department of Linguistics and Philosophy). From 1966 to 1976 he held the Ferrari P. Ward Professorship of Modern Languages and Linguistics, and in 1976 he was appointed Institute Professor. As of 2010, Chomsky has taught at MIT continuously for 55 years.
In February 1967, Chomsky became one of the leading opponents of the Vietnam War with the publication of his essay, "The Responsibility of Intellectuals", in ''The New York Review of Books''. This was followed by his 1969 book, ''American Power and the New Mandarins,'' a collection of essays that established him at the forefront of American dissent. His far-reaching criticisms of U.S. foreign policy and the legitimacy of U.S. power have raised controversy he is frequently sought out for his views by publications and news outlets internationally. In 1977 he delivered the Huizinga Lecture in Leiden, the Netherlands, under the title: ''Intellectuals and the State''.
Chomsky has received death threats because of his criticisms of U.S. foreign policy. He was also on a list of planned targets created by Theodore Kaczynski, better known as the Unabomber; during the period that Kaczynski was at large, Chomsky had all of his mail checked for explosives. He states that he often receives undercover police protection, in particular while on the MIT campus, although he does not agree with the police protection.
Chomsky resides in Lexington, Massachusetts, and travels often, giving lectures on politics.
Contributions to linguistics
Chomskyan linguistics, beginning with his ''Syntactic Structures'', a distillation of his '' Logical Structure of Linguistic Theory'' (1955, 75), challenges structural linguistics and introduces transformational grammar. This approach takes utterances (sequences of words) to have a syntax characterized by a formal grammar; in particular, a context-free grammar extended with transformational rules.Perhaps his most influential and time-tested contribution to the field, is the claim that modeling knowledge of language using a formal grammar accounts for the "productivity" or "creativity" of language. In other words, a formal grammar of a language can explain the ability of a hearer-speaker to produce and interpret an infinite number of utterances, including novel ones, with a limited set of grammatical rules and a finite set of terms. He has always acknowledged his debt to Pāṇini for his modern notion of an explicit generative grammar although it is also related to rationalist ideas of a priori knowledge.
It is a popular misconception that Chomsky proved that language is entirely innate and discovered a "universal grammar" (UG). In fact, Chomsky simply observed that while a human baby and a kitten are both capable of inductive reasoning, if they are exposed to exactly the same linguistic data, the human child will always acquire the ability to understand and produce language, while the kitten will never acquire either ability. Chomsky labeled whatever the relevant capacity the human has which the cat lacks the "language acquisition device" (LAD) and suggested that one of the tasks for linguistics should be to figure out what the LAD is and what constraints it puts on the range of possible human languages. The universal features that would result from these constraints are often termed "universal grammar" or UG.
The Principles and Parameters approach (P&P;)—developed in his Pisa 1979 Lectures, later published as ''Lectures on Government and Binding'' (LGB)—makes strong claims regarding universal grammar: that the grammatical principles underlying languages are innate and fixed, and the differences among the world's languages can be characterized in terms of parameter settings in the brain (such as the pro-drop parameter, which indicates whether an explicit subject is always required, as in English, or can be optionally dropped, as in Spanish), which are often likened to switches. (Hence the term principles and parameters, often given to this approach.) In this view, a child learning a language need only acquire the necessary lexical items (words, grammatical morphemes, and idioms), and determine the appropriate parameter settings, which can be done based on a few key examples.
Proponents of this view argue that the pace at which children learn languages is inexplicably rapid, unless children have an innate ability to learn languages. The similar steps followed by children all across the world when learning languages, and the fact that children make certain characteristic errors as they learn their first language, whereas other seemingly logical kinds of errors never occur (and, according to Chomsky, should be attested if a purely general, rather than language-specific, learning mechanism were being employed), are also pointed to as motivation for innateness.
More recently, in his Minimalist Program (1995), while retaining the core concept of "principles and parameters," Chomsky attempts a major overhaul of the linguistic machinery involved in the LGB model, stripping from it all but the barest necessary elements, while advocating a general approach to the architecture of the human language faculty that emphasizes principles of economy and optimal design, reverting to a derivational approach to generation, in contrast with the largely representational approach of classic P&P.;
Chomsky's ideas have had a strong influence on researchers of the language acquisition in children, though many researchers in this area such as Elizabeth Bates and Michael Tomasello argue very strongly against Chomsky's theories, and instead advocate emergentist or connectionist theories, explaining language with a number of general processing mechanisms in the brain that interact with the extensive and complex social environment in which language is used and learned.
His best-known work in phonology is ''The Sound Pattern of English'' (1968), written with Morris Halle (and often known as simply ''SPE''). This work has had a great significance for the development in the field. While phonological theory has since moved beyond "SPE phonology" in many important respects, the SPE system is considered the precursor of some of the most influential phonological theories today, including autosegmental phonology, lexical phonology and optimality theory. Chomsky no longer publishes on phonology.
Generative grammar
The Chomskyan approach towards syntax, often termed generative grammar, studies grammar as a body of knowledge possessed by language users. Since the 1960s, Chomsky has maintained that much of this knowledge is innate, implying that children need only learn certain parochial features of their native languages. The innate body of linguistic knowledge is often termed universal grammar. From Chomsky's perspective, the strongest evidence for the existence of Universal Grammar is simply the fact that children successfully acquire their native languages in so little time. Furthermore, he argues that there is an enormous gap between the linguistic stimuli to which children are exposed and the rich linguistic knowledge they attain (the "poverty of the stimulus" argument). The knowledge of Universal Grammar would serve to bridge that gap.Chomsky's theories have been immensely influential within linguistics, but they have also received criticism. One recurring criticism of the Chomskyan variety of generative grammar is that it is Anglocentric and Eurocentric, and that often linguists working in this tradition have a tendency to base claims about Universal Grammar on a very small sample of languages, sometimes just one. Initially, the Eurocentrism was exhibited in an overemphasis on the study of English. However, hundreds of different languages have now received at least some attention within Chomskyan linguistic analyses. In spite of the diversity of languages that have been characterized by UG derivations, critics continue to argue that the formalisms within Chomskyan linguistics are Anglocentric and misrepresent the properties of languages that are different from English. Thus, Chomsky's approach has been criticized as a form of linguistic imperialism. In addition, Chomskyan linguists rely heavily on the intuitions of native speakers regarding which sentences of their languages are well-formed. This practice has been criticized on general methodological grounds. Some psychologists and psycholinguists, though sympathetic to Chomsky's overall program, have argued that Chomskyan linguists pay insufficient attention to experimental data from language processing, with the consequence that their theories are not psychologically plausible. Other critics (see language learning) have questioned whether it is necessary to posit Universal Grammar to explain child language acquisition, arguing that domain-general learning mechanisms are sufficient.
Today there are many different branches of generative grammar; one can view grammatical frameworks such as head-driven phrase structure grammar, lexical functional grammar and combinatory categorial grammar as broadly Chomskyan and generative in orientation, but with significant differences in execution.
Chomsky hierarchy
Chomsky is famous for investigating various kinds of formal languages and whether or not they might be capable of capturing key properties of human language. His Chomsky hierarchy partitions formal grammars into classes, or groups, with increasing expressive power, i.e., each successive class can generate a broader set of formal languages than the one before. Interestingly, Chomsky argues that modeling some aspects of human language requires a more complex formal grammar (as measured by the Chomsky hierarchy) than modeling others. For example, while a regular language is powerful enough to model English morphology, it is not powerful enough to model English syntax. In addition to being relevant in linguistics, the Chomsky hierarchy has also become important in computer science (especially in compiler construction and automata theory). Indeed, there is an equivalence between the Chomsky language hierarchy and the different kinds of automata. Thus theorems about languages are often dealt with as either languages (grammars) or automata.An alternate method of dealing with languages is based upon Formal Power series. Formal Power series as well as the relationship between languages and semi-groups continued to occupy M. P. Schützenberger at the Sorbonne. Formal Power Series are similar to the Taylor Series one encounters in a course on Calculus, and is especially useful for languages where words (terminal symbols) are commutative.
Contributions to psychology
Chomsky's work in linguistics has had profound implications for modern psychology. For Chomsky, linguistics is a branch of cognitive psychology; genuine insights in linguistics imply concomitant understandings of aspects of mental processing and human nature. His theory of a universal grammar was seen by many as a direct challenge to the established behaviorist theories of the time and had major consequences for understanding how children learn language and what, exactly, the ability to use language is.In 1959, Chomsky published an influential critique of B.F. Skinner's ''Verbal Behavior'', a book in which Skinner offered a theoretical account of language in functional, behavioral terms. He defined "Verbal Behavior" as learned behavior that has characteristic consequences delivered through the learned behavior of others. This makes for a view of communicative behaviors much larger than that usually addressed by linguists. Skinner's approach focused on the circumstances in which language was used; for example, asking for water was functionally a different response than labeling something as water, responding to someone asking for water, etc. These functionally different kinds of responses, which required in turn separate explanations, sharply contrasted both with traditional notions of language and Chomsky's psycholinguistic approach. Chomsky thought that a functionalist explanation restricting itself to questions of communicative performance ignored important questions. (Chomsky—Language and Mind, 1968). He focused on questions concerning the operation and development of innate structures for syntax capable of creatively organizing, cohering, adapting and combining words and phrases into intelligible utterances.
