
- Order:
- Duration: 2:38
- Published: 08 Nov 2009
- Uploaded: 31 Jul 2011
- Author: AlJazeeraEnglish


















































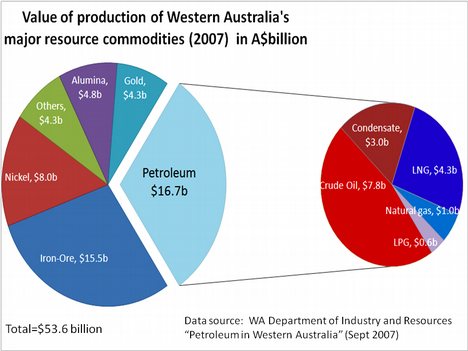













Bauxite is an aluminium ore and is the main provider of aluminium. This form of rock consists mostly of the minerals gibbsite Al(OH)3, boehmite γ-AlO(OH), and diaspore α-AlO(OH), in a mixture with the two iron oxides goethite and hematite, the clay mineral kaolinite, and small amounts of anatase TiO2. Bauxite was named after the village Les Baux in southern France, where it was first recognised as containing aluminium and named by the French geologist Pierre Berthier in 1821.
The lateritic bauxites are found mostly in the countries of the tropics.They were formed by lateritization (see laterite) of various silicate rocks such as granite, gneiss, basalt, syenite, and shale. In comparison with the iron-rich laterites, the formation of bauxites demands even more intense weathering conditions in a location with very good drainage. This enables the dissolution of the kaolinite and the precipitation of the gibbsite. Zones with highest aluminium content are frequently located below a ferruginous surface layer. The aluminium hydroxide in the lateritic bauxite deposits is almost exclusively gibbsite.
In 2007, Australia was one of the top producers of bauxite with almost one-third of the world's production, followed by China, Brazil, Guinea, and India. Although aluminium demand is rapidly increasing, known reserves of its bauxite ore are sufficient to meet the worldwide demands for aluminium for many centuries. Increased aluminium recycling, which has the advantage of lowering the cost in electric power in producing aluminium, will considerably extend the world's bauxite reserves.
In November 2010, Nguyen Tan Dung, the prime minister of Vietnam, announced that Vietnam's bauxite reserves might total 11000Mt; this would be the largest in the world.
Bauxite is usually strip mined because it is almost always found near the surface of the terrain, with little or no overburden. Approximately 95% of the world's bauxite production is processed first into alumina, and then into aluminium by electrolysis. Bauxite rocks are typically classified according to their intended commercial application: metallurgical, abrasive, cement, chemical, and refractory.
Usually, bauxite ore is heated in a pressure vessel along with a sodium hydroxide solution at a temperature of 150 to 200 Celsius. At these temperatures, the aluminium is dissolved as an aluminate (the Bayer process). After separation of ferruginous residue (red mud) by filtering, pure gibbsite is precipitated when the liquid is cooled, and then seeded with fine-grained aluminium hydroxide. The gibbsite is usually converted into aluminium oxide, Al2O3, by heating. This mineral becomes molten at a temperature of about 1000 Celsius, when the mineral cryolite is added as a flux. Next, this molten substance can yield metallic aluminium by passing an electric current through it in the process of electrolysis, which is called the Hall–Héroult process after its American and French discoverers in 1886.
Before Hall and Héroult discovered their process that uses cryolite and electricity, aluminium was separated from its ore—in small quantities—by heating the ore with metallic sodium or potassium in a vacuum. However, those two metals were themselves produced by electrolysis, and the entire procedure was quite complicated and expensive. The Hall-Heroult process greatly simplified the process of refining aluminium and made it economical to produce aluminium from bauxite in very large quantities.
This text is licensed under the Creative Commons CC-BY-SA License. This text was originally published on Wikipedia and was developed by the Wikipedia community.