In the review Chomsky emphasized that the scientific application of behavioral principles from animal research is severely lacking in explanatory adequacy and is furthermore particularly superficial as an account of human verbal behavior because a theory restricting itself to external conditions, to "what is learned," cannot adequately account for generative grammar. Chomsky raised the examples of rapid language acquisition of children, including their quickly developing ability to form grammatical sentences, and the universally creative language use of competent native speakers to highlight the ways in which Skinner's view exemplified under-determination of theory by evidence. He argued that to understand human verbal behavior such as the creative aspects of language use and language development, one must first postulate a genetic linguistic endowment. The assumption that important aspects of language are the product of universal innate ability runs counter to Skinner's radical behaviorism.
Chomsky's 1959 review has drawn fire from a number of critics, the most famous criticism being that of Kenneth MacCorquodale's 1970 paper ''On Chomsky’s Review of Skinner’s Verbal Behavior'' (''Journal of the Experimental Analysis of Behavior,'' volume 13, pages 83–99). MacCorquodale's argument was updated and expanded in important respects by Nathan Stemmer in a 1990 paper, ''Skinner's Verbal Behavior, Chomsky's review, and mentalism'' (''Journal of the Experimental Analysis of Behavior,'' volume 54, pages 307–319). These and similar critiques have raised certain points not generally acknowledged outside of behavioral psychology, such as the claim that Chomsky did not possess an adequate understanding of either behavioral psychology in general, or the differences between Skinner's behaviorism and other varieties. Consequently, it is argued that he made several serious errors. On account of these perceived problems, the critics maintain that the review failed to demonstrate what it has often been cited as doing. As such, it is averred that those most influenced by Chomsky's paper probably either already substantially agreed with Chomsky or never actually read it. The review has been further critiqued for misrepresenting the work of Skinner and others, including by quoting out of context. Chomsky has maintained that the review was directed at the way Skinner's variant of behavioral psychology "was being used in Quinean empiricism and naturalization of philosophy."
It has been claimed that Chomsky's critique of Skinner's methodology and basic assumptions paved the way for the "cognitive revolution", the shift in American psychology between the 1950s through the 1970s from being primarily behavioral to being primarily cognitive. In his 1966 ''Cartesian Linguistics'' and subsequent works, Chomsky laid out an explanation of human language faculties that has become the model for investigation in some areas of psychology. Much of the present conception of how the mind works draws directly from ideas that found their first persuasive author of modern times in Chomsky.
There are three key ideas. First is that the mind is "cognitive", or that the mind actually contains mental states, beliefs, doubts, and so on. Second, he argued that most of the important properties of language and mind are innate. The acquisition and development of a language is a result of the unfolding of innate propensities triggered by the experiential input of the external environment. The link between human innate aptitude to language and heredity has been at the core of the debate opposing Noam Chomsky to Jean Piaget at the Abbaye de Royaumont in 1975 (''Language and Learning. The Debate between Jean Piaget and Noam Chomsky,'' Harvard University Press, 1980). Although links between the genetic setup of humans and aptitude to language have been suggested at that time and in later discussions, we are still far from understanding the genetic bases of human language. Work derived from the model of selective stabilization of synapses set up by Jean-Pierre Changeux, Philippe Courrège and Antoine Danchin, and more recently developed experimentally and theoretically by Jacques Mehler and Stanislas Dehaene in particular in the domain of numerical cognition lend support to the Chomskyan "nativism". It does not, however, provide clues about the type of rules that would organize neuronal connections to permit language competence. Subsequent psychologists have extended this general "nativist" thesis beyond language. Lastly, Chomsky made the concept of "modularity" a critical feature of the mind's cognitive architecture. The mind is composed of an array of interacting, specialized subsystems with limited flows of inter-communication. This model contrasts sharply with the old idea that any piece of information in the mind could be accessed by any other cognitive process (optical illusions, for example, cannot be "turned off" even when they are known to be illusions).
Approach to science
Chomsky sees science as a straightforward search for explanation, and rejects the views of it as a catalog of facts or mechanical explanations. In this light, the majority of his contributions to science have been frameworks and hypotheses, rather than "discoveries."As such, he considers certain so-called post-structuralist or postmodern critiques of logic and reason to be nonsensical:
I have spent a lot of my life working on questions such as these, using the only methods I know of; those condemned here as "science", "rationality," "logic," and so on. I therefore read the papers with some hope that they would help me "transcend" these limitations, or perhaps suggest an entirely different course. I'm afraid I was disappointed. Admittedly, that may be my own limitation. Quite regularly, "my eyes glaze over" when I read polysyllabic discourse on the themes of poststructuralism and postmodernism; what I understand is largely truism or error, but that is only a fraction of the total word count. True, there are lots of other things I don't understand: the articles in the current issues of math and physics journals, for example. But there is a difference. In the latter case, I know how to get to understand them, and have done so, in cases of particular interest to me; and I also know that people in these fields can explain the contents to me at my level, so that I can gain what (partial) understanding I may want. In contrast, no one seems to be able to explain to me why the latest post-this-and-that is (for the most part) other than truism, error, or gibberish, and I do not know how to proceed.
Although Chomsky believes that a scientific background is important to teach proper reasoning, he holds that science in general is "inadequate" to understand complicated problems like human affairs:
Science talks about very simple things, and asks hard questions about them. As soon as things become too complex, science can’t deal with them... But it’s a complicated matter: Science studies what’s at the edge of understanding, and what’s at the edge of understanding is usually fairly simple. And it rarely reaches human affairs. Human affairs are way too complicated.
Debates
Chomsky has been known to vigorously defend and debate his views and opinions, in philosophy, linguistics, and politics. He has had notable debates with Jean Piaget, Michel Foucault, William F. Buckley, Jr., Christopher Hitchens, George Lakoff, Richard Perle, Hilary Putnam, Willard Quine, and Alan Dershowitz, to name a few. In response to his speaking style being criticized as boring, Chomsky said that "I'm a boring speaker and I like it that way.... I doubt that people are attracted to whatever the persona is.... People are interested in the issues, and they're interested in the issues because they are important." "We don't want to be swayed by superficial eloquence, by emotion and so on."
Political views
Chomsky has stated that his "personal visions are fairly traditional anarchist ones, with origins in the Enlightenment and classical liberalism" and he has praised libertarian socialism. Although Chomsky tries to avoid the ambiguity of labels, his political views are often characterized in news accounts as "leftist" or "left-wing," and he has described himself as an anarcho-syndicalist. He is a member of the Campaign for Peace and Democracy and the Industrial Workers of the World international union. He published a book on anarchism titled ''Chomsky on Anarchism'', published by the anarchist book collective AK Press in 2006.Chomsky has engaged in political activism all of his adult life and expressed opinions on politics and world events, which are widely cited, publicized and discussed. Chomsky has in turn argued that his views are those the powerful do not want to hear and for this reason he is considered an American political dissident.
Chomsky asserts that authority, unless justified, is inherently illegitimate and that the burden of proof is on those in authority. If this burden can't be met, the authority in question should be dismantled. Authority for its own sake is inherently unjustified. An example given by Chomsky of a legitimate authority is that exerted by an adult to prevent a young child from wandering into traffic. He contends that there is little moral difference between chattel slavery and renting one's self to an owner or "wage slavery". He feels that it is an attack on personal integrity that undermines individual freedom. He holds that workers should own and control their workplace, a view held (as he notes) by the Lowell Mill Girls.
Chomsky has strongly criticized the foreign policy of the United States. He claims double standards in a foreign policy preaching democracy and freedom for all while allying itself with non-democratic and repressive organizations and states such as Chile under Augusto Pinochet and argues that this results in massive human rights violations. He often argues that America's intervention in foreign nations, including the secret aid given to the Contras in Nicaragua, an event of which he has been very critical, fits any standard description of terrorism, including "official definitions in the US Code and Army Manuals in the early 1980s." Before its collapse, Chomsky also condemned Soviet imperialism; for example in 1986 during a question/answer following a lecture he gave at Universidad Centroamericana in Nicaragua, when challenged about how he could "talk about North American imperialism and Russian imperialism in the same breath," Chomsky responded: "One of the truths about the world is that there are two superpowers, one a huge power which happens to have its boot on your neck; another, a smaller power which happens to have its boot on other people's necks. I think that anyone in the Third World would be making a grave error if they succumbed to illusions about these matters."
Regarding the death of Osama bin Laden, Chomsky stated: "We might ask ourselves how we would be reacting if Iraqi commandos landed at George W. Bush's compound, assassinated him, and dumped his body in the Atlantic. Uncontroversially, his crimes vastly exceed bin Laden’s, and he is not a 'suspect' but uncontroversially the 'decider' who gave the orders to commit the 'supreme international crime differing only from other war crimes in that it contains within itself the accumulated evil of the whole' (quoting the Nuremberg Tribunal) for which Nazi criminals were hanged: the hundreds of thousands of deaths, millions of refugees, destruction of much of the country, [and] the bitter sectarian conflict that has now spread to the rest of the region."
He has argued that the mass media in the United States largely serve as a "bought priesthood" of the U.S. government and U.S.-based corporations, with the three intertwined through common interests. In a famous reference to Walter Lippmann, Chomsky along with his coauthor Edward S. Herman has written that the American media manufactures consent among the public. Chomsky has condemned the 2010 US Supreme Court ''Citizens United'' ruling revoking the limits on campaign finance, calling it a "corporate takeover of democracy."
Chomsky opposes the U.S. global "war on drugs", claiming its language is misleading, and refers to it as "the war on certain drugs." He favors drug policy reform, in education and prevention rather than military or police action as a means of reducing drug use. In an interview in 1999, Chomsky argued that, whereas crops such as tobacco receive no mention in governmental exposition, other non-profitable crops, such as marijuana are attacked because of the effect achieved by persecuting the poor. He has stated:
U.S. domestic drug policy does not carry out its stated goals, and policymakers are well aware of that. If it isn't about reducing substance abuse, what is it about? It is reasonably clear, both from current actions and the historical record, that substances tend to be criminalized when they are associated with the so-called dangerous classes, that the criminalization of certain substances is a technique of social control.
Chomsky is critical of the American "state capitalist" system and big business, he describes himself as a socialist, specifically an anarcho-syndicalist, and is critical of "authoritarian" communist branches of socialism. He also believes that socialist values exemplify the rational and morally consistent extension of original unreconstructed classical liberal and radical humanist ideas to an industrial context. He believes that society should be highly organized and based on democratic control of communities and work places. He believes that the radical humanist ideas of his two major influences, Bertrand Russell and John Dewey, were "rooted in the Enlightenment and classical liberalism, and retain their revolutionary character."
Chomsky has stated that he believes the United States remains the "greatest country in the world", a comment that he later clarified by saying, "Evaluating countries is senseless and I would never put things in those terms, but that some of America's advances, particularly in the area of free speech, that have been achieved by centuries of popular struggle, are to be admired." He has also said "In many respects, the United States is the freest country in the world. I don't just mean in terms of limits on state coercion, though that's true too, but also in terms of individual relations. The United States comes closer to classlessness in terms of interpersonal relations than virtually any society."
Chomsky objects to the criticism that anarchism is inconsistent with support for government welfare, stating in part:
One can, of course, take the position that we don't care about the problems people face today, and want to think about a possible tomorrow. OK, but then don't pretend to have any interest in human beings and their fate, and stay in the seminar room and intellectual coffee house with other privileged people. Or one can take a much more humane position: I want to work, today, to build a better society for tomorrow – the classical anarchist position, quite different from the slogans in the question. That's exactly right, and it leads directly to support for the people facing problems today: for enforcement of health and safety regulation, provision of national health insurance, support systems for people who need them, etc. That is not a sufficient condition for organizing for a different and better future, but it is a necessary condition. Anything else will receive the well-merited contempt of people who do not have the luxury to disregard the circumstances in which they live, and try to survive.
Chomsky holds views that can be summarized as anti-war but not strictly pacifist. He prominently opposed the Vietnam War and most other wars in his lifetime. He expressed these views with tax resistance and peace walks. In 1968, he signed the “Writers and Editors War Tax Protest” pledge, vowing to refuse tax payments in protest against the Vietnam War. He published a number of articles about the war in Vietnam, including "The Responsibility of Intellectuals". He maintains that U.S. involvement in World War II to defeat the Axis powers was probably justified, with the caveat that a preferable outcome would have been to end or prevent the war through earlier diplomacy. He believes that the dropping of nuclear bombs on Hiroshima and Nagasaki were "among the most unspeakable crimes in history".
Chomsky has made many criticisms of the Israeli government, its supporters, the United States' support of the government and its treatment of the Palestinian people, arguing that " 'supporters of Israel' are in reality supporters of its moral degeneration and probable ultimate destruction" and that "Israel's very clear choice of expansion over security may well lead to that consequence." Chomsky disagreed with the founding of Israel as a Jewish state, saying, "I don't think a Jewish or Christian or Islamic state is a proper concept. I would object to the United States as a Christian state." Chomsky hesitated before publishing work critical of Israeli policies while his parents were alive, because he "knew it would hurt them" he says, "mostly because of their friends, who reacted hysterically to views like those expressed in my work." On May 16, 2010, Israeli authorities detained Chomsky and ultimately refused his entry to the West Bank via Jordan. A spokesman for the Israeli Prime Minister indicated that the refusal of entry was simply due to a border guard who "overstepped his authority" and a second attempt to enter would likely be allowed. Chomsky disagreed, saying that the Interior Ministry official who interviewed him was taking instructions from his superiors. Chomsky maintained that based on the several hours of interviewing, he was denied entry because of the things he says and because he was visiting a university in the West Bank but no Israeli universities.
Chomsky has a broad view of free-speech rights, especially in the mass media, and opposes censorship. He has stated that "with regard to freedom of speech there are basically two positions: you defend it vigorously for views you hate, or you reject it and prefer Stalinist/fascist standards". With reference to the United States diplomatic cables leak, Chomsky suggested that "perhaps the most dramatic revelation ... is the bitter hatred of democracy that is revealed both by the U.S. Government -- Hillary Clinton, others -- and also by the diplomatic service." Chomsky refuses to take legal action against those who may have libeled him and prefers to counter libels through open letters in newspapers. One notable example of this approach is his response to an article by Emma Brockes in ''The Guardian'' which alleged he denied the existence of the Srebrenica massacre. Chomsky's complaint prompted The Guardian to publish an apologetic correction and to withdraw the article from the paper's website.
Chomsky has frequently stated that there is no connection between his work in linguistics and his political views and is generally critical of the idea that competent discussion of political topics requires expert knowledge in academic fields. In a 1969 interview, he said regarding the connection between his politics and his work in linguistics:
I still feel myself that there is a kind of tenuous connection. I would not want to overstate it but I think it means something to me at least. I think that anyone's political ideas or their ideas of social organization must be rooted ultimately in some concept of human nature and human needs.
Some critics have accused Chomsky of hypocrisy when, in spite of his political criticism of American and European military imperialism, early research at the institution (MIT) where he did his linguistic research had been substantially funded by the American military. Chomsky makes the argument that because he has received funding from the U.S. military, he has an even greater responsibility to criticize and resist its immoral actions.
He is also an outspoken advocate against the use of the death penalty and has spoken against the execution of Steven Woods.
I think the death penalty is a crime no matter what the circumstances, and it is particularly awful in the Steven Woods case. I strongly oppose the execution of Steven Woods on September 13, 2011.
Influence in other fields
''Chomskyan'' models have been used as a theoretical basis in several other fields. The Chomsky hierarchy is often taught in fundamental computer science courses as it confers insight into the various types of formal languages. This hierarchy can also be discussed in mathematical terms and has generated interest among mathematicians, particularly combinatorialists. Some arguments in evolutionary psychology are derived from his research results.The 1984 Nobel Prize laureate in Medicine and Physiology, Niels K. Jerne, used Chomsky's generative model to explain the human immune system, equating "components of a generative grammar ... with various features of protein structures". The title of Jerne's Stockholm Nobel lecture was "The Generative Grammar of the Immune System".
Nim Chimpsky, a chimpanzee who was the subject of a study in animal language acquisition at Columbia University, was named after Chomsky in reference to his view of language acquisition as a uniquely human ability.
Famous computer scientist Donald Knuth admits to reading Syntactic Structures during his honeymoon and being greatly influenced by it. "...I must admit to taking a copy of Noam Chomsky's Syntactic Structures along with me on my honeymoon in 1961 ... Here was a marvelous thing: a mathematical theory of language in which I could use a computer programmer's intuition!".
Another focus of Chomsky's political work has been an analysis of mainstream mass media (especially in the United States), its structures and constraints, and its perceived role in supporting big business and government interests.
Edward S. Herman and Chomsky's book ''Manufacturing Consent: The Political Economy of the Mass Media'' (1988) explores this topic in depth, presenting their "propaganda model" of the news media with numerous detailed case studies demonstrating it. According to this propaganda model, more democratic societies like the U.S. use subtle, non-violent means of control, unlike totalitarian systems, where physical force can readily be used to coerce the general population. In an often-quoted remark, Chomsky states that "propaganda is to a democracy what the bludgeon is to a totalitarian state." (Media Control)
The model attempts to explain this perceived systemic bias of the mass media in terms of structural economic causes rather than a conspiracy of people. It argues the bias derives from five "filters" that all published news must "pass through," which combine to systematically distort news coverage.
In explaining the first filter, ownership, he notes that most major media outlets are owned by large corporations. The second, funding, notes that the outlets derive the majority of their funding from advertising, not readers. Thus, since they are profit-oriented businesses selling a product—readers and audiences—to other businesses (advertisers), the model expects them to publish news that reflects the desires and values of those businesses. In addition, the news media are dependent on government institutions and major businesses with strong biases as sources (the third filter) for much of their information. Flak, the fourth filter, refers to the various pressure groups that attack the media for supposed bias. Norms, the fifth filter, refer to the common conceptions shared by those in the profession of journalism. (Note: in the original text, published in 1988, the fifth filter was "anticommunism". However, with the fall of the Soviet Union, it has been broadened to allow for shifts in public opinion.) The model describes how the media form a decentralized and non-conspiratorial but nonetheless very powerful propaganda system, that is able to mobilize an elite consensus, frame public debate within elite perspectives and at the same time give the appearance of democratic consent.
Chomsky and Herman test their model empirically by picking "paired examples"—pairs of events that were objectively similar except for the alignment of domestic elite interests. They use a number of such examples to attempt to show that in cases where an "official enemy" does something (like murder of a religious official), the press investigates thoroughly and devotes a great amount of coverage to the matter, thus victims of "enemy" states are considered "worthy". But when the domestic government or an ally does the same thing (or worse), the press downplays the story, thus victims of US or US client states are considered "unworthy."
They also test their model against the case that is often held up as the best example of a free and aggressively independent press, the media coverage of the Tet Offensive during the Vietnam War. Even in this case, they argue that the press was behaving subserviently to elite interests.
Academic achievements, awards and honors
In early 1969, he delivered the John Locke Lectures at Oxford University; in January 1970, the Bertrand Russell Memorial Lecture at University of Cambridge; in 1972, the Nehru Memorial Lecture in New Delhi; in 1977, the Huizinga Lecture in Leiden; in 1988 the Massey Lectures at the University of Toronto, titled "Necessary Illusions: Thought Control in Democratic Societies"; in 1997, The Davie Memorial Lecture on Academic Freedom in Cape Town, and many others.Chomsky has received many honorary degrees from universities around the world, including from the following:
He is a member of the Serbian Academy of Sciences and Arts in Department of Social Sciences.
In 2005, Chomsky received an honorary fellowship from the Literary and Historical Society. In 2007, Chomsky received The Uppsala University (Sweden) Honorary Doctor's degree in commemoration of Carolus Linnaeus. In February 2008, he received the President's Medal from the Literary and Debating Society of the National University of Ireland, Galway. Since 2009 he is an honorary member of IAPTI.
In 2010, Chomsky received the Erich Fromm Prize in Stuttgart, Germany. In April 2010, Chomsky became the third scholar to receive the University of Wisconsin's A.E. Havens Center's Award for Lifetime Contribution to Critical Scholarship.
Chomsky has an Erdős number of four.
Chomsky was voted the leading living public intellectual in The 2005 Global Intellectuals Poll conducted by the British magazine ''Prospect''. He reacted, saying "I don't pay a lot of attention to polls". In a list compiled by the magazine ''New Statesman'' in 2006, he was voted seventh in the list of "Heroes of our time".
Actor Viggo Mortensen with avant-garde guitarist Buckethead dedicated their 2006 album, called ''Pandemoniumfromamerica'', to Chomsky.
On January 22, 2010, a special honorary concert for Chomsky was given at Kresge Auditorium at MIT. The concert, attended by Chomsky and dozens of his family and friends, featured music composed by Edward Manukyan and speeches by Chomsky's colleagues, including David Pesetsky of MIT and Gennaro Chierchia, head of the linguistics department at Harvard University.
In June 2011, Chomsky was awarded the Sydney Peace Prize, which cited his "unfailing courage, critical analysis of power and promotion of human rights".
In 2011, Chomsky was inducted into IEEE Intelligent Systems' AI's Hall of Fame for the "significant contributions to the field of AI and intelligent systems".
Bibliography
Filmography
See also
References
External links
Category:1928 births Category:Living people Category:20th-century philosophers Category:American academics Category:American activists Category:American anarchists Category:American anti–Iraq War activists Category:American anti–Vietnam War activists Category:American dissidents Category:American libertarians Category:American linguists Category:American media critics Category:American people of Belarusian-Jewish descent Category:American people of Ukrainian-Jewish descent Category:American philosophers Category:American philosophy academics Category:American political philosophers Category:American political writers Category:American socialists Category:American tax resisters Category:Analytic philosophers Category:Anarchist academics Category:Anarcho-syndicalists Category:Anti-corporate activists Category:Cognitive scientists Category:Computer pioneers Category:Consciousness researchers and theorists Category:Contemporary philosophers Category:Developmental psycholinguists Category:Drug policy reform activists Category:Fellows of the Royal Society of Canada Category:G7 Welcoming Committee Records artists Category:Generative linguistics Category:Gifford Lecturers Category:Guggenheim Fellows Category:Huizinga Lecturers Category:Industrial Workers of the World members Category:Jewish American social scientists Category:Jewish American writers Category:Jewish anarchists Category:Jewish anti-Zionism Category:Jewish peace activists Category:Jewish philosophers Category:Jewish socialists Category:Lecturers Category:Left-libertarians Category:Libertarian socialists Category:Libertarian theorists Category:Massachusetts Institute of Technology faculty Category:Massey Lecturers Category:Members of the Democratic Socialists of America Category:Members of the Serbian Academy of Sciences and Arts Category:Members of the United States National Academy of Sciences Category:People from Lexington, Massachusetts Category:People from Philadelphia, Pennsylvania Category:Personae non gratae Category:Philosophers of language Category:Philosophers of mind Category:Phonologists Category:Political theorists Category:Political philosophers Category:Propaganda theorists Category:Rationalists Category:Syntacticians Category:University of Pennsylvania alumni Category:Writers from Philadelphia, Pennsylvania
ar:نعوم تشومسكي an:Noam Chomsky ast:Noam Chomsky az:Noam Çomski bn:নোম চম্স্কি zh-min-nan:Noam Chomsky be:Ноам Хомскі be-x-old:Ноам Чомскі bo:ནམ་ཆོམ་སི་ཀེ། bs:Noam Chomsky br:Noam Chomsky bg:Ноам Чомски ca:Noam Chomsky cs:Noam Chomsky cy:Noam Chomsky da:Noam Chomsky de:Noam Chomsky et:Noam Chomsky el:Νόαμ Τσόμσκι es:Noam Chomsky eo:Noam Chomsky ext:Noam Chomski eu:Noam Chomsky fa:نوآم چامسکی hif:Noam Chomsky fr:Noam Chomsky ga:Noam Chomsky gd:Noam Chomsky gl:Noam Chomsky gu:નોઆમ ચોમ્સ્કી ko:노엄 촘스키 hy:Նոամ Չոմսկի hi:नोआम चाम्सकी hr:Noam Chomsky io:Noam Chomsky id:Noam Chomsky ia:Noam Chomsky os:Хомски, Ноам is:Noam Chomsky it:Noam Chomsky he:נועם חומסקי kn:ನೋಅಮ್ ಚಾಮ್ಸ್ಕೀ ka:ნოამ ჩომსკი kk:Ноам Чомски sw:Noam Chomsky ku:Noam Chomsky la:Noam Chomsky lv:Noams Čomskis lb:Noam Chomsky lt:Noam Chomsky jbo:nom.tcomskis hu:Noam Chomsky mk:Ноам Чомски ml:നോം ചോംസ്കി arz:ناعوم تشومسكى ms:Noam Chomsky nl:Noam Chomsky ja:ノーム・チョムスキー no:Noam Chomsky nn:Noam Chomsky oc:Noam Chomsky pnb:نوم چومسکی ps:نوم چومسكي pl:Noam Chomsky pt:Noam Chomsky ro:Noam Chomsky rue:Ноам Чомскі ru:Хомский, Ноам sc:Noam Chomsky sq:Noam Chomsky simple:Noam Chomsky sk:Noam Avram Chomsky cu:Аврамъ Ноамъ Хомьскꙑи sl:Noam Chomsky sr:Ноам Чомски sh:Noam Chomsky su:Noam Chomsky fi:Noam Chomsky sv:Noam Chomsky ta:நோம் சோம்சுக்கி th:โนม ชัมสกี tr:Noam Chomsky uk:Ноам Чомскі vi:Noam Chomsky war:Noam Chomsky yi:נועם כאמסקי yo:Noam Chomsky bat-smg:Noam Chomsky zh:诺姆·乔姆斯基This text is licensed under the Creative Commons CC-BY-SA License. This text was originally published on Wikipedia and was developed by the Wikipedia community.
| name | Kate Bush |
|---|---|
| background | solo_singer |
| birth name | Catherine Bush |
| transformice name | Katebush |
| birth date | July 30, 1958 |
| birth place | Bexleyheath, Kent, England |
| instrument | Vocals, piano, keyboards, bass guitar, guitar, violin |
| genre | Art rock, progressive rock, alternative rock |
| occupation | Musician, vocalist, songwriter, record producer |
| years active | 1975–present |
| label | EMI Records (1975–present)Columbia Records (U.S.) (1989–2009)Legacy Recordings (2010–present) Fish People (division of EMI) 2011– |
| website | |
| notable instruments | Fairlight CMI }} |
Kate Bush (born Catherine Bush 30 July 1958) is an English singer-songwriter, musician and record producer. Her eclectic musical style and idiosyncratic vocal style have made her one of the United Kingdom's most successful solo female performers of the past 30 years. Bush was signed by EMI at the age of 16 after being recommended by Pink Floyd's David Gilmour. In 1978, at age 19, she topped the UK Singles Chart for four weeks with her debut single "Wuthering Heights," becoming the first woman to have a UK number-one with a self-written song. She was also the most photographed woman in the United Kingdom the following year.
After her 1979 tour—the only concert tour of her career—Bush released the 1980 album ''Never for Ever'', which made her the first British solo female artist to top the UK album charts and the first female artist ever to enter the album chart at No. 1. In 1987, she won a BRIT Award for Best British Female Solo Artist. She has released ten albums, three of which topped the UK Albums Chart, and has had twenty-five UK Top 40 hit singles including "Wuthering Heights," "Running Up that Hill," "King of the Mountain," "Babooshka," "The Man with the Child in His Eyes," and "Don't Give Up" (a duet with Peter Gabriel)—all of which reached the Top 10.
In 2002, Bush's songwriting ability was recognised with an Ivor Novello Award for Outstanding Contribution to British Music. In 2005, she released ''Aerial'', her first album in 12 years. The album earned her a BRIT Award nomination for Best Album and another for Best Solo Female Artist. During the course of her career, she has also been nominated for three Grammy Awards. In early 2011, EMI Records also announced an upcoming re-issue of four of Bush's albums (''The Dreaming'', ''Hounds of Love'', ''The Sensual World'' and ''The Red Shoes'') under the name of her own label, Fish People, now that Bush has regained full control over these records. Bush released ''Director's Cut'' on 16 May 2011, which contains reworked material from her albums ''The Sensual World'' (1989) and ''The Red Shoes'' (1993). As of May 2011, Bush was working on an album of new material.
Early life
Bush was born in Bexleyheath, Kent, to English physician Robert Bush and his Irish wife, Hannah Daly. She was raised in their farmhouse in East Wickham, Kent, with her older brothers, John and Paddy. Bush came from an artistic background: her mother was a former Irish folk dancer, her father was an accomplished pianist, Paddy worked as a musical-instrument maker and John was a poet and photographer. Both brothers were involved in the local folk music scene. John was a karateka at Goldsmiths College karate club and Bush also trained there, becoming known as "Ee-ee" because of her squeaky kiai. One of the instructors, Dave Hazard, later noted in his autobiography that her dance moves seemed to owe something to karate. Her family's musical influence inspired the young Kate to teach herself to play the piano at age 11. She also played the organ in a barn behind her parents' house and studied the violin. She soon began writing her own tunes and eventually added lyrics to them.
Career
Bush attended St Joseph's Convent Grammar School (later the St Joseph's campus of Bexley College) and a Catholic girls' school on Woolwich Road in Abbey Wood, London, in the mid-1970s. During this time her family produced a demo tape with over 50 of her compositions, which was turned down by record labels. David Gilmour of Pink Floyd received the demo from Ricky Hopper, a mutual friend of Gilmour and the Bush family. Impressed with what he heard, Gilmour helped Bush get a more professional-sounding demo tape recorded that would be more saleable to the record companies. The tape was produced by Gilmour's friend Andrew Powell, who would go on to produce Bush's first two albums, as well as by sound engineer Geoff Emerick. The tape was sent to EMI executive Terry Slater, who would become famous for signing The Sex Pistols. Slater was impressed by the tape and signed her. At that time, Pink Floyd was an important act to EMI. The British record industry was reaching a point of stagnation. Progressive rock was very popular and visually oriented rock performers were growing in popularity, thus record labels looking for the next big thing were considering experimental acts.Bush was put on retainer for two years by Bob Mercer managing director of EMI group-repertoire division. According to Mercer he felt Bush's material was good enough to be released but felt if the album failed it would be demoralizing and if it was successful Bush was too young to handle it. For the first two years of her contract, Bush spent more time on school work than making an album. She left school after doing her mock A-levels and having gained ten GCE O-Level qualifications. In 2005, Bush stated in an interview with Mark Radcliffe on BBC Radio 2 that she believed EMI signed her before she was ready to make an album so that no other record company could offer her a contract. After the contract signing, EMI forwarded her a sizeable advance which she used to enroll in interpretive dance classes taught by Lindsay Kemp, a former teacher of David Bowie, and mime training with Adam Darius.
Bush also wrote and made demos of close to 200 songs, a few of which today can be found on bootleg recordings and are known as the ''Phoenix Recordings''. From March to August 1977, she fronted the KT Bush Band at public houses around London – specifically at the Rose of Lee public house (now Dirty South) in Lewisham. The other three band members were Del Palmer (bass), Brian Bath (guitar), and Vic King (drums). She began recording her first album in August 1977, although two tracks had been recorded during the summer of 1975.
''The Kick Inside'' and ''Lionheart''
As part of her preparation for entering the studio, Bush toured pubs with the KT Bush Band. However, for her debut album ''The Kick Inside'' (1978) she was persuaded to use established session musicians, some of whom she would retain even after she had brought her band-mates back on board. Her brother Paddy Bush played the harmonica and mandolin, unlike on later albums where he would play more exotic instruments such as the balalaika and didgeridoo. Stuart Elliott played some of the drums and would become her main percussionist on subsequent albums.Bush released ''The Kick Inside'' when she was 19 years old, but some of the songs had been written when she was as young as 13. EMI originally wanted the more rock-oriented track "James and the Cold Gun" to be her debut single, but Bush insisted that it should be "Wuthering Heights". Even at this early stage of her career, she had gained a reputation for her determination to have a say in decisions affecting her work. "Wuthering Heights" topped the UK and Australian charts and became an international hit. Bush became the first woman to reach number one in the UK charts with a self-penned song. A second single, "The Man with the Child in His Eyes", reached number six on the UK charts. It also made it onto the American Billboard Hot 100 where it reached number 85 in early 1979. Bob Mercer felt that Bush's relative lack of success in the United States compared to the rest of the world was due to her music being a poor fit for American radio formats and that there were no outlets for the visual presentation central to Bush's appeal. "The Man with the Child in His Eyes" went on to win her an Ivor Novello Award in 1979 for Outstanding British Lyric. EMI capitalised on Bush's appearance by promoting the album with a poster of her in a tight pink top that emphasised her breasts. In an interview with ''NME'' magazine in 1982, Bush criticised the marketing technique, stating: "People weren't even generally aware that I wrote my own songs or played the piano. The media just promoted me as a female body. It's like I've had to prove that I'm an artist in a female body." In late 1978, EMI persuaded Bush to quickly record a follow-up album, ''Lionheart'', to take advantage of the success of ''The Kick Inside''. Bush has often expressed dissatisfaction with ''Lionheart'', feeling that she needed more time to get it right. The album was rushed out of the studio in Nice on the French Riviera. The album was produced by Andrew Powell, assisted by Bush. While it has its share of hits, most notably "Wow", it did not garner the same reception as her first album, reaching number six in the UK album charts.
Bush was displeased with being rushed into making the second album. She set up her own publishing company, Kate Bush Music, and her own management company, Novercia, to maintain complete control over her work. The board of directors of these companies was herself and members of her family. Following the album's release, she was required by EMI to undertake heavy promotional work and an exhausting tour, the only one of her career. The tour, named The Tour of Life, began in April 1979 and lasted six weeks. This live show was co-devised and performed on stage with magician Simon Drake. Typical of her determination to have control, she was involved in every aspect of the show's production, choreography, set design, and staff recruitment. The shows were noted for her dancing, complex lighting and her 17 costume changes per show. Because of her intention to dance as she sang, her sound engineers used a wire coat hanger and a radio microphone to fashion the first headset mic to be used by a rock performer, at least since the Swedish group Spotnicks used a very primitive version in the early 1960s.
''Never for Ever'' and ''The Dreaming''
Released in September 1980, ''Never for Ever'' saw Bush's second foray into production, co-producing with Jon Kelly. Her first time as a producer was on her ''Live On Stage'' EP, released after her tour the previous year. The first two albums had resulted in a definitive sound evident in every track, with orchestral arrangements supporting the live band sound. The range of styles on ''Never for Ever'' is much more diverse, veering from the straightforward rocker "Violin" to the wistful waltz of hit single "Army Dreamers". ''Never for Ever'' was the first Kate Bush album to feature synthesisers and drum machines, in particular the Fairlight CMI, to which she was introduced when providing backing vocals on Peter Gabriel's third album in early 1980. It was her first record to reach the top position in the UK album charts, also making her the first female British artist to achieve that status, and the first female artist ever to enter the album chart at the top. The top-selling single from the album was "Babooshka", which reached number five in the UK singles chart. In November 1980, she released the Christmas single "December Will Be Magic Again", which reached number 29 in the UK charts.September 1982 saw the release of ''The Dreaming'', the first album Bush produced by herself. It was also a major departure for Bush, being initially composed on the Fairlight CMI rather than piano, with songs extensively revised and rebuilt in the studio, rather than merely arranged there. With her new-found freedom, she experimented with production techniques, creating an album that features a diverse blend of musical styles and is known for its near-exhaustive use of the Fairlight CMI. ''The Dreaming'' received a mixed critical reception in the UK at first. Many were baffled by the dense soundscapes Bush had created, and some critics accused the album of being over-produced. In a 1993 interview with ''Q'', Bush stated: "That was my 'She's gone mad' album." However, the album was hailed as a "masterpiece" and a "musical ''tour-de-force''" by critics in America, and the album became her first to enter the US charts, albeit only reaching number 157. The album entered the UK album chart at no.3, but is to date her lowest selling album, garnering only a gold disc.
"Sat in Your Lap" was the first single from the album to be released. It pre-dated the album by over a year and peaked at number 11 in the UK. The album's title track, featuring the talents of Rolf Harris and Percy Edwards, stalled at number 48, while the third single, "There Goes a Tenner", failed to chart, despite promotion from EMI and Bush. The track "Suspended in Gaffa" was released as a single in Europe, but not in the UK.
Continuing in her storytelling tradition, Bush looked far outside her own personal experience for sources of inspiration. She drew on old crime films for "There Goes A Tenner", a documentary about the war in Vietnam for "Pull Out The Pin", and the plight of Indigenous Australians for "The Dreaming". "Houdini" is about the magician's death, and "Get Out Of My House" was inspired by Stanley Kubrick's film of Stephen King's novel ''The Shining''.
''Hounds of Love'' and ''The Whole Story''
''Hounds of Love'' was released in 1985. Because of the high cost of hiring studio space for her previous album, she built a private studio near her home, where she could work at her own pace. ''Hounds of Love'' ultimately topped the charts in the UK, knocking Madonna's ''Like A Virgin'' from the number one position.The album takes advantage of the vinyl format with two very different sides. The first side, ''Hounds of Love'', contains five "accessible" pop songs, including the four singles "Running Up that Hill," "Cloudbusting," "Hounds of Love," and "The Big Sky." In August 1985, ''NME'' featured Bush in a "Where Are They Now" article. "Running Up that Hill" reached number 3 in the UK charts and also re-introduced Bush to American listeners, climbing to number 30 on the Billboard Hot 100 in November 1985. The second side of the album, ''The Ninth Wave'', takes its name from Tennyson's poem, "Idylls of the King," about the legendary King Arthur's reign, and is one continuous piece of music. The album earned Bush nominations for Best Female Solo Artist, Best Album, Best Single, and Best Producer at the 1986 BRIT Awards. In the same year, Bush and Peter Gabriel had a UK top ten hit with "Don't Give Up," and EMI released her "greatest hits" album, ''The Whole Story'', for which she recorded the single "Experiment IV" and provided new vocals and a refreshed backing track to "Wuthering Heights." Bush won the award for Best Female Solo Artist at the 1987 BRIT Awards.
''The Sensual World'' and ''The Red Shoes''
The increasingly personal tone of her writing continued on 1989's ''The Sensual World'', with songs about unexpressed and unrequited love ("Love and Anger" and "Never Be Mine," respectively), and the pressures on modern relationships ("Between a Man and a Woman"). One of the quirkiest tracks on the album, touched by Bush's black humour, is "Heads We're Dancing," about a woman who dances all night with a charming stranger only to find out in the morning that he is Adolf Hitler. The title track drew its inspiration from James Joyce's novel ''Ulysses''.
''The Sensual World'' went on to become her biggest-selling album in the US, receiving an RIAA Gold certification four years after its release for 500,000 copies sold. In the United Kingdom album charts, it reached the number two position.
In 1990, the boxed-set ''This Woman's Work'' was released and included all of her albums with their original cover art, as well as two discs of all single B sides recorded from 1978–1990. In 1991, Bush released a cover of Elton John's "Rocket Man," which reached number 12 in the UK singles chart and in 2007, was voted the greatest cover ever by readers of ''The Observer'' newspaper. She recorded "Candle in the Wind," as the single's b-side.
''The Red Shoes'' was released in November 1993. ''The Red Shoes'' features more high-profile cameo appearances than Bush's previous efforts, including contributions from composer and conductor Michael Kamen. Comedian Lenny Henry, Prince, Eric Clapton, Gary Brooker of Procol Harum, Trevor Whittaker, and Jeff Beck also contributed to the album. The album gave Bush her highest chart position in the US, reaching number 28, although the only song from the album to make the US singles chart was "Rubberband Girl", which peaked at number 88 in January 1994. In the UK, the album reached number two, and the singles "Rubberband Girl," "The Red Shoes," "Moments of Pleasure," and "And So Is Love" all reached the top 30. That same year, the short film ''The Line, the Cross & the Curve'', written and directed by Bush, and starring Bush and English actress Miranda Richardson, used six of the songs on the album.
The initial plan had been to take the songs out on the road (though a new tour did not transpire), so Bush deliberately aimed for a live-band feel, with less of the studio trickery that had typified her last three albums and that would be difficult to recreate on stage. The result alienated some of her fan base, who enjoyed the intricacy of her earlier compositions, but others found a new complexity in the lyrics and the emotions they expressed.
This was a troubled time for Bush. She had suffered a series of bereavements, including the loss of guitarist Alan Murphy, who had started working with her on The Tour Of Life in 1979, and her mother Hannah, to whom she was exceptionally close. Many of the people she lost are honoured in the ballad "Moments of Pleasure." However, Bush's mother was still alive when "Moments of Pleasure" was written and recorded. Bush describes playing the song to her mother, who thought the line where she is quoted by Bush as saying "Every old sock meets an old shoe", was hilarious and "couldn't stop laughing".
''Aerial''
After the release of ''The Red Shoes'', Bush dropped out of the public eye for many years, although her name occasionally cropped up in the media with rumours of a new album release. Bush had originally intended to take one year off but despite working on material 12 years would pass before her next album release. The press often viewed her as an eccentric recluse, sometimes drawing a comparison with Miss Havisham from Charles Dickens's ''Great Expectations''. In reality, she was trying to give her young son a normal childhood, and needed a quiet place for her creative process to function. In 1998, Bush had given birth to Albert, known as "Bertie", fathered by her guitarist and now-husband Danny McIntosh. After living for many years on Court Road, Eltham, southeast London, the couple and their son moved away from the city and currently have two homes: a £2.5 million house in East Portlemouth on the Devon coast and a mansion on an islet on the Kennet and Avon canal at Sulhamstead in West Berkshire.Bush's eighth studio album, ''Aerial'', was released on double CD and vinyl in November 2005. The first single from the album was "King of the Mountain", which was played for the first time on BBC Radio 2 on 21 September 2005.
As on ''Hounds of Love'' (1985), the album is divided into two sections, each with its own theme and mood. The first disc, subtitled ''A Sea of Honey'', features a set of unrelated themed songs, including "King of the Mountain"; "Bertie", a Renaissance-style ode to her son; and "Joanni", based on the story of Joan of Arc. In the song "π", Bush sings the number to 115 decimal places. The second disc, subtitled ''A Sky of Honey'', features one continuous piece of music describing the experience of being outdoors after waking at dawn, moving through afternoon, dusk, to night, then back to the following dawn of single summer's day. All the pieces in this suite refer or allude to sky and sea the in their lyrical content. Bush mixed her voice with cooing wood pigeons to repeat the phrases "A sea of honey, a sky of honey," and "You're full of beauty" throughout the piece, and uses recordings of actual birdsong throughout. ''A Sky of Honey'' features Rolf Harris playing the didgeridoo on one track, and providing vocals on "The Painter's Link". Other artists making guest appearances on the album include Peter Erskine, Eberhard Weber, Lol Creme, and Gary Brooker. Two tracks feature string arrangements by Michael Kamen, performed by the London Metropolitan Orchestra. A CD release of the single "King of the Mountain" included a cover of "Sexual Healing" by Marvin Gaye.
"King of the Mountain" entered the UK Downloads Chart at number six on 17 October 2005, and by 30 October it had become Bush's third-highest-charting single ever in the UK, peaking at number four on the full chart. ''Aerial'' entered the UK albums chart at number 3, and the US chart at number 48. Bush herself carried out relatively little publicity for the album, only conducting a handful of magazine and radio interviews. ''Aerial'' earned Bush two nominations at the 2006 BRIT Awards, for Best British Female Solo Artist and Best British Album.
In late 2007, Bush composed and recorded a new song, "Lyra", for the soundtrack to the fantasy film ''The Golden Compass''.
''Director's Cut'' and new material
On 16 May 2011, Bush released the album ''Director's Cut''. The album, which Bush has described as an entirely new project rather than a collection of mere remixes, contains 11 tracks of substantially reworked material from her earlier albums ''The Sensual World'' and ''The Red Shoes'', all of which have been recorded using analogue, rather than digital, equipment to create "a warmer sound". All the tracks have new lead vocals, new drums, and radically reworked instrumentation. Some of them have been transposed to a lower key to accommodate her lowering voice. Three of the songs, including "This Woman's Work", have been completely re-recorded, with lyrics often changed in places. The album has been met with a wide range of reviews with most reviewers a bit confused about the concept of the album itself, while responding with varying degrees of enthusiasm about its revamped tracks. Of particular note is the warmer, more intimate tone of the songs and the richer, more mature sound of her voice. This is the first album on her new label, Fish People, a division of EMI Records, with whom she's had a relationship since she started recording. In addition to the album ''Director's Cut'' in both its single CD form and in a box-set with the analog re-mastered ''The Red Shoes'' and ''The Sensual World'', Fish People will be releasing re-mastered editions of ''The Hounds of Love'' and ''The Dreaming''. The album debuted at number 2 on the United Kingdom chart.The song "The Sensual World" has been renamed "Flower of the Mountain" and contains a passage of Molly Bloom's famous soliloquy from James Joyce's novel ''Ulysses''. Bush said, "Originally when I wrote the song "The Sensual World," I had used text from the end of Ulysses. When I asked for permission to use the text I was refused, which was disappointing. I then wrote my own lyrics for the song, although I felt that the original idea had been more interesting. Well, I'm not James Joyce am I? When I came to work on this project I thought I would ask for permission again and this time they said yes."
The first single released from the album was "Deeper Understanding" and contains a new chorus featuring computerized vocals from Bush's son, Albert. A video for the song, directed by Bush, has been released through her channel on YouTube. It features Robbie Coltrane as a man consumed by his relationship with his computer (voiced by Bush's son). Frances Barber plays the man's wife, and Noel Fielding also appears.
As of May 2011, Bush has stated that she is working on an album of new material, most of which has been written and one EMI executive has said, "we have been told to prepare for a November [2011] release."
Musical style
Bush's music is eclectic, using various styles of music even within the same album. Her songs have spanned genres as diverse as rock, pop, alternative and art rock. Even in her earliest works where the piano was a primary instrument, she wove together many diverse influences, melding classical music, rock, and a wide range of ethnic and folk sources, and this has continued throughout her career.In an interview with ''Melody Maker'' magazine in 1977, she revealed that male artists had more influence on her work than females, stating: "Every female you see at a piano is either Lynsey De Paul, or Carole King. And most male music—not all of it but the good stuff—really lays it on you. It really puts you against the wall and that's what I like to do. I'd like my music to intrude. Not many females succeed with that."
The experimental nature of her music has led it to be described as a later, more technological, and more accessible manifestation of the British progressive rock movement. Southern England was the home to the most influential and successful acts of the progressive rock movement and, like other artists in this genre, Bush rejects the classic American style of making pop music, which was adopted by most UK pop artists. Bush's vocals contain elements of British, Anglo-Irish and most prominently (southern) English accents and, in its utilization of musical instruments from many periods and cultures, her music has differed from American pop norms. Elements of Bush's lyrics tend to be more unusual and less clichéd than American-style pop lyrics, often employing historical or literary references and avoiding autobiographical lyrics. She considers herself a storyteller who embodies the character singing the song and strenuously rejects efforts by others to insist that her songs are autobiographical.
Reviewers have used the term "surreal" to describe her music. Many of her songs have a melodramatic emotional and musical surrealism that defies easy categorisation. It has been observed that even the more joyous pieces are often tinged with traces of melancholy, and even the most sorrowful pieces have elements of vitality struggling against all that would oppress them.
Bush is not afraid to tackle sensitive and taboo subjects. "The Kick Inside" is based on a traditional English folk song (''The Ballad of Lucy Wan'') about an incestuous pregnancy and a resulting suicide. "Kashka from Baghdad" is a song about a homosexual male couple; ''Out'' magazine listed two of her albums in their Top 100 Greatest Gayest albums list. "The Infant Kiss" is a song about a haunted, unstable woman's almost paedophile infatuation with a young boy in her care (inspired by Jack Clayton's film ''The Innocents'' (1961), which had been based on Henry James's famous novella ''The Turn of the Screw''); and "Breathing" explores the results of nuclear fallout from the perspective of an unborn child in the womb. Her lyrics have referenced a wide array of subject matter, often relatively obscure, as in "Cloudbusting", which was inspired by Peter Reich's autobiography, "Book of Dreams", about his relationship with his father, Wilhelm Reich, and G. I. Gurdjieff in "Them Heavy People", while "Deeper Understanding", from ''The Sensual World'', portrays a person who stays indoors, obsessively talking to a computer and shunning human contact.
Comedy is also a big influence on her and is a significant component of her work. She has cited Woody Allen, ''Monty Python'', ''Fawlty Towers'', and ''The Young Ones'' as particular favourites. Horror movies are another interest of Bush's and have influenced the gothic nature of several of her songs, such as "Get Out of My House", inspired by Stanley Kubrick's ''The Shining'', and "Hounds of Love", inspired by the 1957 horror movie ''Night of the Demon''. Her songs have occasionally combined comedy and horror to form dark humour, such as murder by poisoning in "Coffee Homeground", an alcoholic mother in "Ran Tan Waltz" and the upbeat "The Wedding List", a song inspired by François Truffaut's 1967 film of Cornell Woolrich's ''The Bride Wore Black'' about the death of a groom and the bride's subsequent revenge against the killer.
Length of time between albums and perception of perfectionism
The length of time in between album releases has led to rumours in the media concerning her health or appearance. In the past, stories of weight gain or mental instability have been disproved by Bush's periodic reappearance. In 2011 Bush told BBC Radio 4 that the amount of time between album releases is extremely stressful noting: "It's very frustrating the albums take as long as they do...I wish there weren't such big gaps between them." In the same interview Bush denied she was a perfectionist in the studio, saying: "I think it's important that things are flawed...That's what makes a piece of art interesting sometimes – the bit that's wrong or the mistake you've made that's led onto an idea you wouldn't have had otherwise," and reiterated her prioritization of her family life.
Live performances
Bush's only tour took place 2 April – 13 May 1979, after which she gave only the occasional live performance. Several reasons have been suggested as to why she abandoned touring, among them her reputed need to be in total control of the final product, which is incompatible with live stage performance, a rumour of a crippling fear of flying, and the suggestion that the death of 21-year-old Bill Duffield severely affected her. Duffield, her lighting director, was killed in an accident during her 2 April 1979 concert at Poole Arts Centre. Bush held a benefit concert on 12 May 1979, with Peter Gabriel and Steve Harley at London's Hammersmith Odeon for his family. Duffield would be honoured in two later songs: "Blow Away" on ''Never for Ever'' and "Moments of Pleasure" on ''The Red Shoes''. Bush explained in a BBC Radio 2 interview with Mark Radcliffe that she actually enjoyed the tour but was consumed with producing her subsequent records.During the same period as her tour, she made numerous television appearances around the world, including ''Top of the Pops'' in the United Kingdom, ''Bios Bahnhof'' in Germany, and ''Saturday Night Live'' in the United States (with Paul Shaffer on piano). On 28 December 1979, BBC TV aired the ''Kate Bush Christmas Special''. It was recorded in October 1979 at the BBC Studios in Birmingham, England; choreography by Anthony Van Laast. As well as playing songs from her first two albums, she played "December Will Be Magic Again", and "Violin" from her forthcoming album, ''Never for Ever''. Peter Gabriel made a guest appearance to play "Here Comes the Flood", and a duet of Roy Harper's "Another Day" with Bush.
After the Tour of Life Bush desired to make two more albums before touring again. At that point she got involved with production techniques and sound experimentation that took up a lot of time and prevented her from touring. Later on there were a couple of instances where she came close to touring again.
In 1982, Bush participated in the first benefit concert in aid of The Prince's Trust alongside artists such as Madness, Midge Ure, Phil Collins, Mick Karn and Pete Townshend. On 25 April 1986 Bush performed live for British charity event Comic Relief, singing "Do Bears... ?", a humorous duet with Rowan Atkinson, and a rendition of "Breathing". Later in the year on 28 June 1986, she made a guest appearance to duet with Peter Gabriel on "Don't Give Up" at Earl's Court, London as part of his "So" tour. In March 1987, Bush sang "Running Up that Hill" at The Secret Policeman's Third Ball.
On 17 January 2002, Bush appeared with her long-time champion, David Gilmour, singing the part of the doctor in "Comfortably Numb" at the Royal Festival Hall in London.
In 2011 Bush told Classic Rock Magazine "I do hope that some time I get a chance to do some shows. Maybe not a tour, but something"
Video projects
In 1979 Bush's one live show, The Tour of Life, was recorded for the BBC and for release on VHS as ''Kate Bush Live at Hammersmith Odeon''.Bush has appeared in innovative music videos designed to accompany her singles releases. Among the best known are those for "Running Up that Hill," "Babooshka," "Breathing," "Wuthering Heights," and "The Man with the Child in His Eyes," and "Cloudbusting," featuring actor Donald Sutherland, who made time during the filming of another project to take part in the video. EMI has released collections of her videos, including ''The Single File'', ''Hair of the Hound'', ''The Whole Story'', a career video overview released in conjunction with the 1986 compilation album of the same title, and ''The Sensual World''.
In 1993, she directed and starred in the short film, ''The Line, the Cross & the Curve'', a musical co-starring Miranda Richardson, featuring music from Bush's album ''The Red Shoes'', which was inspired by the classic movie of the same name. It was released on VHS in the UK in 1994 and also received a small number of cinema screenings around the world. In recent interviews, Bush has said that she considers it a failure, and stated in 2001: "I'm very pleased with four minutes of it, but I'm very disappointed with the rest." In a 2005 interview, she described the film as "A load of bollocks."
In 1994, Bush provided the music used in a series of psychedelic-themed television commercials for the soft drink Fruitopia that appeared in the United States. The same company aired the ads in the United Kingdom, but the British version featured Elizabeth Fraser of Cocteau Twins instead of Bush.
In late 2006, a DVD documentary titled ''Kate Bush Under Review'' was released by Sexy Intellectual, which included archival interviews with Bush, along with interviews with a selection of music historians and journalists (including Phil Sutcliffe, Nigel Williamson, and Morris Pert). The DVD also includes clips from several of Bush's music videos.
On 2 December 2008, the DVD collection of the fourth season of ''Saturday Night Live'', including her performances, was released. A three DVD set of The Secret Policeman's Balls benefit concerts that includes Bush's performance was released on 27 January 2009.
Movie projects
In 1990, Bush starred in the black comedy film ''Les Dogs'', produced by ''The Comic Strip'' for BBC television. Aired on 8 March 1990, Bush plays the bride Angela at a wedding set in a post-apocalyptic version of Britain. While Bush's is a silent presence in a wedding dress throughout most of the film, she does have several lines of dialogue with Peter Richardson in two dream sequences. In another ''Comic Strip Presents'' film, ''GLC'', she produced the theme song "Ken", which includes a vocal performance by Bush. The song was written about Ken Livingstone, the leader of the Greater London Council, who would later be elected as mayor of London and at the time was working with musicians to help the Labour Party garner the youth vote.She also produced all the incidental music, which is synthesiser based. Bush wrote and performed the song "The Magician", in a fairground-like arrangement, for Menahem Golan's 1979 film ''The Magician of Lublin''. In 1985, Bush contributed a darkly melancholic version of the Ary Barroso song "Brazil" to the soundtrack of the Terry Gilliam film ''Brazil''. The track was scored and arranged by Michael Kamen. In 1986, she wrote and recorded "Be Kind To My Mistakes" for the Nicolas Roeg film ''Castaway''. An edited version of this track was used as the B side to her 1989 single "This Woman's Work". In 1988, the song "This Woman's Work" was featured in the John Hughes film ''She's Having a Baby'', and a slightly remixed version appeared on Bush's album ''The Sensual World''. The song has since appeared on numerous television shows, and in 2005 reached number eight on the UK download chart after featuring in a British television advertisement for the charity NSPCC.
In 1999, Bush wrote and recorded a song for the Disney film ''Dinosaur'', but the track was ultimately not included on the soundtrack. According to the winter 1999 issue of ''HomeGround'', a Bush fanzine, it was scrapped when Disney asked her to rewrite the song and she refused. Also in 1999, Bush's song "The Sensual World" was featured prominently in Canadian filmmaker Atom Egoyan's film "Felicia's Journey". "The Man with the Child in His Eyes" is on the soundtrack for the 2007 British romantic comedy film ''Starter for 10''.
Collaborations
Bush provided vocals on two of Peter Gabriel's albums, including the hits "Games Without Frontiers" and "Don't Give Up", as well as "No Self-Control". Gabriel appeared on Bush's 1979 television special, where they sang a duet of Roy Harper's "Another Day". She has sung on two Roy Harper tracks, "You", on his 1979 album, "The Unknown Soldier", and "Once", the title track of his 1990 album. She has also sung on the title song of the 1986 Big Country album ''The Seer'', the Midge Ure song "Sister and Brother" from his 1988 album ''Answers to Nothing'', Go West's 1987 single "The King Is Dead" and two songs with Prince – "Why Should I Love You?", from her 1993 album ''The Red Shoes'', and in 1996, the song "My Computer" from Prince's album ''Emancipation''. In 1987, she sang a verse on the charity single "Let It Be" by Ferry Aid. She sang a line on the charity single "Spirit of the Forest" by Spirit of the Forest in 1989. 1990 saw Kate producing, for the only time in her career, one song for another artist, Alan Stivell's "Kimiad," on his album ''Again''. Stivell had appeared on ''The Sensual World''. In 1995, Bush covered George Gershwin's "The Man I Love" for the tribute album ''The Glory of Gershwin''. In 1996, Bush contributed a version of "Mná na hÉireann" (Irish for Women of Ireland) for the Anglo-Irish folk-rock compilation project ''Common Ground: The Voices of Modern Irish Music''. Bush had to sing the song in Irish, which she learned to do phonetically. Artists who have contributed to Bush's own albums include Eric Clapton, Jeff Beck, David Gilmour, Nigel Kennedy, Gary Brooker, and Prince. Bush provided backing vocals for a song that was recorded during the 1990s titled ''Wouldn't Change a Thing'' by Lionel Azulay, the drummer with the original band that was later to become the KT Bush Band. The song, which was engineered and produced by Del Palmer, is available for download and will be on Azulay’s upcoming CD.Bush declined a request by Erasure to produce one of their albums because "she didn’t feel that that was her area".
In 2010, Bush provided vocals for Rolf Harris's cover of a traditional Irish song entitled "She Moves Through the Fair". Harris, who described the collaboration the "best thing I’ve done," is unsure of how to release the track.
Influence
From the 1980s onward, it has become almost standard for individualistic female singer-songwriters to be compared to Bush by the media. She has been noted as an influence on female artists such as Tori Amos, Björk, Alison Goldfrapp, Nerina Pallot, KT Tunstall, Happy Rhodes, Lily Allen, PJ Harvey, Little Boots, and Florence Welch, in addition to acts as diverse as Muse, OutKast, and Bloc Party. Paula Cole named Bush as an influence while accepting the Best New Artist Grammy in 1996. Ariel Pink wrote a tribute song for her titled "For Kate I Wait" on the album ''The Doldrums''. The trip-hop artist Tricky has said about Bush, "I don't believe in God, but if I did, her music would be my bible". Punk rocker John Lydon, better known as Johnny Rotten of the Sex Pistols, declared her work to be "fucking brilliant" and labelled her "a true original". Rotten once wrote a song for her, titled "Bird in Hand" (about exploitation of parrots) that Bush rejected. Rotten theorised that Bush thought the song contained insulting references aimed at her. Marc Almond chose "Moments of Pleasure" as one of his 10 favourite songs on Radio 2 in June 2007, saying that the song had a profound influence on him when he was combating drug addiction in New York in the 1990s. In November 2006, the singer Rufus Wainwright named Bush as one of his top ten gay icons. Outside music, Bush has been an inspiration to several fashion designers, most notably Hussein Chalayan.Many artists around the world have recorded cover versions of Bush songs, including Charlotte Church, The Futureheads (who had a UK top ten hit with a cover of "Hounds of Love"), Placebo, Pat Benatar, Hayley Westenra, Jane Birkin, Natalie Cole, Ra Ra Riot, Maxwell, The Church and Nada Surf. The British dance act Utah Saints sampled a line from "Cloudbusting" for their single, "Something Good". Artists such as Tori Amos, Nolwenn Leroy, Patrick Wolf and Happy Rhodes (whose upper vocal range has been compared with the one of Kate Bush) have covered her songs in live performances. Coldplay said their track "Speed of Sound" was originally an attempt to re-create "Running Up that Hill". Suede front-man Brett Anderson has stated that "Wuthering Heights" was the first single he ever bought and mentioned "And Dream of Sheep" in Suede's song "These are the Sad Songs". British folk singer Jim Moray also references "And Dream of Sheep" in his self-penned track "Longing for Lucy". Progressive death metal act Novembre also covered "Cloudbusting" on their album ''Novembrine Waltz''. In 2009, John Forté released a hip hop version of "Running Up that Hill". In 2010, Theo Bleckmann has been performing his work ''Hello Earth! The Music of Kate Bush'' and plans to release the project as an album in 2011. In 1998 a collection of independent musicians including Syd Straw recorded the tribute album ''I Wanna Be Kate,'' which was released in CD and mp3 form.
Discography
See also
References
Further reading
External links
Category:English pop singers Category:English singer-songwriters Category:English female singers Category:English pianists Category:English record producers Category:English vegetarians Category:Female rock singers Category:BRIT Award winners Category:Ivor Novello Award winners Category:English people of Irish descent Category:People from Bexleyheath Category:People from South Hams (district) Category:People from Sulhamstead Category:1958 births Category:Living people
br:Kate Bush bg:Кейт Буш ca:Kate Bush cs:Kate Bush da:Kate Bush de:Kate Bush et:Kate Bush es:Kate Bush eo:Kate Bush fa:کیت بوش fr:Kate Bush fy:Kate Bush ga:Kate Bush hr:Kate Bush io:Kate Bush id:Kate Bush it:Kate Bush he:קייט בוש ka:კეიტ ბუში lv:Keita Buša lt:Kate Bush hu:Kate Bush ro:Kate Bush nl:Kate Bush ja:ケイト・ブッシュ no:Kate Bush pl:Kate Bush pt:Kate Bush ru:Буш, Кейт scn:Kate Bush sr:Kejt Buš fi:Kate Bush sv:Kate Bush th:เคต บุช tr:Kate Bush zh:凱特·布希
This text is licensed under the Creative Commons CC-BY-SA License. This text was originally published on Wikipedia and was developed by the Wikipedia community.




![Bush - Swallowed [Widescreen] Bush - Swallowed [Widescreen]](http://web.archive.org./web/20120307164122im_/http://i.ytimg.com/vi/Q7RVp3DvX1o/0.jpg)




